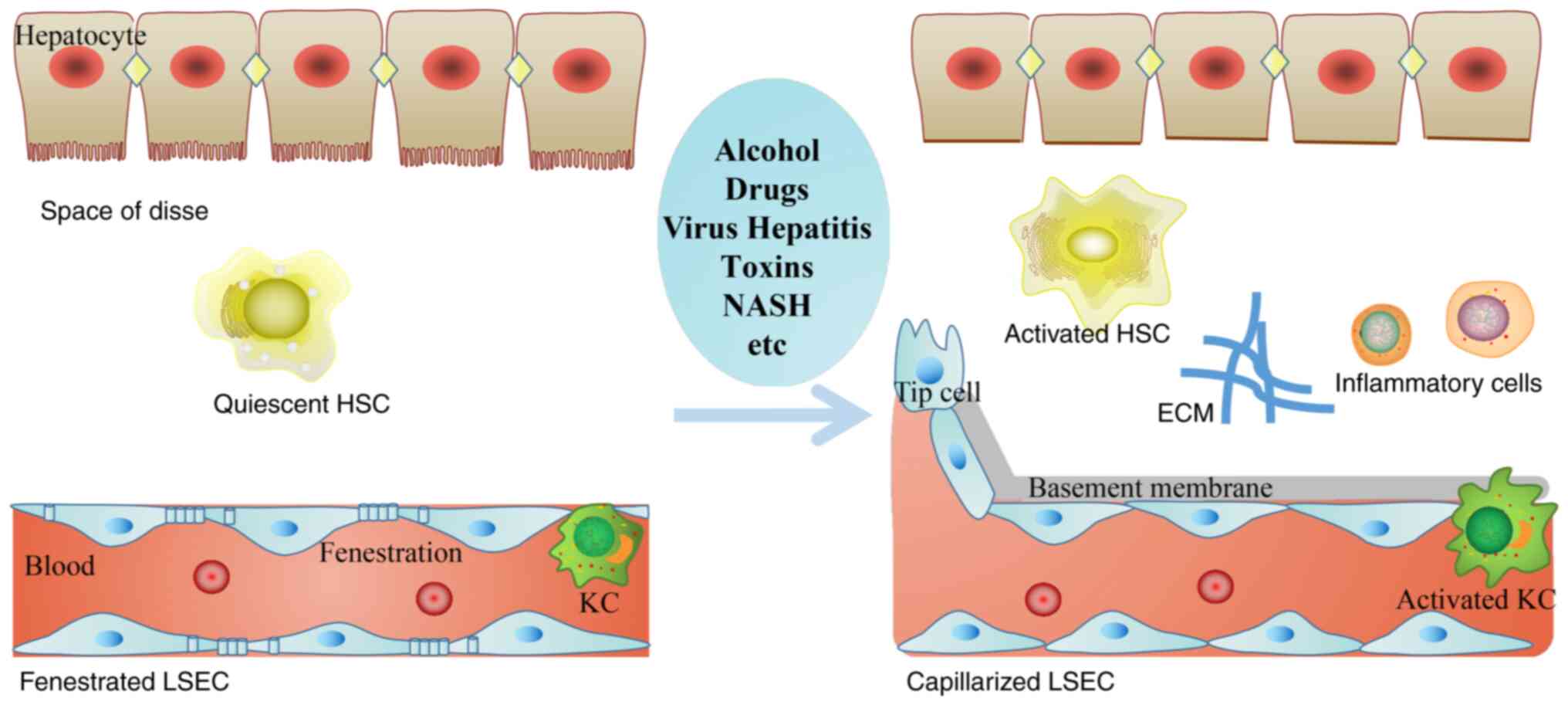
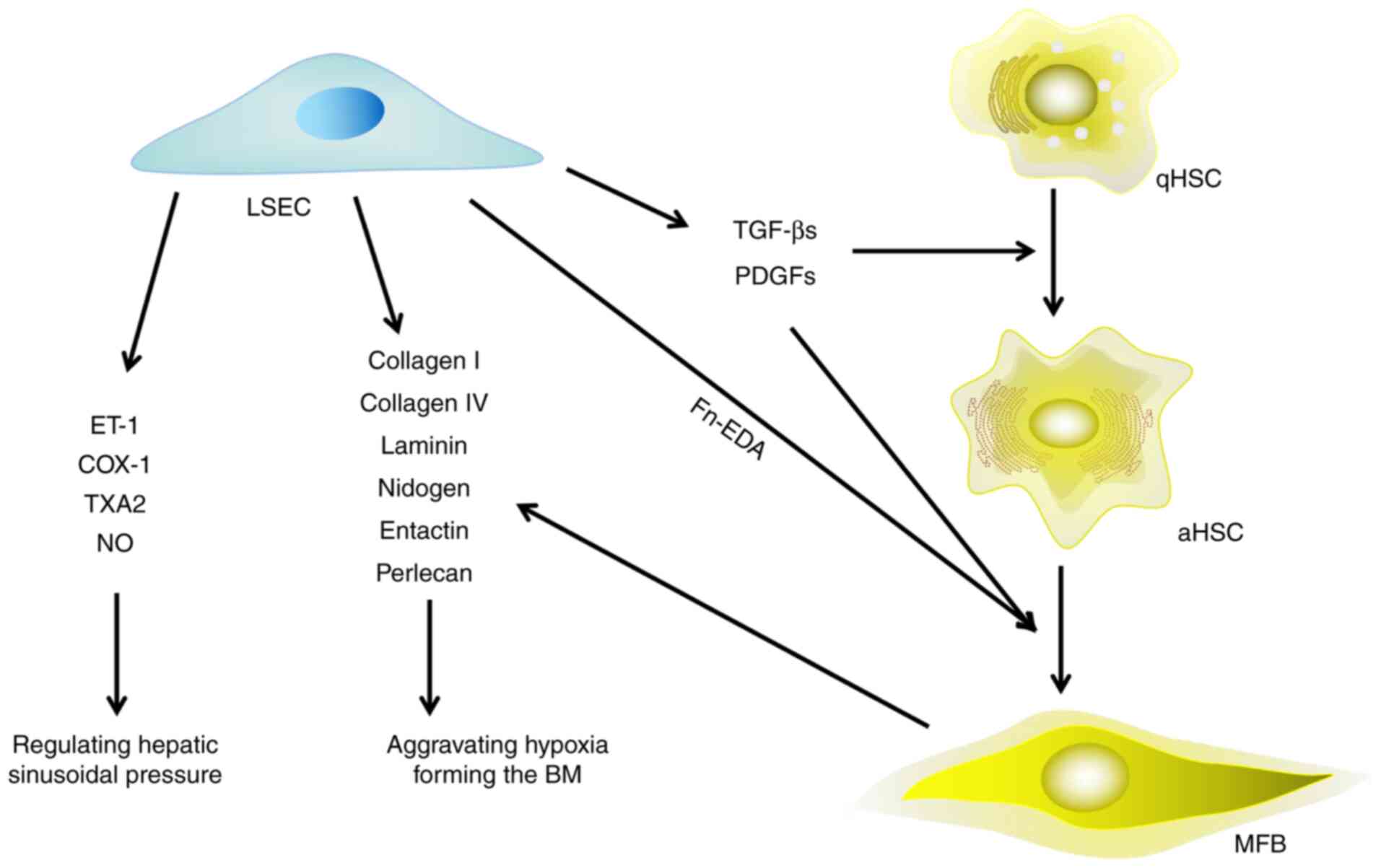
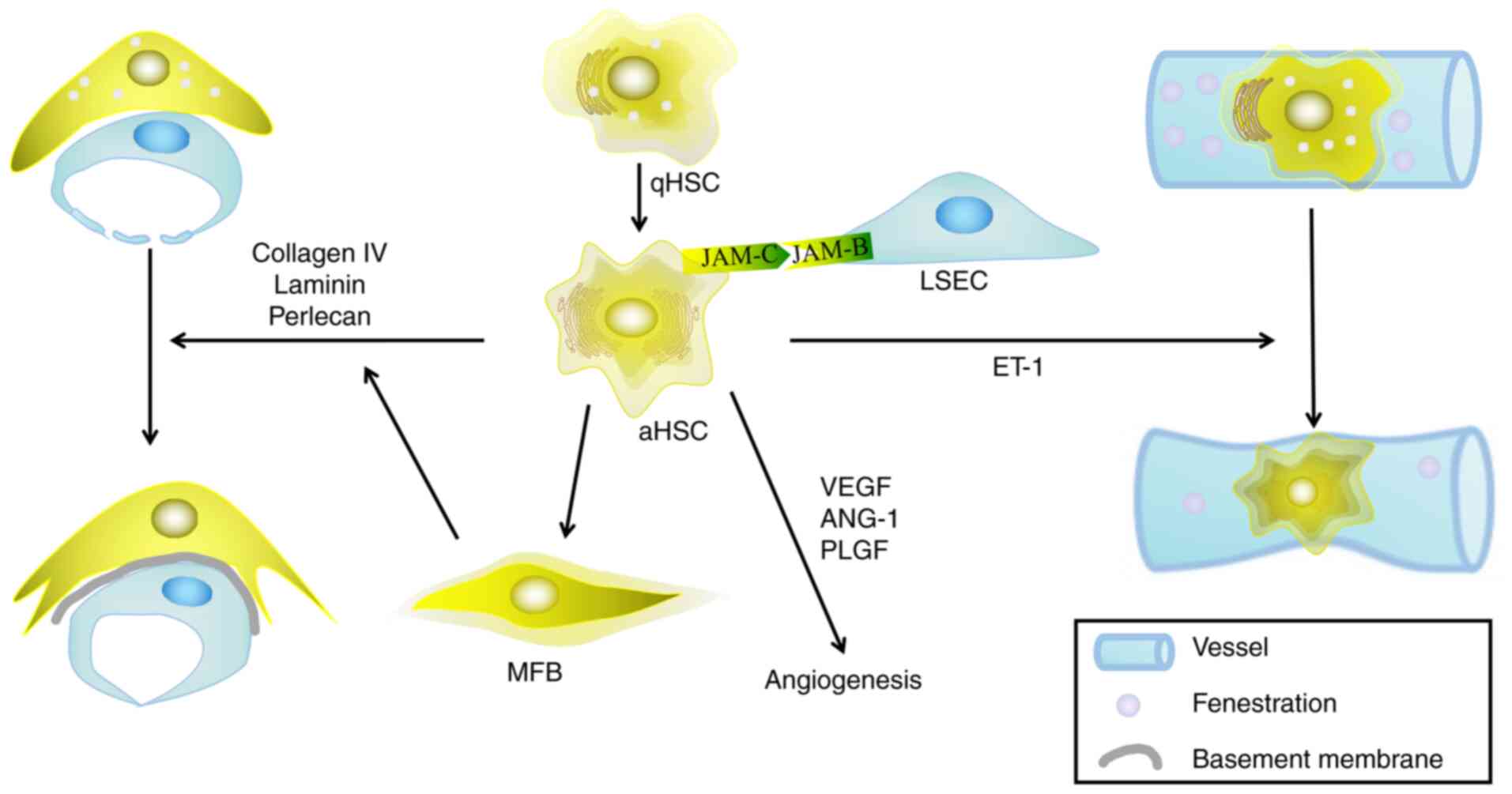
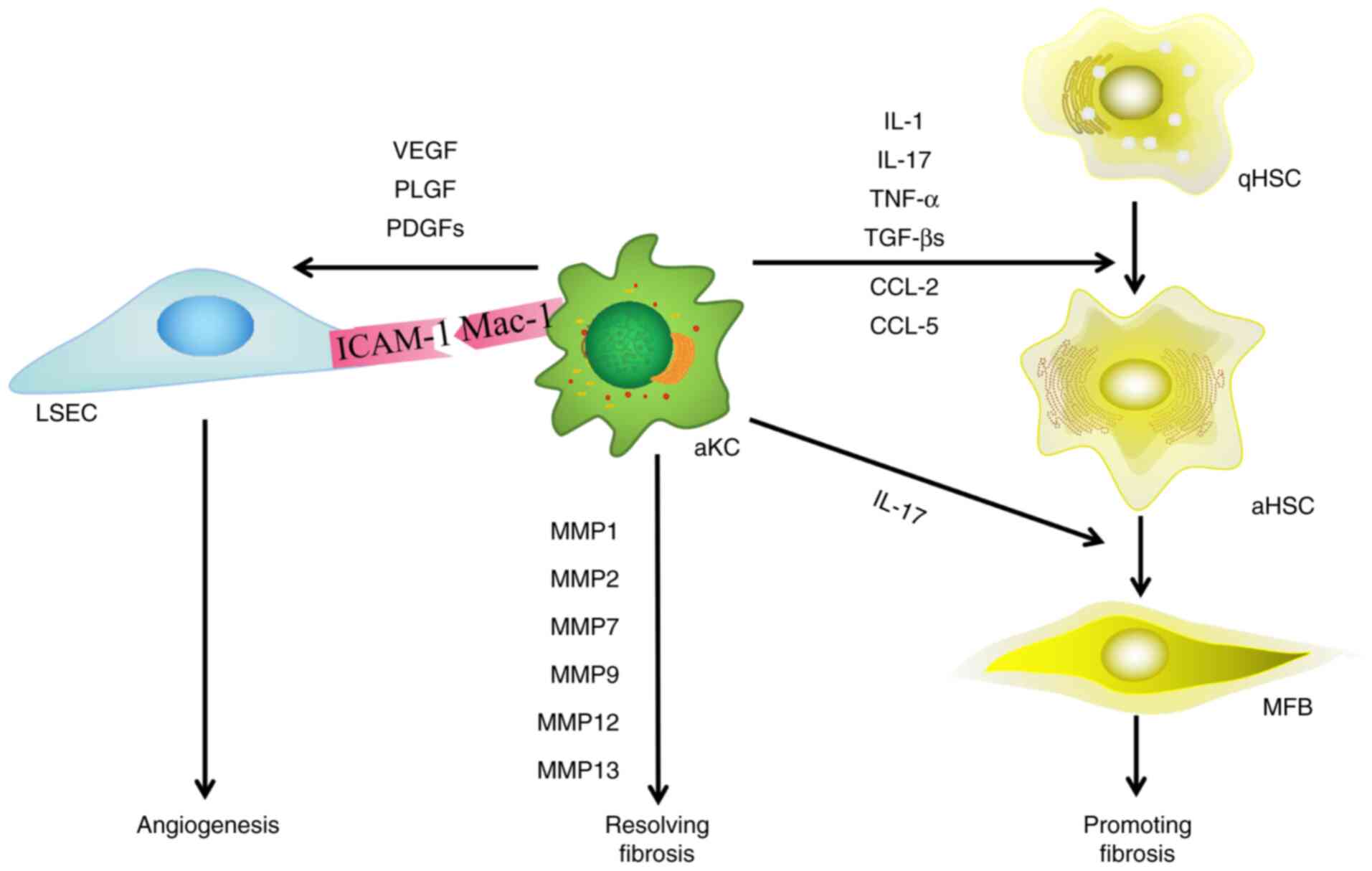
|
1
|
Aydin MM and Akcali KC: Liver fibrosis.
Turk J Gastroenterol. 29:14–21. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Greuter T and Shah VH: Hepatic sinusoids
in liver injury, inflammation, and fibrosis: New pathophysiological
insights. J Gastroenterol. 51:511–519. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Liu X, Hu H and Yin JQ: Therapeutic
strategies against TGF-beta signaling pathway in hepatic fibrosis.
Liver Int. 26:8–22. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Higashi T, Friedman SL and Hoshida Y:
Hepatic stellate cells as key target in liver fibrosis. Adv Drug
Deliv Rev. 121:27–42. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Marrone G, Shah VH and Gracia-Sancho J:
Sinusoidal communication in liver fibrosis and regeneration. J
Hepatol. 65:608–617. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Klenerman P and Ramamurthy N: Liver
sinusoidal endothelial cells: An antiviral ‘defendothelium’.
