|
1
|
Roth GA, Johnson C, Abajobir A, Abd-Allah
F, Abera SF, Abyu G, Ahmed M, Aksut B, Alam T, Alam K, et al:
Global, regional, and national burden of cardiovascular diseases
for 10 causes, 1990 to 2015. J Am Coll Cardiol. 70:1–25. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Wolf MP and Hunziker P: Atherosclerosis:
Insights into vascular pathobiology and outlook to novel
treatments. J Cardiovasc Transl Res. 13:744–757. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Tabas I, Garcia-Cardeña G and Owens GK:
Recent insights into the cellular biology of atherosclerosis. J
Cell Biol. 209:13–22. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Libby P, Buring JE, Badimon L, Hansson GK,
Deanfield J, Bittencourt MS, Tokgözoğlu L and Lewis EF:
Atherosclerosis. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 5:562019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Meng G, Liu Y, Lou C and Yang H: Emodin
suppresses lipopolysaccharide-induced pro-inflammatory responses
and NF-κB activation by disrupting lipid rafts in CD14-negative
endothelial cells. Br J Pharmacol. 161:1628–1644. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Zeng XK, Guan YF, Remick DG and Wang X:
Signal pathways underlying homocysteine-induced production of MCP-1
and IL-8 in cultured human whole blood. Acta Pharmacol Sin.
26:85–91. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Moroni F, Ammirati E, Norata GD, Magnoni M
and Camici PG: The role of monocytes and macrophages in human
atherosclerosis, plaque neoangiogenesis, and atherothrombosis.
Mediators Inflamm. 2019:74343762019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
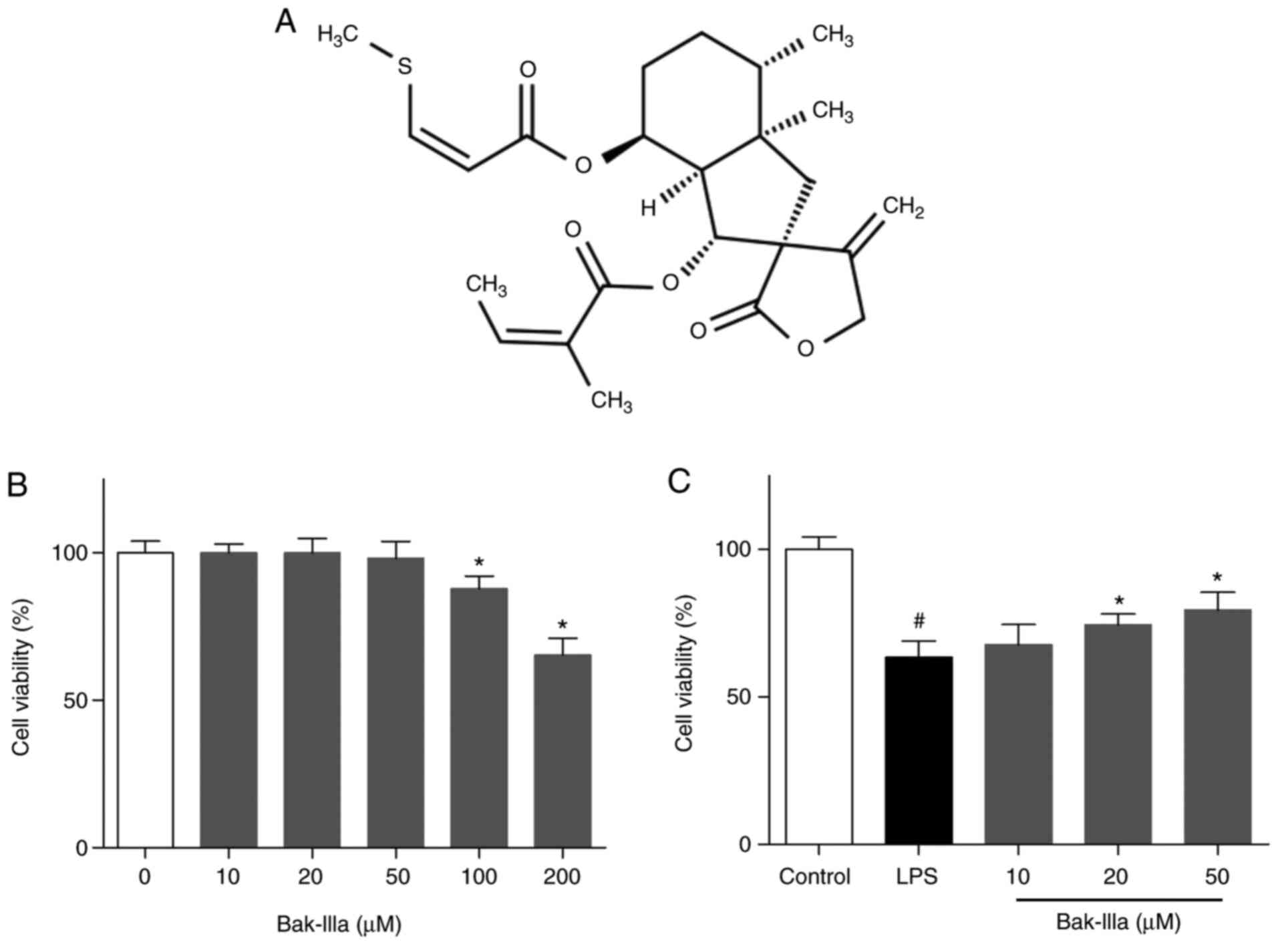
Pei L, Dai D, Bao Y, Chen F, Zheng J, Li
J, Liu S and Chen X: Determination of bakkenolide A in rat plasma
using liquid chromatography/tandem mass spectrometry and its
application to a pharmacokinetic study. J Mass Spectrom.
