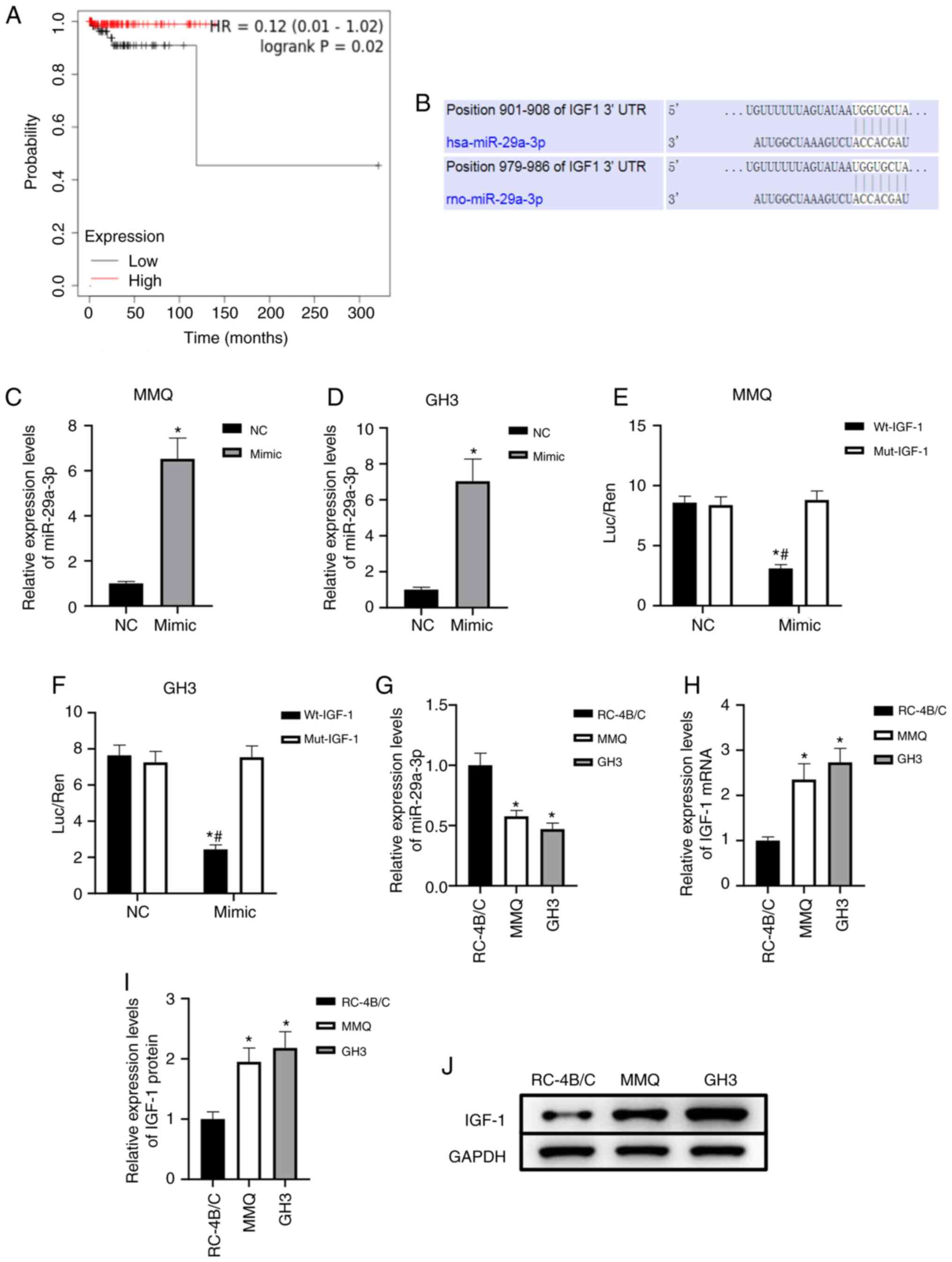
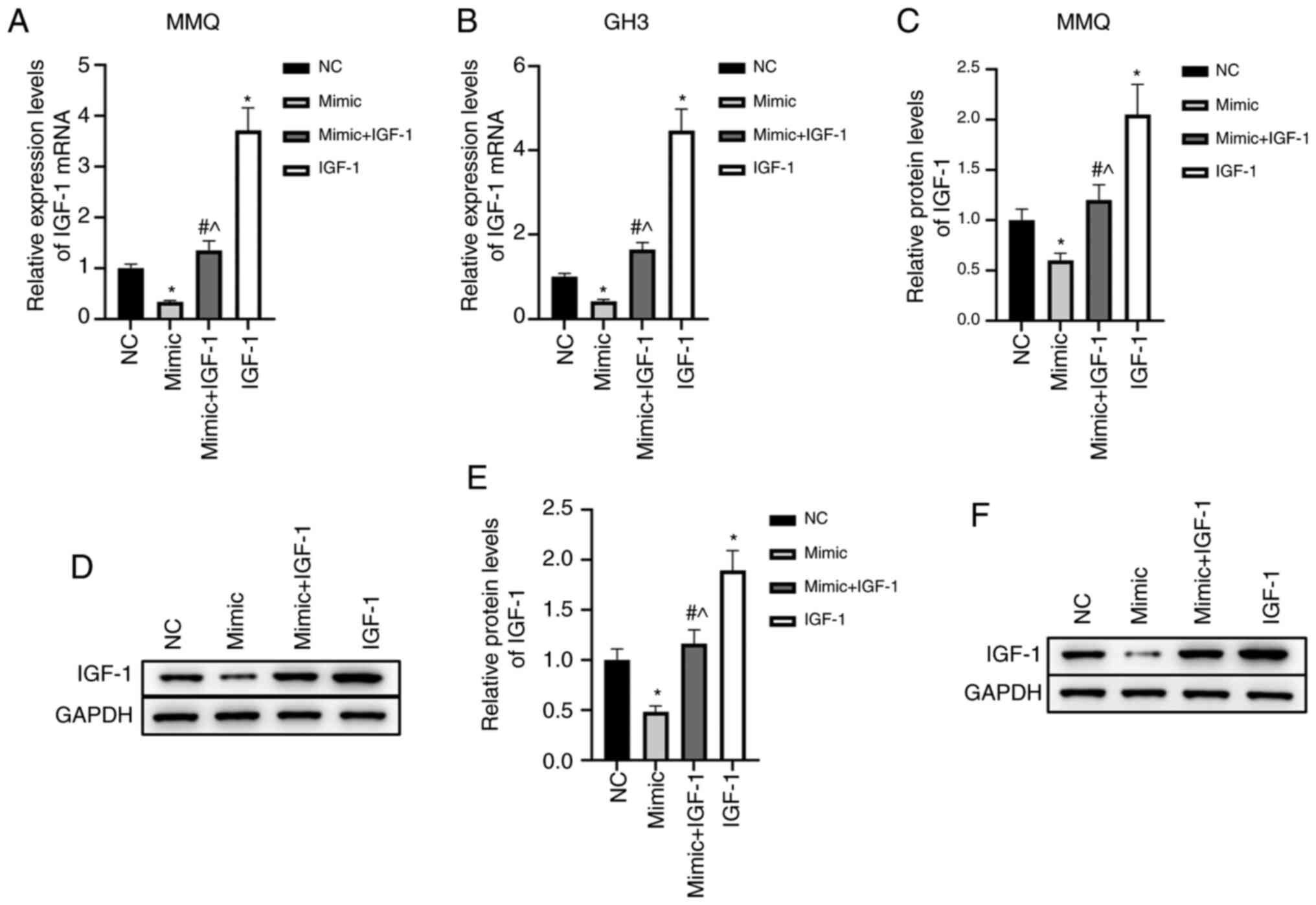
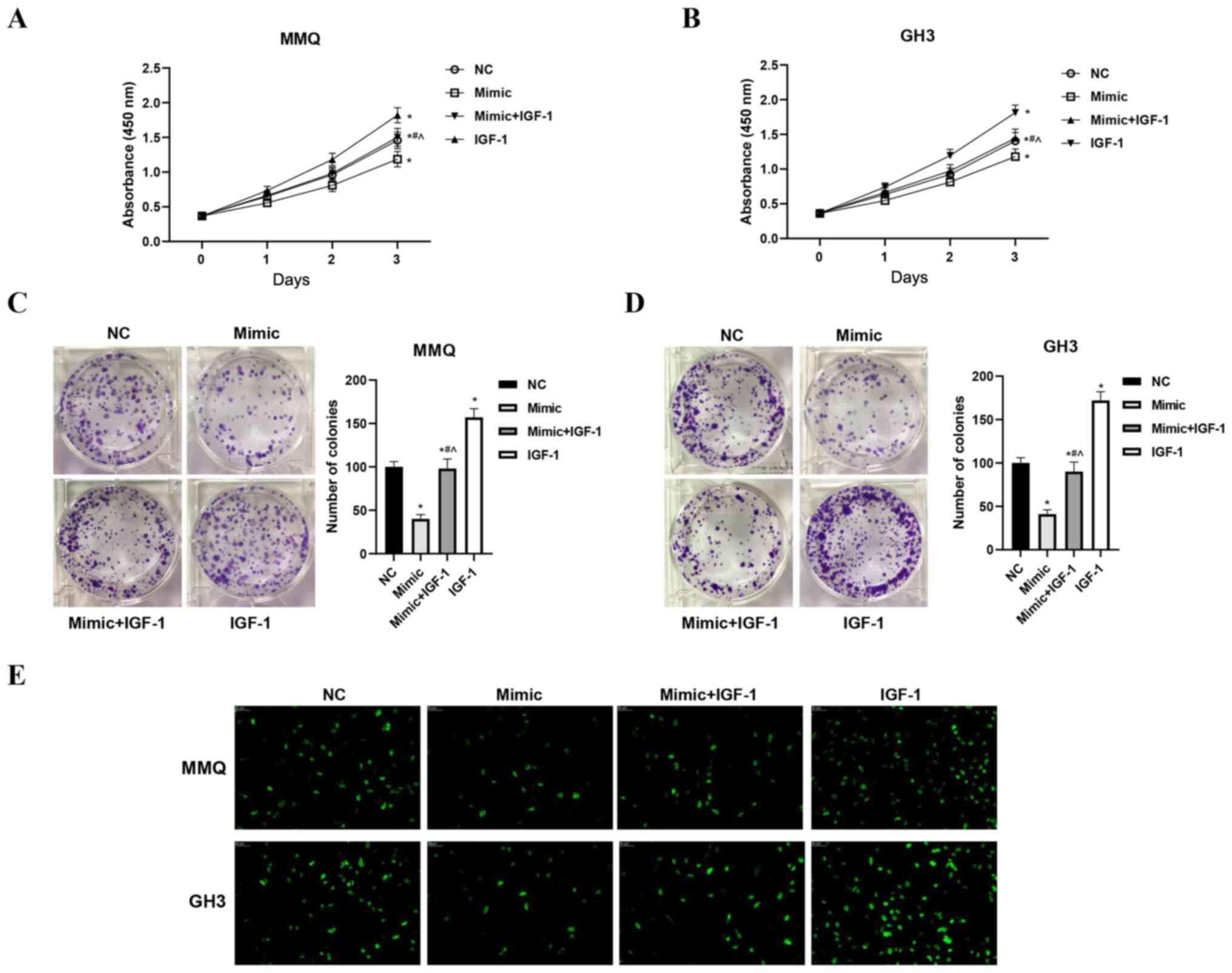
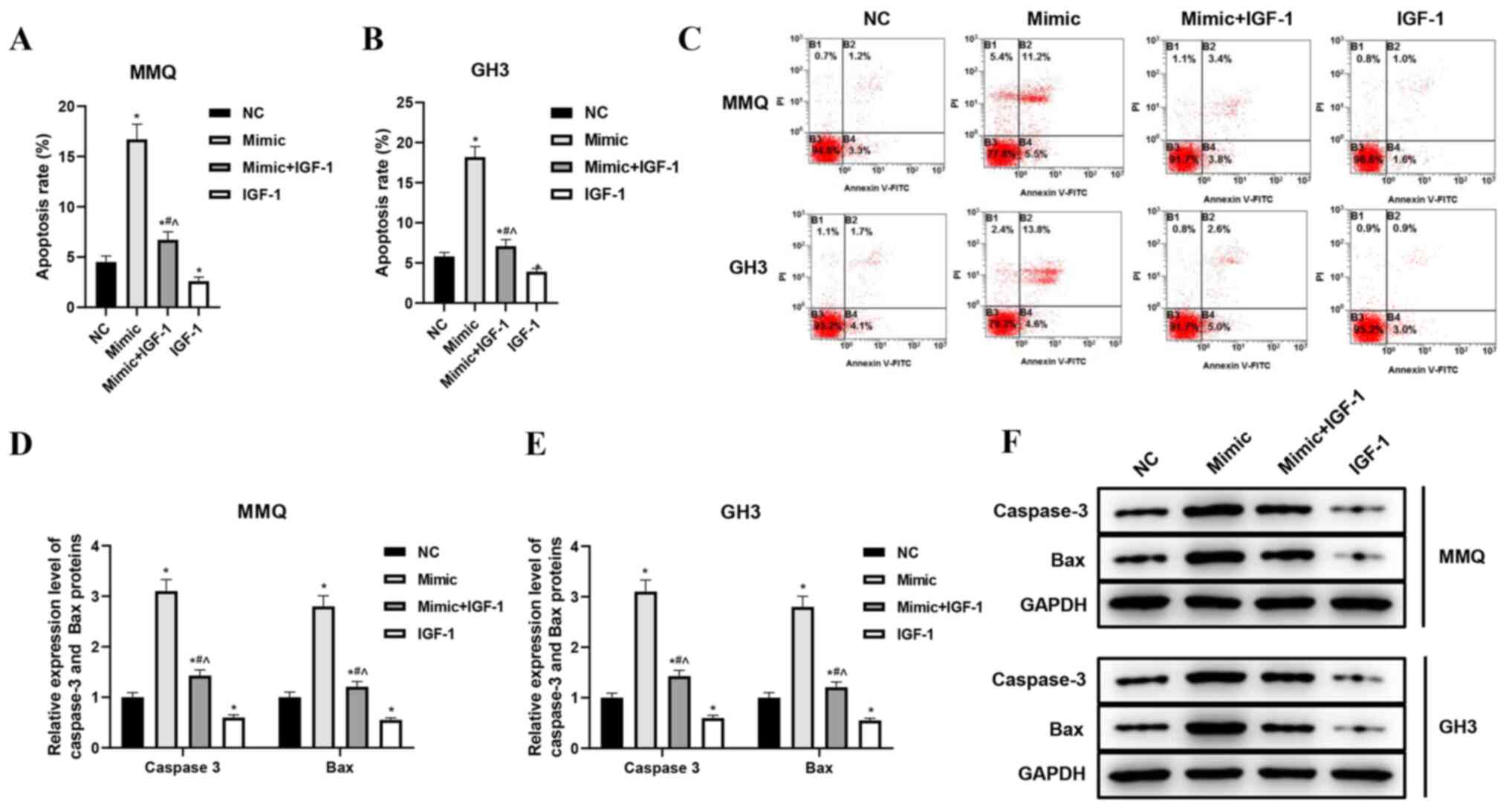
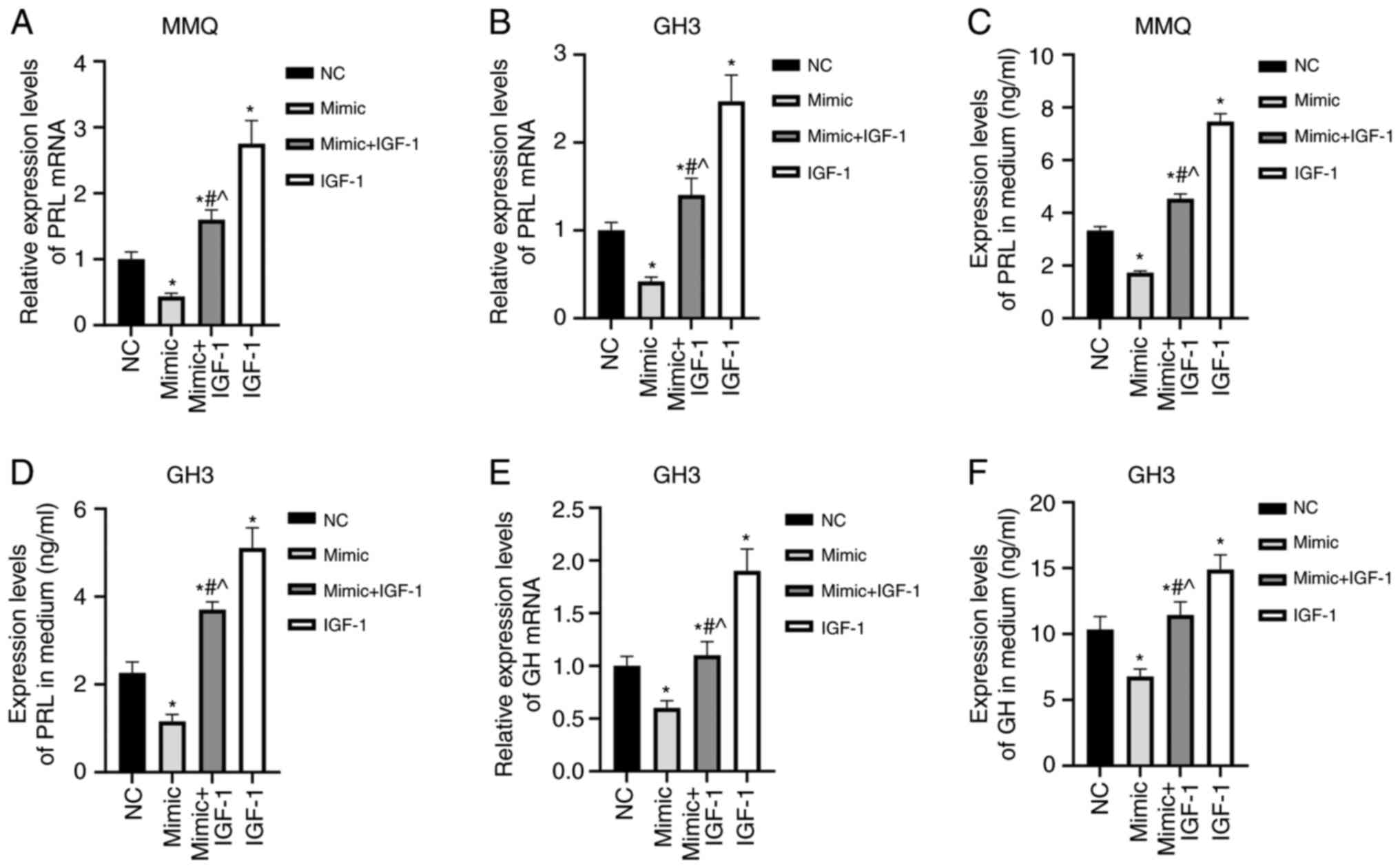
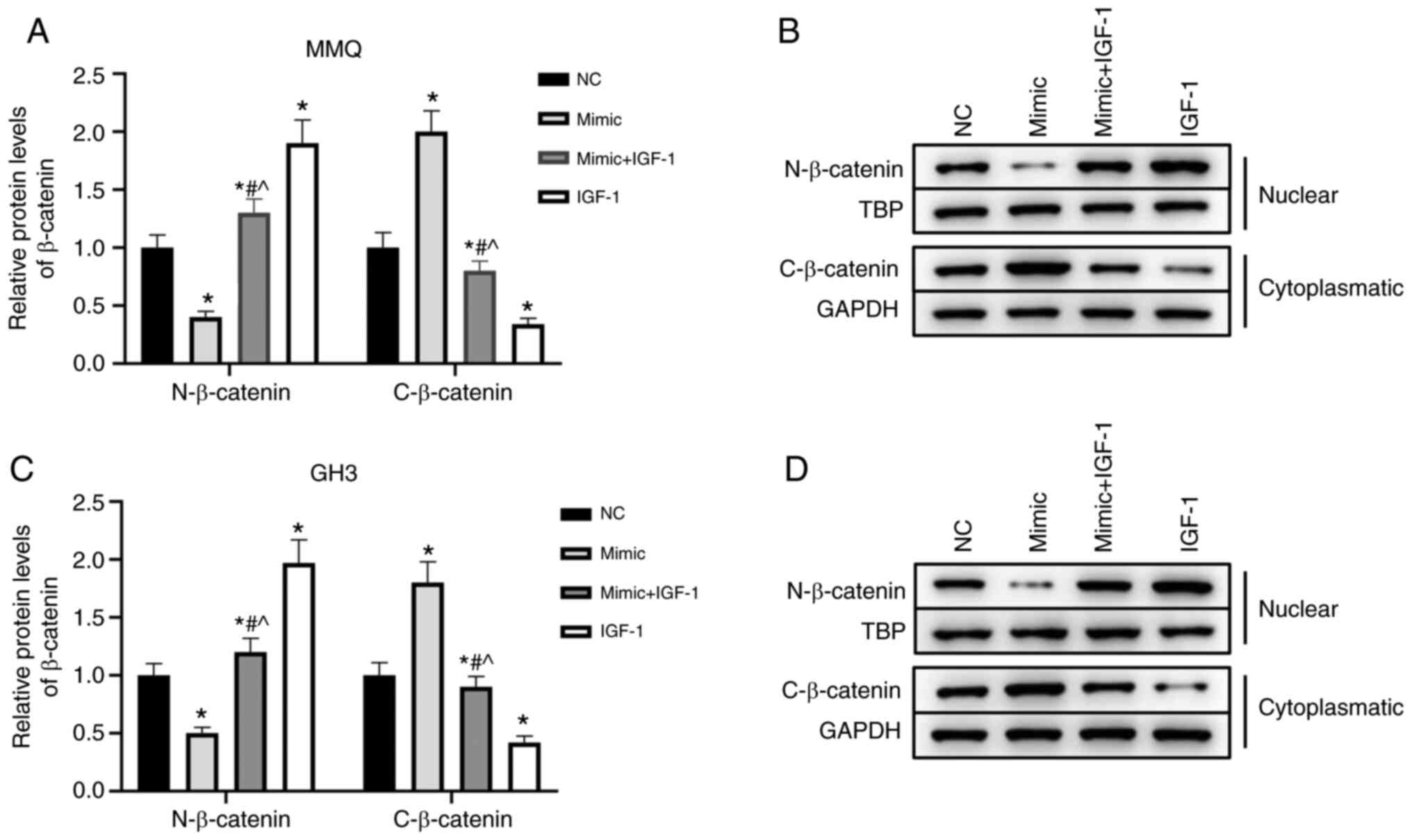
|
1
|
Glezer A and Bronstein MD: Prolactinomas.
Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am. 44:71–78. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Vroonen L, Daly AF and Beckers A:
