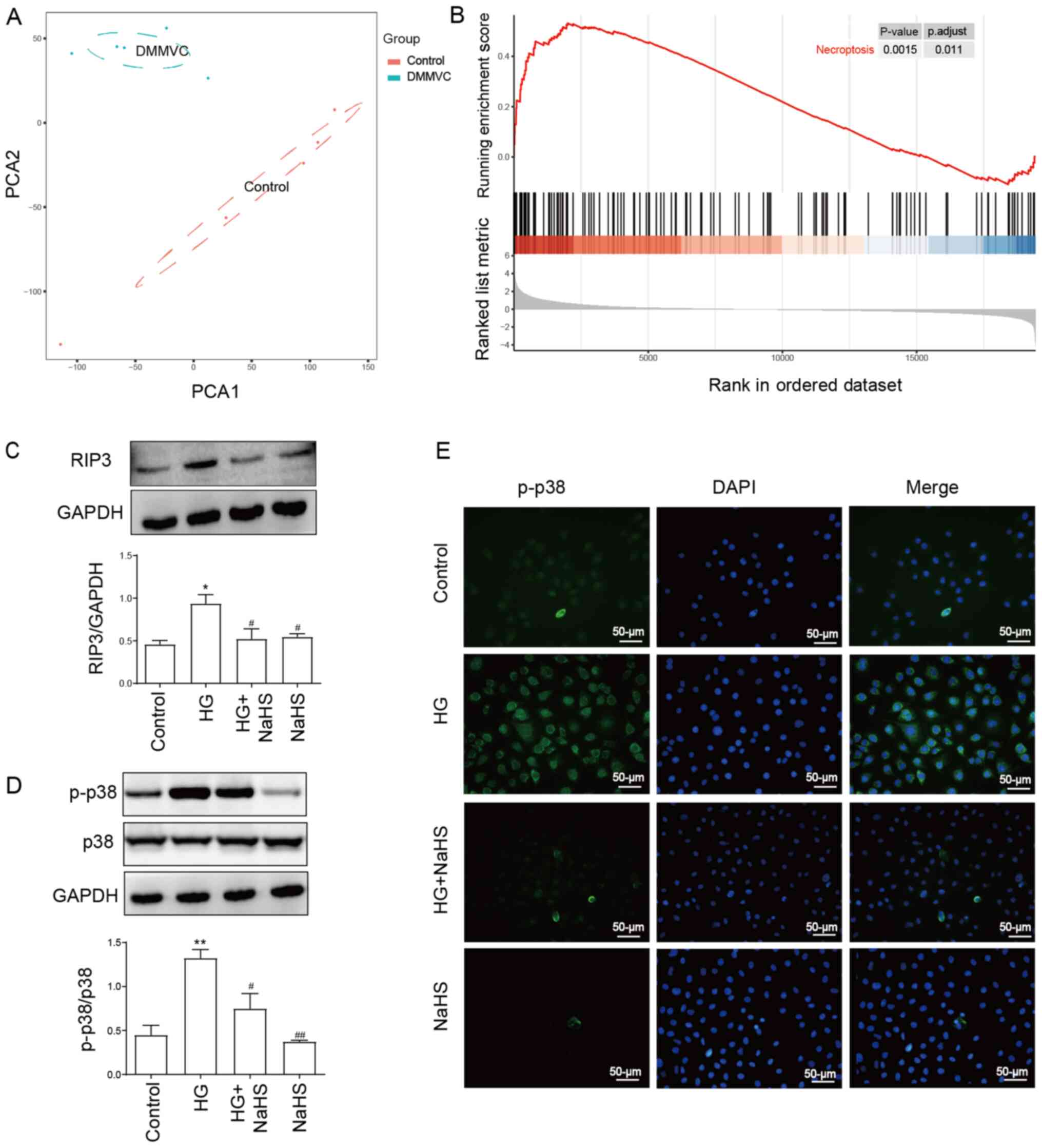
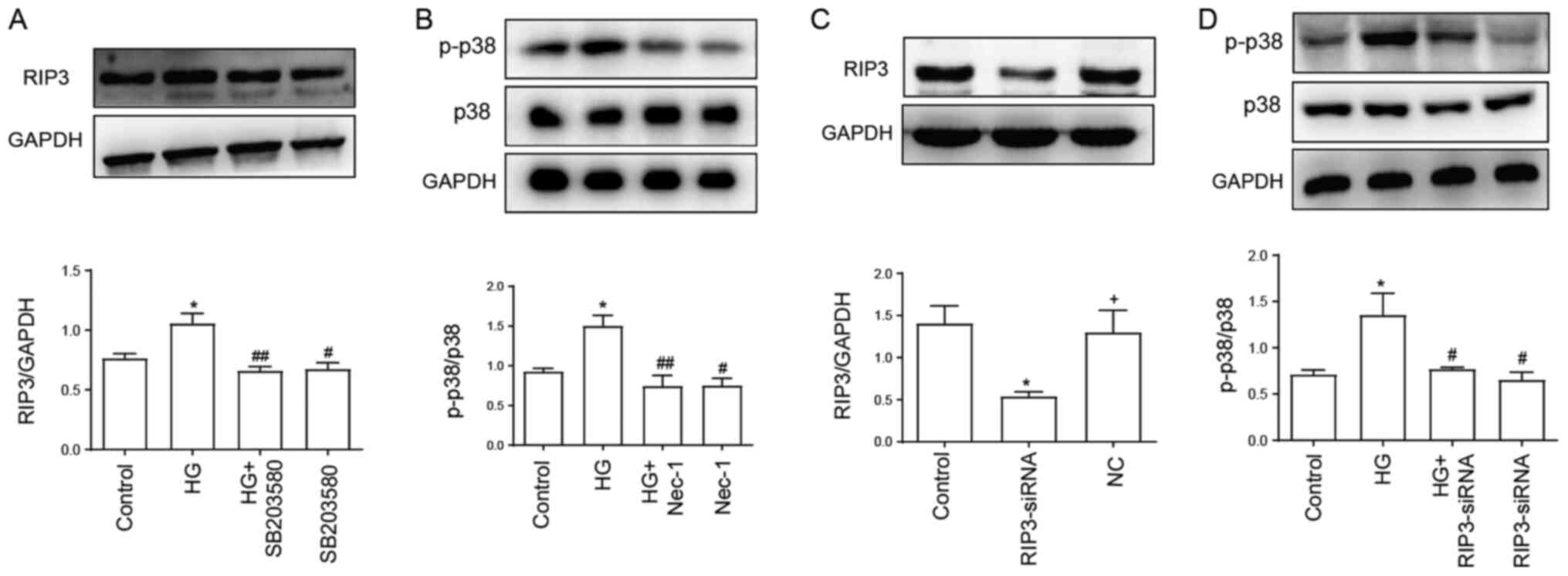
