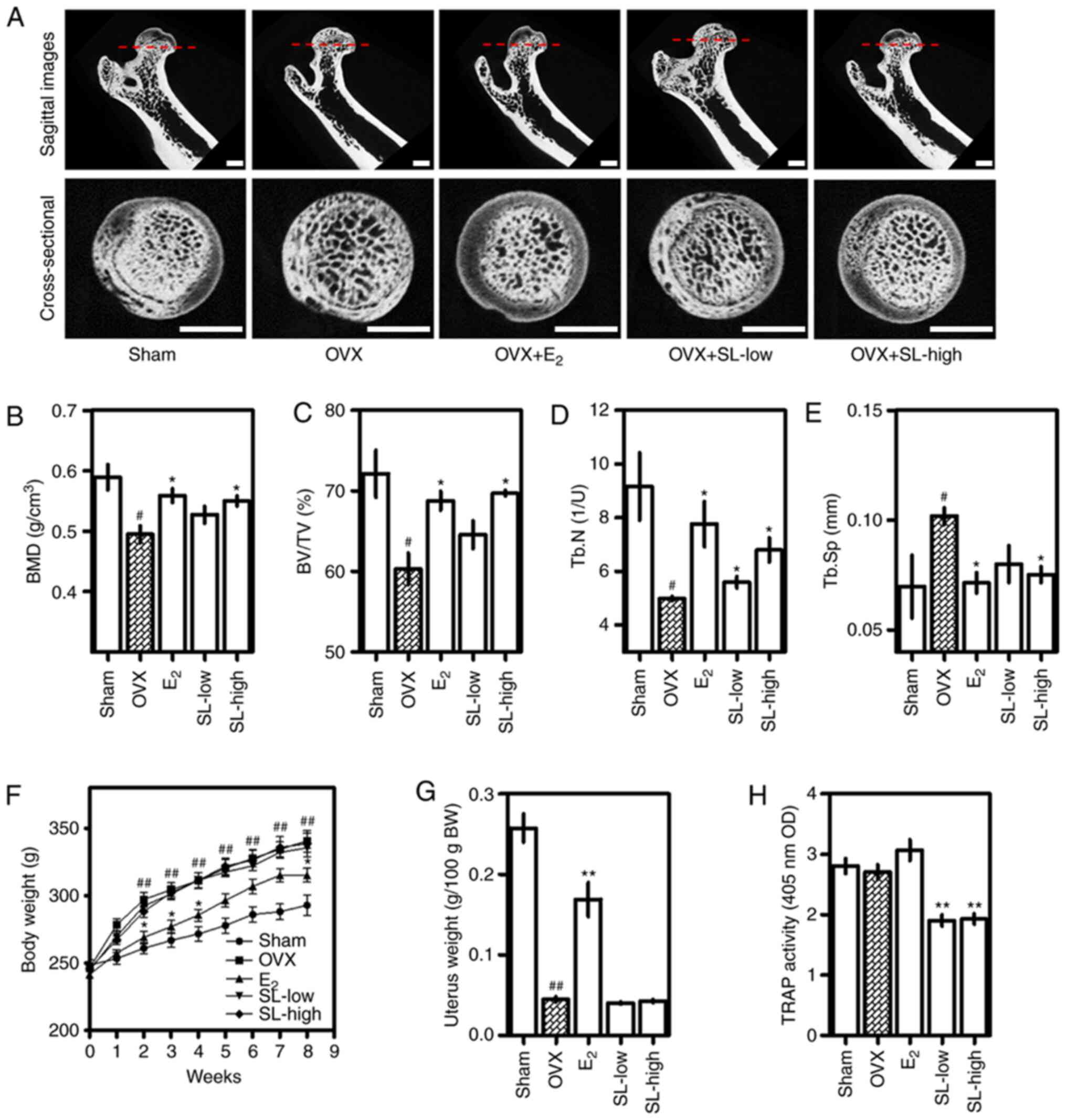
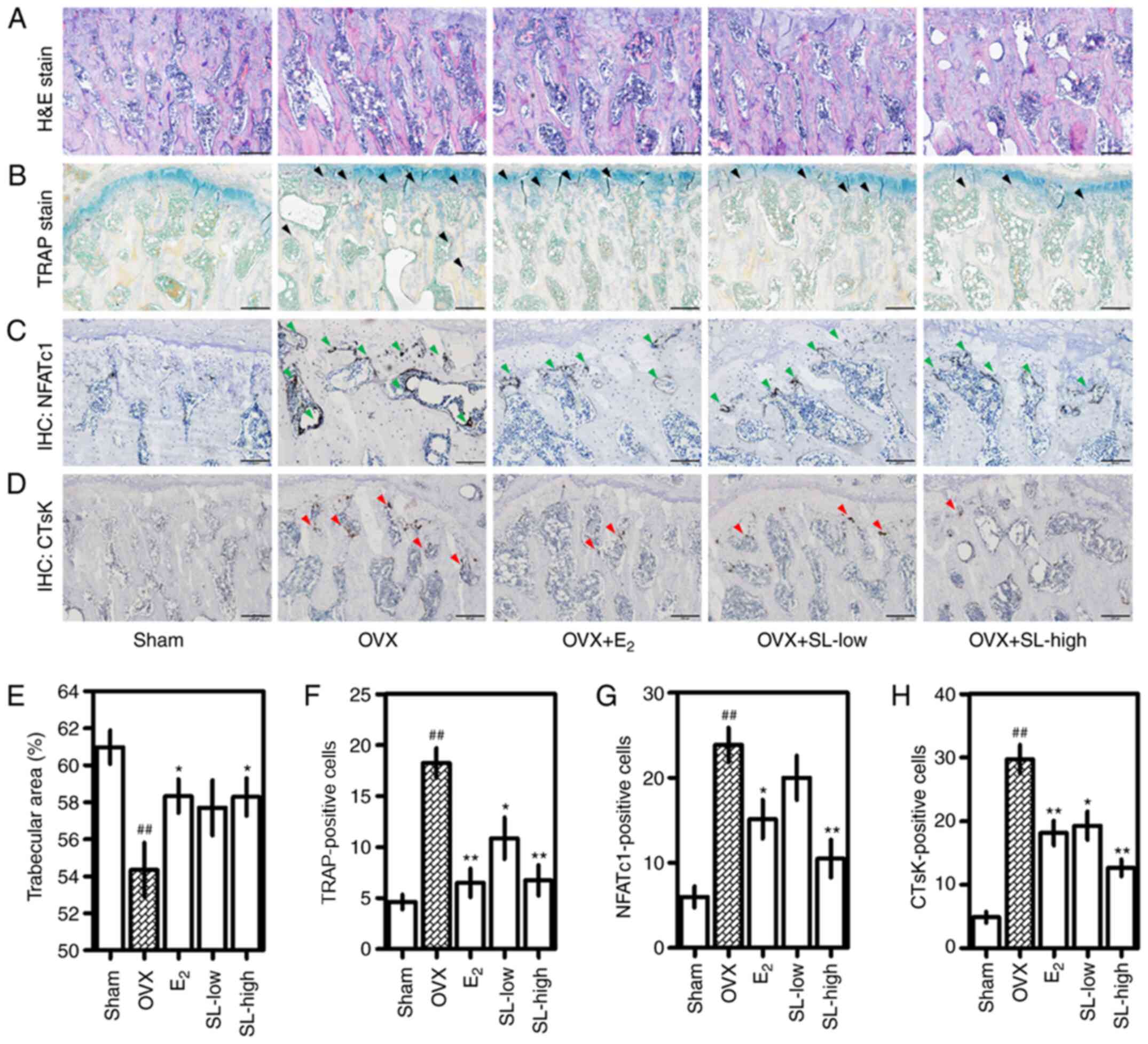
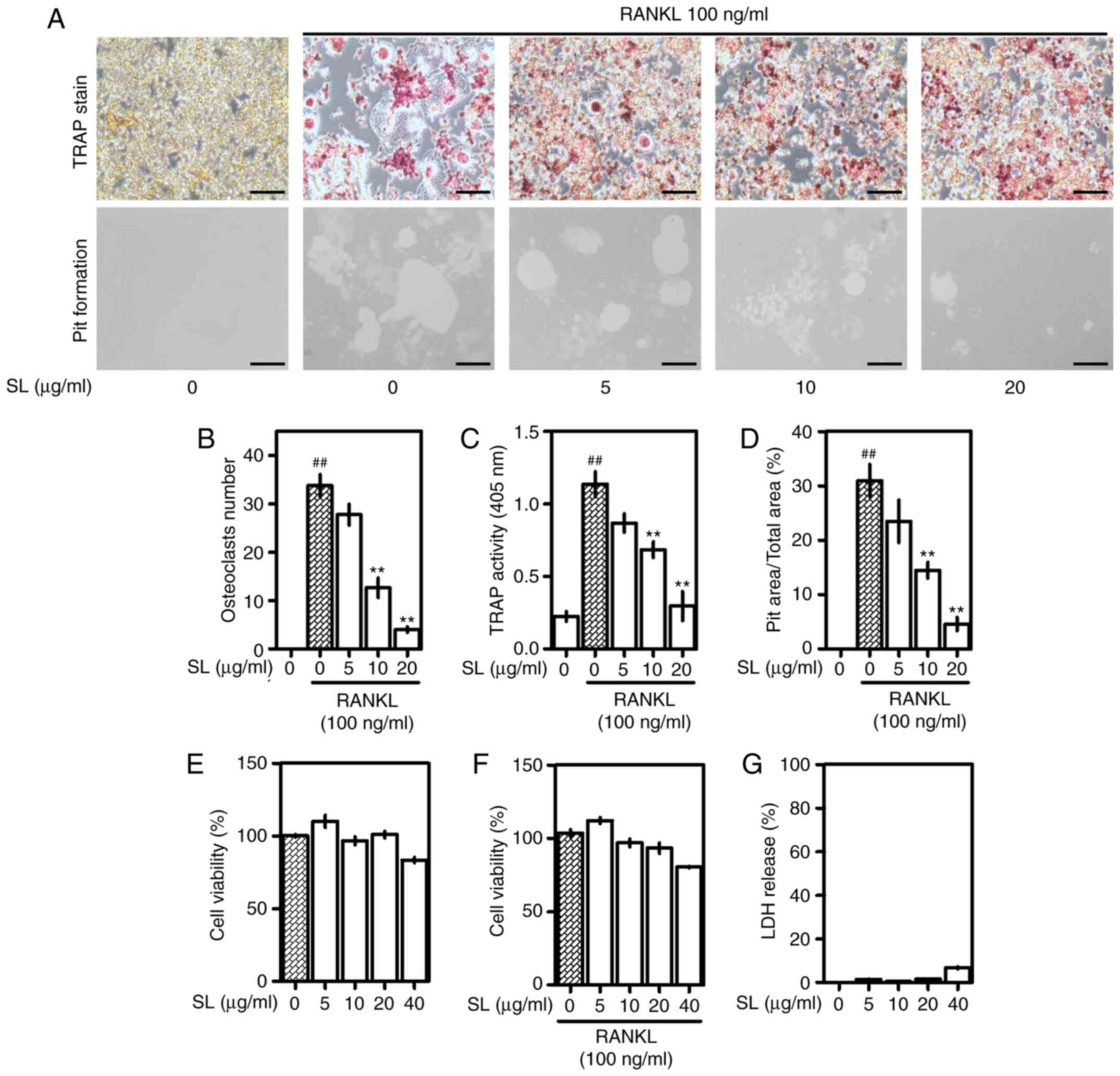
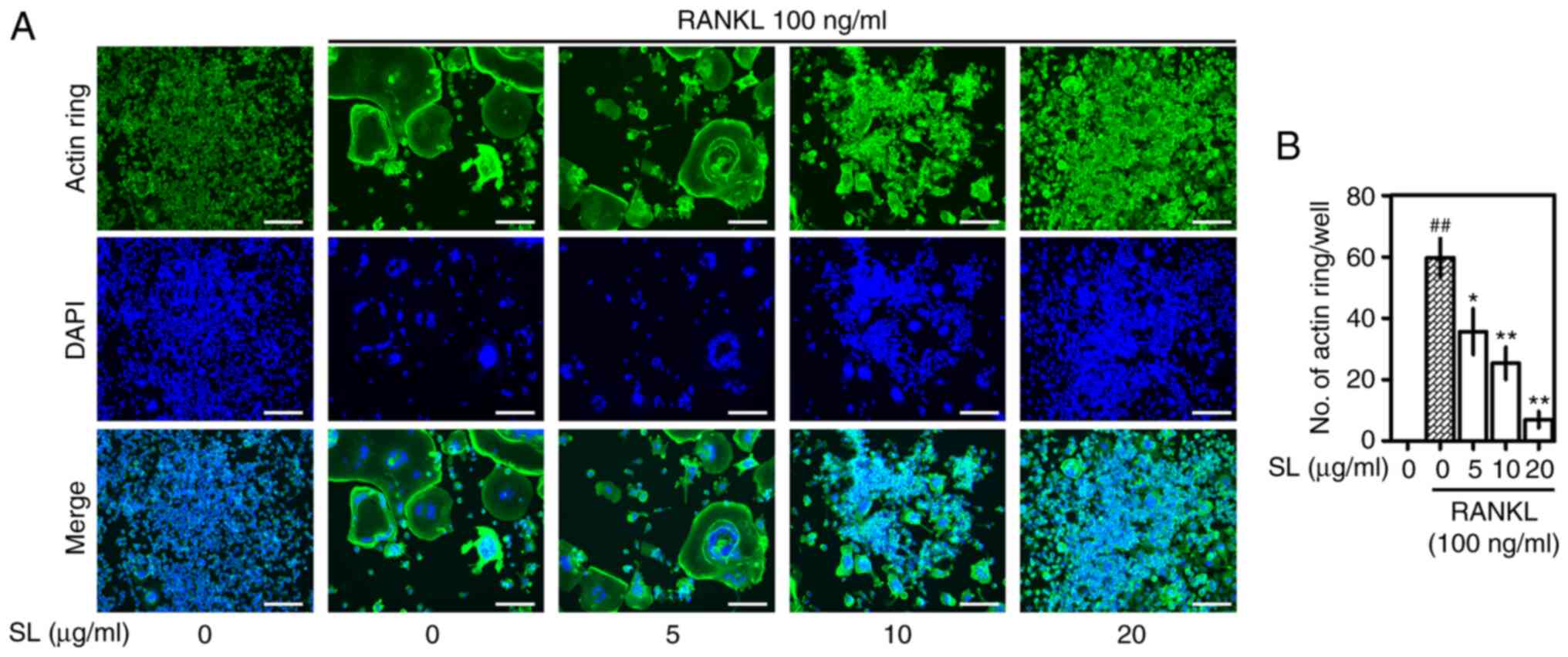
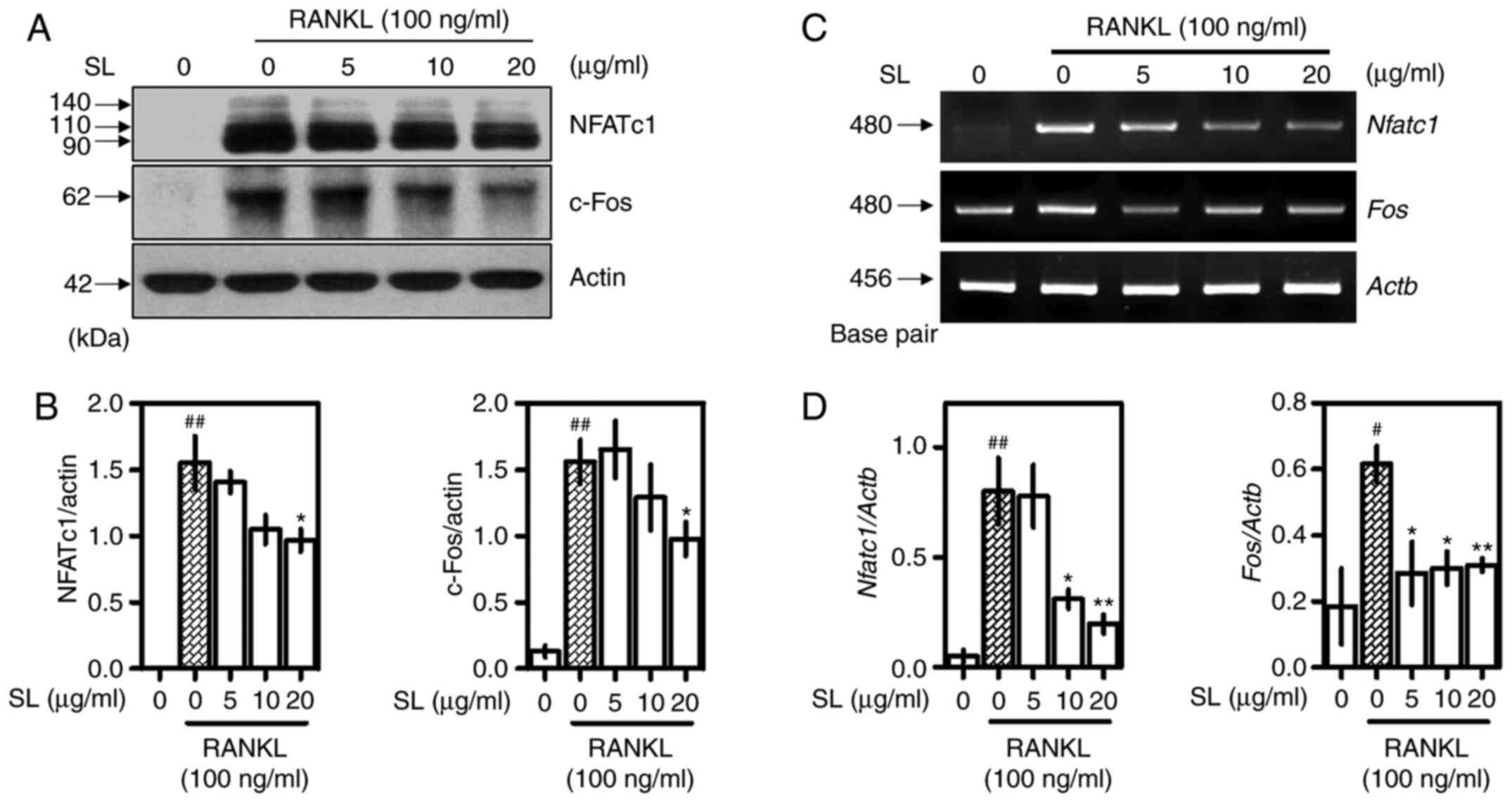
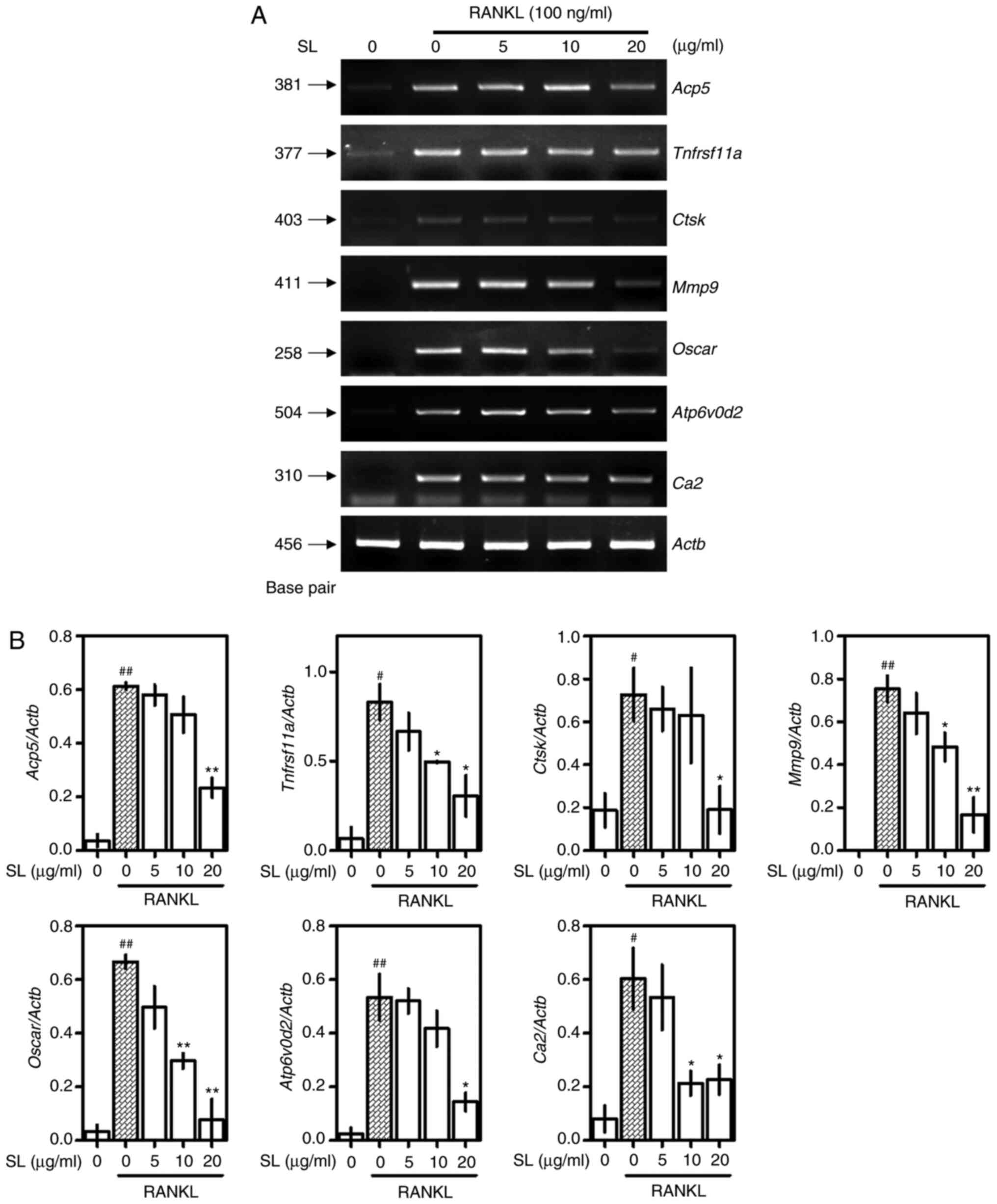
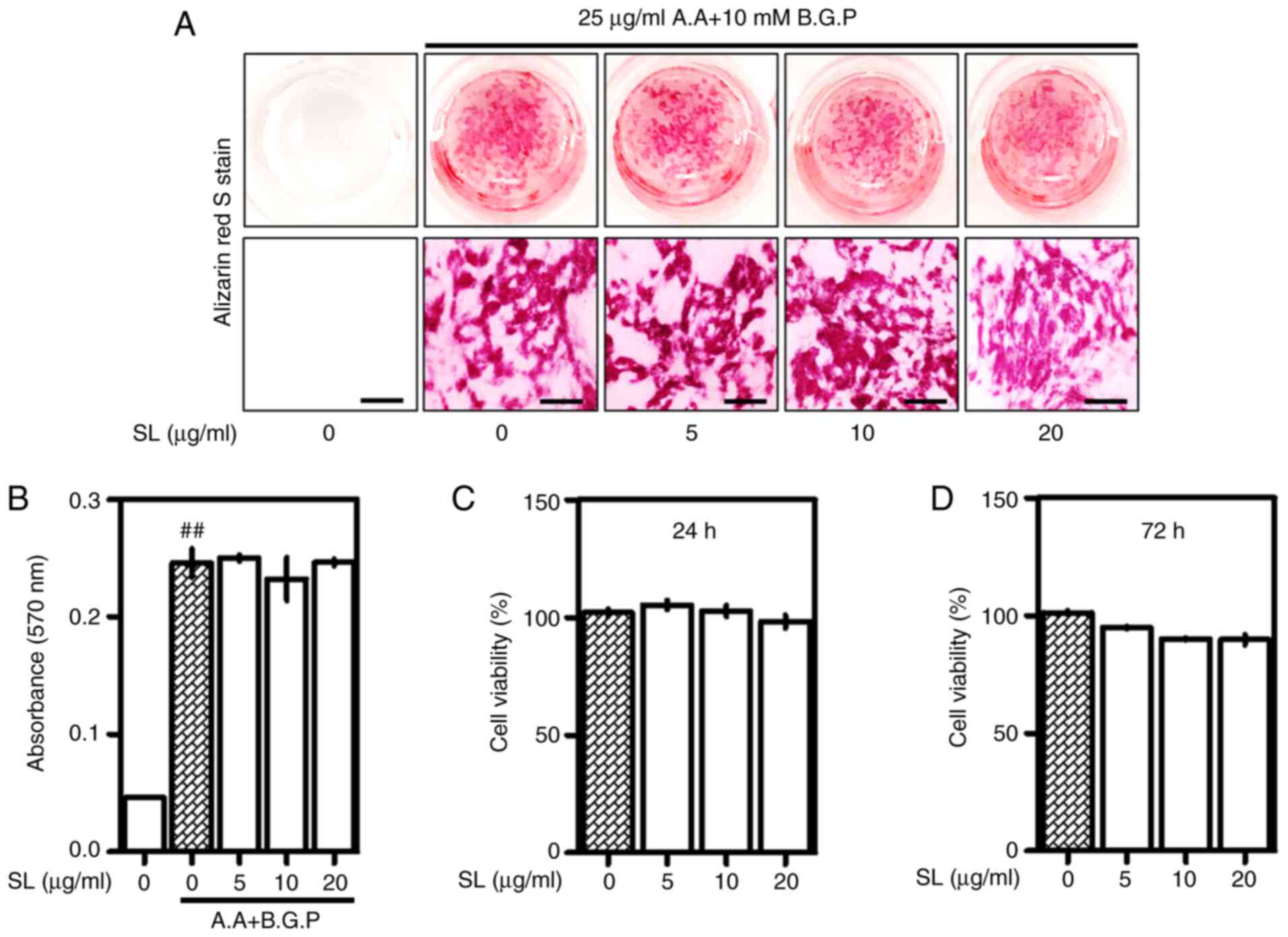
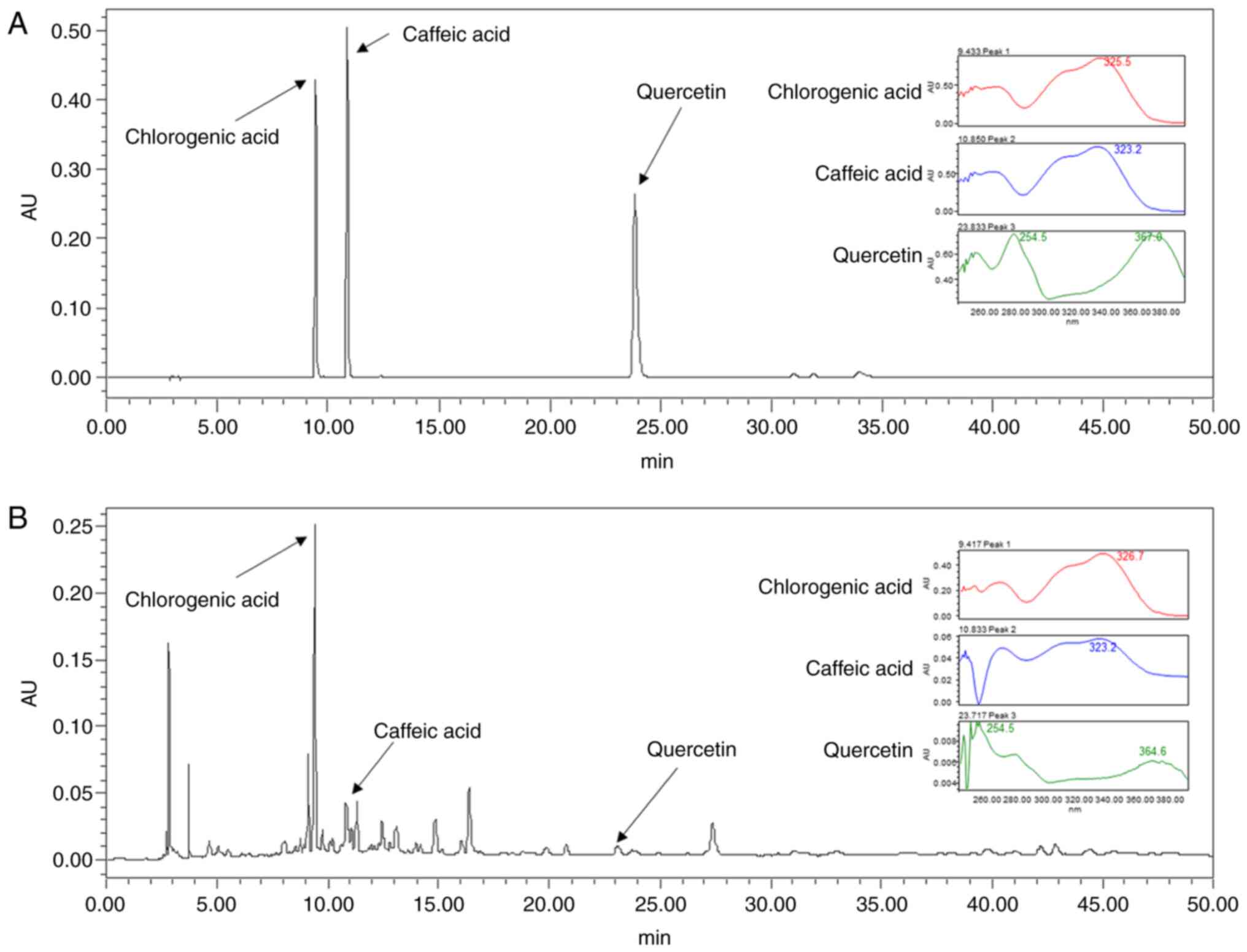
|
1
|
Sözen T, Özışık L and Başaran NC: An
overview and management of osteoporosis. Eur J Rheumatol. 4:46–56.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Boyle WJ, Simonet WS and Lacey DL:
