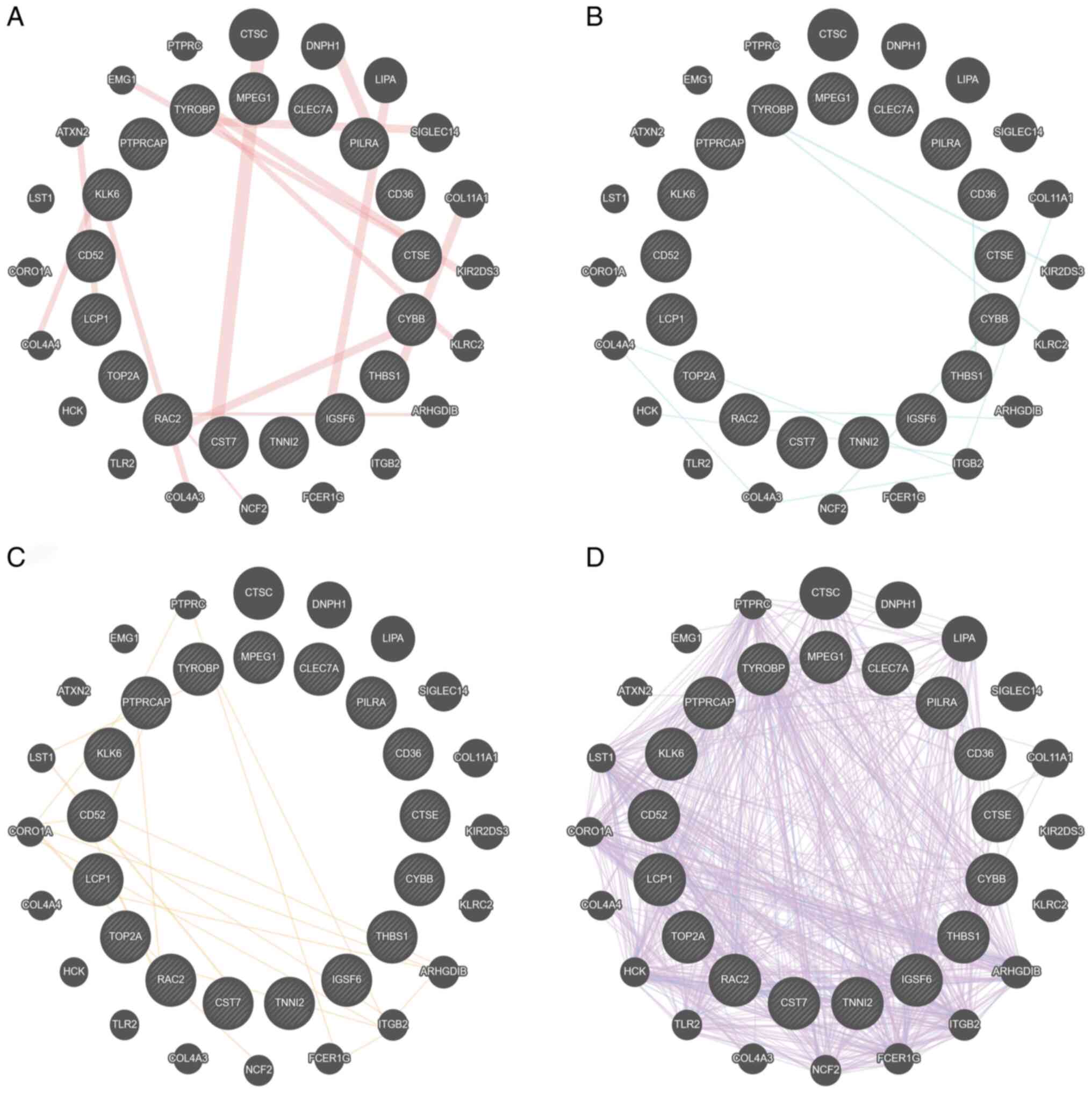
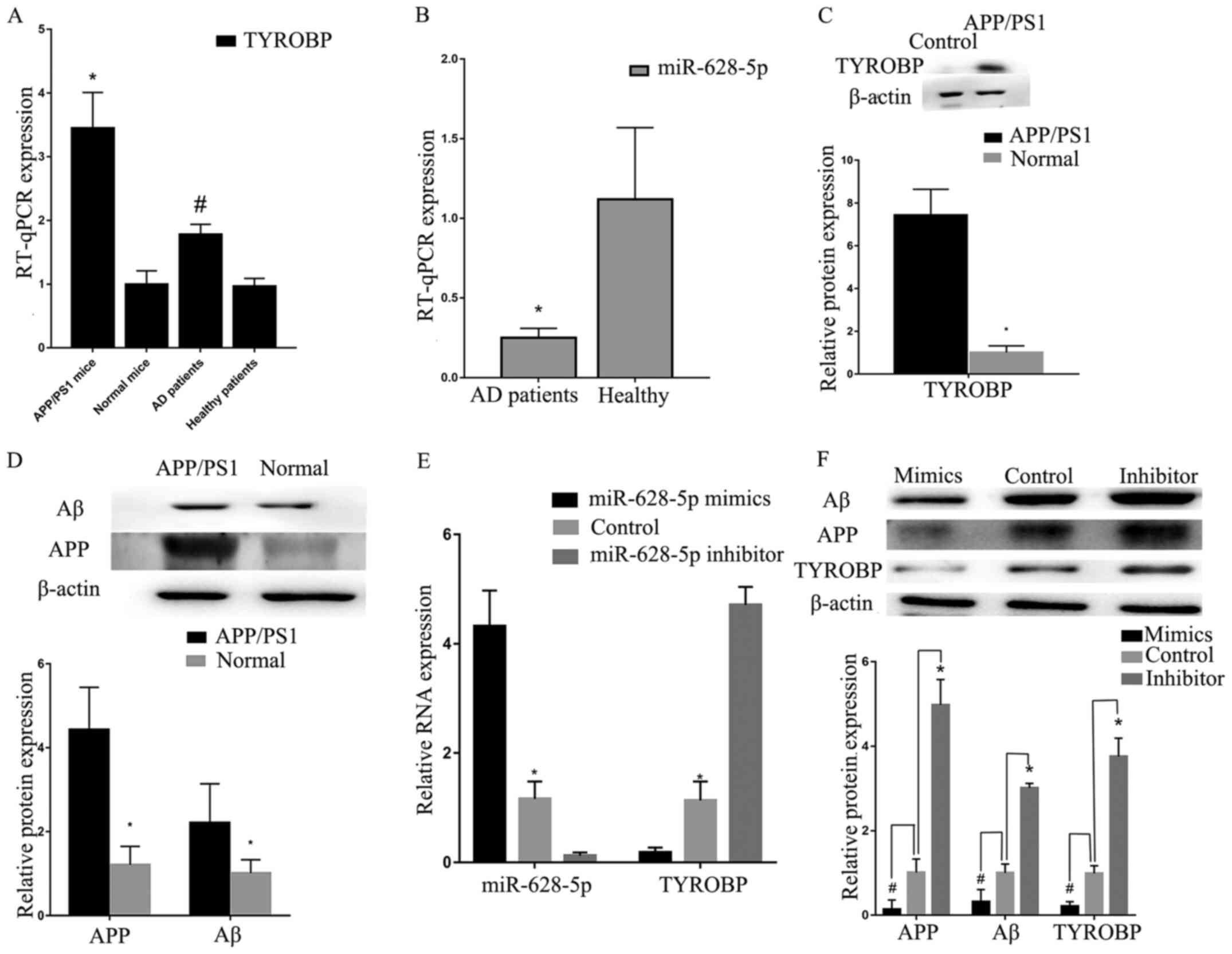
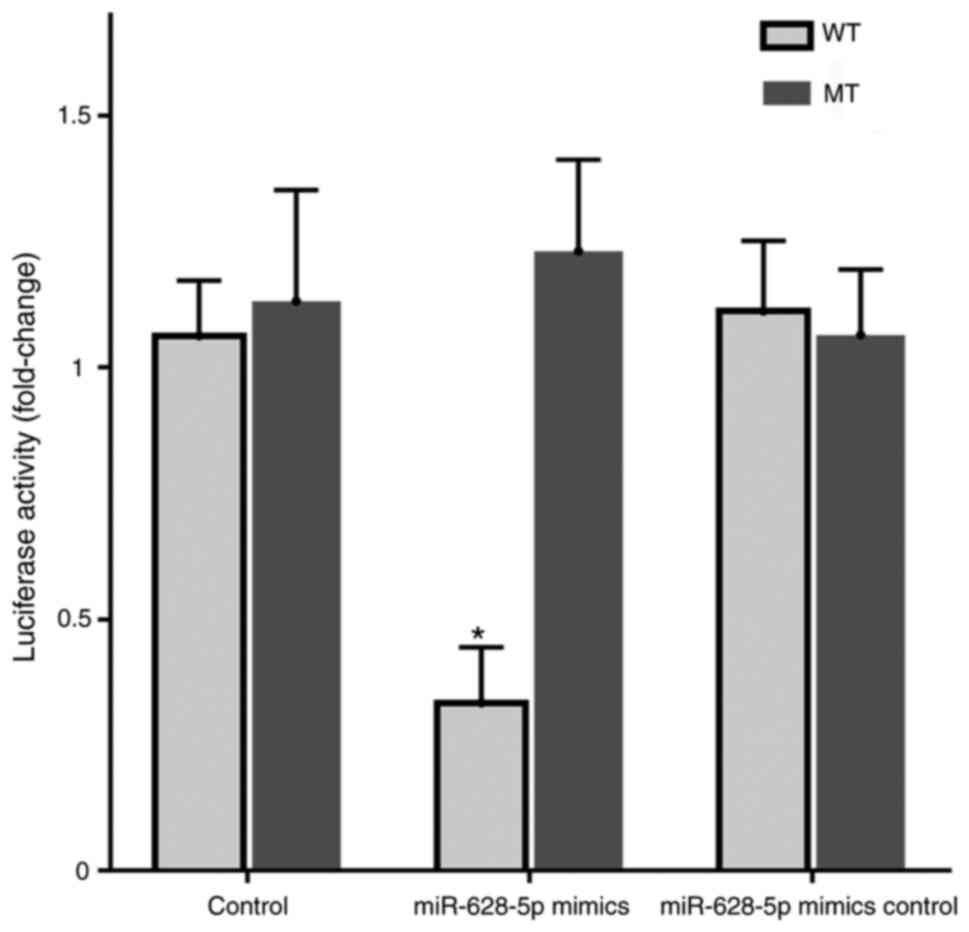
|
1
|
Weiner MW, Veitch DP, Aisen PS, Beckett
LA, Cairns NJ, Green RC, Harvey D, Jack CR, Jagust W, Liu E, et al:
The Alzheimer's disease neuroimaging initiative: A review of papers
published since its inception. Alzheimers Dement. 9:e111–e194.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
De Strooper B: Lessons from a failed
γ-Secretase Alzheimer trial. Cell. 159:721–726. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Mudher A and Lovestone S: Alzheimer's
disease-do tauists and baptists finally shake hands? Trends
Neurosci. 25:22–26. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Karran E and De Strooper B: The amyloid