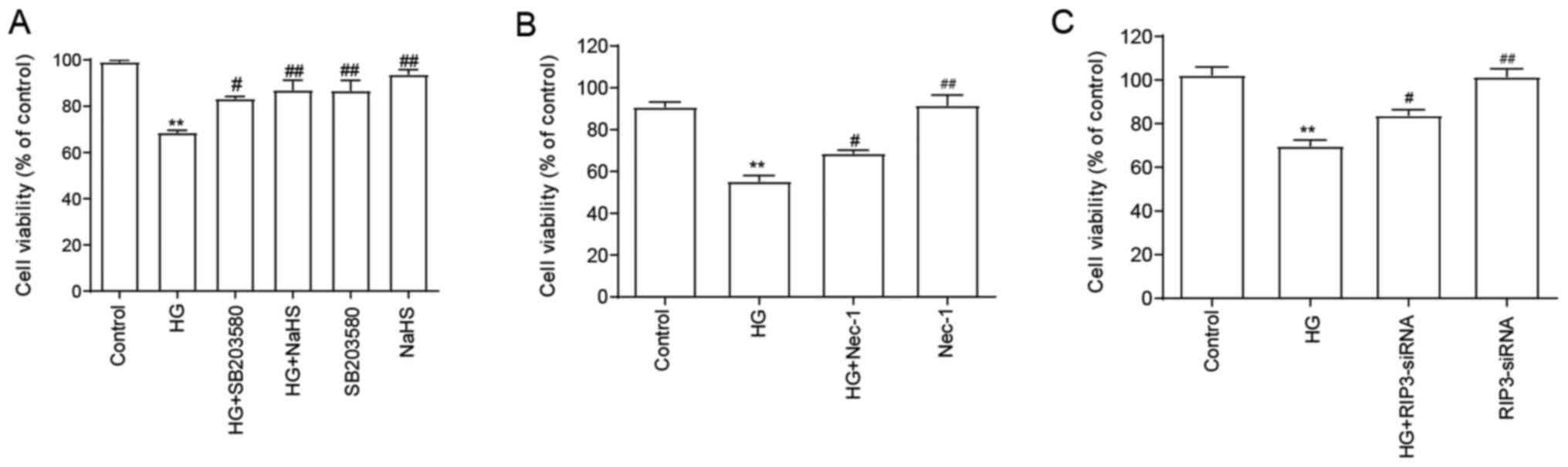
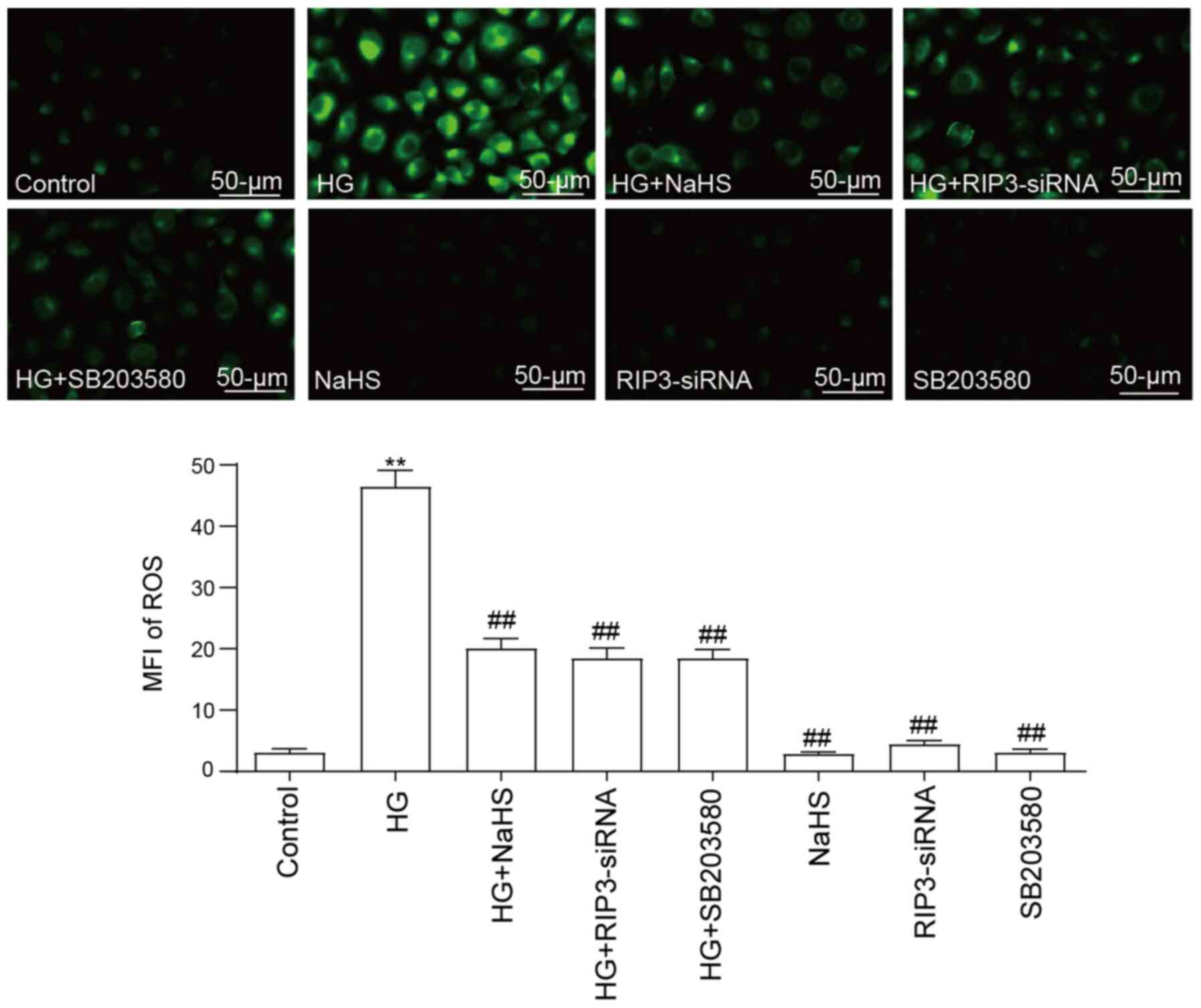
|
1
|
Jeffery N and Harries LW: β-cell
differentiation status in type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Obes Metab.
