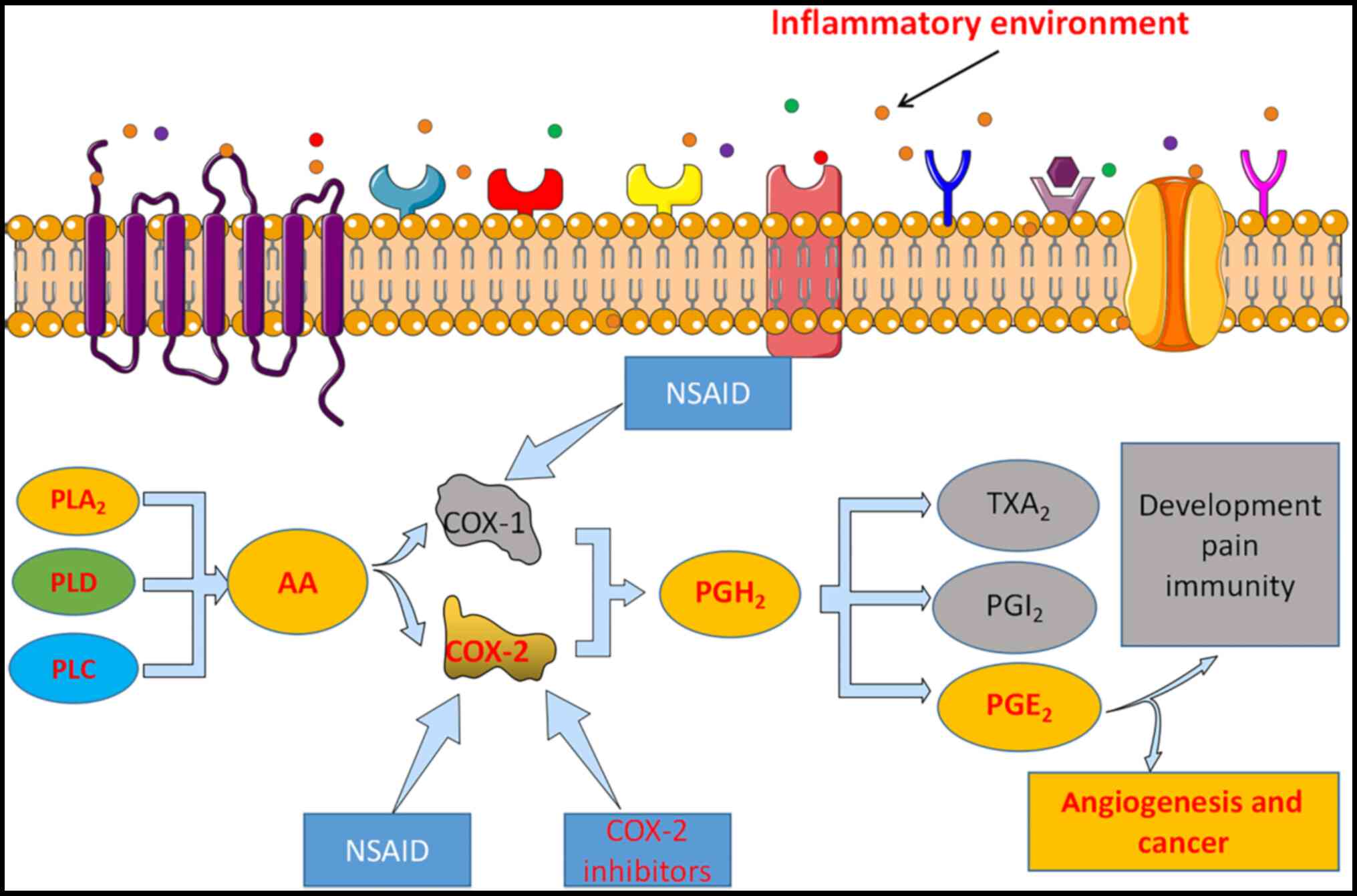
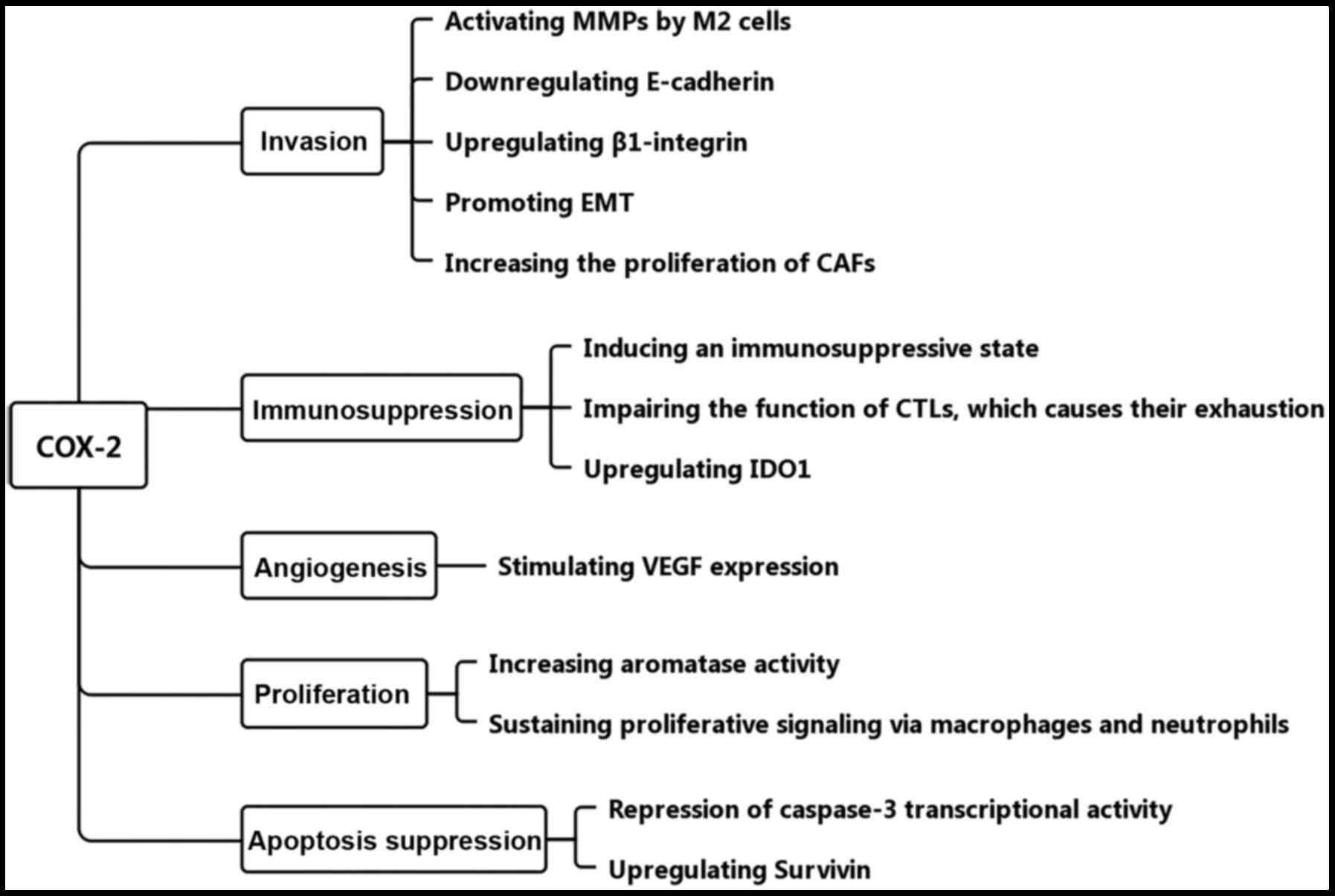
|
1
|
Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel
RL, Torre LA and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN
estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in
185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 68:394–424. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Piotrowski I, Kulcenty K and Suchorska W:
Interplay between inflammation and cancer. Rep Pract Oncol
Radiother. 25:422–427. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Beeghly-Fadiel A, Wilson AJ, Keene S,
Ramahi M, Xu S, Marnett LJ, Fadare O, Crispens MA and Khabele D:
Differential cyclooxygenase expression levels and survival
associations in type I and type II ovarian tumors. J Ovarian Res.
11:172018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Ayiomamitis GD, Notas G, Vasilakaki T,
Tsavari A, Vederaki S, Theodosopoulos T, Kouroumalis E and
Zaravinos A: Understanding the Interplay between COX-2 and hTERT in
colorectal cancer using a multi-omics analysis. Cancers (Basel).