cascade hypothesis: Are we poised for success or failure? J
Neurochem. 139 (Suppl 2):S237–S252. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Gervais F, Paquette J, Morissette C,
Krzywkowski P, Yu M, Azzi M, Lacombe D, Kong X, Aman A, Laurin J,
et al: Targeting soluble Abeta peptide with Tramiprosate for the
treatment of brain amyloidosis. Neurobiol Aging. 28:537–547. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Aisen PS, Gauthier S, Ferris SH, Saumier
D, Haine D, Garceau D, Duong A, Suhy J, Oh J, Lau WC and Sampalis
J: Tramiprosate in mild-to-moderate Alzheimer's disease - a
randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multi-centre study
(the Alphase Study). Arch Med Sci. 7:102–111. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Tomasello E, Olcese L, Vely F, Geourgeon
C, Bléry M, Moqrich A, Gautheret D, Djabali M, Mattei MG and Vivier
E: Gene structure, expression pattern, and biological activity of
mouse killer cell activating receptor-associated protein
(KARAP)/DAP-12. J Biol Chem. 273:34115–34119. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Hamerman JA, Ni M, Killebrew JR, Chu CL
and Lowell CA: The expanding roles of ITAM adapters FcRgamma and
DAP12 in myeloid cells. Immunol Rev. 232:42–58. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Lanier LL, Corliss BC, Wu J, Leong C and
Phillips JH: Immunoreceptor DAP12 bearing a tyrosine-based
activation motif is involved in activating NK cells. Nature.
