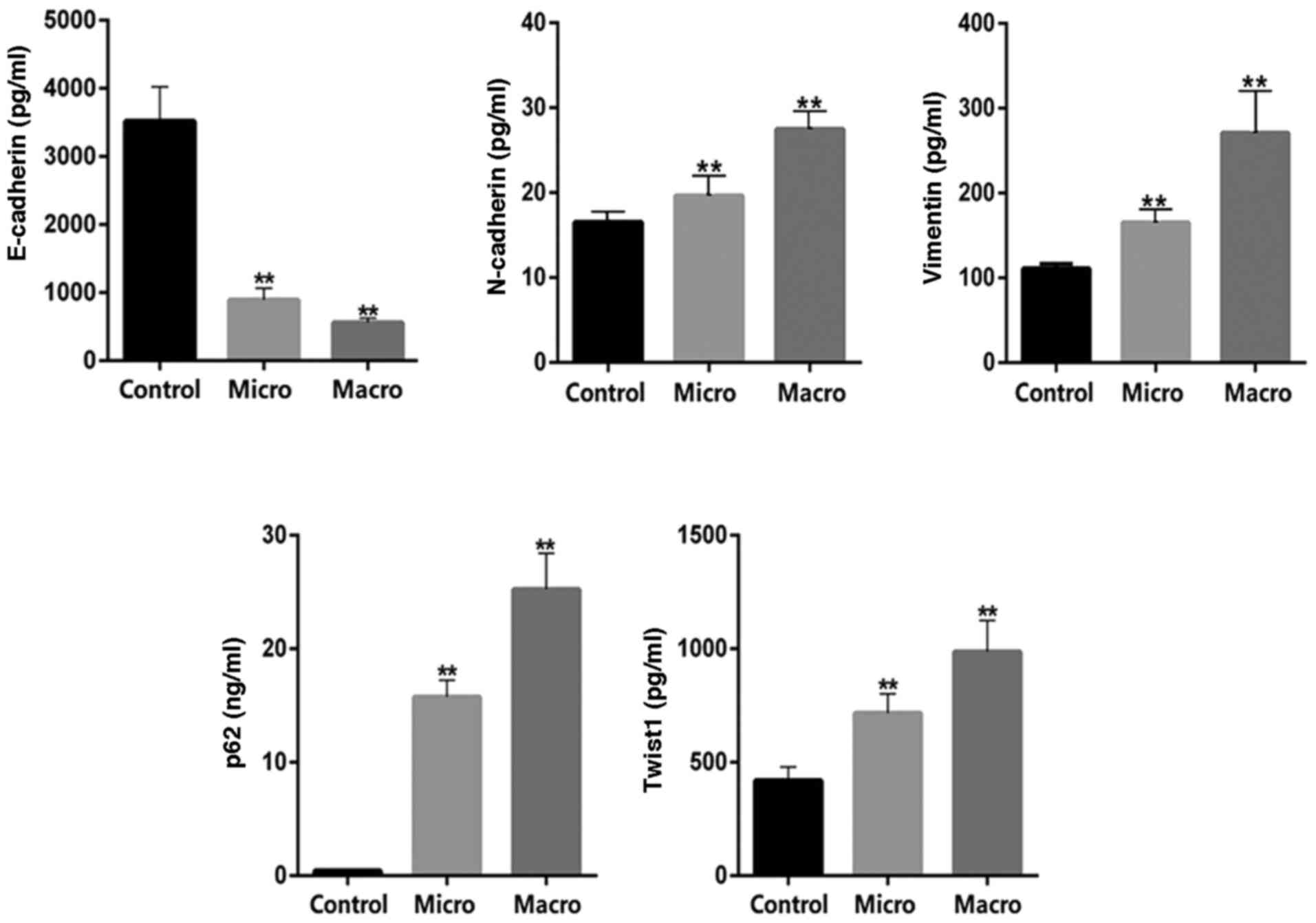
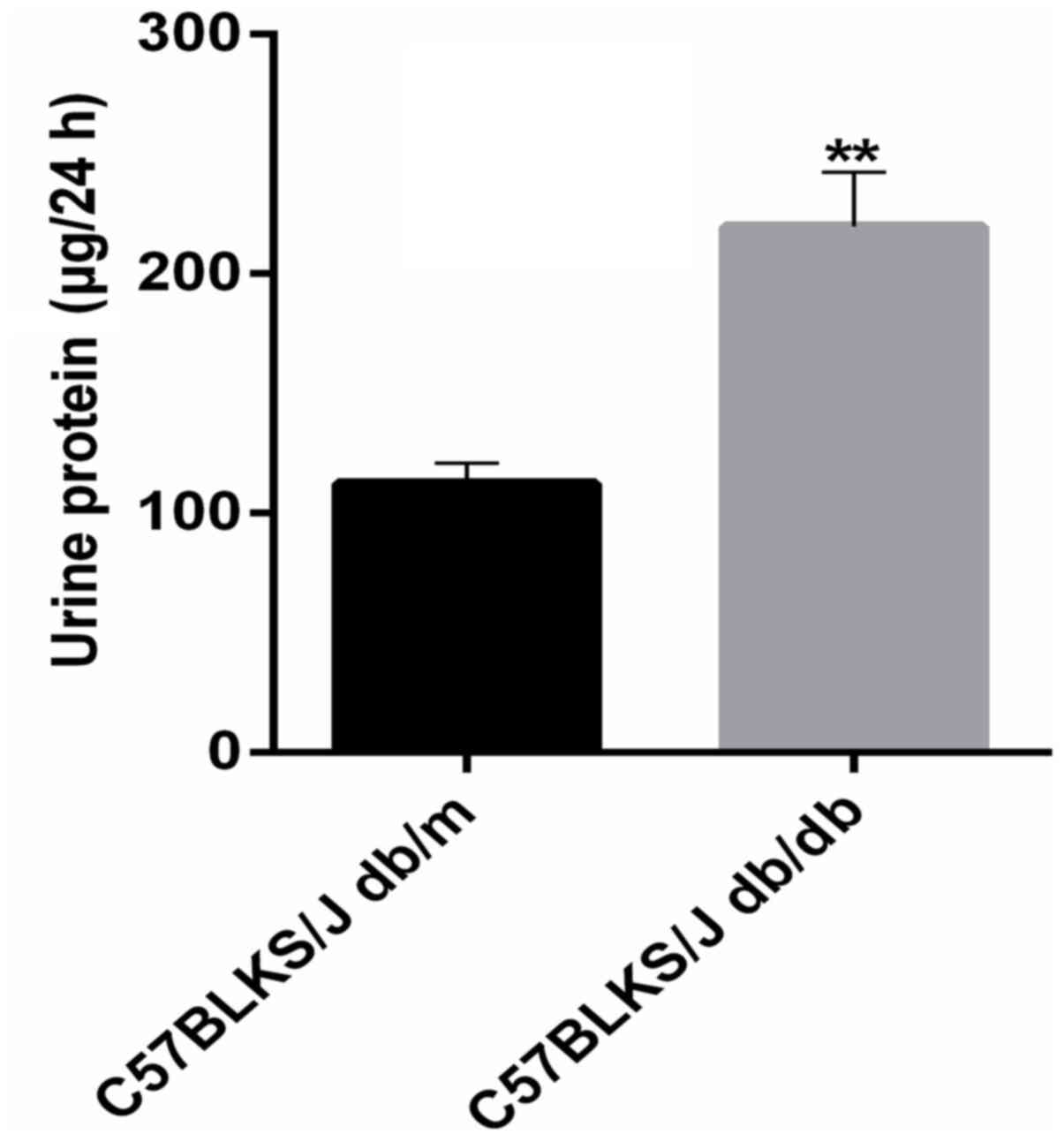
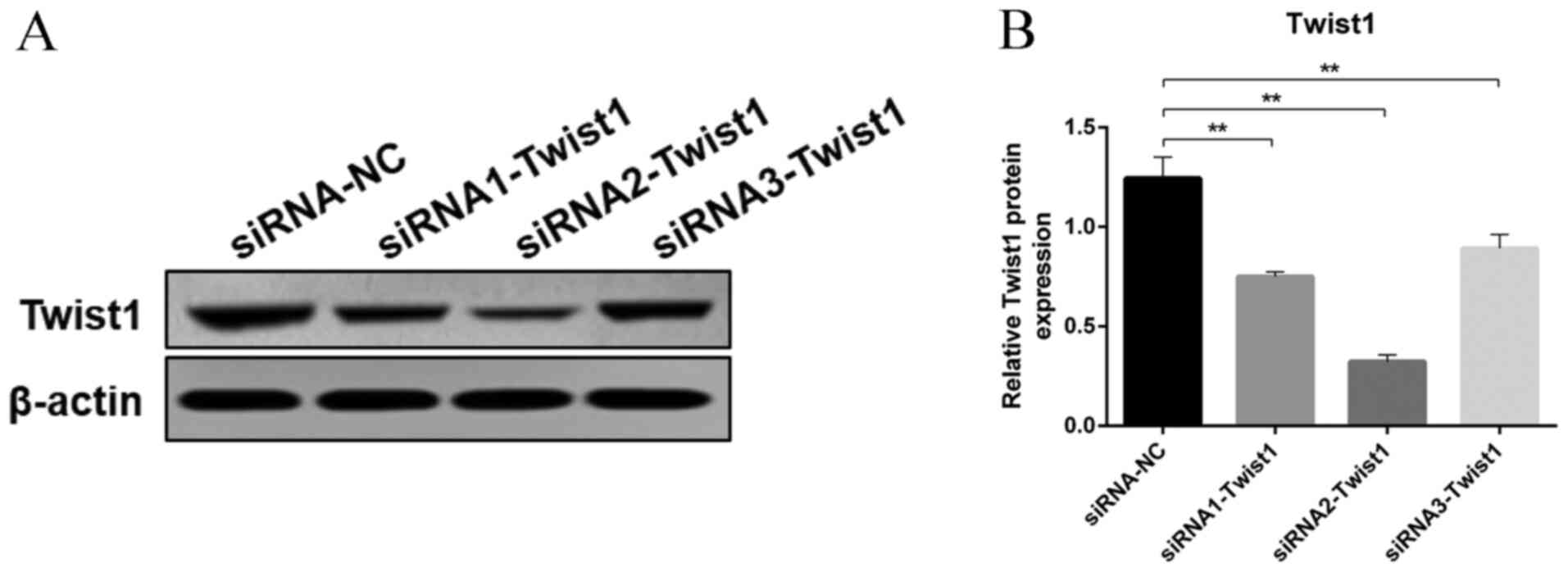
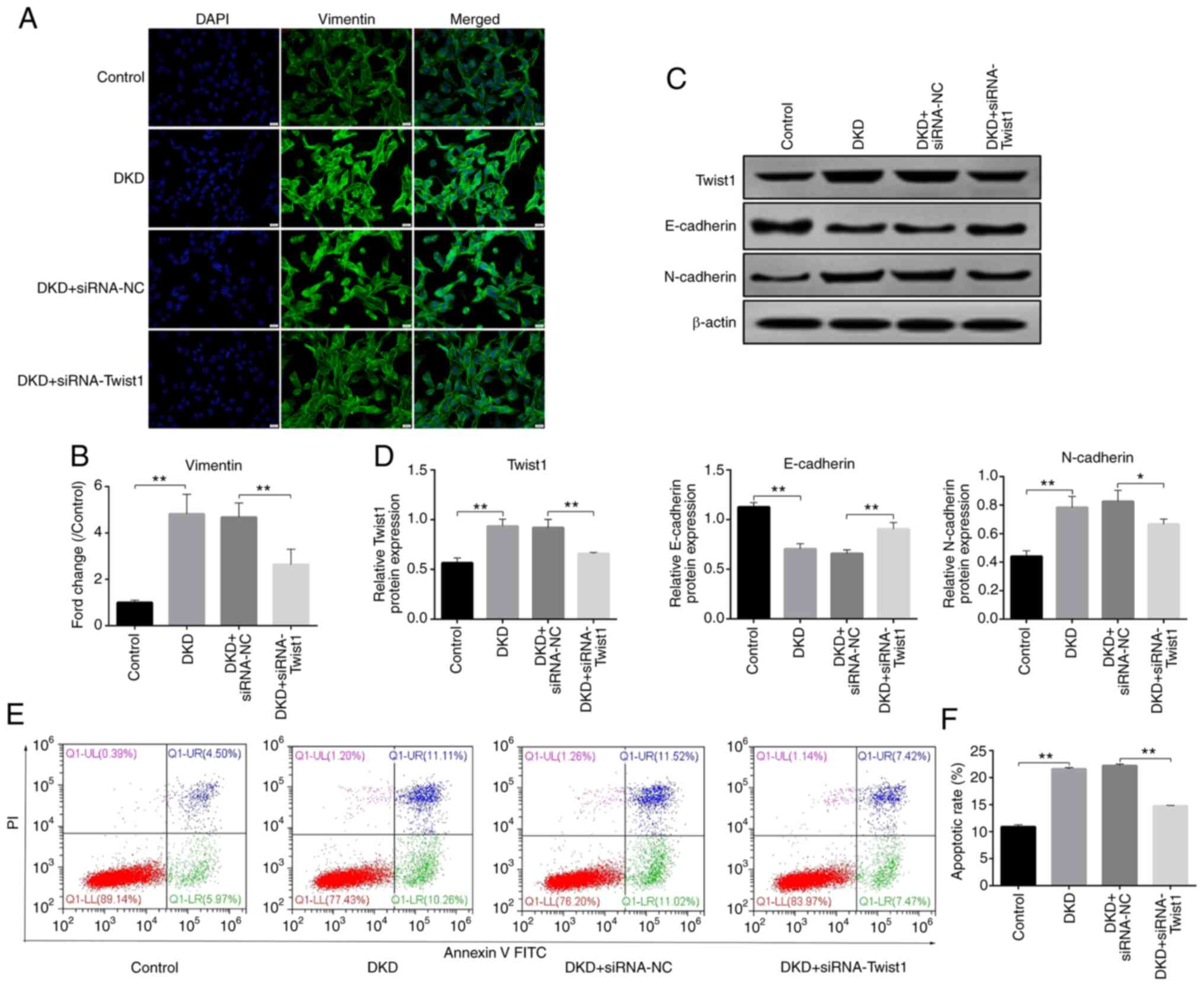
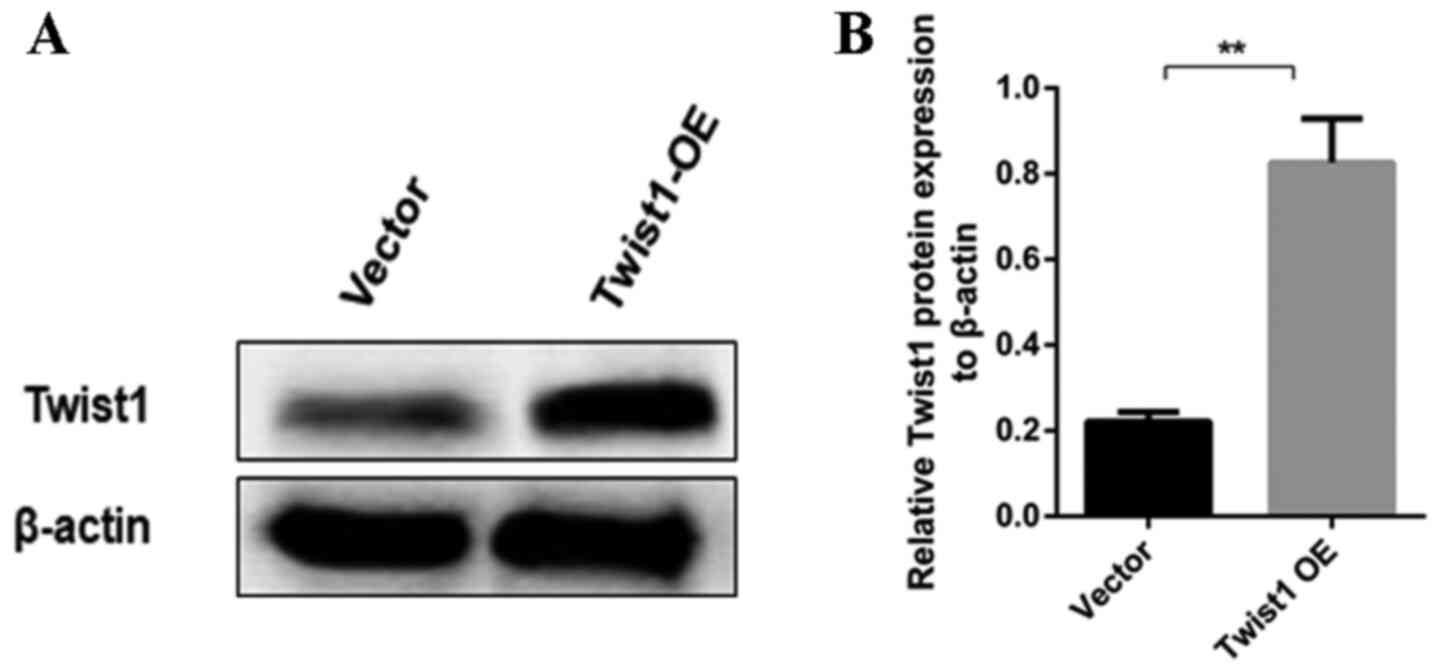
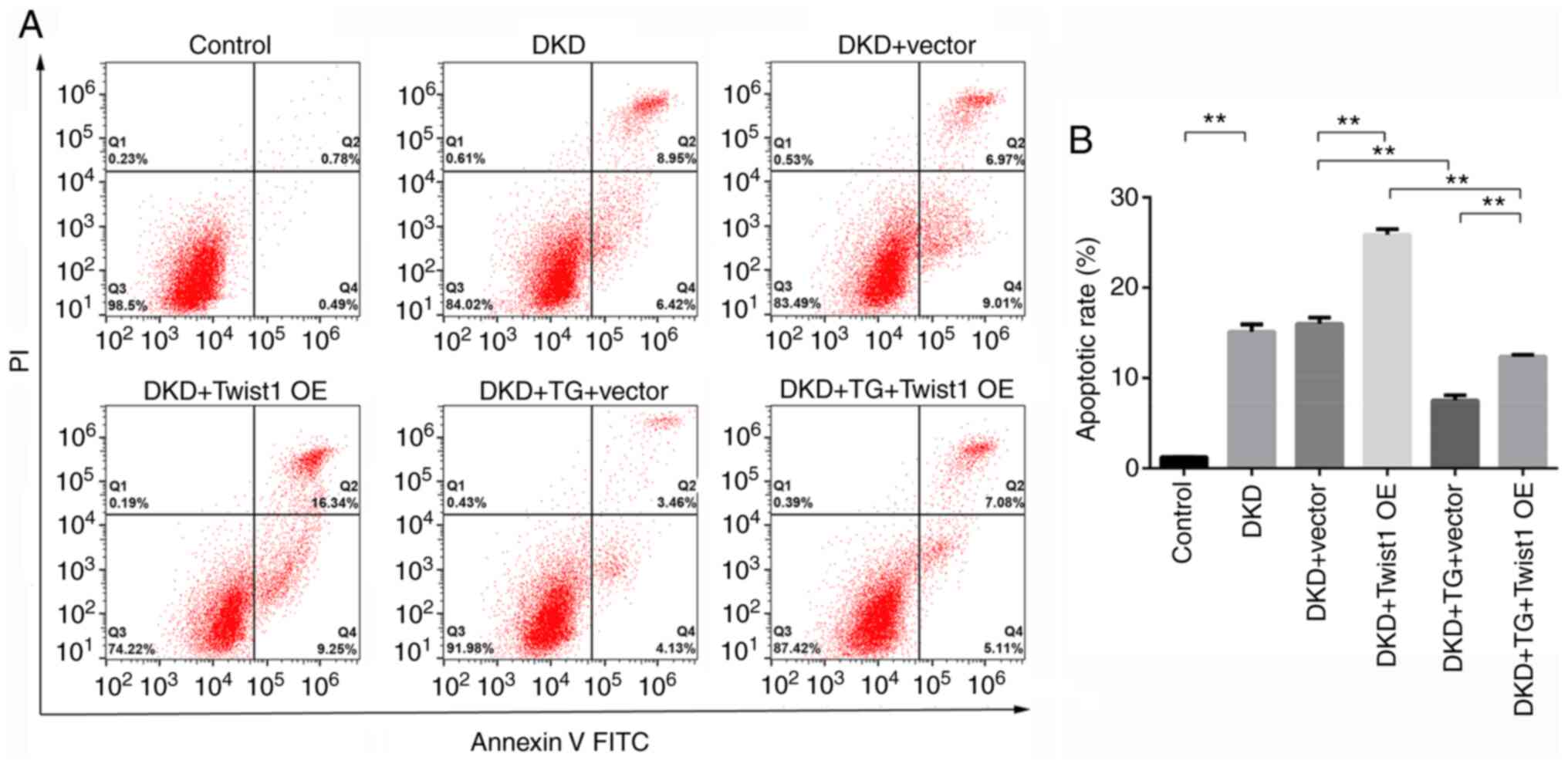
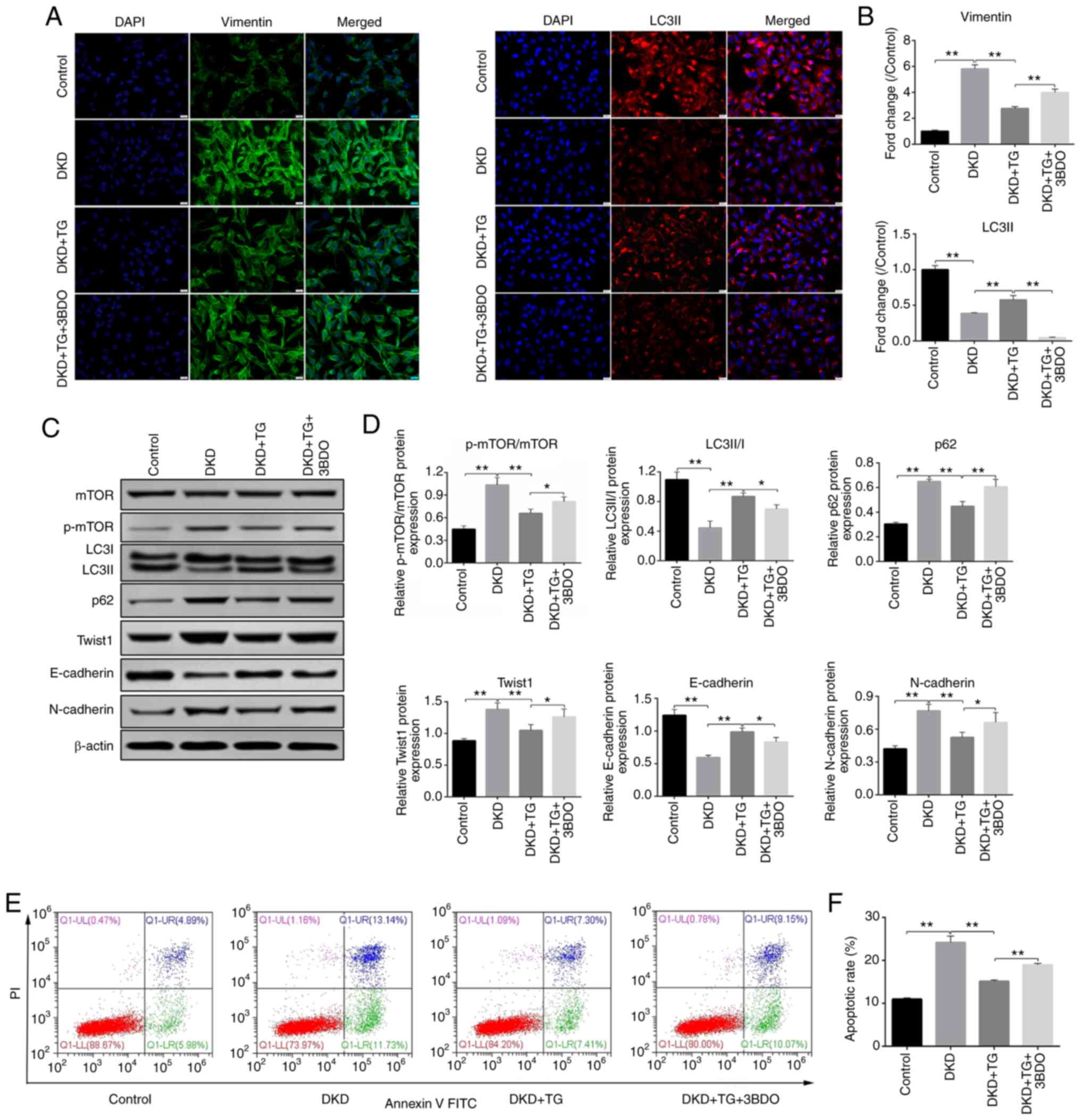
|
1
|
Saran R, Robinson B, Abbott KC, Agodoa
LYC, Albertus P, Ayanian J, Balkrishnan R, Bragg-Gresham J, Cao J,
Chen JL, et al: US Renal Data System 2016 Annual Data Report:
epidemiology of kidney disease in the United States. Am J Kidney
