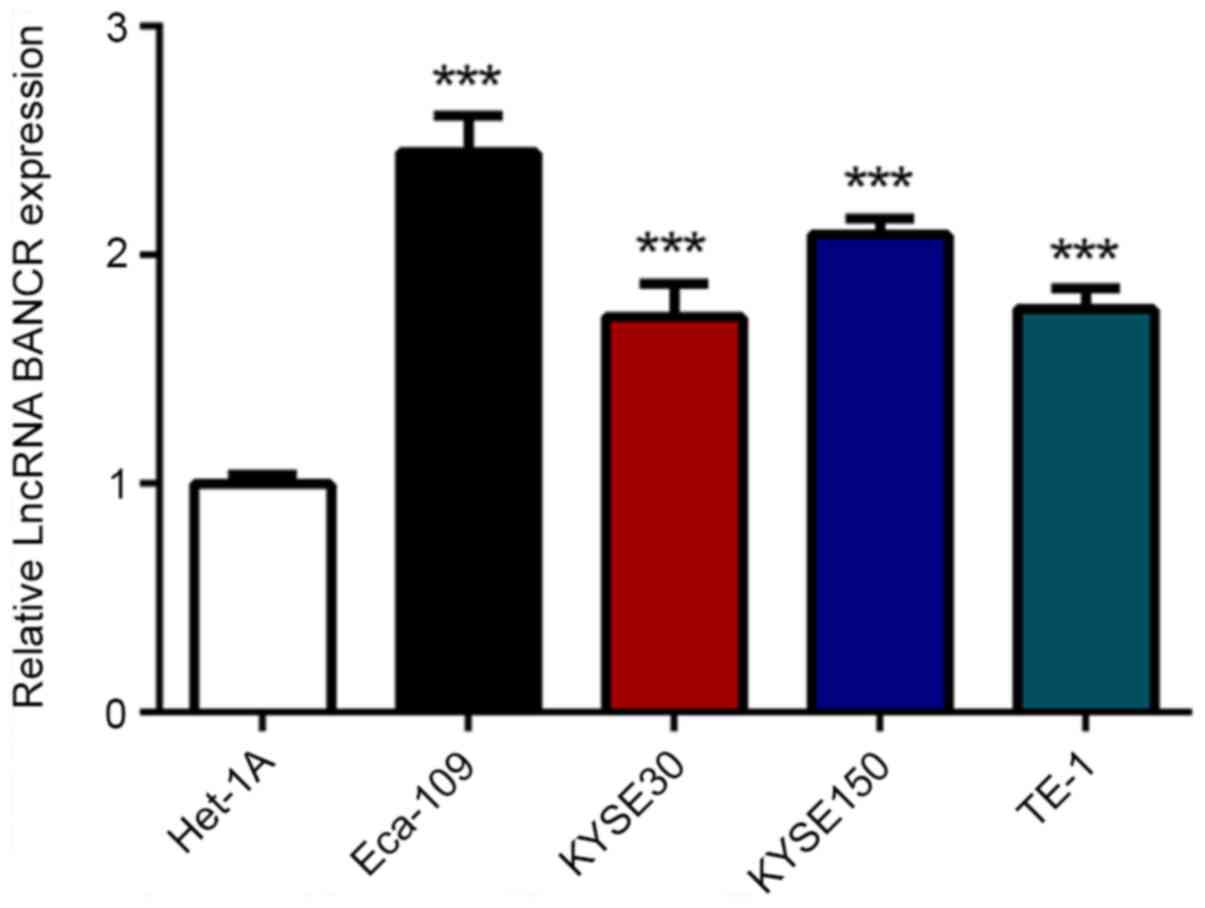
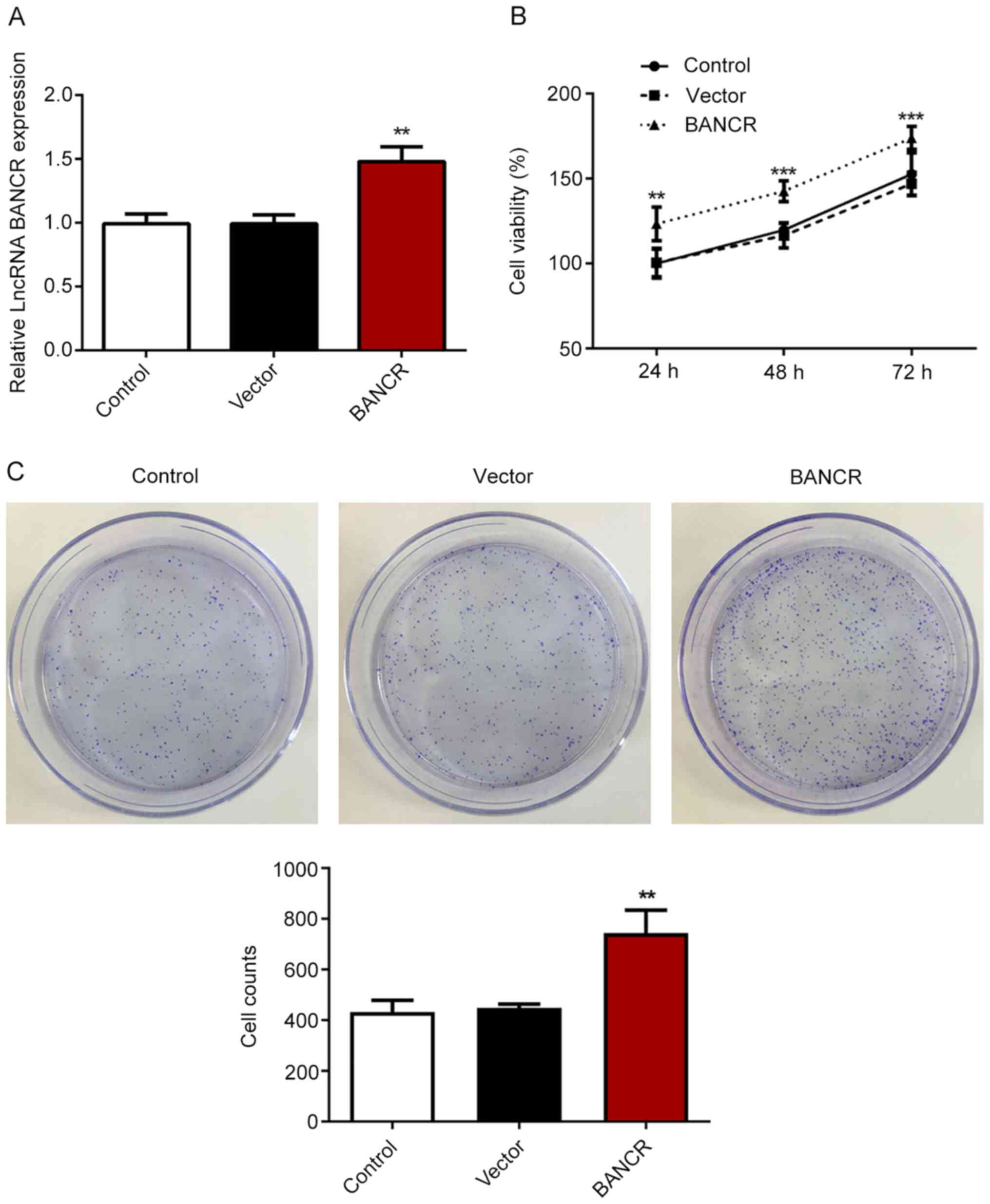
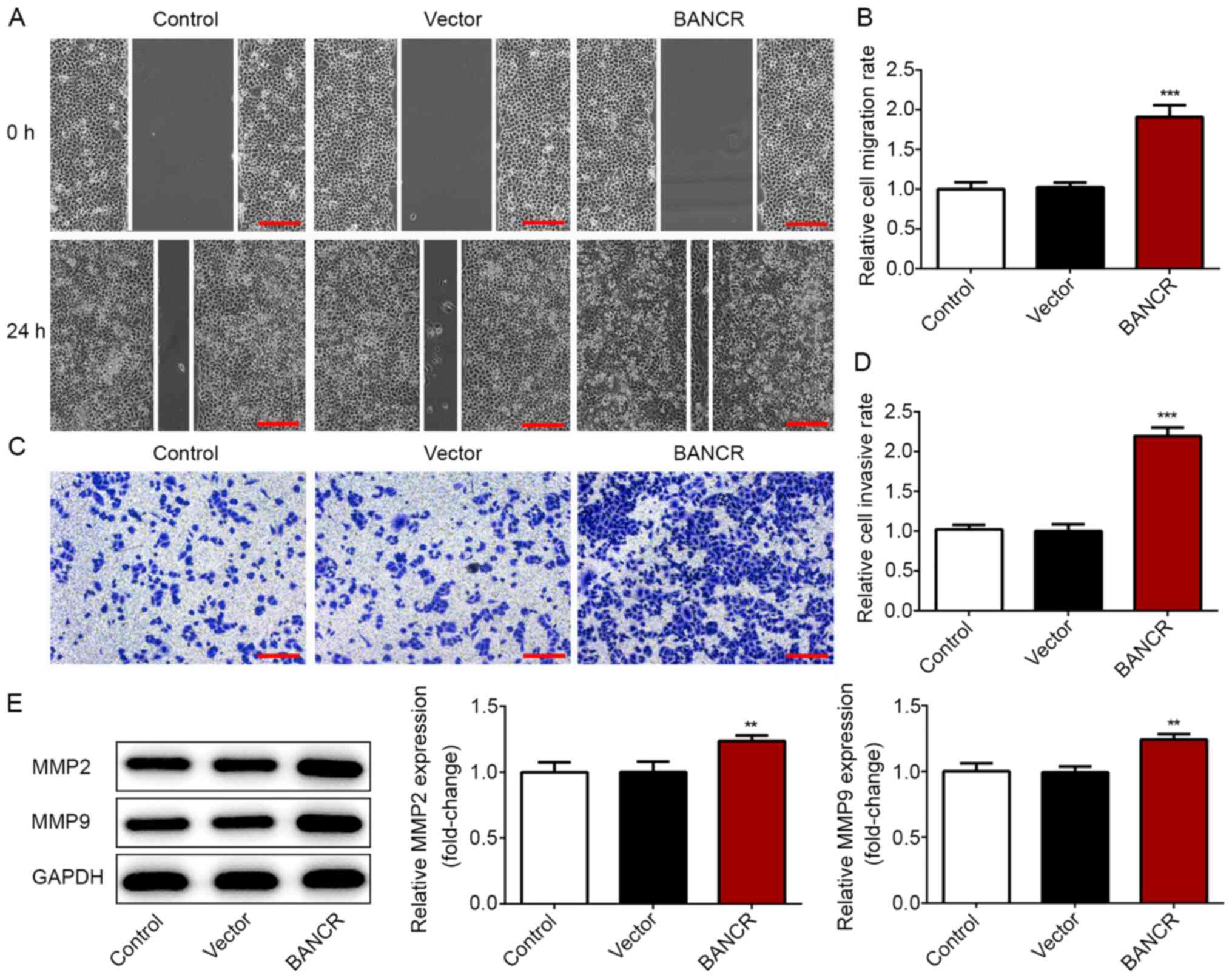
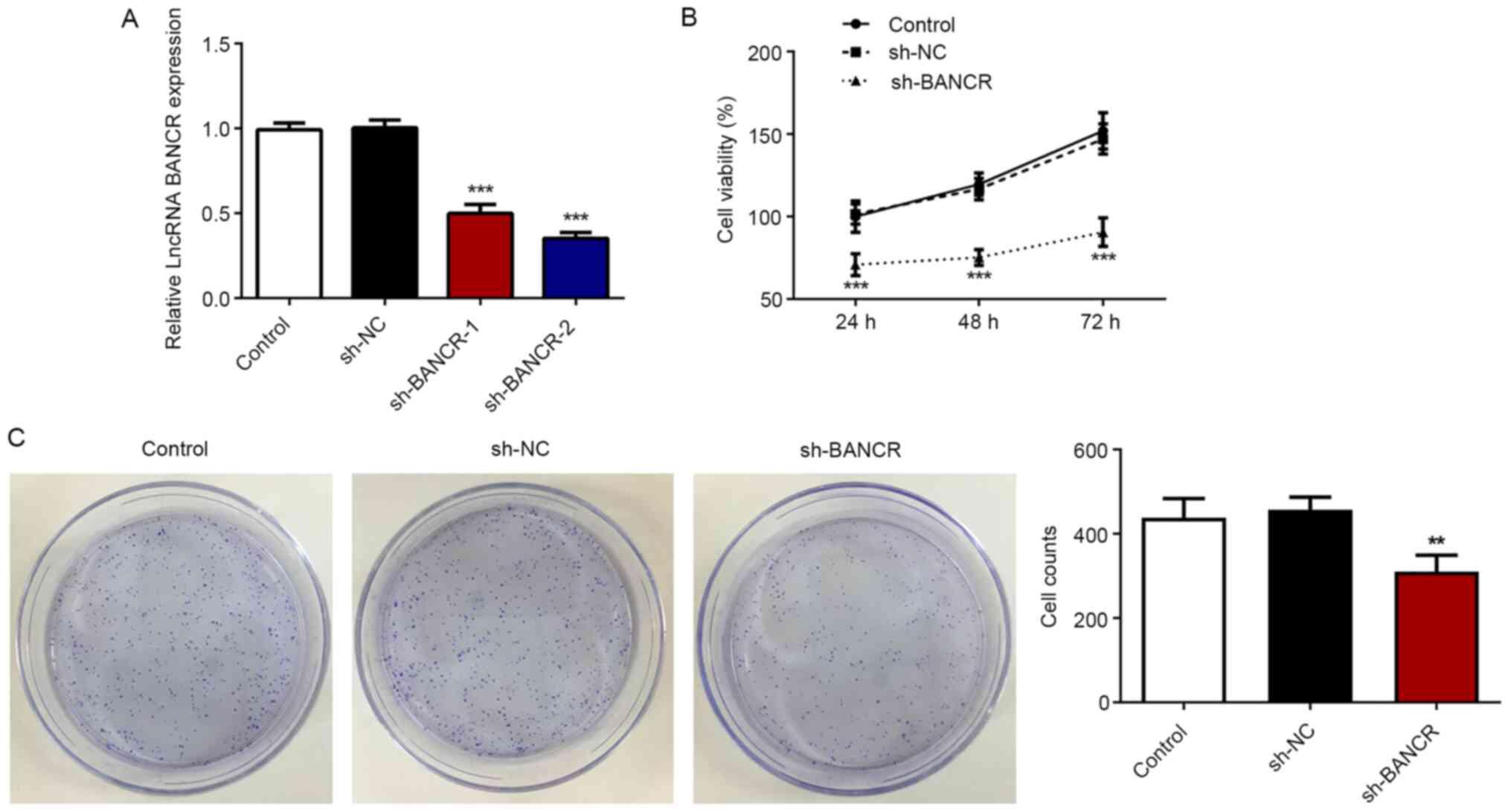
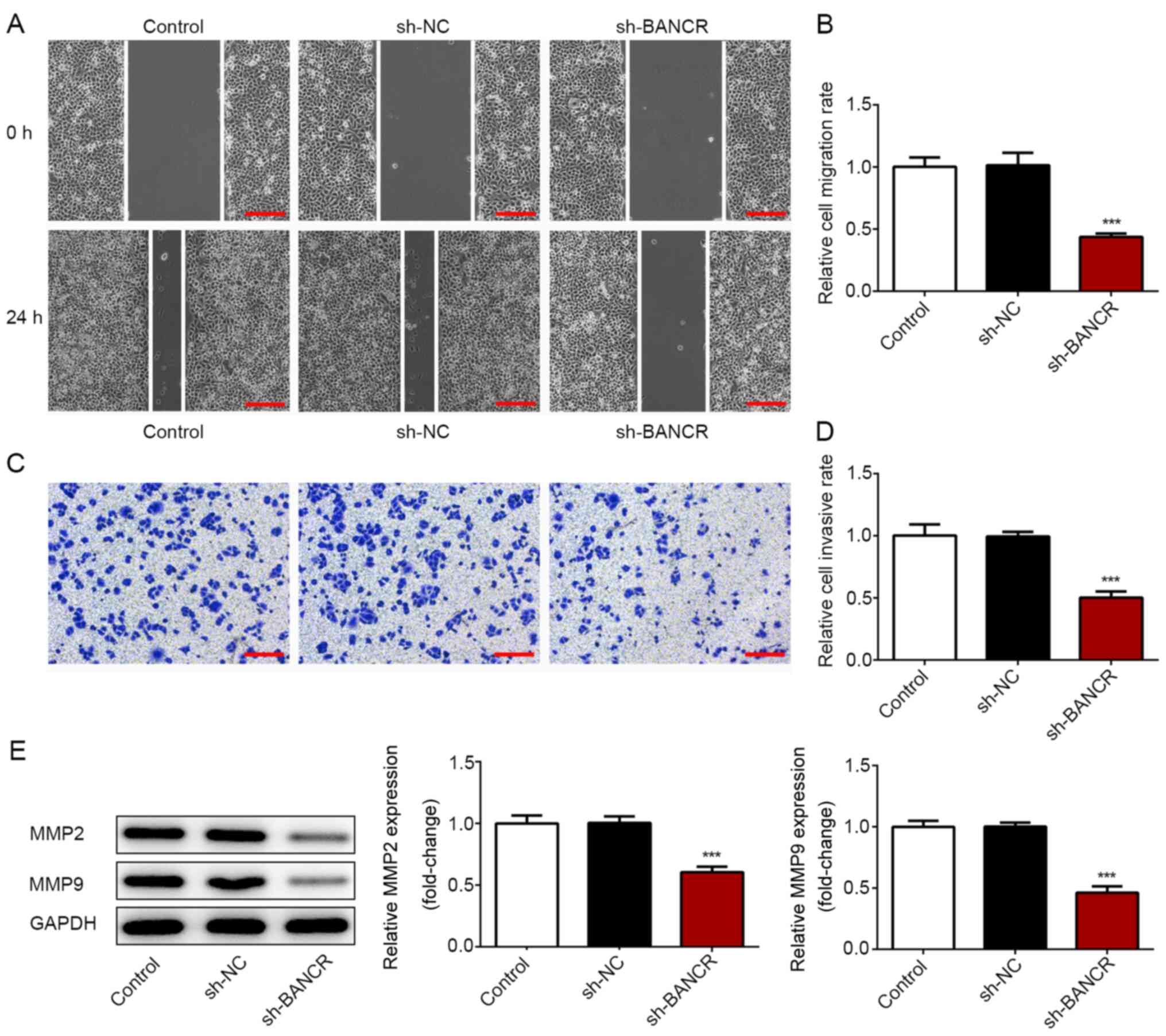
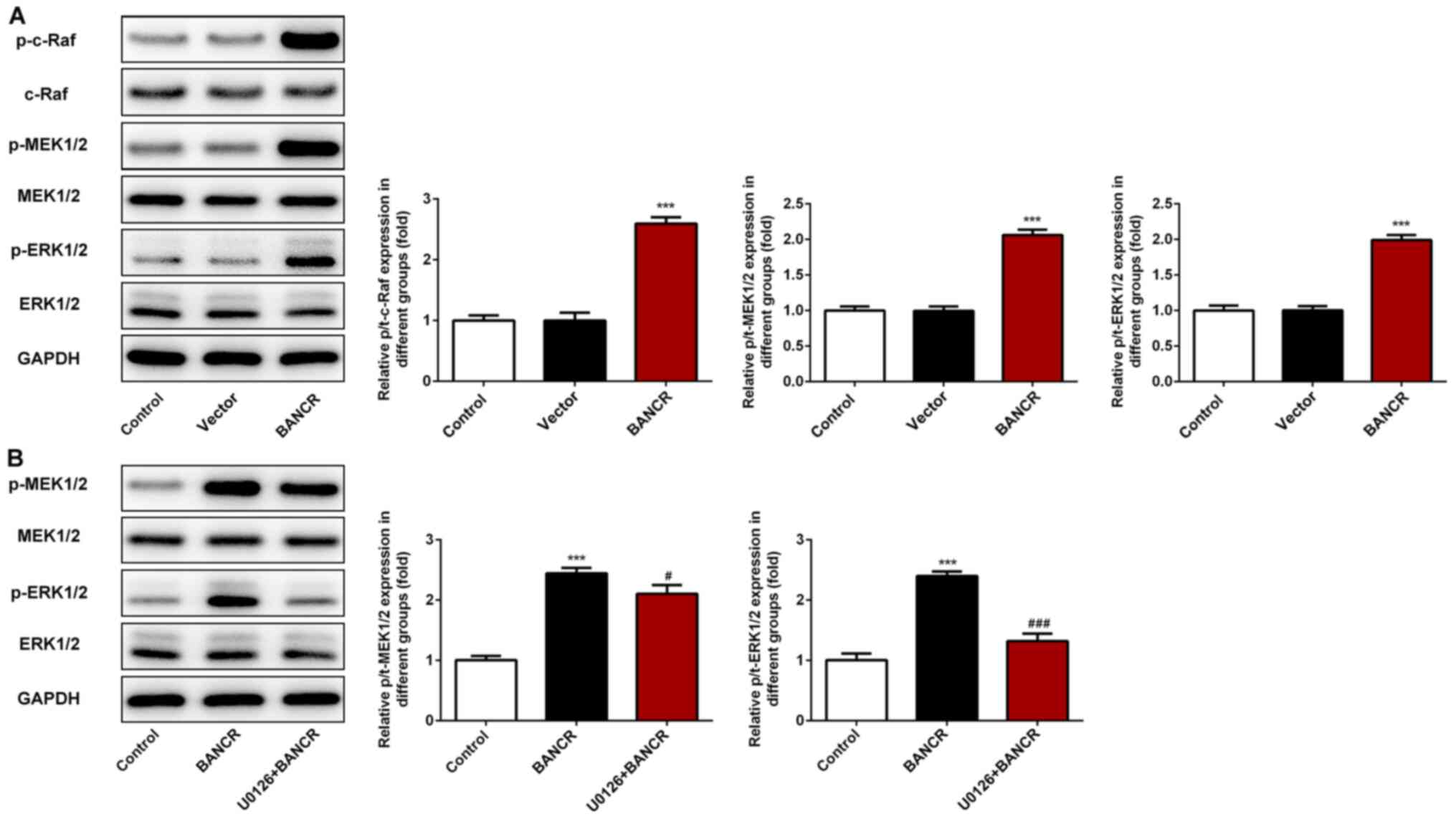
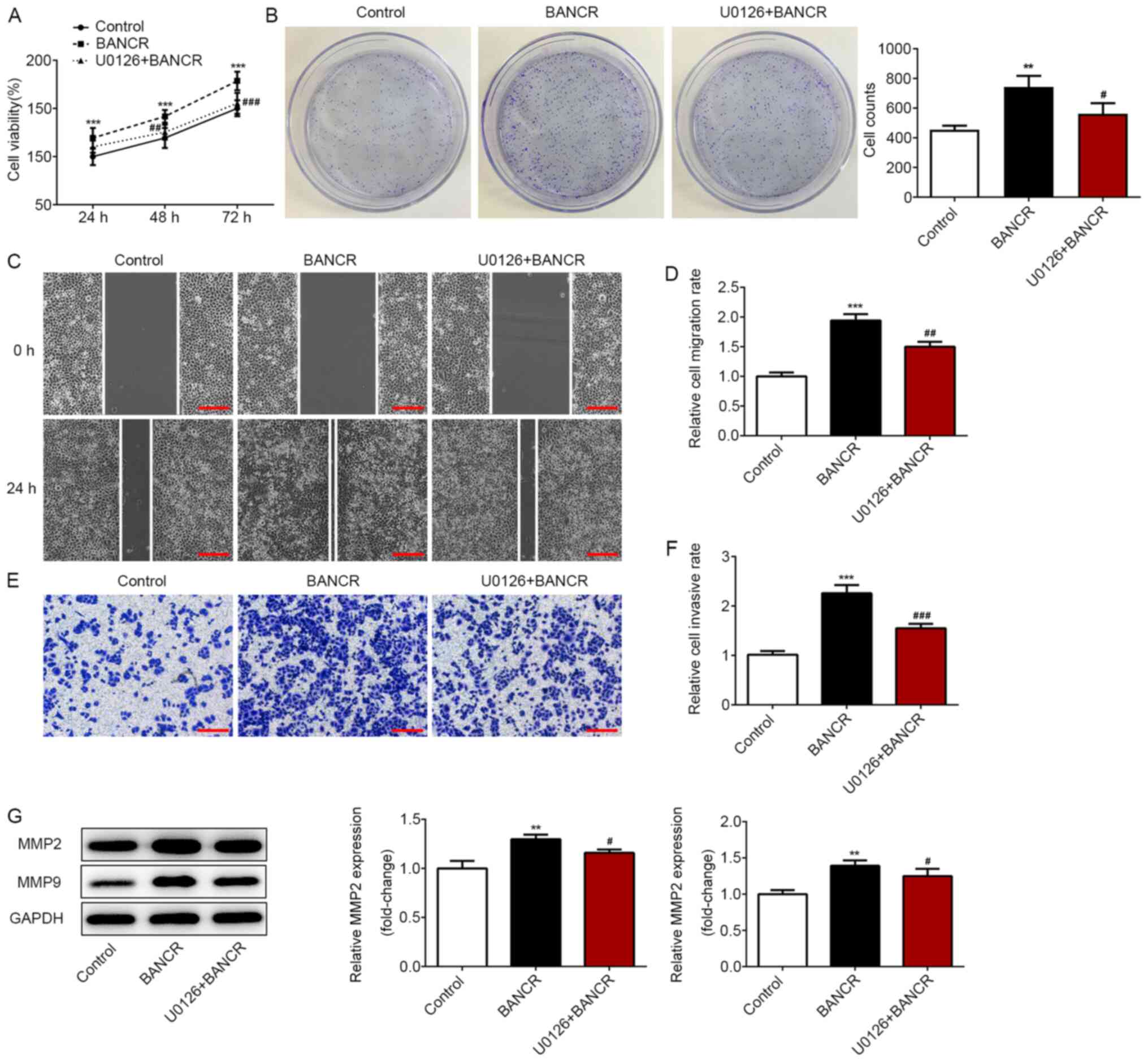
|
1
|
Sadeghpour S and Ghorbian S: Evaluation of
the potential clinical prognostic value of lncRNA-BANCR gene in
esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Mol Biol Rep. 46:991–995. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Li X, Xiao X, Chang R and Zhang C:
Comprehensive bioinformatics analysis identifies lncRNA HCG22 as a