Epidemiology and management challenges in prolactinomas.
Neuroendocrinology. 109:20–27. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Blanco AM: Hypothalamic- and
pituitary-derived growth and reproductive hormones and the control
of energy balance in fish. Gen Comp Endocrinol. 287:1133222020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Silveira MA, Zampieri TT, Furigo IC,
Abdulkader F, Donato J Jr and Frazão R: Acute effects of
somatomammotropin hormones on neuronal components of the
hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal axis. Brain Res. 1714:210–217. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Kubo T, Furujo M, Mori S, Imai K, Ueda Y,
Tsukahara K, Morita H, Ogura K, Fukuhara S, Shimizu J, et al: An
infant case of macroprolactinemia with transient idiopathic central
precocious puberty. Endocr J. 54:825–828. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Tirosh A and Shimon I: Current approach to
treatments for prolactinomas. Minerva Endocrinol. 41:316–323.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Faltermeier CM, Magill ST, Blevins LS Jr
and Aghi MK: Molecular biology of pituitary adenomas. Neurosurg
Clin N Am. 30:391–400. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Donoho DA and Laws ER Jr: The role of
surgery in the management of prolactinomas. Neurosurg Clin N Am.
30:509–514. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Chen T, Zheng F, Tao J, Tan S, Zeng L,
Peng X and Wu B: Insulin-like growth factor-1 contributes to
mucosal repair by β-arrestin2-mediated extracellular signal-related
kinase signaling in experimental colitis. Am J Pathol.
185:2441–2453. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Yoneyama Y, Lanzerstorfer P, Niwa H,
Umehara T, Shibano T, Yokoyama S, Chida K, Weghuber J, Hakuno F and
Takahashi SI: IRS-1 acts as an endocytic regulator of IGF-I
receptor to facilitate sustained IGF signaling. Elife.
