|
1
|
Torre LA, Trabert B, DeSantis CE, Miller
KD, Samimi G, Runowicz CD, Gaudet MM, Jemal A and Siegel RL:
Ovarian cancer statistics, 2018. CA Cancer J Clin. 68:284–296.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2016. CA Cancer J Clin. 66:7–30. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
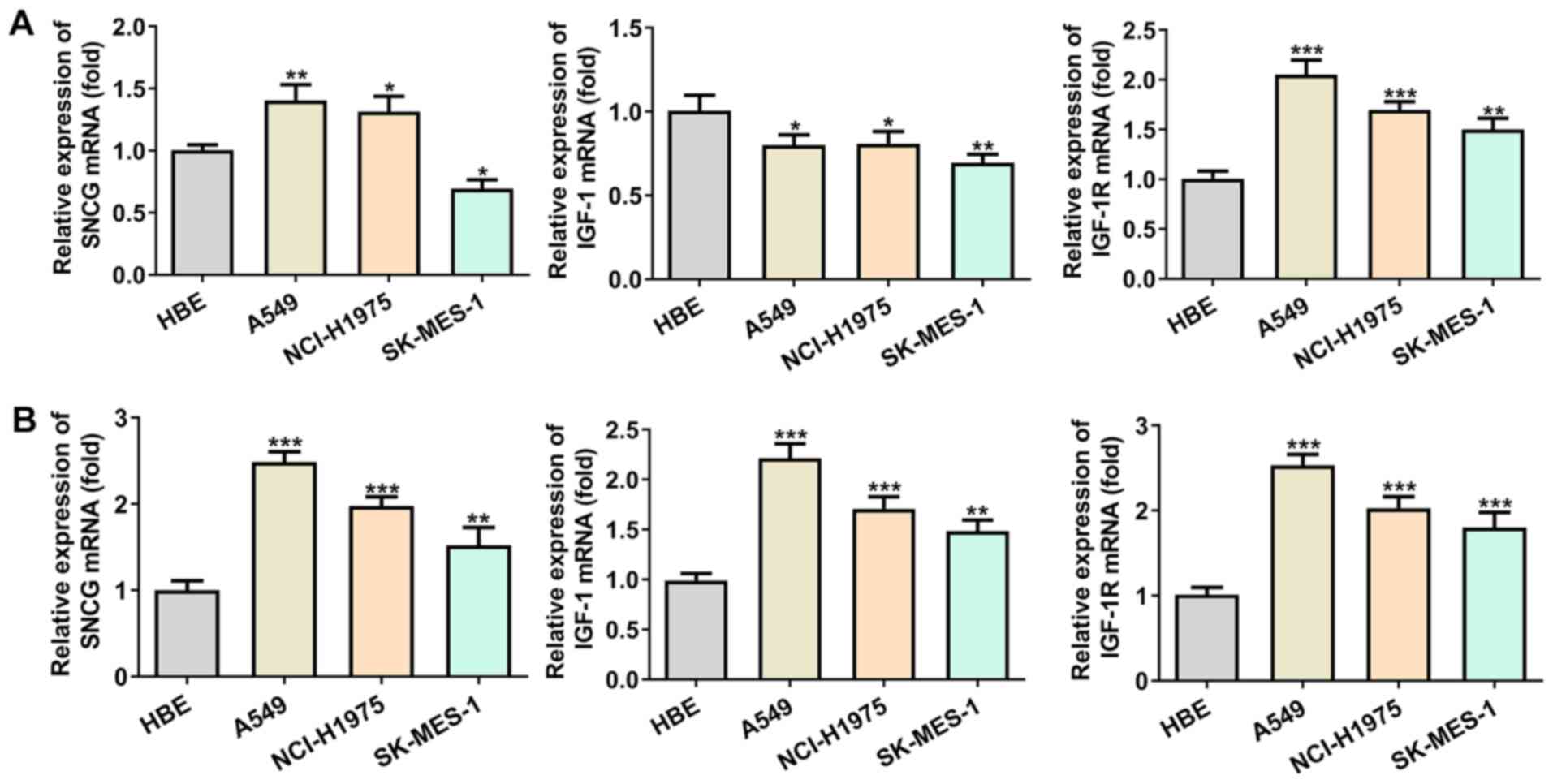
3
|
Edwards BK, Brown ML, Wingo PA, Howe HL,
Ward E, Ries LA, Schrag D, Jamison PM, Jemal A, Wu XC, et al:
Annual report to the nation on the status of cancer, 1975–2002,
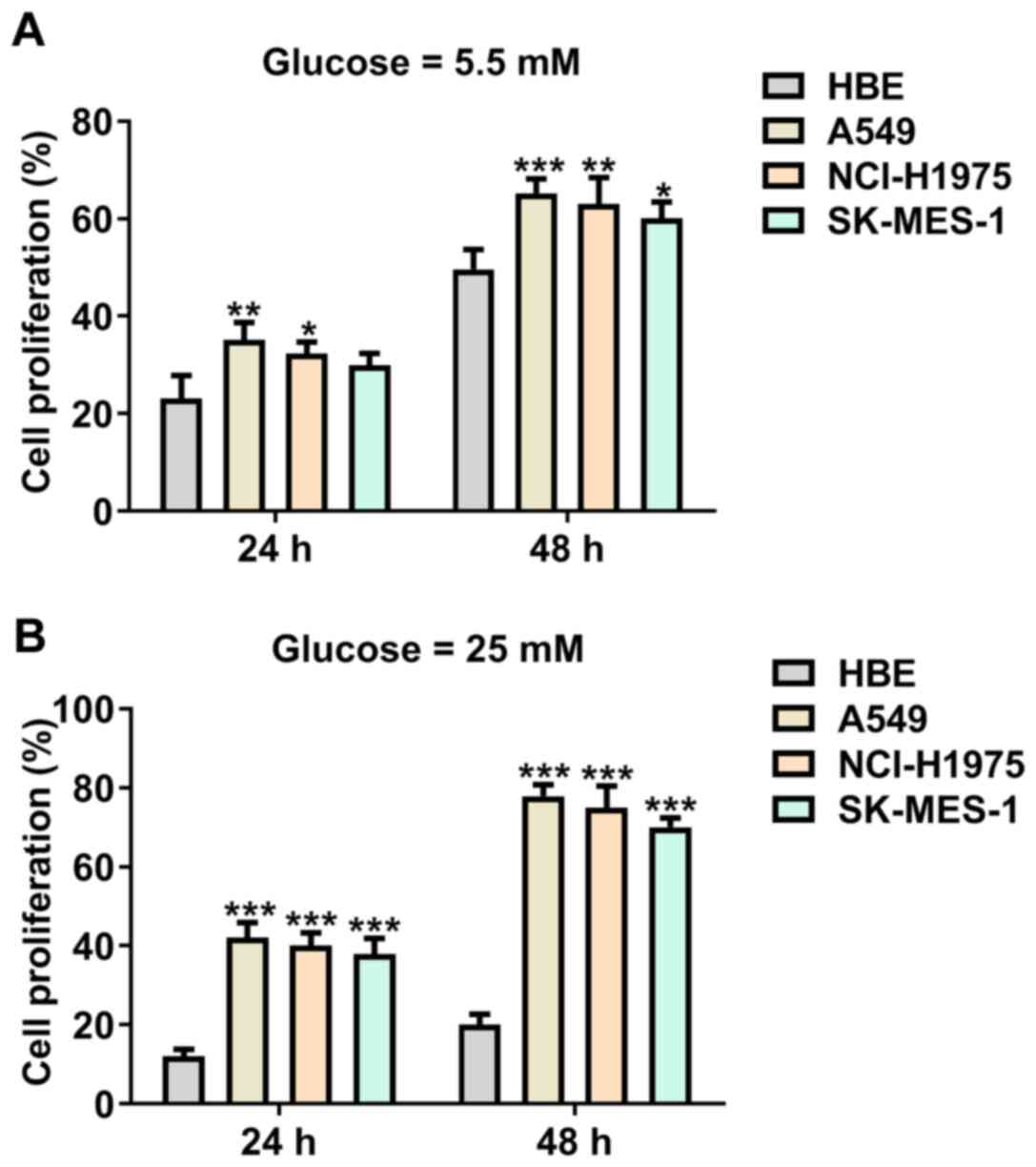
featuring population-based trends in cancer treatment. J Natl
Cancer Inst. 97:1407–1427. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Han C, Zhang M, Luo X, Wang C, Yin L, Pang
C, Feng T, Ren Y, Wang B, Zhang L, et al: Secular trends in the
prevalence of type 2 diabetes in adults in China from 1995 to 2014:
A meta-analysis. J Diabetes. 9:450–461. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Sona MF, Myung SK, Park K and
Jargalsaikhan G: Type 1 diabetes mellitus and risk of cancer: A
meta-analysis of observational studies. Jpn J Clin Oncol.