11:15362019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Pollock JK, Greene LM, Nathwani SM,
Kinsella P, O'Boyle NM, Meegan MJ and Zisterer DM: Involvement of
NF-κB in mediating the anti-tumour effects of combretastatins in T
cells. Invest New Drugs. 36:523–535. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Gurram B, Zhang S, Li M, Li H, Xie Y, Cui
H, Du J, Fan J, Wang J and Peng X: Celecoxib conjugated fluorescent
probe for identification and discrimination of cyclooxygenase-2
enzyme in cancer cells. Anal Chem. 90:5187–5193. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
O'Brien J, Hayder H, Zayed Y and Peng C:
Overview of MicroRNA biogenesis, mechanisms of actions, and
circulation. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 9:4022018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Esquela-Kerscher A and Slack FJ: Oncomirs
microRNAs with a role in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 6:259–269. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Sun X, Ge X, Xu Z and Chen D:
Identification of circular RNA-microRNA-messenger RNA regulatory
network in hepatocellular carcinoma by integrated analysis. J
Gastroenterol Hepatol. 35:157–164. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Griffiths-Jones S, Saini HK, van Dongen S
and Enright AJ: miRBase: Tools for microRNA genomics. Nucleic Acids
Res. 36:D154–D158. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Kim B, Jeong K and Kim VN: Genome-wide
mapping of DROSHA cleavage sites on primary MicroRNAs and
noncanonical substrates. Mol Cell. 66:258–269.e5. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
He L and Hannon GJ: MicroRNAs: Small RNAs
with a big role in gene regulation. Nat Rev Genet. 5:522–531. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Babaei K, Shams S, Keymoradzadeh A, Vahidi
S, Hamami P, Khaksar R, Norollahi SE and Samadani AA: An insight of
microRNAs performance in carcinogenesis and tumorigenesis; an
overview of cancer therapy. Life Sci. 240:1170772020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Calin GA and Croce CM: MicroRNA signatures
in human cancers. Nat Rev Cancer. 6:857–866. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Lu J, Getz G, Miska EA, Alvarez-Saavedra
E, Lamb J, Peck D, Sweet-Cordero A, Ebert BL, Mak RH, Ferrando AA,
et al: MicroRNA expression profiles classify human cancers. Nature.
435:834–838. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Lei X, Lei Y, Li JK, Du WX, Li RG, Yang J,
Li J, Li F and Tan HB: Immune cells within the tumor
microenvironment: Biological functions and roles in cancer
immunotherapy. Cancer Lett. 470:126–133. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Moon H, White AC and Borowsky AD: New
insights into the functions of Cox-2 in skin and esophageal
malignancies. Exp Mol Med. 52:538–547. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Han F, Ren J, Zhang J, Sun Y, Ma F, Liu Z,
Yu H, Jia J and Li W: JMJD2B is required for Helicobacter
pylori-induced gastric carcinogenesis via regulating COX-2
expression. Oncotarget. 7:38626–38637. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Liu Y, Borchert GL, Surazynski A and Phang
JM: Proline oxidase, a p53-induced gene, targets COX-2/PGE2
signaling to induce apoptosis and inhibit tumor growth in
colorectal cancers. Oncogene. 27:6729–6737. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Hashemi Goradel N, Najafi M, Salehi E,
Farhood B and Mortezaee K: Cyclooxygenase-2 in cancer: A review. J
Cell Physiol. 234:5683–5699. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Montezuma MAP, Fonseca FP, Benites BM,
Soares CD, do Amaral-Silva GK, de Almeida OP, Soares FA, Pagano RL
and Fregnani ER: COX-2 as a determinant of lower disease-free
survival for patients affected by ameloblastoma. Pathol Res Pract.
214:907–913. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Han L, Fang S, Li G, Wang M and Yu R:
Total flavonoids suppress lung cancer growth via the COX-2-mediated
Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Oncol Lett. 19:1824–1830.
2020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Conejo-Garcia JR: Breaking barriers for T
cells by targeting the EPHA2/TGF-β/COX-2 axis in pancreatic cancer.
J Clin Invest. 129:3521–3523. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Bourn J, Pandey S, Uddin J, Marnett L and
Cekanova M: Detection of tyrosine kinase inhibitors-induced COX-2
expression in bladder cancer by fluorocoxib A. Oncotarget.
10:5168–5180. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Zhu Y, Shi C, Zeng L, Liu G, Jiang W,
Zhang X, Chen S, Guo J, Jian X, Ouyang J, et al: High COX-2
expression in cancer-associated fibiroblasts contributes to poor
survival and promotes migration and invasiveness in nasopharyngeal
carcinoma. Mol Carcinog. 59:265–280. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Peng Y, Wang Y, Tang N, Sun D, Lan Y, Yu
Z, Zhao X, Feng L, Zhang B, Jin L, et al: Andrographolide inhibits
breast cancer through suppressing COX-2 expression and angiogenesis
via inactivation of p300 signaling and VEGF pathway. J Exp Clin
Cancer Res. 37:2482018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Yang Y, Zhu J, Gou H, Cao D, Jiang M and
Hou M: Clinical significance of Cox-2, Survivin and Bcl-2
expression in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Med Oncol.
