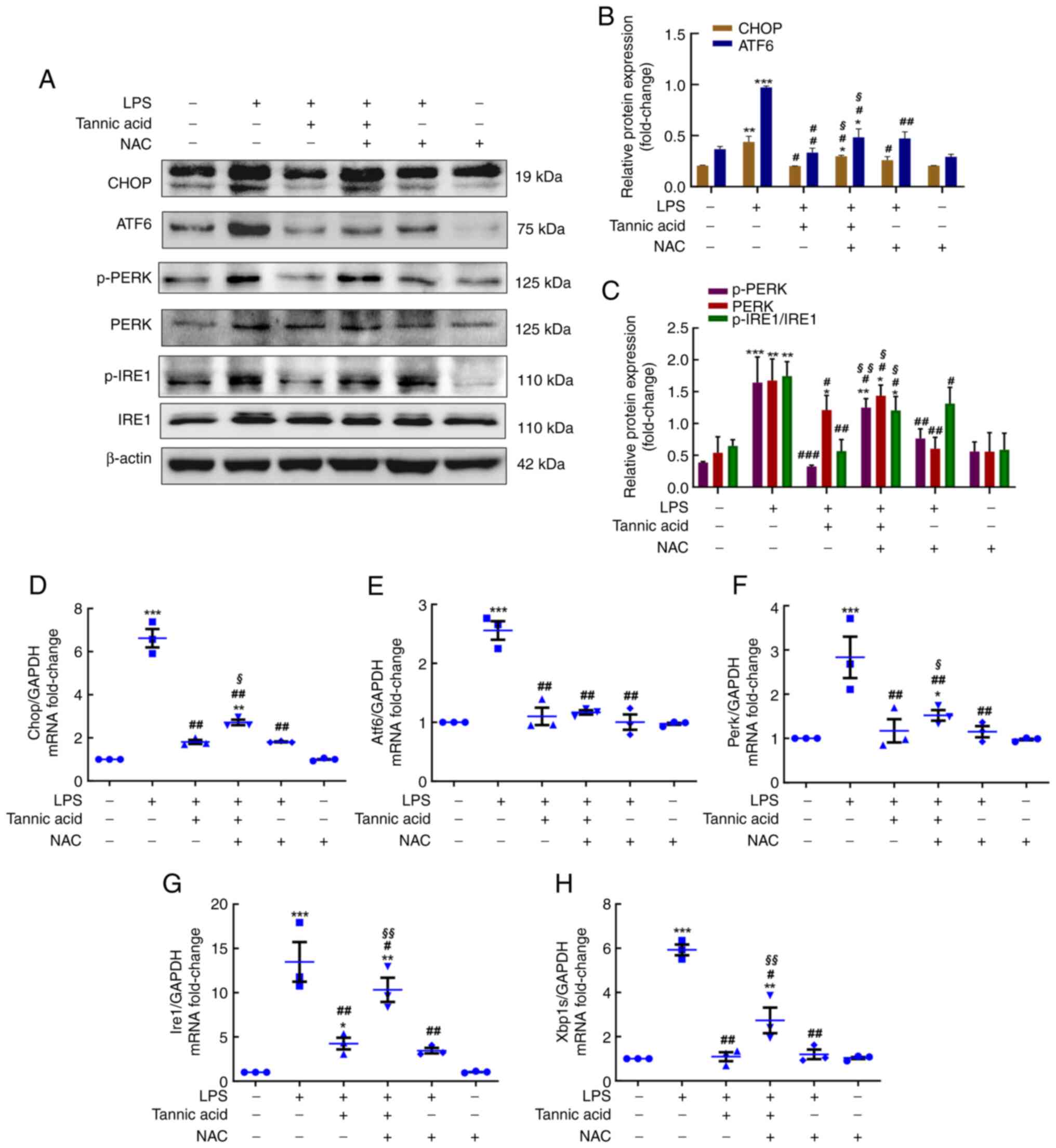
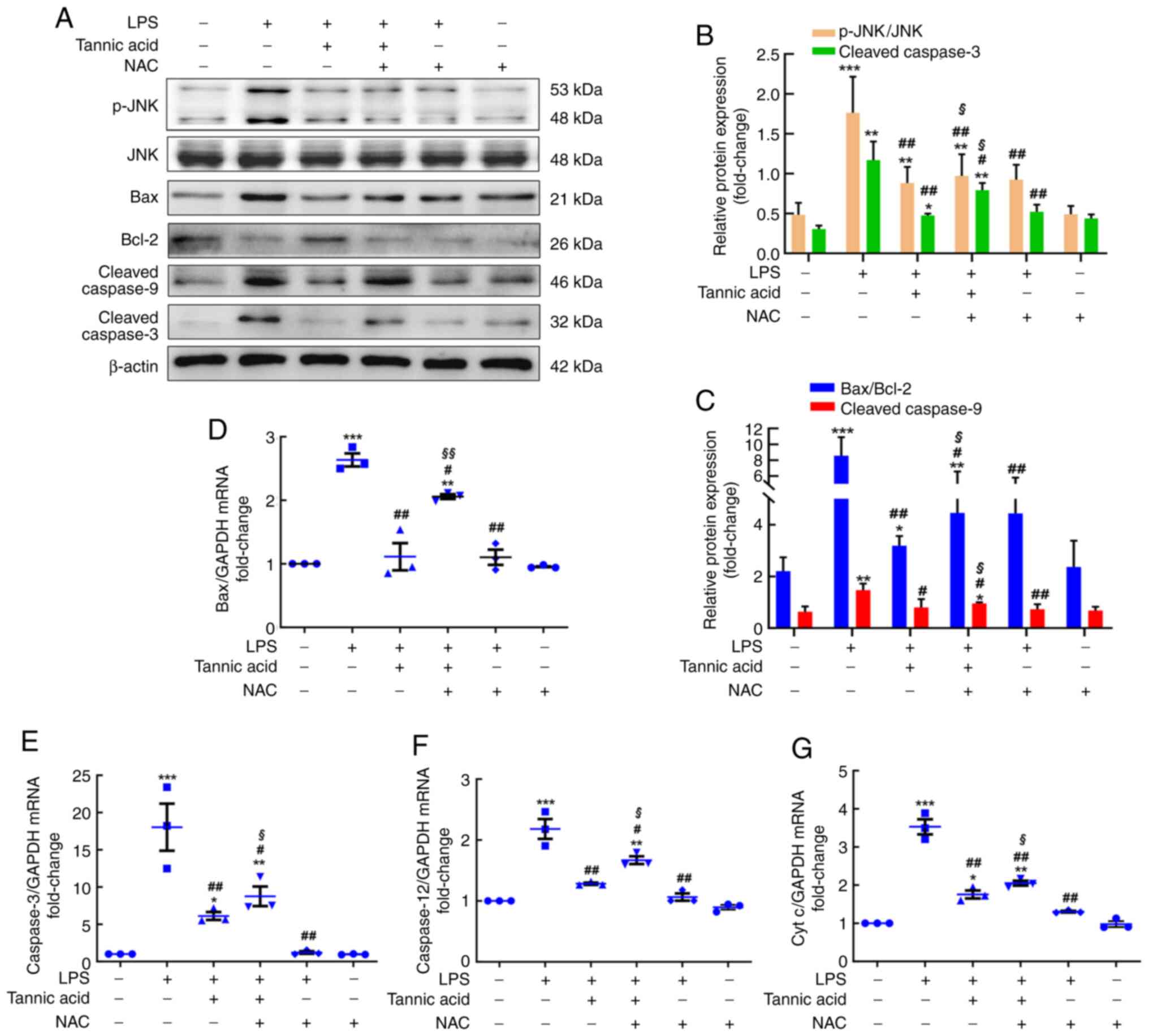
|
1
|
Rocheteau P, Chatre L, Briand D, Mebarki
M, Jouvion G, Bardon J, Crochemore C, Serrani P, Lecci PP, Latil M,
et al: Sepsis induces long-term metabolic and mitochondrial muscle
stem cell dysfunction amenable by mesenchymal stem cell therapy.
