Introduction
Acute kidney injury (AKI) is one common complication
of sepsis with a high mortality rate in critically ill patients
(1). Although great effort has been
made in the mechanism underlying the development of AKI, treatment
of septic AKI remains unsatisfactory (2,3).
Therefore, it is necessary to investigate effective therapeutic
options for sepsis-induced AKI.
Studies have reported that the loss of functional
tubular epithelial cells (TECs) via apoptosis and inflammatory
response are involved in the pathological process of AKI (4–6).
Notably, anti-inflammatory and anti-apoptotic therapy was confirmed
to be beneficial for the treatment of sepsis-induced AKI (7,8).
Lipopolysaccharide (LPS) is a classical ligand for TLR4 and
mediates TLR4-dependent signal transduction to activate NF-κB,
leading to an increase in inflammatory cytokine expression,
including interleukin-1β (IL-1β), IL-6 and tumor necrosis factor-α
(TNF-α) (9). Therefore, an
LPS-induced experimental model was comprehensively used to
investigate and investigate the anti-inflammatory treatment of
sepsis-related AKI.
MicroRNAs (miRNAs/miRs), endogenous small (~22
nucleotides) non-coding RNA, act as unique regulators of gene
expression through either inducing transcript degradation or
inhibiting translation (10,11).
Numerous studies have highlighted the key roles of miRNAs in the
pathological process of AKI (12,13).
For example, Liao et al (14) demonstrated that miR-140-5p improved
cisplatin-induced AKI through suppressing oxidative stress by
activating the Nrf2/ARE pathway in a mouse model. Lan et al
(15) reported that miR-494 may
induce over-activation of inflammatory response and apoptosis in a
mouse AKI model. In addition, several miRNAs, including miR-494
(16), miR-107 (17) in the serum have been proposed to
service as a biomarker of AKI. Recent studies have demonstrated the
protective effects of miRNAs by inhibiting apoptosis and
inflammatory response in various types of renal cells (18,19).
For example, Guo et al (20)
reported that inhibition of miR-709 protected against
cisplatin-induced the proximal tubular cell injury. Yan et
al (21) reported that miR-214
ameliorated ischemic AKI through regulation of mitochondrial
fragmentation and apoptosis in ATP-depleted proximal tubular cells.
Therefore, it was hypothesized that miRNAs may regulate the renal
TECs apoptosis and inflammatory response.
In the present study, a mouse AKI model was
established and microarray analysis was conducted to determine
miRNA expression profiles in kidney tissues. Subsequently, the
function and possible mechanisms of candidate miRNA in regulating
apoptosis, oxidative stress and inflammatory response were
investigated using an AKI cell model. These results should improve
awareness of miR-93 regulation following AKI and inform future
direction of treatments for AKI.
Materials and methods
Animal model
A total of 20 male C57BL6/J mice, aged 10–12 weeks
and weighing 20±2 g, were obtained from the Shanghai SLAC
Laboratory Animal Co., Ltd. All mice were housed under standard
conditions (12-h light-dark cycle, 21±2°C, ~55% humidity) with free
access to food and water. In the AKI group (n=10), LPS in 200 µl
saline was administrated via intraperitoneal (i.p.) injection (10
mg/kg, 0.2 ml/mouse) for 24 h to induce AKI (22), while an equal volume of saline was
given to control mice (n=10). Ethical approval was obtained from
the Animal Experimentation Ethics Committee of the School of
Medicine, Shanghai Jiao Tong University (approval no. 201912033;
Shanghai, China). For miRNA microarray analysis, the sample size
was three; while for reverse transcription-quantitative polymerase
chain reaction (RT-qPCR), the sample size was five.
Renal function measurement
A total of 24 h after the LPS injection, mice were
humanely anesthetized by i.p. injection of pentobarbital sodium (50
mg/kg; Sigma-Aldrich; Merck KGaA). Subsequently, 0.5 ml blood
samples were collected from the eyeballs of mice and placed in
1.5-ml microcentrifuge tubes for 10 min at room temperature. Serum
was obtained by centrifuging at 1,500 × g for 10 min at 4°C and
stored at −80°C. Serum creatinine and blood urea nitrogen (BUN)
were detected by using a creatinine assay kit (cat. no. DICT-500;
BioAssay Systems) and a biochemical analyzer (Roche Diagnostics
GmbH), respectively. The levels of kidney injury molecule-1 (KIM-1)
and neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin (NGAL) were also
measured using a Mouse TIM-1/KIM-1/HAVCR Quantikine ELISA Kit (cat.
no. MKM100) and a Mouse Lipocalin-2/NGAL Quantikine ELISA Kit (cat.
no. MLCN20; both from R&D Systems, Inc.), respectively.
Renal histopathology
A total of 24 h after the LPS injection, mice were
humanely euthanized by i.p. injection of pentobarbital sodium (50
mg/kg; Sigma-Aldrich; Merck KGaA), followed by cervical
dislocation. Subsequently, the right kidney tissue was taken and
fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde in PBS (pH 7.4) for 20 min at 4°C,
embedded in paraffin and sectioned at 4 µm for hematoxylin and
eosin (H&E) staining for 10 min at room temperature. The
morphological changes were observed under a light microscope
(BX-FM; Olympus Corporation; 400× magnification). Tissue damage was
confirmed in a blinded manner and scored as previously described
(23).
MicroRNA expression profiling
Total RNA was extracted from tissues using miRNeasy
mini kit (Qiagen AB). MicroRNA differential expression analysis was
performed using the miRCURY LNA™ Array v. 18.0 (Exiqon; Qiagen,
Inc.) as previously described (24). Briefly, total RNA was labeled using
miRCURY™ Hy3™/Hy5™ power labeling kit (Exiqon; Qiagen, Inc.) and
hybridized on miRCURY™ LNA Array (v 1.8.0). After washing and
staining, the microarray slides were scanned in an Agilent G2565BA
Microarray Scanner System (Agilent Technologies, Inc.). Scanned
images were then imported into GenePix Pro 6.0 software (Molecular
Devices, LLC) for grid alignment and data extraction. Differently
expressed genes were then identified through fold-change
(fold-change ≥2) and P-value (P<0.05). Subsequently, the miRNAs
were measured by Volcano Plot filtering using GraphPad Prism 7.0
software package (GraphPad Software, Inc.). Finally, a hierarchical
cluster heatmap representing expression intensity and direction was
created using a method of hierarchical clustering via GeneSpring
GX, version 7.3 (Agilent Technologies, Inc.).
RT-qPCR analysis
Total RNA was extracted from tissues and cells using
TRIzol Reagent (Invitrogen; Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc.). cDNA
was synthesized using the PrimeScript RT reagent kit (Promega
Corporation) for 1 h at 42°C. For detection of miR-93, qPCR was
conducted using MicroRNAs Quantitation PCR kit (Sangon Biotech Co.,
Ltd.). For detection of mRNA, a SYBR Premix Ex Taq II (Takara Bio,
Inc.) was used for PCR. Sequences for the primers used were as
follows: MiR-93 forward, 5′-AGGCCCAAAGTGCTGTTCGT-3′ and reverse,
5′-GTGCAGGGTCCGAGGT-3′; U6 forward, 5′-GCTTCGGCAGCACATATACTAAAAT-3′
and reverse, 5′-CGCTTCACGAATTTGCGTGTCAT-3′; phosphatase and tensin
homolog deleted on chromosome 10 (PTEN) forward,
5′-CCAGGACCAGAGGAAACCT-3′ and reverse, 5′-GCTAGCCTCTGGATTTGA-3′;
IL-1β forward, 5′-TCTCGCAGCAGCACATCA-3′ and reverse,
5′-CACACACCAGCAGGTTAT-3′; IL-6 forward, 5′-TGGGAAATCGTGGAAATGAG-3′
and reverse, 5′-CTCTGAAGGACTCTGGCTTTG-3′; TNF-α forward,
5′-CCCGGGCTCAGCCTCTTCTCATTC-3′ and reverse,
5′-GGATCCGGTGGTTTGCTACGACGT-3′; and GAPDH forward,
5′-CGAGCCACATCGCTCAGACA-3′ and reverse, 5′-GTGGTGAAGACGCCAGTGGA-3′.
U6 was used as an internal control for detecting miR-93, and GAPDH
was used as an internal control for detecting PTEN. The
thermocycling conditions were as follows: 50°C for 2 min and 95°C
for 10 min, followed by 40 cycles of 95°C for 15 sec and 60°C for
10 min. Fold-changes in expression of each gene were calculated
using the 2−∆∆Cq method (25).
Cell culture and treatment
Mouse kidney epithelial TCMK-1 cells were obtained
from the American Type Culture Collection and were maintained in
Dulbecco's modified Eagle's medium (Gibco; Thermo Fisher
Scientific, Inc.), supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS;
Invitrogen; Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc.) at 37°C and 5%
CO2. LPS, at concentrations of 0, 0.01, 0.1, 1 and 10
µg/ml, was used to treat TCMK-1 cells for 24 h to generate a sepsis
AKI cell model (26).