391:703–707. 1998. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Paloneva J, Kestila M, Wu J, Salminen A,
Böhling T, Ruotsalainen V, Hakola P, Bakker AB, Phillips JH,
Pekkarinen P, et al: Loss-of-function mutations in TYROBP (DAP12)
result in a presenile dementia with bone cysts. Nat Genet.
25:357–361. 2000. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Varnum MM and Ikezu T: The classification
of microglial activation phenotypes on neurodegeneration and
regeneration in Alzheimer's disease brain. Arch Immunol Ther Exp
(Warsz). 60:251–266. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Sessa G, Podini P, Mariani M, Meroni A,
Spreafico R, Sinigaglia F, Colonna M, Panina P and Meldolesi J:
Distribution and signaling of TREM2/DAP12, the receptor system
mutated in human polycystic lipomembraneous osteodysplasia with
sclerosing leukoencephalopathy dementia. Eur J Neurosci.
20:2617–2628. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Satoh J, Shimamura Y and Tabunoki H: Gene
expression profile of THP-1 monocytes following knockdown of DAP12,
a causative gene for Nasu-Hakola disease. Cell Mol Neurobiol.
32:337–343. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Pareek CS, Smoczynski R and Tretyn A:
Sequencing technologies and genome sequencing. J Appl Genet.
52:413–435. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Emilie F, Coelho JE, Zornbach K, Malik E,
Baqi Y, Schneider M, Cellai L, Carvalho K, Sebda S, Figeac M, et
al: Beneficial effect of a selective adenosine a2a
receptor antagonist in the APPswe/PS1dE9 mouse model of Alzheimer's
Disease. Front Mol Neurosci. 11:2352018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Wang W, Liu Q, Wang Y, Piao H, Li B, Zhu
Z, Li D, Wang T, Xu R and Liu K: Integration of gene expression
profile data of human epicardial adipose tissue from coronary
artery disease to verification of hub genes and pathways. Biomed
Res Int. 2019:85673062019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
You J, Qi S, Du Y, Wang C and Su G:
Multiple bioinformatics analyses of integrated gene expression
profiling data and verification of hub genes associated with
diabetic retinopathy. Med Sci Monit. 26:e9231462020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Faivre E, Coelho JE, Zornbach K, Malik E,
Baqi Y, Schneider M, Cellai L, Carvalho K, Sebda S, Figeac M, et
al: Beneficial effect of a selective adenosine A2A
receptor antagonist in the APPswe/PS1dE9 mouse model of Alzheimer's
disease. Front Mol Neurosci. 11:2352018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Liu W, Sun F, Wan M, Jiang F, Bo X, Lin L,
Tang H and Xu S: β-Sheet breaker peptide-HPYD for the treatment of
Alzheimer's disease: Primary studies on behavioral test and
transcriptional profiling. Front Pharmacol. 8:9692018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Shim SR and Kim SJ: Intervention
meta-analysis: Application and practice using R software. Epidemiol
Health. 41:e20190082019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Otto R, Schirrmeister W, Majeed RW,
Greiner F, Lucas B, Röhrig R, Walcher F and Brammen D; AKTIN
Research Group, : Implementation of emergency department
performance benchmarking using R and LaTeX. Stud Health Technol
Inform. 267:238–246. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Huang DW, Sherman BT, Tan Q, Collins JR,
Alvord WG, Roayaei J, Stephens R, Baseler MW, Lane HC and Lempicki
RA: The DAVID gene functional classification tool: A novel
biological module-centric algorithm to functionally analyze large
gene lists. Genome Biol. 8:R1832007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Shannon P, Markiel A, Ozier O, Baliga NS,
Wang JT, Ramage D, Amin N, Schwikowski B and Ideker T: Cytoscape: A
software environment for integrated models of biomolecular
interaction networks. Genome Res. 13:2498–2504. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
McKhann G, Drachman D, Folstein M, Katzman
R, Price D and Stadlan EM: Clinical diagnosis of Alzheimer's
disease: Report of the NINCDS-ADRDA Work Group under the auspices
of the department of health and human services task force on
Alzheimer's disease. Neurology. 34:939–944. 1984. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Zimmermann M: Ethical guidelines for
investigations of experimental pain in conscious animals. Pain.
