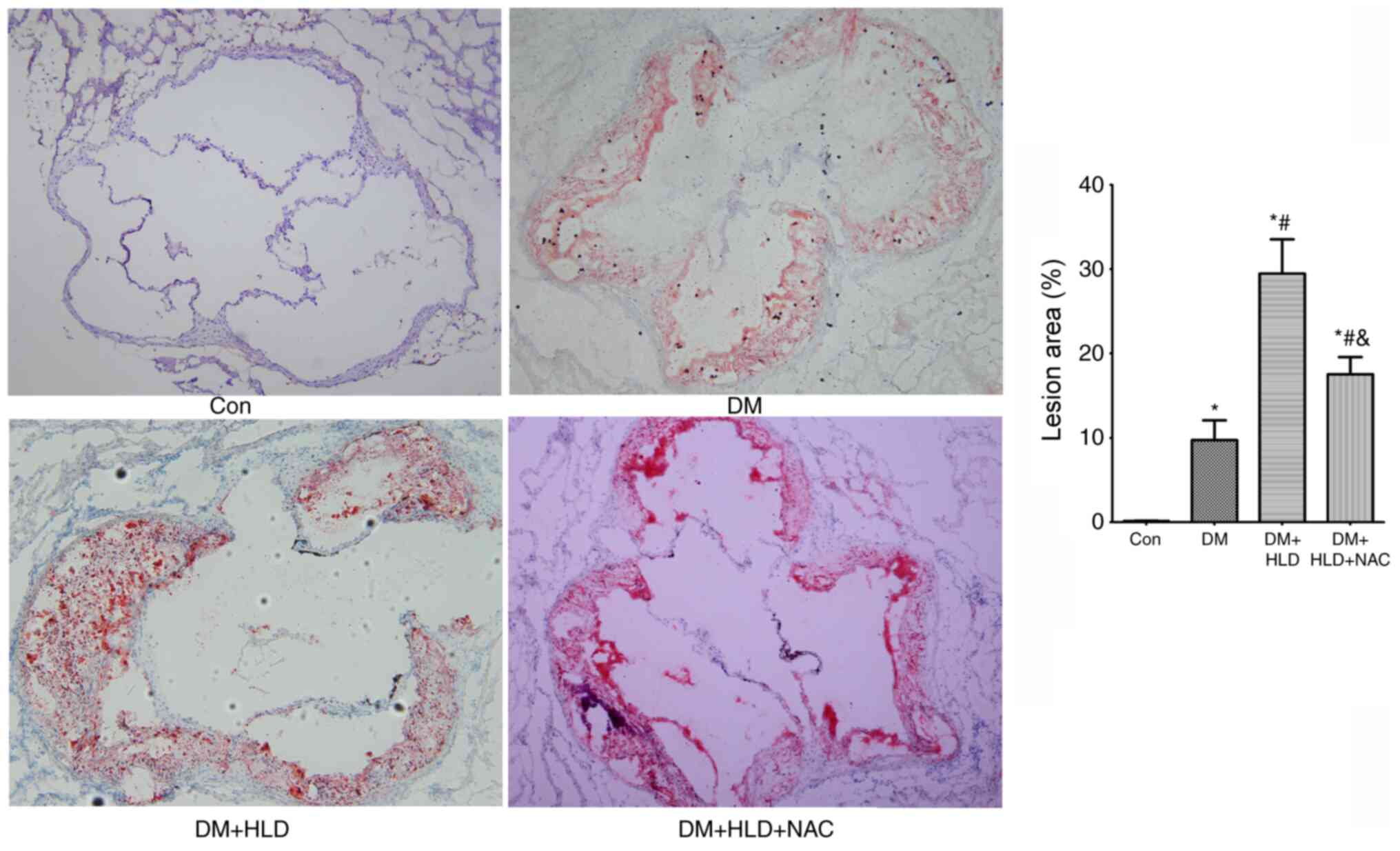
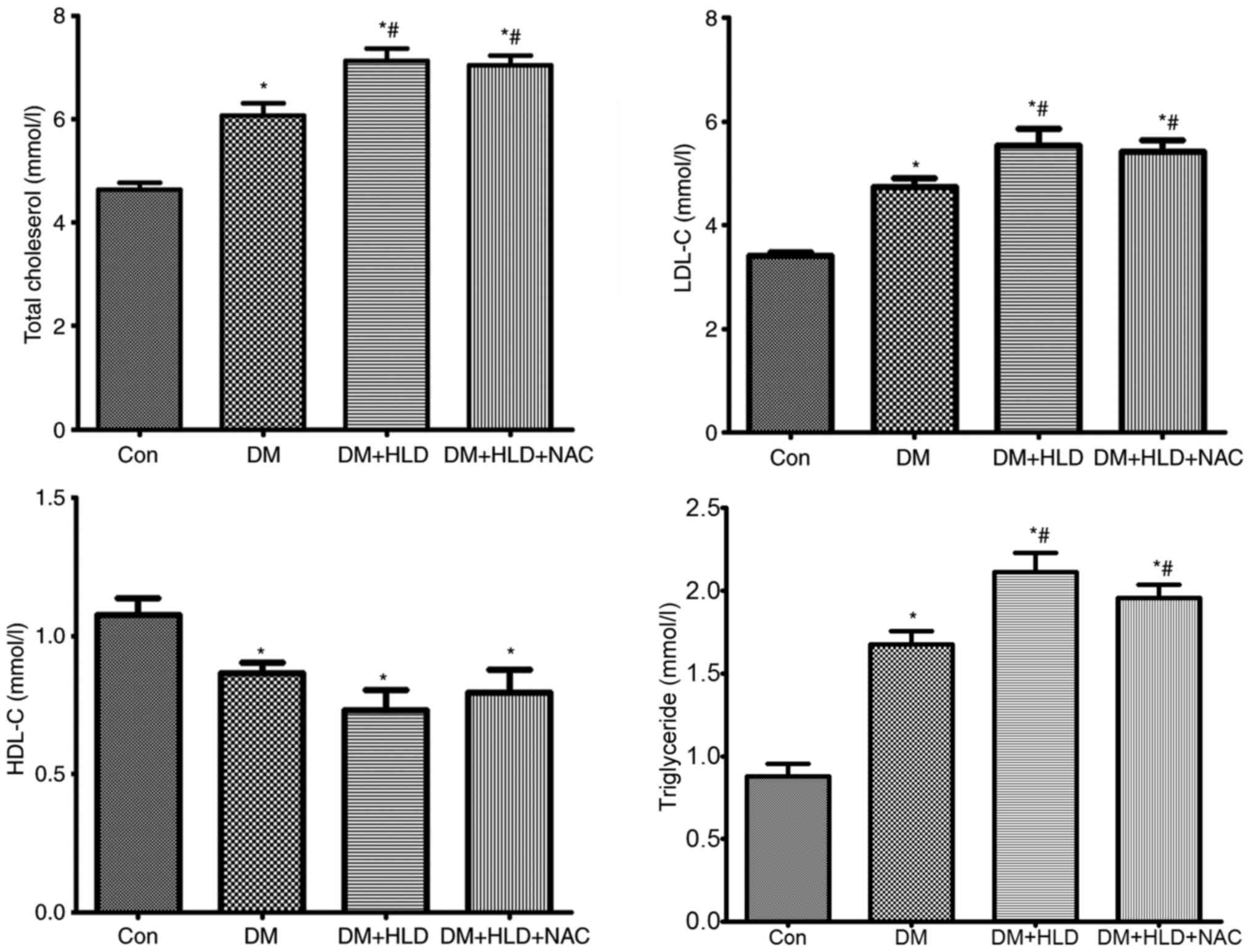
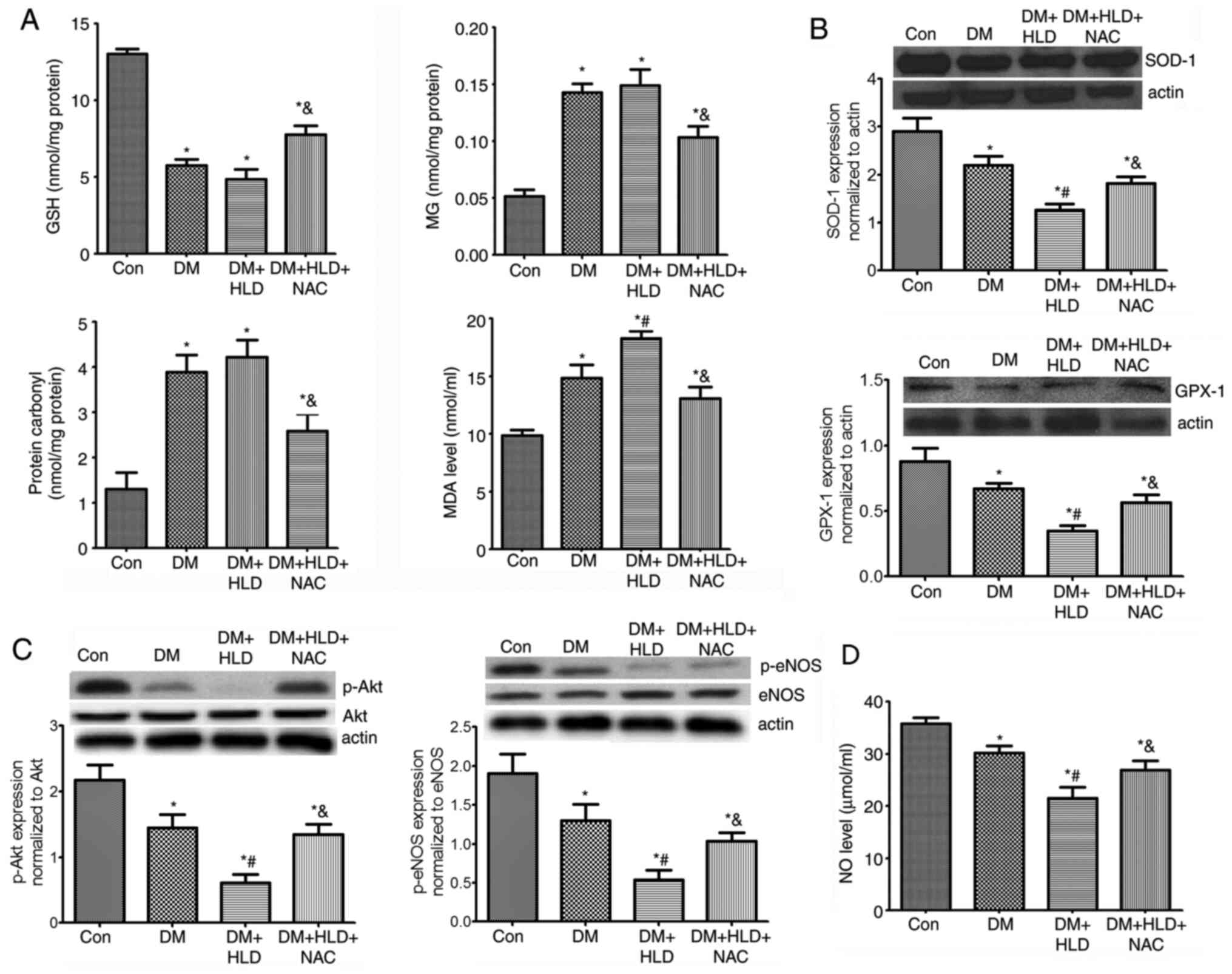
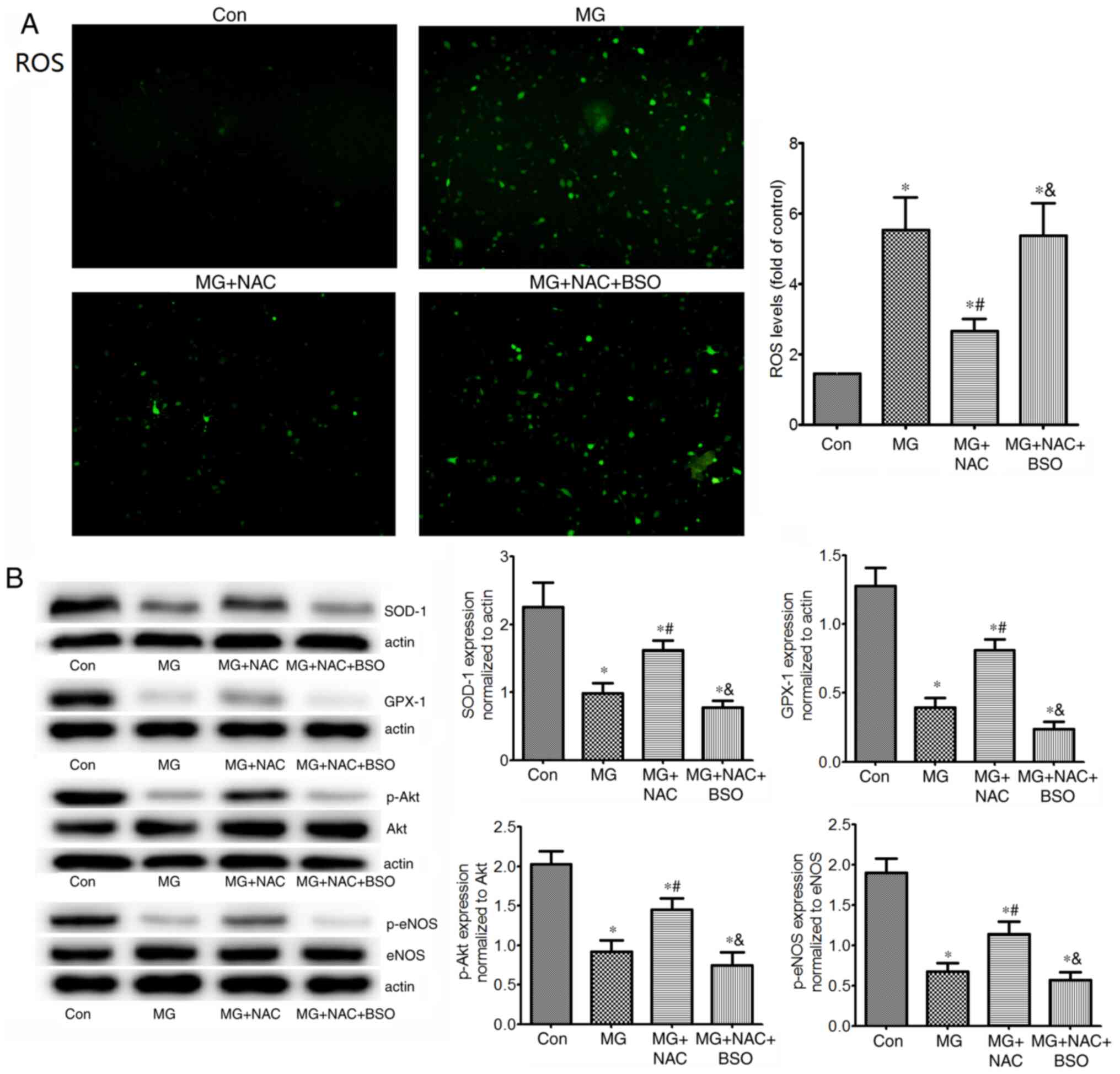
|
1
|
Zimmet P, Alberti KG, Magliano DJ and
Bennett PH: Diabetes mellitus statistics on prevalence and
mortality: Facts and fallacies. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 12:616–622.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Bornfeldt KE: 2013 Russell Ross memorial
lecture in vascular biology: Cellular and molecular mechanisms of
diabetes mellitus-accelerated atherosclerosis. Arterioscler Thromb