Nat Commun. 6:101452015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Paoli CJ, Reynolds MA, Sinha M, Gitlin M
and Crouser E: Epidemiology and costs of sepsis in the United
States-An analysis based on timing of diagnosis and severity level.
Crit Care Med. 46:1889–1897. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Huang M, Cai S and Su J: The Pathogenesis
of sepsis and potential therapeutic targets. Int J Mol Sci.
20:202019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Gaieski DF, Edwards JM, Kallan MJ and Carr
BG: Benchmarking the incidence and mortality of severe sepsis in
the United States. Crit Care Med. 41:1167–1174. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Zhang T, Yan T, Du J, Wang S and Yang H:
Apigenin attenuates heart injury in lipopolysaccharide-induced
endotoxemic model by suppressing sphingosine kinase 1/sphingosine
1-phosphate signaling pathway. Chem Biol Interact. 233:46–55. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Lambden S, Creagh-Brown BC, Hunt J,
Summers C and Forni LG: Definitions and pathophysiology of
vasoplegic shock. Crit Care. 22:1742018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Martin L, Derwall M, Al Zoubi S,
Zechendorf E, Reuter DA, Thiemermann C and Schuerholz T: The Septic
Heart: Current understanding of molecular mechanisms and clinical
implications. Chest. 155:427–437. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Lv X and Wang H: Pathophysiology of
sepsis-induced myocardial dysfunction. Mil Med Res.
3:302016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Liu YC, Yu MM, Shou ST and Chai YF:
Sepsis-induced cardiomyopathy: Mechanisms and treatments. Front
Immunol. 8:10212017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Drosatos K, Lymperopoulos A, Kennel PJ,
Pollak N, Schulze PC and Goldberg IJ: Pathophysiology of
sepsis-related cardiac dysfunction: Driven by inflammation, energy
mismanagement, or both? Curr Heart Fail Rep. 12:130–140. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Bai T, Hu X, Zheng Y, Wang S, Kong J and
Cai L: Resveratrol protects against lipopolysaccharide-induced
cardiac dysfunction by enhancing SERCA2a activity through promoting
the phospholamban oligomerization. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol.
311:H1051–H1062. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Kakihana Y, Ito T, Nakahara M, Yamaguchi K
and Yasuda T: Sepsis-induced myocardial dysfunction:
Pathophysiology and management. J Intensive Care. 4:222016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Tan S, Long Z, Hou X, Lin Y, Xu J, You X,
Wang T and Zhang Y: H2 Protects Against lipopolysaccharide-induced
cardiac dysfunction via blocking TLR4-mediated cytokines
expression. Front Pharmacol. 10:8652019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Turdi S, Han X, Huff AF, Roe ND, Hu N, Gao
F and Ren J: Cardiac-specific overexpression of catalase attenuates
lipopolysaccharide-induced myocardial contractile dysfunction: Role
of autophagy. Free Radic Biol Med. 53:1327–1338. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Jiang W, Luo F, Lu Q, Liu J, Li P, Wang X,
Fu Y, Hao K, Yan T and Ding X: The protective effect of Trillin
LPS-induced acute lung injury by the regulations of inflammation
and oxidative state. Chem Biol Interact. 243:127–134. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Qi XF, Zheng L, Lee KJ, Kim DH, Kim CS,
Cai DQ, Wu Z, Qin JW, Yu YH and Kim SK: HMG-CoA reductase
inhibitors induce apoptosis of lymphoma cells by promoting ROS
generation and regulating Akt, Erk and p38 signals via suppression
of mevalonate pathway. Cell Death Dis. 4:e5182013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Ding W, Yang L, Zhang M and Gu Y: Reactive
oxygen species-mediated endoplasmic reticulum stress contributes to
aldosterone-induced apoptosis in tubular epithelial cells. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 418:451–456. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Liu ZW, Zhu HT, Chen KL, Dong X, Wei J,
Qiu C and Xue JH: Protein kinase RNA-like endoplasmic reticulum
kinase (PERK) signaling pathway plays a major role in reactive
oxygen species (ROS)-mediated endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced
apoptosis in diabetic cardiomyopathy. Cardiovasc Diabetol.