28:796–803. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Garrido MP, Hurtado I,
Valenzuela-Valderrama M, Salvatierra R, Hernández A, Vega M, Selman
A, Quest AFG and Romero C: NGF-enhanced vasculogenic properties of
epithelial ovarian cancer cells is reduced by inhibition of the
COX-2/PGE2 signaling Axis. Cancers (Basel). 11:19702019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Hosseini F, Mahdian-Shakib A,
Jadidi-Niaragh F, Enderami SE, Mohammadi H, Hemmatzadeh M, Mohammed
HA, Anissian A, Kokhaei P, Mirshafiey A and Hassannia H:
Anti-inflammatory and anti-tumor effects of α-l-guluronic acid
(G2013) on cancer-related inflammation in a murine breast cancer
model. Biomed Pharmacother. 98:793–800. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Janakiraman H, House RP, Talwar S,
Courtney SM, Hazard ES, Hardiman G, Mehrotra S, Howe PH, Gangaraju
V and Palanisamy V: Repression of caspase-3 and RNA-binding protein
HuR cleavage by cyclooxygenase-2 promotes drug resistance in oral
squamous cell carcinoma. Oncogene. 36:3137–3148. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Raj V, Bhadauria AS, Singh AK, Kumar U,
Rai A, Keshari AK, Kumar P, Kumar D, Maity B, Nath S, et al: Novel
1,3,4-thiadiazoles inhibit colorectal cancer via blockade of
IL-6/COX-2 mediated JAK2/STAT3 signals as evidenced through
data-based mathematical modeling. Cytokine. 118:144–159. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Krishnamachary B, Stasinopoulos I, Kakkad
S, Penet MF, Jacob D, Wildes F, Mironchik Y, Pathak AP, Solaiyappan
M and Bhujwalla ZM: Breast cancer cell cyclooxygenase-2 expression
alters extracellular matrix structure and function and numbers of
cancer associated fibroblasts. Oncotarget. 8:17981–17994. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Esbona K, Yi Y, Saha S, Yu M, Van Doorn
RR, Conklin MW, Graham DS, Wisinski KB, Ponik SM, Eliceiri KW, et
al: The presence of cyclooxygenase 2, tumor-associated macrophages,
and collagen alignment as prognostic markers for invasive breast
carcinoma patients. Am J Pathol. 188:559–573. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Esbona K, Inman D, Saha S, Jeffery J,
Schedin P, Wilke L and Keely P: COX-2 modulates mammary tumor
progression in response to collagen density. Breast Cancer Res.
18:352016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Hull MA, Cuthbert RJ, Ko CWS, Scott DJ,
Cartwright EJ, Hawcroft G, Perry SL, Ingram N, Carr IM, Markham AF,
et al: Paracrine cyclooxygenase-2 activity by macrophages drives
colorectal adenoma progression in the ApcMin/+ mouse
model of intestinal tumorigenesis. Sci Rep. 7:60742017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Watanabe Y, Imanishi Y, Ozawa H, Sakamoto
K, Fujii R, Shigetomi S, Habu N, Otsuka K, Sato Y, Sekimizu M, et
al: Selective EP2 and Cox-2 inhibition suppresses cell migration by
reversing epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and Cox-2
overexpression and E-cadherin downregulation are implicated in neck
metastasis of hypopharyngeal cancer. Am J Transl Res. 12:1096–1113.
2020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Sorski L, Melamed R, Matzner P, Lavon H,
Shaashua L, Rosenne E and Ben-Eliyahu S: Reducing liver metastases
of colon cancer in the context of extensive and minor surgeries
through beta-adrenoceptors blockade and COX2 inhibition. Brain
Behav Immun. 58:91–98. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Soto MS, O'Brien ER, Andreou K, Scrace SF,
Zakaria R, Jenkinson MD, O'Neill E and Sibson NR: Disruption of
tumour-host communication by downregulation of LFA-1 reduces COX-2
and e-NOS expression and inhibits brain metastasis growth.
