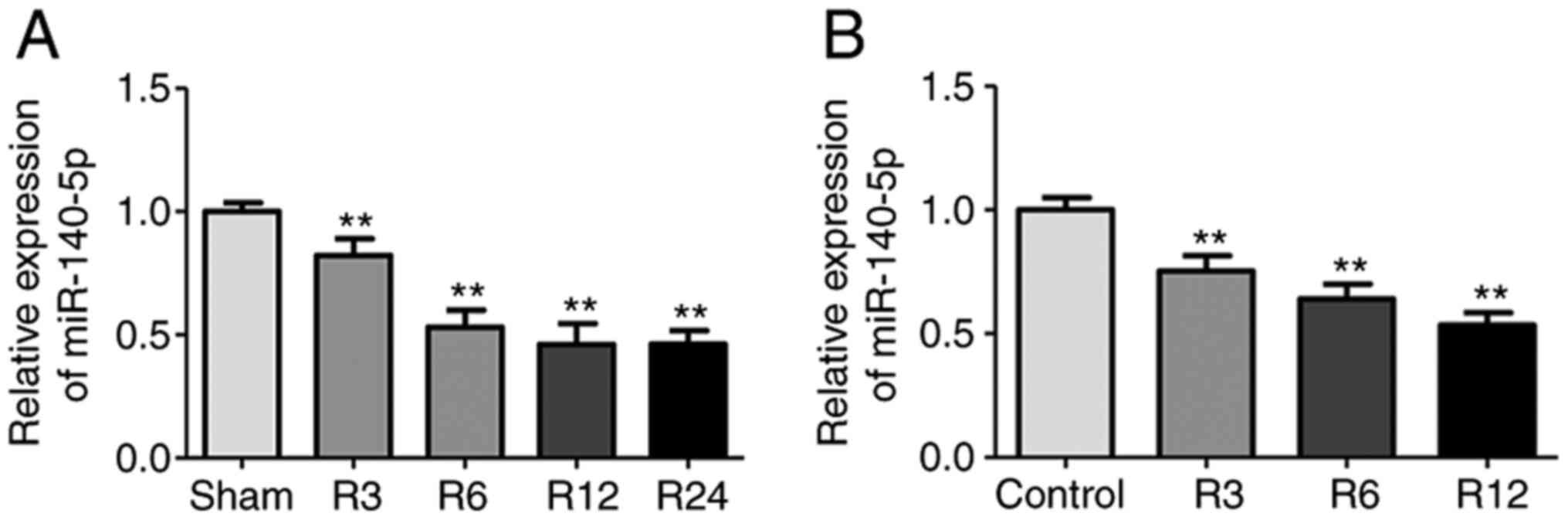
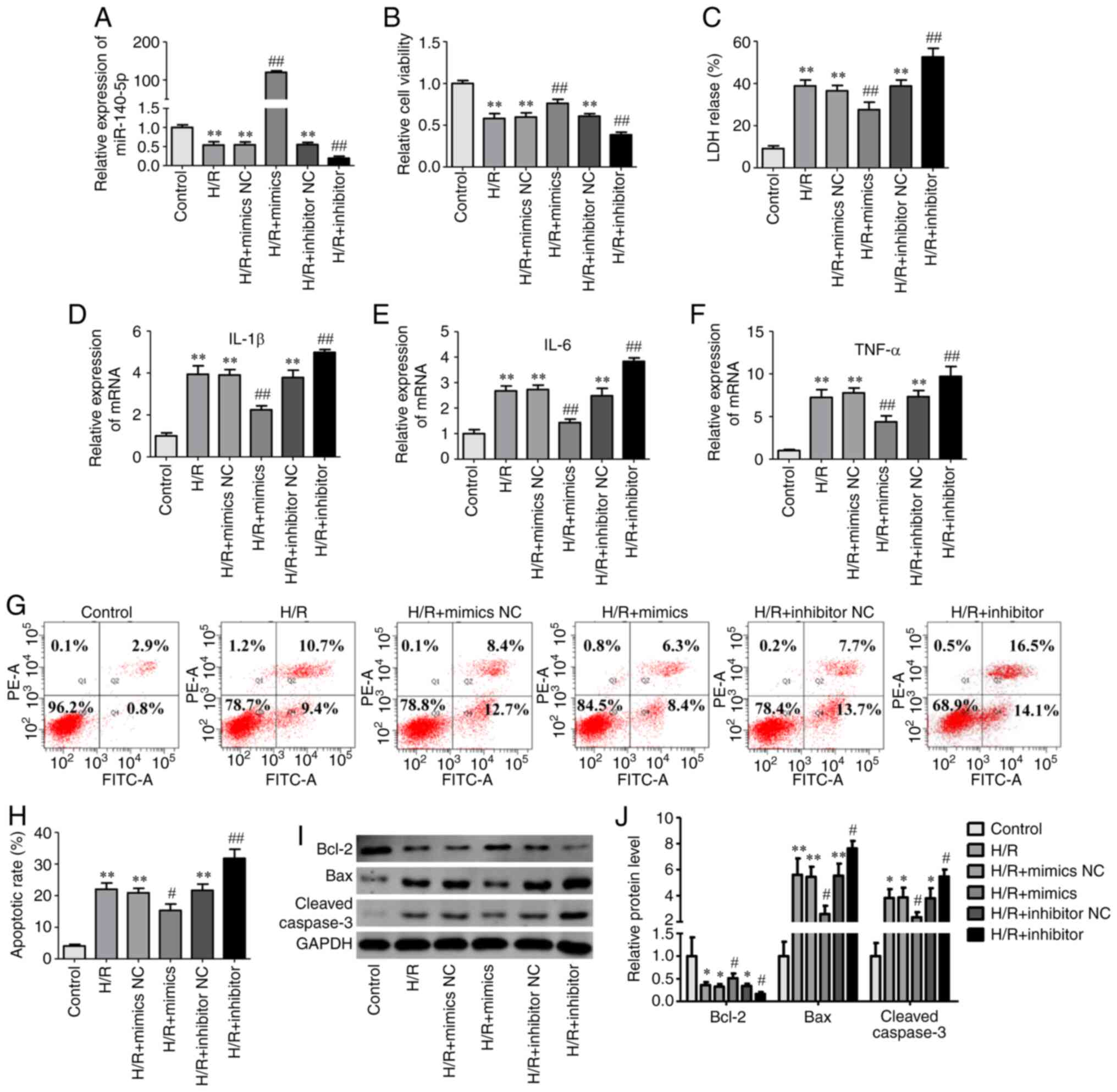
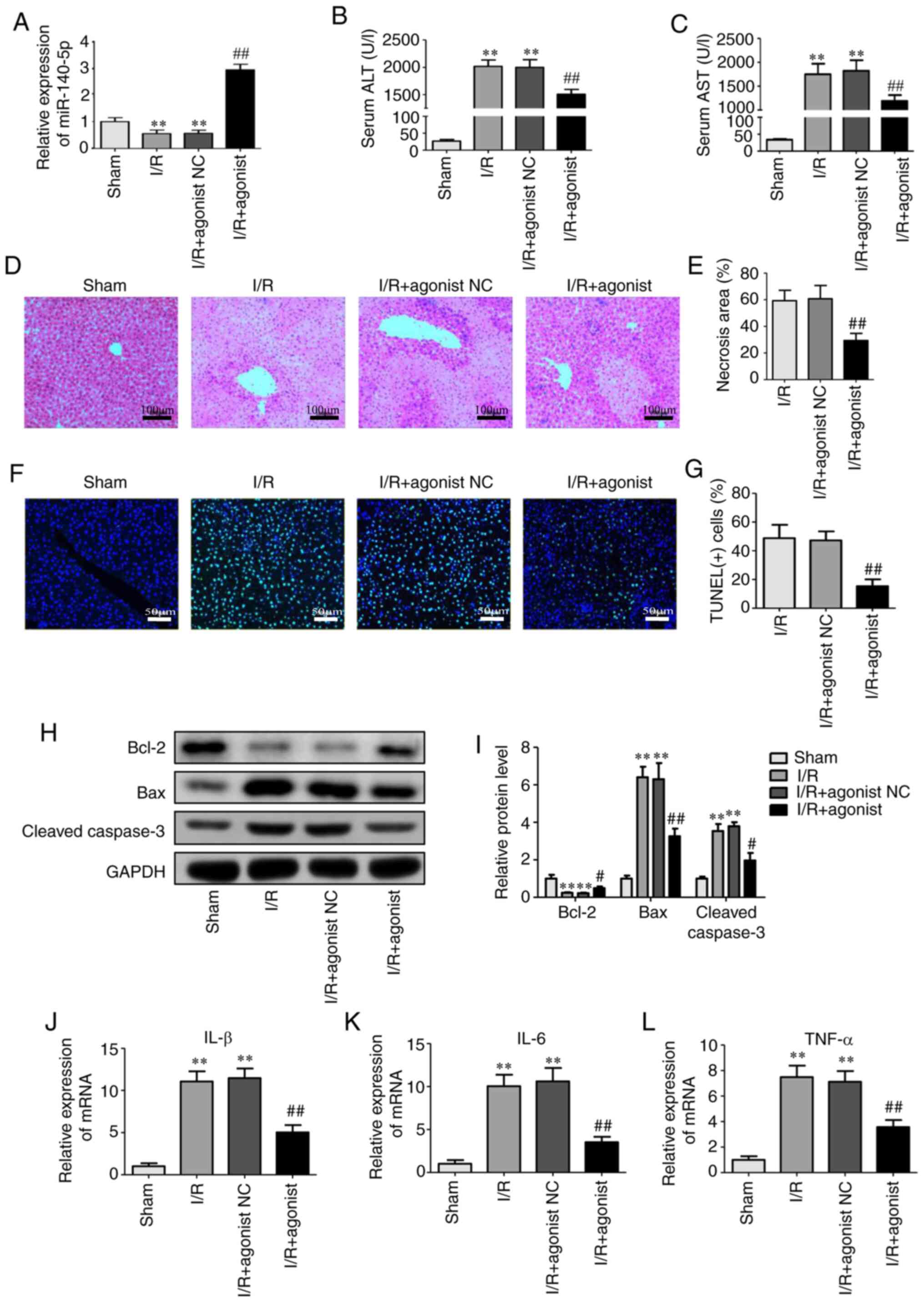
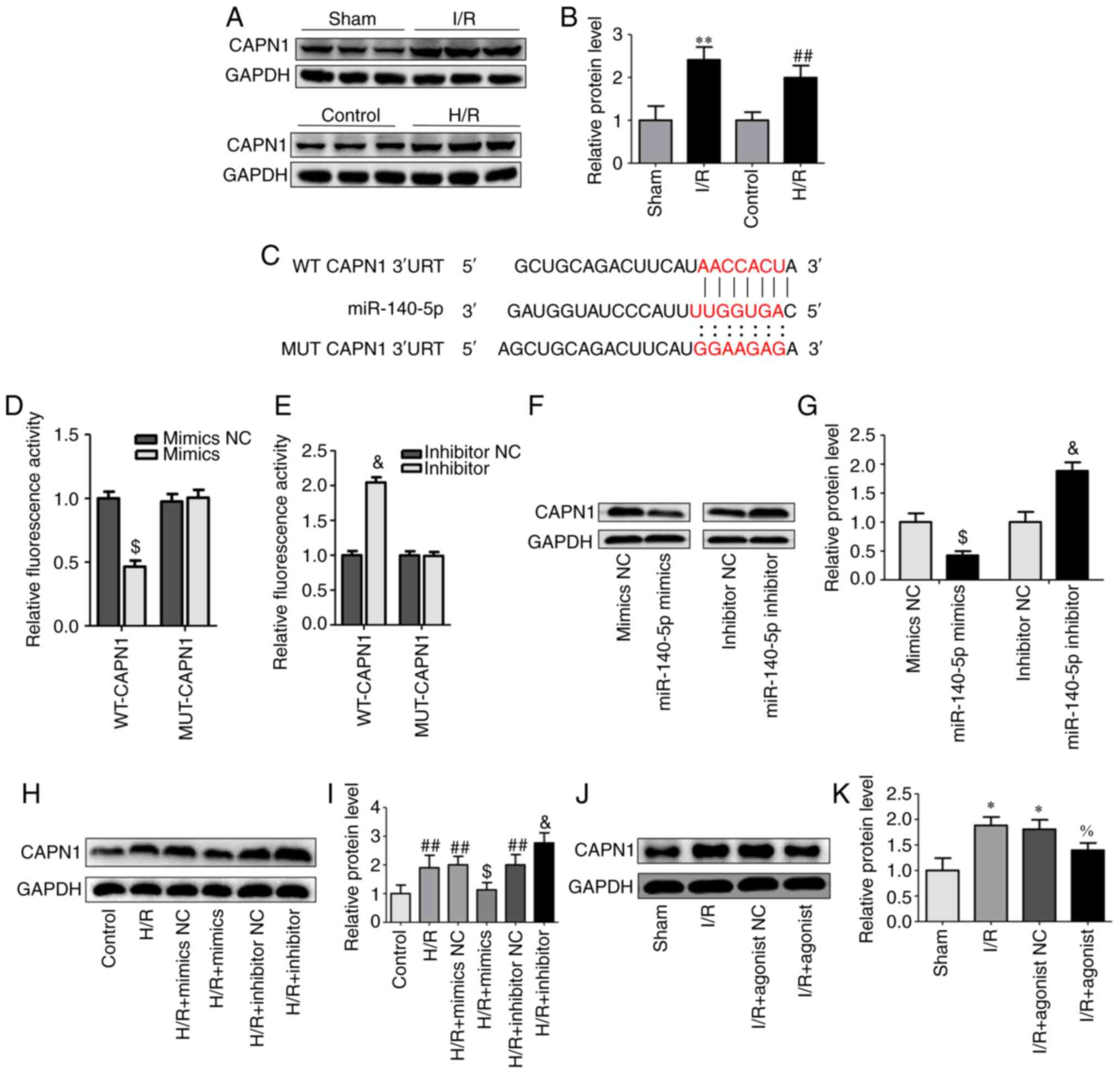
|
1
|
Zhou J, Chen J, Wei Q, Saeb-Parsy K and Xu
X: The role of ischemia/reperfusion injury in early hepatic
allograft dysfunction. Liver Transpl. 26:1034–1048. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Konishi T and Lentsch AB: Hepatic
ischemia/reperfusion: Mechanisms of tissue injury, repair, and
regeneration. Gene Expr. 17:277–287. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Elias-Miró M, Jiménez-Castro MB, Rodés J