Vasc Biol. 34:705–714. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Bairey Merz CN, Alberts MJ, Balady GJ,
Ballantyne CM, Berra K, Black HR, Blumenthal RS, Davidson MH, Fazio
SB, Ferdinand KC, et al American College of Cardiology Foundation;
American Heart Association; American College of Physicians Task
Force on Competence and Training (Writing Committee to Develop a
Competence and Training Statement on Prevention of Cardiovascular
Disease); American Academy of Neurology; American Association of
Cardiovascular and Pulmonary Rehabilitation; American College of
Preventive Medicine; American Diabetes Association; American
Society of Hypertension; Association of Black Cardiologists;
National Lipid Association; Preventive Cardiovascular Nurses
Association: ACCF/AHA/ACP 2009 competence and training statement: a
curriculum on prevention of cardiovascular disease: a report of the
American College of Cardiology Foundation/American Heart
Association/American College of Physicians Task Force on Competence
and Training (Writing Committee to Develop a Competence and
Training Statement on Prevention of Cardiovascular Disease):
developed in collaboration with the American Academy of Neurology;
American Association of Cardiovascular and Pulmonary
Rehabilitation; American College of Preventive Medicine; American
College of Sports Medicine; American Diabetes Association; American
Society of Hypertension; Association of Black Cardiologists;
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention; National Heart, Lung,
and Blood Institute; National Lipid Association; and Preventive
Cardiovascular Nurses Association, : J Am Coll Cardiol.