47:962–968. 2012. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Wang YL, Li RP, Guo ML, Zhang G, Zhang N
and Ma YL: Bakkenolides from Petasites tricholobus and their
neuroprotective effects related to antioxidant activities. Planta
Med. 75:230–235. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Jiang Q, Li RP, Tang Y, Wang YQ, Liu C and
Guo ML: Bakkenolide-IIIa protects against cerebral damage via
inhibiting NF-κB activation. CNS Neurosci Ther. 21:943–952. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Skaper SD, Facci L, Zusso M and Giusti P:
An inflammation-centric view of neurological disease: Beyond the
neuron. Front Cell Neurosci. 12:722018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Aryal B and Suárez Y: Non-coding RNA
regulation of endothelial and macrophage functions during
atherosclerosis. Vascul Pharmacol. 114:64–75. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zhang HN, Xu QQ, Thakur A, Alfred MO,
Chakraborty M, Ghosh A and Yu XB: Endothelial dysfunction in
diabetes and hypertension: Role of microRNAs and long non-coding
RNAs. Life Sci. 213:258–268. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zhu X, Chen D, Liu Y, Yu J, Qiao L, Lin S,
Chen D, Zhong G, Lu X, Wang Y, et al: Long noncoding RNA HOXA-AS3
integrates NF-κB signaling to regulate endothelium inflammation.
Mol Cell Biol. 39:e00139–19. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Cao L, Zhang Z, Li Y, Zhao P and Chen Y:
LncRNA H19/miR-let-7 axis participates in the regulation of
ox-LDL-induced endothelial cell injury via targeting periostin. Int
Immunopharmacol. 72:496–503. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Zhu X, Liu Y, Yu J, Du J, Guo R, Feng Y,
Zhong G, Jiang Y and Lin J: LncRNA HOXA-AS2 represses endothelium
inflammation by regulating the activity of NF-κB signaling.
Atherosclerosis. 281:38–46. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Li S, Sun Y, Zhong L, Xiao Z, Yang M, Chen
M, Wang C, Xie X and Chen X: The suppression of ox-LDL-induced
inflammatory cytokine release and apoptosis of HCAECs by long
non-coding RNA-MALAT1 via regulating microRNA-155/SOCS1 pathway.
Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. 28:1175–1187. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Casper J, Zweig AS, Villarreal C, Tyner C,
Speir ML, Rosenbloom KR, Raney BJ, Lee CM, Lee BT, Karolchik D, et
al: The UCSC genome browser database: 2018 update. Nucleic Acids
Res. 46D:D762–D769. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Tafer H and Hofacker IL: RNAplex: A fast
tool for RNA-RNA interaction search. Bioinformatics. 24:2657–2663.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Song L, Kang C, Sun Y, Huang W, Liu W and
Qian Z: Crocetin inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory
response in human umbilical vein endothelial cells. Cell Physiol
Biochem. 40:443–452. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Yin X, Liang Z, Yun Y and Pei L:
Intravenous transplantation of BMP2-transduced endothelial
progenitor cells attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung
injury in rats. Cell Physiol Biochem. 35:2149–2158. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Uhlig S, Yang Y, Waade J, Wittenberg C,
Babendreyer A and Kuebler WM: Differential regulation of lung
endothelial permeability in vitro and in situ. Cell Physiol
Biochem. 34:1–19. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Kim JH, Jeong JH, Jeon ST, Kim H, Ock J,
Suk K, Kim SI, Song KS and Lee WH: Decursin inhibits induction of
inflammatory mediators by blocking nuclear factor-kappaB activation
in macrophages. Mol Pharmacol. 69:1783–1790. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Zhang M, Pan H, Xu Y, Wang X, Qiu Z and
Jiang L: Allicin decreases lipopolysaccharide-induced oxidative
stress and inflammation in human umbilical vein endothelial cells
through suppression of mitochondrial dysfunction and activation of
Nrf2. Cell Physiol Biochem. 41:2255–2267. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Hou X, Yang S and Yin J: Blocking the
REDD1/TXNIP axis ameliorates LPS-induced vascular endothelial cell
injury through repressing oxidative stress and apoptosis. Am J
Physiol Cell Physiol. 316:C104–C110. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Makó V, Czúcz J, Weiszhár Z, Herczenik E,
Matkó J, Prohászka Z and Cervenak L: Proinflammatory activation
pattern of human umbilical vein endothelial cells induced by IL-1β,
TNF-α, and LPS. Cytometry A. 77:962–970. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Mangoni AA, Zinellu A, Sotgia S, Carru C,
Piga M and Erre GL: Protective effects of methotrexate against
proatherosclerotic cytokines: A review of the evidence. Mediators
Inflamm. 2017:96328462017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Khan R, Rheaume E and Tardif JC: Examining
the role of and treatment directed at IL-1β in atherosclerosis.
