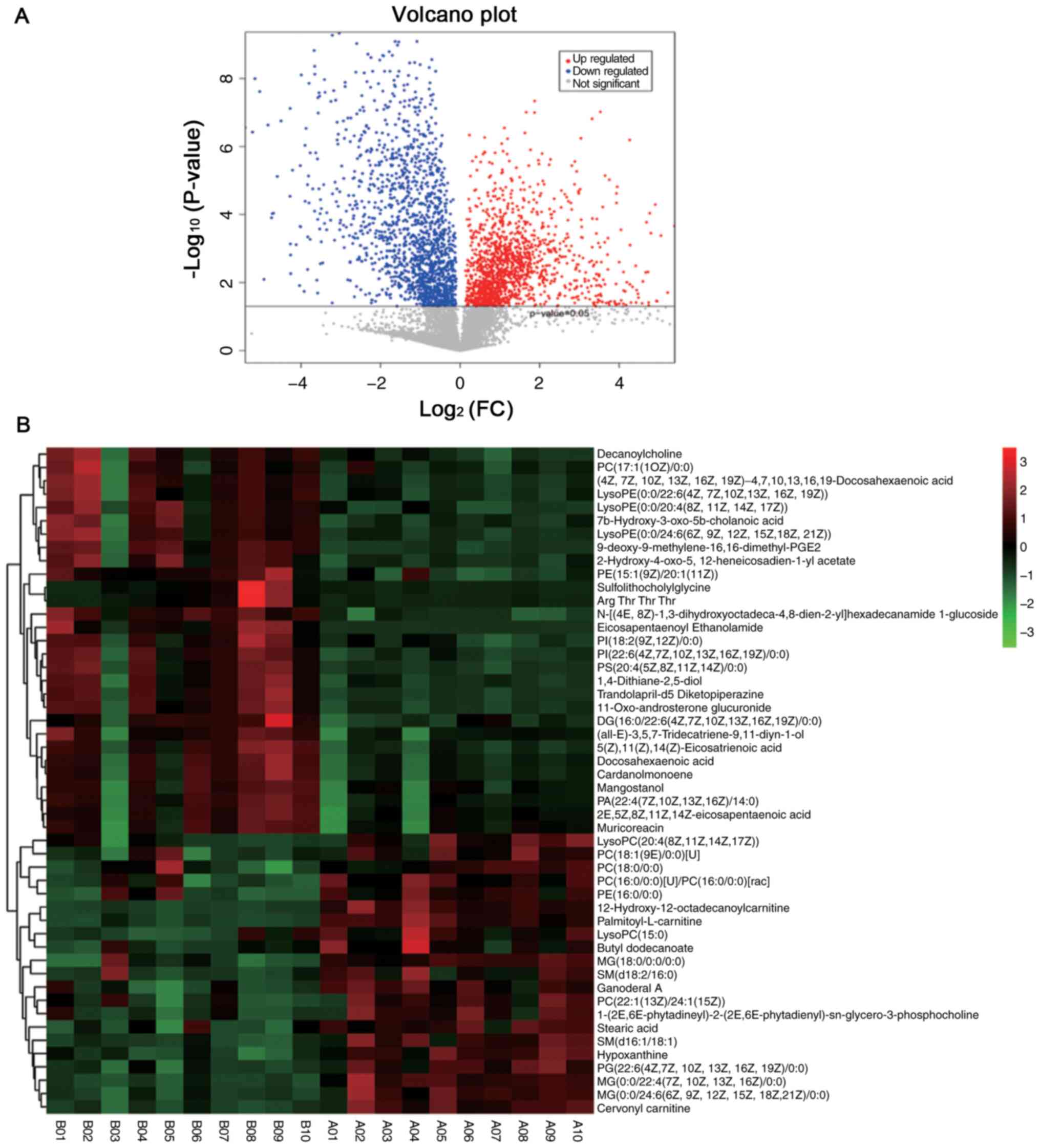
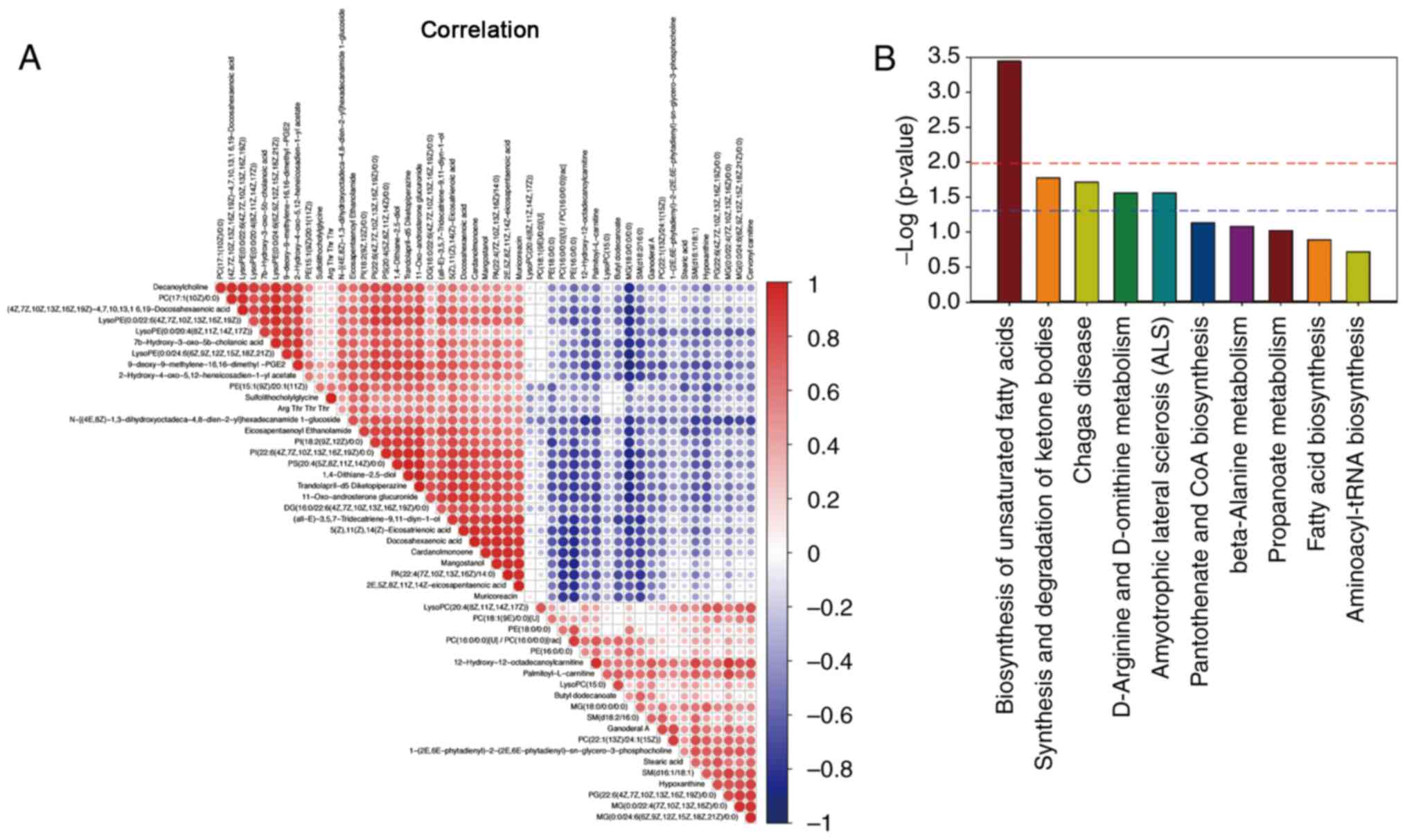
|
1
|
Laitano O, Murray KO and Leon LR:
Overlapping mechanisms of exertional heat stroke and malignant
hyperthermia: Evidence vs.conjecture. Sports Med. 50:1581–1592.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Gaudio FG and Grissom CK: Cooling methods
in heat stroke. J Emerg Med. 50:607–616. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Barriopedro D, Fischer EM, Luterbacher J,
Trigo RM and Garcia-Herrera R: The hot summer of 2010: Redrawing
the temperature record map of Europe. Science. 332:220–224. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Kovats RS and Kristie LE: Heatwaves and
public health in Europe. Eur J Public Health. 16:592–599. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Argaud L, Ferry T, Le QH, Marfisi A,
Ciorba D, Achache P, Ducluzeau R and Robert D: Short- and long-term
outcomes of heatstroke following the 2003 heat wave in Lyon,
France. Arch Intern Med. 167:2177–2183. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Roux-Buisson N, Monnier N, Sagui E, Abriat
A, Brosset C, Bendahan D, Kozak-Ribbens G, Gazzola S, Quesada JL,
Foutrier-Morello C, et al: Identification of variants of the
ryanodine receptor type 1 in patients with exertional heat stroke
and positive response to the malignant hyperthermia in vitro
contracture test. Br J Anaesth. 116:566–568. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Yang M, Zhang Y, Zhao Y and Kang H:
Research progress in the multiple organ dysfunction syndrome caused
by heat stroke. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 29:188–192.
