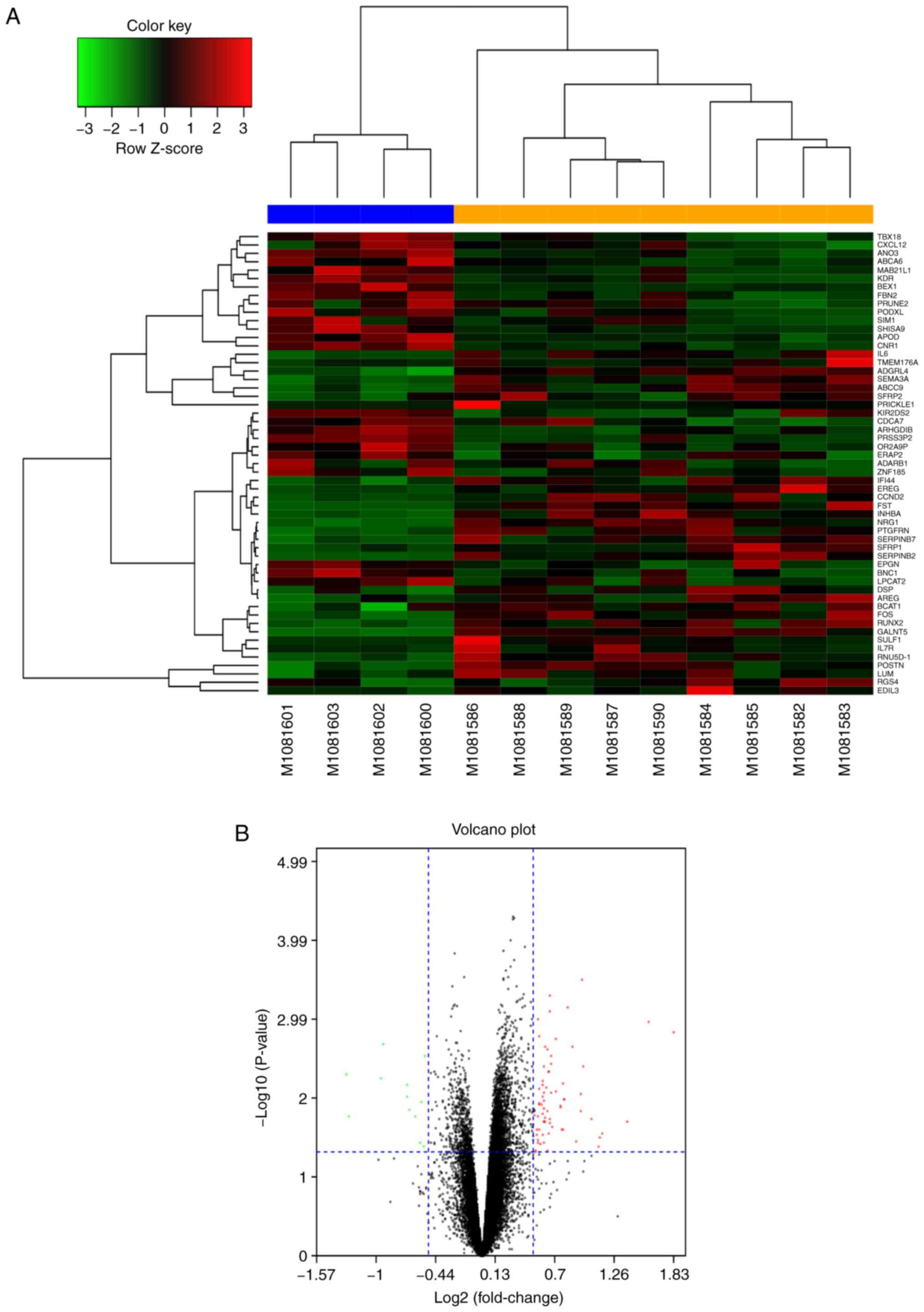
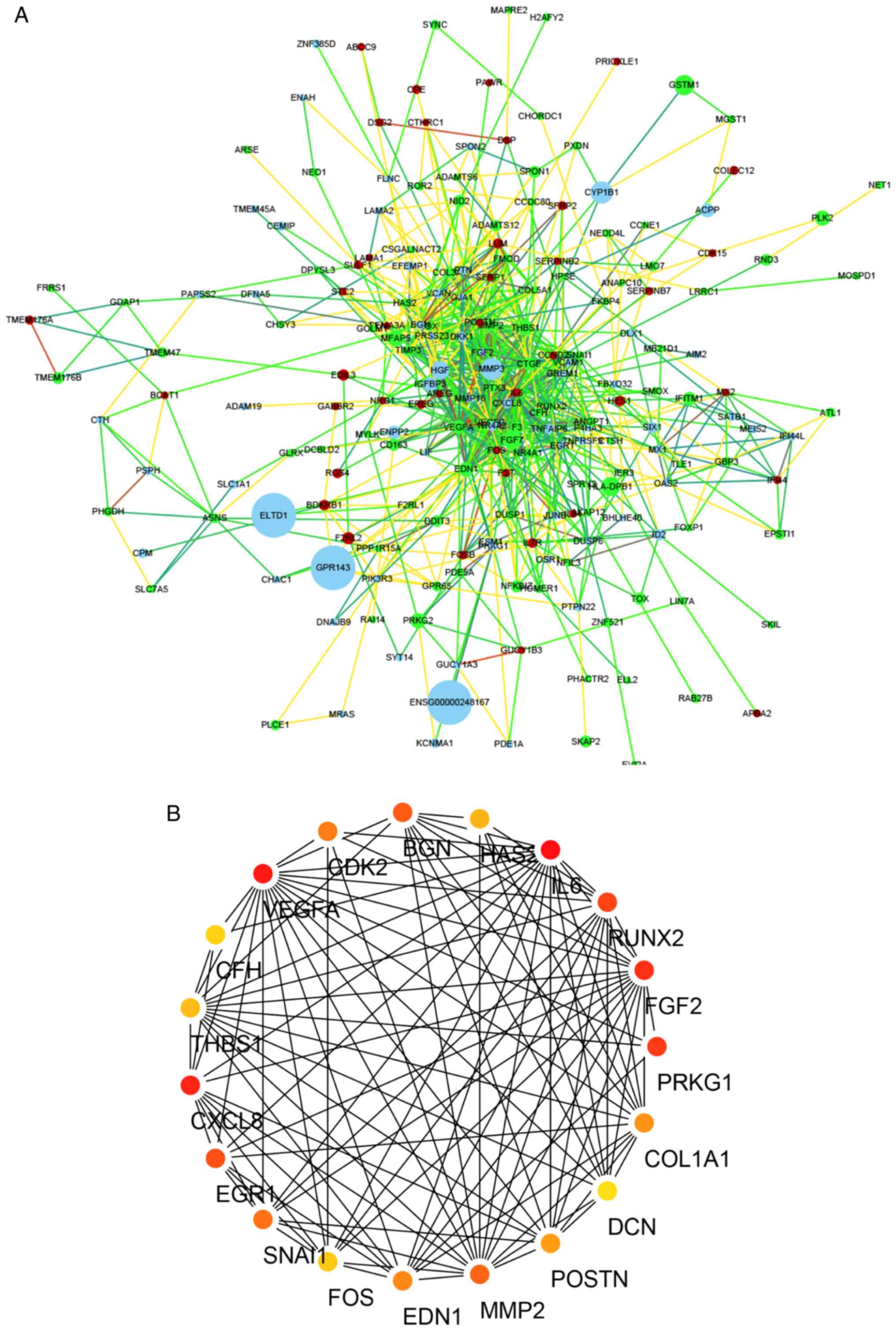
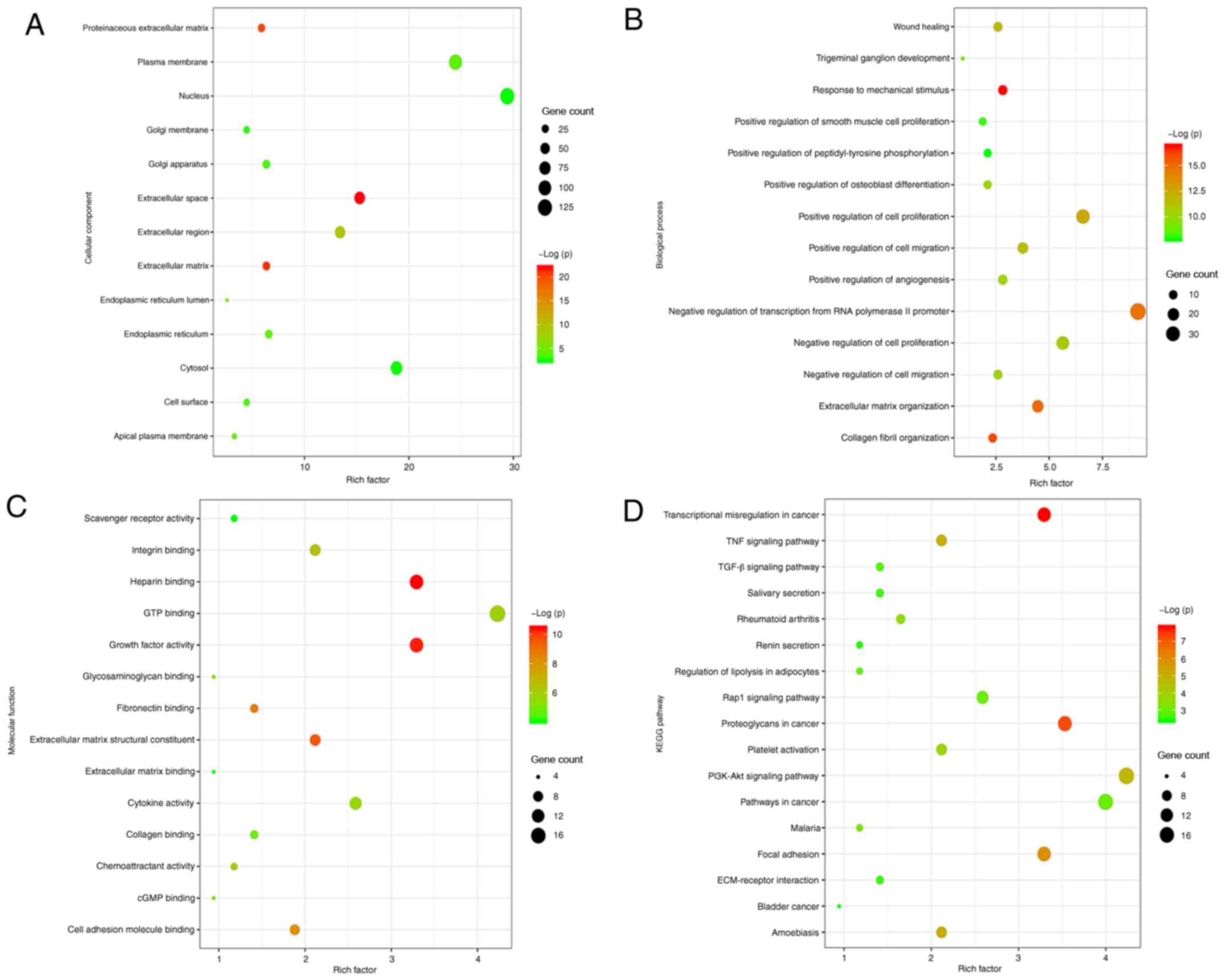
