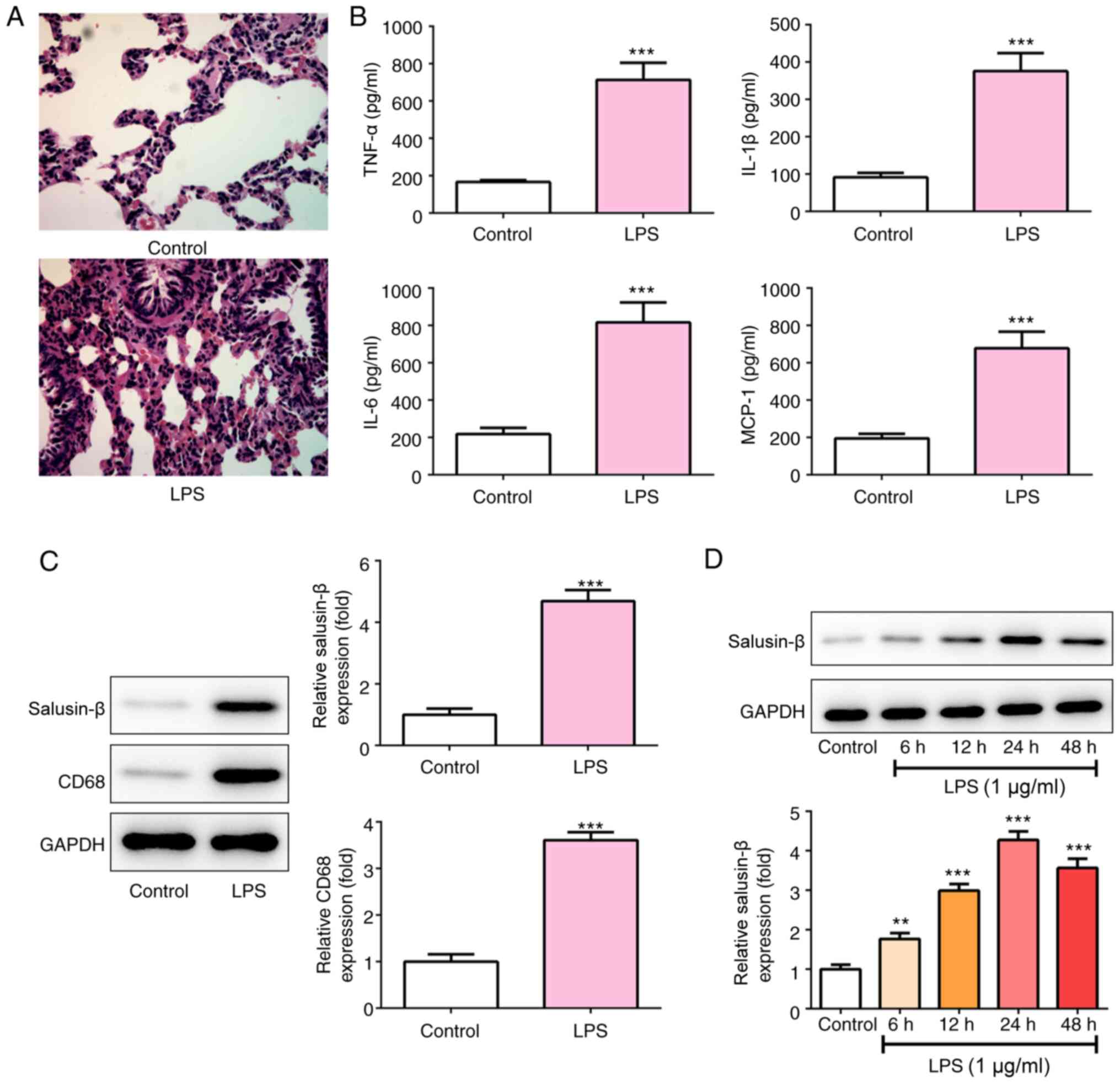
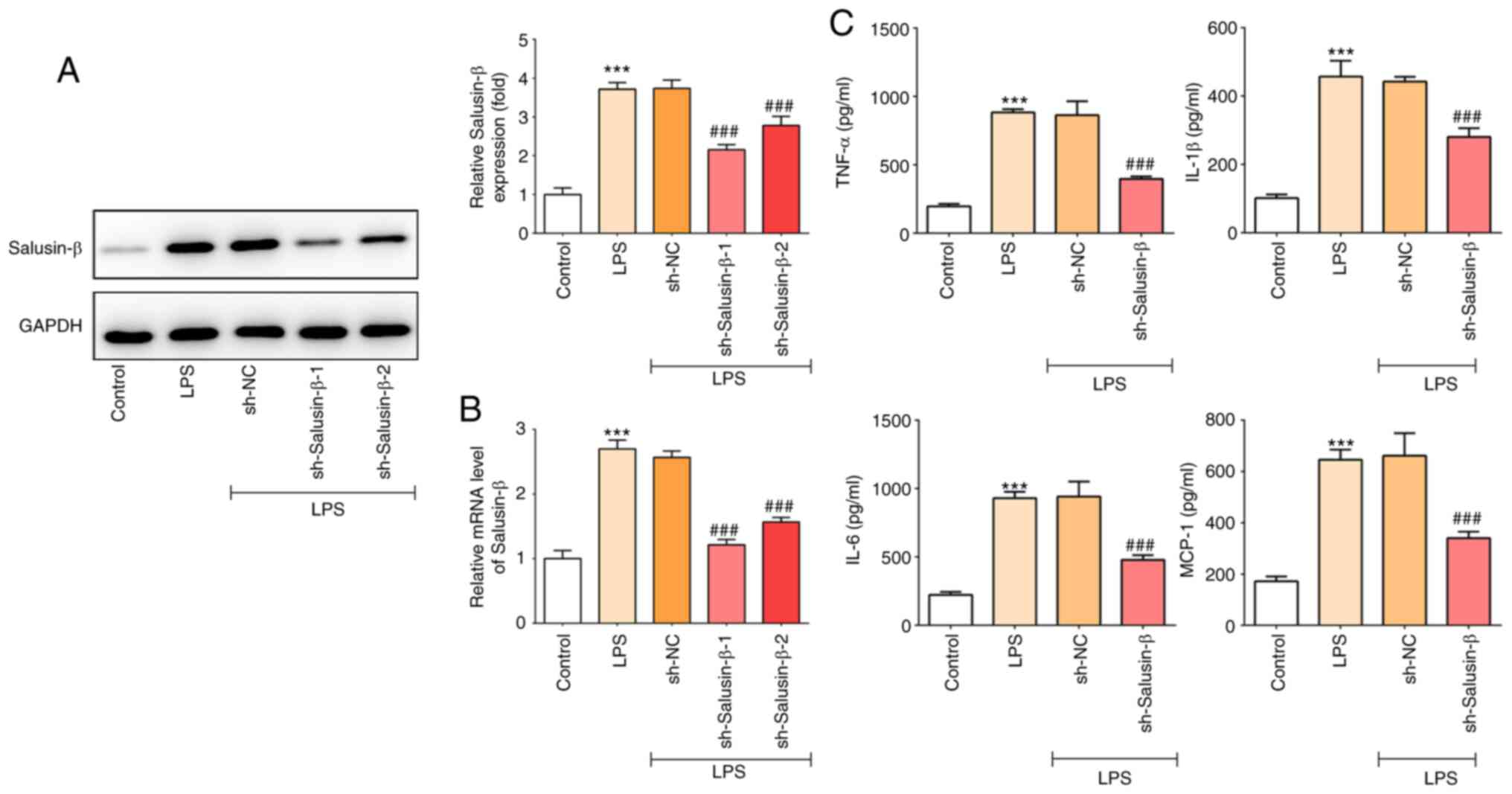
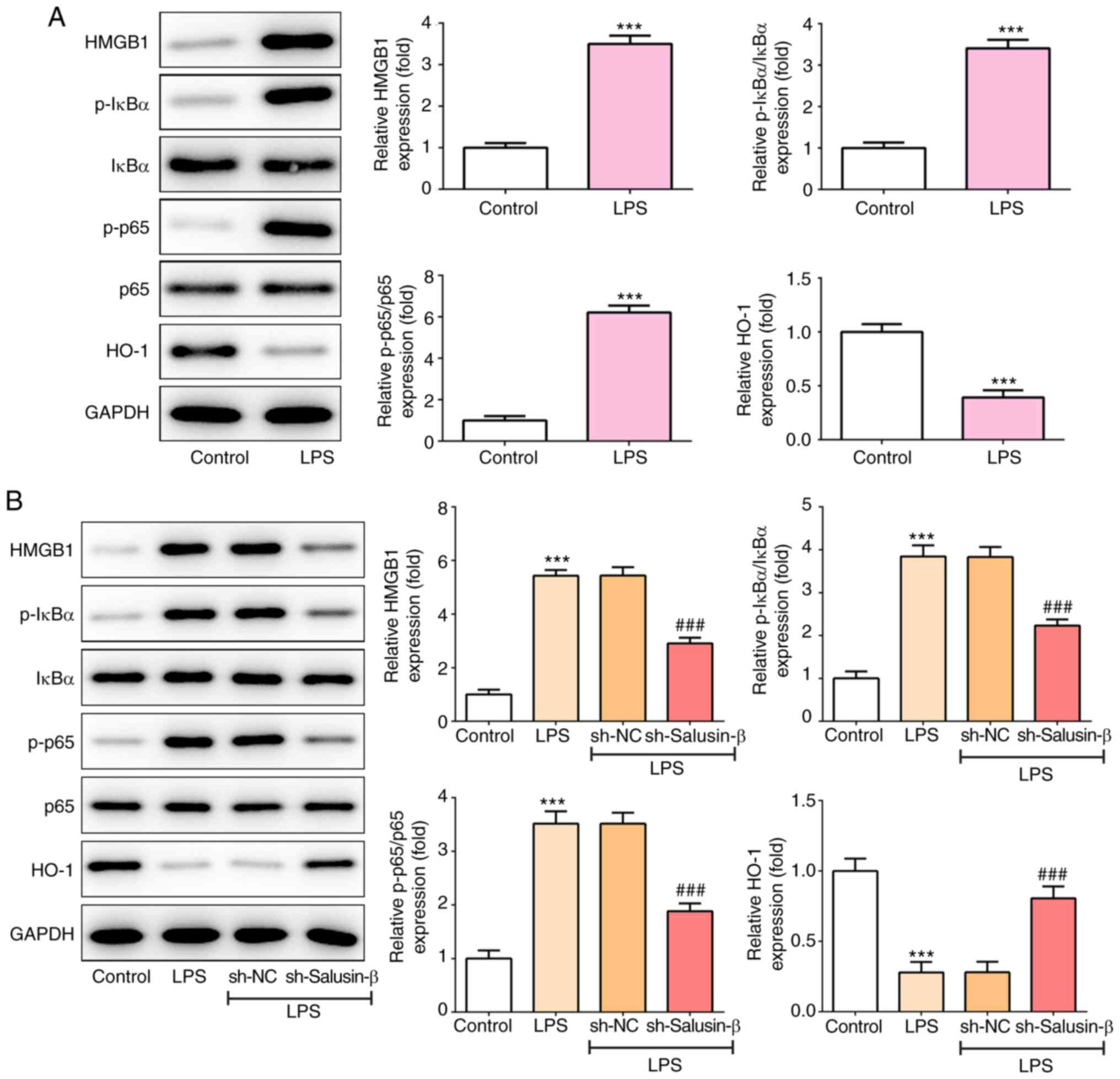
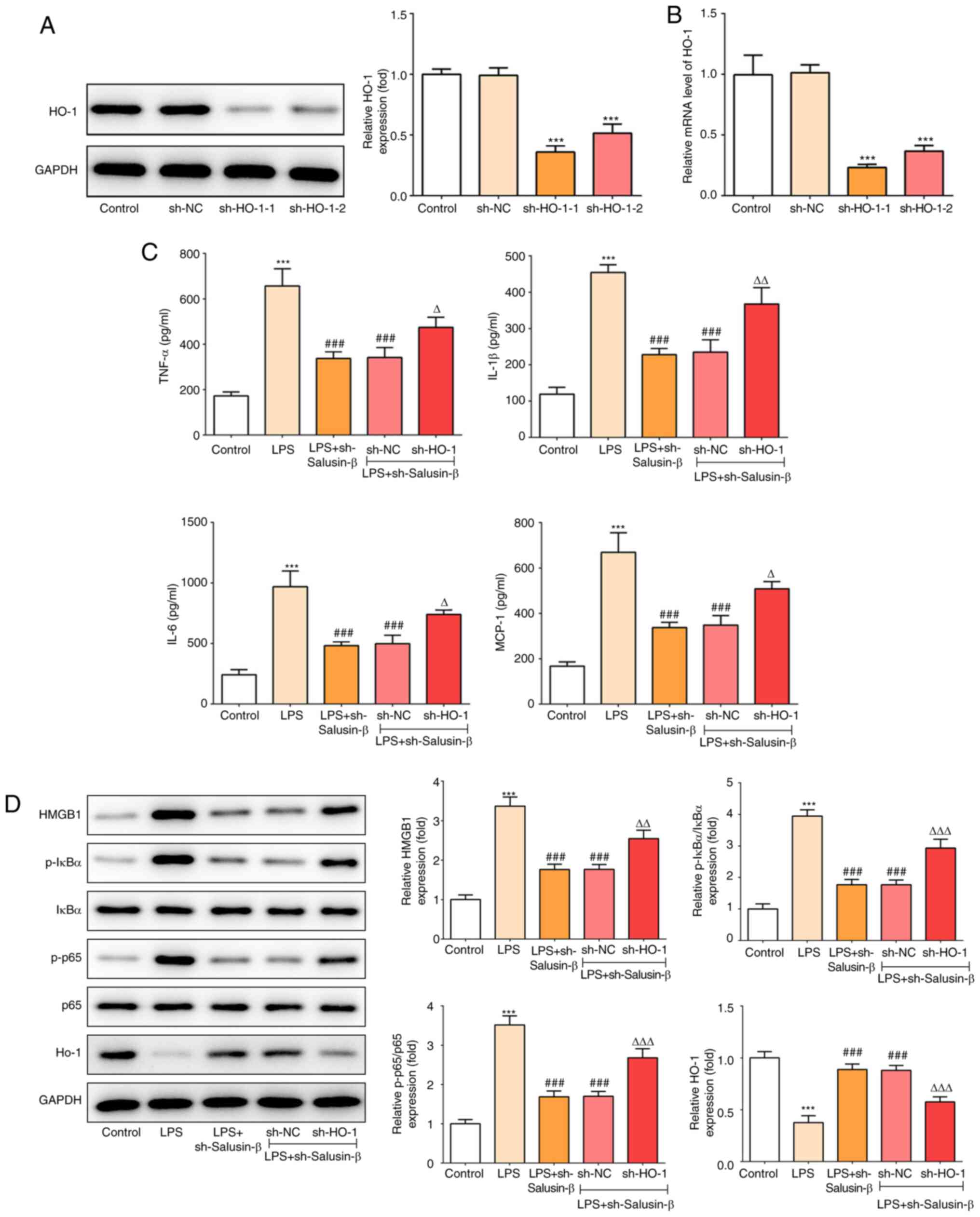
|
1
|
Summers C, Singh NR, Worpole L, Simmonds
R, Babar J, Condliffe AM, Gunning KE, Johnston AJ and Chilvers ER:
Incidence and recognition of acute respiratory distress syndrome in
a UK intensive care unit. Thorax. 71:1050–1051. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Gouda MM and Bhandary YP: Acute lung
injury: IL-17A-mediated inflammatory pathway and its regulation by
curcumin. Inflammation. 42:1160–1169. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Ware LB: Pathophysiology of acute lung
injury and the acute respiratory distress syndrome. Semin Respir
Crit Care Med. 27:337–349. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Laskin DL, Malaviya R and Laskin JD: Role
of macrophages in acute lung injury and chronic fibrosis induced by