Gastroenterology. 148:288–291. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Ray K: Liver: Hepatic stellate cells hold
the key to liver fibrosis. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol.
11:742014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Poisson J, Lemoinne S, Boulanger C, Durand
F, Moreau R, Valla D and Rautou PE: Liver sinusoidal endothelial
cells: Physiology and role in liver diseases. J Hepatol.
66:212–227. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Shetty S, Lalor PF and Adams DH: Liver
sinusoidal endothelial cells-gatekeepers of hepatic immunity. Nat
Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 15:555–567. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Sorensen KK, Simon-Santamaria J, McCuskey
RS and Smedsrod B: Liver Sinusoidal Endothelial Cells. Compr
Physiol. 5:1751–1774. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Ni Y, Li JM, Liu MK, Zhang TT, Wang DP,
Zhou WH, Hu LZ and Lv WL: Pathological process of liver sinusoidal
endothelial cells in liver diseases. World J Gastroenterol.
23:7666–7677. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Friedman SL: Hepatic stellate cells:
Protean, multifunctional, and enigmatic cells of the liver. Physiol
Rev. 88:125–172. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Dixon LJ, Barnes M, Tang H, Pritchard MT
and Nagy LE: Kupffer cells in the liver. Compr Physiol. 3:785–797.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Dou L, Shi X, He X and Gao Y: Macrophage
phenotype and function in liver disorder. Front Immunol.
10:31122019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Liu HL, Lv J, Zhao ZM, Xiong AM, Tan Y,
Glenn JS, Tao YY, Weng HL and Liu CH: Fuzhenghuayu decoction
ameliorates hepatic fibrosis by attenuating experimental sinusoidal
capillarization and liver angiogenesis. Sci Rep. 9:187192019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Brusilovskaya K, Konigshofer P, Schwabl P
and Reiberger T: Vascular targets for the treatment of portal
hypertension. Semin Liver Dis. 39:483–501. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
DeLeve LD: Liver sinusoidal endothelial
cells in hepatic fibrosis. Hepatology. 61:1740–1746. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Tuohetahuntila M, Molenaar MR, Spee B,
Brouwers JF, Wubbolts R, Houweling M, Yan C, Du H, VanderVen BC,
Vaandrager AB and Helms JB: Lysosome-mediated degradation of a
distinct pool of lipid droplets during hepatic stellate cell
activation. J Biol Chem. 292:12436–12448. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Peterova E, Podmolikova L, Rezacova M and
Mrkvicova A: Fibroblast growth Factor-1 suppresses TGF-β-mediated
myofibroblastic differentiation of rat hepatic stellate cells. Acta
Medica (Hradec Kralove). 59:124–132. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Schon HT, Bartneck M, Borkham-Kamphorst E,
Nattermann J, Lammers T, Tacke F and Weiskirchen R: Pharmacological
intervention in hepatic stellate cell activation and hepatic
fibrosis. Front Pharmacol. 7:332016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Ezhilarasan D, Sokal E and Najimi M:
Hepatic fibrosis: It is time to go with hepatic stellate
cell-specific therapeutic targets. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int.
17:192–197. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Cai X, Wang J, Wang J, Zhou Q, Yang B, He
Q and Weng Q: Intercellular crosstalk of hepatic stellate cells in
liver fibrosis: New insights into therapy. Pharmacol Res.
155:1047202020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Ramirez-Pedraza M and Fernandez M:
Interplay between macrophages and angiogenesis: A double-edged
sword in liver disease. Front Immunol. 10:28822019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Lafoz E, Ruart M, Anton A, Oncins A and
Hernández-Gea V: The endothelium as a driver of liver fibrosis and
regeneration. Cells. 9:9292020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Soydemir S, Comella O, Abdelmottaleb D and
Pritchett J: Does mechanocrine signaling by liver sinusoidal
endothelial cells offer new opportunities for the development of
anti-fibrotics? Front Med (Lausanne). 6:3122019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Kaur S and Anita K: Angiogenesis in liver
regeneration and fibrosis: ‘A double-edged sword’. Hepatol Int.
7:959–968. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Wells RG: Cellular sources of
extracellular matrix in hepatic fibrosis. Clin Liver Dis.
12:759–768. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Maher JJ and McGuire RF: Extracellular
matrix gene expression increases preferentially in rat lipocytes
and sinusoidal endothelial cells during hepatic fibrosis in vivo. J
Clin Invest. 86:1641–1648. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Yu F, Dong B, Dong P, He Y, Zheng J and Xu
P: Hypoxia induces the activation of hepatic stellate cells through
the PVT1-miR-152-ATG14 signaling pathway. Mol Cell Biochem.
465:115–123. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Shi YF, Fong CC, Zhang Q, Cheung PY, Tzang
CH, Wu RS and Yang M: Hypoxia induces the activation of human
hepatic stellate cells LX-2 through TGF-beta signaling pathway.
