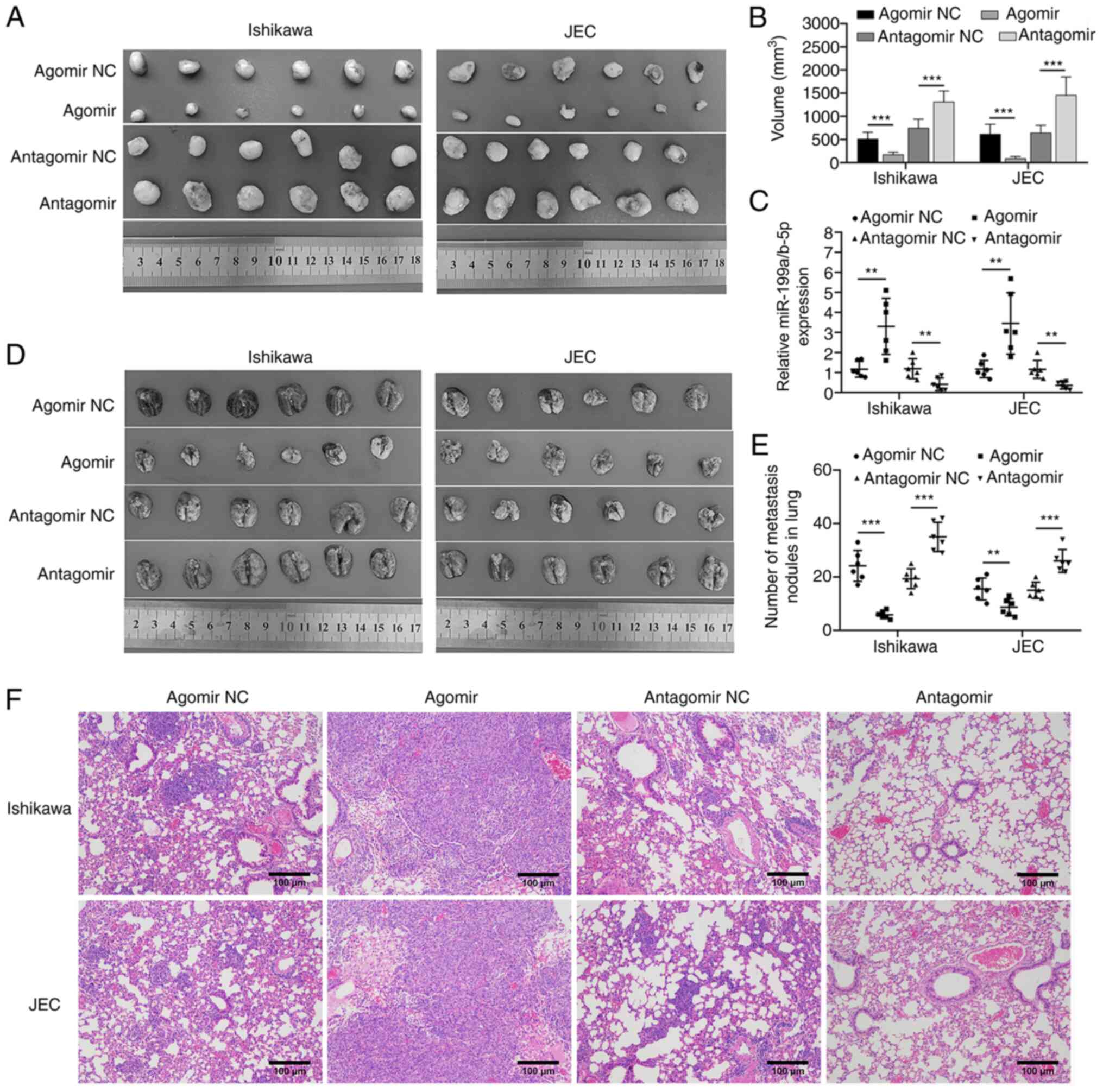
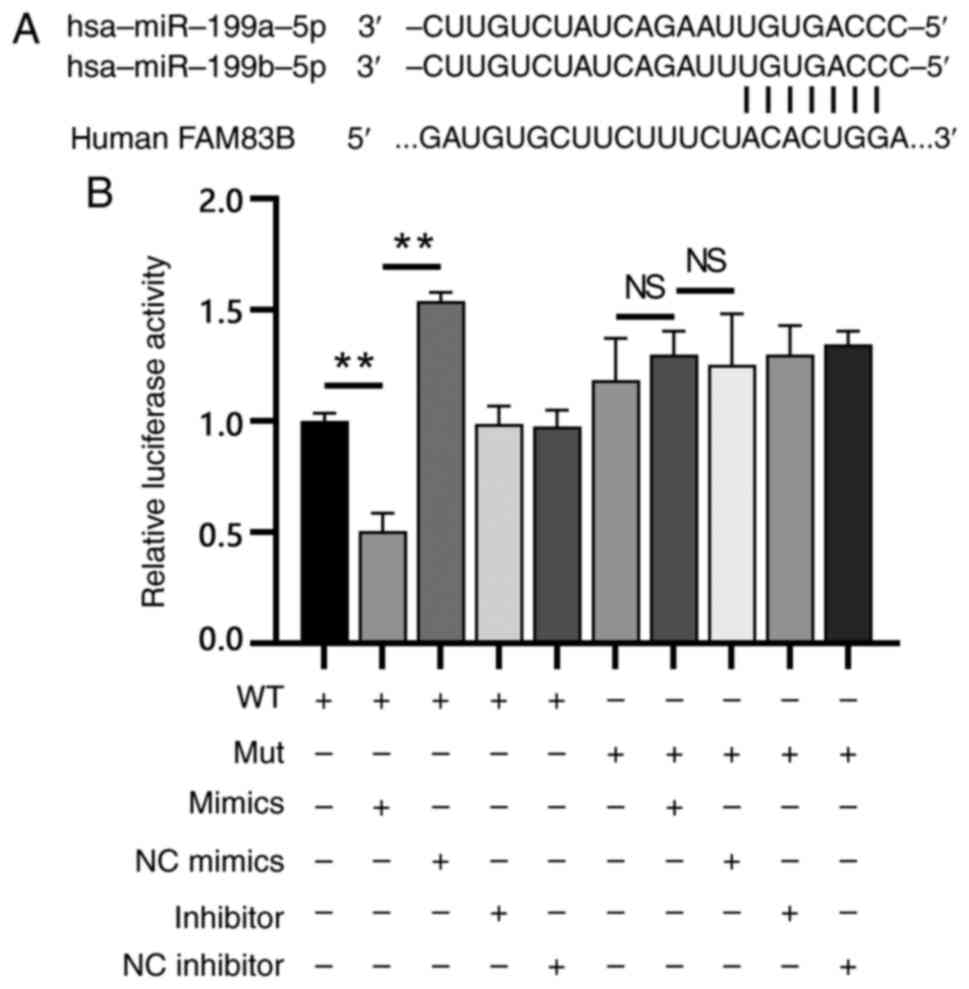
|
1
|
Morice P, Leary A, Creutzberg C,
Abu-Rustum N and Darai E: Endometrial cancer. Lancet.
387:1094–1108. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Geng YH, Wang ZF, Jia YM, Zheng LY, Chen
L, Liu DG, Li XH, Tian XX and Fang WG: Genetic polymorphisms in
CDH1 are associated with endometrial carcinoma susceptibility among
Chinese Han women. Oncol Lett. 16:6868–6878. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Rodriguez AM, Schmeler KM and Kuo YF: Lack
of improvement in survival rates for women under 50 with
endometrial cancer, 2000–2011. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol.
142:783–793. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Zhang HH, Li R, Li YJ, Yu XX, Sun QN, Li
AY and Kong Y: eIF4Erelated miR320a and miR3405p inhibit
endometrial carcinoma cell metastatic capability by preventing
TGF-β-1induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Oncol Rep.