Osteoclast differentiation and activation. Nature. 423:337–342.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Teitelbaum SL: Bone resorption by
osteoclasts. Science. 289:1504–1508. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Tu KN, Lie JD, Wan CKV, Cameron M, Austel
AG, Nguyen JK, Van K and Hyun D: Osteoporosis: A Review of
Treatment Options. P&T. 43:92–104. 2018.
|
|
5
|
Skjødt MK, Frost M and Abrahamsen B: Side
effects of drugs for osteoporosis and metastatic bone disease. Br J
Clin Pharmacol. 85:1063–1071. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Herbology Editorial Committee of Korean
Medicine, . Herbology; Younglimsa, Seoul: 2004
|
|
7
|
Youn YN, Lim E, Lee N, Kim YS, Koo MS and
Choi SY: Screening of Korean medicinal plants for possible
osteoclastogenesis effects in vitro. Genes Nutr. 2:375–380. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Ginaldi L, Di Benedetto MC and De Martinis
M: Osteoporosis, inflammation and ageing. Immun Ageing. 2:142005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Souza PP and Lerner UH: The role of
cytokines in inflammatory bone loss. Immunol Invest. 42:555–622.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Kim K, Lee SH, Ha Kim J, Choi Y and Kim N:
NFATc1 induces osteoclast fusion via up-regulation of Atp6v0d2 and
the dendritic cell-specific transmembrane protein (DC-STAMP). Mol
Endocrinol. 22:176–185. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Kim M, Kim HS, Kim JH, Kim EY, Lee B, Lee
SY, Jun JY, Kim MB, Sohn Y and Jung HS: Chaenomelis fructus
inhibits osteoclast differentiation by suppressing NFATc1
expression and prevents ovariectomy-induced osteoporosis. BMC
Complement Med Ther. 20:352020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Zakaria ZA, Gopalan HK, Zainal H, Mohd
Pojan NH, Morsid NA, Aris A and Sulaiman MR: Antinociceptive,
anti-inflammatory and antipyretic effects of Solanum nigrum
chloroform extract in animal models. Yakugaku Zasshi.
126:1171–1178. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zakaria ZA, Sulaiman MR, Morsid NA, Aris
A, Zainal H, Pojan NH and Kumar GH: Antinociceptive,
anti-inflammatory and antipyretic effects of Solanum nigrum
aqueous extract in animal models. Methods Find Exp Clin Pharmacol.