Cell transfection
The miR-93 mimics (5′-CAAAGUGCUGUUCGUGCAGGUAG-3′),
the mimics negative control (NC; 5′-UUCUCCGAACGUGUCACGUTT-3′),
miR-93 inhibitor (5′-CUACCUGCACGAACAGCACUUUG-3′) and inhibitor NC
(5′-UUGUACUACACAAAAGUACUG-3′) were purchased from Guangzhou RiboBio
Co., Ltd. At 80–90% confluence, miR-93 mimics/inhibitor were
transfected into TCMK-1 cells (5×105) at a final
oligonucleotide concentration of 50 nmol/l. Transfection was
performed using Lipofectamine® 2000 (Invitrogen; Thermo
Fisher Scientific, Inc.), according to the manufacturer's
protocols. After transfection for 24 h, TCMK-1 cells were collected
for subsequent experiments.
Cell proliferation
To detect cell proliferation, TCMK-1 cells were
seeded onto 96-well plates (1,500 cells/well) for 24 h, and then
transfected with miR-93 mimics, followed by treatment with LPS (0,
0.01, 0.1, 1 and 10 µg/ml) for 24 h at 37°C. Then, 10 µl Cell
Counting Kit-8 (CCK-8) solutions (Beyotime Institute of
Biotechnology) were added to cells and cells were incubated for 1.5
h at 37°C and 5% CO2. Next, the OD absorbance was
detected at 450 nm by a micro-plate reader by (Infinite M200; Tecan
Group, Ltd.).
Cell apoptosis
An Annexin V-FITC/PI apoptosis detection kit (Abcam)
was applied to detect cells apoptosis according to the
manufacturer's protocols. Briefly, 48 h after transfection, cells
were centrifuged and washed with PBS, stained with Annexin V and PI
for 15 min at room temperature in the dark. The results of
apoptosis were measured using a FACScan flow cytometer (Beckman
Coulter, Inc.) and then data were analyzed using FlowJo version
8.7.1 software (FlowJo LLC). These results showed healthy viable
cells in the lower left quadrant (Q4) on the scatter plot as
(FITC−/PI−). The lower right quadrant (Q3)
represented the early stage apoptotic cells as
(FITC+/PI−). The upper right quadrant (Q2)
represented necrotic cells and late stage apoptotic cells as
(FITC+/PI+). The following formula was
performed to determine the apoptotic rate: Apoptotic
rate=percentage of early stage apoptotic cells (Q3) + percentage of
late stage apoptotic cells (Q2).
Determination of caspase 3
activity
Following cells being collected and lysed, the
Caspase-3 activity was measured using the Caspase-3 assay kit (cat.
no. ab252897; Abcam) according to the manufacturer's protocols. The
results were determined at 450 nm using a microplate reader
(Bio-Rad Laboratories, Inc.).
Detection of reactive oxygen species
(ROS)
The intracellular ROS levels were tested using a
total ROS detection assay kit (cat. no. K936; BioVision, Inc.),
while the detection of malonaldehyde (MDA), superoxide dismutase
(SOD) and glutathione peroxidase (GPx) was performed using the
detection kits for SOD (cat. no. S0101), MDA (cat. no. S0131S) and
GPx (cat. no. S0058; Beyotime Institute of Biotechnology),
according to the manufacturer's protocols.
Measurement of IL-6, IL-1β and
TNF-α
For cultured cells, the supernatant was carefully
collected by centrifugation 12,000 × g for 10 min at 4°C. The
concentrations of IL-6, IL-1β and TNF-α were analyzed using IL-6
(cat. no. p1330), IL-1β (cat. no. p1305) and TNF-α (cat. no. pt518)
ELISA kits from Beyotime Institute of Biotechnology.
Bioinformatics analysis
miRNA target prediction tools, including PicTar
version 2007 (https://pictar.mdc-berlin.de/) and TargetScan version
7.0 (http://targetscan.org/) were used to
search for the putative targets of miR-93.
Luciferase assay
The luciferase reporter plasmids [wild-type
(wt)-PTEN-UTR-pGL3 or mutant (mut)-PTEN-UTR-pGL3] were synthesized
by Shanghai GenePharma Co., Ltd. 293T cells (8×104)
(American Type Culture Collection) were co-transfected with the
luciferase reporter along with miR-93 mimics/inhibitor using
Lipofectamine 2000 (Invitrogen; Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc.). At
48 h post-transfection, the activity of luciferase was measured
using a Dual-Luciferase Reporter Assay System (Promega
Corporation). Renilla luciferase expression of pRL-TK
plasmids (Promega Corporation) was used for normalization.
Western blotting
Proteins were extracted from cells using RIPA lysis
buffer (EMD Millipore) containing protease inhibitors and
phosphatase inhibitors. In brief, the protein samples (40 µg/lane)
were separated by 12% SDS-PAGE gel, and subsequently transferred to
polyvinylidene difluoride membranes (EMD Millipore). Then, the
membrane was blocked with 5% skimmed milk for 2 h at room
temperature, followed by incubation with antibodies against PTEN
(cat. no. 9559; 1:2,000), phosphorylated (p)-AKT (cat. no. 4060;
1:1,000), AKT (cat. no. 4685; 1:1,000), p-mTOR (cat. no. 5536;
1:1,000), mTOR (cat. no. 2983; 1:2,000) and β-actin (cat. no. 3700;
1:2,000) for an additional 2 h at room temperature. Next, the
membranes were incubated with a goat anti-mouse HRP-conjugated
secondary antibody (cat. no. 91196; 1:2,000) at room temperature
for 1 h. All antibodies were obtained from Cell Signaling
Technology. Detection was performed using ECL reagents (Advansta,
Inc.) and blots were semi-quantified with ImageJ software (version
1.46; National Institutes of Health).
Statistical analysis
SPSS 19.0 software package (IBM Corp.) was used to
analyze the data. All data are presented as the mean ± standard
deviation. Comparisons between multiple groups were analyzed by
one-way analysis of variance, followed by Tukey's post hoc test.
P<0.05 was considered to indicate a statistically significant
difference.
Results
miR-93 is downregulated in kidney
tissues from AKI mice
In the present study, a mouse AKI model was
established, and H&E staining was used to evaluate the
morphological changes of kidney tissues. As shown in Fig. 1A, substantial pathological changes
were observed in the LPS group, including edema of renal TECs,
tubular necrosis and inflammatory cell infiltration, accompanied by
a marked increase in the renal injury scores. Subsequently, the
renal function in the mouse AKI model was investigated. It was
demonstrated that the levels of BUN and Cre, urine KIM-1 and urine
NGAL, which are commonly used biochemical indicators for detecting
renal function were also higher in the AKI group than in the
control group (Fig. 1B-E). This
suggested that LPS-induced AKI animal models were successfully
established.
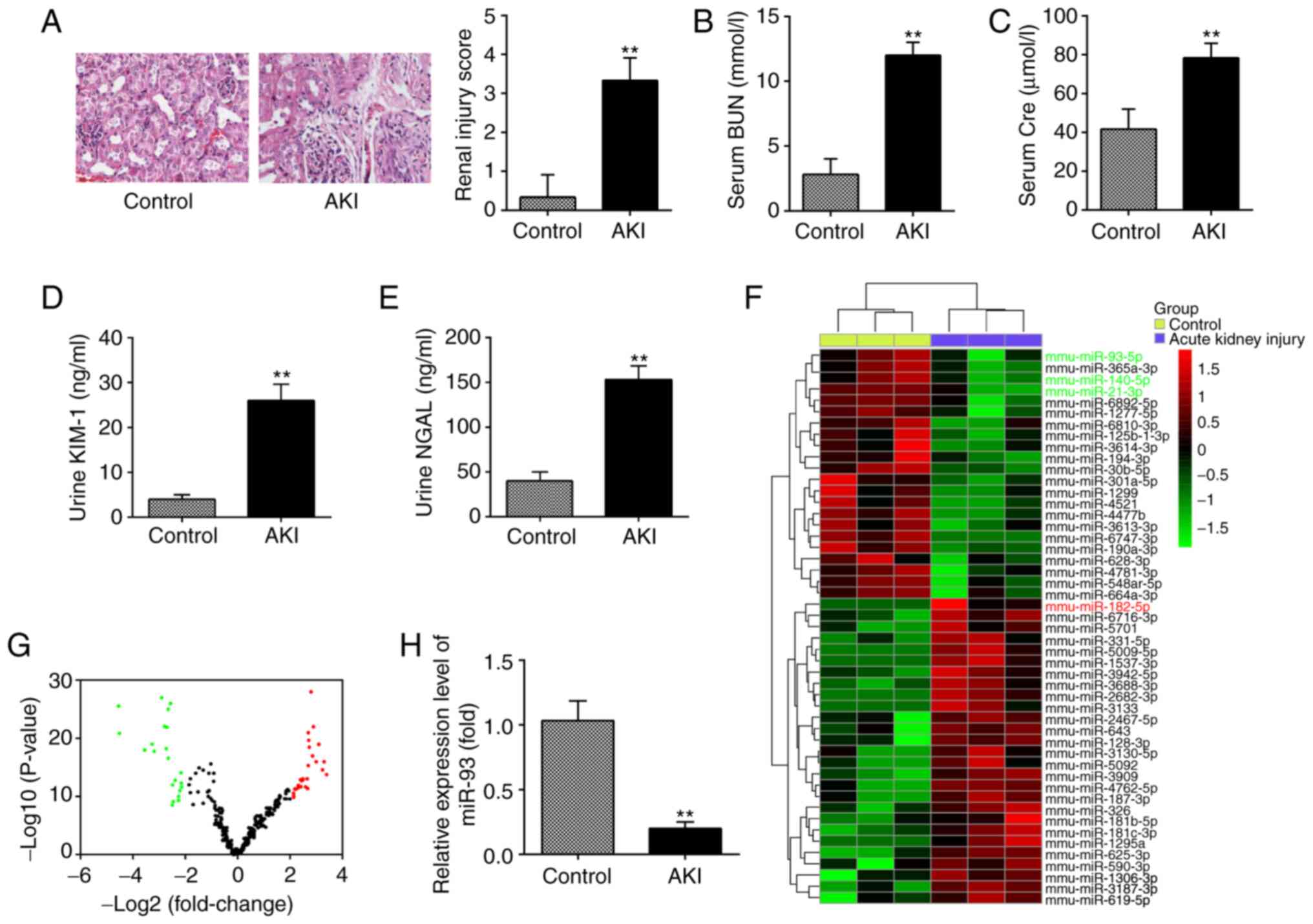 | Figure 1.miR-93 is downregulated in kidney
tissues from AKI mice. (A) H&E staining was used to examine the
histopathological changes of the kidney and evaluation of renal
injury scores was assessed following H&E staining under an
optical microscope (magnification, ×200). The levels of (B) serum
BUN, (C) serum Cre, (D) urine KIM-1 and (E) urine NGAL in mice were
measured using commercial kits. Data are presented as the mean ± SD
of three independent experiments. **P<0.01 vs. Control group.