43:447–460. 2020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Su J, Morgani SM, David CJ, Wang Q, Er EE,
Huang YH, Basnet H, Zou Y, Shu W, Soni RK, et al: TGF-beta
orchestrates fibrogenic and developmental EMTs via the RAS effector
RREB1. Nature. 577:566–571. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Qureshi R, Arora H and Rizvi MA: EMT in
cervical cancer: Its role in tumour progression and response to
therapy. Cancer Lett. 356:321–331. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Mutlu M, Raza U, Saatci O, Eyupoglu E,
Yurdusev E and Sahin O: miR-200c: A versatile watchdog in cancer
progression, EMT, and drug resistance. J Mol Med (Berl).
94:629–644. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Padmanaban V, Krol I, Suhail Y, Szczerba
BM, Aceto N, Bader JS and Ewald AJ: E-cadherin is required for
metastasis in multiple models of breast cancer. Nature.
573:439–444. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Li CF, Chen JY, Ho YH, Hsu WH, Wu LC, Lan
HY, Hsu DS, Tai SK, Chang YC and Yang MH: Snail-induced claudin-11
prompts collective migration for tumour progression. Nat Cell Biol.
21:251–262. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Shen CQ, Yan TT, Liu W, Zhu XQ, Tian XL,
Fu XL, Hua R, Zhang JF, Huo YM, Liu DJ, et al: High expression of
FAM83B predicts poor prognosis in patients with pancreatic ductal
adenocarcinoma and correlates with cell cycle and cell
proliferation. J Cancer. 8:3154–3165. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Zou Z, Ma T, He X, Zhou J, Ma H, Xie M,
Liu Y, Lu D, Di S and Zhang Z: Long intergenic non-coding RNA 00324
promotes gastric cancer cell proliferation via binding with HuR and
stabilizing FAM83B expression. Cell Death Dis. 9:7172018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Cipriano R, Graham J, Miskimen KL, Bryson
BL, Bruntz RC, Scott SA, Brown HA, Stark GR and Jackson MW: FAM83B
mediates EGFR- and RAS-driven oncogenic transformation. J Clin
Invest. 122:3197–3210. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Cipriano R, Miskimen KL, Bryson BL, Foy
CR, Bartel CA and Jackson MW: FAM83B-mediated activation of
PI3K/AKT and MAPK signaling cooperates to promote epithelial cell
transformation and resistance to targeted therapies. Oncotarget.
4:729–738. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Yamaura T, Ezaki J, Okabe N, Takagi H,
Ozaki Y, Inoue T, Watanabe Y, Fukuhara M, Muto S, Matsumura Y, et
al: Family with sequence similarity 83, member B is a predictor of
poor prognosis and a potential therapeutic target for lung
adenocarcinoma expressing wild-type epidermal growth factor
receptor. Oncol Lett. 15:1549–1558. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Lin Q, Chen H, Zhang M, Xiong H and Jiang
Q: Knocking down FAM83B inhibits endometrial cancer cell
proliferation and metastasis by silencing the PI3K/AKT/mTOR
pathway. Biomed Pharmacother. 115:1089392019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Wang Q, Ye B, Wang P, Yao F, Zhang C and
Yu G: Overview of microRNA-199a Regulation in Cancer. Cancer Manag
Res. 11:10327–10335. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Ye H, Pang L, Wu Q, Zhu Y, Guo C, Deng Y
and Zheng X: A critical role of mir-199a in the cell biological
behaviors of colorectal cancer. Diagn Pathol. 10:652015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Hu Y, Liu J, Jiang B, Chen J, Fu Z, Bai F,
Jiang J and Tang Z: MiR-199a-5p loss up-regulated DDR1 aggravated
colorectal cancer by activating epithelial-to-mesenchymal
transition related signaling. Dig Dis Sci. 59:2163–2172. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Torres A, Torres K, Pesci A, Ceccaroni M,
Paszkowski T, Cassandrini P, Zamboni G and Maciejewski R:
Deregulation of miR-100, miR-99a and miR-199b in tissues and plasma
coexists with increased expression of mTOR kinase in endometrioid
endometrial carcinoma. BMC Cancer. 12:3692012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zhang HY, Li CH, Wang XC, Luo YQ, Cao XD
and Chen JJ: MiR-199 inhibits EMT and invasion of hepatoma cells
through inhibition of Snail expression. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci.
