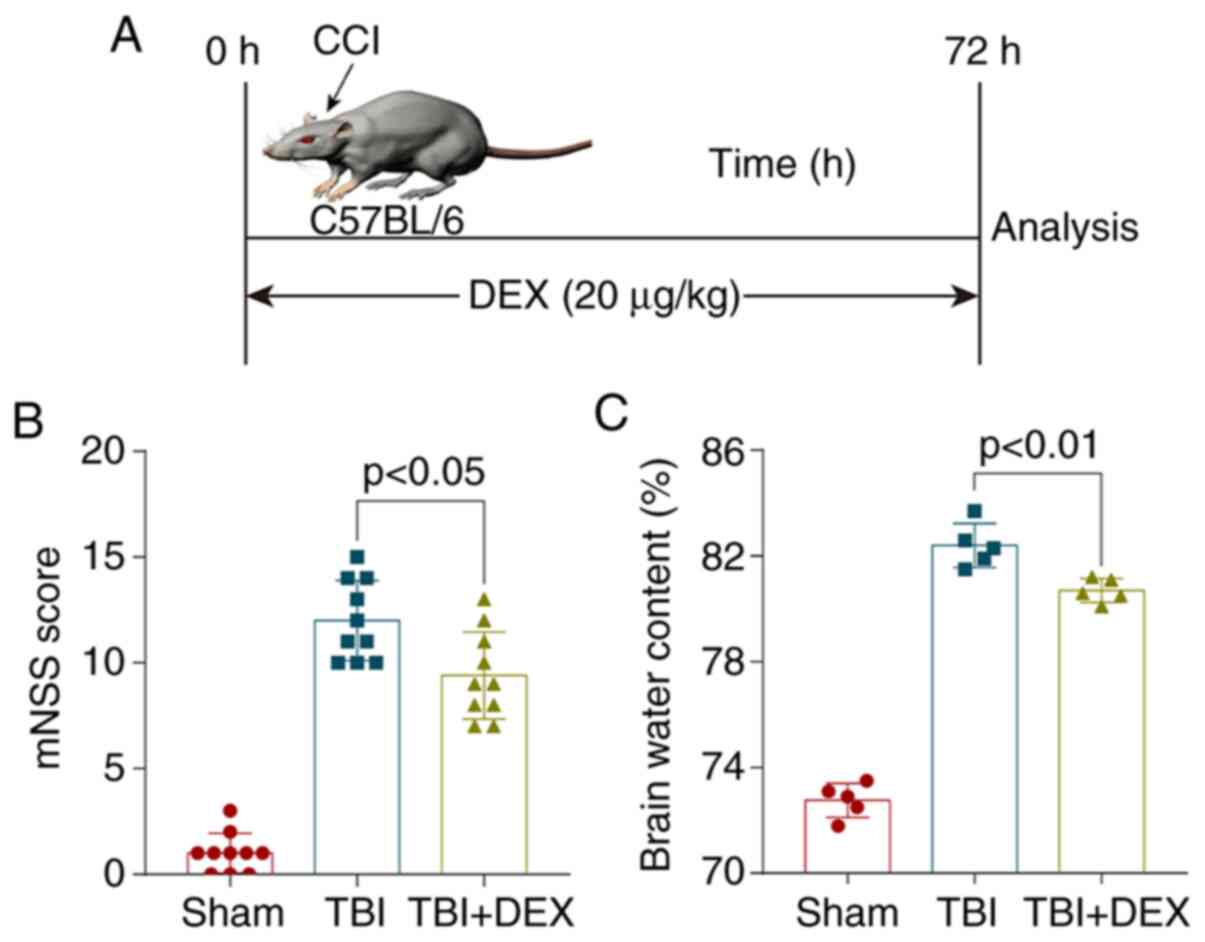
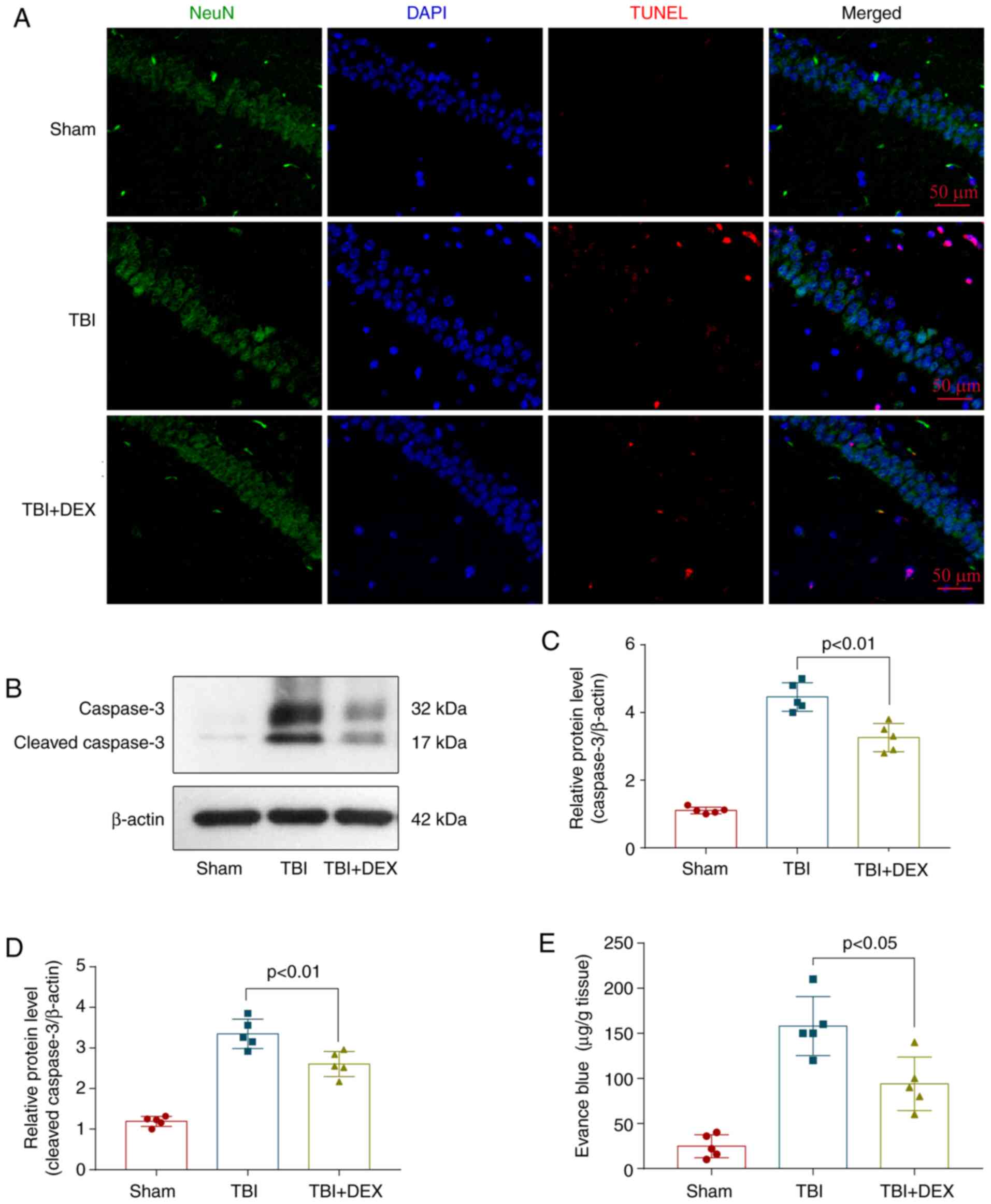
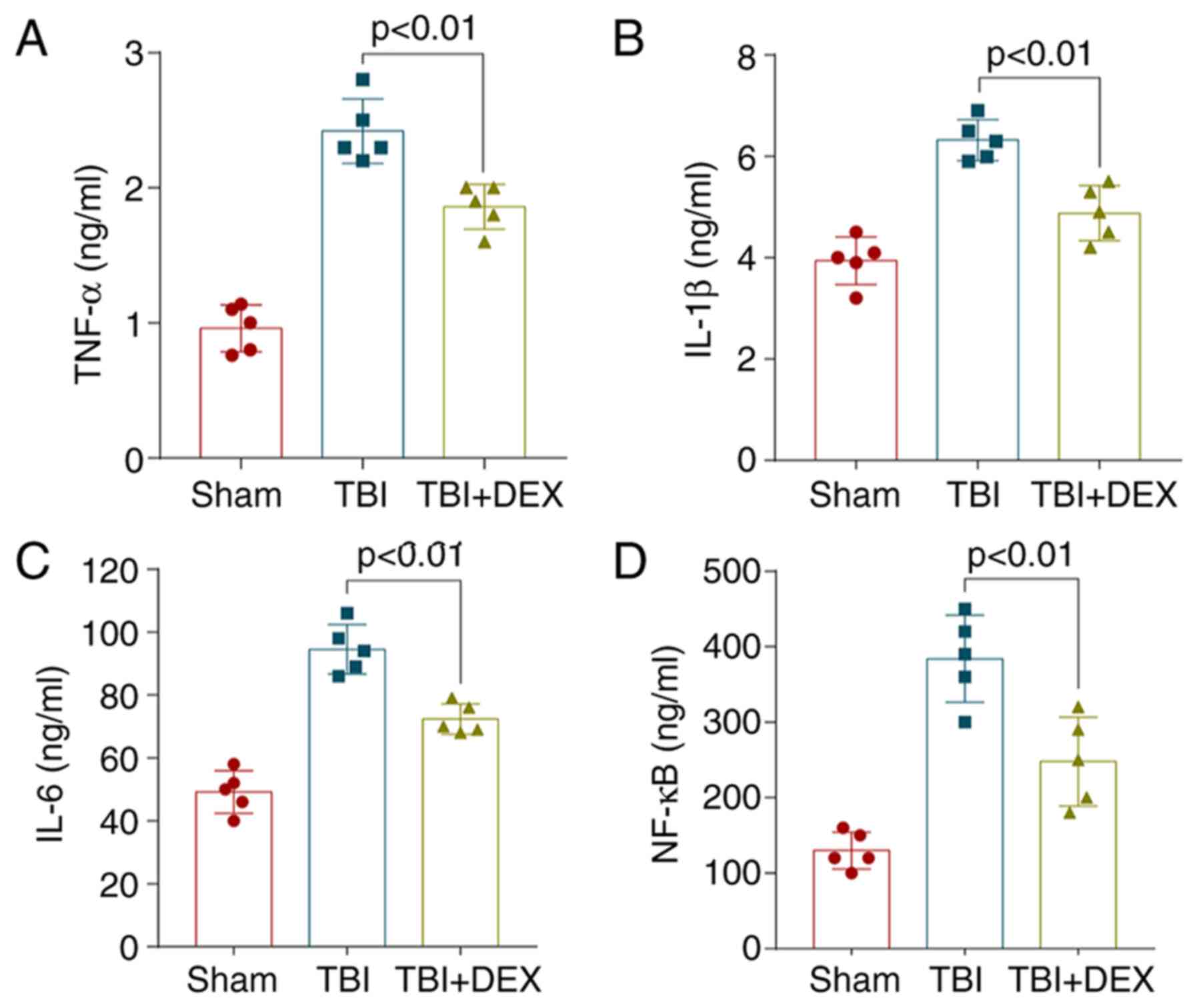
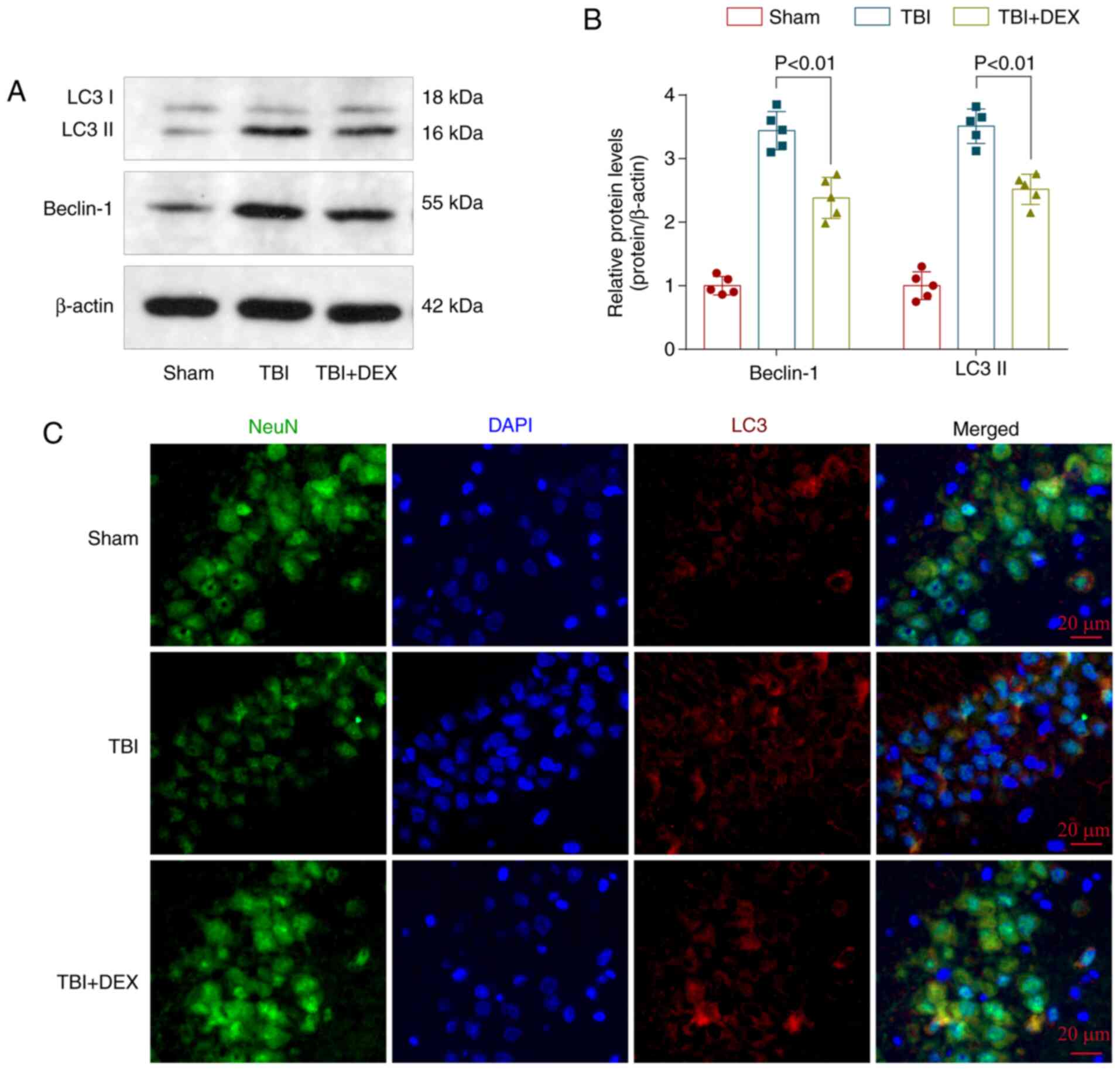