(F) Heatmap of miRNA profiles represented the significantly
regulated miRNAs. The color code in the heatmaps is linear with
green as the lowest and red as the highest. (G) Volcano plot
presenting the differentially expressed miRNAs. Y-axis represents
log transformed P-value, and x-axis indicates the mean expression
differences of miRs between AKI group and control group.
|log2FoldChange| >2 was set as the cut-off criteria. (H) miR-93
expression was validated by reverse transcription-quantitative
polymerase chain reaction in mice following AKI (n=10). Data are
presented as the mean ± SD of three independent experiments.
**P<0.01 vs. Control group. miR/miRNA, micro RNA; AKI, acute
kidney injury; H&E, hematoxylin and eosin; BUN, blood urea
nitrogen; Cre, creatinine; KIM-1, kidney injury molecule-1; NGAL,
neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin; SD, standard
deviation. |
To investigate the potential involvement of miRNA in
AKI, microarray analysis was performed to determine miRNA
expression levels in kidney tissues. It was observed that 22 miRNAs
were significantly downregulated and 26 miRNAs were markedly
upregulated in AKI group, compared with the control group (Fig. 1F). The volcano plot demonstrates all
the differentially expressed miRNAs between the AKI group and the
control group (Fig. 1G). Of these
aberrant miRNAs, miR-93, miR-140 and miR-21 were decreased, while
miR-182 was increased, which was consistent with the results of
previous studies (14,27,28),
indicating the reliability of the microarray used in the present
study. Notably, miR-93 exhibited the most markedly downregulated
expression in the present study. Notably, a previous study reported
that the expression level of miR-93 was correlated with the
severity of oxalic acid-induced AKI (29). In addition, several studies have
demonstrated that miR-93 exerts anti-inflammatory and
anti-apoptotic abilities in several disease models (30,31).
Therefore, RT-qPCR was used to further verify the miR-93 expression
level in kidney tissues of 10 AKI mice and it was observed that
miR-93 expression was significantly decreased in the AKI group,
compared with that in the control group (Fig. 1H). All data indicated that AKI
results in miRNA aberrant expression in kidney tissues and miR-93
may serve an important role in the pathogenesis of AKI.
Overexpression of miR-93 suppresses
LPS-induced renal cell apoptosis
To investigate the roles of miR-93 in AKI, mouse
kidney epithelial TCMK-1 cells were applied for construction of an
AKI cell model under LPS simulation (32). To begin with, expression of miR-93
in TCMK-1 cells was detected under different concentrations of LPS.
It was demonstrated that miR-93 expression was dose-dependently
decreased in TCMK-1 cells and was minimal at 10 µg/ml LPS treatment
(Fig. 2A). Therefore, 10 µg/ml LPS
was selected for the subsequent experiments, which is also
consistent with a previous study (33).
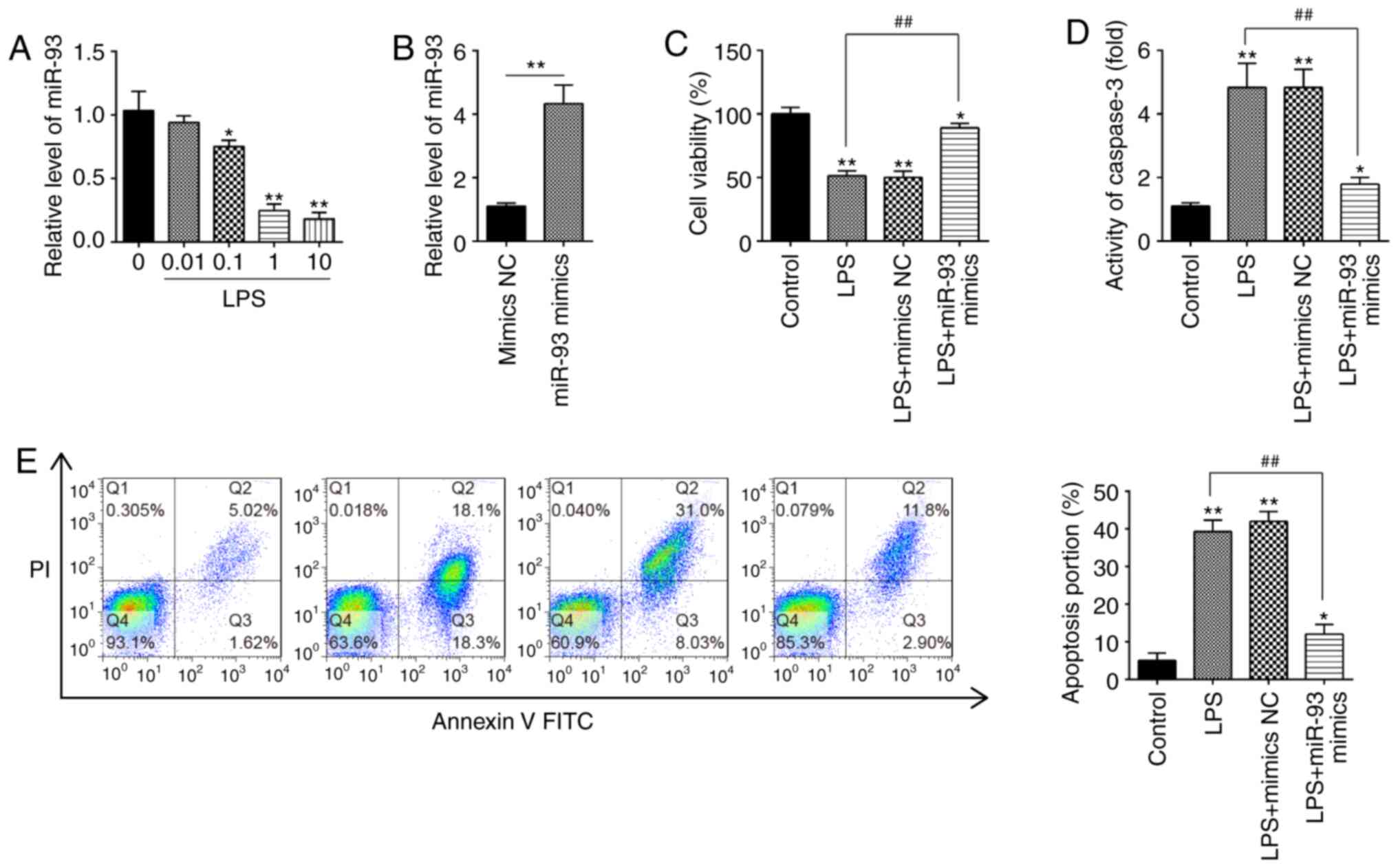 | Figure 2.Overexpression of miR-93 suppresses
LPS-induced renal cell apoptosis. (A) TCMK-1 cells were treated
with different concentrations of LPS (0, 0.01, 0.1, 1 and 10 µg/ml)
for 24 h, and the expression of miR-93 was detected by RT-qPCR. (B)
The transfection efficiency of miR-93 mimics was detected by
RT-qPCR. (C) miR-93 mimics were added to the cultured TCMK-1 cells
for 24 h, and treated with LPS, and then cell viability was
assessed by Cell Counting Kit-8 assay. (D) Activity of Caspase-3
was measured using a Caspase-3 activity assay kit. (E) Apoptosis
was detected by flow cytometry. Data are presented as the mean ±
standard deviation of three independent experiments. *P<0.05,
**P<0.01 vs. Control group; ##P<0.01 vs. LPS
group. miR, microRNA; LPS, lipopolysaccharide; RT-qPCR, reverse
transcription-quantitative polymerase chain reaction; NC, negative
control. |
To investigate the role of miR-93 in LPS-induced
cell injury, miR-93 mimics were transfected into TCMK-1 cells.