7:e328932018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Lyons A, Coleman M, Riis S, Favre C,
O'Flanagan CH, Zhdanov AV, Papkovsky DB, Hursting SD and O'Connor
R: Insulin-like growth factor 1 signaling is essential for
mitochondrial biogenesis and mitophagy in cancer cells. J Biol
Chem. 292:16983–16998. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Chen KC, Chen PH, Ho KH, Shih CM, Chou CM,
Cheng CH and Lee CC: IGF-1-enhanced miR-513a-5p signaling
desensitizes glioma cells to temozolomide by targeting the
NEDD4L-inhibited Wnt/β-catenin pathway. PLoS One. 14:e02259132019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Cónsole GM, Hereñú CB, Camihort GA, Luna
GC, Ferese C and Goya RG: Effect of insulin-like growth factor-I
gene therapy on the somatotropic axis in experimental
prolactinomas. Cells Tissues Organs. 190:20–26. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Castillo AI and Aranda A: Differential
regulation of pituitary-specific gene expression by insulin-like
growth factor 1 in rat pituitary GH4C1 and GH3 cells.
Endocrinology. 138:5442–5451. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Simonson B and Das S: MicroRNA
therapeutics: The next magic bullet? Mini Rev Med Chem. 15:467–474.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Hu B, Mao Z, Du Q, Jiang X, Wang Z, Xiao
Z, Zhu D, Wang X, Zhu Y and Wang H: miR-93-5p targets Smad7 to
regulate the transforming growth factor-β1/Smad3 pathway and
mediate fibrosis in drug-resistant prolactinoma. Brain Res Bull.
149:21–31. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Jian M, Du Q, Zhu D, Mao Z, Wang X, Feng
Y, Xiao Z, Wang H and Zhu Y: Tumor suppressor miR-145-5p sensitizes
prolactinoma to bromocriptine by downregulating TPT1. J Endocrinol
Invest. 42:639–652. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Xiao Z, Wang Z, Hu B, Mao Z, Zhu D, Feng Y
and Zhu Y: MiR-1299 promotes the synthesis and secretion of
prolactin by inhibiting FOXO1 expression in drug-resistant
prolactinomas. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 520:79–85. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zhao X, Hou Y, Tuo Z and Wei F:
Application values of miR-194 and miR-29 in the diagnosis and
prognosis of gastric cancer. Exp Ther Med. 15:4179–4184.
2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Xu W, Li Z, Zhu X, Xu R and Xu Y: miR-29
family inhibits resistance to methotrexate and promotes cell
apoptosis by targeting COL3A1 and MCL1 in osteosarcoma. Med Sci
Monit. 24:8812–8821. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Gao G, Liang X and Ma W: Sinomenine
restrains breast cancer cells proliferation, migration and invasion
via modulation of miR-29/PDCD-4 axis. Artif Cells Nanomed
Biotechnol. 47:3839–3846. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Habibi P, Alihemmatti A, Alipour M,
Nourazar A, Yousefi H, Andalib S and Ahmadiasl N: Effects of
exercise on miR-29 and IGF-1 expression and lipid profile in the
heart of ovariectomized rat. Acta Endocrinol (Buchar). 12:130–136.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Tang H, Zhu D, Zhang G, Luo X and Xie W:
AFAP1-AS1 promotes proliferation of pituitary adenoma cells through
miR-103a-3p to activate PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. World
Neurosurg. 130:e888–e898. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Molitch ME: Diagnosis and treatment of
pituitary adenomas: A review. JAMA. 317:516–524. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Lamberts SW, de Quijada M and Klijn JG:
The effect of tamoxifen on GH and PRL secretion by human pituitary
tumors. J Endocrinol Invest. 3:343–347. 1980. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Watanabe D, Yagasaki H, Kojika S, Ogiwara
M, Kinouchi H, Nakane T and Inukai T: GH/PRL-secreting pituitary
macroadenoma associated with GNAS p.Gln227Leu mutation: Pediatric
case report and review. Endocr J. 66:403–408. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Console GM, Herenu CB, Camihort GA, Luna
GC, Bracamonte MI, Morel GR and Goya RG: Insulin-like growth
factor-I gene therapy reverses morphologic changes and reduces
hyperprolactinemia in experimental rat prolactinomas. Mol Cancer.