Oncotarget. 7:52375–52391. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Majumder M, Landman E, Liu L, Hess D and
Lala PK: COX-2 elevates oncogenic miR-526b in breast cancer by EP4
activation. Mol Cancer Res. 13:1022–1033. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Pan J, Yang Q, Shao J, Zhang L, Ma J, Wang
Y, Jiang BH, Leng J and Bai X: Cyclooxygenase-2 induced β1-integrin
expression in NSCLC and promoted cell invasion via the
EP1/MAPK/E2F-1/FoxC2 signal pathway. Sci Rep. 6:338232016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Lang S, Picu A, Hofmann T, Andratschke M,
Mack B, Moosmann A, Gires O, Tiwari S and Zeidler R: COX-inhibitors
relieve the immunosuppressive effect of tumor cells and improve
functions of immune effectors. Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol.
19:409–419. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Höing B, Kanaan O, Altenhoff P, Petri R,
Thangavelu K, Schlüter A, Lang S, Bankfalvi A and Brandau S:
Stromal versus tumoral inflammation differentially contribute to
metastasis and poor survival in laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma.
Oncotarget. 9:8415–8426. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Mortezaee K: Immune escape: A critical
hallmark in solid tumors. Life Sci. 258:1181102020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Miao J, Lu X, Hu Y, Piao C, Wu X, Liu X,
Huang C, Wang Y, Li D and Liu J: Prostaglandin E 2 and PD-1
mediated inhibition of antitumor CTL responses in the human tumor
microenvironment. Oncotarget. 8:89802–89810. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Hennequart M, Pilotte L, Cane S, Hoffmann
D, Stroobant V, Plaen E and Van den Eynde BJ: Constitutive IDO1
expression in human tumors is driven by cyclooxygenase-2 and
mediates intrinsic immune resistance. Cancer Immunol Res.
5:695–709. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Moon H, Kim D, Donahue LR and White AC:
Phenotypic plasticity of cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma mediated
by cyclooxygenase-2. J Invest Dermatol. 140:1665–1669, e1665. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Moon H, Zhu J, Donahue LR, Choi E and
White AC: Krt5+/Krt15+ foregut basal
progenitors give rise to cyclooxygenase-2-dependent tumours in
response to gastric acid stress. Nat Commun. 10:22252019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Xiang Y, Tian Q, Guan L and Niu SS: The
dual role of miR-186 in cancers: Oncomir battling with tumor
suppressor miRNA. Front Oncol. 10:2332020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Bai J, Xu J, Zhao J and Zhang R: LncRNA
NBR2 suppresses migration and invasion of colorectal cancer cells
by downregulating miRNA-21. Hum Cell. 33:98–103. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Zhang W, Chen J and He G, Xu W and He G:
Impact of mirna-21 on survival prognosis in patients with
pancreatic cancer: A protocol for systematic review and
meta-analysis. Medicine (Baltimore). 99:e220452020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Bascuñán KA, Pérez-Bravo F, Gaudioso G,
Vaira V, Roncoroni L, Elli L, Monguzzi E and Araya M: A miRNA-based
blood and mucosal approach for detecting and monitoring celiac
disease. Dig Dis Sci. 65:1982–1991. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Irimie AI, Braicu C, Sonea L, Zimta AA,
Cojocneanu-Petric R, Tonchev K, Mehterov N, Diudea D, Buduru S and
Berindan-Neagoe I: A looking-glass of non-coding RNAs in oral
cancer. Int J Mol Sci. 18:26202017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Liu Y, Li H, Zhao C and Jia H:
MicroRNA-101 inhibits angiogenesis via COX-2 in endometrial
carcinoma. Mol Cell Biochem. 448:61–69. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Pop-Bica C, Pintea S, Cojocneanu-Petric R,
Del Sal G, Piazza S, Wu ZH, Alencar AJ, Lossos IS, Berindan-Neagoe
I and Calin GA: MiR-181 family-specific behavior in different
cancers: a meta-analysis view. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 37:17–32.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Ruan K, Fang X and Ouyang G: MicroRNAs:
Novel regulators in the hallmarks of human cancer. Cancer Lett.
