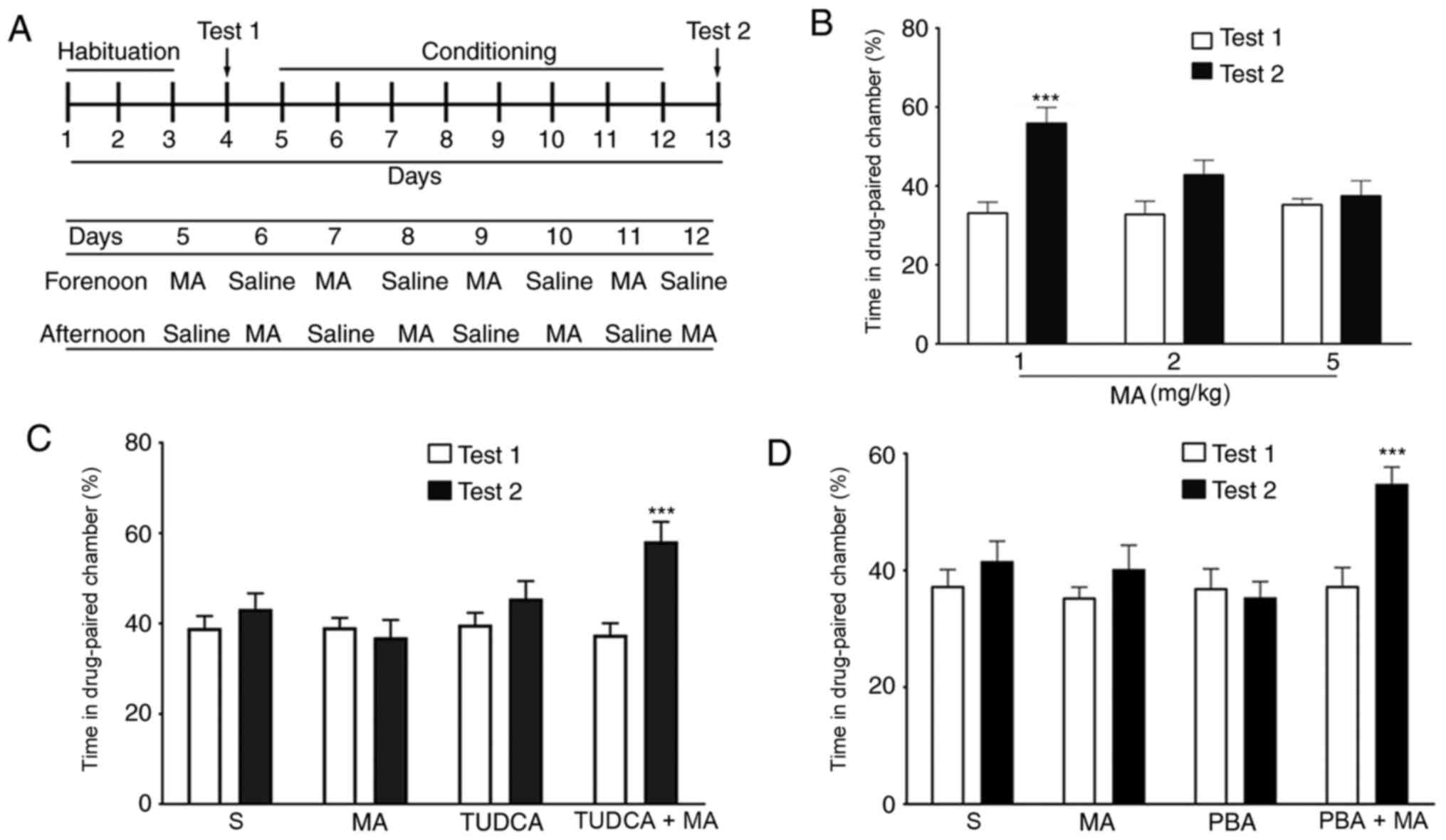
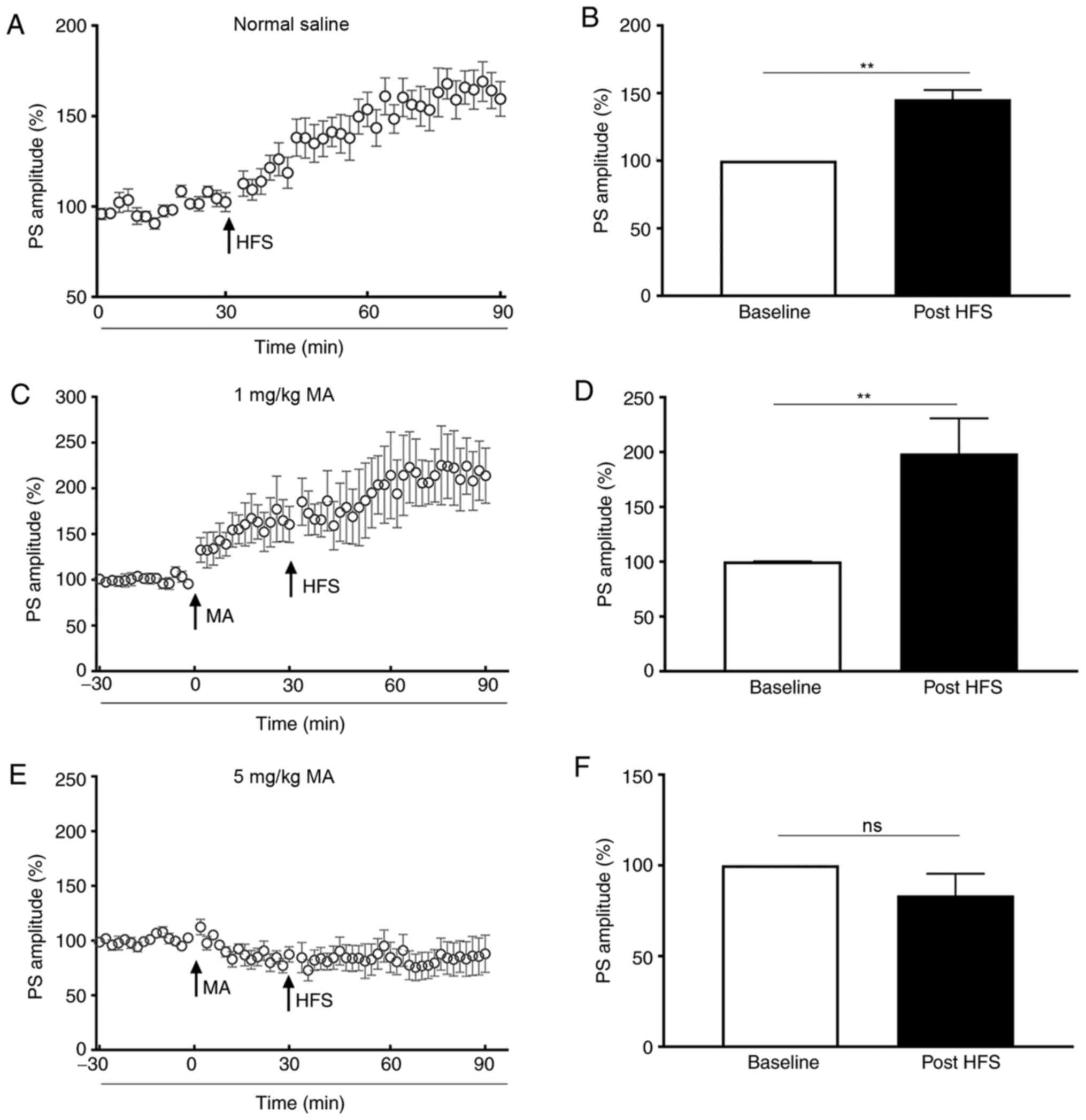
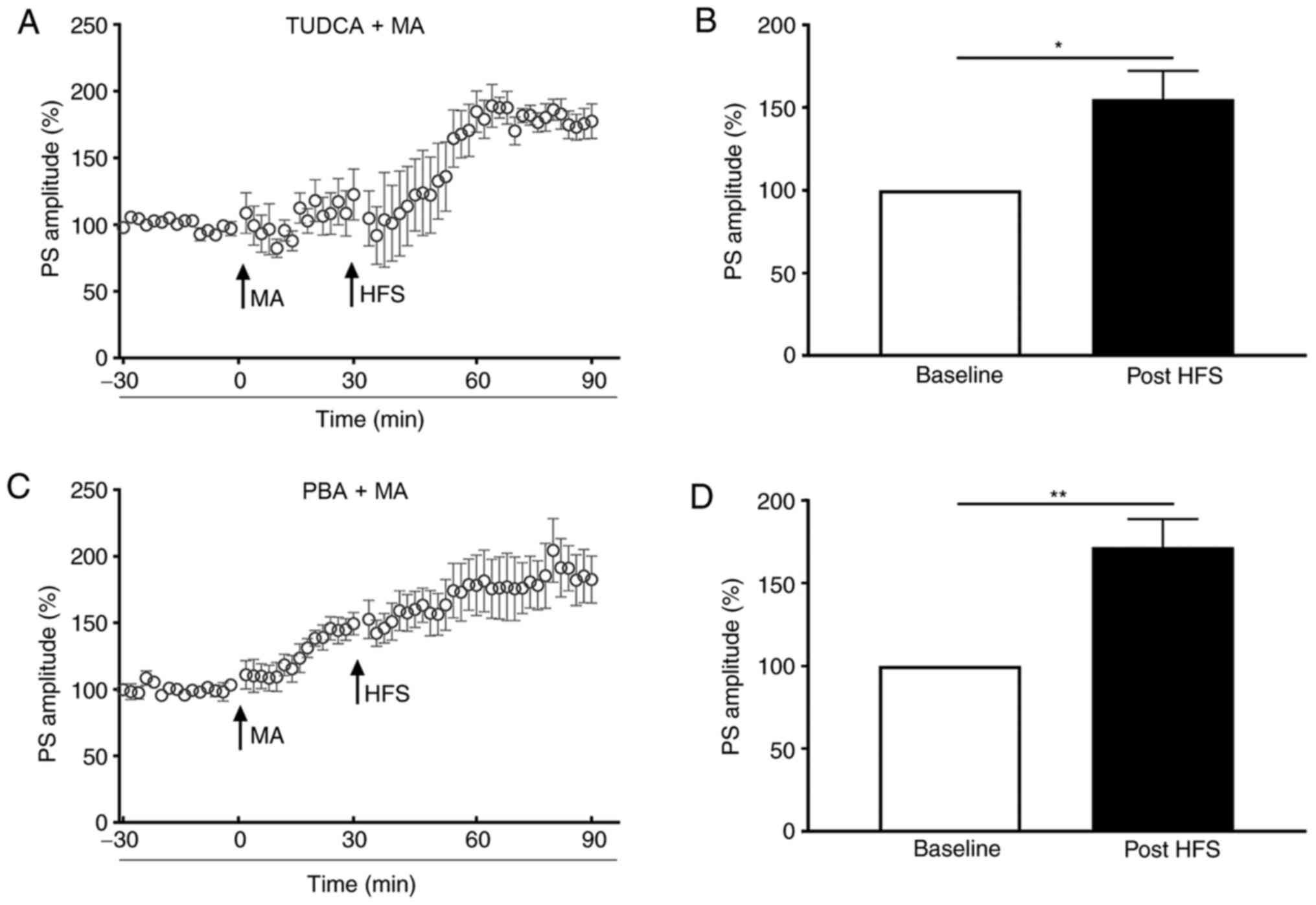
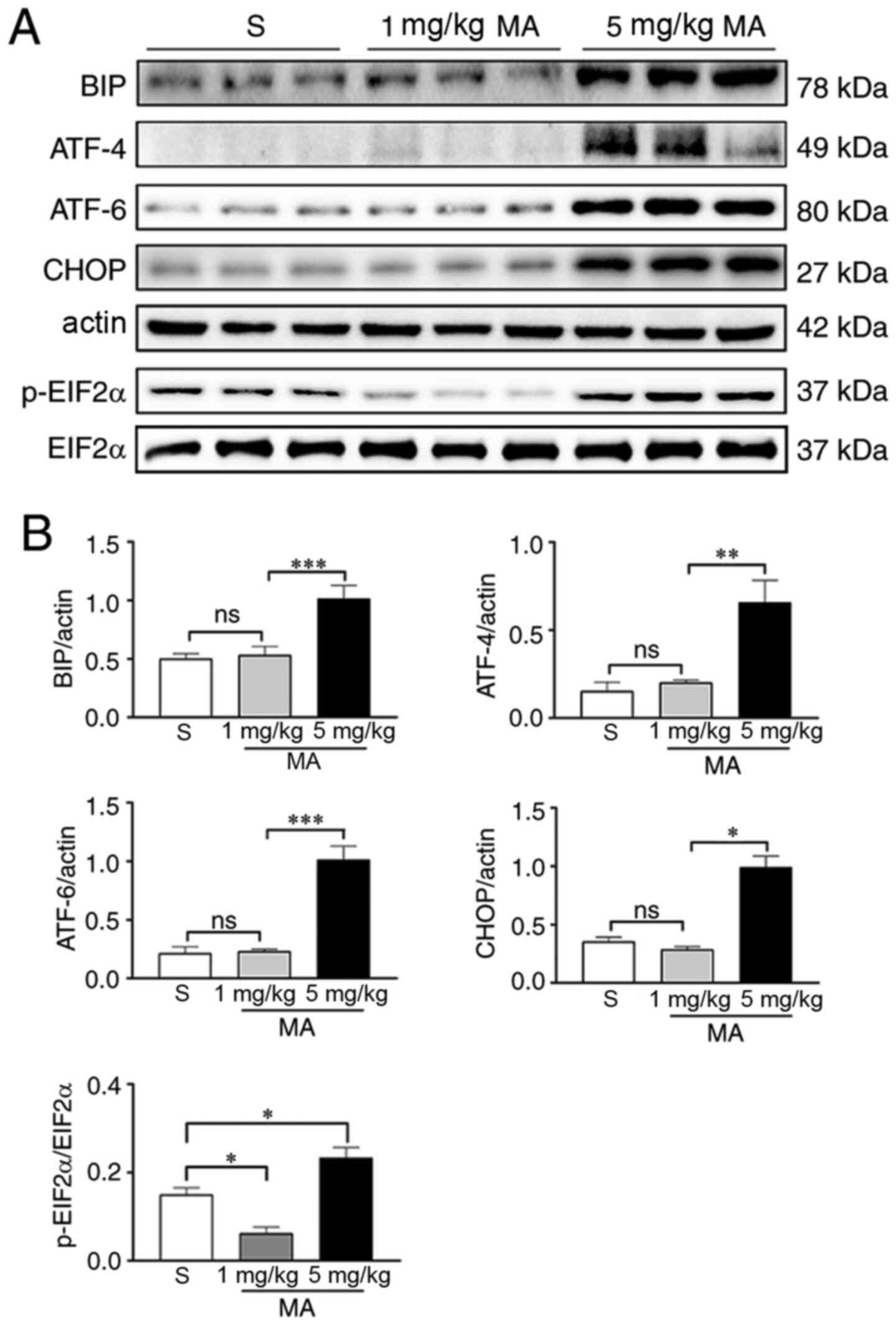