23:7884–7891. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Chu Y, Wang Y, Peng W, Xu L, Liu M, Li J,
Hu X, Li Y, Zuo J and Ye Y: STAT3 activation by IL-6 from
adipose-derived stem cells promotes endometrial carcinoma
proliferation and metastasis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
500:626–631. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
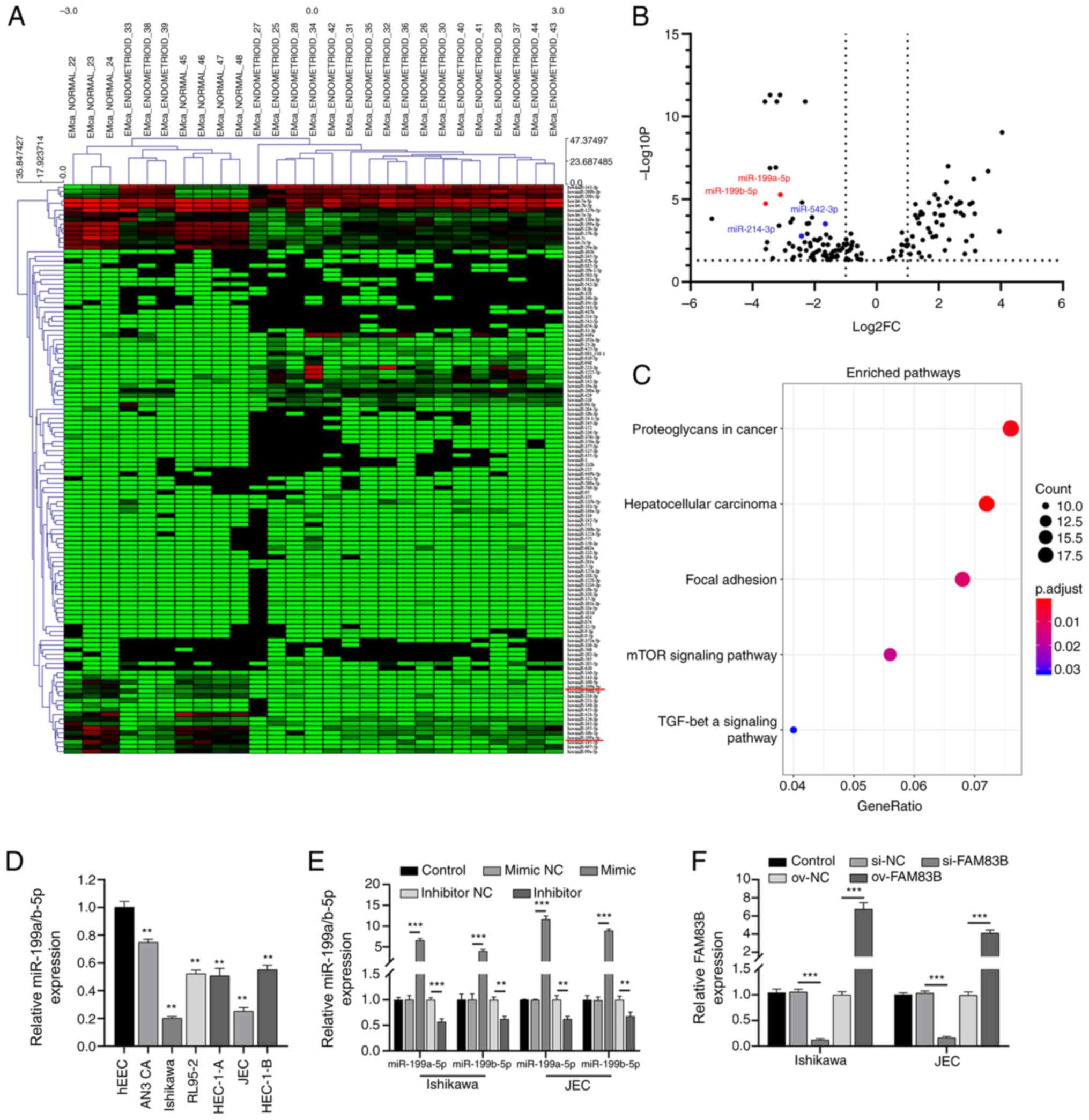
Cai J, Zhang Y, Huang S, Yan M, Li J, Jin
T and Bao S: MiR-100-5p, miR-199a-3p and miR-199b-5p induce
autophagic death of endometrial carcinoma cell through targeting
mTOR. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 10:9262–9272. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Wang Z, Monteiro CD, Jagodnik KM,
Fernandez NF, Gundersen GW, Rouillard AD, Jenkins SL, Feldmann AS,
Hu KS, McDermott MG, et al: Extraction and analysis of signatures
from the Gene Expression Omnibus by the crowd. Nat Commun.