48:426–433. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
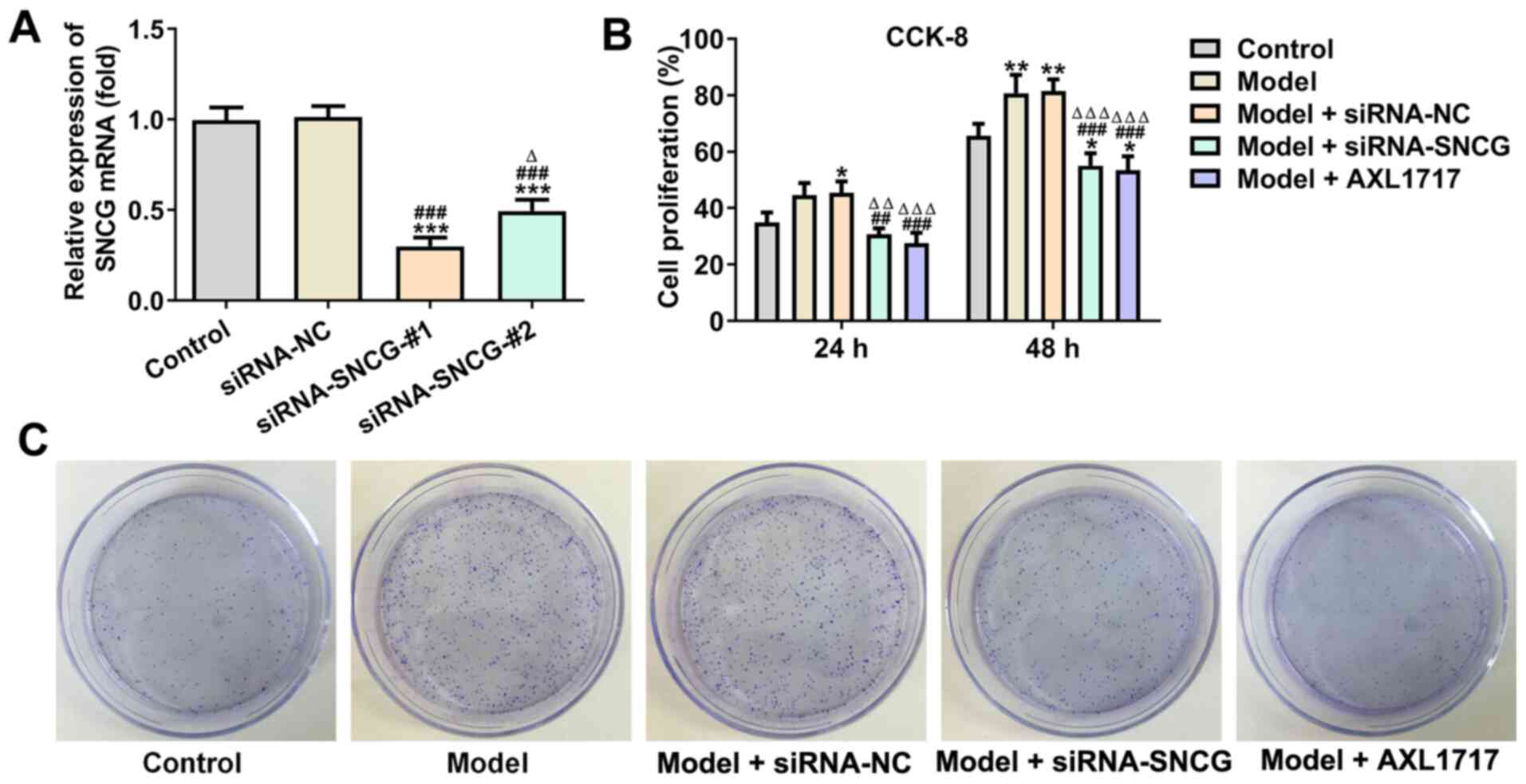
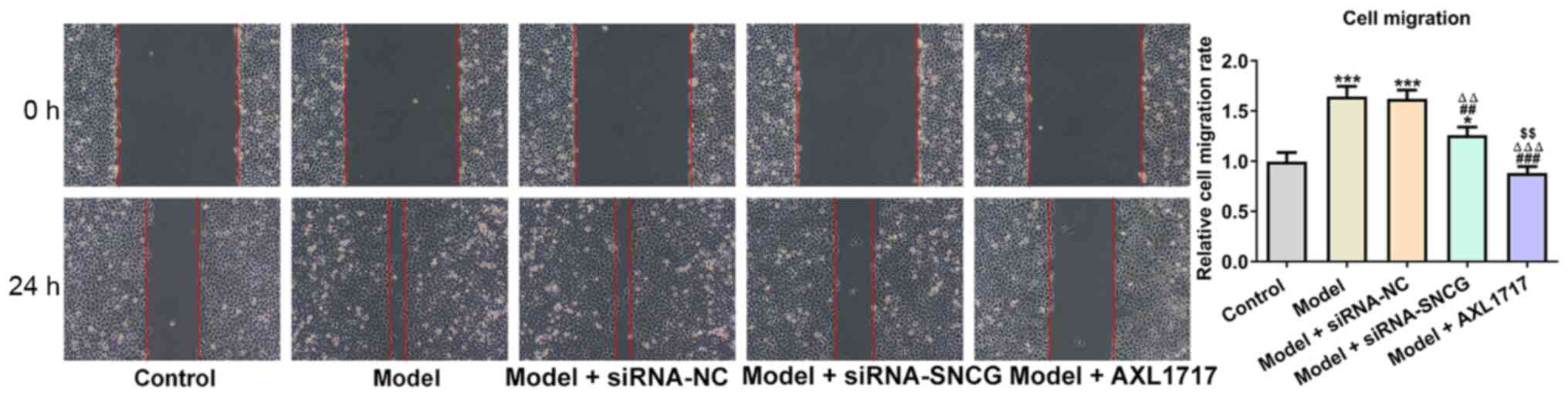
6
|
Luo J, Chen YJ and Chang LJ: Fasting blood
glucose level and prognosis in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC)
patients. Lung Cancer. 76:242–247. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Yu WS, Lee CY, Park SY, Suh JW, Narm KS,
Kim DJ, Chung KY and Lee JG: Prognostic factors for resected
non-small cell lung cancer in patients with type 2 diabetes
mellitus. J Surg Oncol. 117:985–993. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Ji H, Liu YE, Jia T, Wang M, Liu J, Xiao
G, Joseph BK, Rosen C and Shi YE: Identification of a breast
cancer-specific gene, BCSG1, by direct differential cDNA
sequencing. Cancer Res. 57:759–764. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Bruening W, Giasson BI, Klein-Szanto AJP,
Lee VM, Trojanowski JQ and Godwin AK: Synucleins are expressed in
the majority of breast and ovarian carcinomas and in preneoplastic
lesions of the ovary. Cancer. 88:2154–2163. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Gu YM, Tan JX, Lu XW, Ding Y, Han X and
Sun YJ: BCSG1 methylation status and BCSG1 expression in breast
tissues derived from Chinese women with breast cancer. Oncology.
