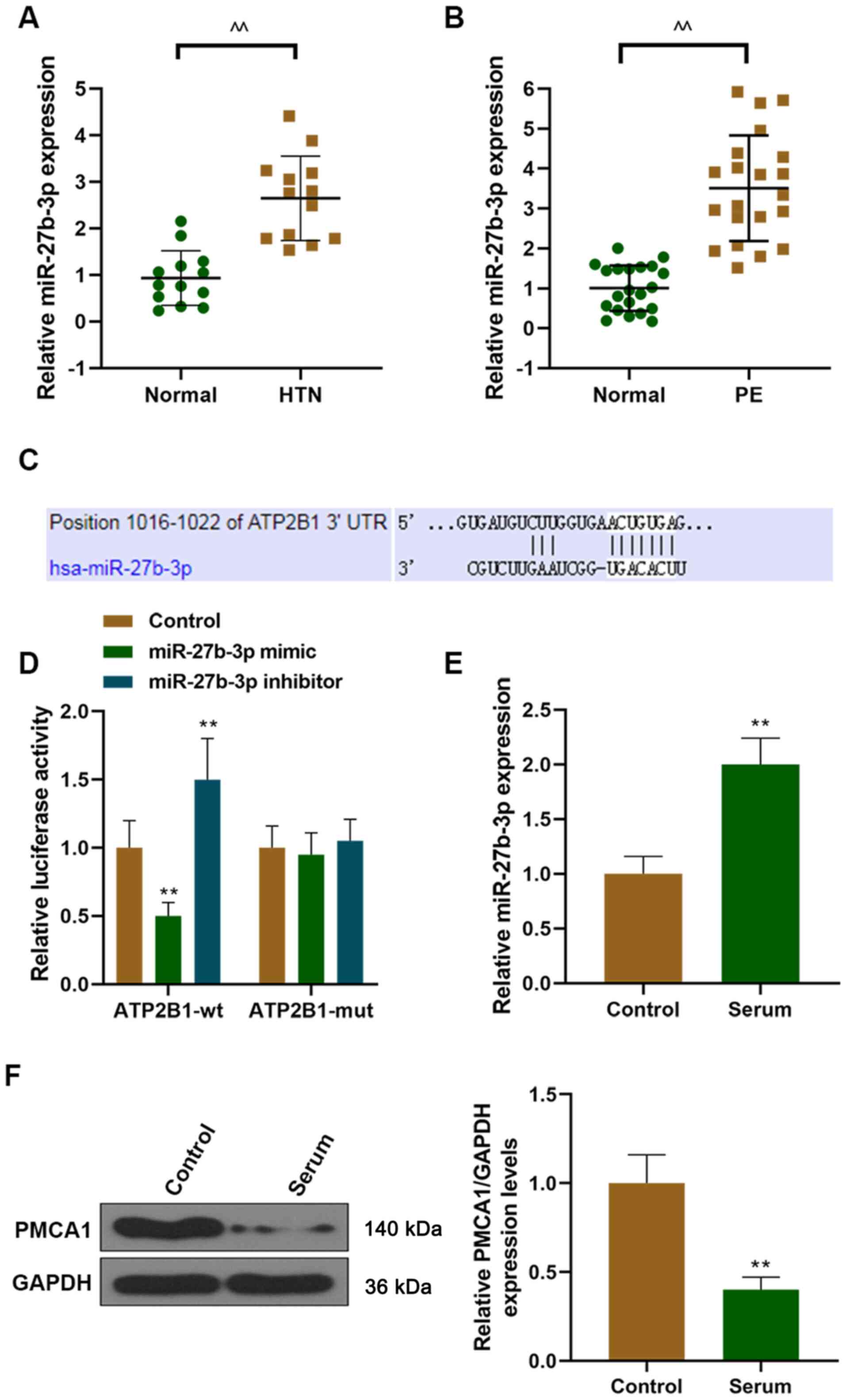
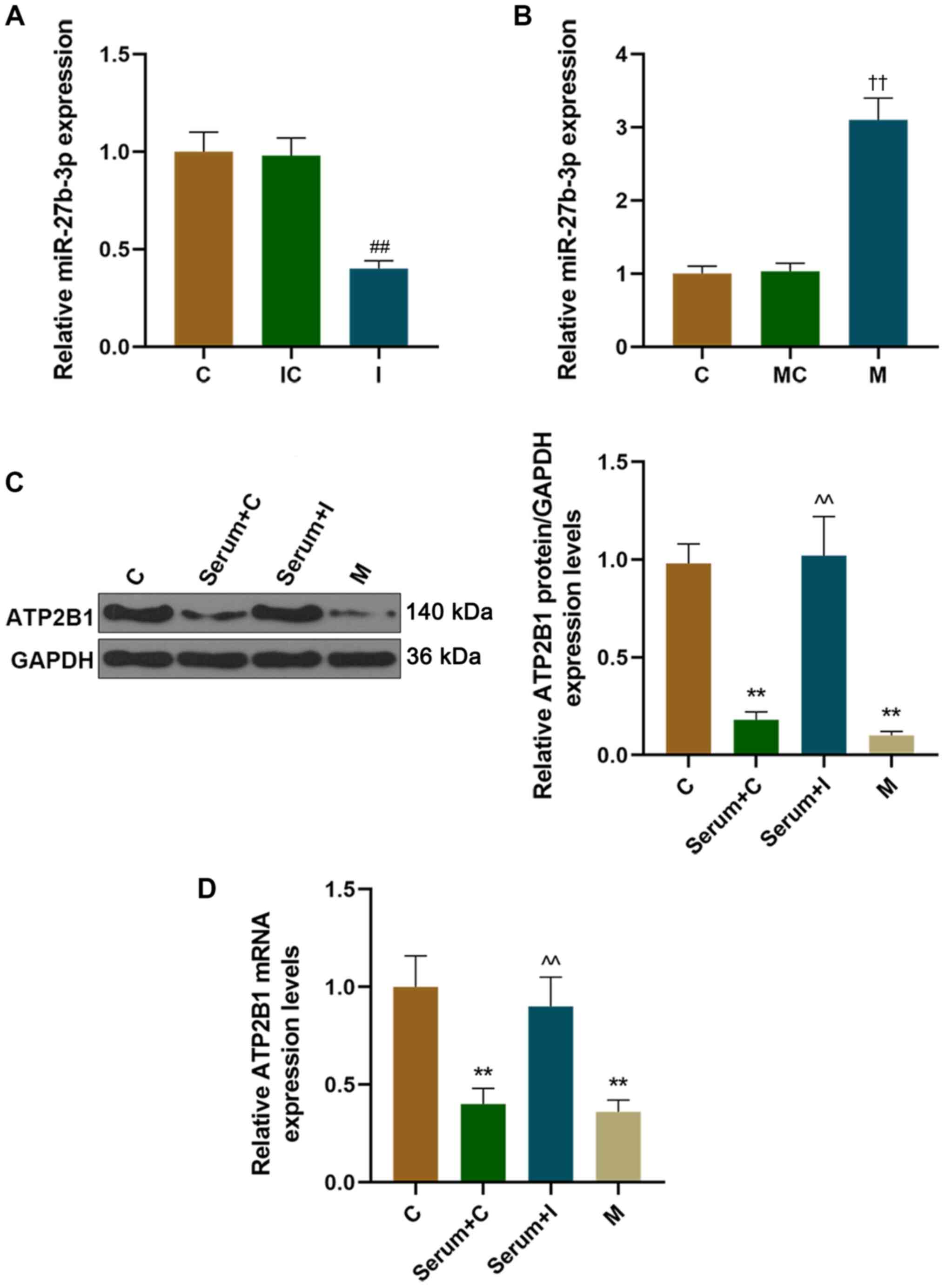
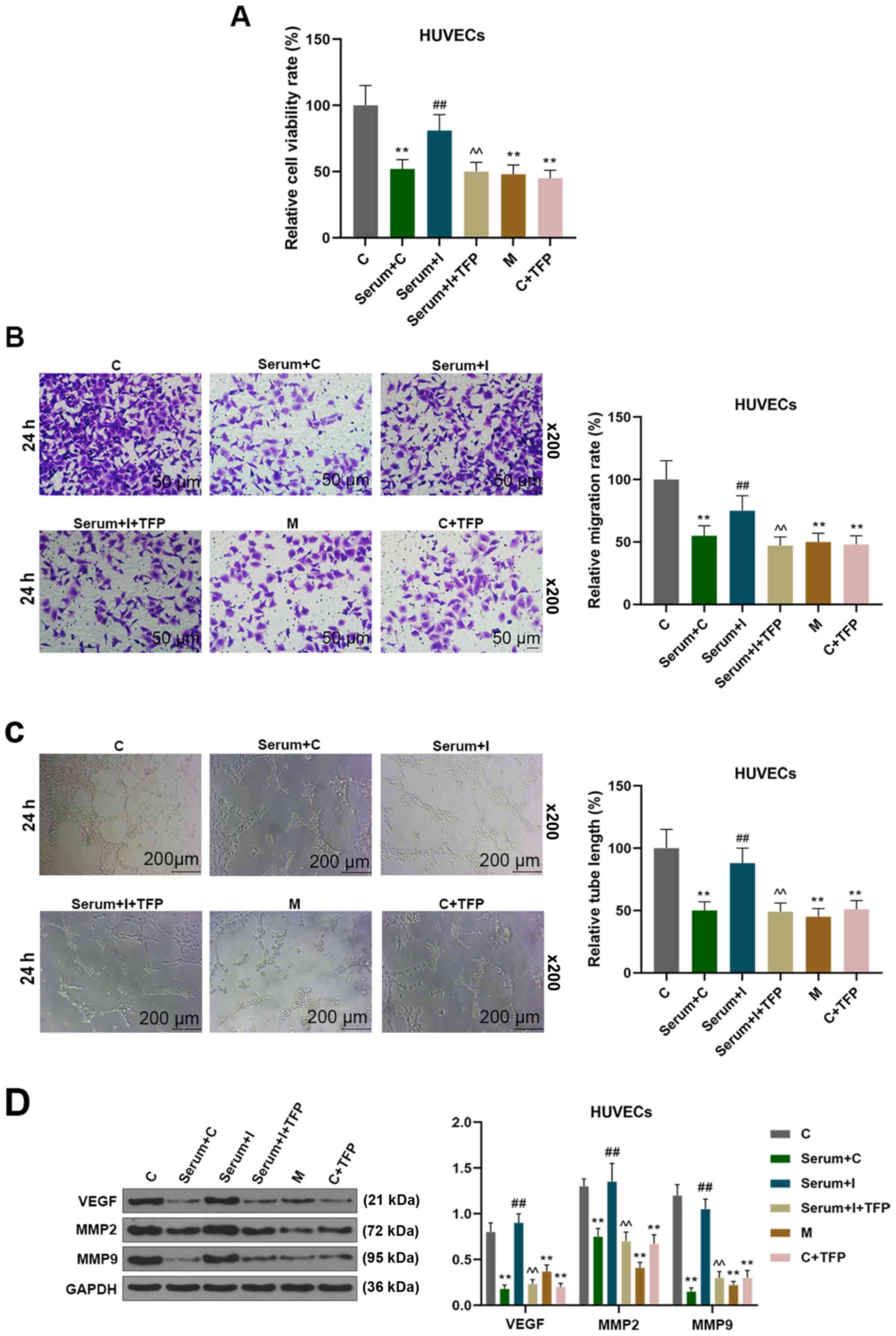
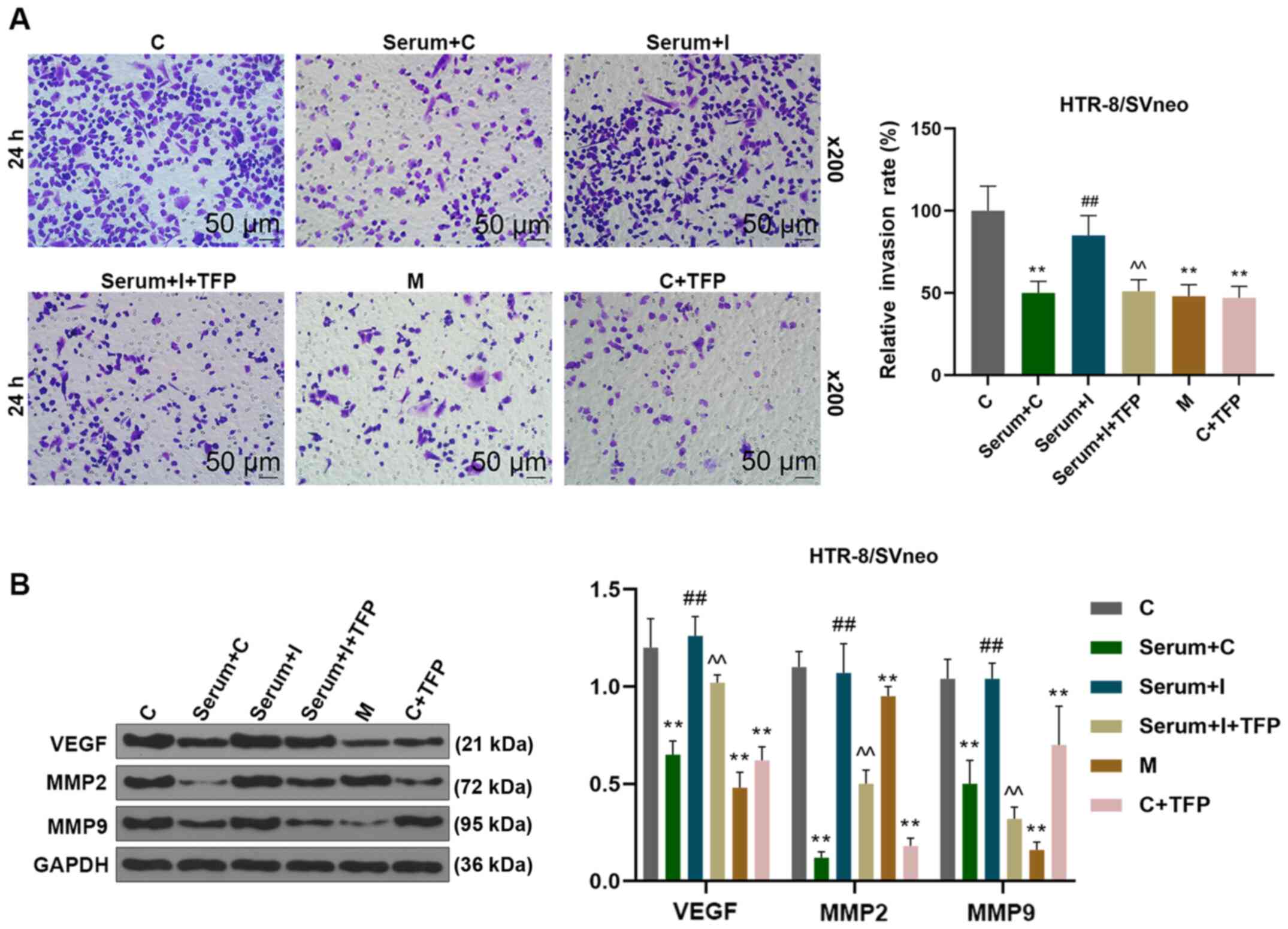
|
1
|
Alrahmani L and Willrich MAV: The
complement alternative pathway and preeclampsia. Curr Hypertens
Rep. 20:402018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Steegers EA, von Dadelszen P, Duvekot JJ