12:1582013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Li D, Cong Z, Yang C and Zhu X: Inhibition
of LPS-induced Nox2 activation by VAS2870 protects alveolar
epithelial cells through eliminating ROS and restoring tight
junctions. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 524:575–581. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Li A, Song NJ, Riesenberg BP and Li Z: The
emerging roles of endoplasmic reticulum stress in balancing
immunity and tolerance in health and diseases: Mechanisms and
opportunities. Front Immunol. 10:31542020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Oyadomari S, Yun C, Fisher EA, Kreglinger
N, Kreibich G, Oyadomari M, Harding HP, Goodman AG, Harant H,
Garrison JL, et al: Cotranslocational degradation protects the
stressed endoplasmic reticulum from protein overload. Cell.
126:727–739. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Wang M and Kaufman RJ: Protein misfolding
in the endoplasmic reticulum as a conduit to human disease. Nature.
529:326–335. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Liu L, Wu H, Zang J, Yang G, Zhu Y, Wu Y,
Chen X, Lan D and Li T: 4-Phenylbutyric acid reveals good
beneficial effects on vital organ function via anti-endoplasmic
reticulum stress in septic rats. Crit Care Med. 44:e689–e701. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Khan MM, Yang WL and Wang P: Endoplasmic
reticulum stress in sepsis. Shock. 44:294–304. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Salminen JP and Karonen M: Chemical
ecology of tannins and other phenolics: We need a change in
approach. Funct Ecol. 25:325–338. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Darvin P, Joung YH, Kang DY, Sp N, Byun
HJ, Hwang TS, Sasidharakurup H, Lee CH, Cho KH, Park KD, et al:
Tannic acid inhibits EGFR/STAT1/3 and enhances p38/STAT1 signalling
axis in breast cancer cells. J Cell Mol Med. 21:720–734. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Pattarayan D, Sivanantham A, Krishnaswami
V, Loganathan L, Palanichamy R, Natesan S, Muthusamy K and
Rajasekaran S: Tannic acid attenuates TGF-β1-induced
epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition by effectively intervening
TGF-β signaling in lung epithelial cells. J Cell Physiol.
233:2513–2525. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Pattarayan D, Sivanantham A, Bethunaickan
R, Palanichamy R and Rajasekaran S: Tannic acid modulates
fibroblast proliferation and differentiation in response to
pro-fibrotic stimuli. J Cell Biochem. 119:6732–6742. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Sivanantham A, Pattarayan D, Bethunaickan
R, Kar A, Mahapatra SK, Thimmulappa RK, Palanichamy R and
Rajasekaran S: Tannic acid protects against experimental acute lung
injury through downregulation of TLR4 and MAPK. J Cell Physiol.
234:6463–6476. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Hu X, Wang H, Lv X, Chu L, Liu Z, Wei X,
Chen Q, Zhu L and Cui W: Cardioprotective effects of tannic acid on
isoproterenol-induced myocardial injury in rats: Further insight
into ‘French Paradox’. Phytother Res. 29:1295–1303. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Zheng Y, Li S, Hu R, Cheng F and Zhang L:
GFI-1 protects against lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory
responses and apoptosis by inhibition of the NF-κB/TNF-α pathway in
H9c2 Cells. Inflammation. 43:74–84. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Shan P, Pu J, Yuan A, Shen L, Shen L, Chai
D and He B: RXR agonists inhibit oxidative stress-induced apoptosis
in H9c2 rat ventricular cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
375:628–633. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Lei Y, Yang Y, Zhao J, Gao H, Chen R, Bai
B, Kang X, He Y, Ding L, Wei T, et al: P-AKT2/SPK1 (P-SPK1) and
P-MEK/P-ERK cell signaling pathways are involved in LPS-induced
macrophage migration. Am J Transl Res. 11:2725–2741.
