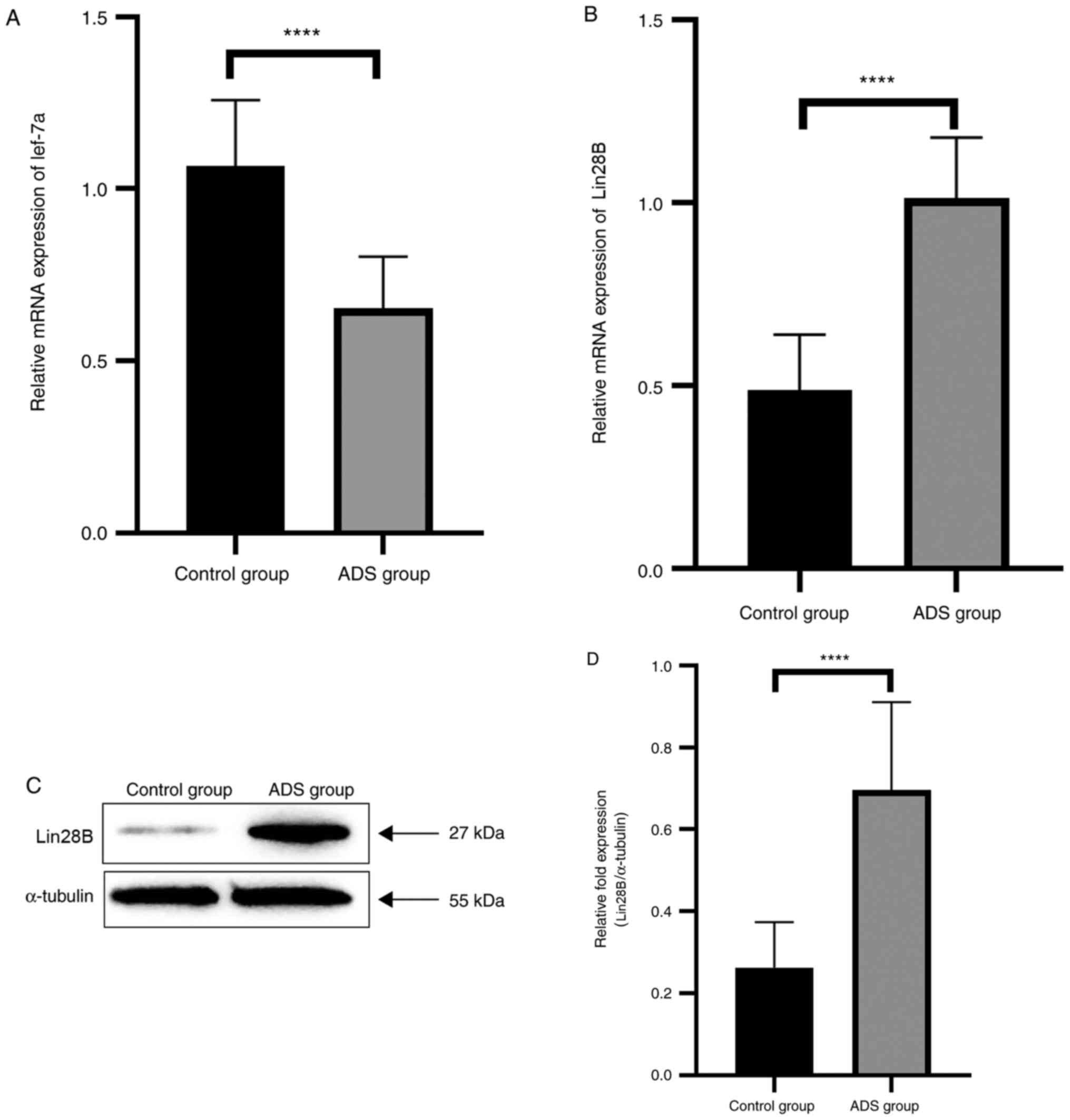
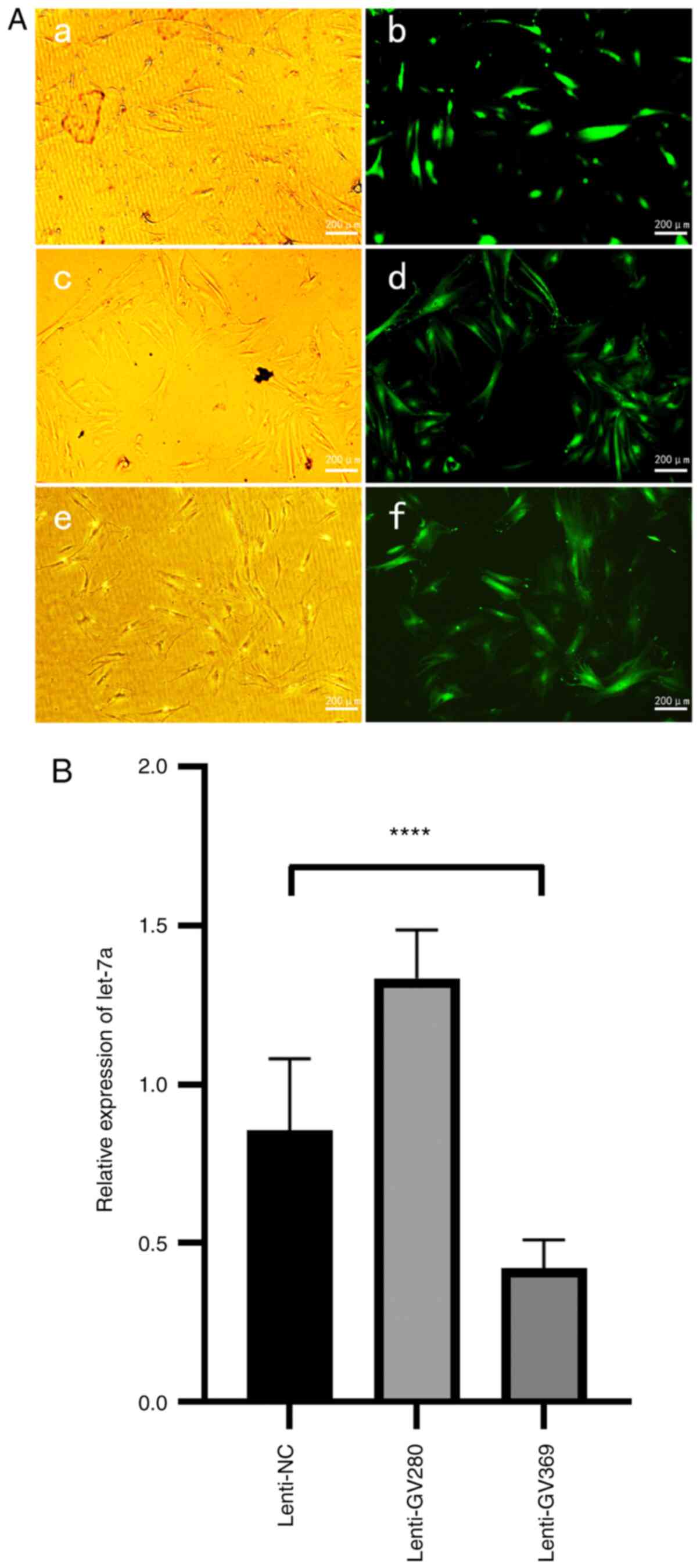
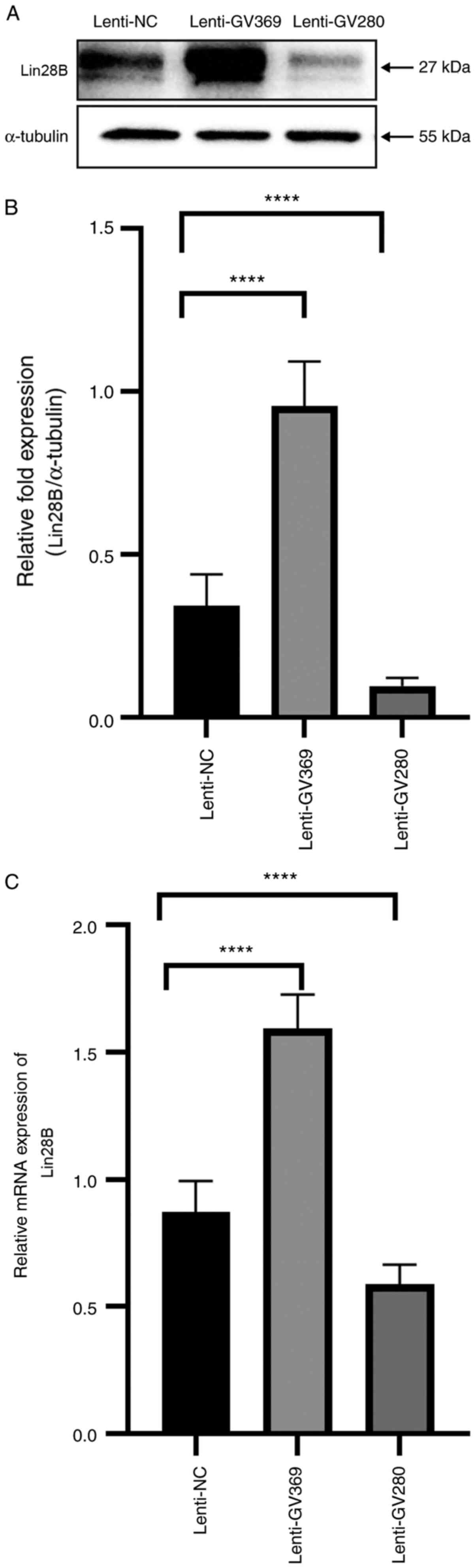
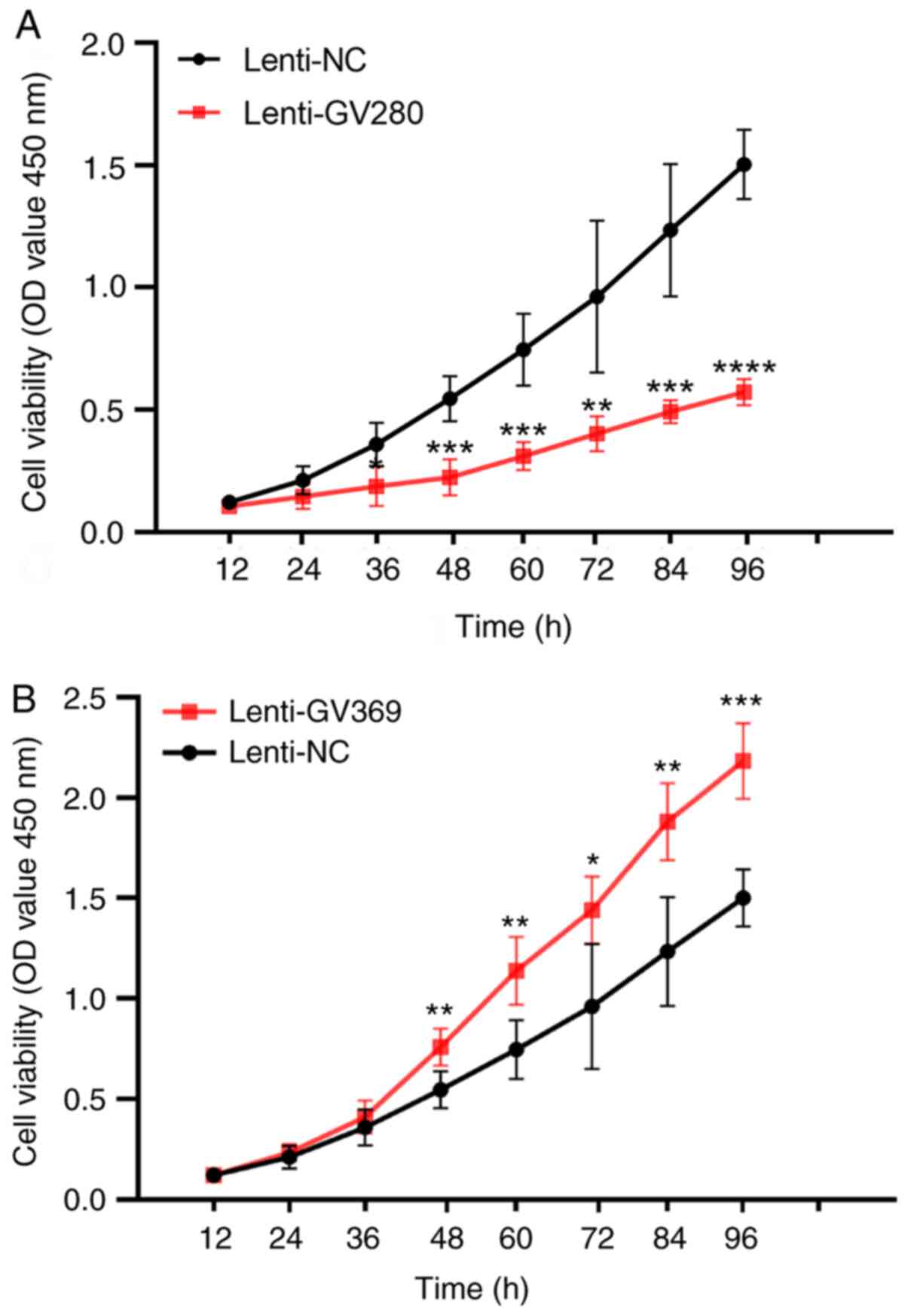
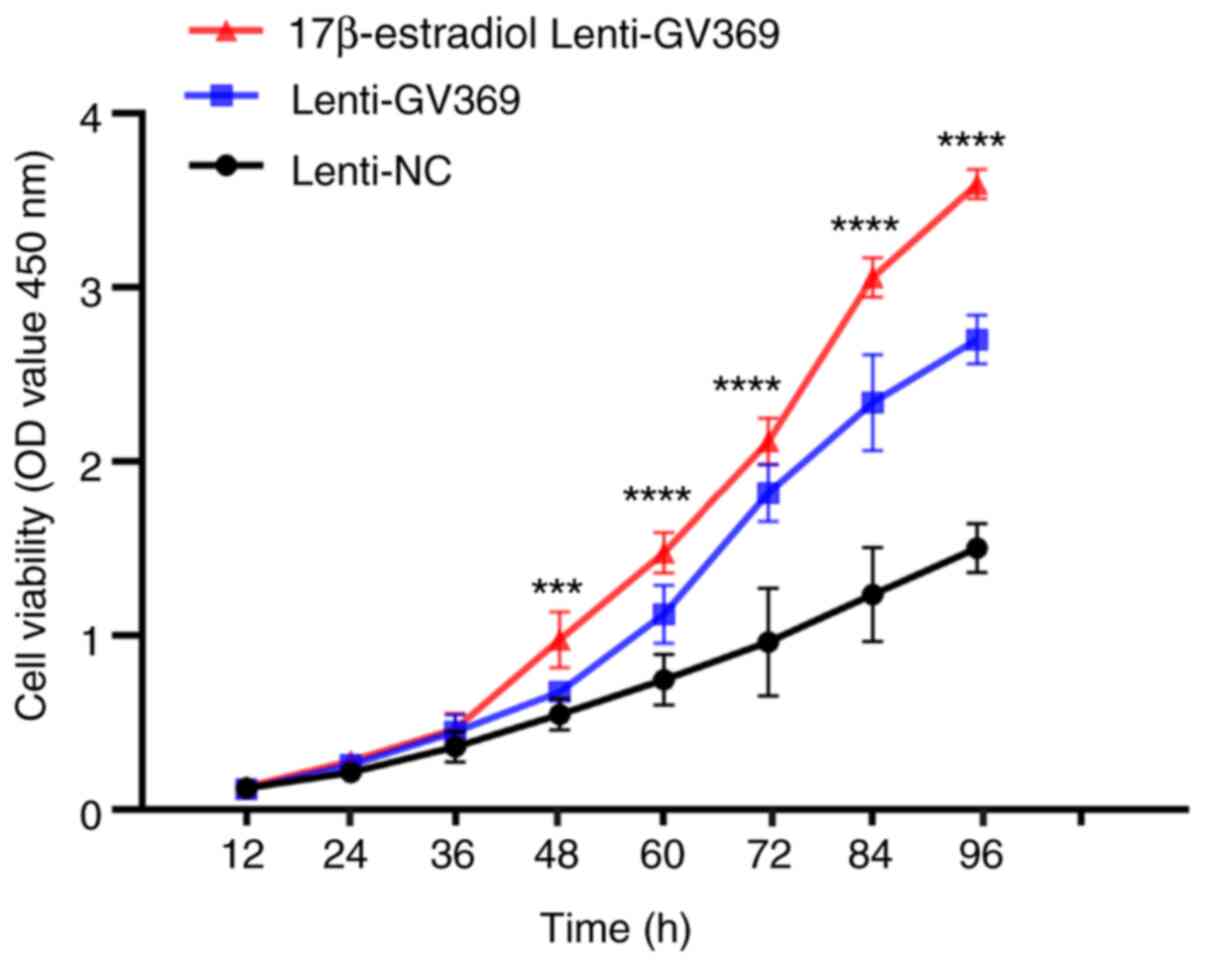
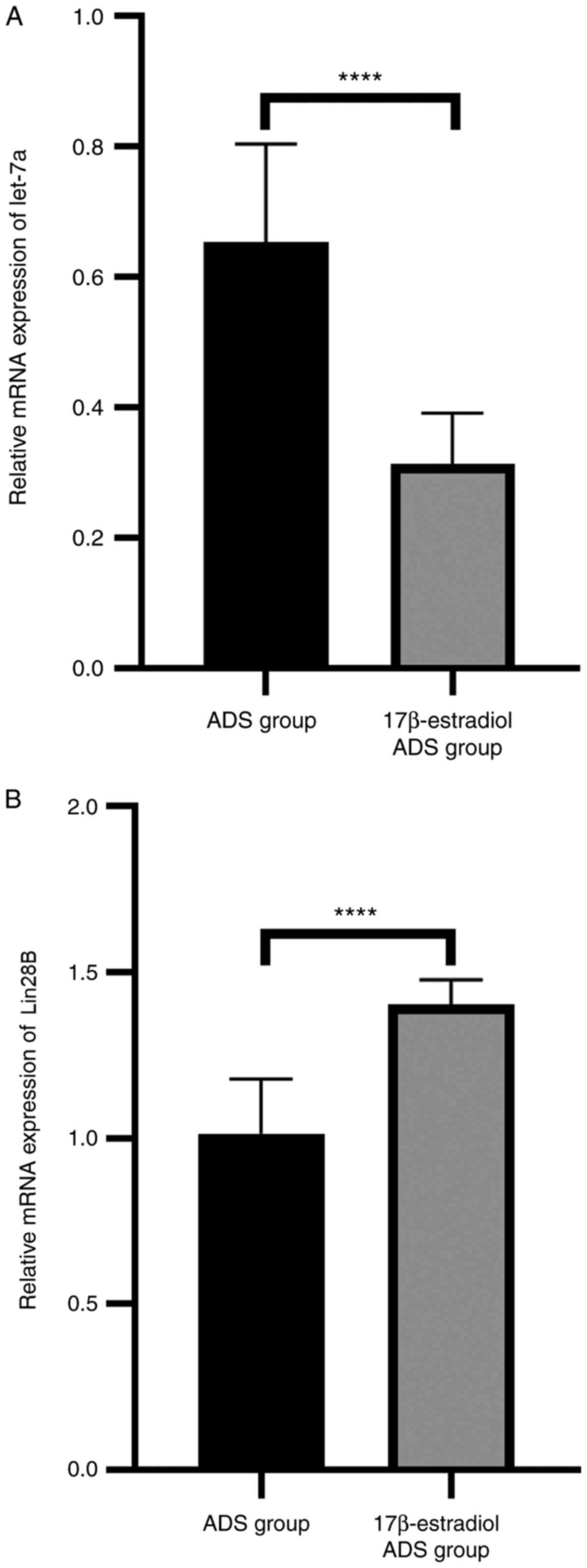
|
1
|
Kitawaki J: Adenomyosis: The
pathophysiology of an oestrogen-dependent disease. Best Pract Res
Clin Obstet Gynaecol. 20:493–502. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Yu O, Schulze-Rath R, Grafton J, Hansen K,
Scholes D and Reed SD: Adenomyosis incidence, prevalence and
treatment: United States population-based study 2006–2015. Am J
Obstet Gynecol. 223:94.e1–94.e10. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Bird CC, McElin TW and Manalo-Estrella P:
The elusive adenomyosis of the uterus - revisited. Am J Obstet
Gynecol. 112:583–593. 1972. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Guo SW: The pathogenesis of adenomyosis
vis-à-vis endometriosis. J Clin Med. 9:4852020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
O'Shea A, Figueiredo G and Lee SI: Imaging
diagnosis of adenomyosis. Semin Reprod Med. 38:119–128. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Brosens JJ, de Souza NM and Barker FG:
Uterine junctional zone: Function and disease. Lancet. 346:558–560.
1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Curtis KM, Hillis SD, Marchbanks PA and
Peterson HB: Disruption of the endometrial-myometrial border during
pregnancy as a risk factor for adenomyosis. Am J Obstet Gynecol.