and Pijnenborg R: Pre-eclampsia. Lancet. 376:631–644. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Kelly RS, Giorgio RT, Chawes BL, Palacios
NI, Gray KJ, Mirzakhani H, Wu A, Blighe K, Weiss ST and Lasky-Su J:
Applications of metabolomics in the study and management of
preeclampsia: A review of the literature. Metabolomics. 13:132017.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Seely EW and Maxwell C: Cardiology patient
page. Chronic hypertension in pregnancy. Circulation.
115:e188–e190. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Tabara Y, Kohara K and Miki T; Millennium
Genome Project for Hypertension, : Hunting for genes for
hypertension: The Millennium Genome Project for Hypertension.
Hypertens Res. 35:567–573. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Tabara Y, Kohara K, Kita Y, Hirawa N,
Katsuya T, Ohkubo T, Hiura Y, Tajima A, Morisaki T, Miyata T, et al
Global Blood Pressure Genetics Consortium, : Common variants in the
ATP2B1 gene are associated with susceptibility to hypertension: The
Japanese Millennium Genome Project. Hypertension. 56:973–980. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Cho YS, Go MJ, Kim YJ, Heo JY, Oh JH, Ban
HJ, Yoon D, Lee MH, Kim DJ, Park M, et al: A large-scale
genome-wide association study of Asian populations uncovers genetic
factors influencing eight quantitative traits. Nat Genet.