pulmonary toxicants. Toxicol Sci. 168:287–301. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Johnson ER and Matthay MA: Acute lung
injury: Epidemiology, pathogenesis, and treatment. J Aerosol Med
Pulm Drug Deliv. 23:243–252. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Wu P, Yan H, Qi J, Jia W, Zhang W, Yao D,
Ding C, Zhang Y, Chen M and Cai X: L6H9 attenuates LPS-induced
acute lung injury in rats through targeting MD2. Drug Dev Res.
81:85–92. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Iwamura H, Inushima K, Takeuchi K,
Kakutani M and Wakitani K: Prophylactic effect of JTE-607 on
LPS-induced acute lung injury in rats with CINC-1 inhibition.
Inflamm Res. 51:160–166. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Sato K, Watanabe R, Itoh F, Shichiri M and
Watanabe T: Salusins: Potential use as a biomarker for
atherosclerotic cardiovascular diseases. Int J Hypertens.
2013:9651402013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Sun H, Zhang F, Xu Y, Sun S, Wang H, Du Q,
Gu C, Black SM, Han Y and Tang H: Salusin-β promotes vascular
calcification via nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide
phosphate/reactive oxygen species-mediated klotho downregulation.
Antioxid Redox Signal. 31:1352–1370. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Sun S, Zhang F, Pan Y, Xu Y, Chen A, Wang
J, Tang H and Han Y: A TOR2A gene product: Salusin-β contributes to
attenuated vasodilatation of spontaneously hypertensive rats.
Cardiovasc Drugs Ther. 2020.(Epub ahead of print). View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Zhou CH, Pan J, Huang H, Zhu Y, Zhang M,
Liu L and Wu Y: Salusin-β, but not salusin-α, promotes human
umbilical vein endothelial cell inflammation via the p38
MAPK/JNK-NF-κB pathway. PLoS One. 9:e1075552014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Zhou CH, Liu L, Liu L, Zhang MX, Guo H,
Pan J, Yin XX, Ma TF and Wu YQ: Salusin-β not salusin-α promotes