Curr Atheroscler Rep. 20:532018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Kopp F and Mendell JT: Functional
classification and experimental dissection of long noncoding RNAs.
Cell. 172:393–407. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Marques RE, Guabiraba R, Russo RC and
Teixeira MM: Targeting CCL5 in inflammation. Expert Opin Ther
Targets. 17:1439–1460. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Nosalski R and Guzik TJ: Perivascular
adipose tissue inflammation in vascular disease. Br J Pharmacol.
174:3496–3513. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Gao Y, Zhang J, Li G, Xu H, Yi Y, Wu Q,
Song M, Bee YM, Huang L, Tan M, et al: Protection of vascular
endothelial cells from high glucose-induced cytotoxicity by emodin.
Biochem Pharmacol. 94:39–45. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Sachdev U and Lotze MT: Perpetual change:
Autophagy, the endothelium, and response to vascular injury. J
Leukoc Biol. 102:221–235. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Cai W, Duan XM, Liu Y, Yu J, Tang YL, Liu
ZL, Jiang S, Zhang CP, Liu JY and Xu JX: Uric acid induces
endothelial dysfunction by activating the HMGB1/RAGE signaling
pathway. Biomed Res Int. 2017:43919202017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Tang ST, Wang F, Shao M, Wang Y and Zhu
HQ: MicroRNA-126 suppresses inflammation in endothelial cells under
hyperglycemic condition by targeting HMGB1. Vascul Pharmacol.
88:48–55. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Kim WH, Lee JW, Suh YH, Lee HJ, Lee SH, Oh
YK, Gao B and Jung MH: AICAR potentiates ROS production induced by
chronic high glucose: Roles of AMPK in pancreatic beta-cell
apoptosis. Cell Signal. 19:791–805. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Bijland S, Mancini SJ and Salt IP: Role of
AMP-activated protein kinase in adipose tissue metabolism and
inflammation. Clin Sci (Lond). 124:491–507. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Ewart MA and Kennedy S: AMPK and
vasculoprotection. Pharmacol Ther. 131:242–253. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Hu R, Wang MQ, Ni SH, Wang M, Liu LY, You
HY, Wu XH, Wang YJ, Lu L and Wei LB: Salidroside ameliorates
endothelial inflammation and oxidative stress by regulating the
AMPK/NF-κB/NLRP3 signaling pathway in AGEs-induced HUVECs. Eur J
Pharmacol. 867:1727972020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Dennhardt S, Finke KR, Huwiler A and
Coldewey SM: Sphingosine-1-phosphate promotes barrier-stabilizing
effects in human microvascular endothelial cells via AMPK-dependent
mechanisms. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 1865:774–781. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Gupta SC, Awasthee N, Rai V, Chava S,
Gunda V and Challagundla KB: Long non-coding RNAs and nuclear
factor-κB crosstalk in cancer and other human diseases. Biochim
Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. 1873:1883162020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Castellanos-Rubio A, Kratchmarov R,
Sebastian M, Garcia-Etxebarria K, Garcia L, Irastorza I and Ghosh
S: Cytoplasmic form of carlr lncRNA facilitates inflammatory gene
expression upon NF-κB activation. J Immunol. 199:581–588. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Özeş AR, Miller DF, Özeş ON, Fang F, Liu
Y, Matei D, Huang T and Nephew KP: NF-κB-HOTAIR axis links DNA
damage response, chemoresistance and cellular senescence in ovarian
cancer. Oncogene. 35:5350–5361. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Chen S, Thorne RF, Zhang XD, Wu M and Liu
L: Non-coding RNAs, guardians of the p53 galaxy. Semin Cancer Biol.
Sep 11–2020.(Epub ahead of print). doi:
10.1016/j.semcancer.2020.09.002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Sun CC, Zhu W, Li SJ, Hu W, Zhang J, Zhuo
Y, Zhang H, Wang J, Zhang Y, Huang SX, et al: FOXC1-mediated
LINC00301 facilitates tumor progression and triggers an
immune-suppressing microenvironment in non-small cell lung cancer
by regulating the HIF1α pathway. Genome Med. 12:772020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Jung TW, Park HS, Choi GH, Kim D, Ahn SH,
Kim DS, Lee T and Jeong JH: Maresin 1 attenuates pro-inflammatory
reactions and ER stress in HUVECs via PPARα-mediated pathway. Mol
Cell Biochem. 448:335–347. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|