Compared with the mimics NC group, miR-93 was significantly
increased in TCMK-1 cells, indicating that miR-93-overexpression
was successful (Fig. 2B). CCK-8
assay demonstrated that, compared with the control group, LPS
treatment resulted in a significant decrease in cell viability;
however, this decrease was reversed by overexpression of miR-93
(Fig. 2C). Furthermore, it was
investigated whether miR-93 modulates cell apoptosis following AKI
induction. As shown in Fig. 2D, the
Caspase-3 activity in the LPS group was significantly upregulated
compared with that in the control group and this increase was
attenuated by overexpression of miR-93. Cell apoptosis was further
analyzed by flow cytometry, and the results demonstrated that LPS
induced a significant increase in cell apoptosis. However, the
increase in apoptosis was significantly decreased by miR-93 mimics
(Fig. 2E). The aforementioned
results indicated that overexpression of miR-93 alleviated cell
apoptosis in the AKI cell model.
Overexpression of miR-93 suppresses
LPS-induced ROS generation
It has been demonstrated that oxidative damage to
tubular cells and renal tissue is associated with renal injury
(34–36). Therefore, the influence of miR-93 on
oxidative stress in LPS-treated TCMK-1 cells was further
investigated. As shown in Fig. 3A,
LPS treatment led to a marked increase in ROS generation; however,
this increase was attenuated by overexpression of miR-93.
Additionally, the levels of MDA, and activities of SOD and GPx were
measured. It was demonstrated that LPS clearly increased the level
of MDA, and decreased the activities of SOD and GPx in the LPS
group, compared with the control group. However, these effects
caused by LPS were reversed by miR-93 upregulation (Fig. 3B-D). All these data indicated that
overexpression of miR-93 may mitigate renal damage through
suppressing oxidative stress.
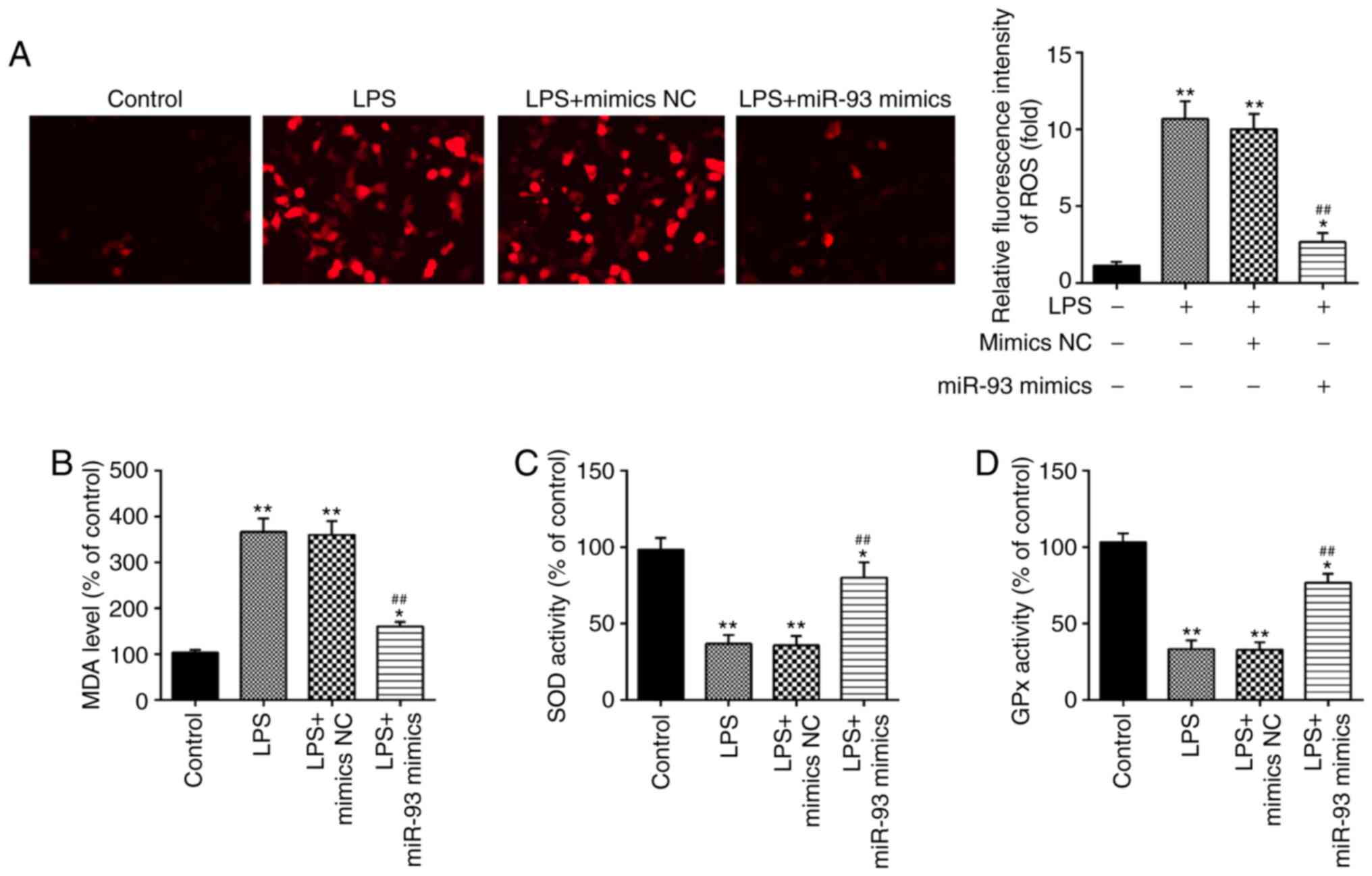 | Figure 3.Overexpression of miR-93 suppresses
LPS-induced ROS generation. miR-93 mimics were added to the
cultured TCMK-1 cells for 24 h and subjected to LPS treatment, and
then cells were harvested for subsequent experiments. (A) Effects
of miR-93 on the intracellular ROS levels in LPS-treated TCMK-1
cells (magnification, ×400). Effects of miR-93 on the (B) MDA, (C)
SOD and (D) GPx levels in LPS-treated TCMK-1 cells. Data are
presented as the mean ± standard deviation of three independent
experiments. *P<0.05, **P<0.01 vs. Control group;
##P<0.01 vs. LPS group. miR, microRNA; LPS,
lipopolysaccharide; ROS, reactive oxygen species; MDA,
malonaldehyde; SOD, superoxide dismutase; GPx, glutathione
peroxidase; NC, negative control. |
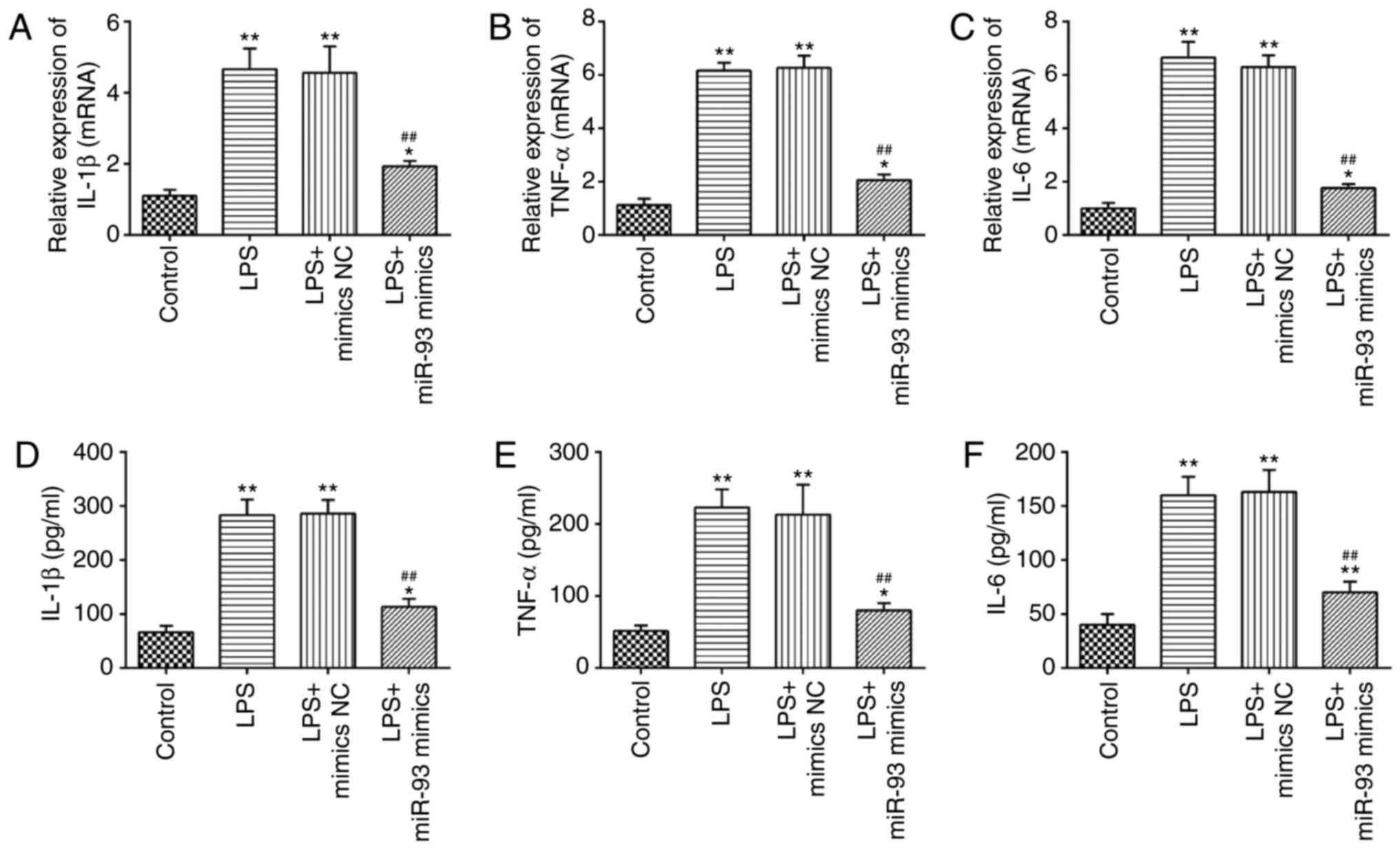
Overexpression of miR-93 suppresses
LPS-induced inflammatory response
A previous study has suggested that the production
of pro-inflammatory cytokines in renal TECs are the main
pathological features of AKI (37).