vascular inflammation in ApoE-deficient mice via the I-kBα/NF-κB
pathway. PLoS One. 9:e914682014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Xu T, Zhang Z, Liu T, Zhang W, Liu J, Wang
W and Wang J: Salusin-β contributes to vascular inflammation
associated with pulmonary arterial hypertension in rats. J Thorac
Cardiovasc Surg. 152:1177–1187. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zhao MX, Zhou B, Ling L, Xiong XQ, Zhang
F, Chen Q, Li YH, Kang YM and Zhu GQ: Salusin-β contributes to
oxidative stress and inflammation in diabetic cardiomyopathy. Cell
Death Dis. 8:e26902017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Li HB, Qin DN, Cheng K, Su Q, Miao YW, Guo
J, Zhang M, Zhu GQ and Kang YM: Central blockade of salusin β
attenuates hypertension and hypothalamic inflammation in
spontaneously hypertensive rats. Sci Rep. 5:111622015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Meng L, Li L, Lu S, Li K, Su Z, Wang Y,
Fan X, Li X and Zhao G: The protective effect of dexmedetomidine on
LPS-induced acute lung injury through the HMGB1-mediated TLR4/NF-κB
and PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathways. Mol Immunol. 94:7–17. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Lan KC, Chao SC, Wu HY, Chiang CL, Wang
CC, Liu SH and Weng TI: Salidroside ameliorates sepsis-induced
acute lung injury and mortality via downregulating NF-κB and HMGB1
pathways through the upregulation of SIRT1. Sci Rep. 7:120262017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Vijayan V, Wagener F and Immenschuh S: The
macrophage heme-heme oxygenase-1 system and its role in
inflammation. Biochem Pharmacol. 153:159–167. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Park J, Chen Y, Zheng M, Ryu J, Cho GJ,
Surh YJ, Sato D, Hamada H, Ryter SW, Kim UH, et al: Pterostilbene
4′-β-glucoside attenuates LPS-induced acute lung injury via
induction of heme oxygenase-1. Oxid Med Cell Longev.
