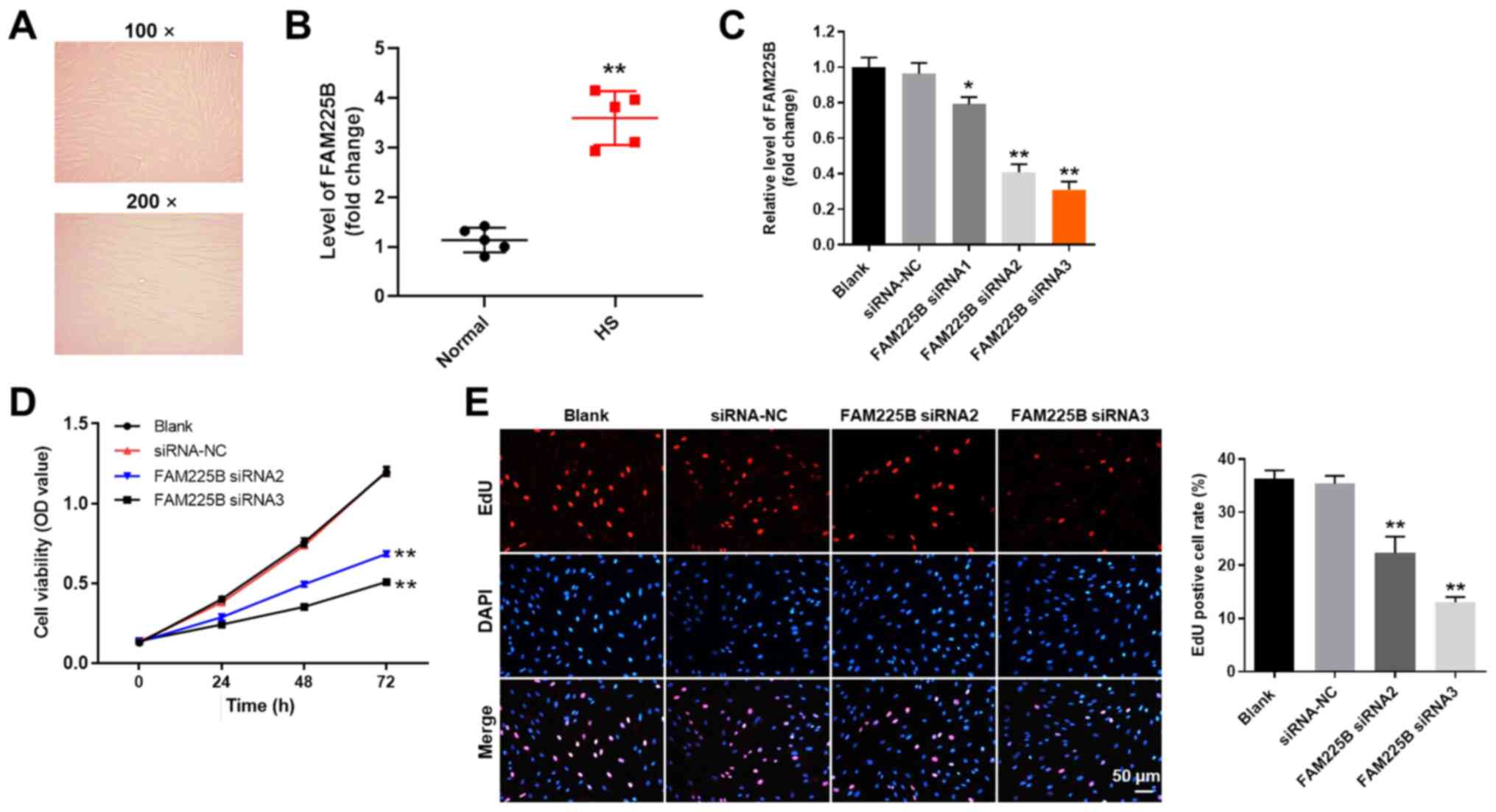
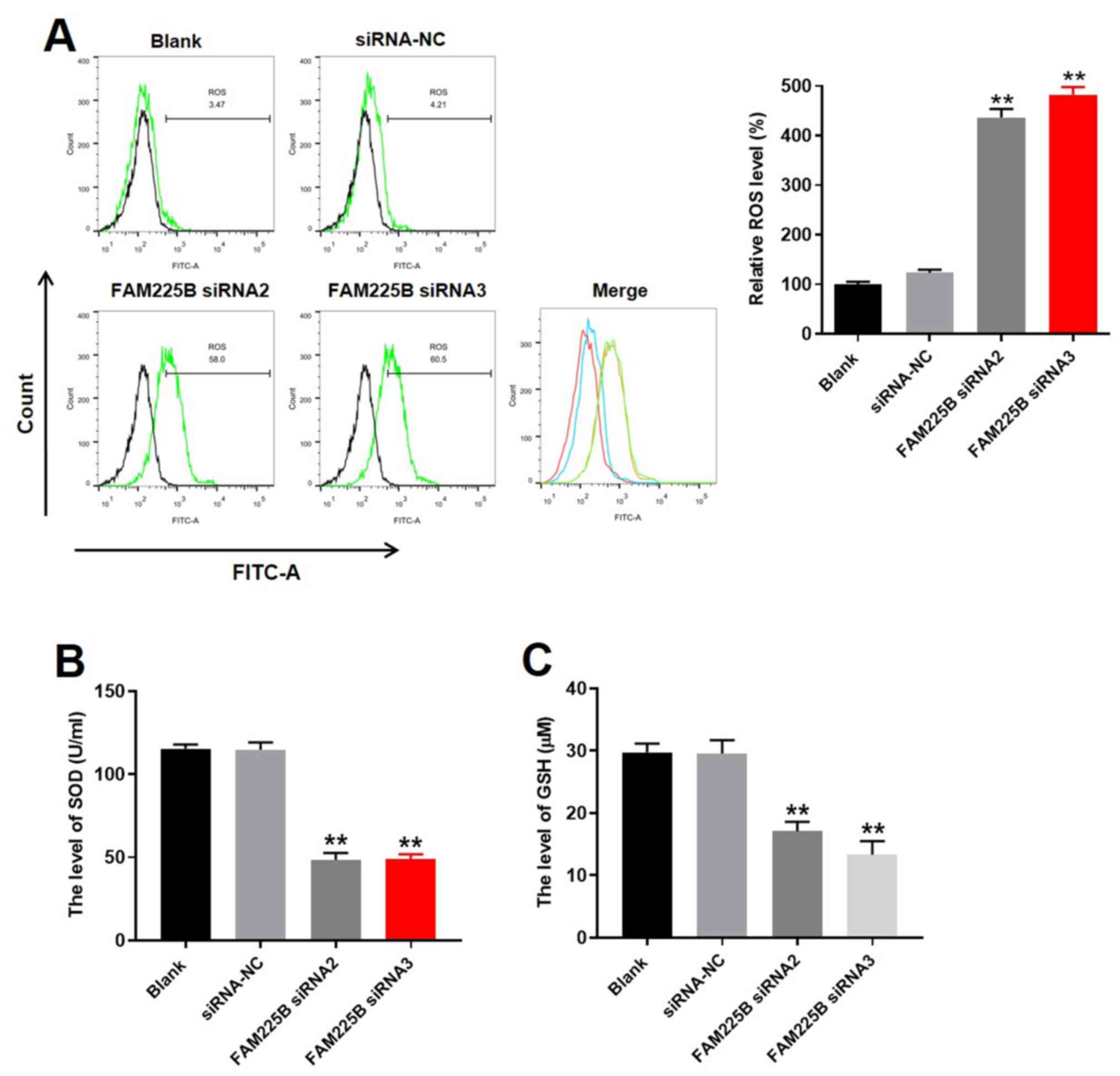
