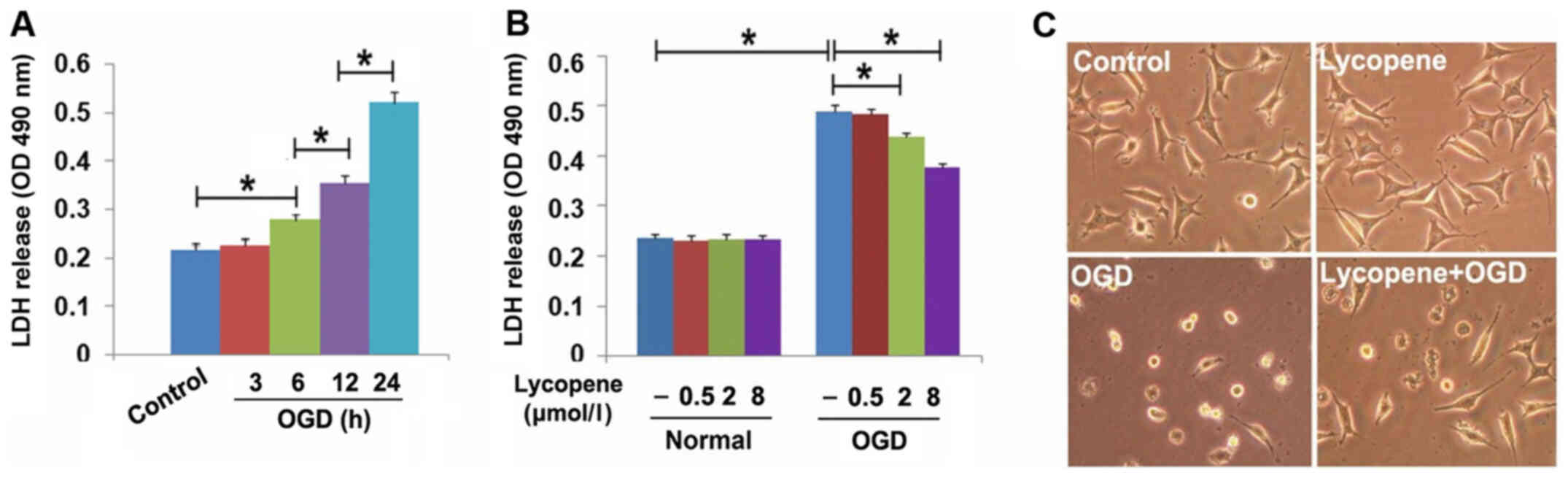
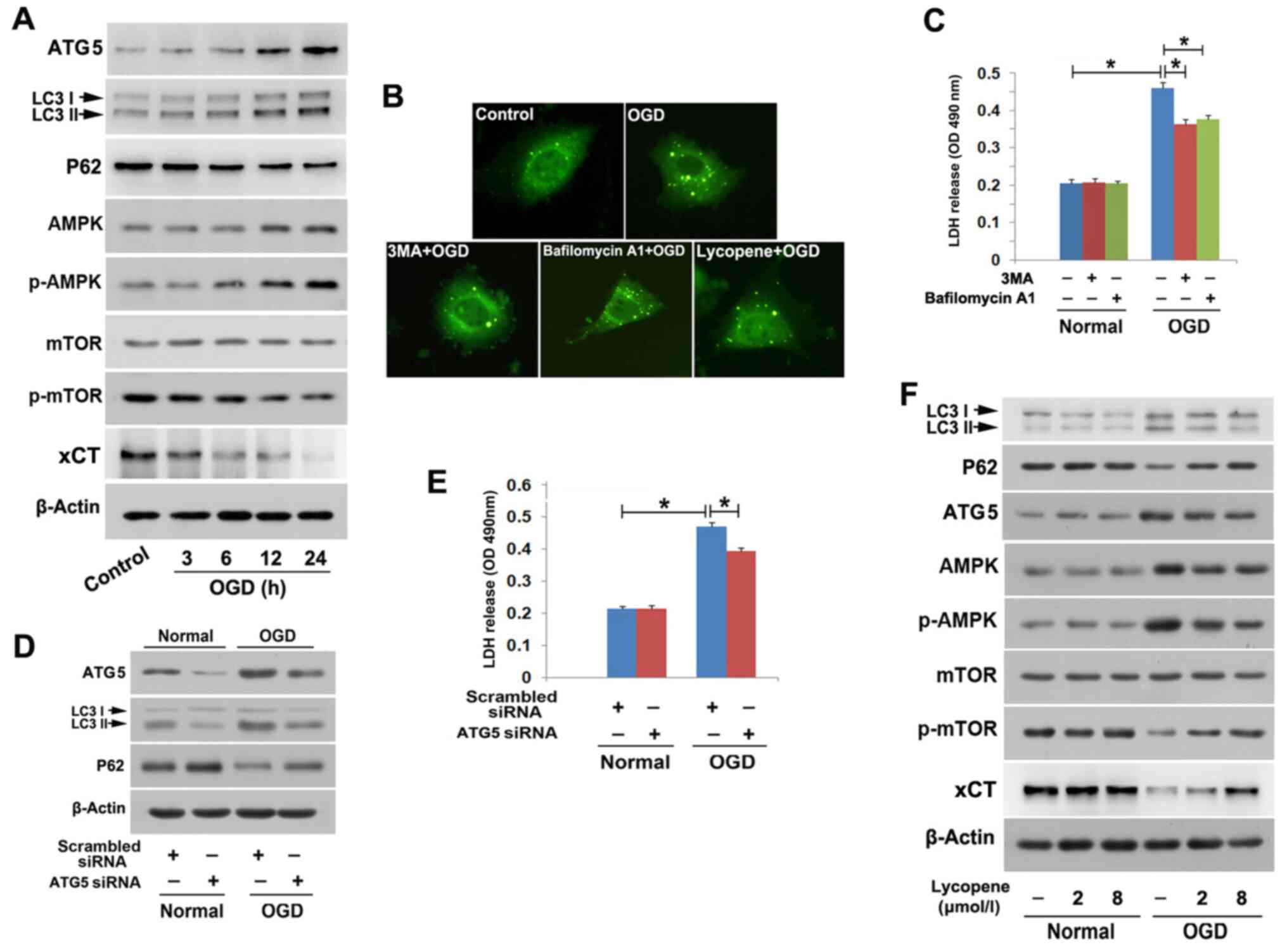
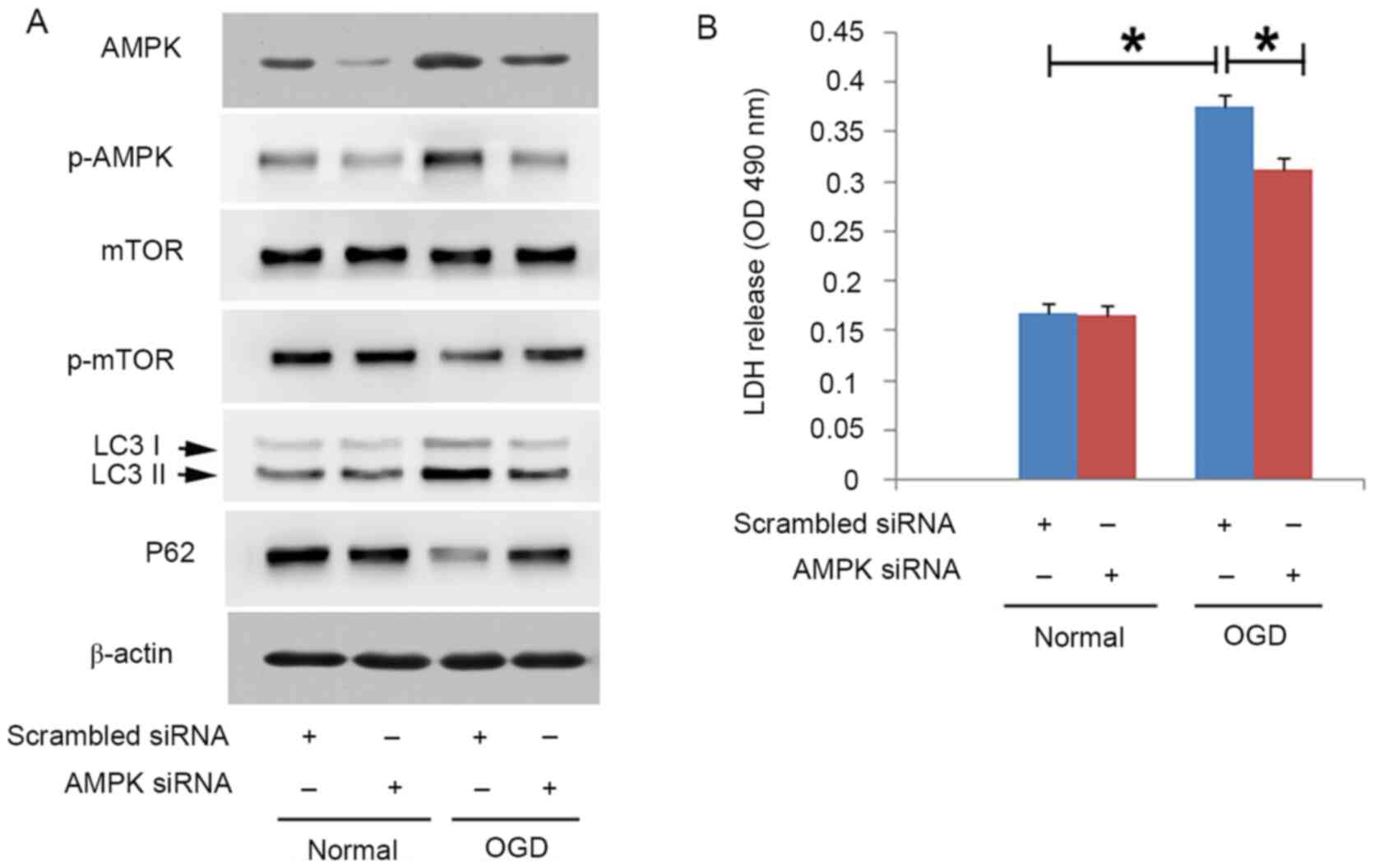
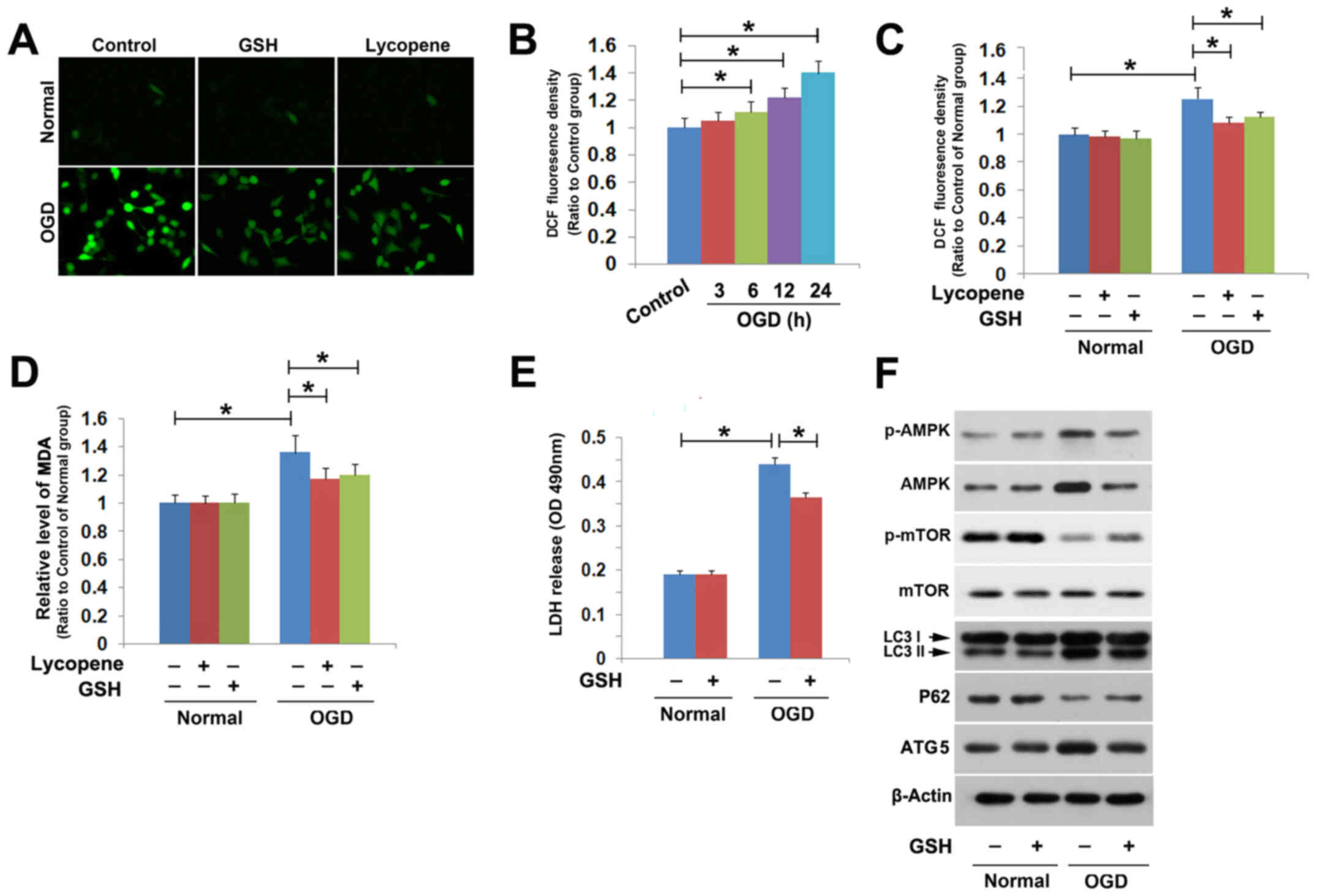
|
1
|
Arumugam TV, Baik SH, Balaganapathy P,
Sobey CG, Mattson MP and Jo DG: Notch signaling and neuronal death
in stroke. Prog Neurobiol. 165-167:103–116. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Kirino T: Delayed neuronal death in the
gerbil hippocampus following ischemia. Brain Res. 239:57–69. 1982.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Li Y, Luo Y, Luo T, Lu B, Wang C, Zhang Y,
Piao M, Feng C and Ge P: Trehalose inhibits protein aggregation
caused by transient ischemic insults through preservation of
