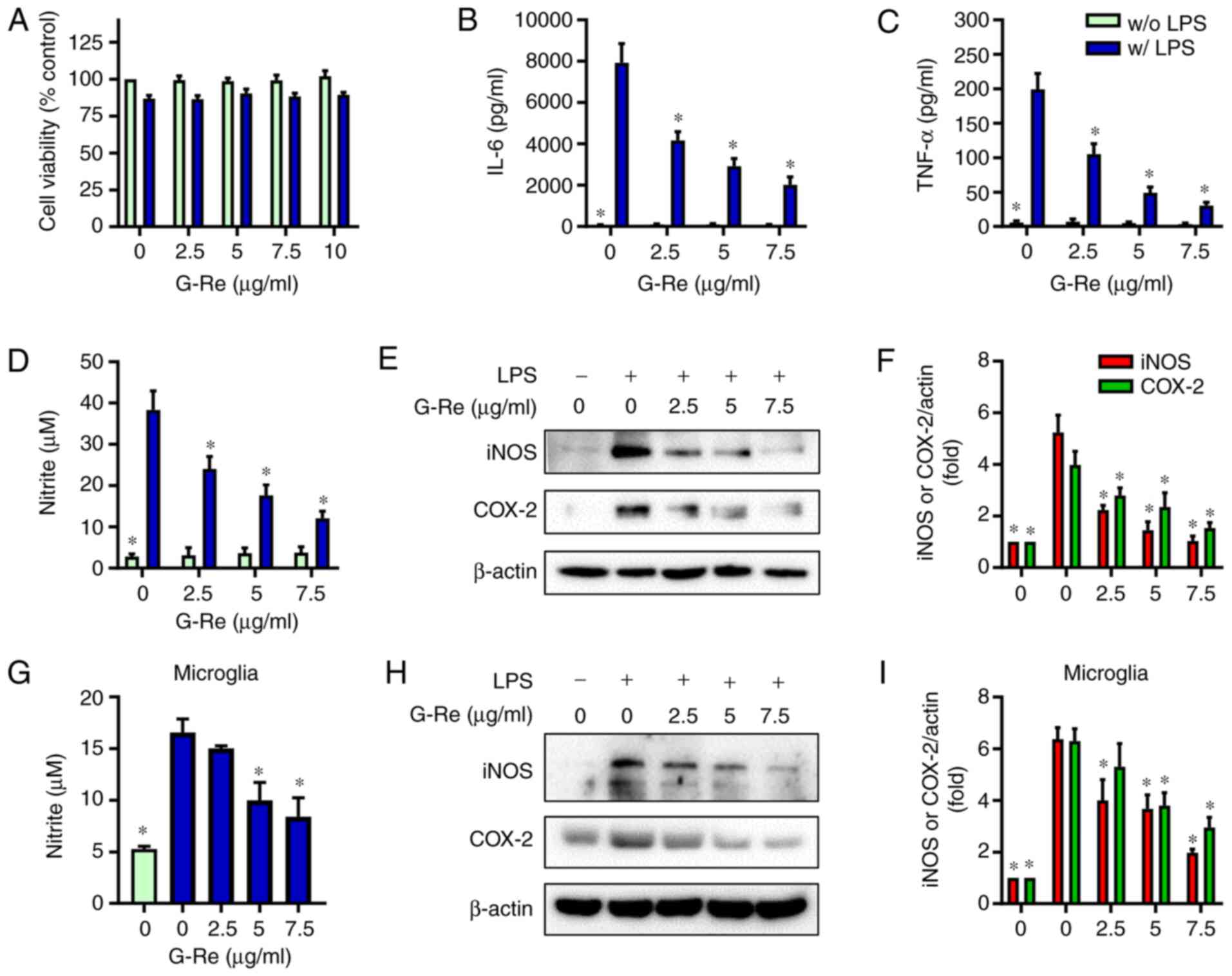