74:61–68. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Tastekin D, Kargin S, Karabulut M, Yaldız
N, Tambas M, Gurdal N, Tatli AM, Arslan D, Gok AF and Aykan F:
Synuclein-gamma predicts poor clinical outcome in esophageal cancer
patients. Tumour Biol. 35:11871–11877. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Ye Q, Wang TF, Peng YF, Xie J, Feng B, Qiu
MY, Li LH, Lu AG, Liu BY and Zheng MH: Expression of α-, β- and
γ-synuclein in colorectal cancer, and potential clinical
significance in progression of the disease. Oncol Rep. 23:429–436.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Liu C, Shi B, Hao C, Wang Q, Lv Q, Xing N,
Shou J, Qu L, Gao Y, Qin C, et al: Urine gamma-synuclein as a
biomarker for the diagnosis of bladder cancer. Oncotarget.
7:43432–43441. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zheng Y, Jiang J, Zhao N, Liu R, Yang C,
Zhang J, Sun M and Zhang X: Expression of γ-synuclein in non-small
cell lung cancer. Zhongguo Laonianxue Zazhi. 31:4771–4773.
2011.
|
|
15
|
Li M, Yin Y, Hua H, Sun X, Luo T, Wang J
and Jiang Y: The reciprocal regulation of γ-synuclein and IGF-I
receptor expression creates a circuit that modulates IGF-I
signaling. J Biol Chem. 285:30480–30488. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Higashi Y, Sukhanov S, Anwar A, Shai SY
and Delafontaine P: Aging, atherosclerosis, and IGF-1. J Gerontol A
Biol Sci Med Sci. 67:626–639. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Xu C: Insulin-like growth factor type 1
receptor and malignancy:An update. Journal of Modern Oncology.
23:706–709. 2015.
|
|
18
|
Annibalini G, Lucertini F, Agostini D,
Vallorani L, Gioacchini A, Barbieri E, Guescini M, Casadei L,
Passalia A, Del Sal M, et al: Concurrent aerobic and resistance
training has anti-inflammatory effects and increases both plasma
and leukocyte levels of IGF-1 in late middle-aged type 2 diabetic
patients. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2017:39378422017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Pollak M: The insulin and insulin-like
growth factor receptor family in neoplasia: An update. Nat Rev
Cancer. 12:159–169. 2012. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Ding CZ, Guo XF, Wang GL, Wang HT, Xu GH,
Liu YY, Wu ZJ, Chen YH, Wang J and Wang WG: High glucose
contributes to the proliferation and migration of non-small cell
lung cancer cells via GAS5-TRIB3 axis. Biosci Rep.
38:BSR201710142018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Zhang J, Luo W, Chi X, Zhang L, Ren Q,
Wang H and Zhang W: IGF2BP1 silencing inhibits proliferation and
induces apoptosis of high glucose-induced non-small cell lung
cancer cells by regulating Netrin-1. Arch Biochem Biophys.
693:1085812020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Hemminki K, Li X, Sundquist J and
Sundquist K: Risk of cancer following hospitalization for type 2
diabetes. Oncologist. 15:548–555. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Cheng X and Han Y: Impact of diabetes
mellitus on lung cancer and its biological mechanism: A Literature
Review. Chin Gen Pract. 21:1779–1784. 2018.
|
|
25
|
Luo J, Hendryx M, Qi L, Ho GY and Margolis
KL: Pre-existing diabetes and lung cancer prognosis. Br J Cancer.