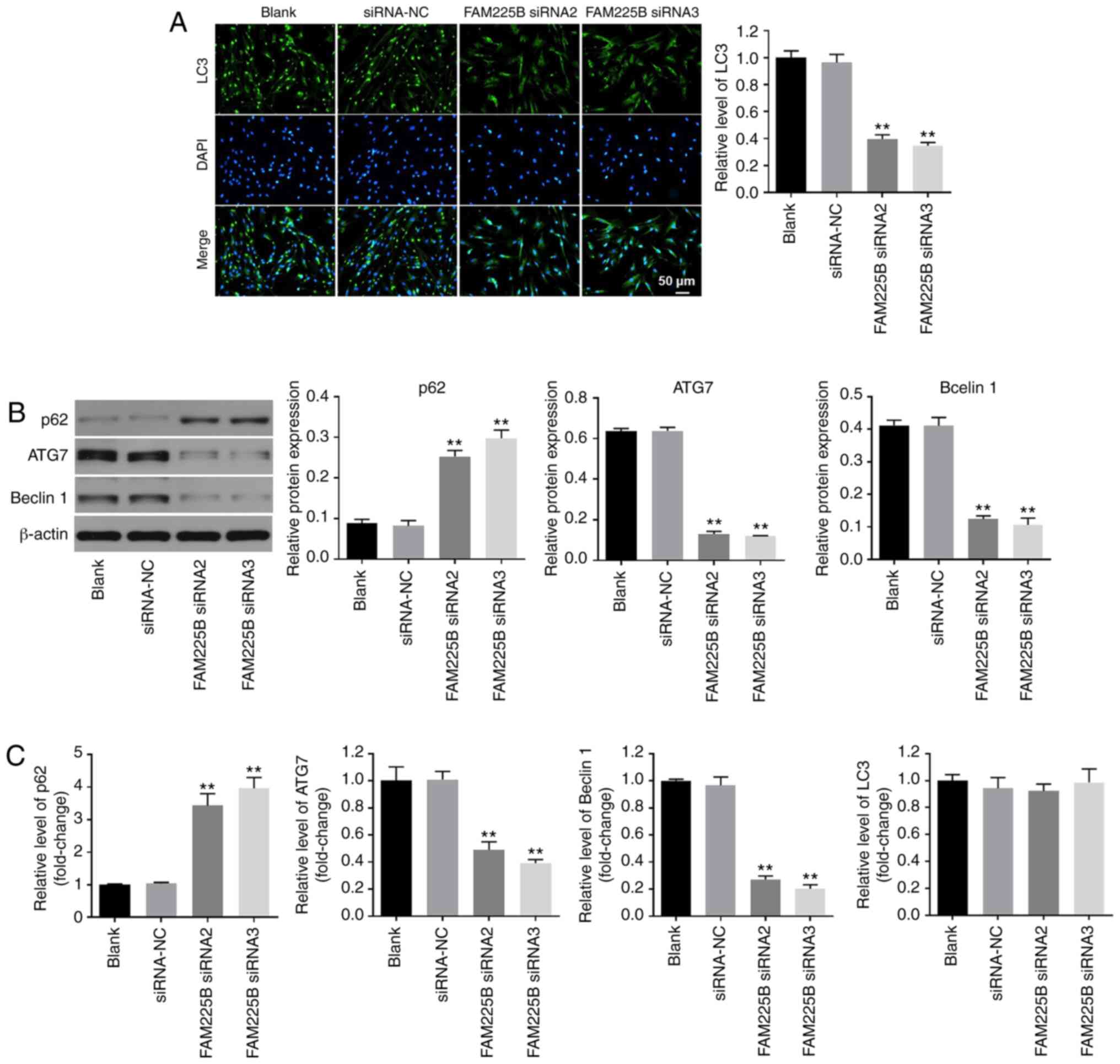
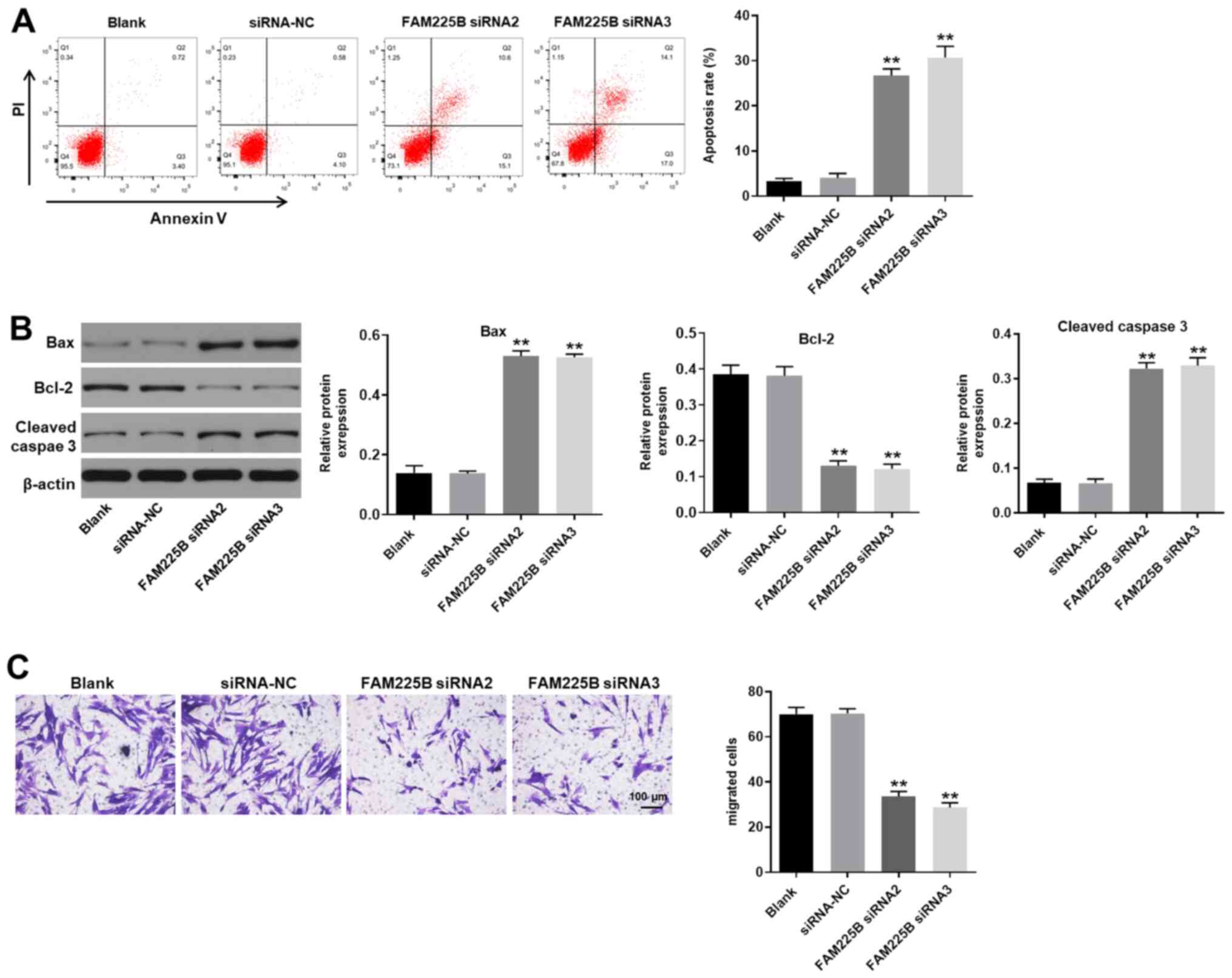
|
1
|
Li X, Leng Y, Jiang Q, Wang Z, Luo P,
Zhang C, Chen L, Wang Y, Wang H, Yue X, et al: Eye drops of
metformin prevents fibrosis after glaucoma filtration surgery in
rats via activating AMPK/Nrf2 signaling pathway. Front Pharmacol.