285:116–126. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Villadsen SB, Bramsen JB, Ostenfeld MS,
Wiklund ED, Fristrup N, Gao S, Hansen TB, Jensen TI, Borre M,
Ørntoft TF, et al: The miR-143/-145 cluster regulates plasminogen
activator inhibitor-1 in bladder cancer. Br J Cancer. 106:366–374.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Aldebasi YH, Rahmani AH, Khan AA and Aly
SM: The effect of vascular endothelial growth factor in the
progression of bladder cancer and diabetic retinopathy. Int J Clin
Exp Med. 6:239–251. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Li X, Zeng Z, Wang J, Wu Y, Chen W, Zheng
L, Xi T, Wang A and Lu Y: MicroRNA-9 and breast cancer. Biomed
Pharmacother. 122:1096872020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Stiegelbauer V, Perakis S, Deutsch A, Ling
H, Gerger A and Pichler M: MicroRNAs as novel predictive biomarkers
and therapeutic targets in colorectal cancer. World J
Gastroenterol. 20:11727–11735. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Hao Y, Gu X, Zhao Y, Greene S, Sha W,
Smoot DT, Califano J, Wu TC and Pang X: Enforced expression of
miR-101 inhibits prostate cancer cell growth by modulating the
COX-2 pathway in vivo. Cancer Prev Res (Phila). 4:1073–1083. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Smits M, Nilsson J, Mir SE, van der Stoop
PM, Hulleman E, Niers JM, de Witt Hamer PC, Marquez VE, Cloos J,
Krichevsky AM, et al: miR-101 is down-regulated in glioblastoma
resulting in EZH2-induced proliferation, migration, and
angiogenesis. Oncotarget. 1:710–720. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Shao Y, Li P, Zhu ST, Yue JP, Ji XJ, He Z,
Ma D, Wang L, Wang YJ, Zong Y, et al: Cyclooxygenase-2, a potential
therapeutic target, is regulated by miR-101 in esophageal squamous
cell carcinoma. PLoS One. 10:e01406422015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Lv P, Zhang P, Li X and Chen Y: Micro
ribonucleic acid (RNA)-101 inhibits cell proliferation and invasion
of lung cancer by regulating cyclooxygenase-2. Thorac Cancer.
6:778–784. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
He XP, Shao Y, Li XL, Xu W, Chen GS, Sun
HH, Xu HC, Xu X, Tang D, Zheng XF, et al: Downregulation of miR-101
in gastric cancer correlates with cyclooxygenase-2 overexpression
and tumor growth. FEBS J. 279:4201–4212. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Nagaraju GP and El-Rayes BF:
Cyclooxygenase-2 in gastrointestinal malignancies. Cancer.
125:1221–1227. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Wang J, Ding Y, Wu Y and Wang X:
Identification of the complex regulatory relationships related to
gastric cancer from lncRNA-miRNA-mRNA network. J Cell Biochem.
121:876–887. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Liu G and Li B: Role of miRNA in
transformation from normal tissue to colorectal adenoma and cancer.
J Cancer Res Ther. 15:278–285. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Takagi T, Iio A, Nakagawa Y, Naoe T,
Tanigawa N and Akao Y: Decreased expression of microRNA-143 and
−145 in human gastric cancers. Oncology. 77:12–21. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Wu XL, Cheng B, Li PY, Huang HJ, Zhao Q,
Dan ZL, Tian DA and Zhang P: MicroRNA-143 suppresses gastric cancer
cell growth and induces apoptosis by targeting COX-2. World J
Gastroenterol. 19:7758–7765. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Yao Q, Gu A, Wang Z and Xue Y:
MicroRNA-144 functions as a tumor suppressor in gastric cancer by
targeting cyclooxygenase-2. Exp Ther Med. 15:3088–3095.
2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Liu X, Ji Q, Zhang C, Liu X, Liu Y, Liu N,
Sui H, Zhou L, Wang S and Li Q: miR-30a acts as a tumor suppressor
by double-targeting COX-2 and BCL9 in H. pylori gastric
cancer models. Sci Rep. 7:71132017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Cheng Y, Li Y, Liu D, Zhang R and Zhang J:
miR-137 effects on gastric carcinogenesis are mediated by targeting
Cox-2-activated PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. FEBS Lett.
588:3274–3281. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Chen P, Wang BL, Pan BS and Guo W:
MiR-1297 regulates the growth, migration and invasion of colorectal
cancer cells by targeting cyclo-oxygenase-2. Asian Pac J Cancer
Prev. 15:9185–9190. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Wang D, Li Y, Zhang C, Li X and Yu J:
MiR-216a-3p inhibits colorectal cancer cell proliferation through
direct targeting COX-2 and ALOX5. J Cell Biochem. 119:1755–1766.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Chakraborty C, Sharma AR, Sharma G and Lee
SS: The interplay among miRNAs, major cytokines, and cancer-related
inflammation. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 20:606–620. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Yang YM, Kim SY and Seki E: Inflammation
and liver cancer: Molecular mechanisms and therapeutic targets.