41:527–534. 2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Kohara K, Tabara Y, Nakura J, Imai Y,
Ohkubo T, Hata A, Soma M, Nakayama T, Umemura S, Hirawa N, et al:
Identification of hypertension-susceptibility genes and pathways by
a systemic multiple candidate gene approach: The millennium genome
project for hypertension. Hypertens Res. 31:203–212. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Levy D, Ehret GB, Rice K, Verwoert GC,
Launer LJ, Dehghan A, Glazer NL, Morrison AC, Johnson AD, Aspelund
T, et al: Genome-wide association study of blood pressure and
hypertension. Nat Genet. 41:677–687. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Wang Y, Zhang Y, Li Y, Zhou X, Wang X, Gao
P, Jin L, Zhang X and Zhu D: Common variants in the ATP2B1 gene are
associated with hypertension and arterial stiffness in Chinese
population. Mol Biol Rep. 40:1867–1873. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Doridot L, Houry D, Gaillard H, Chelbi ST,
Barbaux S and Vaiman D: miR-34a expression, epigenetic regulation,
and function in human placental diseases. Epigenetics. 9:142–151.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Wang Y, Fan H, Zhao G, Liu D, Du L, Wang
Z, Hu Y and Hou Y: miR-16 inhibits the proliferation and
angiogenesis-regulating potential of mesenchymal stem cells in
severe pre-eclampsia. FEBS J. 279:4510–4524. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Xu P, Zhao Y, Liu M, Wang Y, Wang H, Li
YX, Zhu X, Yao Y, Wang H, Qiao J, et al: Variations of microRNAs in
human placentas and plasma from preeclamptic pregnancy.
Hypertension. 63:1276–1284. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Hromadnikova I, Kotlabova K, Hympanova L
and Krofta L: Gestational hypertension, preeclampsia and
intrauterine growth restriction induce dysregulation of
cardiovascular and cerebrovascular disease associated microRNAs in
maternal whole peripheral blood. Thromb Res. 137:126–140. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
JR Jr, Alasztics B, Molvarec A, Nagy B and
Biró O: 11 expression analysis of circulating exosomal hsa miR 210
in hypertensive disorders of pregnancy: Biomarkers, prediction of
preeclampsia. Pregnancy Hypertens An Int J Wom Cardiovasc Health.
6:183. 2016.
|
|
16
|
Liu C, Zhou Y and Zhang Z: miR-210: An
important player in the pathogenesis of preeclampsia? J Cell Mol
Med. 16:943–944. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Tao J, Zhi X, Zhang X, Fu M, Huang H, Fan
Y, Guan W and Zou C: miR-27b-3p suppresses cell proliferation
through targeting receptor tyrosine kinase like orphan receptor 1
in gastric cancer. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 34:1392015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Ruzzo A, Graziano F, Vincenzi B,
Canestrari E, Perrone G, Galluccio N, Catalano V, Loupakis F,
Rabitti C, Santini D, et al: High let-7a microRNA levels in
KRAS-mutated colorectal carcinomas may rescue anti-EGFR therapy
effects in patients with chemotherapy-refractory metastatic
disease. Oncologist. 17:823–829. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Thongon N, Nakkrasae LI, Thongbunchoo J,
Krishnamra N and Charoenphandhu N: Enhancement of calcium transport
in Caco-2 monolayer through PKCzeta-dependent Cav1.3-mediated
transcellular and rectifying paracellular pathways by prolactin. Am
J Physiol Cell Physiol. 296:C1373–C1382. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Little R, Cartwright EJ, Neyses L and
Austin C: Plasma membrane calcium ATPases (PMCAs) as potential
targets for the treatment of essential hypertension. Pharmacol
Ther. 159:23–34. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Gonçalves-Rizzi VH, Possomato-Vieira JS,
Nascimento RA, Caldeira-Dias M and Dias-Junior CA: Maternal
hypertension and feto-placental growth restriction is reversed by
sildenafil: Evidence of independent effects of circulating nitric
oxide levels. Eur J Pharmacol. 822:119–127. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Yan X, Yang Z, Chen Y, Li N, Wang L, Dou
G, Liu Y, Duan J, Feng L, Deng S, et al: Endothelial cells-targeted
soluble human Delta-like 4 suppresses both physiological and
pathological ocular angiogenesis. Sci China Life Sci. 58:425–431.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Beltrame JS, Scotti L, Sordelli MS,
Cañumil VA, Franchi AM, Parborell F and Ribeiro ML:
Lysophosphatidic acid induces the crosstalk between the
endovascular human trophoblast and endothelial cells in vitro. J
Cell Physiol. 234:6274–6285. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Roberts JM, Taylor RN, Musci TJ, Rodgers
GM, Hubel CA and McLaughlin MK: Preeclampsia: An endothelial cell
disorder. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 161:1200–1204. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Huppertz B: Placental origins of
preeclampsia: Challenging the current hypothesis. Hypertension.