2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Zhao J, Lei Y, Yang Y, Gao H, Gai Z and Li
X: Metoprolol alleviates arginine vasopressin-induced cardiomyocyte
hypertrophy by upregulating the AKT1-SERCA2 cascade in H9C2 cells.
Cell Biosci. 10:722020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Song Q, Liu L, Yu J, Zhang J, Xu M, Sun L,
Luo H, Feng Z and Meng G: Dihydromyricetin attenuated Ang II
induced cardiac fibroblasts proliferation related to inhibitory of
oxidative stress. Eur J Pharmacol. 807:159–167. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Kotfis K, Wittebole X, Jaschinski U,
Solé-Violán J, Kashyap R, Leone M, Nanchal R, Fontes LE, Sakr Y and
Vincent JL; ICON Investigators, : A worldwide perspective of sepsis
epidemiology and survival according to age: Observational data from
the ICON audit. J Crit Care. 51:122–132. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Keeley A, Hine P and Nsutebu E: The
recognition and management of sepsis and septic shock: A guide for
non-intensivists. Postgrad Med J. 93:626–634. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Opal SM, Scannon PJ, Vincent JL, White M,
Carroll SF, Palardy JE, Parejo NA, Pribble JP and Lemke JH:
Relationship between plasma levels of lipopolysaccharide (LPS) and
LPS-binding protein in patients with severe sepsis and septic
shock. J Infect Dis. 180:1584–1589. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Li Y, Ge S, Peng Y and Chen X:
Inflammation and cardiac dysfunction during sepsis, muscular
dystrophy, and myocarditis. Burns Trauma. 1:109–121. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Hu D, Yang X, Xiang Y, Li H, Yan H, Zhou
J, Caudle Y, Zhang X and Yin D: Inhibition of Toll-like receptor 9
attenuates sepsis-induced mortality through suppressing excessive
inflammatory response. Cell Immunol. 295:92–98. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Lowes DA, Webster NR, Murphy MP and Galley
HF: Antioxidants that protect mitochondria reduce interleukin-6 and
oxidative stress, improve mitochondrial function, and reduce
biochemical markers of organ dysfunction in a rat model of acute
sepsis. Br J Anaesth. 110:472–480. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Zhang Y, Xu X, Ceylan-Isik AF, Dong M, Pei
Z, Li Y and Ren J: Ablation of Akt2 protects against
lipopolysaccharide-induced cardiac dysfunction: Role of Akt
ubiquitination E3 ligase TRAF6. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 74:76–87. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Luiking YC, Poeze M and Deutz NE: Arginine
infusion in patients with septic shock increases nitric oxide
production without haemodynamic instability. Clinical science.
(London England: 1979). 128:57–67. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Wilson J, Higgins D, Hutting H, Serkova N,
Baird C, Khailova L, Queensland K, Vu Tran Z, Weitzel L and
Wischmeyer PE: Early propranolol treatment induces lung
heme-oxygenase-1, attenuates metabolic dysfunction, and improves
survival following experimental sepsis. Crit Care. 17:R1952013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Nie F, Liang Y, Jiang B, Li X, Xun H, He
W, Lau HT and Ma X: Apoptotic effect of tannic acid on fatty acid
synthase over-expressed human breast cancer cells. Tumour Biol.
37:2137–2143. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Zhang T, Zhang R, Dang M, Qiu S, Gu H, He
P and Guo G: Ameliorative effects of tannic acid on
lipopolysaccharide induced sepsis and acute lung injury in mice.