proteasome activity, not via induction of autophagy. Mol Neurobiol.
54:6857–6869. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Ouyang L, Shi Z, Zhao S, Wang FT, Zhou TT,
Liu B and Bao JK: Programmed cell death pathways in cancer: A
review of apoptosis, autophagy and programmed necrosis. Cell
Prolif. 45:487–498. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Xu Y, Tian Y, Tian Y, Li X and Zhao P:
Autophagy activation involved in hypoxic-ischemic brain injury
induces cognitive and memory impairment in neonatal rats. J
Neurochem. 139:795–805. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Luo CL, Li BX, Li QQ, Chen XP, Sun YX, Bao
HJ, Dai DK, Shen YW, Xu HF, Ni H, et al: Autophagy is involved in
traumatic brain injury-induced cell death and contributes to
functional outcome deficits in mice. Neuroscience. 184:54–63. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Zheng Y, Hou J, Liu J, Yao M, Li L, Zhang
B, Zhu H and Wang Z: Inhibition of autophagy contributes to
melatonin-mediated neuroprotection against transient focal cerebral
ischemia in rats. J Pharmacol Sci. 124:354–364. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Luo T, Liu G, Ma H, Lu B, Xu H, Wang Y, Wu
J, Ge P and Liang J: Inhibition of autophagy via activation of
PI3K/Akt pathway contributes to the protection of ginsenoside Rb1
against neuronal death caused by ischemic insults. Int J Mol Sci.
15:15426–15442. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Chen D, Huang C and Chen Z: A review for
the pharmacological effect of lycopene in central nervous system
disorders. Biomed Pharmacother. 111:791–801. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Tong C, Peng C, Wang L, Zhang L, Yang X,
Xu P, Li J, Delplancke T, Zhang H and Qi H: Intravenous
administration of lycopene, a tomato extract, protects against
myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury. Nutrients. 8:1382016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Kaya C, Karabulut R, Turkyilmaz Z, Sonmez
K, Kulduk G, Gülbahar Ö, Köse F and Basaklar AC: Lycopene has
reduced renal damage histopathologically and biochemically in
experimental renal ischemia-reperfusion injury. Ren Fail.