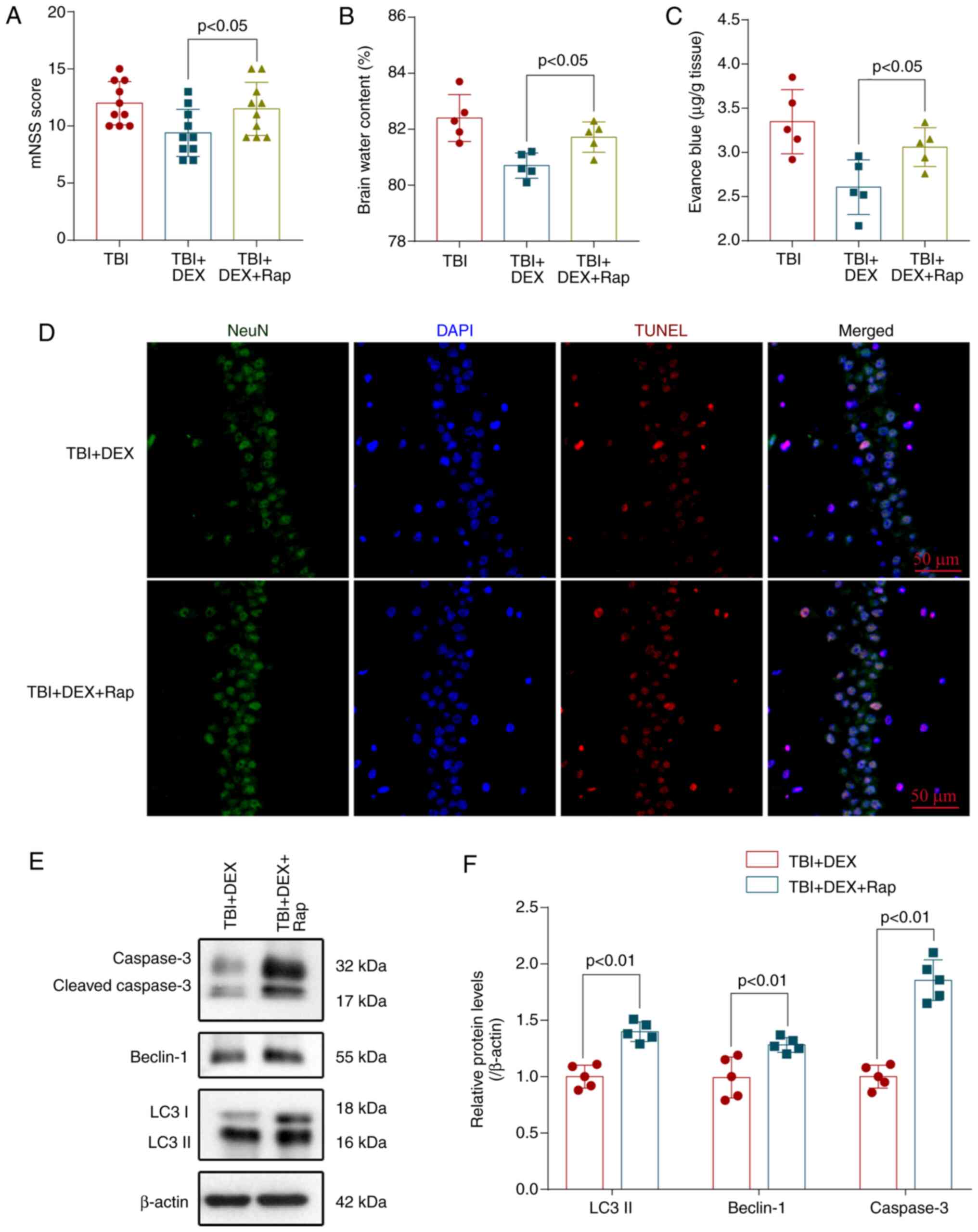
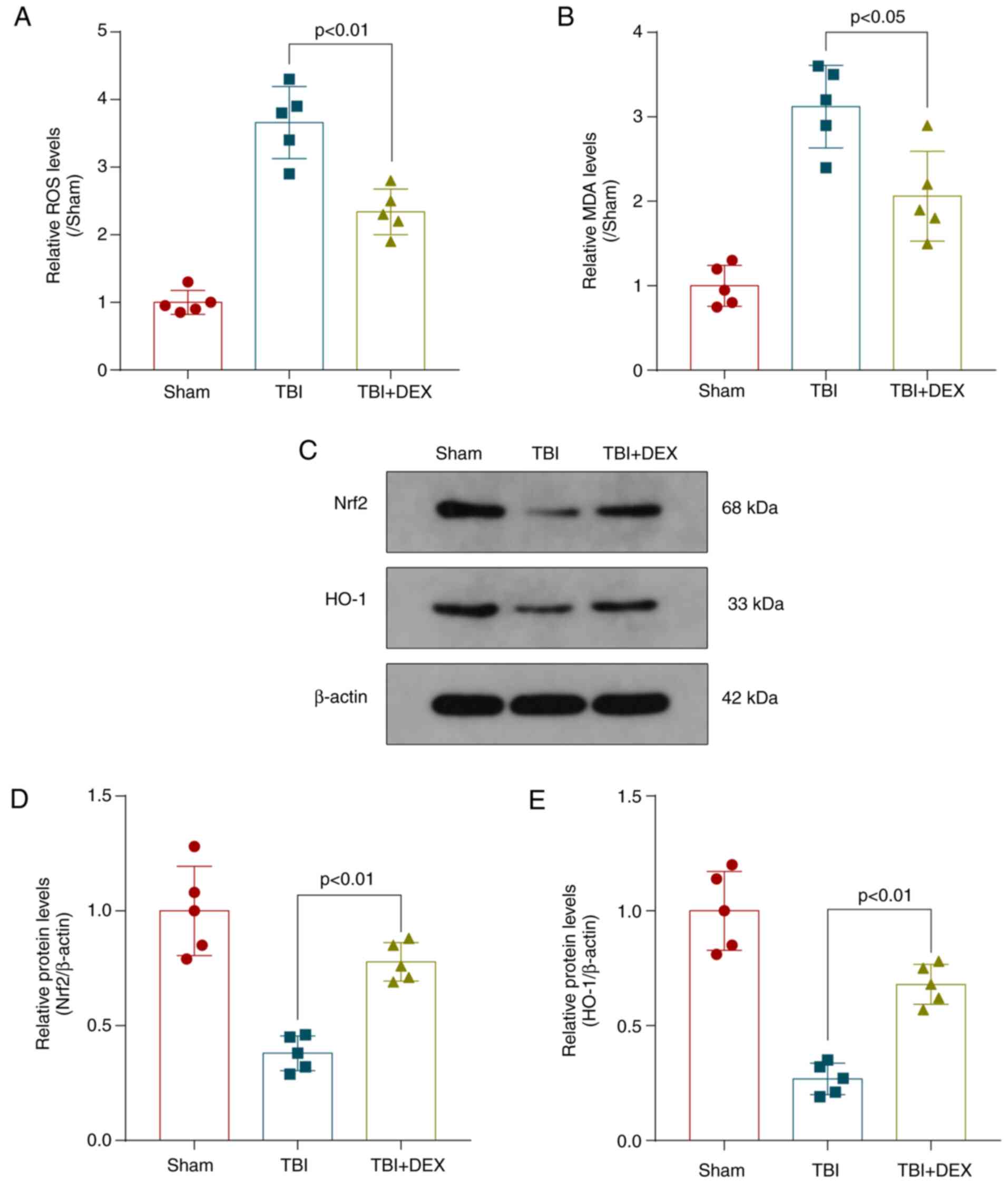
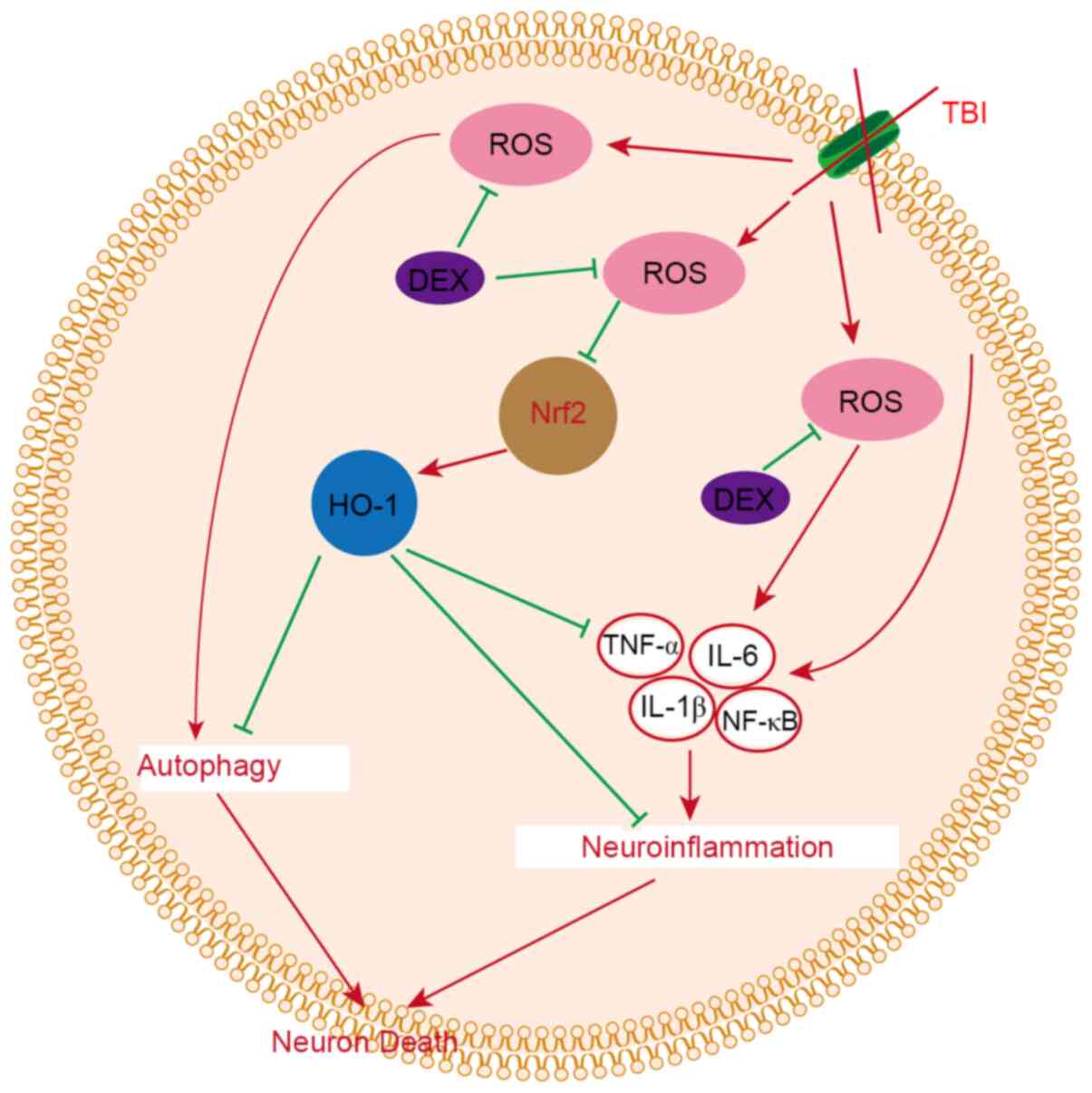
|
1
|
Rowell SE, Meier EN, McKnight B, Kannas D,
May S, Sheehan K, Bulger EM, Idris AH, Christenson J, Morrison LJ,
et al: Effect of out-of-Hospital tranexamic acid vs placebo on
6-month functional neurologic outcomes in patients with moderate or
severe traumatic brain Injury. JAMA. 324:961–974. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Shankar JJ and Vandorpe R: CT perfusion
for confirmation of brain death. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol.