and Peralta C: Current knowledge on oxidative stress in hepatic
ischemia/reperfusion. Free Radic Res. 47:555–568. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Fabian MR, Sonenberg N and Filipowicz W:
Regulation of mRNA translation and stability by microRNAs. Annu Rev
Biochem. 79:351–379. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Huang Z, Zheng D, Pu J, Dai J, Zhang Y,
Zhang W and Wu Z: MicroRNA-125b protects liver from
ischemia/reperfusion injury via inhibiting TRAF6 and NF-κB pathway.
Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 83:829–835. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Mou T, Luo Y, Huang Z, Zheng D, Pu X, Shen
A, Pu J, Li T, Dai J, Chen W and Wu Z: Inhibition of
microRNA-128-3p alleviates liver ischaemia-reperfusion injury in
mice through repressing the Rnd3/NF-κB axis. Innate Immun.
26:528–536. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Li Y, Gao M, Xu LN, Yin LH, Qi Y and Peng
JY: MicroRNA-142-3p attenuates hepatic ischemia/reperfusion injury
via targeting of myristoylated alanine-rich C-kinase substrate.
Pharmacol Res. 156:1047832020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Huang Z, Mou T, Luo Y, Pu X, Pu J, Wan L,
Gong J, Yang H, Liu Y, Li Z, et al: Inhibition of miR-450b-5p
ameliorates hepatic ischemia/reperfusion injury via targeting
CRYAB. Cell Death Dis. 11:4552020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Chi X, Jiang Y, Chen Y, Yang F, Cai Q, Pan
F, Lv L and Zhang X: Suppression of microRNA-27a protects against
liver ischemia/reperfusion injury by targeting PPARgamma and
inhibiting endoplasmic reticulum stress. Mol Med Rep. 20:4003–4012.