18:1167–1175. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
da Rocha Fernandes J, Ogurtsova K,
Linnenkamp U, Guariguata L, Seuring T, Zhang P, Cavan D and
Makaroff LE: IDF diabetes atlas estimates of 2014 global health
expenditures on diabetes. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 117:48–54. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Sahajpal NS, Goel RK, Chaubey A, Aurora R
and Jain SK: Pathological perturbations in diabetic retinopathy:
Hyperglycemia, AGEs, oxidative stress and inflammatory pathways.
Curr Protein Pept Sci. 20:92–110. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Liu H, Wang X, Liu S and Li H, Yuan X,
Feng B, Bai H, Zhao B, Chu Y and Li H: Effects and mechanism of
miR-23b on glucose-mediated epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in
diabetic nephropathy. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 70:149–160. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Laakso M and Kuusisto J: Insulin
resistance and hyperglycaemia in cardiovascular disease
development. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 10:293–302. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Li Y, Shelat H, Wu H, Zhu M, Xu J and Geng
YJ: Low circulating level of IGF-1 is a distinct indicator for the
development of cardiovascular disease caused by combined
hyperglycemia and dyslipidemia. Int J Cardiol. 171:272–273. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Yerra VG, Areti A and Kumar A: Adenosine
monophosphate-activated protein kinase abates
hyperglycaemia-induced neuronal injury in experimental models of
diabetic neuropathy: Effects on mitochondrial biogenesis, autophagy
and neuroinflammation. Mol Neurobiol. 54:2301–2312. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Suzuki K, Olah G, Modis K, Coletta C, Kulp
G, Gerö D, Szoleczky P, Chang T, Zhou Z, Wu L, et al: Hydrogen
sulfide replacement therapy protects the vascular endothelium in
hyperglycemia by preserving mitochondrial function. Proc Natl Acad
Sci USA. 108:13829–13834. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Ceriello A, Novials A, Ortega E, Canivell
S, La Sala L, Pujadas G, Esposito K, Giugliano D and Genovese S:
Glucagon-like peptide 1 reduces endothelial dysfunction,
inflammation, and oxidative stress induced by both hyperglycemia
and hypoglycemia in type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Care. 36:2346–2350.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Chen H, Wan Y, Zhou S, Lu Y, Zhang Z,
Zhang R, Chen F, Hao D, Zhao X, Guo Z, et al: Endothelium-specific
SIRT1 overexpression inhibits hyperglycemia-induced upregulation of
vascular cell senescence. Sci China Life Sci. 55:467–473. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Yokoyama M, Shimizu I, Nagasawa A, Yoshida
Y, Katsuumi G, Wakasugi T, Hayashi Y, Ikegami R, Suda M, Ota Y, et
al: p53 plays a crucial role in endothelial dysfunction associated
with hyperglycemia and ischemia. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 129:105–117.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Song W, Wei L, Du Y, Wang Y and Jiang S:
Protective effect of ginsenoside metabolite compound K against
diabetic nephropathy by inhibiting NLRP3 inflammasome activation
and NF-κB/p38 signaling pathway in high-fat
diet/streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice. Int Immunopharmacol.
