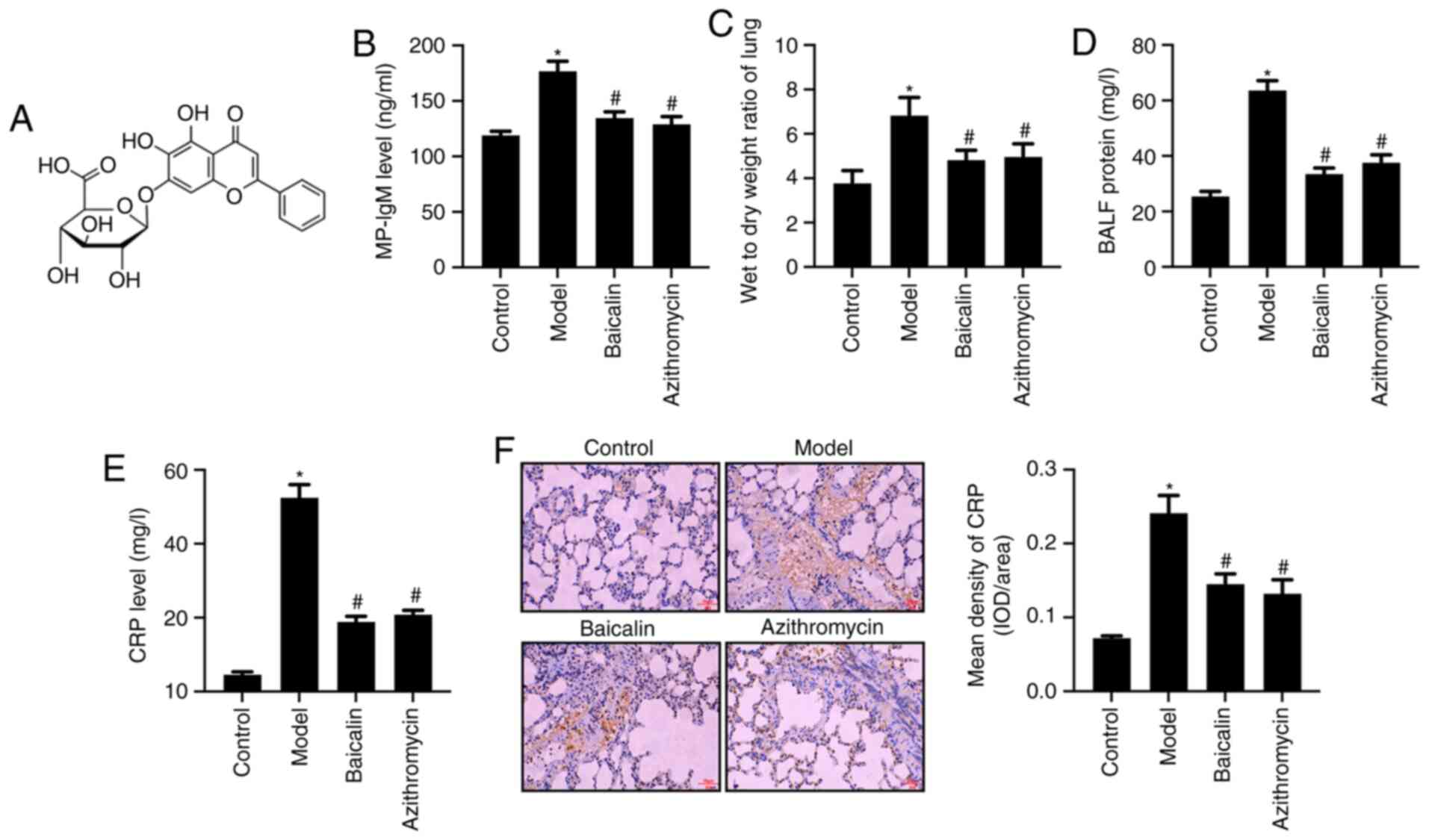
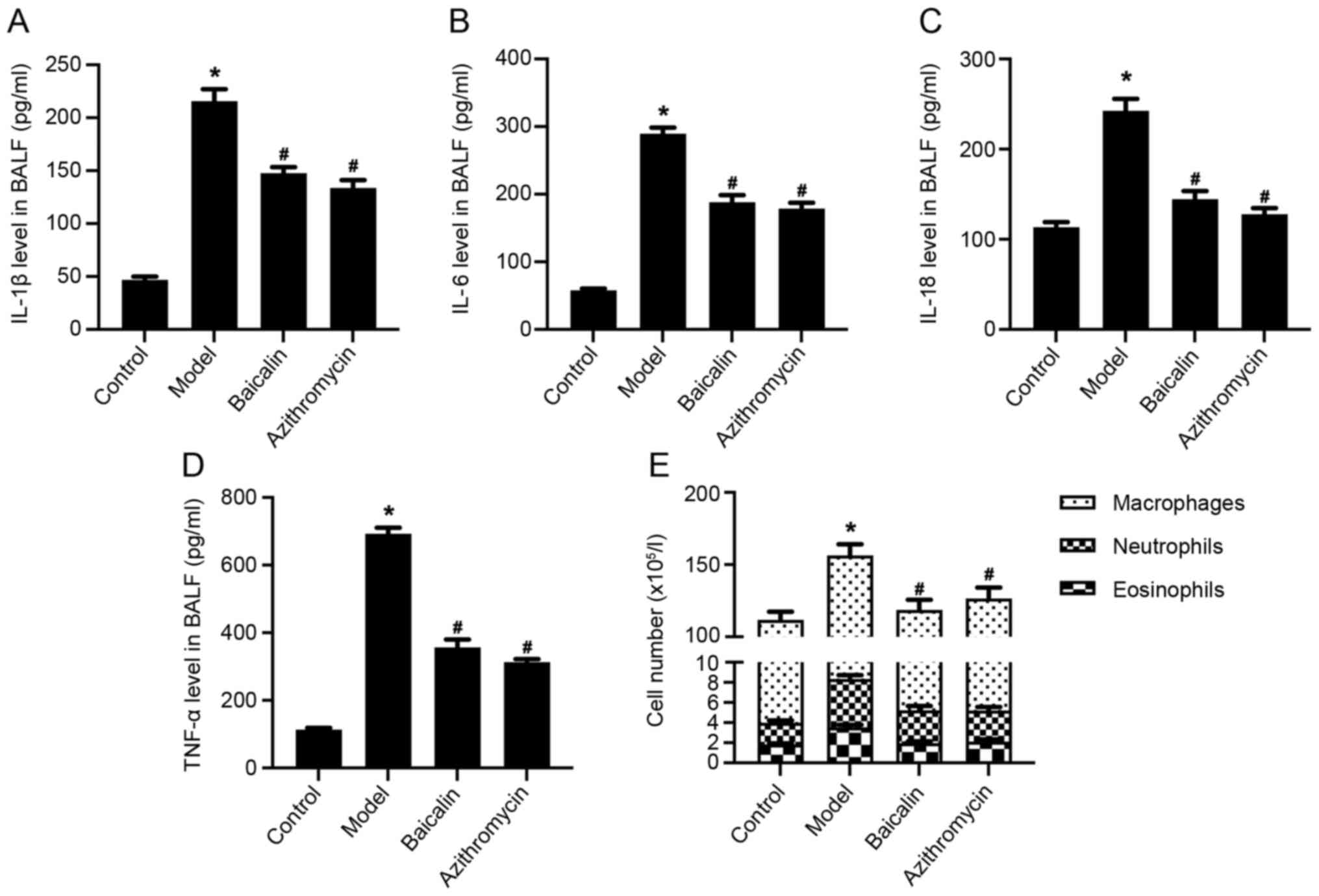
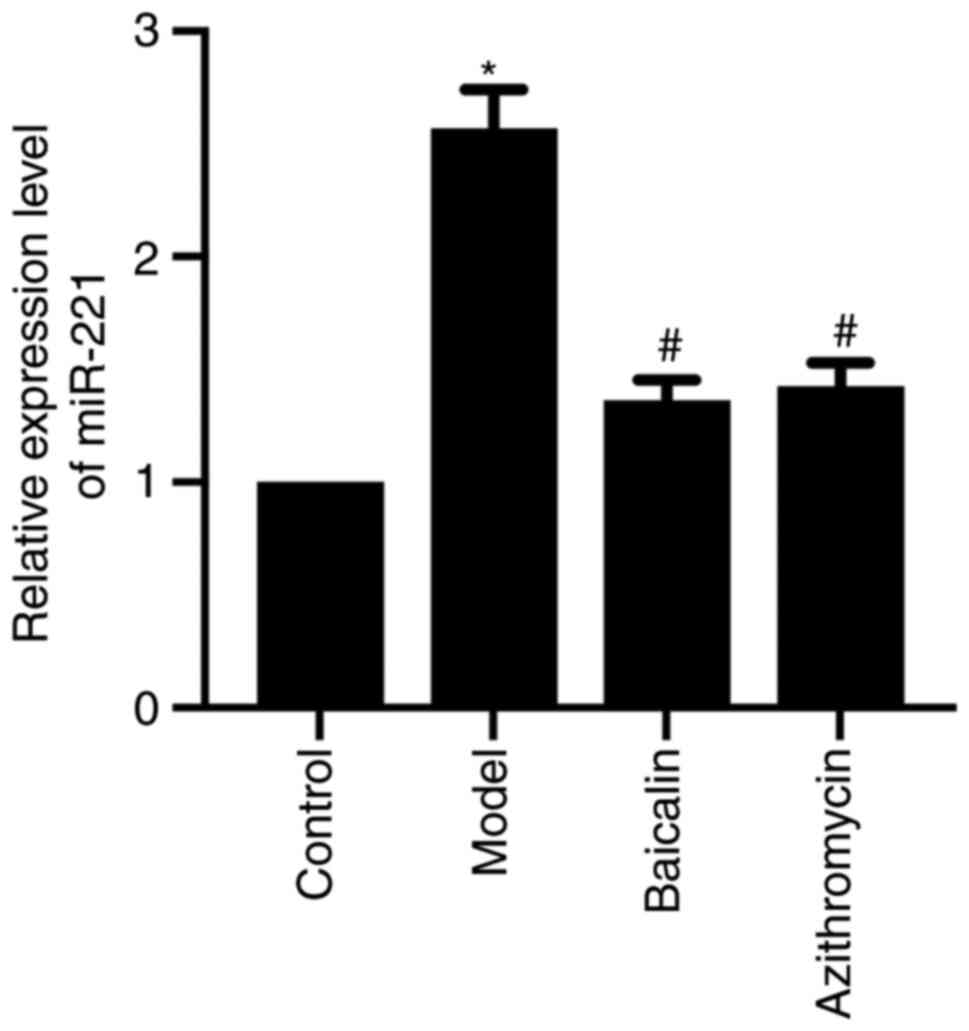
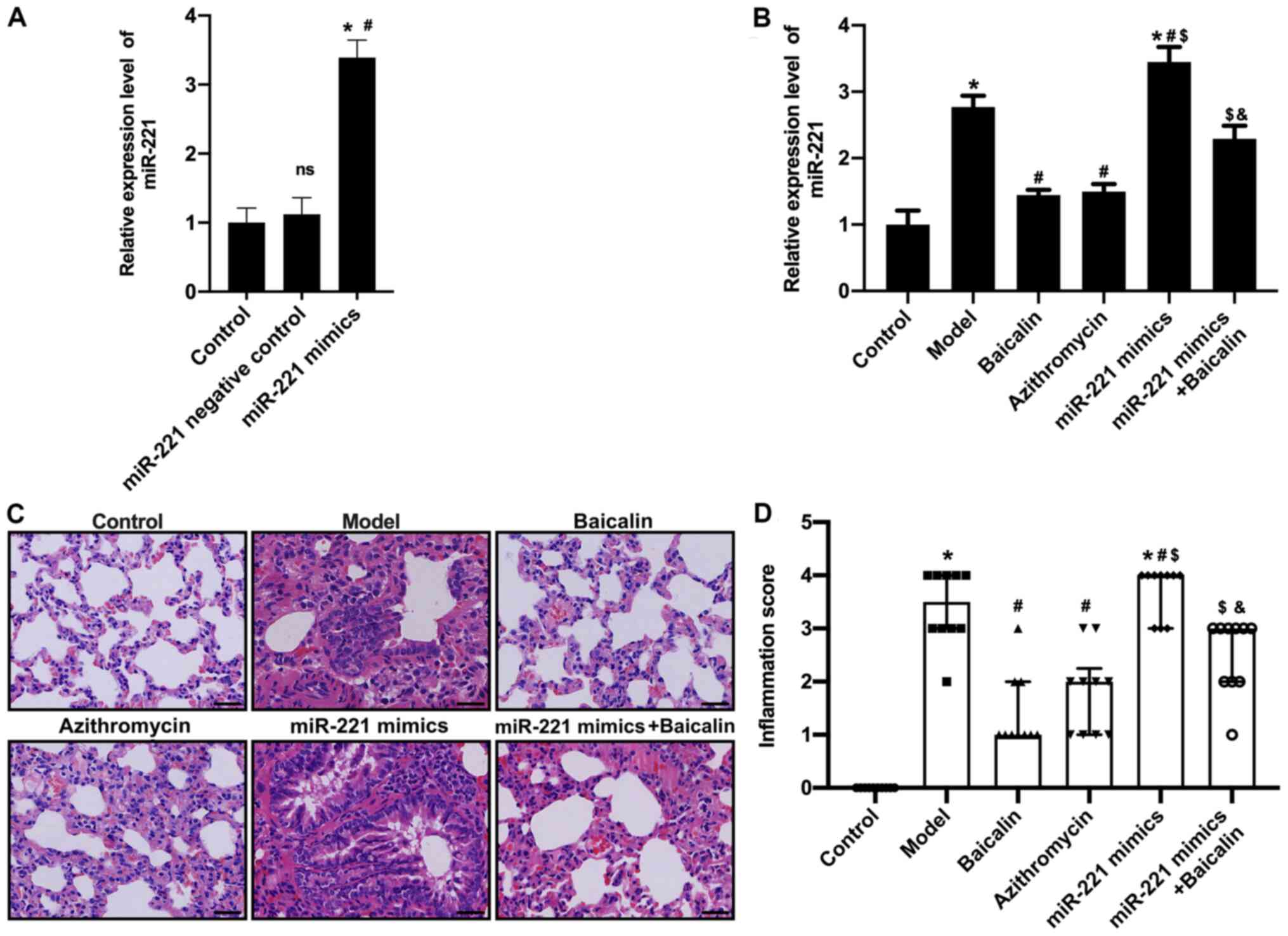
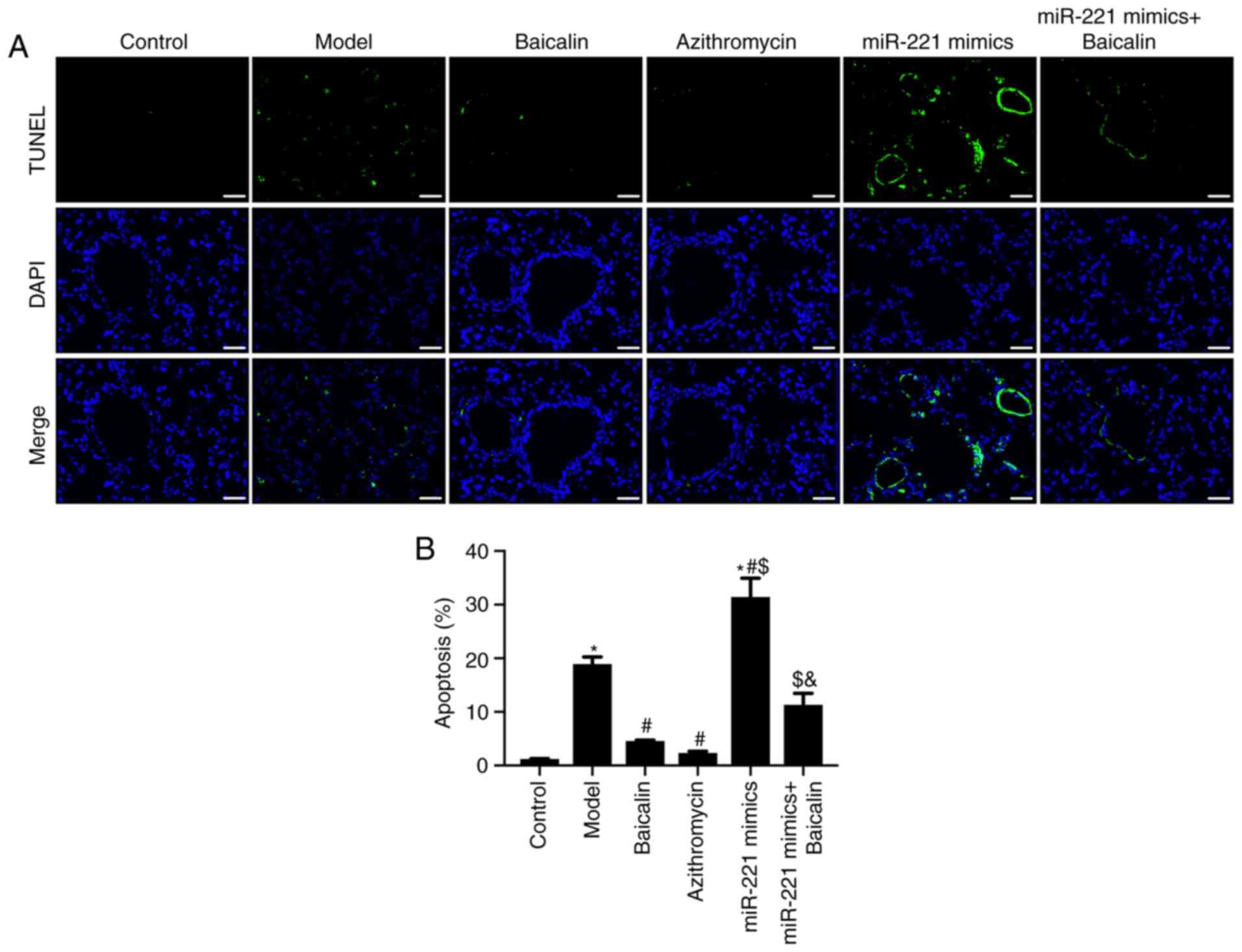
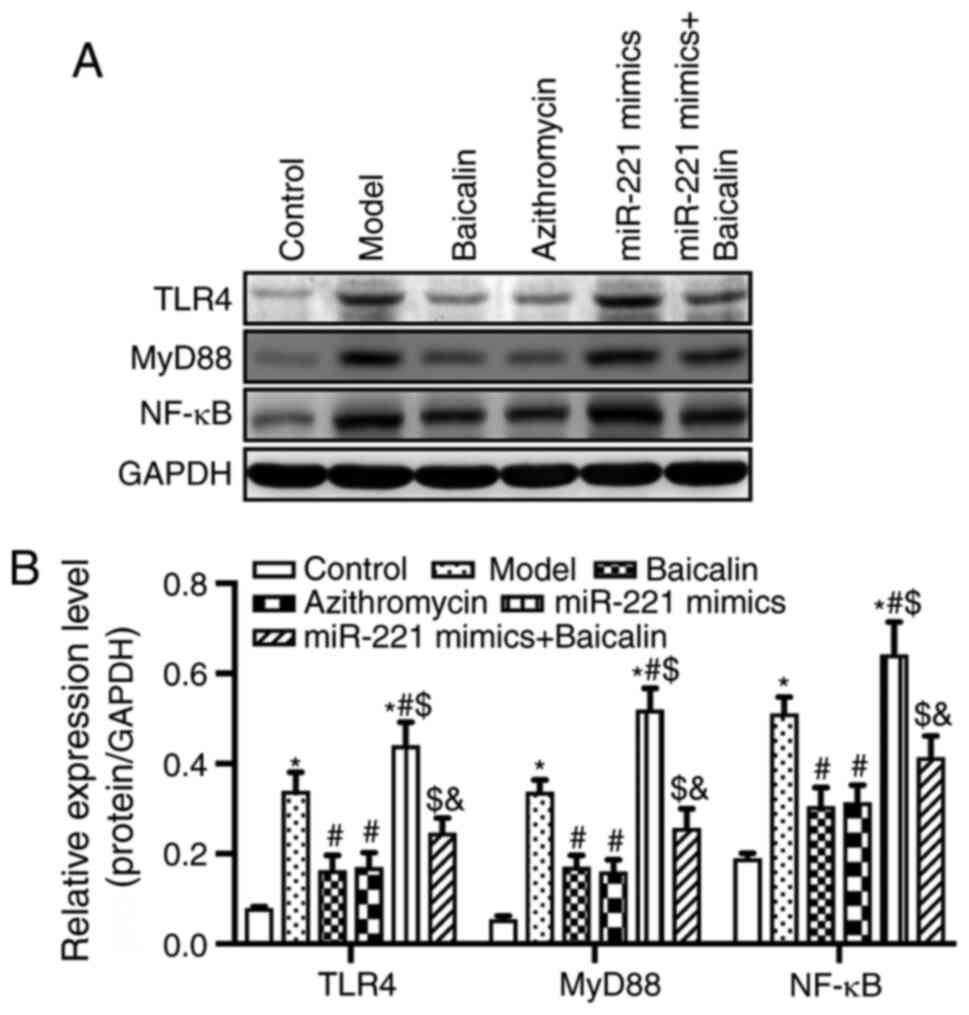
|
1
|
Anjum MU, Riaz H and Tayyab HM: Acute
respiratory tract infections (ARIS); clinico-epidemiolocal profile
in children of less than five years of age. Professional Med J.
24:322–325. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Guillet E, Mas C, Bauvin I, Beze Beyrie P,