11:10382020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Swogger J, Conner IP, Rosano M, Kemmerer
M, Happ-Smith C, Wells A, Schuman JS and Yates CC: Injected versus
sponge-applied mitomycin C (MMC) during modified trabeculectomy in
New Zealand white rabbit model. Transl Vis Sci Technol. 9:232020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Yaman D, Takmaz T, Yüksel N, Dincer SA and
Şahin FI: Evaluation of silent information regulator T (SIRT) 1 and
Forkhead Box O (FOXO) transcription factor 1 and 3a genes in
glaucoma. Mol Biol Rep. 47:9337–9344. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Cheng WS, Chen CL, Chen JT, Lin LT, Pao
SI, Chen YH and Lu DW: AR12286 alleviates TGF-β-related
myofibroblast transdifferentiation and reduces fibrosis after
glaucoma filtration surgery. Molecules. 25:44222020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Yamamoto K, Kokubun T, Sato K, Akaishi T,
Shimazaki A, Nakamura M, Shiga Y, Tsuda S, Omodaka K, Saya H and
Nakazawa T: The DNA topoisomerase II inhibitor amsacrine as a novel
candidate adjuvant in a model of glaucoma filtration surgery. Sci
Rep. 9:192882019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Yu J, Qiu LX, Qing GP, Zhao BW and Wang H:
Modified cortex mori capsules improving the successful rate of
functional filtering blebs after reclinical glaucoma filtering
surgery. World J Clin Cases. 7:3436–3445. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Zhang F, Liu K, Pan Z, Cao M, Zhou D, Liu
H, Huang Y and Duan X: Effects of rosiglitazone/PHBV drug delivery
system on postoperative fibrosis in rabbit glaucoma filtration
surgery model. Drug Deliv. 26:812–819. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Sun J, Liu X, Lei Y, Tang M, Dai Z, Yang
X, Yu X, Yu L, Sun X and Ding J: Sustained subconjunctival delivery
of cyclosporine A using thermogelling polymers for glaucoma
filtration surgery. J Mater Chem B. 5:6400–6411. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Holló G: Wound Healing and Glaucoma
Surgery: Modulating the scarring process with conventional
antimetabolites and new molecules. Dev Ophthalmol. 59:80–89. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Sharma A, Anumanthan G, Reyes M, Chen H,
Brubaker JW, Siddiqui S, Gupta S, Rieger FG and Mohan RR:
Epigenetic modification prevents excessive wound healing and scar
formation after glaucoma filtration surgery. Invest Ophthalmol Vis
Sci. 57:3381–3389. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Zhang H, Li J, Shao W and Shen N: lncRNA
SNHG9 is downregulated in osteoarthritis and inhibits chondrocyte
apoptosis by downregulating miR-34a through methylation. BMC
Musculoskelet Disord. 21:5112020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Wang JH, Wu XJ, Duan YZ and Li F: Circular
RNA_CNST promotes the tumorigenesis of osteosarcoma cells by
sponging miR-421. Cell Transplant. 29:9636897209261472020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Xu YT, Leng YR, Liu MM, Dong RF, Bian J,
Yuan LL, Zhang JG, Xia YZ and Kong LY: MicroRNA and long noncoding
RNA involvement in gout and prospects for treatment. Int
Immunopharmacol. 87:1068422020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Dong Y, Fan G, Li Y and Zhou Q: TUG1
represses apoptosis, autophagy, and inflammatory response by
regulating miR-27a-3p/SLIT2 in LPS-treated vascular endothelial
cells. J Surg Res. 256:345–354. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Li M, Wang J, Liu D and Huang H:
High-throughput sequencing reveals differentially expressed lncRNAs
and circRNAs, and their associated functional network, in human
hypertrophic scars. Mol Med Rep. 18:5669–5682. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Chen J, Zhou R, Liang Y, Fu X, Wang D and
Wang C: Blockade of lncRNA-ASLNCS5088-enriched exosome generation
in M2 macrophages by GW4869 dampens the effect of M2 macrophages on
orchestrating fibroblast activation. FASEB J. 33:12200–12212. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Chen L and Li J, Li Q, Li X, Gao Y, Hua X,
Zhou B and Li J: Overexpression of lncRNA AC067945.2 down-regulates
collagen expression in skin fibroblasts and possibly correlates
with the VEGF and Wnt signalling pathways. Cell Physiol Biochem.