51:970–975. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Brennan L, Morton JS, Quon A and Davidge
ST: Postpartum vascular dysfunction in the reduced uteroplacental
perfusion model of preeclampsia. PLoS One. 11:e01624872016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Shen L, Diao Z, Sun HX, Yan GJ, Wang Z, Li
RT, Dai Y, Wang J, Li J, Ding H, et al: Up-regulation of CD81
inhibits cytotrophoblast invasion and mediates maternal endothelial
cell dysfunction in preeclampsia. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
114:1940–1945. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Granger JP, Alexander BT, Llinas MT,
Bennett WA and Khalil RA: Pathophysiology of hypertension during
preeclampsia linking placental ischemia with endothelial
dysfunction. Hypertension. 38:718–722. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Sánchez-Aranguren LC, Prada CE,
Riaño-Medina CE and Lopez M: Endothelial dysfunction and
preeclampsia: Role of oxidative stress. Front Physiol. 5:3722014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
McDermott AM, Kerin MJ and Miller N:
Identification and validation of miRNAs as endogenous controls for
RQ-PCR in blood specimens for breast cancer studies. PLoS One.
8:e837182013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Cengiz M, Karatas OF, Koparir E, Yavuzer
S, Ali C, Yavuzer H, Kirat E, Karter Y and Ozen M: Differential
expression of hypertension-associated microRNAs in the plasma of
patients with white coat hypertension. Medicine (Baltimore).
94:e6932015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Karolina DS, Tavintharan S, Armugam A,
Sepramaniam S, Pek SLT, Wong MTK, Lim SC, Sum CF and Jeyaseelan K:
Circulating miRNA profiles in patients with metabolic syndrome. J
Clin Endocrinol Metab. 97:E2271–E2276. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Yang Q, Jia C, Wang P, Xiong M, Cui J, Li
L, Wang W, Wu Q, Chen Y and Zhang T: MicroRNA-505 identified from
patients with essential hypertension impairs endothelial cell
migration and tube formation. Int J Cardiol. 177:925–934. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Yang Z, Xiao Z, Guo H, Fang X, Liang J,
Zhu J, Yang J, Li H, Pan R, Yuan S, et al: Novel role of the
clustered miR-23b-3p and miR-27b-3p in enhanced expression of
fibrosis-associated genes by targeting TGFBR3 in atrial
fibroblasts. J Cell Mol Med. 23:3246–3256. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Yu J, Lv Y, Wang F, Kong X, Di W, Liu J,
Sheng Y, Lv S and Ding G: miR-27b-3p inhibition enhances browning
of epididymal fat in high-fat diet induced obese mice. Front
Endocrinol (Lausanne). 10:382019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Lv X, Li J, Hu Y, Wang S, Yang C, Li C and
Zhong G: Overexpression of miR-27b-3p targeting Wnt3a regulates the
signaling pathway of Wnt/β-catenin and attenuates atrial fibrosis
in rats with atrial fibrillation. Oxid Med Cell Longev.
2019:57037642019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Liu Y, Cai Q, Bao PP, Su Y, Cai H, Wu J,
Ye F, Guo X, Zheng W, Zheng Y, et al: Tumor tissue microRNA
expression in association with triple-negative breast cancer
outcomes. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 152:183–191. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Chen D, Si W, Shen J, Du C, Lou W, Bao C,
Zheng H, Pan J, Zhong G, Xu L, et al: miR-27b-3p inhibits
proliferation and potentially reverses multi-chemoresistance by
targeting CBLB/GRB2 in breast cancer cells. Cell Death Dis.
9:1882018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Song C, Yao J, Cao C, Liang X, Huang J,
Han Z, Zhang Y, Qin G, Tao C, Li C, et al: PPARγ is regulated by
miR-27b-3p negatively and plays an important role in porcine oocyte
maturation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 479:224–230. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Xi B, Tang W and Wang Q: Polymorphism near
the ATP2B1 gene is associated with hypertension risk in East
Asians: A meta-analysis involving 15 909 cases and 18 529 controls.