Dis. 69 (Suppl 1):A7–A8. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Matoba K, Takeda Y, Nagai Y, Kawanami D,
Utsunomiya K and Nishimura R: Unraveling the role of inflammation
in the pathogenesis of diabetic kidney disease. Int J Mol Sci.
20:33932019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Stitt-Cavanagh E, MacLeod L and Kennedy C:
The podocyte in diabetic kidney disease. ScientificWorldJournal.
9:1127–1139. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Guo J, Xia N, Yang L, Zhou S, Zhang Q,
Qiao Y and Liu Z: GSK-3beta and vitamin D receptor are involved in
beta-catenin and snail signaling in high glucose-induced
epithelial-mesenchymal transition of mouse podocytes. Cell Physiol
Biochem. 33:1087–1096. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Li Y, Kang YS, Dai C, Kiss LP, Wen X and
Liu Y: Epithelia-to-mesenchymal transition is a potential pathway
leading to podocyte dysfunction and proteinuria. Am J Pathol.
172:299–308. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Liu L, Fu W, Xu J, Shao L and Wang Y:
Effect of BMP7 on podocyte transdifferentiation and Smad7
expression induced by hyperglycemia. Clin Nephrol. 84:95–99. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Dai HY, Zheng M, Tang RN, Ni J, Ma KL, Li
Q and Liu BC: Effects of angiotensin receptor blocker on phenotypic
alterations of podocytes in early diabetic nephropathy. Am J Med
Sci. 341:207–214. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Kang YS, Li Y, Dai C, Kiss LP, Wu C and
Liu Y: Inhibition of integrin-linked kinase blocks podocyte
epithelial-mesenchymal transition and ameliorates proteinuria.
Kidney Int. 78:363–373. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Jin J, Zhang Z, Chen J, Liu Y, Chen Q and
Wang Q: Jixuepaidu Tang-1 inhibits epithelial-mesenchymal
transition and alleviates renal damage in DN mice through
suppressing long non-coding RNA LOC498759. Cell Cycle.
18:3125–3136. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Li CX, Xia M, Han WQ, Li XX, Zhang C,
Boini KM, Liu XC and Li PL: Reversal by growth hormone of
homocysteine-induced epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition through
membrane raft-redox signaling in podocytes. Cell Physiol Biochem.
27:691–702. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Yamaguchi Y, Iwano M, Suzuki D, Nakatani
K, Kimura K, Harada K, Kubo A, Akai Y, Toyoda M, Kanauchi M, et al:
Epithelial-mesenchymal transition as a potential explanation for
podocyte depletion in diabetic nephropathy. Am J Kidney Dis.