7:128462016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Wang Y, Yu D, Liu Z, Zhou F, Dai J, Wu B,
Zhou J, Heng BC, Zou XH, Ouyang H, et al: Exosomes from embryonic
mesenchymal stem cells alleviate osteoarthritis through balancing
synthesis and degradation of cartilage extracellular matrix. Stem
Cell Res Ther. 8:1892017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Sorosky JI: Endometrial cancer. Obstet
Gynecol. 120:383–397. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2020. CA Cancer J Clin. 70:7–30. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Zheng Y and Yang X, Wang C, Zhang S, Wang
Z, Li M, Wang Y, Wang X and Yang X: HDAC6, modulated by miR-206,
promotes endometrial cancer progression through the PTEN/AKT/mTOR
pathway. Sci Rep. 10:35762020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Grant S: FAM83A and FAM83B: Candidate
oncogenes and TKI resistance mediators. J Clin Invest.
122:3048–3051. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Richtmann S, Wilkens D, Warth A,
Lasitschka F, Winter H, Christopoulos P, Herth FJF, Muley T,
Meister M and Schneider MA: FAM83A and FAM83B as prognostic
biomarkers and potential new therapeutic targets in NSCLC. Cancers
(Basel). 11:6522019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Chao CC, Wu PH, Huang HC, Chung HY, Chou
YC, Cai BH and Kannagi R: Downregulation of miR-199a/b-5p is
associated with GCNT2 induction upon epithelial-mesenchymal
transition in colon cancer. FEBS Lett. 591:1902–1917. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Hwang S, Jeong JJ, Kim SH, Chung YJ, Song
SY, Lee YJ and Rhee Y: Differential expression of miRNA199b-5p as a
novel biomarker for sporadic and hereditary parathyroid tumors. Sci
Rep. 8:120162018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Pattabiraman DR, Bierie B, Kober KI, Thiru
P, Krall JA, Zill C, Reinhardt F, Tam WL and Weinberg RA:
Activation of PKA leads to mesenchymal-to-epithelial transition and
loss of tumor-initiating ability. Science. 351:aad36802016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Hamilton G and Rath B:
Mesenchymal-epithelial transition and circulating tumor cells in
small cell lung cancer. Adv Exp Med Biol. 994:229–245. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Dongre A and Weinberg RA: New insights
into the mechanisms of epithelial-mesenchymal transition and
implications for cancer. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 20:69–84. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Wang ZC, Gao Q, Shi JY, Guo WJ, Yang LX,
Liu XY, Liu LZ, Ma LJ, Duan M, Zhao YJ, et al: Protein tyrosine
phosphatase receptor S acts as a metastatic suppressor in
hepatocellular carcinoma by control of epithermal growth factor
receptor-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Hepatology.
62:1201–1214. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Zhou SJ, Liu FY, Zhang AH, Liang HF, Wang
Y, Ma R, Jiang YH and Sun NF: MicroRNA-199b-5p attenuates
TGF-beta1-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition in
hepatocellular carcinoma. Br J Cancer. 117:233–244. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|