Therefore, the present study further investigated the influence of
miR-93 on the LPS-induced inflammatory response. As shown in
Fig. 4A-C, LPS stimulation markedly
promoted the mRNA levels of IL-1β, TNF-α and IL-6, compared with
the control group, but these promoting effects of LPS were
abolished by miR-93-overexpression. Similar results were observed
in the levels of IL-1β, TNF-α and IL-6, as determined by ELISA
(Fig. 4D-F). These data suggested
that miR-93 suppressed the inflammatory response in LPS-treated
TCMK-1 cells.
PTEN is a direct target of miR-93
To elucidate the molecular mechanisms involved in
the protective role of miR-93 in AKI, the target genes of miR-93
were predicted using PicTar and TargetScan, and it was revealed
that miR-93 may target PTEN. PTEN sequences in the 3′-UTR region of
miR-93 are shown in Fig. 5A. To
investigate whether miR-93/PTEN was involved in the pathogenesis of
LPS-induced TCMK-1 injury, a luciferase reporter assay was
performed in TCMK-1 cells to validate PTEN as a direct target of
miR-93. To begin with, it was confirmed that the expression of
miR-93 was significantly decreased following miR-93 inhibitor
transfection in TCMK-1 cells (Fig.
5B). The dual-luciferase reporter assay demonstrated that the
luciferase activity was significantly decreased when PTEN 3′-UTR wt
plasmids were co-transfected with miR-93 mimics in TCMK-1 cells,
but markedly increased when co-transfected with miR-93 inhibitors
(Fig. 5C). However, the luciferase
activity showed no obvious change following TCMK-1 co-transfection
with miR-93 mimics/inhibitor and PTEN 3′-UTR mut plasmids. To
investigate whether PTEN levels were regulated by miR-93, TCMK-1
cells were transfected with miR-93 mimics/inhibitor and the levels
of PTEN mRNA were measured by RT-qPCR. It was demonstrated that
PTEN was significantly downregulated when miR-93 was overexpressed
in TCMK-1 cells, but upregulated following miR-93-knockdown
(Fig. 5D). Subsequent experiments
demonstrated that PTEN levels were significantly increased in the
kidney tissues of the AKI group compared with that in the control
group (Fig. 5E). Furthermore,
whether miR-93 regulates the expression of PTEN was determined in
an AKI cell model. As shown in Fig.
5E, LPS stimulation upregulated the mRNA levels of PTEN and
this increase was attenuated by overexpression of miR-93, but
miR-93-knockdown enhanced the LPS-induced upregulation of PTEN
protein expression (Fig. 5F). All
data indicated that miR-93 may exert its protective effects by
targeting PTEN in the AKI cell model.
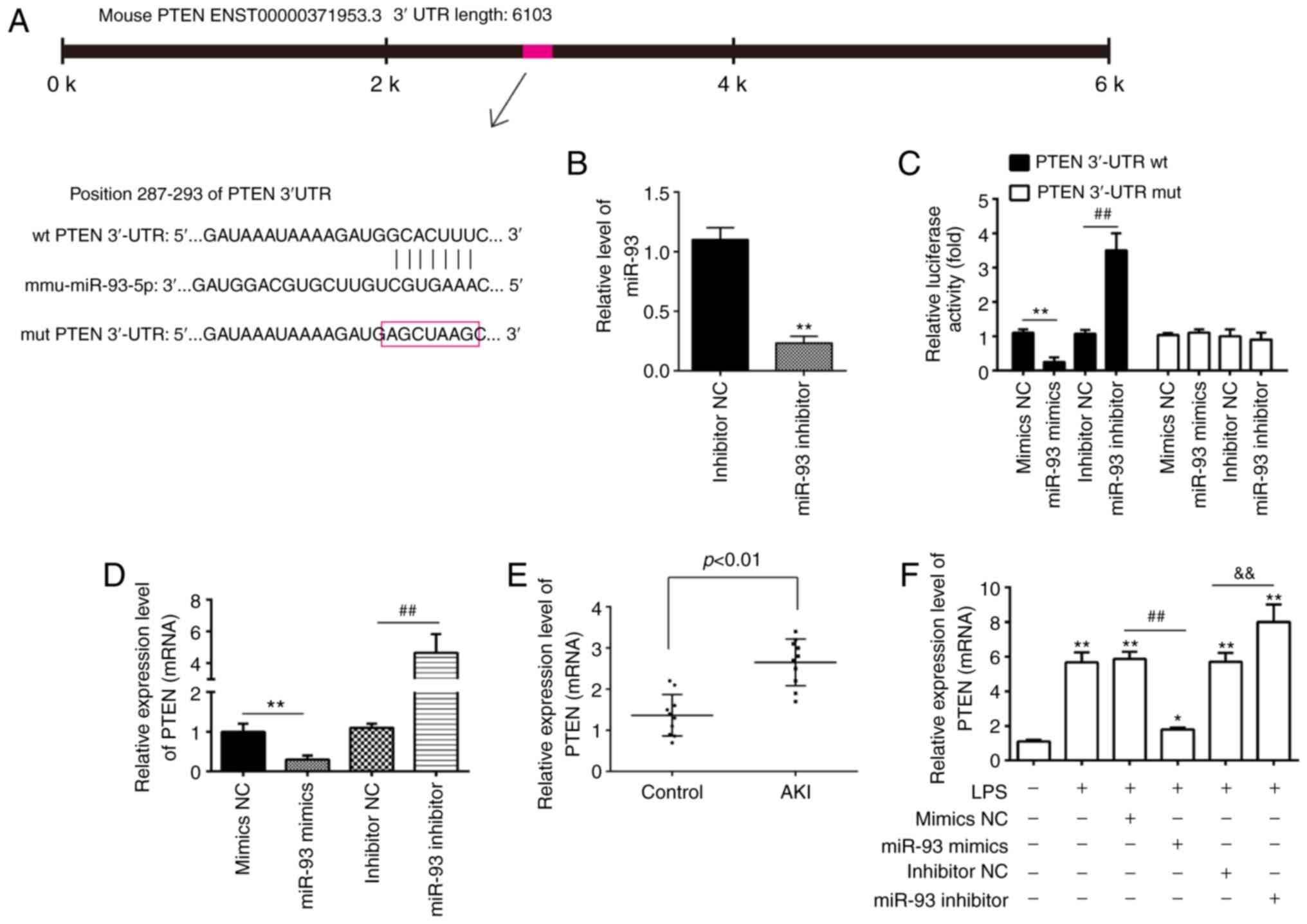 | Figure 5.PTEN is a direct target of miR-93.
(A) Predicted miR-93 targeting sequence in PTEN 3′-UTR (wt PTEN
3′-UTR). Target sequences of PTEN 3′-UTR were mutated (mut PTEN
3′-UTR). (B) Expression of miR-93 was measured by RT-qPCR in TCMK-1
cells following miR-93 inhibitor transfection. **P<0.01 vs.
inhibitor NC group. (C) Luciferase assay of TCMK-1 cells
co-transfected with firefly luciferase constructs containing the
PTEN wt or mut 3′-UTRs and miR-93 mimics, mimic NC, miR-93
inhibitor or inhibitor NC, as indicated (n=3). **P<0.01 vs.
mimics NC group; ##P<0.01 vs. inhibitor NC group. (D)
Expression of PTEN mRNA following transfection with miR-93 mimics
or miR-93 inhibitor was measured by RT-qPCR. Data are presented as
the mean ± SD of three independent experiments. **P<0.01 vs.