7:132008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Gupta P, Rai A, Mukherjee KK, Sachdeva N,
Radotra BD, Punia RPS, Vashista RK, Hota D, Srinivasan A,
Dhandapani S, et al: Imatinib inhibits GH secretion from
somatotropinomas. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 9:4532018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Kempf J, Schmitz A, Meier A, Delfs N,
Mueller B, Fandino J, Schuetz P and Berkmann S: Adenoma size and
postoperative IGF-1 levels predict surgical outcomes in acromegaly
patients: Results of the Swiss pituitary registry (SwissPit). Swiss
Med Wkly. 148:w146532018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
O'Neill BT, Lee KY, Klaus K, Softic S,
Krumpoch MT, Fentz J, Stanford KI, Robinson MM, Cai W, Kleinridders
A, et al: Insulin and IGF-1 receptors regulate FoxO-mediated
signaling in muscle proteostasis. J Clin Invest. 126:3433–3446.
2016. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Cui X, Li M, He Z, Hu L, Liu J, Yan J and
Hua L: MiR-302b-5p enhances the neuroprotective effect of IGF-1 in
methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine-induced Parkinson's
disease by regulating inducible nitric-oxide synthase. Cell Biochem
Funct. 38:1025–1035. 2020. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Wang T, Liu Y, Lv M, Xing Q, Zhang Z, He
X, Xu Y, Wei Z and Cao Y: miR-323-3p regulates the steroidogenesis
and cell apoptosis in polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) by targeting
IGF-1. Gene. 683:87–100. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Zhou Y, Li S, Li J, Wang D and Li Q:
Effect of microRNA-135a on cell proliferation, migration, invasion,
apoptosis and tumor angiogenesis through the IGF-1/PI3K/Akt
signaling pathway in non-small cell lung cancer. Cell Physiol
Biochem. 42:1431–1446. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Liu Y, Hu Q, Ao J, Li H and Li M: Role of
miR-92a-3p/PTEN axis in regulation of pancreatic cancer cell
proliferation and metastasis. Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban.
45:280–289. 2020.(In English, Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Wang Y, Zhao R, Liu W, Wang Z, Rong J,
Long X, Liu Z, Ge J and Shi B: Exosomal circHIPK3 released from
hypoxia-pretreated cardiomyocytes regulates oxidative damage in
cardiac microvascular endothelial cells via the miR-29a/IGF-1
pathway. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2019:79546572019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Shastri AA, Saleh A, Savage JE, DeAngelis
T, Camphausen K and Simone NL: Dietary alterations modulate the
microRNA 29/30 and IGF-1/AKT signaling axis in breast cancer liver
metastasis. Nutr Metab (Lond). 17:232020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Li Z, Jiang R, Yue Q and Peng H:
MicroRNA-29 regulates myocardial microvascular endothelial cells
proliferation and migration in association with IGF1 in type 2
diabetes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 487:15–21. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Cao L, Gao H, Li P, Gui S and Zhang Y: The
Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway is involved in the antitumor effect
of fulvestrant on rat prolactinoma MMQ cells. Tumour Biol.
35:5121–5127. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Chauvet N, Romanò N, Meunier AC, Galibert
E, Fontanaud P, Mathieu MN, Osterstock G, Osterstock P, Baccino E,
Rigau V, et al: Combining cadherin expression with molecular
markers discriminates invasiveness in growth hormone and prolactin
pituitary adenomas. J Neuroendocrinol. 28:123522016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Wang C, Tan C, Wen Y, Zhang D, Li G, Chang
L, Su J and Wang X: FOXP1-induced lncRNA CLRN1-AS1 acts as a tumor
suppressor in pituitary prolactinoma by repressing the autophagy
via inactivating Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Cell Death Dis.
10:4992019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Lei C, Jing G, Jichao W, Xiaohui L, Fang
Q, Hua G, Yazhou M and Zhang Y: MiR-137′s tumor suppression on
prolactinomas by targeting MITF and modulating Wnt signaling
pathway. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 104:6391–6402. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|