FEBS Lett. 581:203–210. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Jin Y, Bai Y, Ni H, Qiang L, Ye L, Shan Y
and Zhou M: Activation of autophagy through calcium-dependent
AMPK/mTOR and PKCθ pathway causes activation of rat hepatic
stellate cells under hypoxic stress. FEBS Lett. 590:672–682. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Chen W, Rock JB, Yearsley MM, Ferrell LD
and Frankel WL: Different collagen types show distinct rates of
increase from early to late stages of hepatitis C-related liver
fibrosis. Hum Pathol. 45:160–165. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Ghafoory S, Varshney R, Robison T,
Kouzbari K, Woolington S, Murphy B, Xia L and Ahamed J: Platelet
TGF-β1 deficiency decreases liver fibrosis in a mouse model of
liver injury. Blood Adv. 2:470–480. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Baghy K, Iozzo RV and Kovalszky I:
Decorin-TGFβ axis in hepatic fibrosis and cirrhosis. J Histochem
Cytochem. 60:262–268. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Hayes BJ, Riehle KJ, Shimizu-Albergine M,
Bauer RL, Hudkins KL, Johansson F, Yeh MM, Mahoney WJ, Yeung RS and
Campbell JS: Activation of platelet-derived growth factor receptor
alpha contributes to liver fibrosis. PLoS One. 9:e929252014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Ying HZ, Chen Q, Zhang WY, Zhang HH, Ma Y,
Zhang SZ, Fang J and Yu CH: PDGF signaling pathway in hepatic
fibrosis pathogenesis and therapeutics (Review). Mol Med Rep.
16:7879–7889. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Borkham-Kamphorst E and Weiskirchen R: The
PDGF system and its antagonists in liver fibrosis. Cytokine Growth
Factor Rev. 28:53–61. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Borkham-Kamphorst E, Meurer SK, Van de
Leur E, Haas U, Tihaa L and Weiskirchen R: PDGF-D signaling in
portal myofibroblasts and hepatic stellate cells proves identical
to PDGF-B via both PDGF receptor type alpha and β. Cell Signal.
27:1305–1314. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Kocabayoglu P, Lade A, Lee YA, Dragomir A,
Sun X, Fiel MI, Thung S, Aloman C, Soriano P, Hoshida Y and
Friedman SL: β-PDGF receptor expressed by hepatic stellate cells
regulates fibrosis in murine liver injury, but not carcinogenesis.
J Hepatol. 63:141–147. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Thabut D and Shah V: Intrahepatic
angiogenesis and sinusoidal remodeling in chronic liver disease:
New targets for the treatment of portal hypertension? J Hepatol.
53:976–980. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Lim BJ, Lee WK, Lee HW, Lee KS, Kim JK,
Chang HY and Lee JI: Selective deletion of hepatocyte
platelet-derived growth factor receptor α and development of liver
fibrosis in mice. Cell Commun Signal. 16:932018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Serini G, Bochaton-Piallat ML, Ropraz P,
Geinoz A, Borsi L, Zardi L and Gabbiani G: The fibronectin domain
ED-A is crucial for myofibroblastic phenotype induction by
transforming growth factor-beta1. J Cell Biol. 142:873–881. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Gabbiani G: The myofibroblast in wound
healing and fibrocontractive diseases. J Pathol. 200:500–503. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Bocca C, Novo E, Miglietta A and Parola M:
Angiogenesis and Fibrogenesis in chronic liver diseases. Cell Mol
Gastroenterol Hepatol. 1:477–488. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Kardum D, Fabijanic D, Lukic A, Romic Z,
Petrovecki M, Bogdanovic Z, Juric K, Urek-Crncevic M and Banic M:
Correlation of endothelin-1 concentration and
angiotensin-converting enzyme activity with the staging of liver
fibrosis. Coll Antropol. 36:413–418. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Yokomori H, Oda M, Ogi M, Kamegaya Y,
Tsukada N, Nakamura M and Ishii H: Enhanced expression of
endothelin receptor subtypes in cirrhotic rat liver. Liver.
21:114–122. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Koda M, Bauer M, Krebs A, Hahn EG,
Schuppan D and Murawaki Y: Endothelin-1 enhances fibrogenic gene
expression, but does not promote DNA synthesis or apoptosis in
hepatic stellate cells. Comp Hepatol. 5:52006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Pinzani M, Milani S, De Franco R, Grappone
C, Caligiuri A, Gentilini A, Tosti-Guerra C, Maggi M, Failli P,
Ruocco C and Gentilini P: Endothelin 1 is overexpressed in human
cirrhotic liver and exerts multiple effects on activated hepatic
stellate cells. Gastroenterology. 110:534–548. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Das A, Shergill U, Thakur L, Sinha S,
Urrutia R, Mukhopadhyay D and Shah VH: Ephrin B2/EphB4 pathway in
hepatic stellate cells stimulates Erk-dependent VEGF production and
sinusoidal endothelial cell recruitment. Am J Physiol Gastrointest
Liver Physiol. 298:G908–G915. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Li G, Peng Y, Zhao T, Lin J, Duan X, Wei Y
and Ma J: Plumbagin alleviates capillarization of hepatic sinusoids
in vitro by downregulating ET-1, VEGF, LN, and type IV collagen.
Biomed Res Int. 2017:56032162017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Lee JS, Semela D, Iredale J and Shah VH:
Sinusoidal remodeling and angiogenesis: A new function for the
liver-specific pericyte? Hepatology. 45:817–825. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Rockey DC: Hepatic blood flow regulation
by stellate cells in normal and injured liver. Semin Liver Dis.