mimics NC group; ##P<0.01 vs. inhibitor NC group. (E)
PTEN expression was measured by RT-qPCR in mouse kidneys following
AKI (n=5). (F) The miR-93 mimics/inhibitor and corresponding NC
were added to TCMK-1 cells, followed by 10 ng/ml LPS stimulation
for 24 h, and then the mRNA levels of PTEN were detected by
RT-qPCR. Data are presented as the mean ± SD of three independent
experiments. *P<0.05, **P<0.01 vs. Control group;
##P<0.01 vs. LPS + mimics NC group;
&&P<0.01 vs. LPS + inhibitor NC group. PTEN,
phosphatase and tensin homolog deleted on chromosome 10; miR,
microRNA; UTR, untranslated region; RT-qPCR, reverse
transcription-quantitative polymerase chain reaction; NC, negative
control; SD, standard deviation; wt, wild-type; mut, mutant; AKI,
acute kidney injury; LPS, lipopolysaccharide. |
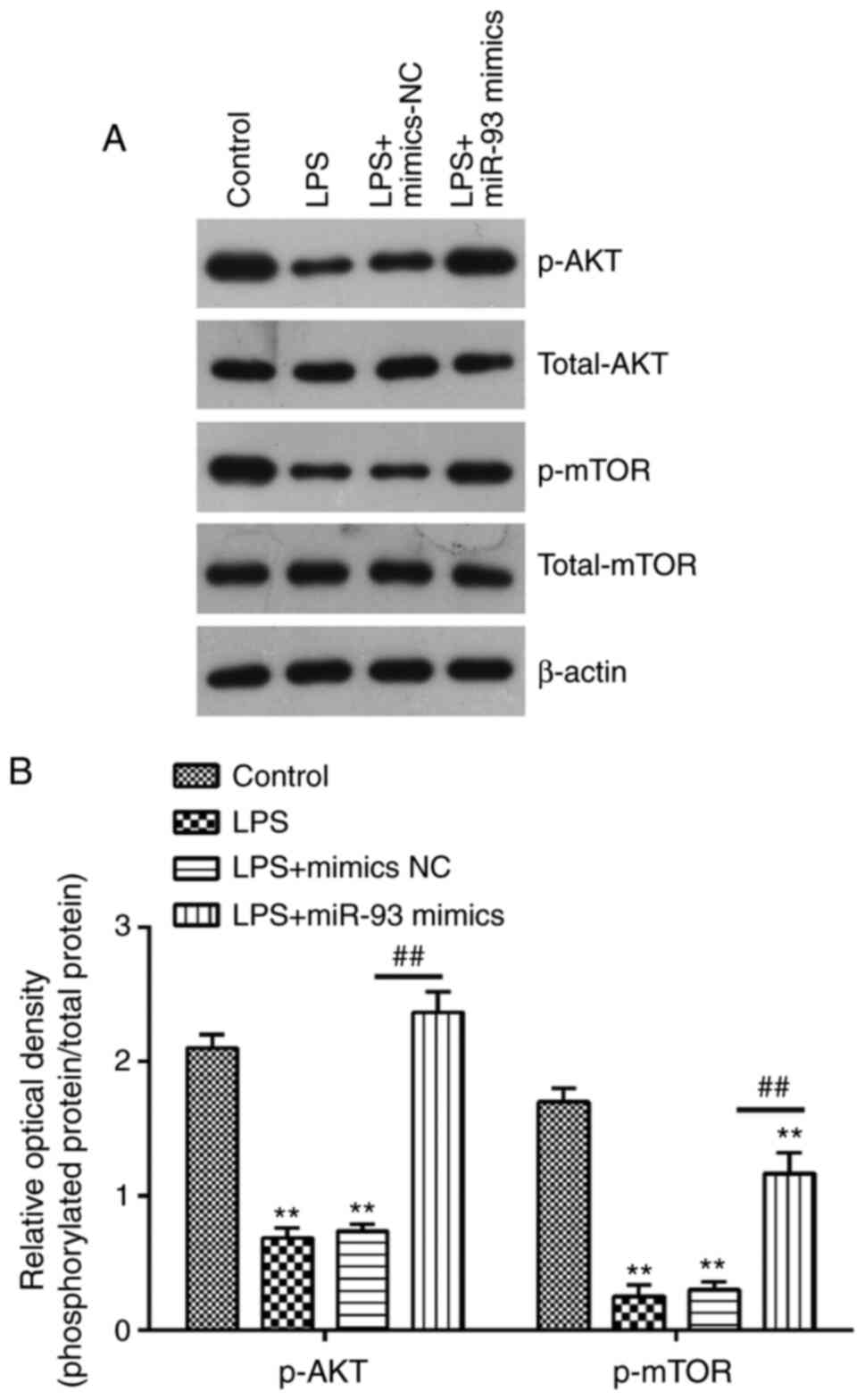
miR-93 reactivates the AKT/mTOR
pathway in the AKI cell model
It is well-known that PTEN is a negative regulator
of AKT/mTOR pathway, which is directly associated with apoptosis
(38,39). Therefore, the present study further
investigated whether miR-93 affected the activation of AKT/mTOR in
the AKI cell model. The results of western blotting demonstrated
that the protein levels of p-AKT and p-mTOR were decreased in
LPS-treated TCMK-1 cells, compared with that in the control group,
but these inhibitory effects of LPS on the protein levels of p-AKT
and p-mTOR were reversed by miR-93 upregulation (Fig. 6A and B). These findings suggested
that miR-93 may re-activate the AKT/mTOR pathway through
suppressing PTEN.
Discussion
In the present study, miR-93 was revealed to be
significantly downregulated in kidney tissues from an AKI mouse
model. These results demonstrated that overexpression of miR-124
alleviates LPS-induced TEC cell injury by suppressing apoptosis,
oxidative stress and inflammation. In addition, it was demonstrated
that overexpression of miR-93 may exert protective effects against
AKI by reactivating the PTEN/AKT/mTOR pathway. The results of the
present study suggested that miR-93 may serve as a potential future
therapeutic target for AKI treatment.
There are several AKI animal models that have been
generated and widely used in research, which have provided
significant information on the post-AKI pathophysiological changes
and molecular mechanisms (40,41).
All types of models of AKI have their own advantages in clinical
difficulty, stability and feasibility, and at the same time, there
are certain deficiencies in the process of modeling. The animal
models of renal ischemia-reperfusion injury-induced AKI generated
by temporary unilateral or bilateral clamping of renal pedicles or
renal arteries have been well established and broadly used in the
study of AKI pathogenesis and drug efficacy evaluation (42,43).
Furthermore, the cecal ligation and puncture mouse model of sepsis
is also used to investigate the pathogenesis of septic AKI
(44). Of note, the LPS model
differs substantially from the ischemia and maleate models in that
LPS does not induce significant proximal tubule necrosis. A
previous study has reported that the loss of functional TECs via
inflammatory response in the pathological process of AKI (4). Notably, anti-inflammatory and
anti-apoptotic therapy was confirmed to be beneficial for the
treatment of sepsis-induced AKI (5,6). LPS
is a classical ligand for TLR4 and mediates TLR4-dependent signal
transduction to activate NF-κB, leading to an increase in
inflammatory cytokine expression, including IL-1β, IL-6 and TNF-α
(7). Therefore, an LPS-induced
experimental model was comprehensively used to investigate and
evaluate the anti-inflammatory treatment of sepsis-related AKI.
Future studies should aim to further verify the results of the
present study using different AKI models.
Growing evidence has revealed that miRNAs are
abnormally expressed in renal tissues and are often associated with
renal injury responses, including apoptosis, oxidative stress and
inflammation (45–48). For example, Li et al
(49) demonstrated that
miR-25-overexpression may ameliorate high glucose (HG)-induced
oxidative stress and apoptosis in renal TECs. Qu and Zhang
(50) reported that downregulation
of miR-122 alleviated renal ischemic reperfusion injury through
inhibiting apoptosis and ROS generation in rat renal TECs. Song
et al (27) reported that
miR-21-overexpression protects against AKI by preventing epithelial
cell apoptosis. Therefore, clarification of the role and regulation
of miRNAs in AKI may generate a potential therapeutic strategy for
AKI. In the present study, using an miRNA microarray revealed that
a large set of miRNAs were abnormally expressed; in particular,
miR-93 was identified as the most downregulated miRNA in kidney
tissues from AKI mice, suggesting that miR-93 may be involved in
the development of AKI.
Several studies have demonstrated that miR-93 exerts
protective effects in various injury models. For example, Ma et
al (51) reported that miR-93
decreased the cardiac microvascular endothelial cell injury via
inactivation of the NF-κB signaling pathway. Yan et al
(52) demonstrated that miR-93
inhibition ameliorated oxygen-glucose deprivation/reoxygenation
injury in cardiomyocytes by targeting Nrf2. Xiong et al
(30) reported that overexpression
of miR-93 alleviated hepatic injury by suppressing apoptosis and
inflammatory response. In a clinical study, miR-93 has been
proposed to serve as a biomarker for early detection of AKI
(29). However, the regulatory
roles of miR-93 in AKI remain unknown. In the present study, an
LPS-induced TCMK-1 cell model revealed that overexpression of
miR-93 suppressed the apoptosis, oxidative stress and inflammatory
response. Taken together, these data revealed that miR-93
upregulation has a protective effect in AKI via suppressing the
apoptosis, oxidative stress and inflammatory response, indicating
that miR-93 may be a potential candidate target for AKI therapy.
However, the molecular mechanism requires further
clarification.
It is recognized that identifying the downstream
target gene(s) is a key to elucidating the pathophysiological role
of an miRNA. In the present study, using computational algorithms,
PTEN was identified as a target of miR-93. PTEN has been found to
serve important roles in renal injury (53). For example, Li et al
(49) demonstrated that
overexpression of PTEN promoted the apoptosis of renal TECs in a
HG-induced cell damage model. Zhang et al (54) reported that activation of PTEN/AKT
signaling alleviated tubular cell apoptosis, thereby protecting
animals from Cis-induced AKI. Notably, PTEN has been reported to be
a direct target of miR-93 in myocardial ischemia/reperfusion (I/R)
injury (55). The present study
demonstrated that PTEN is also a direct target of miR-93 in renal
TECs and its protein expression was negatively regulated by miR-93
in TCMK-1 cells and in kidney tissues of AKI mice. These results
suggested that miR-93 may exert its protective effect in AKI via
reactivating the PTEN/AKT/mTOR pathway.