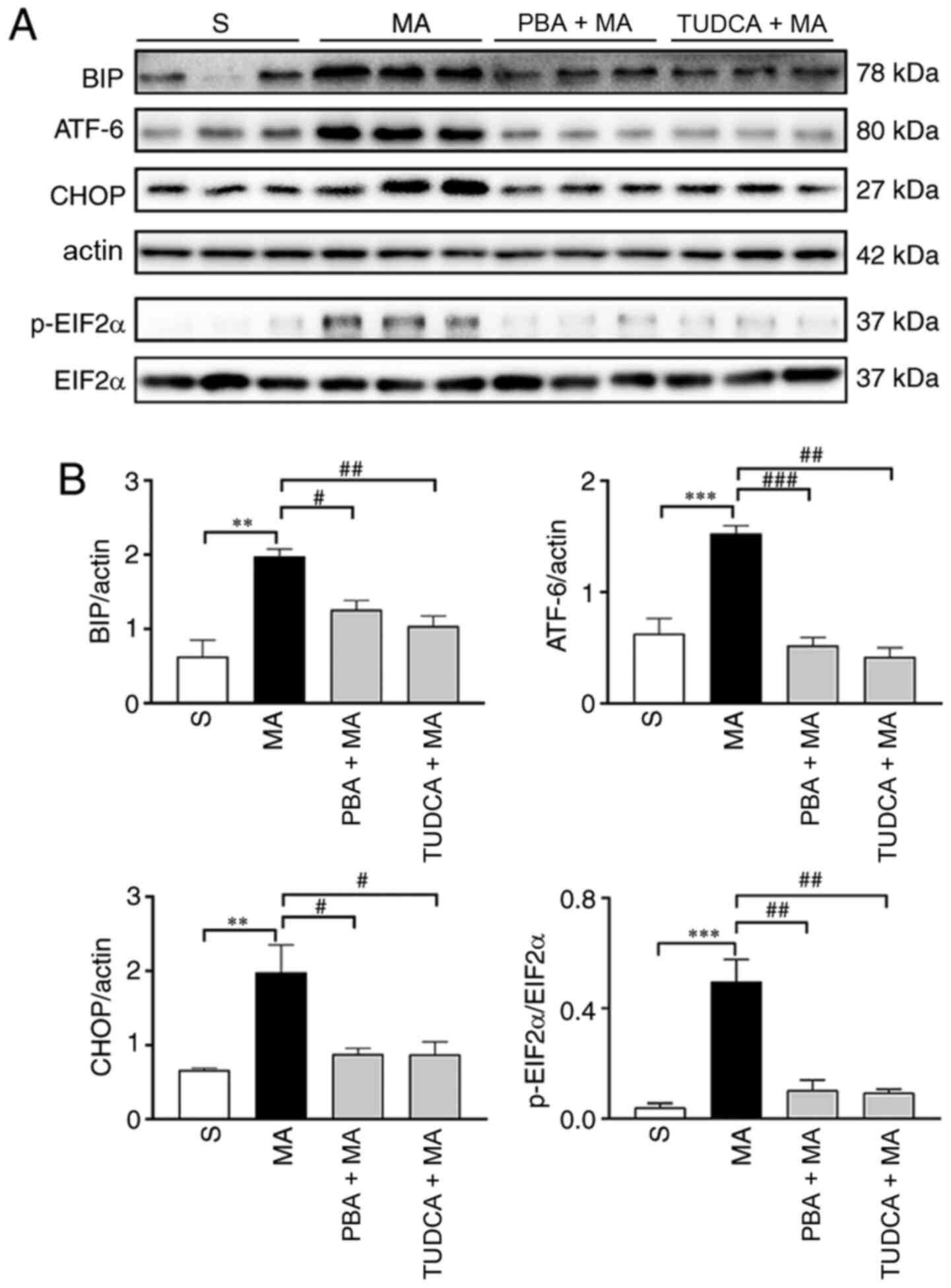
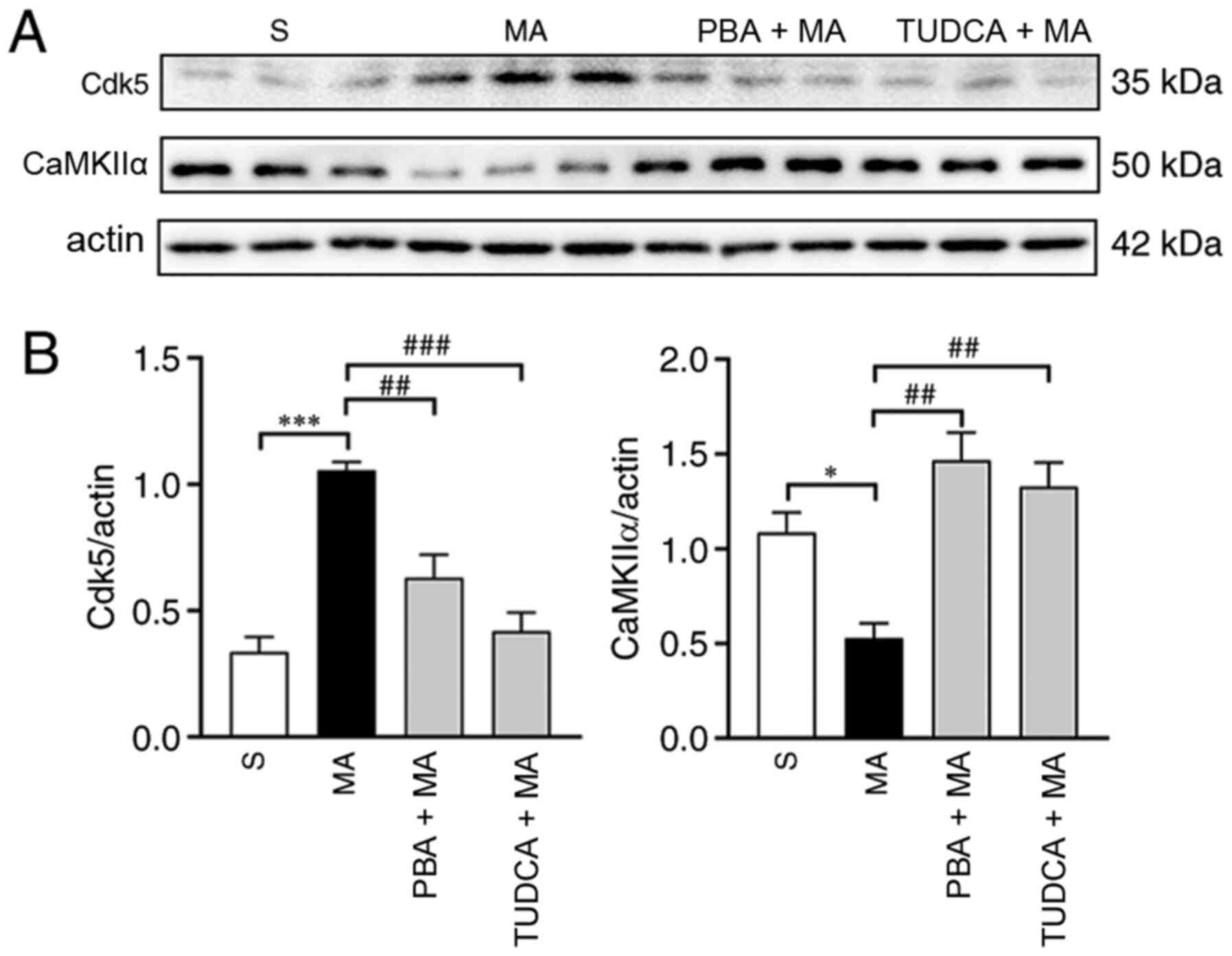
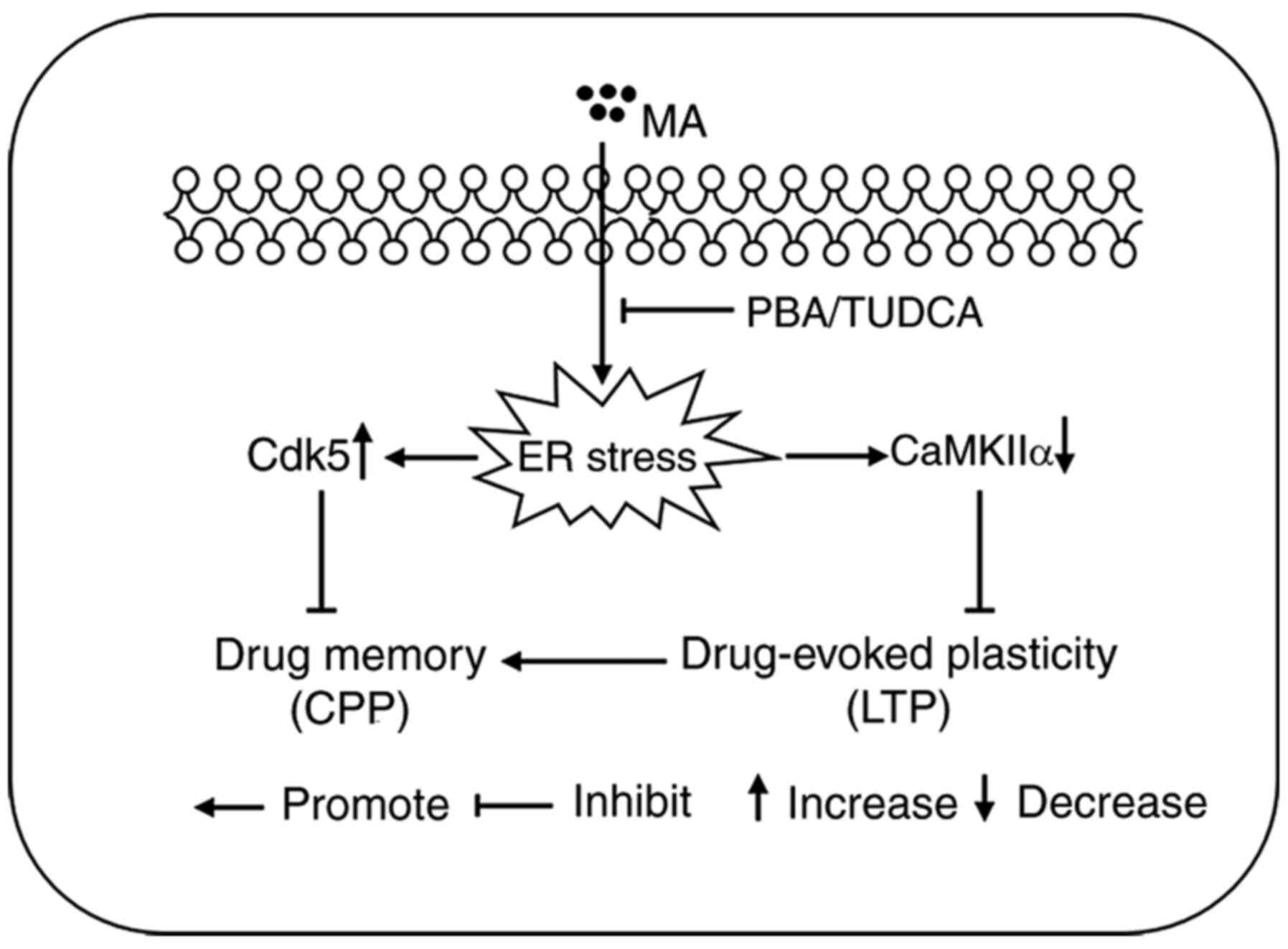
|
1
|
Joffe ME, Grueter CA and Grueter BA:
Biological substrates of addiction. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Cogn Sci.
5:151–171. 2014. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Koob GF and Volkow ND: Neurocircuitry of
addiction. Neuropsychopharmacology. 35:217–238. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Di Chiara G, Bassareo V, Fenu S, De Luca
MA, Spina L, Cadoni C, Acquas E, Carboni E, Valentini V and Lecca
D: Dopamine and drug addiction: The nucleus accumbens shell
connection. Neuropharmacology. 47 (Suppl 1):S227–S241. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Gipson CD, Kupchik YM and Kalivas PW:
Rapid, transient synaptic plasticity in addiction.