63:227–238. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Chen P, Yuan Y, Zhang T, Xu B, Gao Q and
Guan T: Pentosan polysulfate ameliorates apoptosis and inflammation
by suppressing activation of the p38 MAPK pathway in high
glucose-treated HK-2 cells. Int J Mol Med. 41:908–914.
2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Chen Y, Wang JJ, Li J, Hosoya KI, Ratan R,
Townes T and Zhang SX: Activating transcription factor 4 mediates
hyperglycaemia-induced endothelial inflammation and retinal
vascular leakage through activation of STAT3 in a mouse model of
type 1 diabetes. Diabetologia. 55:2533–2545. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Perkins JM, Joy NG, Tate DB and Davis SN:
Acute effects of hyperinsulinemia and hyperglycemia on vascular
inflammatory biomarkers and endothelial function in overweight and
obese humans. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 309:E168–E176. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Jung UJ and Choi MS: Obesity and its
metabolic complications: The role of adipokines and the
relationship between obesity, inflammation, insulin resistance,
dyslipidemia and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Int J Mol Sci.
15:6184–6223. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Li J, Bao L, Zha D, Zhang L, Gao P, Zhang
J and Wu X: Oridonin protects against the inflammatory response in
diabetic nephropathy by inhibiting the TLR4/p38-MAPK and TLR4/NF-κB
signaling pathways. Int Immunopharmacol. 55:9–19. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Arcambal A, Taïlé J, Rondeau P,
Viranaïcken W, Meilhac O and Gonthier MP: Hyperglycemia modulates
redox, inflammatory and vasoactive markers through specific
signaling pathways in cerebral endothelial cells: Insights on
insulin protective action. Free Radic Biol Med. 130:59–70. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Shanmuganathan S and Angayarkanni N:
Chebulagic acid chebulinic acid and Gallic acid, the active
principles of Triphala, inhibit TNFα induced pro-angiogenic and
pro-inflammatory activities in retinal capillary endothelial cells
by inhibiting p38, ERK and NFkB phosphorylation. Vascul Pharmacol.
108:23–35. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Dhuriya YK and Sharma D: Necroptosis: A
regulated inflammatory mode of cell death. J Neuroinflammation.
15:1992018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Zhe-Wei S, Li-Sha G and Yue-Chun L: The
role of necroptosis in cardiovascular disease. Front Pharmacol.
9:7212018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Chan FKM, Luz NF and Moriwaki K:
Programmed necrosis in the cross talk of cell death and
inflammation. Annu Rev Immunol. 33:79–106. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
He S, Wang L, Miao L, Wang T, Du F, Zhao L
and Wang X: Receptor interacting protein kinase-3 determines
cellular necrotic response to TNF-alpha. Cell. 137:1100–1111. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Cho YS, Challa S, Moquin D, Genga R, Ray
TD, Guildford M and Chan FKM: Phosphorylation-driven assembly of
the RIP1-RIP3 complex regulates programmed necrosis and
virus-induced inflammation. Cell. 137:1112–1123. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Newton K and Manning G: Necroptosis and
inflammation. Annu Rev Biochem. 85:743–763. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Silke J, Rickard JA and Gerlic M: The
diverse role of RIP kinases in necroptosis and inflammation. Nat
Immunol. 16:689–697. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Negroni A, Colantoni E, Pierdomenico M,
Palone F, Costanzo M, Oliva S, Tiberti A, Cucchiara S and Stronati
L: RIP3 AND pMLKL promote necroptosis-induced inflammation and
alter membrane permeability in intestinal epithelial cells. Dig
Liver Dis. 49:1201–1210. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Wang L, Wang T, Li H, Liu Q, Zhang Z, Xie
W, Feng Y, Socorburam T, Wu G, Xia Z and Wu Q: Receptor interacting
protein 3-mediated necroptosis promotes lipopolysaccharide-induced
inflammation and acute respiratory distress syndrome in mice. PLoS
One. 11:e01557232016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Lin J, Chen M, Liu D, Guo R, Lin K, Deng
H, Zhi X, Zhang W, Feng J and Wu W: Exogenous hydrogen sulfide
protects human umbilical vein endothelial cells against high
glucoseinduced injury by inhibiting the necroptosis pathway. Int J
Mol Med. 41:1477–1486. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Feng T, Chen W, Zhang C, Xiang J, Ding HM,
Wu LL and Geng D: The p38/CYLD pathway is involved in necroptosis
induced by oxygen-glucose deprivation combined with ZVAD in primary
cortical neurons. Neurochem Res. 42:2294–2304. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Qin S, Yang C, Huang W, Du S, Mai H, Xiao
J and Lü T: Sulforaphane attenuates microglia-mediated neuronal
necroptosis through down-regulation of MAPK/NF-κB signaling
pathways in LPS-activated BV-2 microglia. Pharmacol Res.