115:76–79. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Zhu L, Cao H, Zhang T, Shen H, Dong W,
Wang L and Du J: The effect of diabetes mellitus on lung cancer
prognosis: A PRISMA-compliant meta-analysis of cohort studies.
Medicine (Baltimore). 95:e35282016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Renehan AG, Frystyk J and Flyvbjerg A:
Obesity and cancer risk: The role of the insulin-IGF axis. Trends
Endocrinol Metab. 17:328–336. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Papa V, Pezzino V, Costantino A, Belfiore
A, Giuffrida D, Frittitta L, Vannelli GB, Brand R, Goldfine ID and
Vigneri R: Elevated insulin receptor content in human breast
cancer. J Clin Invest. 86:1503–1510. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Pollak MN, Schernhammer ES and Hankinson
SE: Insulin-like growth factors and neoplasia. Nat Rev Cancer.
4:505–518. 2004. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Giovannucci E, Harlan DM, Archer MC,
Bergenstal RM, Gapstur SM, Habel LA, Pollak M, Regensteiner JG and
Yee D: Diabetes and cancer: A consensus report. Diabetes Care.
33:1674–1685. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Li F, Liu Y, Ren L, Sun Q and Luo YX:
IGF-1 regulates Ang II and VEGF signaling pathways in retinal
neovascularization. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 22:6175–6180.
2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Surgucheva IG, Sivak JM, Fini ME, Palazzo
RE and Surguchov AP: Effect of gamma-synuclein overexpression on
matrix metalloproteinases in retinoblastoma Y79 cells. Arch Biochem
Biophys. 410:167–176. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Jiang Y, Liu YE, Goldberg ID and Shi YE: γ
synuclein, a novel heat-shock protein-associated chaperone,
stimulates ligand-dependent estrogen receptor α signaling and
mammary tumorigenesis. Cancer Res. 64:4539–4546. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Shen P-H, Fan Q-X, Li Y-W, Zhang W, He XK,
Wang Z and Zhang YH: SNCG shRNA suppressed breast cancer cell
xenograft formation and growth in nude mice. Chin Med J (Engl).
124:1524–1528. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Alexa A, Gógl G, Glatz G, Garai Á, Zeke A,
Varga J, Dudás E, Jeszenői N, Bodor A, Hetényi C, et al: Structural
assembly of the signaling competent ERK2-RSK1 heterodimeric protein
kinase complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 112:2711–2716. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Liu K, Lu R, Zhao Q, Du J, Li Y, Zheng M
and Zhang S: Association and clinicopathologic significance of
p38MAPK-ERK-JNK-CDC25C with polyploid giant cancer cell formation.
Med Oncol. 37:62019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Yang T, Wang Y, Zhan S, Jia Q and Wang X:
Effects of ERK gene overexpression on proliferation, migration and
invasion of lung cancer A549 Cells. J Ningxia Med Univ. 42:332–338.
2020.
|
|
38
|
Eisinger-Mathason TSK, Andrade J and
Lannigan DA: RSK in tumorigenesis: Connections to steroid
signaling. Steroids. 75:191–202. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Jian W, Xue-zhong H, Jing L and Jing G:
The molecular mechanism of miR23a promotes apoptosis of lung cancer
cell line A549 Caspase-3 expression. Anat Res. 40:494–497.
2018.
|
|
40
|
Fan C, Liu J, Tian J, Zhang Y, Yan M and
Zhu C: siRNA Targeting of the SNCG gene inhibits the growth of
gastric carcinoma SGC7901 cells in vitro and in vivo by
downregulating the phosphorylation of AKT/ERK. Cytogenet Genome
Res. 154:209–216. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Man GCW, Wang J, Song Y, Wong JH, Zhao Y,
Lau TS, Leung KT, Chan TH, Wang H, Kwong J, et al: Therapeutic
potential of a novel prodrug of green tea extract in induction of
apoptosis via ERK/JNK and Akt signaling pathway in human
endometrial cancer. BMC Cancer. 20:9642020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|