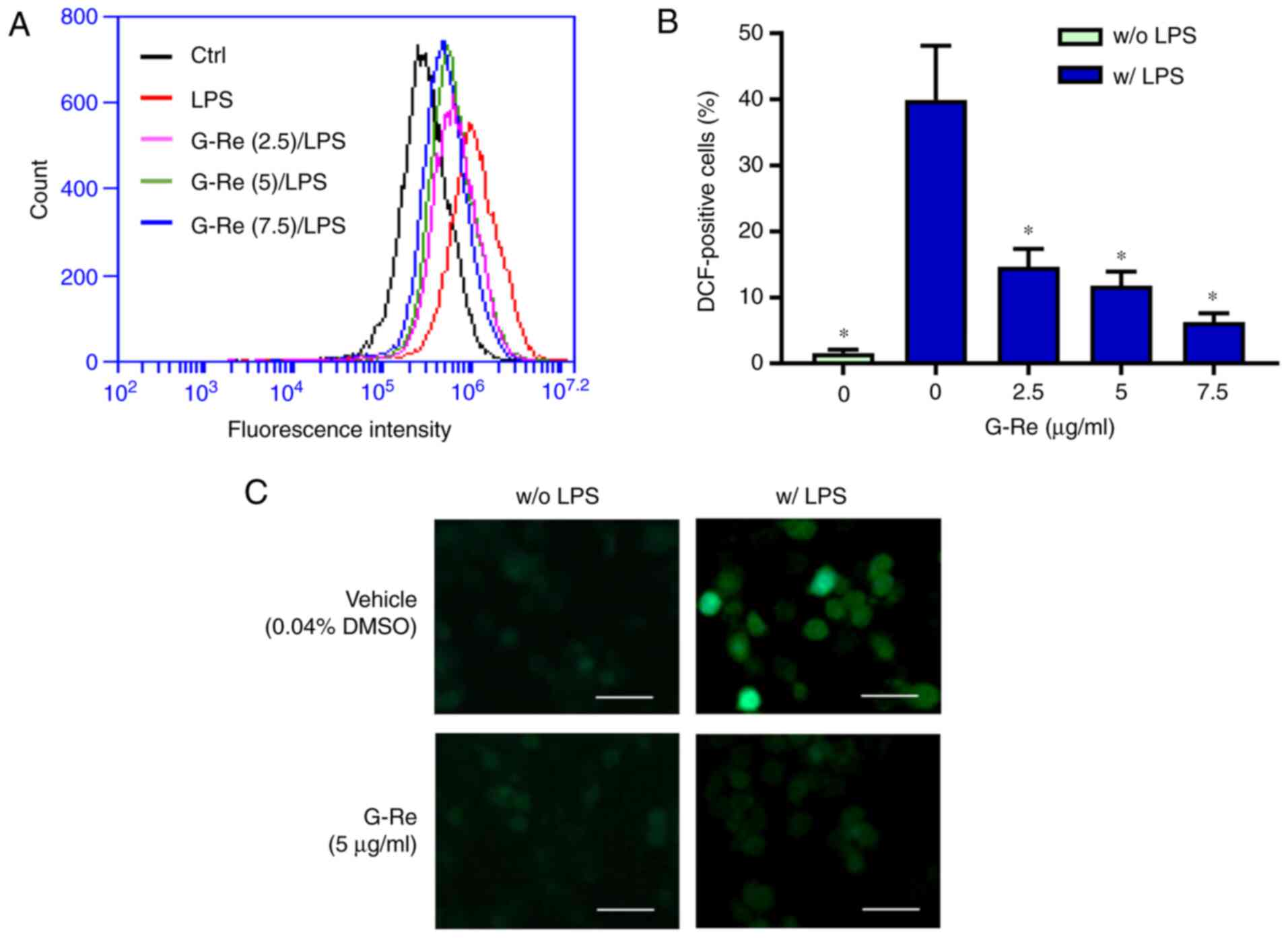