Numerous signaling pathways are downstream of PTEN.
One important pathway, the endogenous PI3K/AKT pathway, regulates
negative feedback in response to LPS stimuli (56,57).
The PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway is ubiquitous in cells and is involved in
the modulation of a series of physiological activities associated
with AKI, including cell apoptosis, oxidative indices and
inflammatory response (58,59). A previous study has demonstrated
that AKT/mTOR signaling activation markedly attenuated
inflammation, mitochondrial damage and apoptosis caused by
ischemia/reperfusion (I/R)-induced AKI (60). Zhang et al (61) demonstrated that activation of the
PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway may prevent the apoptosis and inflammation in
tubular epithelial cells following I/R injury. Of note, miR-93 may
protect against I/R-induced cardiomyocyte apoptosis by inhibiting
the PTEN/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway (55). Therefore, the present study aimed to
investigate whether miR-93 affects the PTEN/AKT/mTOR signaling
pathway in an AKI cell model. In the present study, it was
demonstrated that overexpression of miR-93 decreased the increased
protein levels of p-AKT and p-mTOR induced by LPS in TCMK-1 cells.
Taken together, these results suggested that miR-93 may exert its
protective effects on AKI by promoting the PTEN/AKT/mTOR signaling
pathway.
However, there are certain limitations to the
present study. For example, only the AKT/mTOR signaling pathway was
investigated, while other pathways may also be associated with the
pathogenesis of AKI. Additionally, the number of experimental
animals was limited. In the future, further systematic and in-depth
studies investigating the pathogenesis of AKI will be
conducted.
In conclusion, the results of the present study
demonstrated that upregulation of miR-93 protects against
LPS-induced TEC apoptosis, oxidative stress and inflammatory
response in an in vitro model of AKI. The underlying
molecular mechanism is mediated via promoting the activation of the
PTEN/AKT/mTOR pathway. These findings may provide a novel direction
for the treatment of AKI.
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Funding
The present study was supported by the Clinical
Innovation and Multi-discipline Integrated Medical Construction
Project of South Campus, Renji Hospital, School of Medicine,
Shanghai Jiaotong University (grant no. 2014MDT02) and Cultivating
Funds of Medicine, Shanghai Jiaotong University (grant no.
2017PYQB05).
Availability of data and materials
All data generated or analyzed during this study are
included in this published article.
Authors' contributions
YZ, MZ, SL, JL and ZN performed all the experiments
and collected the data. YZ, HC and WZ confirm the authenticity of
all the raw data. YZ, HC and WZ conceived and designed the study.
YZ HC and WZ wrote the main manuscript and analyzed the data. All
authors read and approved the final version of the manuscript.
Ethics approval and consent to
participate
The present study was approved by the Animal
Experimentation Ethics Committee of the School of Medicine,
Shanghai Jiao Tong University (Shanghai, China).
Patient consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing
interests.
References
|
1
|
Bonventre JV and Yang L: Cellular
pathophysiology of ischemic acute kidney injury. J Clin Invest.
121:4210–4221. 2011. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Moreth K, Frey H, Hubo M, Zeng-Brouwers J,
Nastase MV, Hsieh LT, Haceni R, Pfeilschifter J, Iozzo RV and
Schaefer L: Biglycan-triggered TLR-2- and TLR-4-signaling
exacerbates the pathophysiology of ischemic acute kidney injury.
Matrix Biol. 35:143–151. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Sharfuddin AA and Molitoris BA:
Pathophysiology of ischemic acute kidney injury. Nat Rev Nephrol.
7:189–200. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Scharnweber T, Alhilali L and Fakhran S:
Contrast-induced acute kidney injury: Pathophysiology,
manifestations, prevention, and management. Magn Reson Imaging Clin
N Am. 25:743–753. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Peng X, Wang Y, Li H, Fan J, Shen J, Yu X,
Zhou Y and Mao H: ATG5-mediated autophagy suppresses NF-κB
signaling to limit epithelial inflammatory response to kidney
injury. Cell Death Dis. 10:2532019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Zhi D, Zhang M, Lin J, Liu P and Duan M:
GPR120 ameliorates apoptosis and inhibits the production of
inflammatory cytokines in renal tubular epithelial cells.
Inflammation. 44:493–505. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Souza AC, Volpini RA, Shimizu MH, Sanches
TR, Camara NO, Semedo P, Rodrigues CE, Seguro AC and Andrade L:
Erythropoietin prevents sepsis-related acute kidney injury in rats
by inhibiting NF-κB and upregulating endothelial nitric oxide
synthase. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 302:F1045–F1054. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Xie C, Liu L, Wang Z, Xie H, Feng Y, Suo
J, Wang M, Shang W and Feng G: Icariin improves sepsis-induced
mortality and acute kidney injury. Pharmacology. 102:196–205. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Wang C, Sun H, Song Y, Ma Z, Zhang G, Gu X
and Zhao L: Pterostilbene attenuates inflammation in rat heart
subjected to ischemia-reperfusion: Role of TLR4/NF-kappaB signaling
pathway. Int J Clin Exp Med. 8:1737–1746. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Thomson DW and Dinger ME: Endogenous
microRNA sponges: Evidence and controversy. Nat Rev Genet.
17:272–283. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Dragomir MP, Knutsen E and Calin GA:
SnapShot: Unconventional miRNA functions. Cell. 174:1038–1038.e1.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Ren GL, Zhu J, Li J and Meng XM: Noncoding
RNAs in acute kidney injury. J Cell Physiol. 234:2266–2276. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Bhatt K, Mi QS and Dong Z: MicroRNAs in
kidneys: Biogenesis, regulation, and pathophysiological roles. Am J
Physiol Renal Physiol. 300:F602–F610. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Liao W, Fu Z, Zou Y, Wen D, Ma H, Zhou F,
Chen Y, Zhang M and Zhang W: MicroRNA-140-5p attenuated oxidative
stress in Cisplatin induced acute kidney injury by activating
Nrf2/ARE pathway through a Keap1-independent mechanism. Exp Cell
Res. 360:292–302. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Lan YF, Chen HH, Lai PF, Cheng CF, Huang
YT, Lee YC, Chen TW and Lin H: MicroRNA-494 reduces ATF3 expression
and promotes AKI. J Am Soc Nephrol. 23:2012–2023. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Wu R, Wu Y, Yang L, Deng Y and Chen D:
Value of serum level of microRNA-494 in predicting prognosis of
acute renal injury after cardiac surgery in children. Zhonghua Wei
Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 31:1469–1473. 2019.(In Chinese).
PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Wang S, Zhang Z, Wang J and Miao H:
MiR-107 induces TNF-α secretion in endothelial cells causing
tubular cell injury in patients with septic acute kidney injury.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 483:45–51. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Lv LL, Feng Y, Wu M, Wang B, Li ZL, Zhong
X, Wu WJ, Chen J, Ni HF, Tang TT, et al: Exosomal miRNA-19b-3p of
tubular epithelial cells promotes M1 macrophage activation in
kidney injury. Cell Death Differ. 27:210–226. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Jiang L, Liu XQ, Ma Q, Yang Q, Gao L, Li
HD, Wang JN, Wei B, Wen J, Li J, et al: hsa-miR-500a-3P alleviates
kidney injury by targeting MLKL-mediated necroptosis in renal
epithelial cells. FASEB J. 33:3523–3535. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Guo Y, Ni J, Chen S, Bai M, Lin J, Ding G,
Zhang Y, Sun P, Jia Z, Huang S, et al: MicroRNA-709 mediates acute
tubular injury through effects on mitochondrial function. J Am Soc
Nephrol. 29:449–461. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Yan Y, Ma Z, Zhu J, Zeng M, Liu H and Dong
Z: MiR-214 represses mitofusin-2 to promote renal tubular apoptosis
in ischemic acute kidney injury. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol.
318:F878–F887. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Chen X, Zhang X, Xu J, Zhao Y, Bao J,
Zheng Z and Han J: AZD4547 attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced
acute kidney injury by inhibiting inflammation: The Role of FGFR1
in renal tubular epithelial cells. Drug Des Devel Ther. 14:833–844.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Tang C, Han H, Yan M, Zhu S, Liu J, Liu Z,
He L, Tan J, Liu Y, Liu H, et al: PINK1-PRKN/PARK2 pathway of
mitophagy is activated to protect against renal
ischemia-reperfusion injury. Autophagy. 14:880–897. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Mei LL, Wang WJ, Qiu YT, Xie XF, Bai J and
Shi ZZ: MiR-125b-5p functions as a tumor suppressor gene partially
by regulating HMGA2 in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. PLoS
One. 12:e01856362017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Xu J, Ma X, Yu K, Wang R, Wang S, Liu R,
Liu H, Gao H, Yu K and Wang C: Lactate up-regulates the expression
of PD-L1 in kidney and causes immunosuppression in septic acute
renal injury. J Microbiol Immunol Infect. S1684-1182:30168–30169.