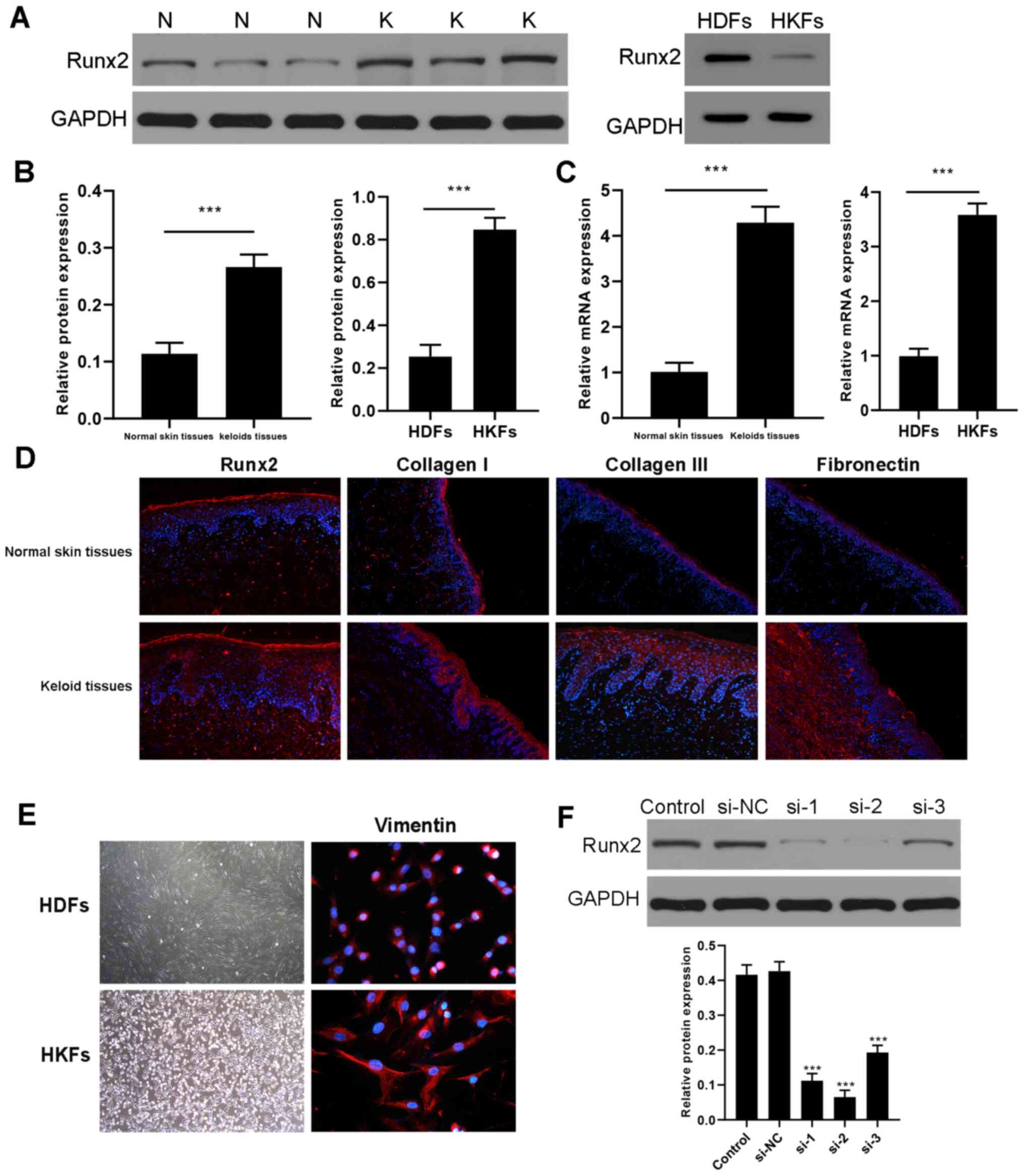
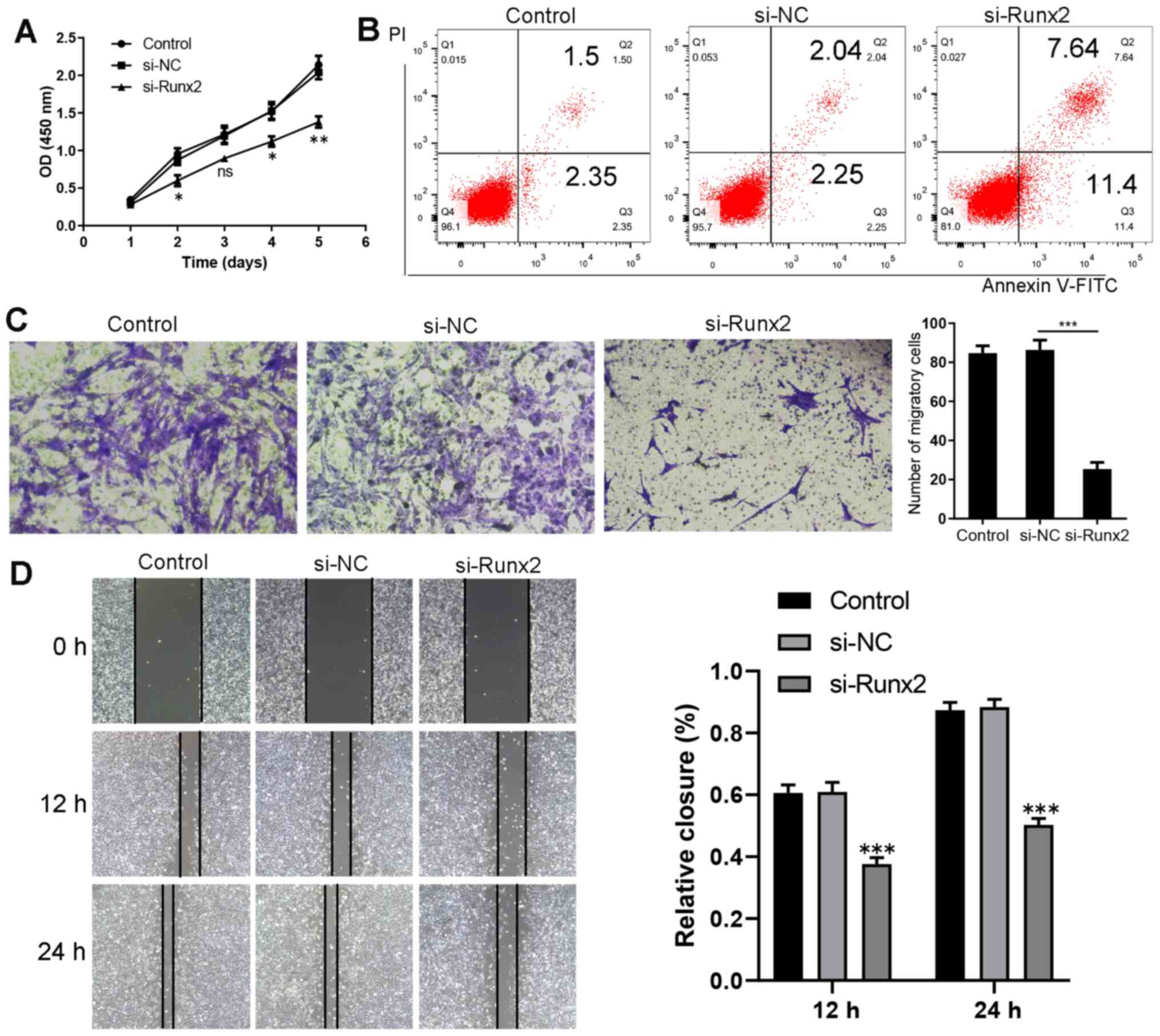
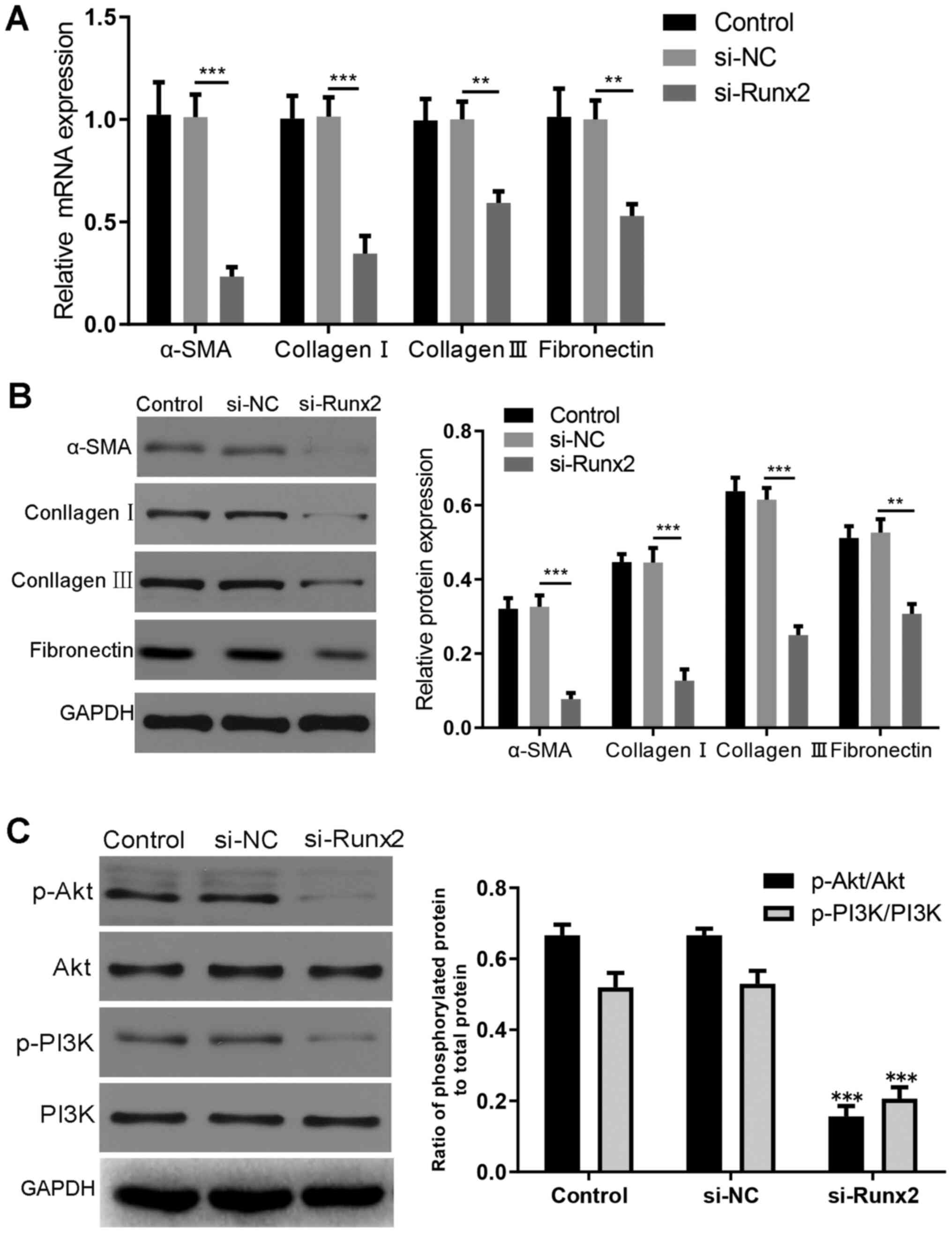
|
1
|
Ud-Din S and Bayat A: New insights on
keloids, hypertrophic scars, and striae. Dermatol Clin. 32:193–209.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
de Oliveira GV and Gold MH: Hydrocolloid
dressings can be used to treat hypertrophic scars: An outpatient
dermatology service devoted to treat keloids and challenging scars.