2017.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Chen CM, Hou CC, Cheng KC, Tian RL, Chang
CP and Lin MT: Activated protein C therapy in a rat heat stroke
model. Crit Care Med. 34:1960–1966. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Ren MQ, Kazman JB, Abraham PA, Atias-Varon
D, Heled Y and Deuster PA: Gene expression profiling of humans
under exertional heat stress: Comparisons between persons with and
without exertional heat stroke. J Therm. 85:1024232019.
|
|
10
|
Lumlertgul D, Chuaychoo B, Thitiarchakul
S, Srimahachota S, Sangchun K and Keoplung M: Heat stroke-induced
multiple organ failure. Ren Fail. 14:77–80. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Deutsch M, Koskinas J, Emmanuel T,
Kountouras D and Hadziyannis S: Heat stroke and multi-organ failure
with liver involvement in an asylum-seeking refugee. J Emerg Med.
31:255–257. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
McGeehin MA and Mirabelli M: The potential
impacts of climate variability and change on temperature-related
morbidity and mortality in the United States. Environ Health
Perspect. 109 (Suppl 2):S185–S189. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Bouchama A and Knochel JP: Heat stroke. N
Engl J Med. 346:1978–1988. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Woodrow G, Brownjohn AM and Turney JH: The
clinical and biochemical features of acute renal failure due to
rhabdomyolysis. Ren Fail. 17:467–474. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Chen GM, Chen YH, Zhang W, Yu Y, Chen JH
and Chen J: Therapy of severe heatshock in combination with
multiple organ dysfunction with continuous renal replacement
therapy: A clinical study. Medicine (Baltimore). 94:e12122015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Inoue N, Sato A, Ikawa Y, Shimizu M,
Okajima M, Taniguchi T and Yachie A: Successful treatment of
exertional heat stroke using continuous plasma diafiltration. J
Clin Apher. 31:490–492. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Hamaya H, Hifumi T, Kawakita K, Okazaki T,
Kiridume K, Shinohara N, Abe Y, Takano K, Hagiike M and Kuroda Y:
Successful management of heat stroke associated with multiple-organ
dysfunction by active intravascular cooling. Am J Emerg Med.
33:124.e5–e7. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Ye J, Mo W, Chen Y and Yang A: An analysis
of laboratory results of parameters of organ function in patients
with heat stroke. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue.
27:658–661. 2015.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zhao JJ, Zhou JJ, Hu J, Zhou FH, Kang HJ,
Liu H, Pan L and Song Q: Analysis of risk factors affecting
prognosis of exertional heat stroke. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu
Yi Xue. 25:515–518. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Segev G, Bruchim Y, Berl N, Cohen A and
Aroch I: Effects of fenoldopam on kidney function parameters and
its therapeutic efficacy in the management of acute kidney injury
in dogs with heatstroke. J Vet Intern Med. 32:1109–1115. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Peng N, Geng Y, Zhang S, Tang Y, Wen Q,
Tong H, Liu Y, Liu Z and Su L: Correlation of kidney injury and
inflammatory response in rats with classic severe heatstroke.
Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 27:327–331. 2015.(In
Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Protasi F, Paolini C and Dainese M:
Calsequestrin-1: A new candidate gene for malignant hyperthermia
and exertional/environmental heat stroke. J Physiol. 587:3095–3100.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Leon LR and Helwig BG: Heat stroke: Role
of the systemic inflammatory response. J Appl Physiol (1985).
109:1980–1988. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Roberts GT, Ghebeh H, Chishti MA,
Al-Mohanna F, El-Sayed R, Al-Mohanna F and Bouchama A:
Microvascular injury, thrombosis, inflammation, and apoptosis in
the pathogenesis of heatstroke: A study in baboon model.
Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 28:1130–1136. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Rosendal L, Langberg H, Skov-Jensen A and
Kjaer M: Incidence of injury and physical performance adaptations
during military training. Clin J Sport Med. 13:157–163. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Yang PC, He SH and Zheng PY: Investigation
into the signal transduction pathway via which heat stress impairs
intestinal epithelial barrier function. J Gastroenterol Hepatol.
22:1823–1831. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Mittal R and Coopersmith CM: Redefining
the gut as the motor of critical illness. Trends Mol Med.