2019.(Epub ahead of print).
|
|
27
|
Song N, Zhang T, Xu X, Lu Z, Yu X, Fang Y,
Hu J, Jia P, Teng J and Ding X: MiR-21 protects against
ischemia/reperfusion-induced acute kidney injury by preventing
epithelial cell apoptosis and inhibiting dendritic cell maturation.
Front Physiol. 9:7902018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Li H, Ma Y, Chen B and Shi J: MiR-182
enhances acute kidney injury by promoting apoptosis involving the
targeting and regulation of TCF7L2/Wnt/β-catenins pathway. Eur J
Pharmacol. 831:20–27. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Shihana F, Joglekar MV, Raubenheimer J,
Hardikar AA, Buckley NA and Seth D: Circulating human microRNA
biomarkers of oxalic acid-induced acute kidney injury. Arch
Toxicol. 94:1725–1737. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Xiong L, Yu KH and Zhen SQ: MiR-93 blocks
STAT3 to alleviate hepatic injury after ischemia-reperfusion. Eur
Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 22:5295–5304. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Wang P, Liang X, Lu Y, Zhao X and Liang J:
MicroRNA-93 downregulation ameliorates cerebral ischemic injury
through the Nrf2/HO-1 defense pathway. Neurochem Res. 41:2627–2635.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Shen Y, Yu J, Jing Y and Zhang J: MiR-106a
aggravates sepsis-induced acute kidney injury by targeting THBS2 in
mice model. Acta Cir Bras. 34:e2019006022019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Zhu Y, Wei SW, Ding A, Zhu WP, Mai MF, Cui
TX, Yang H and Zhang H: The long noncoding RNA ANRIL promotes cell
apoptosis in lipopolysaccharide-induced acute kidney injury
mediated by the TLR4/nuclear factor-kappa B pathway. Kidney Blood
Press Res. 45:209–221. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Paller MS, Hoidal JR and Ferris TF: Oxygen
free radicals in ischemic acute renal failure in the rat. J Clin
Invest. 74:1156–1164. 1984. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Baliga R, Ueda N, Walker PD and Shah SV:
Oxidant mechanisms in toxic acute renal failure. Drug Metab Rev.
31:971–997. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Brezniceanu ML, Lau CJ, Godin N, Chénier
I, Duclos A, Ethier J, Filep JG, Ingelfinger JR, Zhang SL and Chan
JS: Reactive oxygen species promote caspase-12 expression and
tubular apoptosis in diabetic nephropathy. J Am Soc Nephrol.
21:943–954. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Li GS, Chen XL, Zhang Y, He Q, Wang F,
Hong DQ, Zhang P, Pu L, Zhang Y, Yang XC and Wang L: Malnutrition
and inflammation in acute kidney injury due to earthquake-related
crush syndrome. BMC Nephrol. 11:42010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Yang P, Peairs JJ, Tano R and Jaffe GJ:
Oxidant-mediated Akt activation in human RPE cells. Invest
Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 47:4598–4606. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Byeon SH, Lee SC, Choi SH, Lee HK, Lee JH,
Chu YK and Kwon OW: Vascular endothelial growth factor as an
autocrine survival factor for retinal pigment epithelial cells
under oxidative stress via the VEGF-R2/PI3K/Akt. Invest Ophthalmol
Vis Sci. 51:1190–1197. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Skrypnyk NI, Voziyan P, Yang H, de
Caestecker CR, Theberge MC, Drouin M, Hudson B, Harris RC and de
Caestecker MP: Pyridoxamine reduces postinjury fibrosis and
improves functional recovery after acute kidney injury. Am J
Physiol Renal Physiol. 311:F268–F277. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Zager RA, Johnson AC and Becker K: Acute
unilateral ischemic renal injury induces progressive renal
inflammation, lipid accumulation, histone modification, and
‘end-stage’ kidney disease. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol.
301:F1334–F1345. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Gall JM, Wong V, Pimental DR, Havasi A,
Wang Z, Pastorino JG, Bonegio RG, Schwartz JH and Borkan SC:
Hexokinase regulates Bax-mediated mitochondrial membrane injury
following ischemic stress. Kidney Int. 79:1207–1216. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Lee HT, Park SW, Kim M, Ham A, Anderson
LJ, Brown KM, D'Agati VD and Cox GN: Interleukin-11 protects
against renal ischemia and reperfusion injury. Am J Physiol Renal
Physiol. 303:F1216–F1224. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Schrier RW and Wang W: Acute renal failure
and sepsis. N Engl J Med. 351:159–169. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Saikumar J, Hoffmann D, Kim TM, Gonzalez
VR, Zhang Q, Goering PL, Brown RP, Bijol V, Park PJ, Waikar SS and
Vaidya VS: Expression, circulation, and excretion profile of
microRNA-21, −155, and −18a following acute kidney injury. Toxicol
Sci. 129:256–267. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Szeto CC, Ching-Ha KB, Ka-Bik L, Mac-Moune
LF, Cheung-Lung CP, Gang W, Kai-Ming C and Kam-Tao LP: Micro-RNA
expression in the urinary sediment of patients with chronic kidney
diseases. Dis Markers. 33:137–144. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Chen W, Ruan Y, Zhao S, Ning J, Rao T, Yu
W, Zhou X, Liu C, Qi Y and Cheng F: MicroRNA-205 inhibits the
apoptosis of renal tubular epithelial cells via the PTEN/Akt
pathway in renal ischemia-reperfusion injury. Am J Transl Res.
11:7364–7375. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Wu H, Huang T, Ying L, Han C, Li D, Xu Y,
Zhang M, Mou S and Dong Z: MiR-155 is involved in renal
ischemia-reperfusion injury via direct targeting of FoxO3a and
regulating renal tubular cell pyroptosis. Cell Physiol Biochem.
40:1692–1705. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Li H, Zhu X, Zhang J and Shi J:
MicroRNA-25 inhibits high glucose-induced apoptosis in renal
tubular epithelial cells via PTEN/AKT pathway. Biomed Pharmacother.
96:471–479. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Qu XH and Zhang K: MiR-122 regulates cell
apoptosis and ROS by targeting DJ-1 in renal ischemic reperfusion
injury rat models. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 22:8830–8838.
2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Ma SX, Bai ZF, Wang W and Wu HY: Effects
of microrna-93 on mouse cardiac microvascular endothelial cells
injury and inflammatory response by mediating SPP1 through the
NF-ΚB pathway. J Cell Biochem. 120:2847–2858. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Yan LJ, Fan XW, Yang HT, Wu JT, Wang SL
and Qiu CG: MiR-93 inhibition ameliorates OGD/R induced
cardiomyocyte apoptosis by targeting Nrf2. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol
Sci. 21:5456–5461. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Gao S, Zhu Y, Li H, Xia Z, Wu Q, Yao S,
Wang T and Yuan S: Remote ischemic postconditioning protects
against renal ischemia/reperfusion injury by activation of
T-LAK-cell-originated protein kinase (TOPK)/PTEN/Akt signaling
pathway mediated anti-oxidation and anti-inflammation. Int
Immunopharmacol. 38:395–401. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Zhang W, Chen C, Jing R, Liu T and Liu B:
Remote ischemic preconditioning protects cisplatin-induced acute
kidney injury through the PTEN/AKT signaling pathway. Oxid Med Cell
Longev. 2019:76293962019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Ke ZP, Xu P, Shi Y and Gao AM: MicroRNA-93
inhibits ischemia-reperfusion induced cardiomyocyte apoptosis by
targeting PTEN. Oncotarget. 7:28796–28805. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Zhong J, Qiu X, Yu Q, Chen H and Yan C: A
novel polysaccharide from Acorus tatarinowii protects against
LPS-induced neuroinflammation and neurotoxicity by inhibiting
TLR4-mediated MyD88/NF-κB and PI3K/Akt signaling pathways. Int J
Biol Macromol. 163:464–475. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Liu F, Huang X, He JJ, Song C, Peng L,
Chen T and Wu BL: Plantamajoside attenuates inflammatory response
in LPS-stimulated human gingival fibroblasts by inhibiting PI3K/AKT
signaling pathway. Microb Pathog. 127:208–211. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Meng L, Li L, Lu S, Li K, Su Z, Wang Y,
Fan X, Li X and Zhao G: The protective effect of dexmedetomidine on
LPS-induced acute lung injury through the HMGB1-mediated TLR4/NF-κB
and PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathways. Mol Immunol. 94:7–17. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Liu HB, Meng QH, Huang C, Wang JB and Liu
XW: Nephroprotective effects of polydatin against
ischemia/reperfusion injury: A role for the PI3K/Akt signal
pathway. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2015:3621582015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Yingjie K, Haihong Y, Lingwei C, Sen Z,
Yuanting D, Shasha C, Liutong P, Ying W and Min Z: Apoptosis
repressor with caspase recruitment domain deficiency accelerates
ischemia/reperfusion (I/R)-induced acute kidney injury by
suppressing inflammation and apoptosis: The role of AKT/mTOR
signaling. Biomed Pharmacother. 112:1086812019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Zhang G, Wang Q, Wang W, Yu M, Zhang S, Xu
N, Zhou S, Cao X, Fu X, Ma Z, et al: Tempol protects against acute
renal injury by regulating PI3K/Akt/mTOR and GSK3β signaling
cascades and afferent arteriolar activity. Kidney Blood Press Res.
43:904–913. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|