187:543–544. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Guo SW, Mao X, Ma Q and Liu X:
Dysmenorrhea and its severity are associated with increased uterine
contractility and overexpression of oxytocin receptor (OTR) in
women with symptomatic adenomyosis. Fertil Steril. 99:231–240.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Fusi L, Cloke B and Brosens JJ: The
uterine junctional zone. Best Pract Res Clin Obstet Gynaecol.
20:479–491. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Tanos V, Lingwood L and Balami S:
Junctional zone endometrium morphological characteristics and
functionality: Review of the literature. Gynecol Obstet Invest.
85:107–117. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Imaoka I, Ascher SM, Sugimura K, Takahashi
K, Li H, Cuomo F, Simon J and Arnold LL: MR imaging of diffuse
adenomyosis changes after GnRH analog therapy. J Magn Reson
Imaging. 15:285–290. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Khan KN, Kitajima M, Hiraki K, Fujishita
A, Nakashima M, Ishimaru T and Masuzaki H: Cell proliferation
effect of GnRH agonist on pathological lesions of women with
endometriosis, adenomyosis and uterine myoma. Hum Reprod.
25:2878–2890. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zhang Y, Zhou L, Li TC, Duan H, Yu P and
Wang HY: Ultrastructural features of endometrial-myometrial
interface and its alteration in adenomyosis. Int J Clin Exp Pathol.
7:1469–1477. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Wang S, Duan H, Zhang Y and Sun FQ:
Abnormal activation of RhoA/ROCK-I signaling in junctional zone
smooth muscle cells of patients with adenomyosis. Reprod Sci.
23:333–341. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Sun FQ, Duan H, Wang S, Li JJ and FQ S:
17β-estradiol induces overproliferation in adenomyotic human
uterine smooth muscle cells of the junctional zone through
hyperactivation of the estrogen receptor-enhanced RhoA/ROCK
signaling pathway. Reprod Sci. 22:1436–1444. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Leyendecker G, Kunz G, Wildt L, Beil D and
Deininger H: Uterine hyperperistalsis and dysperistalsis as
dysfunctions of the mechanism of rapid sperm transport in patients
with endometriosis and infertility. Hum Reprod. 11:1542–1551. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Kunz G, Noe M, Herbertz M and Leyendecker
G: Uterine peristalsis during the follicular phase of the menstrual
cycle: Effects of oestrogen, antioestrogen and oxytocin. Hum Reprod
Update. 4:647–654. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Leyendecker G and Wildt L: A new concept
of endometriosis and adenomyosis: Tissue injury and repair (TIAR).
Horm Mol Biol Clin Investig. 5:125–142. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Liu X, Zou H, Zhao Y, Chen H, Liu T, Wu Z,
Yang C, Li Q and Li Y: Tanshinone inhibits NSCLC by downregulating
AURKA through Let-7a-5p. Front Genet. 11:8382020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Leyendecker G, Wildt L and Mall G: The
pathophysiology of endometriosis and adenomyosis: Tissue injury and
repair. Arch Gynecol Obstet. 280:529–538. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Reinhart BJ, Slack FJ, Basson M,
Pasquinelli AE, Bettinger JC, Rougvie AE, Horvitz HR and Ruvkun G:
The 21-nucleotide let-7 RNA regulates developmental timing in
Caenorhabditis elegans. Nature. 403:901–906. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Jiang J, Lee EJ, Gusev Y and Schmittgen
TD: Real-time expression profiling of microRNA precursors in human
cancer cell lines. Nucleic Acids Res. 33:5394–5403. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Jiang S and Baltimore D: RNA-binding
protein Lin28 in cancer and immunity. Cancer Lett. 375:108–113.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Balzeau J, Menezes MR, Cao S and Hagan JP:
The LIN28/let-7 Pathway in Cancer. Front Genet. 8:312017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Shyh-Chang N and Daley GQ; N S, : Lin28:
Primal regulator of growth and metabolism in stem cells. Cell Stem
Cell. 12:395–406. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Hikasa H, Sekido Y and Suzuki A; H H, :
Merlin/NF2-Lin28B-let-7 is a tumor-suppressive pathway that is
cell-density dependent and hippo independent. Cell Rep.