20:214–223. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Clayton TA, Lindon JC, Cloarec O, Antti H,
Charuel C, Hanton G, Provost JP, Le Net JL, Baker D, Walley RJ, et
al: Pharmaco-metabonomic phenotyping and personalized drug
treatment. Nature. 440:1073–1077. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Kork F, Holthues J, Hellweg R, Jankowski
V, Tepel M, Ohring R, Heuser I, Bierbrauer J, Peters O, Schlattmann
P, et al: A possible new diagnostic biomarker in early diagnosis of
Alzheimer's disease. Curr Alzheimer Res. 6:519–524. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Laitano O, Garcia CK, Mattingly AJ,
Robinson GP, Murray KO, King MA, Ingram B, Ramamoorthy S, Leon LR
and Clanton TL: Delayed metabolic dysfunction in myocardium
following exertional heat stroke in mice. J Physiol. 598:967–985.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Li Y, Zhu X, Zhang M, Tong H and Su L:
Heatstroke-induced hepatocyte exosomes promote liver injury by
activating the NOD-like receptor signaling pathway in mice. PeerJ.
7:e82162019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Tai PA, Chang CK, Niu KC, Lin MT, Chiu WT
and Lin JW: Reduction of ischemic and oxidative damage to the
hypothalamus by hyperbaric oxygen in heatstroke mice. J Biomed
Biotechnol. 2010:6095262010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Umemura Y, Ogura H, Matsuura H, Ebihara T,
Shimizu K and Shimazu T: Bone marrow-derived mononuclear cell
therapy can attenuate systemic inflammation in rat heatstroke.
Scand J Trauma Resusc Emerg Med. 26:972018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Yeh CH, Chen ZC, Hsu CC, Lin MT and Chen
CC: Protection in rats with heatstroke: Hyperbaric oxygen vs
activated protein C therapy. Eur J Pharmacol. 635:103–108. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Yayi H, Yeda X, Huaxin W, Yang W, Qian S
and Zhongyuan X: Toll-like receptor 7 involves the injury in acute
kidney ischemia/reperfusion of STZ-induced diabetic rats. Acta Cir
Bras. 31:448–455. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Satirapoj B, Kongthaworn S, Choovichian P
and Supasyndh O: Electrolyte disturbances and risk factors of acute
kidney injury patients receiving dialysis in exertional heat
stroke. BMC Nephrol. 17:552016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
López-Ibáñez J, Pazos F and Chagoyen M:
MBROLE 2.0-functional enrichment of chemical compounds. Nucleic
Acids Res. 44((W1)): W201–W204. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Kanehisa M, Sato Y, Furumichi M, Morishima
K and Tanabe M: New approach for understanding genome variations in
KEGG. Nucleic Acids Res. 47(D1): D590–D595. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Alele F, Malau-Aduli B, Malau-Aduli A and
Crowe M: Systematic review of gender differences in the
epidemiology and risk factors of exertional heat illness and heat
tolerance in the armed forces. BMJ Open. 10:e0318252020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Li L, Tan H, Zou Z, Gong J, Zhou J, Peng
N, Su L, Maegele M, Cai D and Gu Z: Preventing necroptosis by
scavenging ROS production alleviates heat stress-induced intestinal
injury. Int J Hyperthermia. 37:517–530. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Thongprayoon C, Qureshi F, Petnak T,
Cheungpasitporn W, Chewcharat A, Cato LD, Boonpheng B, Bathini T,
Hansrivijit P, Vallabhajosyula S and Kaewput W: Impact of acute
kidney injury on outcomes of hospitalizations for heat stroke in
the United States. Diseases. 8:282020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Weigand K, Riediger C, Stremmel W,
Flechtenmacher C and Encke J: Are heat stroke and physical
exhaustion underestimated causes of acute hepatic failure? World J
Gastroenterol. 13:306–309. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Hu J, Kang HJ, Liu C, Hu P, Yang MM and
Zhou FH: Response of regulatory T cells to classic heat stroke in
mice. Exp Ther Med. 16:4609–4615. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Shapiro Y, Alkan M, Epstein Y, Newman F
and Magazanik A: Increase in rat intestinal permeability to
endotoxin during hyperthermia. Eur J Appl Physiol Occup Physiol.
55:410–412. 1986. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Gathiram P, Wells MT, Raidoo D, Brock-Utne
JG and Gaffin SL: Portal and systemic plasma lipopolysaccharide
concentrations in heat-stressed primates. Circ Shock. 25:223–230.
1988.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Gathiram P, Wells MT, Brock-Utne JG and
Gaffin SL: Antilipopolysaccharide improves survival in primates
subjected to heat stroke. Circ Shock. 23:157–164. 1987.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Huisse MG, Pease S, Hurtado-Nedelec M,
Arnaud B, Malaquin C, Wolff M, Gougerot-Pocidalo MA, Kermarrec N,
Bezeaud A, Guillin MC, et al: Leukocyte activation: The link
between inflammation and coagulation during heatstroke. A study of
patients during the 2003 heat wave in Paris. Crit Care Med.