34:1175–1179. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Jiang JY, Gao GY, Feng JF, Mao Q, Chen LG,
Yang XF, Liu JF, Wang YH, Qiu BH and Huang XJ: Traumatic brain
injury in China. Lancet Neurol. 18:286–295. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Chen J, Li M, Chen L, Chen W, Zhang C,
Feng Y, Wang Y and Chen Q: The effect of controlled decompression
for severe traumatic brain injury: A randomized, controlled trial.
Front Neurol. 11:1072020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Chen JH, Li PP, Yang LK, Chen L, Zhu J, Hu
X and Wang YH: Value of ventricular intracranial pressure
monitoring for traumatic bifrontal contusions. World Neurosurg.
113:e690–e701. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Nichol A, French C, Little L, Haddad S,
Presneill J, Arabi Y, Bailey M, Cooper DJ, Duranteau J, Huet O, et
al: Erythropoietin in traumatic brain injury (EPO-TBI): A
double-blind randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 386:2499–2506.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Hutchinson PJ, Kolias AG, Timofeev IS,
Corteen EA, Czosnyka M, Timothy J, Anderson I, Bulters DO, Belli A,
Eynon CA, et al: Trial of decompressive craniectomy for traumatic
intracranial hypertension. N Engl J Med. 375:1119–1130. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Cooper DJ, Nichol AD, Bailey M, Bernard S,
Cameron PA, Pili-Floury S, Forbes A, Gantner D, Higgins AM, Huet O,
et al: Effect of early sustained prophylactic hypothermia on
neurologic outcomes among patients with severe traumatic brain
injury: The POLAR randomized clinical trial. JAMA. 320:2211–2220.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Wright DW, Yeatts SD, Silbergleit R,
Palesch YY, Hertzberg VS, Frankel M, Goldstein FC, Caveney AF,
Howlett-Smith H, Bengelink EM, et al: Very early administration of
progesterone for acute traumatic brain injury. N Engl J Med.
371:2457–2466. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Robertson CS, Hannay HJ, Yamal JM,
Gopinath S, Goodman JC, Tilley BC; Epo Severe TBI Trial
Investigators, ; Baldwin A, Rivera Lara L, Saucedo-Crespo H, et al:
Effect of erythropoietin and transfusion threshold on neurological
recovery after traumatic brain injury: A randomized clinical trial.
JAMA. 312:36–47. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Wang Y, Wang L, Hu T, Wang F, Han Z, Yin
Z, Ge X, Xie K and Lei P: Hydrogen improves cell viability partly
through inhibition of autophagy and activation of PI3K/Akt/GSK3β
signal pathway in a microvascular endothelial cell model of
traumatic brain injury. Neurol Res. 42:487–496. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Li H, Lu C, Yao W, Xu L, Zhou J and Zheng
B: Dexmedetomidine inhibits inflammatory response and autophagy
through the circLrp1b/miR-27a-3p/Dram2 pathway in a rat model of
traumatic brain injury. Aging (Albany NY). 12:21687–21705. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Wang Y, Zhao M, Shang L, Zhang Y, Huang C,
He Z, Luo M, Wu B, Song P, Wang M and Duan F: Homer1a protects
against neuronal injury via PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway. Int J
Neurosci. 130:621–630. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Ceccariglia S, Cargnoni A, Silini AR and
Parolini O: Autophagy: A potential key contributor to the
therapeutic action of mesenchymal stem cells. Autophagy. 16:28–37.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Tang C, Shan Y, Hu Y, Fang Z, Tong Y, Chen
M, Wei X, Fu X and Xu X: FGF2 attenuates neural cell death via
suppressing autophagy after rat mild traumatic brain injury. Stem
Cells Int. 2017:29231822017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Fang J, Zhu Y, Wang H, Cao B, Fei M, Niu
W, Zhou Y, Wang X, Li X and Zhou M: Baicalin protects mice brain
from apoptosis in traumatic brain injury model through activation
of autophagy. Front Neurosci. 12:10062018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Zhao M, Gao J, Cui C, Zhang Y, Jiang X and
Cui J: Inhibition of PTEN ameliorates secondary hippocampal injury
and cognitive deficits after intracerebral hemorrhage: Involvement
of AKT/FoxO3a/ATG-mediated autophagy. Oxid Med Cell Longev.