Semin Liver Dis. 39:26–42. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Agra Andrieu N, Motiño O, Mayoral R,
Llorente Izquierdo C, Fernández-Alvarez A, Boscá L, Casado M and
Martín-Sanz P: Cyclooxygenase-2 is a target of microRNA-16 in human
hepatoma cells. PLoS One. 7:e509352012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Jia H, Wang H, Yao Y, Wang C and Li P:
miR-136 inhibits malignant progression of hepatocellular carcinoma
cells by targeting cyclooxygenase 2. Oncol Res. 26:967–976. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Li J, Lu X, Zou X, Jiang Y, Yao J, Liu H,
Ni B and Ma H: COX-2 rs5275 and rs689466 polymorphism and risk of
lung cancer: A PRISMA-compliant meta-analysis. Medicine
(Baltimore). 97:e118592018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Zago M, Rico de Souza A, Hecht E, Rousseau
S, Hamid Q, Eidelman DH and Baglole CJ: The NF-κB family member
RelB regulates microRNA miR-146a to suppress cigarette
smoke-induced COX-2 protein expression in lung fibroblasts. Toxicol
Lett. 226:107–116. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Xia M, Duan ML, Tong JH and Xu JG: MiR-26b
suppresses tumor cell proliferation, migration and invasion by
directly targeting COX-2 in lung cancer. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci.
19:4728–4737. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Kwon Y, Kim Y, Eom S, Kim M, Park D, Kim
H, Noh K, Lee H, Lee YS, Choe J, et al:
MicroRNA-26a/-26b-COX-2-MIP-2 loop regulates allergic inflammation
and allergic inflammation-promoted enhanced tumorigenic and
metastatic potential of cancer cells. J Biol Chem. 290:14245–14266.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Wu C, Li X, Zhang D, Xu B, Hu W, Zheng X,
Zhu D, Zhou Q, Jiang J and Wu C: IL-1β-mediated Up-regulation of
WT1D via miR-144-3p and their synergistic effect with
NF-κB/COX-2/HIF-1α pathway on cell proliferation in LUAD. Cell
Physiol Biochem. 48:2493–2502. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Li B, Lu Y, Yu L, Han X, Wang H, Mao J,
Shen J, Wang B, Tang J, Li C and Song B: miR-221/222 promote cancer
stem-like cell properties and tumor growth of breast cancer via
targeting PTEN and sustained Akt/NF-κB/COX-2 activation. Chem Biol
Interact. 277:33–42. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Majumder M, Dunn L, Liu L, Hasan A,
Vincent K, Brackstone M, Hess D and Lala PK: COX-2 induces
oncogenic micro RNA miR655 in human breast cancer. Sci Rep.
8:3272018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Liao H, Zhou Q, Gu Y, Duan T and Feng Y:
Luteinizing hormone facilitates angiogenesis in ovarian epithelial
tumor cells and metformin inhibits the effect through the mTOR
signaling pathway. Oncol Rep. 27:1873–1878. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Lai Y, Zhang X, Zhang Z, Shu Y, Luo X,
Yang Y, Wang X, Yang G, Li L and Feng Y: The microRNA-27a:
ZBTB10-specificity protein pathway is involved in follicle
stimulating hormone-induced VEGF, Cox2 and survivin expression in
ovarian epithelial cancer cells. Int J Oncol. 42:776–784. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Lin Y and Wu Z: MicroRNA-128 inhibits
proliferation and invasion of glioma cells by targeting COX-2.
Gene. 658:63–69. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Chen ZG, Zheng CY, Cai WQ, Li DW, Ye FY,
Zhou J, Wu R and Yang K: miR-26b mimic inhibits glioma
proliferation in vitro and in vivo suppressing COX-2 expression.
Oncol Res. 27:147–155. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Shields CL and Shields JA: Retinoblastoma
management: Advances in enucleation, intravenous chemoreduction,
and intra-arterial chemotherapy. Curr Opin Ophthalmol. 21:203–212.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Zhang J, He J and Zhang L: The
down-regulation of microRNA-137 contributes to the up-regulation of
retinoblastoma cell proliferation and invasion by regulating
COX-2/PGE2 signaling. Biomed Pharmacother. 106:35–42. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Yu Q, Zhang K, Wang X, Liu X and Zhang Z:
Expression of transcription factors snail, slug, and twist in human
bladder carcinoma. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 29:1192010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Song T, Zhang X, Wang C, Wu Y, Dong J, Gao
J, Cai W and Hong B: Expression of miR-143 reduces growth and
migration of human bladder carcinoma cells by targeting
cyclooxygenase-2. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 12:9292011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Xu L, Shen B, Chen T and Dong P: miR-203
is involved in the laryngeal carcinoma pathogenesis via targeting
VEGFA and Cox-2. Onco Targets Ther. 9:4629–4637. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Tołoczko-Iwaniuk N, Dziemiańczyk-Pakieła
D, Nowaszewska BK, Celińska-Janowicz K and Miltyk W: Celecoxib in
cancer therapy and prevention-review. Curr Drug Targets.