45:761–771. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Tu L, Huang Q, Fu S and Liu D: Aberrantly
expressed long noncoding RNAs in hypertrophic scar fibroblasts
in vitro: A microarray study. Int J Mol Med. 41:1917–1930.
2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Yamoto M, Alganabi M, Chusilp S, Lee D,
Yazaki Y, Lee C, Li B and Pierro A: Lysosomal overloading and
necrotizing enterocolitis. Pediatr Surg Int. 36:1157–1165. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Li Y, Zhang J, Zhou K, Xie L, Xiang G,
Fang M, Han W, Wang X and Xiao J: Elevating sestrin2 attenuates
endoplasmic reticulum stress and improves functional recovery
through autophagy activation after spinal cord injury. Cell Biol
Toxicol. Aug 1–2020.(Epub ahead of print). doi:
10.1007/s10565-020-09550-4. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Gutjahr A, Papagno L, Vernejoul F, Lioux
T, Jospin F, Chanut B, Perouzel E, Rochereau N, Appay V, Verrier B
and Paul S: New chimeric TLR7/NOD2 agonist is a potent adjuvant to
induce mucosal immune responses. EBioMedicine. 58:1029222020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Fu H, Chung KR, Liu X and Li H: Aaprb1, a
subtilsin-like protease, required for autophagy and virulence of
the tangerine pathotype of Alternaria alternata. Microbiol
Res. 240:1265372020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Shi J, Xiao H, Li J, Zhang J, Li Y, Zhang
J, Wang X, Bai X, Tao K, Hu D and Guan H: Wild-type p53-modulated
autophagy and autophagic fibroblast apoptosis inhibit hypertrophic
scar formation. Lab Invest. 98:1423–1437. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Liu X, Xu Q, Long X, Liu W, Zhao Y,
Hayashi T, Hattori S, Fujisaki H, Ogura T, Tashiro SI, et al:
Silibinin-induced autophagy mediated by PPARα-sirt1-AMPK pathway
participated in the regulation of type I collagen-enhanced
migration in murine 3T3-L1 preadipocytes. Mol Cell Biochem.
450:1–23. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Kyun S, Yoo C, Park HY, Kim J and Lim K:
The effects of exogenous lactate administration on the
IGF1/Akt/mTOR pathway in rat skeletal muscle. Int J Environ Res
Public Health. 17:78052020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Wang XC, Wang T, Zhang Y, Wang LL, Zhao RY
and Tan W: Tacrolimus inhibits proliferation and induces apoptosis
by decreasing survivin in scar fibroblasts after glaucoma surgery.
Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 22:2934–2940. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Jammal AA, Berchuck SI, Thompson AC, Costa
VP and Medeiros FA: The effect of age on increasing susceptibility
to retinal nerve fiber layer loss in glaucoma. Invest Ophthalmol
Vis Sci. 61:82020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Mu Y: Correlation analysis between TCM
syndromes of primary angle-closure glaucoma and type A personality.
Chin J Tradit Chin Ophthalmol. 10:23–30. 2020.
|
|
29
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Ye Q, Wu J, Wu P, Wang J, Niu W, Yang S,
Chen M, Rehman S and Zhu N: Enhancing peroxymonosulfate activation
of Fe-Al layered double hydroxide by dissolved organic matter:
Performance and mechanism. Water Res. 185:1162462020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Wei Z, Wang Y, Jiang L, Ji N, Wang Y, Chen
F, Li T, Li J, Xu H, Zeng X and Chen Q: miR-223 regulates oral
squamous cell carcinoma metastasis through the Wnt/β-catenin
signaling pathway. Oral Oncol. 109:1049412020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Liu YP, Wan J, Long F, Tian J and Zhang C:
circPVT1 facilitates invasion and metastasis by regulating
miR-205-5p/c-FLIP axis in osteosarcoma. Cancer Manag Res.