54:1336–1363. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Patel A, MacMahon S, Chalmers J, Neal B,
Billot L, Woodward M, Marre M, Cooper M, Glasziou P, Grobbee D, et
al ADVANCE Collaborative Group, : Intensive blood glucose control
and vascular outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes. N Engl J
Med. 358:2560–2572. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Lachin JM, Genuth S, Cleary P, Davis MD
and Nathan DM; Diabetes Control and Complications
Trial/Epidemiology of Diabetes Interventions and Complications
Research Group, : Retinopathy and nephropathy in patients with type
1 diabetes four years after a trial of intensive therapy. N Engl J
Med. 342:381–389. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Fullerton B, Jeitler K, Seitz M, Horvath
K, Berghold A and Siebenhofer A: Intensive glucose control versus
conventional glucose control for type 1 diabetes mellitus. Cochrane
Database Syst Rev. (2):CD0091222014.
|
|
7
|
Schmidt AM and Stern D: Atherosclerosis
and diabetes: The RAGE connection. Curr Atheroscler Rep. 2:430–436.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Cushman WC, Evans GW, Byington RP, Goff DC
Jr, Grimm RH Jr, Cutler JA, Simons-Morton DG, Basile JN, Corson MA,
Probstfield JL, et al ACCORD Study Group, : Effects of intensive
blood-pressure control in type 2 diabetes mellitus. N Engl J Med.
362:1575–1585. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Rabbani N, Xue M and Thornalley PJ:
Methylglyoxal-induced dicarbonyl stress in aging and disease: First
steps towards glyoxalase 1-based treatments. Clin Sci (Lond).
130:1677–1696. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Turk Z: Glycotoxines, carbonyl stress and
relevance to diabetes and its complications. Physiol Res.
59:147–156. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Watson AM, Soro-Paavonen A, Sheehy K, Li
J, Calkin AC, Koitka A, Rajan SN, Brasacchio D, Allen TJ, Cooper
ME, et al: Delayed intervention with AGE inhibitors attenuates the
progression of diabetes-accelerated atherosclerosis in diabetic
apolipoprotein E knockout mice. Diabetologia. 54:681–689. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Lapolla A, Flamini R, Dalla Vedova A,
Senesi A, Reitano R, Fedele D, Basso E, Seraglia R and Traldi P:
Glyoxal and methylglyoxal levels in diabetic patients: Quantitative
determination by a new GC/MS method. Clin Chem Lab Med.
41:1166–1173. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
McLellan AC, Thornalley PJ, Benn J and
Sonksen PH: Glyoxalase system in clinical diabetes mellitus and
correlation with diabetic complications. Clin Sci (Lond). 87:21–29.
1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Rabbani N, Godfrey L, Xue M, Shaheen F,
Geoffrion M, Milne R and Thornalley PJ: Glycation of LDL by
methylglyoxal increases arterial atherogenicity: A possible
contributor to increased risk of cardiovascular disease in
diabetes. Diabetes. 60:1973–1980. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Nigro C, Leone A, Raciti GA, Longo M,
Mirra P, Formisano P, Beguinot F and Miele C:
Methylglyoxal-glyoxalase 1 balance: the root of vascular damage.