migration inhibitor in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. J Cell
Biochem. 121:468–481. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel
RL, Torre LA and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN
estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in
185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 68:394–424. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Shang QX, Yang YS, Yuan Y, Gu YM, Zhang
HL, Ji AF and Chen LQ: Clinical and prognostic effects of adjuvant
therapy on less advanced esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
patients. Ann Palliat Med. 9:681–699. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Liu Z, Yang T, Xu Z and Cao X:
Upregulation of the long non-coding RNA BANCR correlates with tumor
progression and poor prognosis in esophageal squamous cell
carcinoma. Biomed Pharmacother. 82:406–412. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Zhu Y, Yuan T, Zhang Y, Shi J, Bai L, Duan
X, Tong R and Zhong L: AR-42: A pan-HDAC inhibitor with antitumor
and antiangiogenic activities in esophageal squamous cell
carcinoma. Drug Des Devel Ther. 13:4321–4330. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Shapiro J, van Lanschot JJB, Hulshof M,
van Hagen P, van Berge Henegouwen MI, Wijnhoven BPL, van Laarhoven
HWM, Nieuwenhuijzen GAP, Hospers GAP, Bonenkamp JJ, et al:
Neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy plus surgery versus surgery alone for
oesophageal or junctional cancer (CROSS): Long-term results of a
randomised controlled trial. Lancet Oncol. 16:1090–1098. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Tachimori Y, Ozawa S, Numasaki H, Ishihara
R, Matsubara H, Muro K, Oyama T, Toh Y, Udagawa H and Uno T;