Pharmacogn Mag. 15:152019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Chu L, Li P, Song T, Han X, Zhang X, Song
Q, Liu T, Zhang Y and Zhang J: Protective effects of tannic acid on
pressure overload-induced cardiac hypertrophy and underlying
mechanisms in rats. J Pharm Pharmacol. 69:1191–1207. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Zhang J, Cui L, Han X, Zhang Y, Zhang X,
Chu X, Zhang F, Zhang Y and Chu L: Protective effects of tannic
acid on acute doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity: Involvement of
suppression in oxidative stress, inflammation, and apoptosis.
Biomed Pharmacother. 93:1253–1260. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Fiers W, Beyaert R, Declercq W and
Vandenabeele P: More than one way to die: Apoptosis, necrosis and
reactive oxygen damage. Oncogene. 18:7719–7730. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Sakon S, Xue X, Takekawa M, Sasazuki T,
Okazaki T, Kojima Y, Piao JH, Yagita H, Okumura K, Doi T, et al:
NF-kappaB inhibits TNF-induced accumulation of ROS that mediate
prolonged MAPK activation and necrotic cell death. EMBO J.
22:3898–3909. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Quoilin C, Mouithys-Mickalad A, Lécart S,
Fontaine-Aupart MP and Hoebeke M: Evidence of oxidative stress and
mitochondrial respiratory chain dysfunction in an in vitro model of
sepsis-induced kidney injury. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1837:1790–1800.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Wible DJ and Bratton SB: Reciprocity in
ROS and autophagic signaling. Curr Opin Toxicol. 7:28–36. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Bardaweel SK, Gul M, Alzweiri M, Ishaqat
A, ALSalamat HA and Bashatwah RM: Reactive oxygen species: The dual
role in physiological and pathological conditions of the human
body. Eurasian J Med. 50:193–201. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
L'Heureux M, Sternberg M, Brath L,
Turlington J and Kashiouris MG: Sepsis-induced cardiomyopathy: A
comprehensive review. Curr Cardiol Rep. 22:352020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Prauchner CA: Oxidative stress in sepsis:
Pathophysiological implications justifying antioxidant co-therapy.
Burns. 43:471–485. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Xu Y, Liu P, Xu S, Koroleva M, Zhang S, Si
S and Jin ZG: Tannic acid as a plant-derived polyphenol exerts
vasoprotection via enhancing KLF2 expression in endothelial cells.
Sci Rep. 7:66862017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Li YH, Zhang WL, Zhou HY, Yu DW, Sun XN
and Hu Q: Halofuginone protects against advanced glycation end
products induced injury of H9C2 cells via alleviating endoplasmic
reticulum stress associated apoptosis and inducing autophagy. Mol
Med Rep. 20:3131–3139. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Cheng YC, Chen CA and Chen HC: Endoplasmic
reticulum stress-induced cell death in podocytes. Nephrology
(Carlton). 22 (Suppl 4):43–49. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Tabas I and Ron D: Integrating the
mechanisms of apoptosis induced by endoplasmic reticulum stress.
Nat Cell Biol. 13:184–190. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Yang J, Wu Q, Lv J and Nie H: 4-Phenyl
butyric acid prevents glucocorticoid-induced osteoblast apoptosis
by attenuating endoplasmic reticulum stress. J Bone Miner Metab.
35:366–374. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Nagesh PKB, Hatami E, Chowdhury P, Kashyap
VK, Khan S, Hafeez BB, Chauhan SC, Jaggi M and Yallapu MM: Tannic
acid induces endoplasmic reticulum stress-mediated apoptosis in
prostate cancer. Cancers (Basel). 10:102018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
62
|
Nagesh PKB, Chowdhury P, Hatami E, Jain S,
Dan N, Kashyap VK, Chauhan SC, Jaggi M and Yallapu MM: Tannic acid
inhibits lipid metabolism and induce ROS in prostate cancer cells.
Sci Rep. 10:9802020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|