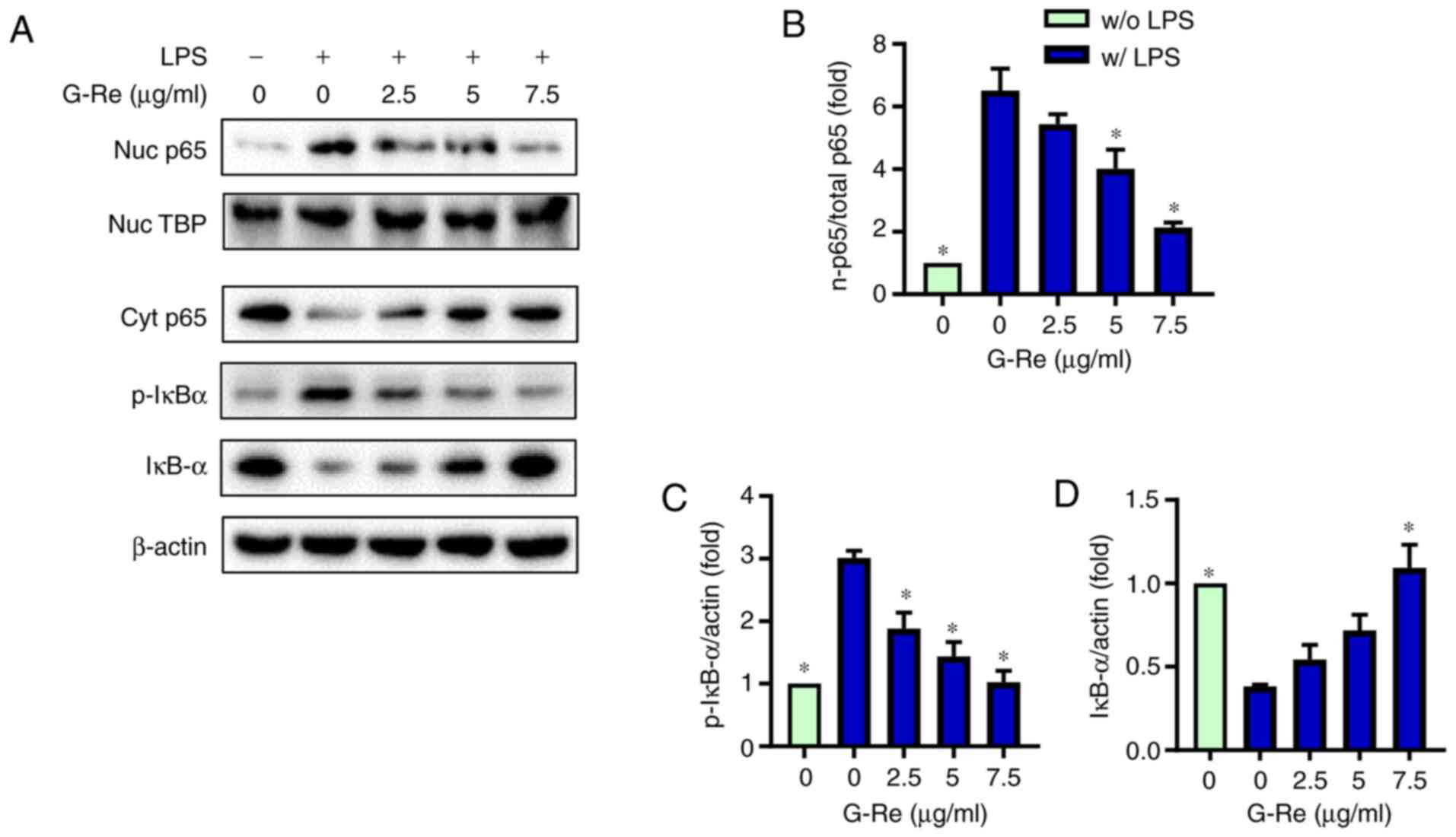