Registration Committee for Esophageal Cancer of the Japan
Esophageal Society, : Comprehensive registry of esophageal cancer
in Japan, 2011. Esophagus. 15:127–152. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
van Hagen P, Hulshof MC, van Lanschot JJ,
Steyerberg EW, van Berge Henegouwen MI, Wijnhoven BP, Richel DJ,
Nieuwenhuijzen GA, Hospers GA, Bonenkamp JJ, et al: Preoperative
chemoradiotherapy for esophageal or junctional cancer. N Engl J
Med. 366:2074–2084. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
He LR, Liu MZ, Li BK, Jia WH, Zhang Y,
Liao YJ, Chen YC, Zhang LJ, Guan XY, Zeng YX, et al: High
expression of EZH2 is associated with tumor aggressiveness and poor
prognosis in patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
treated with definitive chemoradiotherapy. Int J Cancer.
127:138–147. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Luo J, Wang W, Tang Y, Zhou D, Gao Y,
Zhang Q, Zhou X, Zhu H, Xing L and Yu J: mRNA and methylation
profiling of radioresistant esophageal cancer cells: The
involvement of Sall2 in acquired aggressive phenotypes. J Cancer.
8:646–656. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Ghorbian S and Ardekani AM: Non-invasive
detection of esophageal cancer using genetic changes in circulating
cell-free DNA. Avicenna J Med Biotechnol. 4:3–13. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Liu J, Zhao SY, Jiang Q, Qu Y, Huang X, Du
J, Sun W and Ye Q: Long noncoding RNA MYLK-AS1 promotes growth and
invasion of hepatocellular carcinoma through the EGFR/HER2-ERK1/2
signaling pathway. Int J Biol Sci. 16:1989–2000. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Liu JQ, Deng M, Xue NN, Li TX, Guo YX, Gao
L, Zhao D and Fan RT: lncRNA KLF3-AS1 suppresses cell migration and
invasion in ESCC by impairing miR-185-5p-targeted KLF3 inhibition.
Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 20:231–241. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Wu D, He X, Wang W, Hu X, Wang K and Wang
M: Long noncoding RNA SNHG12 induces proliferation, migration,
epithelial-mesenchymal transition and stemness of esophageal
squamous cell carcinoma cells via post-transcriptional regulation
of BMI1 and CTNNB1. Mol Oncol. 14:2332–2351. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Ma S, Yang D, Liu Y, Wang Y, Lin T, Li Y,
Yang S, Zhang W and Zhang R: LncRNA BANCR promotes tumorigenesis
and enhances adriamycin resistance in colorectal cancer. Aging
(Albany NY). 10:2062–2078. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Wang Y, Gu J, Lin X, Yan W, Yang W and Wu
G: lncRNA BANCR promotes EMT in PTC via the Raf/MEK/ERK signaling
pathway. Oncol Lett. 15:5865–5870. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Wang D, Wang D, Wang N, Long Z and Ren X:
Long non-coding RNA BANCR promotes endometrial cancer cell
proliferation and invasion by regulating MMP2 and MMP1 via ERK/MAPK
signaling pathway. Cell Physiol Biochem. 40:644–656. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Chen Q, Zheng Y, Wu B, Chen X, Sun F, Ge P
and Wang P: BANCR regulates the cell invasion and migration in
esophageal squamous cell carcinoma through Wnt/beta-catenin
signaling pathway. Onco Targets Ther. 12:9319–9327. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Song W, Wang K, Yang X, Dai W and Fan Z:
Long non-coding RNA BANCR mediates esophageal squamous cell
carcinoma progression by regulating the IGF1R/Raf/MEK/ERK pathway
via miR-338-3p. Int J Mol Med. 46:1377–1388. 2020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Peng WX, Koirala P and Mo YY:
LncRNA-mediated regulation of cell signaling in cancer. Oncogene.
36:5661–5667. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Cossu AM, Mosca L, Zappavigna S, Misso G,
Bocchetti M, De Micco F, Quagliuolo L, Porcelli M, Caraglia M and
Boccellino M: Long non-coding RNAs as important biomarkers in
laryngeal cancer and other head and neck tumours. Int J Mol Sci.
20:34442019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Mahmoudian-Sani MR, Jalali A, Jamshidi M,
Moridi H, Alghasi A, Shojaeian A and Mobini GR: Long non-coding
RNAs in thyroid cancer: Implications for pathogenesis, diagnosis,
and therapy. Oncol Res Treat. 42:136–142. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Wu X, Xia T, Cao M, Zhang P, Shi G, Chen
L, Zhang J, Yin J, Wu P, Cai B, et al: LncRNA BANCR promotes
pancreatic cancer tumorigenesis via modulating
MiR-195-5p/Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Technol Cancer Res
Treat. 18:15330338198879622019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Yang L and Liu G: lncRNA BANCR suppresses
cell viability and invasion and promotes apoptosis in
non-small-cell lung cancer cells in vitro and in vivo. Cancer Manag
Res. 11:3565–3574. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Xu X, Pan L, Zhuo M, Yang X, Zhang W, Sun
D, Zeng N and Zhang D: Increased expression of LncRNA BANCR and its
prognostic significance in human epithelial ovarian cancer. Eur J
Gynaecol Oncol. 38:449–452. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Su S, Gao J, Wang T, Wang J, Li H and Wang
Z: Long non-coding RNA BANCR regulates growth and metastasis and is
associated with poor prognosis in retinoblastoma. Tumour Biol.
36:7205–7211. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Roberts PJ and Der CJ: Targeting the
Raf-MEK-ERK mitogen-activated protein kinase cascade for the
treatment of cancer. Oncogene. 26:3291–3310. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Wang Z, Ma L, Su M, Zhou Y, Mao K, Li C,
Peng G, Zhou C, Shen B and Dou J: Baicalin induces cellular
senescence in human colon cancer cells via upregulation of DEPP and
the activation of Ras/Raf/MEK/ERK signaling. Cell Death Dis.
9:2172018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Wu GJ, Pen J, Huang Y, An S, Liu Y, Yang
Y, Hao Q, Guo XX and Xu TR: KAP1 inhibits the Raf-MEK-ERK pathway
to promote tumorigenesis in A549 lung cancer cells. Mol Carcinog.
57:1396–1407. 2018. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Yin X, Zhang J, Li X, Liu D, Feng C, Liang
R, Zhuang K, Cai C, Xue X, Jing F, et al: DADS suppresses human
esophageal xenograft tumors through RAF/MEK/ERK and
mitochondria-dependent pathways. Int J Mol Sci. 15:12422–12441.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|