21:337–349. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Henderson NC and Iredale JP: Liver
fibrosis: Cellular mechanisms of progression and resolution. Clin
Sci (Lond). 112:265–280. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Knittel T, Mehde M, Kobold D, Saile B,
Dinter C and Ramadori G: Expression patterns of matrix
metalloproteinases and their inhibitors in parenchymal and
non-parenchymal cells of rat liver: Regulation by TNF-alpha and
TGF-beta1. J Hepatol. 30:48–60. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Liu T, Xu L, Wang C, Chen K, Xia Y, Li J,
Li S, Wu L, Feng J, Xu S, et al: Alleviation of hepatic fibrosis
and autophagy via inhibition of transforming growth factor-β1/Smads
pathway through shikonin. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 34:263–276.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Gupta G, Khadem F and Uzonna JE: Role of
hepatic stellate cell (HSC)-derived cytokines in hepatic
inflammation and immunity. Cytokine. 124:1545422019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Marchand M, Monnot C, Muller L and Germain
S: Extracellular matrix scaffolding in angiogenesis and capillary
homeostasis. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 89:147–156. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Mokkapati S, Fleger-Weckmann A, Bechtel M,
Koch M, Breitkreutz D, Mayer U, Smyth N and Nischt R: Basement
membrane deposition of nidogen 1 but not nidogen 2 requires the
nidogen binding module of the laminin gamma1 chain. J Biol Chem.
286:1911–1918. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Mak KM and Mei R: Basement membrane type
IV collagen and laminin: An overview of their biology and value as
fibrosis biomarkers of liver disease. Anat Rec (Hoboken).
300:1371–1390. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
McGuire RF, Bissell DM, Boyles J and Roll
FJ: Role of extracellular matrix in regulating fenestrations of
sinusoidal endothelial cells isolated from normal rat liver.
Hepatology. 15:989–997. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Braet F and Wisse E: Structural and
functional aspects of liver sinusoidal endothelial cell fenestrae:
A review. Comp Hepatol. 1:12002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Natarajan V, Harris EN and Kidambi S: SECs
(Sinusoidal Endothelial Cells), liver microenvironment, and
fibrosis. Biomed Res Int. 2017:40972052017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
DeLeve LD, Wang X, Hu L, McCuskey MK and
McCuskey RS: Rat liver sinusoidal endothelial cell phenotype is
maintained by paracrine and autocrine regulation. Am J Physiol
Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 287:G757–G763. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Desroches-Castan A, Tillet E, Ricard N,
Ouarne M, Mallet C, Belmudes L, Coute Y, Boillot O, Scoazec JY,
Bailly S and Feige JJ: Bone morphogenetic protein 9 is a paracrine
factor controlling liver sinusoidal endothelial cell fenestration
and protecting against hepatic fibrosis. Hepatology. 70:1392–1408.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Soon RJ and Yee HJ: Stellate cell
contraction: Role, regulation, and potential therapeutic target.
Clin Liver Dis. 12:791–803. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Hintermann E, Bayer M, Ehser J,
Aurrand-Lions M, Pfeilschifter JM, Imhof BA and Christen U: Murine
junctional adhesion molecules JAM-B and JAM-C mediate endothelial
and stellate cell interactions during hepatic fibrosis. Cell Adh
Migr. 10:419–433. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Hintermann E, Bayer M, Conti CB, Fuchs S,
Fausther M, Leung PS, Aurrand-Lions M, Taubert R, Pfeilschifter JM,
Friedrich-Rust M, et al: Junctional adhesion molecules JAM-B and
JAM-C promote autoimmune-mediated liver fibrosis in mice. J
Autoimmun. 91:83–96. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Saiman Y, Agarwal R, Hickman DA, Fausther
M, El-Shamy A, Dranoff JA, Friedman SL and Bansal MB: CXCL12
induces hepatic stellate cell contraction through a
calcium-independent pathway. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver
Physiol. 305:G375–G382. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Sohail MA, Hashmi AZ, Hakim W, Watanabe A,
Zipprich A, Groszmann RJ, Dranoff JA, Torok NJ and Mehal WZ:
Adenosine induces loss of actin stress fibers and inhibits
contraction in hepatic stellate cells via Rho inhibition.
Hepatology. 49:185–194. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Zhang Z, Zhang F, Lu Y and Zheng S: Update
on implications and mechanisms of angiogenesis in liver fibrosis.
Hepatol Res. 45:162–178. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Budny T, Palmes D, Stratmann U, Minin E,
Herbst H and Spiegel HU: Morphologic features in the regenerating
liver-a comparative intravital, lightmicroscopical and
ultrastructural analysis with focus on hepatic stellate cells.
Virchows Arch. 451:781–791. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Coulon S, Heindryckx F, Geerts A, Van
Steenkiste C, Colle I and Van Vlierberghe H: Angiogenesis in
chronic liver disease and its complications. Liver Int. 31:146–162.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Karkkainen MJ and Petrova TV: Vascular
endothelial growth factor receptors in the regulation of
angiogenesis and lymphangiogenesis. Oncogene. 19:5598–5605. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Xie G, Wang X, Wang L, Wang L, Atkinson
RD, Kanel GC, Gaarde WA and Deleve LD: Role of differentiation of
liver sinusoidal endothelial cells in progression and regression of
hepatic fibrosis in rats. Gastroenterology. 142:918–927. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Deleve LD, Wang X and Guo Y: Sinusoidal
endothelial cells prevent rat stellate cell activation and promote
reversion to quiescence. Hepatology. 48:920–930. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Li X, Yao Q, Liu H, Jin Q, Xu B, Zhang S
and Tu C: Placental growth factor silencing ameliorates liver
fibrosis and angiogenesis and inhibits activation of hepatic
stellate cells in a murine model of chronic liver disease. J Cell
Mol Med. 21:2370–2385. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Dewerchin M and Carmeliet P: PlGF: A
multitasking cytokine with disease-restricted activity. Cold Spring
Harb Perspect Med. 2:a0110562012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Li X, Jin Q, Yao Q, Zhou Y, Zou Y, Li Z,
Zhang S and Tu C: Placental growth factor contributes to liver
inflammation, angiogenesis, Fibrosis in mice by promoting hepatic
macrophage recruitment and activation. Front Immunol. 8:8012017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Reif S, Lang A, Lindquist JN, Yata Y,
Gabele E, Scanga A, Brenner DA and Rippe RA: The role of focal
adhesion kinase-phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-akt signaling in
hepatic stellate cell proliferation and type I collagen expression.