2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Wienholds E, Kloosterman WP, Miska E,
Alvarez-Saavedra E, Berezikov E, de Bruijn E, Horvitz HR, Kauppinen
S and Plasterk RH: MicroRNA expression in zebrafish embryonic
development. Science. 309:310–311. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Tuddenham L, Wheeler G, Ntounia-Fousara S,
Waters J, Hajihosseini MK, Clark I and Dalmay T: The cartilage
specific microRNA-140 targets histone deacetylase 4 in mouse cells.
Febs Lett. 580:4214–4217. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Miyaki S, Nakasa T, Otsuki S, Grogan SP,
Higashiyama R, Inoue A, Kato Y, Sato T, Lotz MK and Asahara H:
MicroRNA-140 is expressed in differentiated human articular
chondrocytes and modulates interleukin-1 responses. Arthritis
Rheum. 60:2723–2730. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zhu D, Lv W, Zhou X, He Y, Yao H, Yu Y,
Zhang G and Zhang Q: Long non-coding RNA TMPO-AS1 promotes tumor
progression via sponging miR-140-5p in breast cancer. Exp Ther Med.
21:172021.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zhuo E, Cai C, Liu W, Li K and Zhao W:
Downregulated microRNA-140-5p expression regulates apoptosis,
migration and invasion of lung cancer cells by targeting zinc
finger protein 800. Oncol Lett. 20:3902020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Mei J, Liu G, Wang W, Xiao P, Yang D, Bai
H and Li R: OIP5-AS1 modulates epigenetic regulator HDAC7 to
enhance non-small cell lung cancer metastasis via miR-140-5p. Oncol
Lett. 20:72020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Mao Z, Wang Z, Zhang S, Pu Y, Wang J,
Zhang T, Long Y, Liu Y, Ma Y and Zhu J: LRP4 promotes migration and
invasion of gastric cancer under the regulation of microRNA-140-5p.
Cancer Biomark. 29:245–253. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Cai RD, Zhang CC, Xie LL, Wang PC, Huang
CX, Chen JL and Lv HT: SNHG1 promotes malignant progression of
glioma by targeting miR-140-5p and regulating PI3K/AKT pathway.
Cancer Manag Res. 12:12011–12020. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Fan L, Huang X, Chen J, Zhang K, Gu YH,
Sun J and Cui SY: Long noncoding RNA MALAT1 contributes to
sorafenib resistance by targeting miR-140-5p/Aurora-A signaling in
hepatocellular carcinoma. Mol Cancer Ther. 19:1197–1209. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Yang Y, Liu D, Xi Y and Li J, Liu B and Li
J: Upregulation of miRNA-140-5p inhibits inflammatory cytokines in
acute lung injury through the MyD88/NF-kappaB signaling pathway by
targeting TLR4. Exp Ther Med. 16:3913–3920. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Wang S, Cui Y, Xu J and Gao H: miR-140-5p
Attenuates Neuroinflammation and Brain Injury in Rats Following
Intracerebral Hemorrhage by Targeting TLR4. Inflammation.
42:1869–1877. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Wang Y, Shen S, Li Z, Li W and Weng X:
MIR-140-5p affects chondrocyte proliferation, apoptosis, and
inflammation by targeting HMGB1 in osteoarthritis. Inflamm Res.
69:63–73. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Liao W, Fu Z, Zou Y, Wen D, Ma H, Zhou F,
Chen Y, Zhang M and Zhang W: MicroRNA-140-5p attenuated oxidative
stress in Cisplatin induced acute kidney injury by activating
Nrf2/ARE pathway through a Keap1-independent mechanism. Exp Cell
Res. 360:292–302. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Liu H, Mao Z, Zhu J, Shen M and Chen F:
miR-140-5p inhibits oxidized low-density lipoprotein-induced
oxidative stress and cell apoptosis via targeting toll-like
receptor 4. Gene Ther. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Sun J, Tao S, Liu L, Guo D, Xia Z and
Huang M: miR-140-5p regulates angiogenesis following ischemic
stroke by targeting VEGFA. Mol Med Rep. 13:4499–4505. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Demarchi F and Schneider C: The calpain
system as a modulator of stress/damage response. Cell Cycle.