36:2288–2295. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Tong HS, Tang YQ, Chen Y, Qiu JM, Wen Q
and Su L: Early elevated HMGB1 level predicting the outcome in
exertional heatstroke. J Trauma. 71:808–814. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Pozner RG, Ure AE, Jaquenod de Giusti C,
D'Atri LP, Italiano JE, Torres O, Romanowski V, Schattner M and
Gómez RM: Junín virus infection of human hematopoietic progenitors
impairs in vitro proplatelet formation and platelet release via a
bystander effect involving type I IFN signaling. PLoS Pathog.
6:e10008472010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Chen HS, Tong HS, Zhao Y, Hong CY, Bin JP
and Su L: Differential expression pattern of exosome long
non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) and MicroRNAs (miRNAs) in vascular
endothelial cells under heat stroke. Med Sci Monit. 24:7965–7974.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Thulesius O: Thermal reactions of blood
vessels in vascular stroke and heatstroke. Med Princ Pract.
15:316–321. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Fan H, Zhao Y, Zhu JH, Song FC, Ye JH,
Wang ZY and Le JW: Thrombocytopenia as a predictor of severe acute
kidney injury in patients with heat stroke. Ren Fail. 37:877–881.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Michels S, Buchholz HG, Rosar F, Heinrich
I, Hoffmann MA, Schweiger S, Tüscher O and Schreckenberger M:
18F-FDG PET/CT: An unexpected case of Huntington's disease. BMC
Neurol. 19:782019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Wan Y, Sun SS, Fu HY, Xu YK, Liu Q, Yin JT
and Wan B: Adjuvant rhubarb alleviates organs dysfunction and
inhibits inflammation in heat stroke. Exp Ther Med. 16:1493–1498.
2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Yang TH, Shih MF, Wen YS, Ho WY, Leu KL,
Wang MY and Liu CC: Attenuation of circulatory shock and cerebral
ischemia injury in heat stroke by combination treatment with
dexamethasone and hydroxyethyl starch. Exp Transl Stroke Med.
2:192010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Kurts C, Panzer U, Anders HJ and Rees AJ:
The immune system and kidney disease: Basic concepts and clinical
implications. Nat Rev Immunol. 13:738–753. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Chen Q, Guan X, Zuo X, Wang J and Yin W:
The role of high mobility group box 1 (HMGB1) in the pathogenesis
of kidney diseases. Acta Pharm Sin B. 6:183–188. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Liu GQ, Zuo XH, Jiang LN, Zhang YP, Zhang
LM, Zhao ZG and Niu CY: Inhibitory effect of post-hemorrhagic shock
mesenteric lymph drainage on the HMGB1 and RAGE in mouse kidney.
Ren Fail. 38:131–136. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Miriyala S, Thippakorn C, Chaiswing L, Xu
Y, Noel T, Tovmasyan A, Batinic-Haberle I, Vander Kooi CW, Chi W,
Latif AA, et al: Novel role of 4-hydroxy-2-nonenal in
AIFm2-mediated mitochondrial stress signaling. Free Radic Biol Med.
91:68–80. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Qin S, Wang H, Yuan R, Li H, Ochani M,
Ochani K, Rosas-Ballina M, Czura CJ, Huston JM, Miller E, et al:
Role of HMGB1 in apoptosis-mediated sepsis lethality. J Exp Med.
203:1637–1642. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Adato B, Dubnov-Raz G, Gips H, Heled Y and
Epstein Y: Fatal heat stroke in children found in parked cars:
Autopsy findings. Eur J Pediatr. 175:1249–1252. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Xu L, Zhao K, Shen X, Fan XX, Ding K, Liu
RM and Wang F: Blockade of extracellular high-mobility group box 1
attenuates systemic inflammation and coagulation abnormalities in
rats with acute traumatic coagulopathy. Med Sci Monit.
22:2561–2570. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Xiao G, Yuan F, Geng Y, Qiu X, Liu Z, Lu
J, Tang L, Zhang Y and Su L: Eicosapentaenoic acid enhances
heatstroke-impaired intestinal epithelial barrier function in rats.
Shock. 44:348–356. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Wei W, Chen M, Zhu Y, Wang J, Zhu P, Li Y
and Li J: Down-regulation of vascular HMGB1 and RAGE expression by
n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids is accompanied by amelioration of
chronic vasculopathy of small bowel allografts. J Nutr Biochem.
23:1333–1340. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Ying S, Xiao X, Chen T and Lou J: PPAR
ligands function as suppressors that target biological actions of
HMGB1. PPAR Res. 2016:26127432016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|