J Biol Chem. 278:8083–8090. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Van Steenkiste C, Ribera J, Geerts A,
Pauta M, Tugues S, Casteleyn C, Libbrecht L, Olievier K, Schroyen
B, Reynaert H, et al: Inhibition of placental growth factor
activity reduces the severity of fibrosis, inflammation, and portal
hypertension in cirrhotic mice. Hepatology. 53:1629–1640. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Augustin HG, Koh GY, Thurston G and
Alitalo K: Control of vascular morphogenesis and homeostasis
through the angiopoietin-Tie system. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol.
10:165–177. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Gurnik S, Devraj K, Macas J, Yamaji M,
Starke J, Scholz A, Sommer K, Di Tacchio M, Vutukuri R, Beck H, et
al: Angiopoietin-2-induced blood-brain barrier compromise and
increased stroke size are rescued by VE-PTP-dependent restoration
of Tie2 signaling. Acta Neuropathol. 131:753–773. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Wynn TA and Barron L: Macrophages: Master
regulators of inflammation and fibrosis. Semin Liver Dis.
30:245–257. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Ma PF, Gao CC, Yi J, Zhao JL, Liang SQ,
Zhao Y, Ye YC, Bai J, Zheng QJ, Dou KF, et al: Cytotherapy with
M1-polarized macrophages ameliorates liver fibrosis by modulating
immune microenvironment in mice. J Hepatol. 67:770–779. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Tacke F: Targeting hepatic macrophages to
treat liver diseases. J Hepatol. 66:1300–1312. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Varol C, Mildner A and Jung S:
Macrophages: Development and tissue specialization. Annu Rev
Immunol. 33:643–675. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
You Q, Holt M, Yin H, Li G, Hu CJ and Ju
C: Role of hepatic resident and infiltrating macrophages in liver
repair after acute injury. Biochem Pharmacol. 86:836–843. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Vollmar B, Siegmund S, Richter S and
Menger MD: Microvascular consequences of Kupffer cell modulation in
rat liver fibrogenesis. J Pathol. 189:85–91. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Wehr A, Baeck C, Heymann F, Niemietz PM,
Hammerich L, Martin C, Zimmermann HW, Pack O, Gassler N, Hittatiya
K, et al: Chemokine receptor CXCR6-dependent hepatic NK T cell
accumulation promotes inflammation and liver fibrosis. J Immunol.
190:5226–5236. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Tacke F and Zimmermann HW: Macrophage
heterogeneity in liver injury and fibrosis. J Hepatol.
60:1090–1096. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Zhou WC, Zhang QB and Qiao L: Pathogenesis
of liver cirrhosis. World J Gastroenterol. 20:7312–7324. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Koyama Y and Brenner DA: Liver
inflammation and fibrosis. J Clin Invest. 127:55–64. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Luckey SW and Petersen DR: Activation of
Kupffer cells during the course of carbon tetrachloride-induced
liver injury and fibrosis in rats. Exp Mol Pathol. 71:226–240.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Weiskirchen R and Tacke F: Cellular and
molecular functions of hepatic stellate cells in inflammatory
responses and liver immunology. Hepatobiliary Surg Nutr. 3:344–363.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Wang J, Leclercq I, Brymora JM, Xu N,
Ramezani-Moghadam M, London RM, Brigstock D and George J: Kupffer
cells mediate leptin-induced liver fibrosis. Gastroenterology.
137:713–723. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
96
|
Meng F, Wang K, Aoyama T, Grivennikov SI,
Paik Y, Scholten D, Cong M, Iwaisako K, Liu X, Zhang M, et al:
Interleukin-17 signaling in inflammatory, Kupffer cells, and
hepatic stellate cells exacerbates liver fibrosis in mice.
Gastroenterology. 143:765–776. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Seki E and Brenner DA: Recent advancement
of molecular mechanisms of liver fibrosis. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat
Sci. 22:512–518. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98
|
Hara M, Kono H, Furuya S, Hirayama K,
Tsuchiya M and Fujii H: Interleukin-17A plays a pivotal role in
cholestatic liver fibrosis in mice. J Surg Res. 183:574–582. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
99
|
Mochida S, Ishikawa K, Toshima K, Inao M,
Ikeda H, Matsui A, Shibuya M and Fujiwara K: The mechanisms of
hepatic sinusoidal endothelial cell regeneration: A possible
communication system associated with vascular endothelial growth
factor in liver cells. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 13 (Suppl 1):S1–S5.