Int J Mol Sci. 18:1882017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Tikellis C, Pickering RJ, Tsorotes D, Huet
O, Cooper ME, Jandeleit-Dahm K and Thomas MC: Dicarbonyl stress in
the absence of hyperglycemia increases endothelial inflammation and
atherogenesis similar to that observed in diabetes. Diabetes.
63:3915–3925. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Wu L and Juurlink BH: Increased
methylglyoxal and oxidative stress in hypertensive rat vascular
smooth muscle cells. Hypertension. 39:809–814. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Sena CM, Matafome P, Crisóstomo J,
Rodrigues L, Fernandes R, Pereira P and Seiça RM: Methylglyoxal
promotes oxidative stress and endothelial dysfunction. Pharmacol
Res. 65:497–506. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Tachi Y, Okuda Y, Bannai C, Okamura N,
Bannai S and Yamashita K: High concentration of glucose causes
impairment of the function of the glutathione redox cycle in human
vascular smooth muscle cells. FEBS Lett. 421:19–22. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Tachi Y, Okuda Y, Bannai C, Bannai S,
Shinohara M, Shimpuku H, Yamashita K and Ohura K: Hyperglycemia in
diabetic rats reduces the glutathione content in the aortic tissue.
Life Sci. 69:1039–1047. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Sung HJ, Kim J, Kim Y, Jang SW and Ko J:
N-acetyl cysteine suppresses the foam cell formation that is
induced by oxidized low density lipoprotein via regulation of gene
expression. Mol Biol Rep. 39:3001–3007. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Wang B, Aw TY and Stokes KY: The
protection conferred against ischemia-reperfusion injury in the
diabetic brain by N-acetylcysteine is associated with decreased
dicarbonyl stress. Free Radic Biol Med. 96:89–98. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Soro-Paavonen A, Watson AM, Li J, Paavonen
K, Koitka A, Calkin AC, Barit D, Coughlan MT, Drew BG, Lancaster
GI, et al: Receptor for advanced glycation end products (RAGE)
deficiency attenuates the development of atherosclerosis in
diabetes. Diabetes. 57:2461–2469. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Kotur-Stevuljevic J, Memon L, Stefanovic
A, Spasic S, Spasojevic-Kalimanovska V, Bogavac-Stanojevic N,
Kalimanovska-Ostric D, Jelić-Ivanovic Z and Zunic G: Correlation of
oxidative stress parameters and inflammatory markers in coronary
artery disease patients. Clin Biochem. 40:181–187. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Institute of Laboratory Animal Resources
Commission on Life Sciences National Research Council, . Guide for
the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals. National Academy Press;
Washington, DC: pp. 8–78. 1996
|
|
26
|
Traslavina RP, King EJ, Loar AS, Riedel
ER, Garvey MS, Ricart-Arbona R, Wolf FR and Couto SS: Euthanasia by
CO2 inhalation affects potassium levels in mice. J Am
Assoc Lab Anim Sci. 49:316–322. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Overmyer KA, Thonusin C, Qi NR, Burant CF
and Evans CR: Impact of anesthesia and euthanasia on metabolomics
of mammalian tissues: Studies in a C57BL/6J mouse model. PLoS One.
10:e01172322015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Fuentes JM, Talamini MA, Fulton WB, Hanly
EJ, Aurora AR and De Maio A: General anesthesia delays the
inflammatory response and increases survival for mice with
endotoxic shock. Clin Vaccine Immunol. 13:281–288. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Yang XP, Liu YH, Rhaleb NE, Kurihara N,
Kim HE and Carretero OA: Echocardiographic assessment of cardiac
function in conscious and anesthetized mice. Am J Physiol.
277:H1967–H1974. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Guan S and Wang B: Effects of fosinopril
and valsartan on expressions of ICAM-1 and NO in human umbilical
vein endothelial cells. Chin Med J (Engl). 116:923–927.