Neuropharmacology. 76(Pt B): 276–286. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
McLellan AT, Lewis DC, O'Brien CP and
Kleber HD: Drug dependence, a chronic medical illness: Implications
for treatment, insurance, and outcomes evaluation. JAMA.
284:1689–1695. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Tronson N and Taylor J: Molecular
mechanisms of memory reconsolidation. Nat Rev Neurosci. 8:262–275.
2007. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
de Carvalho C and Takahashi R: Cannabidiol
disrupts the reconsolidation of contextual drug-associated memories
in Wistar rats. Addict Biol. 22:742–751. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Hyman S: Addiction: A disease of learning
and memory. Am J Psychiatry. 162:1414–1422. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Hyman S and Malenka R: Addiction and the
brain: The neurobiology of compulsion and its persistence. Nat Rev
Neurosci. 2:695–703. 2001. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Berke J and Hyman S: Addiction, dopamine,
and the molecular mechanisms of memory. Neuron. 25:515–532. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Grimm JW, Hope BT, Wise RA and Shaham Y:
Neuroadaptation. Incubation of cocaine craving after withdrawal.
Nature. 412:141–142. 2001. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Zhang Y, Xue Y, Meng S, Luo Y, Liang J, Li
J, Ai S, Sun C, Shen H, Zhu W, et al: Inhibition of lactate
transport erases drug memory and prevents drug relapse. Biol
Psychiatry. 79:928–939. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Hyman S, Malenka R and Nestler E: Neural
mechanisms of addiction: The role of reward-related learning and
memory. Annu Rev Neurosci. 29:565–598. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Kelley AE: Memory and addiction: Shared
neural circuitry and molecular mechanisms. Neuron. 44:161–179.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Frey U and Morris RG: Synaptic tagging and
long-term potentiation. Nature. 385:533–536. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Whitlock J, Heynen A, Shuler M and Bear M:
Learning induces long-term potentiation in the hippocampus.
Science. 313:1093–1097. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Pastalkova E, Serrano P, Pinkhasova D,
Wallace E, Fenton AA and Sacktor TC: Storage of spatial information
by the maintenance mechanism of LTP. Science. 313:1141–1144. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Luscher C and Malenka RC: Drug-evoked
synaptic plasticity in addiction: From molecular changes to circuit
remodeling. Neuron. 69:650–663. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Grueter B, Rothwell P and Malenka R:
Integrating synaptic plasticity and striatal circuit function in
addiction. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 22:545–551. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Courtney KE and Ray LA: Methamphetamine:
An update on epidemiology, pharmacology, clinical phenomenology,
and treatment literature. Drug Alcohol Depend. 143:11–21. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
North A, Swant J, Salvatore M,
Gamble-George J, Prins P, Butler B, Mittal MK, Heltsley R, Clark JT
and Khoshbouei H: Chronic methamphetamine exposure produces a
delayed, long-lasting memory deficit. Synapse. 67:245–257. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Naidoo N: ER and aging-Protein folding and
the ER stress response. Ageing Res Rev. 8:150–159. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Zhang Z, Qin P, Deng Y, Ma Z, Guo H, Guo
H, Hou Y, Wang S, Zou W, Sun Y, et al: The novel estrogenic
receptor GPR30 alleviates ischemic injury by inhibiting
TLR4-mediated microglial inflammation. J Neuroinflammation.
15:2062018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Wakida N, Kiguchi N, Saika F, Nishiue H,
Kobayashi Y and Kishioka S: CC-chemokine ligand 2 facilitates
conditioned place preference to methamphetamine through the
activation of dopamine systems. J Pharmacol Sci. 125:68–73. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Gureviciene I, Ikonen S, Gurevicius K,
Sarkaki A, van Groen T, Pussinen R, Ylinen A and Tanila H: Normal
induction but accelerated decay of LTP in APP+PS1 transgenic mice.
Neurobiol Dis. 15:188–195. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Marquardt N, Feja M, Hünigen H, Plendl J,
Menken L, Fink H and Bert B: Euthanasia of laboratory mice: Are
isoflurane and sevoflurane real alternatives to carbon dioxide?