31:81–88. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Miyamoto T and Suda T: Differentiation and
function of osteoclasts. Keio J Med. 52:1–7. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Clohisy JC, Frazier E, Hirayama T and
Abu-Amer Y: RANKL is an essential cytokine mediator of
polymethylmethacrylate particle-induced osteoclastogenesis. J
Orthop Res. 21:202–212. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Takayanagi H: The role of NFAT in
osteoclast formation. Ann NY Acad Sci. 1116:227–237. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Kim JH, Kim EY, Lee B, Min JH, Song DU,
Lim JM, Eom JW, Yeom M, Jung HS and Sohn Y: The effects of Lycii
Radicis Cortex on RANKL-induced osteoclast differentiation and
activation in RAW 264.7 cells. Int J Mol Med. 37:649–658. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Lee KY, Kim JH, Kim EY, Yeom M, Jung HS
and Sohn Y: Water extract of Cnidii Rhizoma suppresses
RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis in RAW 264.7 cell by inhibiting
NFATc1/c-Fos signaling and prevents ovariectomized bone loss in
SD-rat. BMC Complement Altern Med. 19:2072019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Yeom M, Kim EY, Kim JH, Jung HS and Sohn
Y: High doses of Bupleurum falcatum partially prevents
estrogen deficiency-induced bone loss with anti-osteoclastogenic
activity due to enhanced iNOS/NO signaling. Front Pharmacol.
9:13142018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Tschöp MH, Speakman JR, Arch JR, Auwerx J,
Brüning JC, Chan L, Eckel RH, Farese RV Jr, Galgani JE, Hambly C,
et al: A guide to analysis of mouse energy metabolism. Nat Methods.
9:57–63. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Chan FK, Moriwaki K and De Rosa MJ:
Detection of necrosis by release of lactate dehydrogenase activity.
Methods Mol Biol. 979:65–70. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Hayman AR: Tartrate-resistant acid
phosphatase (TRAP) and the osteoclast/immune cell dichotomy.
Autoimmunity. 41:218–223. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Campisi A, Acquaviva R, Raciti G, Duro A,
Rizzo M and Santagati NA: Antioxidant activities of Solanum
Nigrum L. leaf extracts determined in in vitro cellular models.
Foods. 8:82019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Huang HC, Syu KY and Lin JK: Chemical
composition of Solanum nigrum linn extract and induction of
autophagy by leaf water extract and its major flavonoids in AU565
breast cancer cells. J Agric Food Chem. 58:8699–8708. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Matsubara T, Myoui A, Ikeda F, Hata K,
Yoshikawa H, Nishimura R and Yoneda T: Critical role of cortactin
in actin ring formation and osteoclastic bone resorption. J Bone
Miner Metab. 24:368–372. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Burstein AH, Reilly DT and Martens M:
Aging of bone tissue: Mechanical properties. J Bone Joint Surg Am.
58:82–86. 1976. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Osterhoff G, Morgan EF, Shefelbine SJ,
Karim L, McNamara LM and Augat P: Bone mechanical properties and
changes with osteoporosis. Injury. 47 (Suppl 2):S11–S20. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Kalu DN: The ovariectomized rat model of
postmenopausal bone loss. Bone Miner. 15:175–191. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Kim EY, Kim JH, Kim M, Park JH, Sohn Y and
Jung HS: Abeliophyllum distichum Nakai alleviates
postmenopausal osteoporosis in ovariectomized rats and prevents
RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis in vitro. J Ethnopharmacol.
257:1128282020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Yousefzadeh N, Kashfi K, Jeddi S and
Ghasemi A: Ovariectomized rat model of osteoporosis: A practical
guide. EXCLI J. 19:89–107. 2020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Taciak B, Białasek M, Braniewska A, Sas Z,
Sawicka P, Kiraga Ł, Rygiel T and Król M: Evaluation of phenotypic
and functional stability of RAW 264.7 cell line through serial
passages. PLoS One. 13:e01989432018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Funk JL, Feingold KR, Moser AH and
Grunfeld C: Lipopolysaccharide stimulation of RAW 264.7 macrophages
induces lipid accumulation and foam cell formation.
Atherosclerosis. 98:67–82. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Kong L, Smith W and Hao D: Overview of
RAW264.7 for osteoclastogensis study: Phenotype and stimuli. J Cell
Mol Med. 23:3077–3087. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Yeom M, Kim JH, Min JH, Hwang MK, Jung HS
and Sohn Y: Xanthii fructus inhibits inflammatory responses in
LPS-stimulated RAW 264.7 macrophages through suppressing NF-κB and
JNK/p38 MAPK. J Ethnopharmacol. 176:394–401. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Collin-Osdoby P and Osdoby P:
RANKL-mediated osteoclast formation from murine RAW 264.7 cells.
Methods Mol Biol. 816:187–202. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Ballanti P, Minisola S, Pacitti MT,
Scarnecchia L, Rosso R, Mazzuoli GF and Bonucci E:
Tartrate-resistant acid phosphate activity as osteoclastic marker:
Sensitivity of cytochemical assessment and serum assay in
comparison with standardized osteoclast histomorphometry.
Osteoporos Int. 7:39–43. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Kim JH and Kim N: Regulation of NFATc1 in
osteoclast differentiation. J Bone Metab. 21:233–241. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Aliprantis AO, Ueki Y, Sulyanto R, Park A,
Sigrist KS, Sharma SM, Ostrowski MC, Olsen BR and Glimcher LH:
NFATc1 in mice represses osteoprotegerin during osteoclastogenesis
and dissociates systemic osteopenia from inflammation in cherubism.
J Clin Invest. 118:3775–3789. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Takayanagi H, Kim S, Koga T, Nishina H,
Isshiki M, Yoshida H, Saiura A, Isobe M, Yokochi T, Inoue J, et al:
Induction and activation of the transcription factor NFATc1 (NFAT2)
integrate RANKL signaling in terminal differentiation of
osteoclasts. Dev Cell. 3:889–901. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Zhao Q, Wang X, Liu Y, He A and Jia R:
NFATc1: Functions in osteoclasts. Int J Biochem Cell Biol.