1998. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
100
|
Zhang CY, Yuan WG, He P, Lei JH and Wang
CX: Liver fibrosis and hepatic stellate cells: Etiology,
pathological hallmarks and therapeutic targets. World J
Gastroenterol. 22:10512–10522. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
101
|
Lee UE and Friedman SL: Mechanisms of
hepatic fibrogenesis. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol.
25:195–206. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
102
|
Melgar-Lesmes P and Edelman ER:
Monocyte-endothelial cell interactions in the regulation of
vascular sprouting and liver regeneration in mouse. J Hepatol.
63:917–925. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
103
|
Hoefer IE, van Royen N, Rectenwald JE,
Deindl E, Hua J, Jost M, Grundmann S, Voskuil M, Ozaki CK, Piek JJ
and Buschmann IR: Arteriogenesis proceeds via ICAM-1/Mac-1-mediated
mechanisms. Circ Res. 94:1179–1185. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
104
|
Schubert SY, Benarroch A, Monter-Solans J
and Edelman ER: Primary monocytes regulate endothelial cell
survival through secretion of angiopoietin-1 and activation of
endothelial Tie2. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 31:870–875. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
105
|
Priya MK, Sahu G, Soto-Pantoja DR, Goldy
N, Sundaresan AM, Jadhav V, Barathkumar TR, Saran U, Jaffar AB,
Roberts DD, et al: Tipping off endothelial tubes: Nitric oxide
drives tip cells. Angiogenesis. 18:175–189. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
106
|
De Smet F, Segura I, De Bock K,
Hohensinner PJ and Carmeliet P: Mechanisms of vessel branching:
Filopodia on endothelial tip cells lead the way. Arterioscler
Thromb Vasc Biol. 29:639–649. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
107
|
Gao B and Radaeva S: Natural killer and
natural killer T cells in liver fibrosis. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1832:1061–1069. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
108
|
Connolly MK, Bedrosian AS, Mallen-St CJ,
Mitchell AP, Ibrahim J, Stroud A, Pachter HL, Bar-Sagi D, Frey AB
and Miller G: In liver fibrosis, dendritic cells govern hepatic
inflammation in mice via TNF-alpha. J Clin Invest. 119:3213–3225.
2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
109
|
Ehrlich L, Scrushy M, Meng F, Lairmore TC,
Alpini G and Glaser S: Biliary epithelium: A neuroendocrine
compartment in cholestatic liver disease. Clin Res Hepatol
Gastroenterol. 42:296–305. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
110
|
Gao B, Radaeva S and Park O: Liver natural
killer and natural killer T cells: Immunobiology and emerging roles
in liver diseases. J Leukoc Biol. 86:513–528. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
111
|
Wang H and Yin S: Natural killer T cells
in liver injury, inflammation and cancer. Expert Rev Gastroenterol
Hepatol. 9:1077–1085. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
112
|
Radaeva S, Sun R, Jaruga B, Nguyen VT,
Tian Z and Gao B: Natural killer cells ameliorate liver fibrosis by
killing activated stellate cells in NKG2D-dependent and tumor
necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand-dependent
manners. Gastroenterology. 130:435–452. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
113
|
Peng Y, Yang T, Huang K, Shen L, Tao Y and
Liu C: Salvia miltiorrhiza ameliorates liver fibrosis by activating
hepatic natural killer cells in vivo and in vitro. Front Pharmacol.
9:7622018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
114
|
Cheng JT, Deng YN, Yi HM, Wang GY, Fu BS,
Chen WJ, Liu W, Tai Y, Peng YW and Zhang Q: Hepatic
carcinoma-associated fibroblasts induce IDO-producing regulatory
dendritic cells through IL-6-mediated STAT3 activation.
Oncogenesis. 5:e1982016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
115
|
Jiao J, Sastre D, Fiel MI, Lee UE,
Ghiassi-Nejad Z, Ginhoux F, Vivier E, Friedman SL, Merad M and
Aloman C: Dendritic cell regulation of carbon tetrachloride-induced
murine liver fibrosis regression. Hepatology. 55:244–255. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
116
|
Sato K, Meng F, Giang T, Glaser S and
Alpini G: Mechanisms of cholangiocyte responses to injury. Biochim
Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 1864:1262–1269. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
117
|
Omenetti A, Syn WK, Jung Y, Francis H,
Porrello A, Witek RP, Choi SS, Yang L, Mayo MJ, Gershwin ME, et al:
Repair-related activation of hedgehog signaling promotes
cholangiocyte chemokine production. Hepatology. 50:518–527. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
118
|
Parola M and Pinzani M: Liver fibrosis:
Pathophysiology, pathogenetic targets and clinical issues. Mol
Aspects Med. 65:37–55. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
119
|
Sohrabpour AA, Mohamadnejad M and
Malekzadeh R: Review article: The reversibility of cirrhosis.
Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 36:824–832. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
120
|
Poilil SS, George TR, Moon MJ and Jeong
YY: Nanoparticles for the treatment of liver fibrosis. Int J
Nanomedicine. 12:6997–7006. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
121
|
Feng R, Yuan X, Shao C, Ding H, Liebe R
and Weng HL: Are we any closer to treating liver fibrosis (and if
no, why not)? J Dig Dis. 19:118–126. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
122
|
Gracia-Sancho J, Marrone G and
Fernandez-Iglesias A: Hepatic microcirculation and mechanisms of
portal hypertension. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 16:221–234.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|