6:136–138. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Lu HT, Feng RQ, Tang JK, Zhou JJ, Gao F
and Ren J: CaMKII/calpain interaction mediates ischemia/reperfusion
injury in isolated rat hearts. Cell Death Dis. 11:3882020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Yue RC, Lu SZ, Luo Y, Wang T, Liang H,
Zeng J, Liu J and Hu HX: Calpain silencing alleviates myocardial
ischemia-reperfusion injury through the NLRP3/ASC/Caspase-1 axis in
mice. Life Sci. 233:1166312019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Zhao H, Xu M and Chu G: Association
between myocardial cell apoptosis and calpain-1/caspase-3
expression in rats with hypoxic-ischemic brain damage. Mol Med Rep.
15:2727–2731. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
National Research Council, . Guide for the
Care and Use of Laboratory Animals. National Academies Press;
Washington, DC: 2010
|
|
30
|
Guo WZ, Fang HB, Cao SL, Chen SY, Li J,
Shi JH, Tang HW, Zhang Y, Wen PH, Zhang JK, et al:
Six-transmembrane epithelial antigen of the prostate 3 Deficiency
in hepatocytes protects the liver against ischemia-reperfusion
injury by suppressing transforming growth factor-β-activated kinase
1. Hepatology. 71:1037–1054. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Yi Z, Deng M, Scott MJ, Fu G, Loughran PA,
Lei Z, Li S, Sun P, Yang C, Li W, et al: Immune-responsive gene
1/itaconate activates nuclear factor Erythroid 2-related factor 2
in hepatocytes to protect against liver ischemia-reperfusion
injury. Hepatology. 72:1394–1411. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Kohli V, Madden JF, Bentley RC and Clavien
PA: Calpain mediates ischemic injury of the liver through
modulation of apoptosis and necrosis. Gastroenterology.
116:168–178. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Li W and He F: Monocyte to macrophage
differentiation-associated (MMD) targeted by miR-140-5p regulates
tumor growth in non-small cell lung cancer. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 450:844–850. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Kai Y, Peng W, Ling W, Jiebing H and Zhuan
B: Reciprocal effects between microRNA-140-5p and ADAM10 suppress
migration and invasion of human tongue cancer cells. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 448:308–314. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Rothman AM, Arnold ND, Pickworth JA,
Iremonger J, Ciuclan L, Allen RM, Guth-Gundel S, Southwood M,
Morrell NW, Thomas M, et al: MicroRNA-140-5p and SMURF1 regulate
pulmonary arterial hypertension. J Clin Invest. 126:2495–2508.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Güllü G, Peker I, Haholu A, Eren F,
Küçükodaci Z, Güleç B, Baloglu H, Erzik C, Özer A and Akkiprik M:
Clinical significance of miR-140-5p and miR-193b expression in
patients with breast cancer and relationship to IGFBP5. Genet Mol
Biol. 38:21–29. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Han XR, Wen X, Wang YJ, Wang S, Shen M,
Zhang ZF, Fan SH, Shan Q, Wang L, Li MQ, et al: MicroRNA-140-5p
elevates cerebral protection of dexmedetomidine against
hypoxic-ischaemic brain damage via the Wnt/beta-catenin signalling
pathway. J Cell Mol Med. 22:3167–3182. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Sorimachi H, Hata S and Ono Y: Calpain
chronicle-an enzyme family under multidisciplinary
characterization. Proc Jpn Acad Ser B Phys Biol Sci. 87:287–327.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Kuchay SM and Chishti AH: Calpain-mediated
regulation of platelet signaling pathways. Curr Opin Hematol.
14:249–254. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Kakurina GV, Kolegova ES, Shashova EE,
Cheremisina OV, Choynzonov EL and Kondakova IV: Relationship
between the mRNA expression levels of calpains 1/2 and proteins
involved in cytoskeleton remodeling. Acta Naturae. 12:110–113.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Kling A, Jantos K, Mack H, Hornberger W,
Drescher K, Nimmrich V, Relo A, Wicke K, Hutchins CW, Lao Y, et al:
Discovery of novel and highly selective inhibitors of calpain for
the treatment of Alzheimer's disease:
2-(3-Phenyl-1H-pyrazol-1-yl)-nicotinamides. J Med Chem.
60:7123–7138. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|