37:1390–1395. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Hekimoglu A, Kurcer Z, Aral F, Baba F,
Sahna E and Atessahin A: Lycopene, an antioxidant carotenoid,
attenuates testicular injury caused by ischemia/reperfusion in
rats. Tohoku J Exp Med. 218:141–147. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Bayramoglu G, Bayramoglu A, Altuner Y,
Uyanoglu M and Colak S: The effects of lycopene on hepatic
ischemia/reperfusion injury in rats. Cytotechnology. 67:487–491.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Hsiao G, Fong TH, Tzu NH, Lin KH, Chou DS
and Sheu JR: A potent antioxidant, lycopene, affords
neuroprotection against microglia activation and focal cerebral
ischemia in rats. In Vivo. 18:351–356. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Lei X, Lei L, Zhang Z and Cheng Y:
Neuroprotective effects of lycopene pretreatment on transient
global cerebral ischemia reperfusion in rats: The role of the
Nrf2/HO 1 signaling pathway. Mol Med Rep. 13:412–418. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Fujita K, Yoshimoto N, Kato T, Imada H,
Matsumoto G, Inakuma T, Nagata Y and Miyachi E: Lycopene inhibits
ischemia/reperfusion-induced neuronal apoptosis in gerbil
hippocampal tissue. Neurochem Res. 38:461–469. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Prakash A and Kumar A: Lycopene protects
against memory impairment and mito-oxidative damage induced by
colchicine in rats: An evidence of nitric oxide signaling. Eur J
Pharmacol. 721:373–381. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Kaur H, Chauhan S and Sandhir R:
Protective effect of lycopene on oxidative stress and cognitive
decline in rotenone induced model of Parkinson's disease. Neurochem
Res. 36:1435–1443. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Qu M, Nan X, Gao Z, Guo B, Liu B and Chen
Z: Protective effects of lycopene against methylmercury-induced
neurotoxicity in cultured rat cerebellar granule neurons. Brain
Res. 1540:92–102. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Qu M, Li L, Chen C, Li M, Pei L, Chu F,
Yang J, Yu Z, Wang D and Zhou Z: Protective effects of lycopene
against amyloid β-induced neurotoxicity in cultured rat cortical
neurons. Neurosci Lett. 505:286–290. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Qu M, Zhou Z, Chen C, Li M, Pei L, Chu F,
Yang J, Wang Y, Li L, Liu C, et al: Lycopene protects against
trimethyltin-induced neurotoxicity in primary cultured rat
hippocampal neurons by inhibiting the mitochondrial apoptotic
pathway. Neurochem Int. 59:1095–1103. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
di Matteo V, Pierucci M, Di Giovanni G,
Dragani LK, Murzilli S, Poggi A and Esposito E: Intake of
tomato-enriched diet protects from 6-hydroxydopamine-induced
degeneration of rat nigral dopaminergic neurons. J Neural Transm
Suppl. 73:333–341. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Zhao Y, Xin Z, Li N, Chang S, Chen Y, Geng
L, Chang H, Shi H and Chang YZ: Nano-liposomes of lycopene reduces
ischemic brain damage in rodents by regulating iron metabolism.
Free Radic Biol Med. 124:1–11. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Chen F, Sun ZW, Ye LF, Fu GS, Mou Y and Hu
SJ: Lycopene protects against apoptosis in hypoxia/reoxygenation
induced H9C2 myocardioblast cells through increased autophagy. Mol
Med Rep. 11:1358–1365. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Zeng YC, Peng LS, Zou L, Huang SF, Xie Y,
Mu GP, Zeng XH, Zhou XL and Zeng YC: Protective effect and
mechanism of lycopene on endothelial progenitor cells (EPCs) from
type 2 diabetes mellitus rats. Biomed Pharmacother. 92:86–94. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Wang HF, Wang ZQ, Ding Y, Piao MH, Feng
CS, Chi GF, Luo YN and Ge PF: Endoplasmic reticulum stress
regulates oxygen-glucose deprivation-induced parthanatos in human
SH-SY5Y cells via improvement of intracellular ROS. CNS Neurosci
Ther. 24:29–38. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Cui L, Li C, Gao G, Zhuo Y, Yang L, Cui N
and Zhang S: FTY720 inhibits the activation of pancreatic stellate
cells by promoting apoptosis and suppressing autophagy via the
AMPK/mTOR pathway. Life Sci. 217:243–250. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Gao Z, Wang H, Zhang B, Wu X, Zhang Y, Ge
P, Chi G and Liang J: Trehalose inhibits
H2O2-induced autophagic death in dopaminergic
SH-SY5Y cells via mitigation of ROS-dependent endoplasmic reticulum
stress and AMPK activation. Int J Med Sci. 15:1014–1024. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Shin CS, Mishra P, Watrous JD, Carelli V,
D'Aurelio M, Jain M and Chan DC: The glutamate/cystine xCT
antiporter antagonizes glutamine metabolism and reduces nutrient
flexibility. Nat Commun. 8:150742017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Mariño G, Madeo F and Kroemer G: Autophagy
for tissue homeostasis and neuroprotection. Curr Opin Cell Biol.