Mansir T and Guérin B: Extrarespiratory manifestations of
Mycoplasma pneumoniae: A case report. Arch Pediatr.
21:381–383. 2014.(In French). View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Hanzawa F, Fuchigami T, Ishii W, Nakajima
S, Kawamura Y, Endo A, Arakawa C, Kohira R, Fujita Y and Takahashi
S: A 3-year-old boy with Guillain-Barré syndrome and encephalitis
associated with Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection. J Infect
Chemother. 20:134–138. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Esposito S, Blasi F, Arosio C, Fioravanti
L, Fagetti L, Droghetti R, Tarsia P, Allegra L and Principi N:
Importance of acute Mycoplasma pneumoniae and chlamydia
pneumoniae infections in children with wheezing. Eur Respir J.
16:1142–1146. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Liu WK, Liu Q, Chen DH, Liang HX, Chen XK,
Chen MX, Qiu SY, Yang ZY and Zhou R: Epidemiology of acute
respiratory infections in children in Guangzhou: A three-year
study. PLoS One. 9:e966742014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Gullsby K and Bondeson K: No detection of
macrolide-resistant Mycoplasma pneumoniae from Swedish
patients, 1996–2013. Infect Ecol Epidemiol. 6:313742016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Lu A, Wang C, Zhang X, Wang L and Qian L:
Lactate dehydrogenase as a biomarker for prediction of refractory
Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia in children. Respir Care.
60:1469–1475. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Yang JY, Li M, Zhang CL and Liu D:
Pharmacological properties of baicalin on liver diseases: A
narrative review. Pharmacol Rep. Feb 17–2021.(Epub ahead of print).
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Hu Q, Zhang W, Wu Z, Tian X, Xiang J, Li
L, Li Z, Peng X, Wei S, Ma X and Zhao Y: Baicalin and the liver-gut
system: Pharmacological bases explaining its therapeutic effects.