Blood Press. 21:134–138. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Drost JT, Maas AH, van Eyck J and van der
Schouw YT: Preeclampsia as a female-specific risk factor for
chronic hypertension. Maturitas. 67:321–326. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Sibai BM: Diagnosis and management of
gestational hypertension and preeclampsia. Obstet Gynecol.
102:181–192. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Daily JW, Kim BC, Liu M and Park S: People
with the major alleles of ATP2B1 rs17249754 increases the risk of
hypertension in high ratio of sodium and potassium, and low calcium
intakes. J Hum Hypertens. 31:787–794. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Ryan ZC, Craig TA, Filoteo AG, Westendorf
JJ, Cartwright EJ, Neyses L, Strehler EE and Kumar R: Deletion of
the intestinal plasma membrane calcium pump, isoform 1, Atp2b1, in
mice is associated with decreased bone mineral density and impaired
responsiveness to 1, 25-dihydroxyvitamin D3. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 467:152–156. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Long Y, Chen SW, Gao CL, He XM, Liang GN,
Wu J, Jiang CX, Liu X, Wang F and Chen F: ATP2B1 gene silencing
increases NO production under basal conditions through the
Ca2+/calmodulin/eNOS signaling pathway in endothelial
cells. Hypertens Res. 41:246–252. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Zhang Y, Fei M, Xue G, Zhou Q, Jia Y, Li
L, Xin H and Sun S: Elevated levels of hypoxia-inducible
microRNA-210 in pre-eclampsia: New insights into molecular
mechanisms for the disease. J Cell Mol Med. 16:249–259. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Zhou Y, McMaster M, Woo K, Janatpour M,
Perry J, Karpanen T, Alitalo K, Damsky C and Fisher SJ: Vascular
endothelial growth factor ligands and receptors that regulate human
cytotrophoblast survival are dysregulated in severe preeclampsia
and hemolysis, elevated liver enzymes, and low platelets syndrome.
Am J Pathol. 160:1405–1423. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Cross JC, Hemberger M, Lu Y, Nozaki T,
Whiteley K, Masutani M and Adamson SL: Trophoblast functions,
angiogenesis and remodeling of the maternal vasculature in the
placenta. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 187:207–212. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Zhang M, Muralimanoharan S, Wortman AC and
Mendelson CR: Primate-specific miR-515 family members inhibit key
genes in human trophoblast differentiation and are upregulated in
preeclampsia. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA:. 113:E7069–E7076. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Melincovici CS, Boşca AB, Şuşman S,
Mărginean M, Mihu C, Istrate M, Moldovan IM, Roman AL and Mihu CM:
Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) - key factor in normal
and pathological angiogenesis. Rom J Morphol Embryol. 59:455–467.
2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
VanKlompenberg MK, Manjarín R, Donovan CE,
Trott JF and Hovey RC: Regulation and localization of vascular
endothelial growth factor within the mammary glands during the
transition from late gestation to lactation. Domest Anim
Endocrinol. 54:37–47. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Thangapazham RL, Sharma A, Gaddipati JP,
Singh AK and Maheshwari RK: Inhibition of tumor angiogenesis by
Brahma Rasayana (BR). J Exp Ther Oncol. 6:13–21. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Zhong T, Chen J, Ling Y, Yang B, Xie X, Yu
D, Zhang D, Ouyang J and Kuang H: Down-Regulation of neuropathy
target esterase in preeclampsia placenta inhibits human trophoblast
cell invasion via modulating MMP-9 levels. Cell Physiol Biochem.
45:1013–1022. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Lee DY, Deng Z, Wang CH and Yang BB:
MicroRNA-378 promotes cell survival, tumor growth, and angiogenesis
by targeting SuFu and Fus-1 expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
104:20350–20355. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Shen X, Fang J, Lv X, Pei Z, Wang Y, Jiang
S and Ding K: Heparin impairs angiogenesis through inhibition of
microRNA-10b. J Biol Chem. 286:26616–26627. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Rong X, Ge D, Shen D, Chen X, Wang X,
Zhang L, Jia C, Zeng J, He Y, Qiu H, et al: miR-27b suppresses
endothelial cell proliferation and migration by targeting Smad7 in
Kawasaki disease. Cell Physiol Biochem. 48:1804–1814. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Adu-Gyamfi EA, Fondjo LA, Owiredu WKBA,
Czika A, Nelson W, Lamptey J, Wang YX and Ding YB: The role of
adiponectin in placentation and preeclampsia. Cell Biochem Funct.
38:106–117. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|