16:109–110. 1983. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Shen J and Kelleher RJ III: The presenilin
hypothesis of Alzheimer's disease: Evidence for a loss-of-function
pathogenic mechanism. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 104:403–409. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Francis PT, Palmer AM, Snape M and Wilcock
GK: The cholinergic hypothesis of Alzheimer's disease: A review of
progress. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 66:137–147. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Hardy J and Allsop D: Amyloid deposition
as the central event in the aetiology of Alzheimer's disease.
Trends Pharmacol Sci. 12:383–388. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Goedert M, Spillantini MG and Crowther RA:
Tau proteins and neurofibrillary degeneration. Brain Pathol.
1:279–286. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Chen J, Qi Y, Liu CF, Lu JM, Shi J and Shi
Y: MicroRNA expression data analysis to identify key miRNAs
associated with Alzheimer's disease. J Gene Med. 20:e30142018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Sagy-Bross C, Hadad N and Levy R:
Cytosolic phospholipase A2α upregulation mediates apoptotic
neuronal death induced by aggregated amyloid-β peptide1-42.
Neurochem Int. 63:541–550. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Heneka MT, Kummer MP, Stutz A, Delekate A,
Schwartz S, Vieira-Saecker A, Griep A, Axt D, Remus A, Tzeng TC, et
al: NLRP3 is activated in Alzheimer's disease and contributes to
pathology in APP/PS1 mice. Nature. 493:674–678. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Sarma JV and Ward PA: The compliment
system. Cell Tissue Res. 343:227–235. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Rogers J, Cooper NR, Webster S, Schultz J,
McGeer PL, Styren SD, Civin WH, Brachova L, Bradt B, Ward P, et al:
Complement activation by beta-amyloid in Alzheimer disease. Proc
Natl Acad Sci USA. 89:10016–10020. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Schöll M, Lockhart SN, Schonhaut DR,
O'Neil JP, Janabi M, Ossenkoppele R, Baker SL, Vogel JW, Faria J,
Schwimmer HD, et al: PET imaging of tau deposition in the aging
human brain. Neuron. 89:971–982. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Jiang Y, Li Z, Ma H, Cao X, Liu F, Tian A,
Sun X, Li X and Wang J: Upregulation of TREM2 ameliorates
neuroinflammatory responses and improves cognitive deficits
triggered by surgical trauma in Appswe/PS1dE9 mice. Cell Physiol
Biochem. 46:1398–1411. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Sekiya M, Wang M, Fujisaki N, Sakakibara
Y, Quan X, Ehrlich ME, De Jager PL, Bennett DA, Schadt EE, Gandy S,
et al: Integrated biology approach reveals molecular and
pathological interactions among Alzheimer's Aβ42, Tau, TREM2, and
TYROBP in drosophila models. Genome Med. 10:262018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Haure-Mirande JV, Audrain M, Fanutza T,
Kim SH, Klein WL, Glabe C, Readhead B, Dudley JT, Blitzer RD, Wang
M, et al: Deficiency of TYROBP, an adapter protein for TREM2 and
CR3 receptors, is neuroprotective in a mouse model of early
Alzheimer's pathology. Acta Neuropathol. 134:769–788. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Ma J, Jiang T, Tan L and Yu JT: TYROBP in
Alzheimer's disease. Mol Neurobiol. 51:820–826. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Haure-Mirande JV, Wang M, Audrain M,
Fanutza T, Kim SH, Heja S, Readhead B, Dudley JT, Blitzer RD,
Schadt EE, et al: Integrative approach to sporadic Alzheimer's
disease: Deficiency of Tyrobp in cerebral Abeta amyloidosis mouse
normalizes clinical phenotype and complement subnetwork molecular
pathology without reducing Abeta burden. Mol Psychiatry.