12:1229–1240. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Zhang Y, Chang B, Zhang J and Wu X: lncRNA
SOX2OT alleviates the high glucose-induced podocytes injury through
autophagy induction by the miR-9/SIRT1 axis. Exp Mol Pathol.
110:1042832019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Perez Vidakovics MLA, Ure AE, Arrias PN,
Romanowski V and Gómez RM: Junin virus induces autophagy in human
A549 cells. PLoS One. 14:e02187302019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Neubert P, Weichselbaum A, Reitinger C,
Schatz V, Schröder A, Ferdinand JR, Simon M, Bär AL, Brochhausen C,
Gerlach RG, et al: HIF1A and NFAT5 coordinate
Na+-boosted antibacterial defense via enhanced autophagy
and autolysosomal targeting. Autophagy. 15:1899–1916. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Nong Q, Li S, Wu Y and Liu D: lncRNA
COL1A2-AS1 inhibits the scar fibroblasts proliferation via
regulating miR-21/Smad7 pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
495:319–324. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Wang X, Chu J, Wen CJ, Fu SB, Qian YL, Wo
Y, Wang C and Wang DR: Functional characterization of TRAP1-like
protein involved in modulating fibrotic processes mediated by
TGF-β/Smad signaling in hypertrophic scar fibroblasts. Exp Cell
Res. 332:202–211. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Pang K, Li B, Tang Z, Yang W, Hao L, Shi
Z, Zhang J, Cai L, Li R, Liu Y, et al: Resveratrol inhibits
hypertrophic scars formation by activating autophagy via the
miR-4654/Rheb axis. Mol Med Rep. 22:3440–3452. 2020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Shi W, Wu Y and Bian D: p75NTR silencing
inhibits proliferation, migration and extracellular matrix
deposition of hypertrophic scar fibroblasts by activating autophagy
through inhibiting PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway. Can J Physiol Pharmacol.
Jul 29–2020.(Epub ahead of print). doi: 10.1139/cjpp-2020-0219.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
De Risi M, Torromino G, Tufano M, Moriceau
S, Pignataro A, Rivagorda M, Carrano N, Middei S, Settembre C,
Ammassari-Teule M, et al: Mechanisms by which autophagy regulates
memory capacity in ageing. Aging Cell. 19:e131892020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Lanzillotta C, Zuliani I, Vasavda C,
Snyder SH, Paul BD, Perluigi M, Di Domenico F and Barone E: BVR-A
deficiency leads to autophagy impairment through the dysregulation
of AMPK/mTOR axis in the brain-implications for neurodegeneration.
Antioxidants (Basel). 9:6712020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Long J and Pi X: Polyphyllin I promoted
melanoma cells autophagy and apoptosis via PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling
pathway. Biomed Res Int. 2020:51494172020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Luo M, Liu Y, Liu N, Shao W, Ming L, Liu J
and Xie Y: Proscillaridin A inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma
progression through inducing mitochondrial damage and autophagy.
Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). Nov 17–2020.(Epub ahead of
print). doi: 10.1093/abbs/gmaa139. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Yang J, Wang B, Xu Q, Yang Y, Hou L, Yin
K, Guo Q, Hua Y, Zhang L, Li Y, et al: TMEM166 inhibits cell
proliferation, migration and invasion in hepatocellular carcinoma
via upregulating TP53. Mol Cell Biochem. Nov 16–2020.(Epub ahead of
print). doi: 10.1007/s11010-020-03979-1. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Yang Z, Tang Y, Lu H, Shi B, Ye Y, Xu G
and Zhao Q: Long non-coding RNA reprogramming (lncRNA-ROR)
regulates cell apoptosis and autophagy in chondrocytes. J Cell
Biochem. 119:8432–8440. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Urut F, Dede S, Yuksek V, Cetin S, Usta A
and Taspinar M: In vitro evaluation of the apoptotic, autophagic,
and necrotic molecular pathways of fluoride. Biol Trace Elem Res.
Nov 16–2020.(Epub ahead of print). doi: 10.1007/s12011-020-02491-3.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|