PLoS One. 13:e02037932018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Cai D, Huang E, Luo B, Yang Y, Zhang F,
Liu C, Lin Z, Xie WB and Wang H: Nupr1/Chop signal axis is involved
in mitochondrion-related endothelial cell apoptosis induced by
methamphetamine. Cell Death Dis. 7:e21612016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Anderson S, Famous KR, Sadri-Vakili G,
Kumaresan V, Schmidt HD, Bass CE, Terwilliger EF, Cha JH and Pierce
RC: CaMKII: A biochemical bridge linking accumbens dopamine and
glutamate systems in cocaine seeking. Nat Neurosci. 11:344–353.
2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Mlewski E, Krapacher F, Ferreras S and
Paglini G: Transient enhanced expression of Cdk5 activator p25
after acute and chronic d-amphetamine administration. Ann N Y Acad
Sci. 1139:89–102. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Koob G, Ahmed S, Boutrel B, Chen SA, Kenny
PJ, Markou A, O'Dell LE, Parsons LH and Sanna PP: Neurobiological
mechanisms in the transition from drug use to drug dependence.
Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 27:739–749. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
White NM: Addictive drugs as reinforcers:
Multiple partial actions on memory systems. Addiction. 91:921–949;
discussion 951–965. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Li FQ, Xue YX, Wang JS, Fang Q, Li YQ, Zhu
WL, He YY, Liu JF, Xue LF, Shaham Y and Lu L: Basolateral amygdala
cdk5 activity mediates consolidation and reconsolidation of
memories for cocaine cues. J Neurosci. 30:10351–10359. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Boury-Jamot B, Carrard A, Martin JL,
Halfon O, Magistretti PJ and Boutrel B: Disrupting astrocyte-neuron
lactate transfer persistently reduces conditioned responses to
cocaine. Mol Psychiatry. 21:1070–1076. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Moncada D and Viola H: Induction of
long-term memory by exposure to novelty requires protein synthesis:
Evidence for a behavioral tagging. J Neurosci. 27:7476–7481. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Sun L, Song R, Chen Y, Yang RF, Wu N, Su
RB and Li J: A selective D3 receptor antagonist YQA14 attenuates
methamphetamine-induced behavioral sensitization and conditioned
place preference in mice. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 37:157–165. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Sweatt JD: Hippocampal function in
cognition. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 174:99–110. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Lisman J and Grace A: The hippocampal-VTA
loop: Controlling the entry of information into long-term memory.
Neuron. 46:703–713. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Keleta Y and Martinez J: Brain circuits of
methamphetamine place reinforcement learning: The role of the
hippocampus-VTA Loop. Brain Behav. 2:128–141. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Ricoy U and Martinez J Jr: Local
hippocampal methamphetamine-induced reinforcement. Front Behav
Neurosci. 3:472009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Lüscher C: Drug-evoked synaptic plasticity
causing addictive behavior. J Neurosci. 33:17641–17646. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Ungless M, Whistler J, Malenka R and Bonci
A: Single cocaine exposure in vivo induces long-term potentiation
in dopamine neurons. Nature. 411:583–587. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Benavides DR, Quinn JJ, Zhong P, Hawasli
AH, DiLeone RJ, Kansy JW, Olausson P, Yan Z, Taylor JR and Bibb JA:
Cdk5 modulates cocaine reward, motivation, and striatal neuron
excitability. J Neurosci. 27:12967–12976. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Wang L, Lv Z, Hu Z, Sheng J, Hui B, Sun J
and Ma L: Chronic cocaine-induced H3 acetylation and
transcriptional activation of CaMKIIalpha in the nucleus accumbens
is critical for motivation for drug reinforcement.
Neuropsychopharmacology. 35:913–928. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Huang W, Placzek A, Viana Di Prisco G,
Khatiwada S, Sidrauski C, Krnjević K, Walter P, Dani JA and
Costa-Mattioli M: Translational control by eIF2alpha
phosphorylation regulates vulnerability to the synaptic and
behavioral effects of cocaine. Elife. 5:e120522016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Placzek A, Molfese D, Khatiwada S, Viana
Di Prisco G, Huang W, Sidrauski C, Krnjević K, Amos CL, Ray R, Dani
JA, et al: Translational control of nicotine-evoked synaptic
potentiation in mice and neuronal responses in human smokers by
eIF2α. eLife. 5:e120562016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Placzek A, Prisco G, Khatiwada S, Sgritta
M, Huang W, Krnjević K, Kaufman RJ, Dani JA, Walter P and
Costa-Mattioli M: eIF2α-mediated translational control regulates
the persistence of cocaine-induced LTP in midbrain dopamine
neurons. Elife. 5:e175172016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Fan HY, Cherng CG, Yang FY, Cheng LY, Tsai
CJ, Lin LC and Yu L: Systemic treatment with protein synthesis
inhibitors attenuates the expression of cocaine memory. Behavi
Brain Res. 208:522–527. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|