54:653–664. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Doublier S, Salvidio G, Lupia E,
Ruotsalainen V, Verzola D, Deferrari G and Camussi G: Nephrin
expression is reduced in human diabetic nephropathy: Evidence for a
distinct role for glycated albumin and angiotensin II. Diabetes.
52:1023–1030. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Ravikumar B, Sarkar S, Davies JE, Futter
M, Garcia-Arencibia M, Green-Thompson ZW, Jimenez-Sanchez M,
Korolchuk VI, Lichtenberg M, Luo S, et al: Regulation of mammalian
autophagy in physiology and pathophysiology. Physiol Rev.
90:1383–1435. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Yasuda-Yamahara M, Kume S, Tagawa A,
Maegawa H and Uzu T: Emerging role of podocyte autophagy in the
progression of diabetic nephropathy. Autophagy. 11:2385–2386. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Li G, Li CX, Xia M, Ritter JK, Gehr TW,
Boini K and Li PL: Enhanced epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition
associated with lysosome dysfunction in podocytes: role of
p62/Sequestosome 1 as a signaling hub. Cell Physiol Biochem.
35:1773–1786. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Shibue T and Weinberg RA: EMT, CSCs, and
drug resistance: The mechanistic link and clinical implications.
Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 14:611–629. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Meng J, Chen S, Han JX, Qian B, Wang XR,
Zhong WL, Qin Y, Zhang H, Gao WF, Lei YY, et al: Twist1 regulates
vimentin through Cul2 circular RNA to promote EMT in hepatocellular
carcinoma. Cancer Res. 78:4150–4162. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Liu W, Zhang B, Xu N, Wang MJ and Liu Q:
miR-326 regulates EMT and metastasis of endometrial cancer through
targeting TWIST1. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 21:3787–3793.
2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Qiang L and He YY: Autophagy deficiency
stabilizes TWIST1 to promote epithelial-mesenchymal transition.
Autophagy. 10:1864–1865. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Cui J, Chen X and Su JC: Advanced progress
of main pharmacology activities of triptolide. Zhongguo Zhongyao
Zazhi. 42:2655–2658. 2017.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Zhang H, Sun W, Wan Y, Che X, He F, Pu H
and Dou C: Preventive effects of multi-glycoside of Tripterygium
wilfordii on glomerular lesions in experimental diabetic
nephropathy. Zhongguo Zhongyao Zazhi. 35:1460–1465. 2010.(In
Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Ma RX, Zhao N and Zhang W: The effects and
mechanism of Tripterygium wilfordii Hook F combination with
irbesartan on urinary podocyte excretion in diabetic nephropathy
patients. Zhonghua Nei Ke Za Zhi. 52:469–473. 2013.(In Chinese).
PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Sethi S, Haas M, Markowitz GS, D'Agati VD,
Rennke HG, Jennette JC, Bajema IM, Alpers CE, Chang A, Cornell LD,
et al: Mayo clinic/renal pathology society consensus report on
pathologic classification, diagnosis, and reporting of GN. J Am Soc
Nephrol. 27:1278–1287. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
de Cabo R, Fürer-Galbán S, Anson RM,
Gilman C, Gorospe M and Lane MA: An in vitro model of caloric
restriction. Exp Gerontol. 38:631–639. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
National Research Council Committee for
the Update of the Guide for the C and Use of Laboratory A, . The
National Academies Collection: Reports funded by National
Institutes of Health. Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory
Animals National Academies Press Copyright© 2011.
National Academy of Sciences; Washington, DC: 2011
|
|
26
|
Zhan H, Jin J, Liang S, Zhao L, Gong J and
He Q: Tripterygium glycoside protects diabetic kidney disease mouse
serum-induced podocyte injury by upregulating autophagy and
downregulating β-arrestin-1. Histol Histopathol. 34:943–952.
2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Xia M, Conley SM, Li G, Li PL and Boini
KM: Inhibition of hyperhomocysteinemia-induced inflammasome
activation and glomerular sclerosis by NLRP3 gene deletion. Cell
Physiol Biochem. 34:829–841. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Rastaldi MP, Ferrario F, Giardino L,
Dell'Antonio G, Grillo C, Grillo P, Strutz F, Müller GA, Colasanti
G and D'Amico G: Epithelial-mesenchymal transition of tubular
epithelial cells in human renal biopsies. Kidney Int. 62:137–146.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Zeisberg M and Kalluri R: The role of
epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in renal fibrosis. J Mol Med
(Berl). 82:175–181. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Reidy K and Susztak K:
Epithelial-mesenchymal transition and podocyte loss in diabetic
kidney disease. Am J Kidney Dis. 54:590–593. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Srivastava SP, Koya D and Kanasaki K:
MicroRNAs in kidney fibrosis and diabetic nephropathy: Roles on EMT
and EndMT. BioMed Res Int. 2013:1254692013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Loeffler I and Wolf G:
Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in diabetic nephropathy: Fact
or Fiction? Cells. 4:631–652. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Hills CE and Squires PE: The role of TGF-β
and epithelial-to mesenchymal transition in diabetic nephropathy.
Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 22:131–139. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Li XY, Wang SS, Han Z, Han F, Chang YP,
Yang Y, Xue M, Sun B and Chen LM: Triptolide restores autophagy to
alleviate diabetic renal fibrosis through the
miR-141-3p/PTEN/Akt/mTOR pathway. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 9:48–56.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Liu Y: New insights into
epithelial-mesenchymal transition in kidney fibrosis. J Am Soc
Nephrol. 21:212–222. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Dai H, Liu Q and Liu B: Research progress
on mechanism of podocyte depletion in diabetic nephropathy. J
Diabetes Res. 2017:26152862017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Wang J, Chen N, Fang L, Feng Z, Li G,
Mucelli A, Zhang X and Zhou X: A systematic review about the
efficacy and safety of Tripterygium wilfordii Hook.f.
preparations used for the management of rheumatoid arthritis. Evid
Based Complement Alternat Med. 2018:15674632018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Gao Q, Shen W, Qin W, Zheng C, Zhang M,
Zeng C, Wang S, Wang J, Zhu X and Liu Z: Treatment of db/db
diabetic mice with triptolide: A novel therapy for diabetic
nephropathy. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 25:3539–3547. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Ge Y, Xie H, Li S, Jin B, Hou J, Zhang H,
Shi M and Liu Z: Treatment of diabetic nephropathy with
Tripterygium wilfordii Hook F extract: A prospective,
randomized, controlled clinical trial. J Transl Med. 11:134. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Guo H, Pan C, Chang B, Wu X, Guo J, Zhou
Y, Liu H, Zhu Z, Chang B and Chen L: Triptolide Improves Diabetic
Nephropathy by Regulating Th Cell Balance and Macrophage
Infiltration in Rat Models of Diabetic Nephropathy. Exp Clin
Endocrinol Diabetes. 124:389–398. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Chen ZH, Qin WS, Zeng CH, Zheng CX, Hong
YM, Lu YZ, Li LS and Liu ZH: Triptolide reduces proteinuria in
experimental membranous nephropathy and protects against
C5b-9-induced podocyte injury in vitro. Kidney Int. 77:974–988.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Gong J, Jin J, Zhao L, Li Y, Li Y and He
Q: Tripterygium glycoside protects against puromycin amino
nucleoside-induced podocyte injury by upregulating autophagy. Int J
Mol Med. 42:115–122. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Chan SF, Chen YY, Lin JJ, Liao CL, Ko YC,
Tang NY, Kuo CL, Liu KC and Chung JG: Triptolide induced cell death
through apoptosis and autophagy in murine leukemia WEHI-3 cells in
vitro and promoting immune responses in WEHI-3 generated leukemia
mice in vivo. Environ Toxicol. 32:550–568. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Zhao F, Huang W, Zhang Z, Mao L, Han Y,
Yan J and Lei M: Triptolide induces protective autophagy through
activation of the CaMKKβ-AMPK signaling pathway in prostate cancer
cells. Oncotarget. 7:5366–5382. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Xin W, Li Z, Xu Y, Yu Y, Zhou Q, Chen L
and Wan Q: Autophagy protects human podocytes from high
glucose-induced injury by preventing insulin resistance.
Metabolism. 65:1307–1315. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Rodon J, Dienstmann R, Serra V and
Tabernero J: Development of PI3K inhibitors: Lessons learned from
early clinical trials. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 10:143–153. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Han F, Xue M, Chang Y, Li X, Yang Y, Sun B
and Chen L: Triptolide suppresses glomerular mesangial cell
proliferation in diabetic nephropathy is associated with inhibition
of PDK1/Akt/mTOR pathway. Int J Biol Sci. 13:1266–1275. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Lamouille S and Derynck R: Cell size and
invasion in TGF-beta-induced epithelial to mesenchymal transition
is regulated by activation of the mTOR pathway. J Cell Biol.
178:437–451. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Wang F, Li H, Yan XG, Zhou ZW, Yi ZG, He
ZX, Pan ST, Yang YX, Wang ZZ, Zhang X, et al: Alisertib induces
cell cycle arrest and autophagy and suppresses
epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition involving PI3K/Akt/mTOR and
sirtuin 1-mediated signaling pathways in human pancreatic cancer
cells. Drug Des Devel Ther. 9:575–601. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|