J Cosmet Dermatol. Oct 26–2020.(Epub ahead of print). doi:
10.1111/jocd.13792 2020.
|
|
3
|
Li Y, Liu H, Liang Y, Peng P, Ma X and
Zhang X: DKK3 regulates cell proliferation, apoptosis and collagen
synthesis in keloid fibroblasts via TGF-β1/Smad signaling pathway.
Biomed Pharmacother. 91:174–180. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Lee JY, Yang CC, Chao SC and Wong TW:
Histopathological differential diagnosis of keloid and hypertrophic
scar. Am J Dermatopathol. 26:379–384. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Lee YS, Liang YC, Wu P, Kulber DA, Tanabe
K, Chuong CM, Widelitz R and Tuan TL: STAT3 signalling pathway is
implicated in keloid pathogenesis by preliminary transcriptome and
open chromatin analyses. Exp Dermatol. 28:480–484. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Zhang Q, Cai L, Wang M, Ke X, Zhao X and
Huang Y: Identification of a novel mutation in the
mechanoreceptor-encoding gene CXCR1 in patients with keloid. Arch
Dermatol Res. 310:561–566. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Liu J, Zhu H, Wang H, Li J, Han F, Liu Y,
Zhang W, He T, Li N, Zheng Z, et al: Methylation of secreted
frizzled-related protein 1 (SFRP1) promoter downregulates
Wnt/β-catenin activity in keloids. J Mol Histol. 49:185–193. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Bijlard E, Kouwenberg CA, Timman R, Hovius
SE, Busschbach JJ and Mureau MA: Burden of Keloid Disease: A
Cross-sectional Health-related Quality of Life Assessment. Acta
Derm Venereol. 97:225–229. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Chen L, Zhang YH, Wang S, Zhang Y, Huang T
and Cai YD: Prediction and analysis of essential genes using the
enrichments of gene ontology and KEGG pathways. PLoS One.
12:e01841292017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Liu W, Huang X, Liang X, Zhou Y, Li H, Yu
Q and Li Q: Identification of Key Modules and Hub Genes of Keloids
with Weighted Gene Coexpression Network Analysis. Plast Reconstr
Surg. 139:376–390. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Fagone P, Mazzon E, Cavalli E, Bramanti A,
Petralia MC, Mangano K, Al-Abed Y, Bramati P and Nicoletti F:
Contribution of the macrophage migration inhibitory factor
superfamily of cytokines in the pathogenesis of preclinical and
human multiple sclerosis: In silico and in vivo evidences. J
Neuroimmunol. 322:46–56. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Presti M, Mazzon E, Basile MS, Petralia
MC, Bramanti A, Colletti G, Bramanti P, Nicoletti F and Fagone P:
Overexpression of macrophage migration inhibitory factor and
functionally-related genes, D-DT, CD74, CD44, CXCR2 and CXCR4, in
glioblastoma. Oncol Lett. 16:2881–2886. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Mevel R, Draper JE, Lie ALM, Kouskoff V
and Lacaud G: RUNX transcription factors: orchestrators of
development. Development. 146:dev1482962019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Mümmler C, Burgy O, Hermann S, Mutze K,
Günther A and Königshoff M: Cell-specific expression of
runt-related transcription factor 2 contributes to pulmonary
fibrosis. FASEB J. 32:703–716. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Herreño AM, Ramírez AC, Chaparro VP,
Fernandez MJ, Cañas A, Morantes CF, Moreno OM, Brugés RE, Mejía JA,
Bustos FJ, et al: Role of RUNX2 transcription factor in epithelial
mesenchymal transition in non-small cell lung cancer lung cancer:
Epigenetic control of the RUNX2 P1 promoter. Tumour Biol.