Pharmacol Res. 165:1054442021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Singh S, Meena A and Luqman S: Baicalin
mediated regulation of key signaling pathways in cancer. Pharmacol
Res. 164:1053872021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Yu FY, Huang SG, Zhang HY, Ye H, Chi HG,
Zou Y, Lv RX and Zheng XB: Effects of baicalin in CD4 + CD29 + T
cell subsets of ulcerative colitis patients. World J Gastroenterol.
20:15299–15309. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Wang CZ, Zhang CF, Chen L, Anderson S, Lu
F and Yuan CS: Colon cancer chemopreventive effects of baicalein,
an active enteric microbiome metabolite from baicalin. Int J Oncol.
47:1749–1758. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Lee W, Ku SK and Bae JS: Anti-inflammatory
effects of baicalin, baicalein, and wogonin in vitro and in vivo.
Inflammation. 38:110–125. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Huang X, Mao W, Zhang T, Wang M, Wang X,
Li Y, Zhang L, Yao D, Cai X and Wang L: Baicalin promotes apoptosis
and inhibits proliferation and migration of hypoxia-induced
pulmonary artery smooth muscle cells by up-regulating A2a receptor
via the SDF-1/CXCR4 signaling pathway. BMC Complement Altern Med.
18:3302018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Wang G, Mohammadtursun N, Lv Y, Zhang H,
Sun J and Dong J: Baicalin exerts anti-airway inflammation and
anti-remodelling effects in severe stage rat model of chronic
obstructive pulmonary disease. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med.
2018:75913482018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Bai C, Li T, Sun Q, Xin Q, Xu T, Yu J,
Wang Y and Wei L: Protective effect of baicalin against severe
burn-induced remote acute lung injury in rats. Mol Med Rep.
17:2689–2694. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Chaudhry R, Ghosh A and Chandolia A:
Pathogenesis of Mycoplasma pneumoniae: An update. Indian J
Med Microbiol. 34:7–16. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Martin RJ, Kraft M, Chu HW, Berns EA and
Cassell GH: A link between chronic asthma and chronic infection. J
Allergy Clin Immunol. 107:595–601. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Ramien M: Reactive infectious
mucocutaneous eruption: Mycoplasma pneumoniae-induced rash
and mucositis and other parainfectious eruptions. Clin Exp
Dermatol. 46:420–429. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Jiang Z, Li S, Zhu C, Zhou R and Leung
PHM: Mycoplasma pneumoniae infections: Pathogenesis and
vaccine development. Pathogens. 10:1192021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Saraya T, Kurai D, Nakagaki K, Sasaki Y,
Niwa S, Tsukagoshi H, Nunokawa H, Ohkuma K, Tsujimoto N, Hirao S,
et al: Novel aspects on the pathogenesis of Mycoplasma
pneumoniae pneumonia and therapeutic implications. Front
Microbiol. 5:4102014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Yano T, Komatsu S, Araki K, Kuboshiro M,
Ichikawa Y, Ohizumi K and Arai S: Role of transiently accumulated
neutrophils in the lung of hamster in development of pneumonia due
to Mycoplasma pneumoniae. Kansenshogaku Zasshi. 65:365–373.
1991.(In Japanese). View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Wang Z, Liao Y, Wang L, Lin Y, Ye Z, Zeng
X, Liu X, Wei F and Yang N: Small RNA deep sequencing reveals novel
miRNAs in peripheral blood mononuclear cells from patients with IgA
nephropathy. Mol Med Rep. 22:3378–3386. 2020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Duan Q, Mao X, Xiao Y, Liu Z, Wang Y, Zhou
H, Zhou Z, Cai J, Xia K, Zhu Q, et al: Super enhancers at the
miR-146a and miR-155 genes contribute to self-regulation of
inflammation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1859:564–571. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Yamamoto M, Singh A, Ruan J, Gauvreau GM,
O'Byrne PM, Carlsten CR, FitzGerald JM, Boulet LP and Tebbutt SJ:
Decreased miR-192 expression in peripheral blood of asthmatic
individuals undergoing an allergen inhalation challenge. BMC
Genomics. 13:6552012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Zhou Y, Yang Q, Xu H, Zhang J, Deng H, Gao
H, Yang J, Zhao D and Liu F: miRNA-221-3p enhances the secretion of
interleukin-4 in mast cells through the phosphatase and tensin
homolog/p38/nuclear factor-kappaB pathway. PLoS One.
11:e01488212016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Amarante-Mendes GP, Adjemian S, Branco LM,
Zanetti LC, Weinlich R and Bortoluci KR: Pattern recognition
receptors and the host cell death molecular machinery. Front
Immunol. 9:23792018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Poddighe D: Mycoplasma
pneumoniae-related hepatitis in children. Microb Pathog.