14:2950–2961. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Farzaneh M, Attari F and Khoshnam SE:
Concise review: LIN28/let-7 signaling, a critical double-negative
feedback loop during pluripotency, reprogramming, and
tumorigenicity. Cell Reprogram. 19:289–293. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Shamsuzzama LK, Kumar L, Haque R and Nazir
A: Role of MicroRNA Let-7 in modulating multifactorial aspect of
neurodegenerative diseases: An Overview. Mol Neurobiol.
53:2787–2793. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Chien CS, Wang ML, Chu PY, Chang YL, Liu
WH, Yu CC, Lan YT, Huang PI, Lee YY, Chen YW, et al: Lin28B/Let-7
regulates expression of Oct4 and Sox2 and reprograms oral squamous
cell carcinoma cells to a stem-like state. Cancer Res.
75:2553–2565. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Peng F, Li TT, Wang KL, Xiao GQ, Wang JH,
Zhao HD, Kang ZJ, Fan WJ, Zhu LL, Li M, et al: H19/let-7/LIN28
reciprocal negative regulatory circuit promotes breast cancer stem
cell maintenance. Cell Death Dis. 8:e25692017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Yin J, Zhao J, Hu W, Yang G, Yu H, Wang R,
Wang L, Zhang G, Fu W, Dai L, et al: Disturbance of the let-7/LIN28
double-negative feedback loop is associated with radio- and
chemo-resistance in non-small cell lung cancer. PLoS One.
12:e01727872017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Cho S, Mutlu L, Grechukhina O and Taylor
HS: Circulating microRNAs as potential biomarkers for
endometriosis. Fertil Steril. 103:1252–60.e1. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Cho S, Mutlu L, Zhou Y and Taylor HS:
Aromatase inhibitor regulates let-7 expression and let-7f-induced
cell migration in endometrial cells from women with endometriosis.
Fertil Steril. 106:673–680. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Lin SL, Duan H, Wang S and Li JJ; SL L, :
Overexpression of Lin28B promoted the proliferation of adenomyotic
smooth muscle cells of the junctional zone via regulating Let-7a.
Reprod Sci. 27:1156–1163. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Schmittgen TD and Livak KJ: Analyzing
real-time PCR data by the comparative C(T) method. Nat Protoc.
3:1101–1108. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Reinhold C, McCarthy S, Bret PM, Mehio A,
Atri M, Zakarian R, Glaude Y, Liang L and Seymour RJ: Diffuse
adenomyosis: Comparison of endovaginal US and MR imaging with
histopathologic correlation. Radiology. 199:151–158. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
de Souza NM, Brosens JJ, Schwieso JE,
Paraschos T and Winston RM: The potential value of magnetic
resonance imaging in infertility. Clin Radiol. 50:75–79. 1995.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Reinhold C, Tafazoli F, Mehio A, Wang L,
Atri M, Siegelman ES and Rohoman L: Uterine adenomyosis:
Endovaginal US and MR imaging features with histopathologic
correlation. Radiographics. 19 (Suppl 1):S147–S160. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Benagiano G, Brosens I and Habiba M:
Structural and molecular features of the endomyometrium in
endometriosis and adenomyosis. Hum Reprod Update. 20:386–402. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Chen YJ, Li HY, Huang CH, Twu NF, Yen MS,
Wang PH, Chou TY, Liu YN, Chao KC and Yang MH: Oestrogen-induced
epithelial-mesenchymal transition of endometrial epithelial cells
contributes to the development of adenomyosis. J Pathol.
222:261–270. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Huang TS, Chen YJ, Chou TY, Chen CY, Li
HY, Huang BS, Tsai HW, Lan HY, Chang CH, Twu NF, et al:
Oestrogen-induced angiogenesis promotes adenomyosis by activating
the Slug-VEGF axis in endometrial epithelial cells. J Cell Mol Med.
18:1358–1371. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Daels J: Uterine contractility patterns of
the outer and inner zones of the myometrium. Obstet Gynecol.
44:315–326. 1974.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Brosens JJ, Barker FG and de Souza NM:
Myometrial zonal differentiation and uterine junctional zone
hyperplasia in the non-pregnant uterus. Hum Reprod Update.
4:496–502. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
McCarthy S, Tauber C and Gore J: Female
pelvic anatomy: MR assessment of variations during the menstrual
cycle and with use of oral contraceptives. Radiology. 160:119–123.