24:431–446. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Pottier C, Ravenscroft TA, Brown PH, Finch
NA, Baker M, Parsons M, Asmann YW, Ren Y, Christopher E, Levitch D,
et al: TYROBP genetic variants in early-onset Alzheimer's disease.
Neurobiol Aging. 48:222.e9–222.e15. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Mori Y, Yoshino Y, Ochi S, Yamazaki K,
Kawabe K, Abe M, Kitano T, Ozaki Y, Yoshida T, Numata S, et al:
TREM2 mRNA expression in leukocytes is increased in Alzheimer's
disease and schizophrenia. PLoS One. 10:e01368352015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Kempthorne L, Yoon H, Madore C, Smith S,
Wszolek ZK, Rademakers R, Kim J, Butovsky O and Dickson DW: Loss of
homeostatic microglial phenotype in CSF1R-related
Leukoencephalopathy. Acta Neuropathol Commun. 8:722020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Malik M, Parikh I, Vasquez JB, Smith C,
Tai L, Bu G, LaDu MJ, Fardo DW, Rebeck GW and Estus S: Genetics
ignite focus on microglial inflammation in Alzheimer's disease. Mol
Neurodegener. 10:522015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Rademakers R, Baker M, Nicholson AM,
Rutherford NJ, Finch N, Soto-Ortolaza A, Lash J, Wider C, Wojtas A,
DeJesus-Hernandez M, et al: Mutations in the colony stimulating
factor 1 receptor (CSF1R) gene cause hereditary diffuse
leukoencephalopathy with spheroids. Nat Genet. 44:200–205. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Audrain M, Haure-Mirande JV, Wang M, Kim
SH, Fanutza T, Chakrabarty P, Fraser P, St George-Hyslop PH, Golde
TE, Blitzer RD, et al: Integrative approach to sporadic Alzheimer's
disease: Deficiency of TYROBP in a tauopathy mouse model reduces
C1q and normalizes clinical phenotype while increasing spread and
state of phosphorylation of tau. Mol Psychiatry. 24:1383–1397.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Agarwal V, Bell GW, Nam JW and Bartel DP:
Predicting effective microRNA target sites in mammalian mRNAs.
Elife. 4:e050052015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Chen WL, Jiang L, Wang JS and Liao CX:
Circ-0001801 contributes to cell proliferation, migration, invasion
and epithelial to mesenchymal transition (EMT) in glioblastoma by
regulating miR-628-5p/HMGB3 axis. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci.
23:10874–10885. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Srivastava A, Goldberger H, Dimtchev A,
Marian C, Soldin O, Li X, Collins SP, Suy S and Kumar D:
Circulatory miR-628-5p is downregulated in prostate cancer
patients. Tumour Biol. 35:4867–4873. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Li M, Qian Z, Ma X, Lin X, You Y, Li Y,
Chen T and Jiang H: miR-628-5p decreases the tumorigenicity of
epithelial ovarian cancer cells by targeting at FGFR2. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 495:2085–2091. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Xie P, Wang Y, Liao Y, Han Q, Qiu Z, Chen
Y and Zuo X: MicroRNA-628-5p inhibits cell proliferation in glioma
by targeting DDX59. J Cell Biochem. 120:17293–17302. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|