2018:27470182018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Yin H, Li X, Yuan B, Zhang B, Hu S, Gu H,
Jin X and Zhu J: Heme oxygenase-1 ameliorates LPS-induced acute
lung injury correlated with downregulation of interleukin-33. Int
Immunopharmacol. 11:2112–2117. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Zhang X, Feng J, Zhu P and Zhao Z:
Ketamine inhibits calcium elevation and hydroxyl radical and nitric
oxide production in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated NR8383 alveolar
macrophages. Inflammation. 36:1094–1100. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Ko IG, Hwang JJ, Chang BS, Kim SH, Jin JJ,
Hwang L, Kim CJ and Choi CW: Polydeoxyribonucleotide ameliorates
lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury via modulation of the
MAPK/NF-κB signaling pathway in rats. Int Immunopharmacol.
83:1064442020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Liang Y, Luo J, Yang N, Wang S, Ye M and
Pan G: Activation of the IL-1β/KLF2/HSPH1 pathway promotes STAT3
phosphorylation in alveolar macrophages during LPS-induced acute
lung injury. Biosci Rep. 40:BSR201935722020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Fisher AB, Dodia C, Chatterjee S and
Feinstein SI: A peptide inhibitor of NADPH oxidase (NOX2)
activation markedly decreases mouse lung injury and mortality
following administration of lipopolysaccharide (LPS). Int J Mol
Sci. 20:23952019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Liang Y, Yang N, Pan G, Jin B, Wang S and
Ji W: Elevated IL-33 promotes expression of MMP2 and MMP9 via
activating STAT3 in alveolar macrophages during LPS-induced acute
lung injury. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 23:522018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Yan J, Li J, Zhang L, Sun Y, Jiang J,
Huang Y, Xu H, Jiang H and Hu R: Nrf2 protects against acute lung
injury and inflammation by modulating TLR4 and Akt signaling. Free
Radic Biol Med. 121:78–85. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Çakır M, Sabah-Özcan S and Saçmacı H:
Increased level of plasma salusin-α and salusin-β in patients with
multiple sclerosis. Mult Scler Relat Disord. 30:76–80. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Joe Y, Kim SK, Chen Y, Yang JW, Lee JH,
Cho GJ, Park JW and Chung HT: Tristetraprolin mediates
anti-inflammatory effects of carbon monoxide on
lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury. Am J Pathol.
185:2867–2874. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Sarady JK, Zuckerbraun BS, Bilban M,
Wagner O, Usheva A, Liu F, Ifedigbo E, Zamora R, Choi AMK and
Otterbein LE: Carbon monoxide protection against endotoxic shock
involves reciprocal effects on iNOS in the lung and liver. FASEB J.
18:854–856. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Gong Q, Yin H, Fang M, Xiang Y, Yuan CL,
Zheng GY, Yang H, Xiong P, Chen G, Gong FL and Zheng F: Heme
oxygenase-1 upregulation significantly inhibits TNF-alpha and Hmgb1
releasing and attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung
injury in mice. Int Immunopharmacol. 8:792–798. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|