139:1038632020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Naghib M, Hatam-Jahromi M, Niktab M,
Ahmadi R and Kariminik A: Mycoplasma pneumoniae and
toll-like receptors: A mutual avenue. Allergol Immunopathol (Madr).
46:508–513. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Shimizu T: Inflammation -inducing Factors
of Mycoplasma pneumoniae. Front Microbiol. 7:4142016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Pal S, Ausar SF, Tifrea DF, Cheng C,
Gallichan S, Sanchez V, de la Maza LM and Visan L: Protection of
outbred mice against a vaginal challenge by a chlamydia trachomatis
serovar E recombinant major outer membrane protein vaccine is
dependent on phosphate substitution in the adjuvant. Hum Vaccin
Immunother. 16:2537–2547. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Chandler CE and Ernst RK: Bacterial
lipids: Powerful modifiers of the innate immune response. F1000Res.
6:F10002017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Dickson K and Lehmann C: Inflammatory
response to different toxins in experimental sepsis models. Int J
Mol Sci. 20:43412019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Narita M: Pathogenesis of extrapulmonary
manifestations of Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection with
special reference to pneumonia. J Infect Chemother. 16:162–169.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Sun H, Zhang L, Shi C, Hu P, Yan W, Wang
Z, Duan Q, Lu F, Qin L, Lu T, et al: TOPK is highly expressed in
circulating tumor cells, enabling metastasis of prostate cancer.
Oncotarget. 6:12392–12404. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Meng Y, Yang Y, Lu W, Wang Y, Qian F, Wang
X, Zhang Z and Wang W: The inhibition of Platycodin D on
Mycoplasma pneumoniae proliferation and its effect on
promoting cell growth after anti-Mycoplasma pneumoniae
treatment. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 4:1922015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Liu Y, Miao Y, Gao X, Wang YY, Wang H,
Zheng YW and Zhao ZY: MicroRNA-200a affects the proliferation of
airway smooth muscle cells and airway remodeling by targeting FOXC1
via the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway in ovalbumin-induced asthmatic
mice. Cell Physiol Biochem. 50:2365–2389. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Kita H: Eosinophils: Multifaceted
biological properties and roles in health and disease. Immunol Rev.
242:161–177. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Zhang Y, Yang X, Qian J, Gu X, Zhang J,
Liu J and Hu Z: Simultaneous detection of Mycoplasma
pneumoniae IgG and IgM using dual-label time resolved
fluoroimmunoassay. Anal Biochem. 548:1–6. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Seo YH, Kim JS, Seo SC, Seo WH, Yoo Y,
Song DJ and Choung JT: Predictive value of C-reactive protein in
response to macrolides in children with macrolide-resistant
Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia. Korean J Pediatr.
57:186–192. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Miyashita N, Obase Y, Ouchi K, Kawasaki K,
Kawai Y, Kobashi Y and Oka M: Clinical features of severe
Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia in adults admitted to an
intensive care unit. J Med Microbiol. 56:1625–1629. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Yang M, Meng F, Wang K, Gao M, Lu R, Li M,
Zhao F, Huang L, Zhang Y, Cheng G and Wang X: Interleukin 17A as a
good predictor of the severity of Mycoplasma pneumoniae
pneumonia in children. Sci Rep. 7:129342017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Wang YC, Liu JS, Tang HK, Nie J, Zhu JX,
Wen LL and Guo QL: miR-221 targets HMGA2 to inhibit
bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis by regulating
TGF-β1/Smad3-induced EMT. Int J Mol Med. 38:1208–1216. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Perry MM, Baker JE, Gibeon DS, Adcock IM
and Chung KF: Airway smooth muscle hyperproliferation is regulated
by microRNA-221 in severe asthma. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol.
50:7–17. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Lino Cardenas CL, Kaminski N and Kass DJ:
Micromanaging microRNAs: Using murine models to study microRNAs in
lung fibrosis. Drug Discov Today Dis Models. 10:e145–e151. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Zhu L, Gong X, Gong J, Xuan Y, Fu T, Ni S,
Xu L and Ji N: Notoginsenoside R1 upregulates miR-221-3p expression
to alleviate ox-LDL-induced apoptosis, inflammation, and oxidative
stress by inhibiting the TLR4/NF-κB pathway in HUVECs. Braz J Med
Biol Res. 53:e93462020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Gu H, Zhu Y, Zhou Y, Huang T, Zhang S,
Zhao D and Liu F: LncRNA MALAT1 affects Mycoplasma
pneumoniae pneumonia via NF-κB regulation. Front Cell Dev Biol.
8:5636932020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Wang CZ, Li XL, Wang QF, Mehendale SR and
Yuan CS: Selective fraction of Scutellaria baicalensis and
its chemopreventive effects on MCF-7 human breast cancer cells.