42:576–579. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Saftig P, Hunziker E, Wehmeyer O, Jones S,
Boyde A, Rommerskirch W, Moritz JD, Schu P and von Figura K:
Impaired osteoclastic bone resorption leads to osteopetrosis in
cathepsin-K-deficient mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 95:13453–13458.
1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Kim K, Kim JH, Lee J, Jin HM, Lee SH,
Fisher DE, Kook H, Kim KK, Choi Y and Kim N: Nuclear factor of
activated T cells c1 induces osteoclast-associated receptor gene
expression during tumor necrosis factor-related activation-induced
cytokine-mediated osteoclastogenesis. J Biol Chem. 280:35209–35216.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Wu H, Xu G and Li YP: Atp6v0d2 is an
essential component of the osteoclast-specific proton pump that
mediates extracellular acidification in bone resorption. J Bone
Miner Res. 24:871–885. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Han G, Zuo J and Holliday LS: Specialized
roles for actin in osteoclasts: Unanswered questions and
therapeutic opportunities. Biomolecules. 9:92019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Anderson DM, Maraskovsky E, Billingsley
WL, Dougall WC, Tometsko ME, Roux ER, Teepe MC, DuBose RF, Cosman D
and Galibert L: A homologue of the TNF receptor and its ligand
enhance T-cell growth and dendritic-cell function. Nature.
390:175–179. 1997. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Matsuo K, Galson DL, Zhao C, Peng L,
Laplace C, Wang KZ, Bachler MA, Amano H, Aburatani H, Ishikawa H,
et al: Nuclear factor of activated T-cells (NFAT) rescues
osteoclastogenesis in precursors lacking c-Fos. J Biol Chem.
279:26475–26480. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
David JP, Rincon M, Neff L, Horne WC and
Baron R: Carbonic anhydrase II is an AP-1 target gene in
osteoclasts. J Cell Physiol. 188:89–97. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Kim M, Kim M, Kim JH, Hong S, Kim DH, Kim
S, Kim EY, Jung HS and Sohn Y: Crataegus pinnatifida bunge
inhibits RANKL-induced osteoclast differentiation in RAW 264.7
cells and prevents bone loss in an ovariectomized rat model. Evid
Based Complement Alternat Med. 2021:55215622021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Lehenkari P, Hentunen TA, Laitala-Leinonen
T, Tuukkanen J and Väänänen HK: Carbonic anhydrase II plays a major
role in osteoclast differentiation and bone resorption by effecting
the steady state intracellular pH and Ca2+. Exp Cell
Res. 242:128–137. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Manolagas SC: Steroids and osteoporosis:
The quest for mechanisms. J Clin Invest. 123:1919–1921. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Rochira V, Balestrieri A, Madeo B, Zirilli
L, Granata AR and Carani C: Osteoporosis and male age-related
hypogonadism: Role of sex steroids on bone (patho)physiology. Eur J
Endocrinol. 154:175–185. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Tella SH and Gallagher JC: Prevention and
treatment of postmenopausal osteoporosis. J Steroid Biochem Mol
Biol. 142:155–170. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Thulkar J and Singh S: Overview of
research studies on osteoporosis in menopausal women since the last
decade. J Midlife Health. 6:104–107. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Christensen K, Doblhammer G, Rau R and
Vaupel JW: Ageing populations: The challenges ahead. Lancet.
374:1196–1208. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Gu XY, Shen XF, Wang L, Wu ZW, Li F, Chen
B, Zhang GL and Wang MK: Bioactive steroidal alkaloids from the
fruits of Solanum nigrum. Phytochemistry. 147:125–131. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Shen KH, Liao AC, Hung JH, Lee WJ, Hu KC,
Lin PT, Liao RF and Chen PS: α-Solanine inhibits invasion of human
prostate cancer cell by suppressing epithelial-mesenchymal
transition and MMPs expression. Molecules. 19:11896–11914. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Zhao L, Wang L, Di SN, Xu Q, Ren QC, Chen
SZ, Huang N, Jia D and Shen XF: Steroidal alkaloid solanine A from
Solanum nigrum Linn. exhibits anti-inflammatory activity in
lipopolysaccharide/interferon γ-activated murine macrophages and
animal models of inflammation. Biomed Pharmacother. 105:606–615.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Lin HM, Tseng HC, Wang CJ, Lin JJ, Lo CW
and Chou FP: Hepatoprotective effects of Solanum nigrum Linn
extract against CCl(4)-induced oxidative damage in rats. Chem Biol
Interact. 171:283–293. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Doss HM, Samarpita S, Ganesan R and Rasool
M: Ferulic acid, a dietary polyphenol suppresses osteoclast
differentiation and bone erosion via the inhibition of RANKL
dependent NF-κB signalling pathway. Life Sci. 207:284–295. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Shishodia S and Aggarwal BB: Diosgenin
inhibits osteoclastogenesis, invasion, and proliferation through
the downregulation of Akt, I kappa B kinase activation and NF-kappa
B-regulated gene expression. Oncogene. 25:1463–1473. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Wu YX, Wu TY, Xu BB, Xu XY, Chen HG, Li XY
and Wang G: Protocatechuic acid inhibits osteoclast differentiation
and stimulates apoptosis in mature osteoclasts. Biomed
Pharmacother. 82:399–405. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Kyung TW, Lee JE, Shin HH and Choi HS:
Rutin inhibits osteoclast formation by decreasing reactive oxygen
species and TNF-alpha by inhibiting activation of NF-kappaB. Exp
Mol Med. 40:52–58. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|