133:218–235. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Wang D, Zhao M, Chen G, Cheng X, Han X,
Lin S, Zhang X and Yu X: The histone deacetylase inhibitor
vorinostat prevents TNFα-induced necroptosis by regulating multiple
signaling pathways. Apoptosis. 18:1348–1362. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Łowicka E and Bełtowski J: Hydrogen
sulfide (H2S)-the third gas of interest for pharmacologists.
Pharmacol Rep. 59:4–24. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Gemici B, Elsheikh W, Feitosa KB, Costa
SK, Muscara MN and Wallace JL: H2S-releasing drugs:
Anti-inflammatory, cytoprotective and chemopreventative potential.
Nitric Oxide. 46:25–31. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Citi V, Piragine E, Testai L, Breschi MC,
Calderone V and Martelli A: The role of hydrogen sulfide and
H2S-donors in myocardial protection against ischemia/reperfusion
injury. Curr Med Chem. 25:4380–4401. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Xu S, Liu Z and Liu P: Targeting hydrogen
sulfide as a promising therapeutic strategy for atherosclerosis.
Int J Cardiol. 172:313–317. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Kumar M and Sandhir R: Hydrogen sulfide
suppresses homocysteine-induced glial activation and inflammatory
response. Nitric Oxide. 90:15–28. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Huang Z, Dong X, Zhuang X, Hu X, Wang L
and Liao X: Exogenous hydrogen sulfide protects against high
glucose-induced inflammation and cytotoxicity in H9c2 cardiac
cells. Mol Med Rep. 14:4911–4917. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Zhang L, Jia YH, Zhao XS, Zhou FH, Pan YY,
Wan Q, Cui XB, Sun XG, Chen YY, Zhang Y and Cheng SB:
Trichosanatine alleviates oxidized low-density lipoprotein induced
endothelial cells injury via inhibiting the LOX-1/p38 MAPK pathway.
Am J Transl Res. 8:5455–5464. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Daniele G, Guardado Mendoza R, Winnier D,
Fiorentino TV, Pengou Z, Cornell J, Andreozzi F, Jenkinson C,
Cersosimo E, Federici M, et al: The inflammatory status score
including IL-6, TNF-α, osteopontin, fractalkine, MCP-1 and
adiponectin underlies whole-body insulin resistance and
hyperglycemia in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Acta Diabetol.
51:123–131. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Smith RP and Gosselin RE: Hydrogen sulfide
poisoning. J Occup Med. 21:93–97. 1979. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Chatzianastasiou A, Bibli SI, Andreadou I,
Efentakis P, Kaludercic N, Wood ME, Whiteman M, Di Lisa F, Daiber
A, Manolopoulos VG, et al: Cardioprotection by H2S donors: Nitric
oxide-dependent and -independent mechanisms. J Pharmacol Exp Ther.