Phytomedicine. 17:63–68. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Takahashi H, Chen MC, Pham H, Angst E,
King JC, Park J, Brovman EY, Ishiguro H, Harris DM, Reber HA, et
al: Baicalein, a component of Scutellaria baicalensis,
induces apoptosis by Mcl-1 down-regulation in human pancreatic
cancer cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1813:1465–1474. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Chen LG, Hung LY, Tsai KW, Pan YS, Tsai
YD, Li YZ and Liu YW: Wogonin, a bioactive flavonoid in herbal tea,
inhibits inflammatory cyclooxygenase-2 gene expression in human
lung epithelial cancer cells. Mol Nutr Food Res. 52:1349–1357.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Ku SK and Bae JS: Baicalin, baicalein and
wogonin inhibits high glucose-induced vascular inflammation in
vitro and in vivo. BMB Rep. 48:519–524. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Yuan H, et al: Study on inhibitory effect
of baicalein on mycoplasma pneumonia and protection mechanism of
pulmonary epithelial cells of mice. J Chin Phys. 919–922.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Meng Y, Huo J, Lu W, Wang X, Zhang J and
Wang W: Modulation of P1 and EGF expression by baicalin. Int J Mol
Sci. 14:146–157. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Waites KB: New concepts of Mycoplasma
pneumoniae infections in children. Pediatr Pulmonol.
36:267–278. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Rottem S: Interaction of mycoplasmas with
host cells. Physiol Rev. 83:417–432. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Dimitrov DS, Franzoso G, Salman M,
Blumenthal R, Tarshis M, Barile MF and Rottem S: Mycoplasma
fermentans (incognitus strain) cells are able to fuse with T
lymphocytes. Clin Infect Dis. 17 (Suppl 1):S305–S308. 1993.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Chan ED and Welsh CH: Fulminant
Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia. West J Med. 162:133–142.
1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Lee H, Yun KW, Lee HJ and Choi EH:
Antimicrobial therapy of macrolide-resistant Mycoplasma
pneumoniae pneumonia in children. Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther.
16:23–34. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Ingle PV and Patel DM: C-reactive protein
in various disease condition-an overview. Asian J Pharm Clin Res.
4:9–13. 2011.
|
|
61
|
Dulay AT, Buhimschi IA, Zhao G, Bahtiyar
MO, Thung SF, Cackovic M and Buhimschi CS: Compartmentalization of
acute phase reactants interleukin-6, C-reactive protein and
procalcitonin as biomarkers of intra-amniotic infection and
chorioamnionitis. Cytokine. 76:236–243. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Baumeister D, Akhtar R, Ciufolini S,
Pariante CM and Mondelli V: Childhood trauma and adulthood
inflammation: A meta-analysis of peripheral C-reactive protein,
interleukin-6 and tumour necrosis factor-α. Mol Psychiatry.
21:642–649. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Meylan E, Tschopp J and Karin M:
Intracellular pattern recognition receptors in the host response.
Nature. 442:39–44. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Kolsuz M, Erginel S, Alataş O, Alataş F,
Metintaş M, Uçgun I, Harmanci E and Colak O: Acute phase reactants
and cytokine levels in unilateral community-acquired pneumonia.
Respiration. 70:615–622. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
O'Neill LA and Bowie AG: The family of
five: TIR-domain-containing adaptors in Toll-like receptor
signalling. Nat Rev Immunol. 7:353–364. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
66
|
Huang C, Pan L, Lin F, Dai H and Fu R:
Monoclonal antibody against Toll-like receptor 4 attenuates
ventilator-induced lung injury in rats by inhibiting MyD88- and
NF-κB-dependent signaling. Int J Mol Med. 39:693–700. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Prakash A, Mesa KR, Wilhelmsen K, Xu F,
Dodd-o JM and Hellman J: Alveolar macrophages and Toll-like
receptor 4 mediate ventilated lung ischemia reperfusion injury in
mice. Anesthesiology. 117:822–835. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
He Z, Gao Y, Deng Y, Li W, Chen Y, Xing S,
Zhao X, Ding J and Wang X: Lipopolysaccharide induces lung
fibroblast proliferation through Toll-like receptor 4 signaling and
the phosphoinositide3-kinase-Akt pathway. PLoS One. 7:e359262012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Fuchs Y and Steller H: Programmed cell
death in animal development and disease. Cell. 147:742–758. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Liu Y, Yin H, Zhao M and Lu Q: TLR2 and
TLR4 in autoimmune diseases: A comprehensive review. Clin Rev
Allergy Immunol. 47:136–147. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Perkins DJ and Vogel SN: Inflammation:
Species-specific TLR signalling-insight into human disease. Nat Rev
Rheumatol. 12:198–200. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
So EY, Kim SH, Park HH, Cho BS and Lee CE:
Corticosteroid inhibits IL-4 signaling through down-regulation of
IL-4 receptor and STAT6 activity. FEBS Lett. 518:53–59. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|