41:1010428319851014. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Fagone P, Mangano K, Pesce A, Portale TR,
Puleo S and Nicoletti F: Emerging therapeutic targets for the
treatment of hepatic fibrosis. Drug Discov Today. 21:369–375. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Fagone P, Mangano K, Mammana S, Pesce A,
Pesce A, Caltabiano R, Giorlandino A, Portale TR, Cavalli E,
Lombardo GA, et al: Identification of novel targets for the
diagnosis and treatment of liver fibrosis. Int J Mol Med.
36:747–752. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Chen J, Lin Y and Sun Z: Deficiency in the
anti-aging gene Klotho promotes aortic valve fibrosis through
AMPKα-mediated activation of RUNX2. Aging Cell. 15:853–860. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Tchetina EV, Demidova NV, Markova GA,
Taskina EA, Glukhova SI and Karateev DE: Increased baseline RUNX2,
caspase 3 and p21 gene expressions in the peripheral blood of
disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drug-naïve rheumatoid arthritis
patients are associated with improved clinical response to
methotrexate therapy. Int J Rheum Dis. 20:1468–1480. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Hahn JM, Glaser K, McFarland KL, Aronow
BJ, Boyce ST and Supp DM: Keloid-derived keratinocytes exhibit an
abnormal gene expression profile consistent with a distinct causal
role in keloid pathology. Wound Repair Regen. 21:530–544. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Chen YT, Yao JN, Qin YT, Hu K, Wu F and
Fang YY: Biological role and clinical value of miR-99a-5p in head
and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC): A bioinformatics-based
study. FEBS Open Bio. 8:1280–1298. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Kang SU, Kim YS, Kim YE, Park JK, Lee YS,
Kang HY, Jang JW, Ryeo JB, Lee Y, Shin YS, et al: Opposite effects
of non-thermal plasma on cell migration and collagen production in
keloid and normal fibroblasts. PLoS One. 12:e01879782017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Garcia-Morales V, Friedrich J, Jorna LM,
Campos-Toimil M, Hammes HP, Schmidt M and Krenning G: The
microRNA-7-mediated reduction in EPAC-1 contributes to vascular
endothelial permeability and eNOS uncoupling in murine experimental
retinopathy. Acta Diabetol. 54:581–591. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Fang B, Liu Y, Zheng D, Shan S, Wang C,
Gao Y, Wang J, Xie Y, Zhang Y and Li Q: The effects of mechanical
stretch on the biological characteristics of human adipose-derived
stem cells. J Cell Mol Med. 23:4244–4255. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Zhang M, Zeng J, Zhao Z and Liu Z: Loss of
MiR-424-3p, not miR-424-5p, confers chemoresistance through
targeting YAP1 in non-small cell lung cancer. Mol Carcinog.
56:821–832. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Rotgers E, Nurmio M, Pietilä E,
Cisneros-Montalvo S and Toppari J: E2F1 controls germ cell
apoptosis during the first wave of spermatogenesis. Andrology.
3:1000–1014. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Gene Ontology C; Gene Ontology Consortium,
: Gene Ontology Consortium: Going forward. Nucleic Acids Res.
43D:D1049–D1056. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Kanehisa M, Furumichi M, Tanabe M, Sato Y
and Morishima K: KEGG: New perspectives on genomes, pathways,
diseases and drugs. Nucleic Acids Res. 45D1:D353–D361. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Cavalli E, Battaglia G, Basile MS, Bruno
V, Petralia MC, Lombardo SD, Pennisi M, Kalfin R, Tancheva L,
Fagone P, et al: Exploratory Analysis of iPSCS-Derived Neuronal
Cells as Predictors of Diagnosis and Treatment of Alzheimer
Disease. Brain Sci. 10:1662020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Zhang Y, Cheng C, Wang S, Xu M, Zhang D
and Zeng W: Knockdown of FOXM1 inhibits activation of keloid
fibroblasts and extracellular matrix production via inhibition of
TGF-β1/Smad pathway. Life Sci. 232:1166372019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Berman B, Maderal A and Raphael B: Keloids
and Hypertrophic Scars: Pathophysiology, Classification, and
Treatment. Dermatol Surg. 43 (Suppl 1):S3–S18. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Bock O, Schmid-Ott G, Malewski P and
Mrowietz U: Quality of life of patients with keloid and
hypertrophic scarring. Arch Dermatol Res. 297:433–438. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Liu Q, Wang X and Jia Y: Heat Shock
Protein 90 Inhibitor Decreases Collagen Synthesis of Keloid
Fibroblasts and Attenuates the Extracellular Matrix on the Keloid
Spheroid Model. Plast Reconstr Surg. 137:759e–760e. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Philandrianos C, Kerfant N, Jaloux C Jr,
Martinet L, Bertrand B and Casanova D: Keloid scars (part I):
Clinical presentation, epidemiology, histology and pathogenesis.