2021:54726052021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Chen JH, Wu T, Xia WY, Shi ZH, Zhang CL,
Chen L, Chen QX and Wang YH: An early neuroprotective effect of
atorvastatin against subarachnoid hemorrhage. Neural Regen Res.
15:1947–1954. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Aron R, Pellegrini P, Green EW, Maddison
DC, Opoku-Nsiah K, Oliveira AO, Wong JS, Daub AC, Giorgini F,
Muchowski P and Finkbeiner S: Deubiquitinase Usp12 functions
noncatalytically to induce autophagy and confer neuroprotection in
models of Huntington's disease. Nat Commun. 9:31912018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Yang T, Feng X, Zhao Y, Zhang H, Cui H,
Wei M, Yang H and Fan H: Dexmedetomidine enhances autophagy via
α2-AR/AMPK/mTOR pathway to inhibit the activation of NLRP3
inflammasome and subsequently alleviates lipopolysaccharide-induced
acute kidney injury. Front Pharmacol. 11:7902020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Subramaniam B, Shankar P, Shaefi S,
Mueller A, O'Gara B, Banner-Goodspeed V, Gallagher J, Gasangwa D,
Patxot M, Packiasabapathy S, et al: Effect of intravenous
acetaminophen vs placebo combined with propofol or dexmedetomidine
on postoperative delirium among older patients following cardiac
surgery: The DEXACET randomized clinical trial. JAMA. 321:686–696.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Huang GR and Hao FG: Dexmedetomidine
inhibits inflammation to alleviate early neuronal injury via
TLR4/NF-κB pathway in rats with traumatic brain injury. Crit Rev
Eukaryot Gene Expr. 31:41–47. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Bilodeau V, Saavedra-Mitjans M, Frenette
AJ, Burry L, Albert M, Bernard F and Williamson DR: Safety of
dexmedetomidine for the control of agitation in critically ill
traumatic brain injury patients: A descriptive study. J Clin Pharm
Ther. 46:1020–1026. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Li F, Wang X, Zhang Z, Zhang X and Gao P:
Dexmedetomidine attenuates neuroinflammatory-induced apoptosis
after traumatic brain injury via Nrf2 signaling pathway. Ann Clin
Transl Neurol. 6:1825–1835. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Zhao Y, Feng X, Li B, Sha J, Wang C, Yang
T, Cui H and Fan H: Dexmedetomidine protects against
lipopolysaccharide-induced acute kidney injury by enhancing
autophagy through inhibition of the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway. Front
Pharmacol. 11:1282020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Bu LL, Liu YQ, Shen Y, Fan Y, Yu WB, Jiang
DL, Tang YL, Yang YJ, Wu P, Zuo CT, et al: Neuroprotection of
exendin-4 by enhanced autophagy in a parkinsonian rat model of
α-synucleinopathy. Neurotherapeutics. Mar 15–2021.(Epub ahead of
print). View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Dou R, Qian J, Wu W, Zhang Y, Yuan Y, Guo
M, Wei R, Yang S, Jurczyszyn A, Janz S, et al: Suppression of
steroid 5α-reductase type I promotes cellular apoptosis and
autophagy via PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway in multiple myeloma. Cell Death
Dis. 12:2062021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Li J, Tian M, Hua T, Wang H, Yang M, Li W,
Zhang X and Yuan H: Combination of autophagy and NFE2L2/NRF2
activation as a treatment approach for neuropathic pain. Autophagy.
April 9–2021.(Epub ahead of print). View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Shi J, Yu T, Song K, Du S, He S, Hu X, Li
X, Li H, Dong S, Zhang Y, et al: Dexmedetomidine ameliorates
endotoxin-induced acute lung injury in vivo and in vitro by
preserving mitochondrial dynamic equilibrium through the
HIF-1a/HO-1 signaling pathway. Redox Biol. 41:1019542021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Chen J, Wang Y, Wu J, Yang J, Li M and
Chen Q: The potential value of targeting ferroptosis in early brain
injury after acute CNS disease. Front Mol Neurosci. 13:1102020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Chen J, Zhang C, Yan T, Yang L, Wang Y,
Shi Z, Li M and Chen Q: Atorvastatin ameliorates early brain injury
after subarachnoid hemorrhage via inhibition of pyroptosis and
neuroinflammation. J Cell Physiol. Mar 3–2021.(Epub ahead of
print). View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
National Research Council (US) Institute
for Laboratory Animal Research, . Guide for the Care and Use of
Laboratory Animals. National Academies Press (US); Washington, DC:
1996
|
|
33
|
Flierl MA, Stahel PF, Beauchamp KM, Morgan
SJ, Smith WR and Shohami E: Mouse closed head injury model induced
by a weight-drop device. Nat Protoc. 4:1328–1337. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Tian J, Yang L, Wang P, Yang L and Fan Z:
Exogenous CGRP regulates apoptosis and autophagy to alleviate
traumatic brain injury through Akt/mTOR signalling pathway.