358:431–440. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Liu X, Ma D, Zheng S, Zha K, Feng J, Cai
Y, Jiang F, Li J and Fan Z: The roles of nitric oxide and hydrogen
sulfide in the anti-atherosclerotic effect of atorvastatin. J
Cardiovasc Med (Hagerstown). 16:22–28. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Bełtowski J, Wójcicka G and
Jamroz-Wiśniewska A: Hydrogen sulfide in the regulation of insulin
secretion and insulin sensitivity: Implications for the
pathogenesis and treatment of diabetes mellitus. Biochem Pharmacol.
149:60–76. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Wang Y, Zhao X, Jin H, Wei H, Li W, Bu D,
Tang X, Ren Y, Tang C and Du J: Role of hydrogen sulfide in the
development of atherosclerotic lesions in apolipoprotein E knockout
mice. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 29:173–179. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Guo R, Wu K, Chen J, Mo L, Hua X, Zheng D,
Chen P, Chen G, Xu W and Feng J: Exogenous hydrogen sulfide
protects against doxorubicin-induced inflammation and cytotoxicity
by inhibiting p38MAPK/NFκB pathway in H9c2 cardiac cells. Cell
Physiol Biochem. 32:1668–1680. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Yang C, Yang Z, Zhang M, Dong Q, Wang X,
Lan A, Zeng F, Chen P, Wang C and Feng J: Hydrogen sulfide protects
against chemical hypoxia-induced cytotoxicity and inflammation in
HaCaT cells through inhibition of ROS/NF-κB/COX-2 pathway. PLoS
One. 6:e219712011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Degterev A, Huang Z, Boyce M, Li Y, Jagtap
P, Mizushima N, Cuny GD, Mitchison TJ, Moskowitz MA and Yuan J:
Chemical inhibitor of nonapoptotic cell death with therapeutic
potential for ischemic brain injury. Nat Chem Biol. 1:112–119.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Lin J, Li H, Yang M, Ren J, Huang Z, Han
F, Huang J, Ma J, Zhang D, Zhang Z, et al: A role of RIP3-mediated
macrophage necrosis in atherosclerosis development. Cell Rep.
3:200–210. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Murakami Y, Matsumoto H, Roh M, Suzuki J,
Hisatomi T, Ikeda Y, Miller JW and Vavvas DG: Receptor interacting
protein kinase mediates necrotic cone but not rod cell death in a
mouse model of inherited degeneration. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
109:14598–14603. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Luedde M, Lutz M, Carter N, Sosna J,
Jacoby C, Vucur M, Gautheron J, Roderburg C, Borg N, Reisinger F,
et al: RIP3, a kinase promoting necroptotic cell death, mediates
adverse remodelling after myocardial infarction. Cardiovasc Res.
103:206–216. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Cao L, Chen X, Xiao X, Ma Q and Li W:
Resveratrol inhibits hyperglycemia-driven ROS-induced invasion and
migration of pancreatic cancer cells via suppression of the ERK and
p38 MAPK signaling pathways. Int J Oncol. 49:735–743. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Xu W, Wu W, Chen J, Guo R, Lin J, Liao X
and Feng J: Exogenous hydrogen sulfide protects H9c2 cardiac cells
against high glucose-induced injury by inhibiting the activities of
the p38 MAPK and ERK1/2 pathways. Int J Mol Med. 32:917–925. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Perry MM, Tildy B, Papi A, Casolari P,
Caramori G, Rempel KL, Halayko AJ, Adcock I and Chung KF: The
anti-proliferative and anti-inflammatory response of COPD airway
smooth muscle cells to hydrogen sulfide. Respir Res. 19:852018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Koike A, Hanatani M and Fujimori K:
Pan-caspase inhibitors induce necroptosis via ROS-mediated
activation of mixed lineage kinase domain-like protein and p38 in
classically activated macrophages. Exp Cell Res. 380:171–179. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Mazrouei S, Sharifpanah F, Caldwell RW,
Franz M, Shatanawi A, Muessig J, Fritzenwanger M, Schulze PC and
Jung C: Regulation of MAP kinase-mediated endothelial dysfunction
in hyperglycemia via arginase I and eNOS dysregulation. Biochim
Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res. 1866:1398–1411. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|