1986. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Slack FJ, Basson M, Liu Z, Ambros V,
Horvitz HR and Ruvkun G: The lin-41 RBCC gene acts in the C.
elegans heterochronic pathway between the let-7 regulatory RNA
and the LIN-29 transcription factor. Mol Cell. 5:659–669. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Moss EG, Lee RC and Ambros V: The cold
shock domain protein LIN-28 controls developmental timing in C.
elegans and is regulated by the lin-4 RNA. Cell. 88:637–646.
1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Luo C, Zhang J, Zhang Y, Zhang X, Chen Y
and Fan W: Low expression of miR-let-7a promotes cell growth and
invasion through the regulation of c-Myc in oral squamous cell
carcinoma. Cell Cycle. 19:1983–1993. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Yang Q, Jie Z, Cao H, Greenlee AR, Yang C,
Zou F and Jiang Y: Low-level expression of let-7a in gastric cancer
and its involvement in tumorigenesis by targeting RAB40C.
Carcinogenesis. 32:713–722. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Re M, Magliulo G, Gioacchini FM,
Bajraktari A, Bertini A, Çeka A, Rubini C, Ferrante L, Procopio AD
and Olivieri F: Expression levels and clinical significance of
miR-21-5p, miR-let-7a, and miR-34c-5p in laryngeal squamous cell
carcinoma. BioMed Res Int. 2017:39212582017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Liu TP, Huang CC, Yeh KT, Ke TW, Wei PL,
Yang JR and Cheng YW: Down-regulation of let-7a-5p predicts lymph
node metastasis and prognosis in colorectal cancer: Implications
for chemotherapy. Surg Oncol. 25:429–434. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Viswanathan SR and Daley GQ; SR V, :
Lin28: A microRNA regulator with a macro role. Cell. 140:445–449.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
King CE, Cuatrecasas M, Castells A,
Sepulveda AR, Lee JS and Rustgi AK: LIN28B promotes colon cancer
progression and metastasis. Cancer Res. 71:4260–4268. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
West JA, Viswanathan SR, Yabuuchi A,
Cunniff K, Takeuchi A, Park IH, Sero JE, Zhu H, Perez-Atayde A,
Frazier AL, et al: A role for Lin28 in primordial germ-cell
development and germ-cell malignancy. Nature. 460:909–913. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Zhou J, Ng SB and Chng WJ: LIN28/LIN28B:
An emerging oncogenic driver in cancer stem cells. Int J Biochem
Cell Biol. 45:973–978. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
García-Solares J, Donnez J, Donnez O and
Dolmans MM: Pathogenesis of uterine adenomyosis: Invagination or
metaplasia? Fertil Steril. 109:371–379. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Herndon CN, Aghajanova L, Balayan S,
Erikson D, Barragan F, Goldfien G, Vo KC, Hawkins S and Giudice LC:
Global transcriptome abnormalities of the eutopic endometrium from
women with adenomyosis. Reprod Sci. 23:1289–1303. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Mijatovic V, Florijn E, Halim N, Schats R
and Hompes P: Adenomyosis has no adverse effects on IVF/ICSI
outcomes in women with endometriosis treated with long-term
pituitary down-regulation before IVF/ICSI. Eur J Obstet Gynecol
Reprod Biol. 151:62–65. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Levgur M: Diagnosis of adenomyosis: A
review. J Reprod Med. 52:177–193. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Halvorsen TB and Moen MH: The extent and
clinical significance of adenomyotic lesions in the uterine wall. A
quantitative assessment. APMIS. 101:907–913. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Bohlman ME, Ensor RE and Sanders RC:
Sonographic findings in adenomyosis of the uterus. AJR Am J
Roentgenol. 148:765–766. 1987. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Ma HB, Yao YN, Yu JJ, Chen XX and Li HF:
Extensive profiling of circular RNAs and the potential regulatory
role of circRNA-000284 in cell proliferation and invasion of
cervical cancer via sponging miR-506. Am J Transl Res. 10:592–604.
2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Guo J, Chen M, Ai G, Mao W, Li H and Zhou
J: Hsa_circ_0023404 enhances cervical cancer metastasis and
chemoresistance through VEGFA and autophagy signaling by sponging
miR-5047. Biomed Pharmacother. 115:1089572019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Liu J, Wang D, Long Z, Liu J and Li W:
CircRNA8924 promotes cervical cancer cell proliferation, migration
and invasion by competitively binding to MiR-518d-5p/519-5p family
and modulating the expression of CBX8. Cell Physiol Biochem.
48:173–184. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|