2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Paigen B, Morrow A, Holmes PA, Mitchell D
and Williams RA: Quantitative assessment of atherosclerotic lesions
in mice. Atherosclerosis. 68:231–240. 1987. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Friedewald WT, Levy RI and Fredrickson DS:
Estimation of the concentration of low-density lipoprotein
cholesterol in plasma, without use of the preparative
ultracentrifuge. Clin Chem. 18:499–502. 1972. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Reed DJ, Babson JR, Beatty PW, Brodie AE,
Ellis WW and Potter DW: High-performance liquid chromatography
analysis of nanomole levels of glutathione, glutathione disulfide,
and related thiols and disulfides. Anal Biochem. 106:55–62. 1980.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Dhar A, Desai K, Liu J and Wu L:
Methylglyoxal, protein binding and biological samples: Are we
getting the true measure? J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life
Sci. 877:1093–1100. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Levine RL, Garland D, Oliver CN, Amici A,
Climent I, Lenz AG, Ahn BW, Shaltiel S and Stadtman ER:
Determination of carbonyl content in oxidatively modified proteins.
Methods Enzymol. 186:464–478. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Zhu ZX, Cai WH, Wang T, Ye HB, Zhu YT, Chi
LS, Duan YM, Sun CC, Xuan YH and Jin LT: bFGF-regulating MAPKs are
involved in high glucose-mediated ROS production and delay of
vascular endothelial cell migration. PLoS One. 10:e01444952015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Kannel WB, Castelli WP, Gordon T and
McNamara PM: Serum cholesterol, lipoproteins, and the risk of
coronary heart disease. The Framingham study. Ann Intern Med.
74:1–12. 1971. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Keys A: Coronary heart disease in seven
countries. 1970. Nutrition. 13:250–252; discussion 249, 253. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Valdovinos-Flores C, Limón-Pacheco JH,
León-Rodríguez R, Petrosyan P, Garza-Lombó C and Gonsebatt ME:
Systemic L-buthionine-S-R-sulfoximine treatment increases plasma
NGF and upregulates L-cys/L-cys2 transporter and γ-glutamylcysteine
ligase mRNAs through the NGF/TrkA/Akt/Nrf2 pathway in the striatum.
Front Cell Neurosci. 13:3252019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Nascimento NR, Costa-e-Forti A, Peter AA
and Fonteles MC: Free radical scavengers improve the impaired
endothelium-dependent responses in aorta and kidneys of diabetic
rabbits. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 61:145–153. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Muniyappa R and Srinivas PR: Dicarbonyl
stress and atherosclerosis: Is it all RAGE? Diabetes. 63:3587–3589.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Serafini M and Del Rio D: Understanding
the association between dietary antioxidants, redox status and
disease: is the Total Antioxidant Capacity the right tool? Redox
Rep. 9:145–152. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Peluso I, Morabito G, Urban L, Ioannone F
and Serafini M: Oxidative stress in atherosclerosis development:
The central role of LDL and oxidative burst. Endocr Metab Immune
Disord Drug Targets. 12:351–360. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Matough FA, Budin SB, Hamid ZA, Alwahaibi
N and Mohamed J: The role of oxidative stress and antioxidants in
diabetic complications. Sultan Qaboos Univ Med J. 12:5–18. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Wang B, Yee Aw T and Stokes KY:
N-acetylcysteine attenuates systemic platelet activation and
cerebral vessel thrombosis in diabetes. Redox Biol. 14:218–228.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Sit M, Yilmaz EE, Tosun M and Aktas G:
Effects of N-acetyl cysteine on lipid levels and on leukocyte and
platelet count in rats after splenectomy. Niger J Clin Pract.
17:343–345. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Franceschini G, Werba JP, Safa O, Gikalov
I and Sirtori CR: Dose-related increase of HDL-cholesterol levels
after N-acetylcysteine in man. Pharmacol Res. 28:213–218. 1993.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Violi F, Loffredo L, Carnevale R,
Pignatelli P and Pastori D: Atherothrombosis and oxidative stress:
mechanisms and management in elderly. Antioxid Redox Signal.
27:1083–1124. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Pignatelli P, Menichelli D, Pastori D and
Violi F: Oxidative stress and cardiovascular disease: New insights.
Kardiol Pol. 76:713–722. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|