20:302–315. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
96
|
Jackson AL, Bartz SR, Schelter J,
Kobayashi SV, Burchard J, Mao M, Li B, Cavet G and Linsley PS:
Expression profiling reveals off-target gene regulation by RNAi.
Nat Biotechnol. 21:635–637. 2003. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Strillacci A, Griffoni C, Valerii MC,
Lazzarini G, Tomasi V and Spisni E: RNAi-based strategies for
cyclooxygenase-2 inhibition in cancer. J Biomed Biotechnol.
2010:8280452010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98
|
Liu X, Wu Y, Zhou Z, Huang M, Deng W, Wang
Y, Zhou X, Chen L, Li Y, Zeng T, et al: Celecoxib inhibits the
epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in bladder cancer via the
miRNA-145/TGFBR2/Smad3 axis. Int J Mol Med. 44:683–693.
2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
99
|
Ghose J and Bhattacharyya NP:
Transcriptional regulation of microRNA-100, −146a, and −150 genes
by p53 and NFκB p65/RelA in mouse striatal STHdh(Q7)/Hdh(Q7) cells
and human cervical carcinoma HeLa cells. RNA Biol. 12:457–477.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
100
|
DA Costa RM, Bastos MM, Medeiros R and
Oliveira PA: The NFkB signaling pathway in papillomavirus-induced
lesions: Friend or foe? Anticancer Res. 36:2073–2083.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
101
|
DA Costa RMG, Araújo R, Santos JMO,
Fernandes M, Neto T, Sousa H, Ribeiro J, Bastos MMSM, Oliveira PA,
Carmo D, et al: Regulation of miRNA-146a and miRNA-150 Levels by
celecoxib in premalignant lesions of K14-HPV16 mice. Anticancer
Res. 37:2913–2918. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
102
|
Saito Y, Suzuki H, Imaeda H, Matsuzaki J,
Hirata K, Tsugawa H, Hibino S, Kanai Y, Saito H and Hibi T: The
tumor suppressor microRNA-29c is downregulated and restored by
celecoxib in human gastric cancer cells. Int J Cancer.
132:1751–1760. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
103
|
Mott JL, Kobayashi S, Bronk SF and Gores
GJ: mir-29 regulates Mcl-1 protein expression and apoptosis.
Oncogene. 26:6133–6140. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
104
|
Hunter S, Nault B, Ugwuagbo KC, Maiti S
and Majumder M: Chemicall induced hypoxia enhances miRNA functions
in breast cancer. Cancers (Basel). 12:20082020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
105
|
Najafi M, Farhood B, Mortezaee K,
Kharazinejad E, Majidpoor J and Ahadi R: Hypoxia in solid tumors: A
key promoter of cancer stem cell (CSC) resistance. J Cancer Res
Clin Oncol. 146:19–31. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
106
|
Xiong W, Li WH, Jiang YX, Liu S, Ai YQ,
Liu R, Chang L, Zhang M, Wang XL, Bai H, et al: Parecoxib: An
enhancer of radiation therapy for colorectal cancer. Asian Pac J
Cancer Prev. 16:627–633. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
107
|
Zagani R, Hamzaoui N, Cacheux W, de
Reyniès A, Terris B, Chaussade S, Romagnolo B, Perret C and
Lamarque D: Cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitors down-regulate osteopontin
and Nr4A2-new therapeutic targets for colorectal cancers.
Gastroenterology. 137:1358–1366.e1-3. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
108
|
Li LY, Xiao J, Liu Q and Xia K: Parecoxib
inhibits glioblastoma cell proliferation, migration and invasion by
up-regulating miRNA-29c. Biol Open. 6:311–316. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
109
|
Nissen SE, Yeomans ND, Solomon DH, Lüscher
TF, Libby P, Husni ME, Graham DY, Borer JS, Wisniewski LM, Wolski
KE, et al: Cardiovascular safety of celecoxib, naproxen, or
ibuprofen for arthritis. N Engl J Med. 375:2519–2529. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|