Neurochem Res. 45:2926–2938. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Chen J, Xuan Y, Chen Y, Wu T, Chen L, Guan
H, Yang S, He J, Shi D and Wang Y: Netrin-1 alleviates subarachnoid
haemorrhage-induced brain injury via the PPAR gamma/NF-KB
signalling pathway. J Cell Mol Med. 23:2256–2262. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Li G, Dong Y, Liu D, Zou Z, Hao G, Gao X,
Pan P and Liang G: NEK7 coordinates rapid neuroinflammation after
subarachnoid hemorrhage in mice. Front Neurol. 11:5512020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Das S, Chattopadhyay D, Chatterjee SK,
Mondal SA, Majumdar SS, Mukhopadhyay S, Saha N, Velayutham R,
Bhattacharya S and Mukherjee S: Increase in PPARγ inhibitory
phosphorylation by Fetuin-A through the activation of Ras-MEK-ERK
pathway causes insulin resistance. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis
Dis. 1867:1660502021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Zhao S, Cheng L, Shi Y, Li J, Yun Q and
Yang H: MIEF2 reprograms lipid metabolism to drive progression of
ovarian cancer through ROS/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway. Cell Death
Dis. 12:182021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Dando I, Pacchiana R, Pozza ED, Cataldo I,
Bruno S, Conti P, Cordani M, Grimaldi A, Butera G, Caraglia M, et
al: UCP2 inhibition induces ROS/Akt/mTOR axis: Role of GAPDH
nuclear translocation in genipin/everolimus anticancer synergism.
Free Radic Biol Med. 113:176–189. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Dick RW: Is there a gender difference in
concussion incidence and outcomes? Br J Sports Med. 43 (Suppl
1):i46–i50. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Gupte R, Brooks W, Vukas R, Pierce J and
Harris J: Sex differences in traumatic brain injury: What We Know
and What We Should Know. J Neurotrauma. 36:3063–3091. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Biegon A: Considering biological sex in
traumatic brain injury. Front Neurol. 12:5763662021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Kawazoe Y, Miyamoto K, Morimoto T,
Yamamoto T, Fuke A, Hashimoto A, Koami H, Beppu S, Katayama Y, Itoh
M, et al: Effect of dexmedetomidine on mortality and
ventilator-free days in patients requiring mechanical ventilation
with sepsis: A randomized clinical trial. JAMA. 317:1321–1328.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Skrobik Y, Duprey MS, Hill NS and Devlin
JW: Low-Dose nocturnal dexmedetomidine prevents ICU delirium. A
Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Trial. Am J Respir Crit Care Med.
197:1147–1156. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Chen J, Wang J, Li C, Ding H, Ye J and Xia
Z: Dexmedetomidine reverses MTX-induced neurotoxicity and
inflammation in hippocampal HT22 cell lines via NCOA4-mediated
ferritinophagy. Aging (Albany NY). 13:6182–6193. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Chen X, Chen D, Li Q, Wu S, Pan J, Liao Y,
Zheng X and Zeng W: Dexmedetomidine alleviates hypoxia-induced
synaptic loss and cognitive impairment via inhibition of microglial
NOX2 activation in the hippocampus of neonatal rats. Oxid Med Cell
Longev. 2021:66431712021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Mei B, Li J and Zuo Z: Dexmedetomidine
attenuates sepsis-associated inflammation and encephalopathy via
central α2A adrenoceptor. Brain Behav Immun. 91:296–314. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Yang YF, Wang H, Song N, Jiang YH, Zhang
J, Meng XW, Feng XM, Liu H, Peng K and Ji FH: Dexmedetomidine
attenuates ischemia/reperfusion-induced myocardial inflammation and
apoptosis through inhibiting endoplasmic reticulum stress
signaling. J Inflamm Res. 14:1217–1233. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Gao Y, Zhang Y, Dong Y, Wu X and Liu H:
Dexmedetomidine mediates neuroglobin Up-regulation and alleviates
the hypoxia/reoxygenation injury by inhibiting neuronal apoptosis
in developing rats. Front Pharmacol. 11:5555322020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Sun YB, Zhao H, Mu DL, Zhang W, Cui J, Wu
L, Alam A, Wang DX and Ma D: Dexmedetomidine inhibits astrocyte
pyroptosis and subsequently protects the brain in in vitro and in
vivo models of sepsis. Cell Death Dis. 10:1672019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Shen R, Pan D, Wang Z, Jin X, Li Z and
Wang H: The effects of dexmedetomidine post-conditioning on cardiac
and neurological outcomes after cardiac arrest and resuscitation in
swine. Shock. 55:388–395. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Nixon RA: The role of autophagy in
neurodegenerative disease. Nat Med. 19:983–997. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Zeng Z, Zhang Y, Jiang W, He L and Qu H:
Modulation of autophagy in traumatic brain injury. J Cell Physiol.
235:1973–1985. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Xue H, Wu Z, Xu Y, Gao Q, Zhang Y, Li C
and Zhao P: Dexmedetomidine post-conditioning ameliorates long-term
neurological outcomes after neonatal hypoxic ischemia: The role of
autophagy. Life Sci. 270:1189802021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Wang M, Ke Y, Li Y, Shan Z, Mi W, Cao Y,
Feng W and Zheng X: The nephroprotective effects and mechanisms of
rehmapicrogenin include ROS inhibition via an oestrogen-like
pathway both in vivo and in vitro. Biomed Pharmacother.
138:1113052021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Cui G, Li Z, Cao F, Li P, Jin M, Hou S,
Yang X, Mu Y, Peng C, Shao H and Du Z: Activation of Nrf2/HO-1
signaling pathway attenuates ROS-mediated autophagy induced by
silica nanoparticles in H9c2 cells. Environ Toxicol. 36:1389–1401.
2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|