Ann Chir Plast Esthet. 61:128–135. 2016.(In French). View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Chen J, Liu K, Liu Y, Wang X and Zhang Z:
Targeting mTORC1/2 with OSI-027 inhibits proliferation and
migration of keloid keratinocytes. Exp Dermatol. 28:270–275. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Ogawa R: Keloid and Hypertrophic Scars Are
the Result of Chronic Inflammation in the Reticular Dermis. Int J
Mol Sci. 18:6062017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Komori T: Regulation of Proliferation,
Differentiation and Functions of Osteoblasts by Runx2. Int J Mol
Sci. 20:16942019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Li G, Li YY, Sun JE, Lin WH and Zhou RX:
ILK-PI3K/AKT pathway participates in cutaneous wound contraction by
regulating fibroblast migration and differentiation to
myofibroblast. Lab Invest. 96:741–751. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Evangelisti C, Evangelisti C, Chiarini F,
Lonetti A, Buontempo F, Bressanin D, Cappellini A, Orsini E,
McCubrey JA and Martelli AM: Therapeutic potential of targeting
mTOR in T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (review). Int J Oncol.
45:909–918. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Sharma VR, Gupta GK and Sharma AK, Batra
N, Sharma DK, Joshi A and Sharma AK: PI3K/Akt/mTOR Intracellular
Pathway and Breast Cancer: Factors, Mechanism and Regulation. Curr
Pharm Des. 23:1633–1638. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Steelman LS, Martelli AM, Cocco L, Libra
M, Nicoletti F, Abrams SL and McCubrey JA: The therapeutic
potential of mTOR inhibitors in breast cancer. Br J Clin Pharmacol.
82:1189–1212. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Ge F, Wang F, Yan X, Li Z and Wang X:
Association of BAFF with PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling in lupus
nephritis. Mol Med Rep. 16:5793–5798. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Fagone P, Ciurleo R, Lombardo SD,
Iacobello C, Palermo CI, Shoenfeld Y, Bendtzen K, Bramanti P and
Nicoletti F: Transcriptional landscape of SARS-CoV-2 infection
dismantles pathogenic pathways activated by the virus, proposes
unique sex-specific differences and predicts tailored therapeutic
strategies. Autoimmun Rev. 19:1025712020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Nicoletti F, Fagone P, Meroni P, McCubrey
J and Bendtzen K: mTOR as a multifunctional therapeutic target in
HIV infection. Drug Discov Today. 16:715–721. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Tu T, Huang J, Lin M, Gao Z, Wu X, Zhang
W, Zhou G, Wang W and Liu W: CUDC 907 reverses pathological
phenotype of keloid fibroblasts in vitro and in vivo via
dual inhibition of PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling and HDAC2. Int J Mol
Med. 44:1789–1800. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Aragona M and Blanpain C: Gene therapy:
Transgenic stem cells replace skin. Nature. 551:306–307. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Mavilio F, Pellegrini G, Ferrari S, Di
Nunzio F, Di Iorio E, Recchia A, Maruggi G, Ferrari G, Provasi E,
Bonini C, et al: Correction of junctional epidermolysis bullosa by
transplantation of genetically modified epidermal stem cells. Nat
Med. 12:1397–1402. 2006. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Wang W, Qu M, Xu L, Wu X, Gao Z, Gu T,
Zhang W, Ding X, Liu W and Chen YL: Sorafenib exerts an anti-keloid
activity by antagonizing TGF-β/Smad and MAPK/ERK signaling
pathways. J Mol Med (Berl). 94:1181–1194. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Tian Y, Jin L, Zhang W, Ya Z, Cheng Y and
Zhao H: AMF siRNA treatment of keloid through inhibition signaling
pathway of RhoA/ROCK1. Genes Dis. 6:185–192. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|