23:198–206. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Wang T, Zhu L, Liu H, Yu G and Guo Y:
Picroside II protects SH-SY5Y cells from autophagy and apoptosis
following oxygen glucose deprivation/reoxygen injury by inhibiting
JNK signal pathway. Anat Rec (Hoboken). 302:2245–2254. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Ding C, Zhang J, Li B, Ding Z, Cheng W,
Gao F, Zhang Y, Xu Y and Zhang S: Cornin protects SH SY5Y cells
against oxygen and glucose deprivation induced autophagy through
the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway. Mol Med Rep. 17:87–92. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Hwang S, Lim JW and Kim H: Inhibitory
effect of lycopene on amyloid-β-induced apoptosis in neuronal
cells. Nutrients. 9:92017.
|
|
34
|
Wu A, Liu R, Dai W, Jie Y, Yu G, Fan X and
Huang Q: Lycopene attenuates early brain injury and inflammation
following subarachnoid hemorrhage in rats. Int J Clin Exp Med.
8:14316–14322. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Lin CJ, Chen TH, Yang LY and Shih CM:
Resveratrol protects astrocytes against traumatic brain injury
through inhibiting apoptotic and autophagic cell death. Cell Death
Dis. 5:e11472014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Wang M, Li YJ, Ding Y, Zhang HN, Sun T,
Zhang K, Yang L, Guo YY, Liu SB, Zhao MG, et al: Silibinin prevents
autophagic cell death upon oxidative stress in cortical neurons and
cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury. Mol Neurobiol. 53:932–943.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Li YY, Xiang Y, Zhang S, Wang Y, Yang J,
Liu W and Xue FT: Thioredoxin-2 protects against oxygen-glucose
deprivation/reperfusion injury by inhibiting autophagy and
apoptosis in H9c2 cardiomyocytes. Am J Transl Res. 9:1471–1482.
2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Zhang L, Wei J, Ren L, Zhang J, Wang J,
Jing L, Yang M, Yu Y, Sun Z and Zhou X: Endosulfan induces
autophagy and endothelial dysfunction via the AMPK/mTOR signaling
pathway triggered by oxidative stress. Environ Pollut. 220:843–852.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Wang L, Mao N, Tan RZ, Wang HL, Wen J, Liu
YH, Furhad M and Fan JM: Ginsenoside Rg1 reduces
aldosterone-induced autophagy via the AMPK/mTOR pathway in NRK-52E
cells. Int J Mol Med. 36:518–526. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Sun B, Ou H, Ren F, Huan Y, Zhong T, Gao M
and Cai H: Propofol inhibited autophagy through
Ca2+/CaMKKβ/AMPK/mTOR pathway in OGD/R-induced neuron
injury. Mol Med. 24:582018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Niu G, Zhu D, Zhang X, Wang J, Zhao Y and
Wang X: Role of hypoxia-inducible factors 1α (HIF1α) in SH-SY5Y
cell autophagy induced by oxygen-glucose deprivation. Med Sci
Monit. 24:2758–2766. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Upadhyay J, Kesharwani RK and Misra K:
Comparative study of antioxidants as cancer preventives through
inhibition of HIF-1 alpha activity. Bioinformation. 4:233–236.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Feng C, Luo T, Zhang S, Liu K, Zhang Y,
Luo Y and Ge P: Lycopene protects human SH SY5Y neuroblastoma cells
against hydrogen peroxide induced death via inhibition of oxidative
stress and mitochondria associated apoptotic pathways. Mol Med Rep.
13:4205–4214. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Xiang C, Wang Y, Zhang H and Han F: The
role of endoplasmic reticulum stress in neurodegenerative disease.
Apoptosis. 22:1–26. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Xu J, Hu H, Chen B, Yue R, Zhou Z, Liu Y,
Zhang S, Xu L, Wang H and Yu Z: Lycopene protects against
hypoxia/reoxygenation injury by alleviating er stress induced
apoptosis in neonatal mouse cardiomyocytes. PLoS One.
10:e01364432015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Gao Y, Jia P, Shu W and Jia D: The
protective effect of lycopene on hypoxia/reoxygenation-induced
endoplasmic reticulum stress in H9C2 cardiomyocytes. Eur J
Pharmacol. 774:71–79. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|