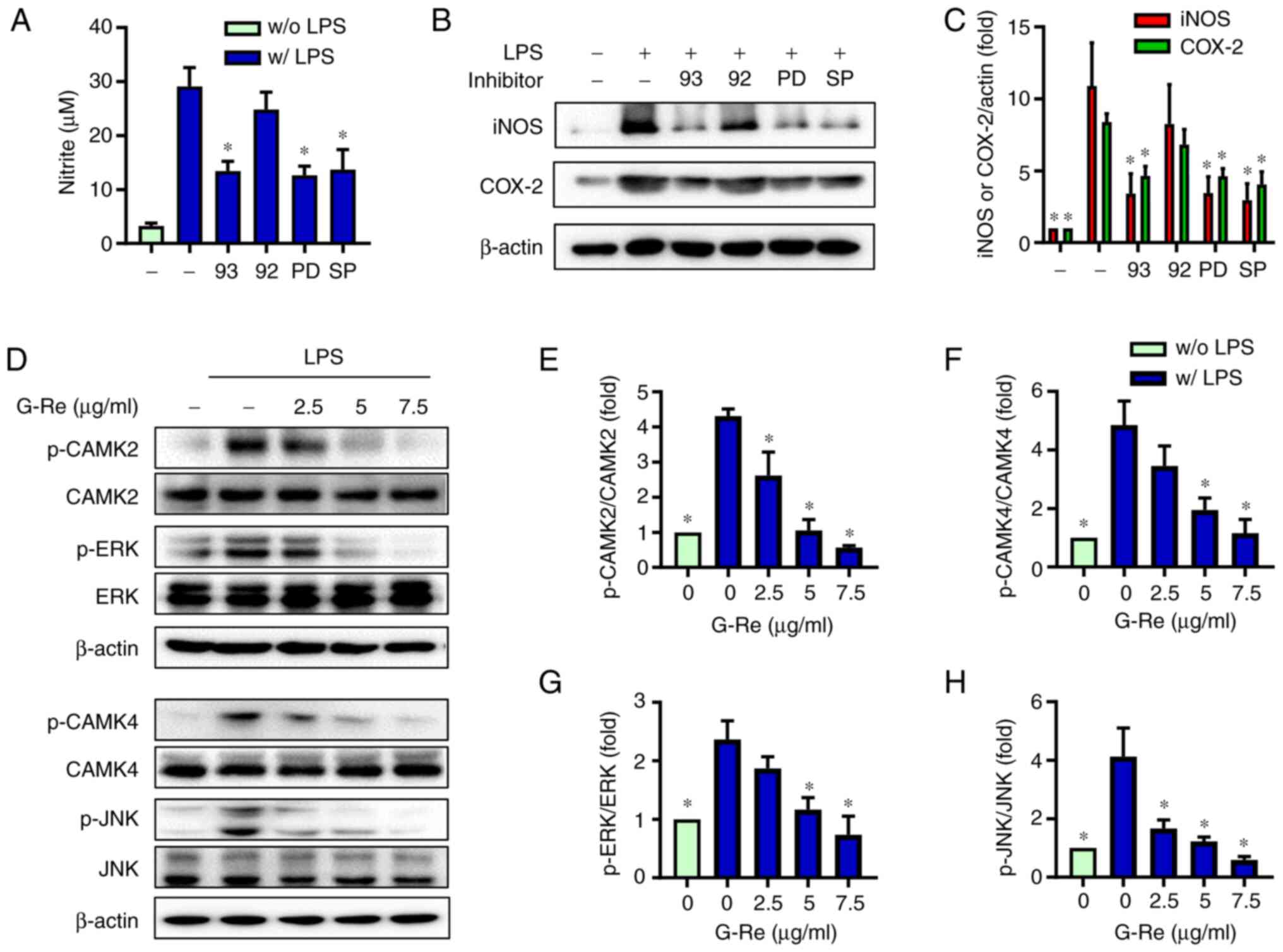
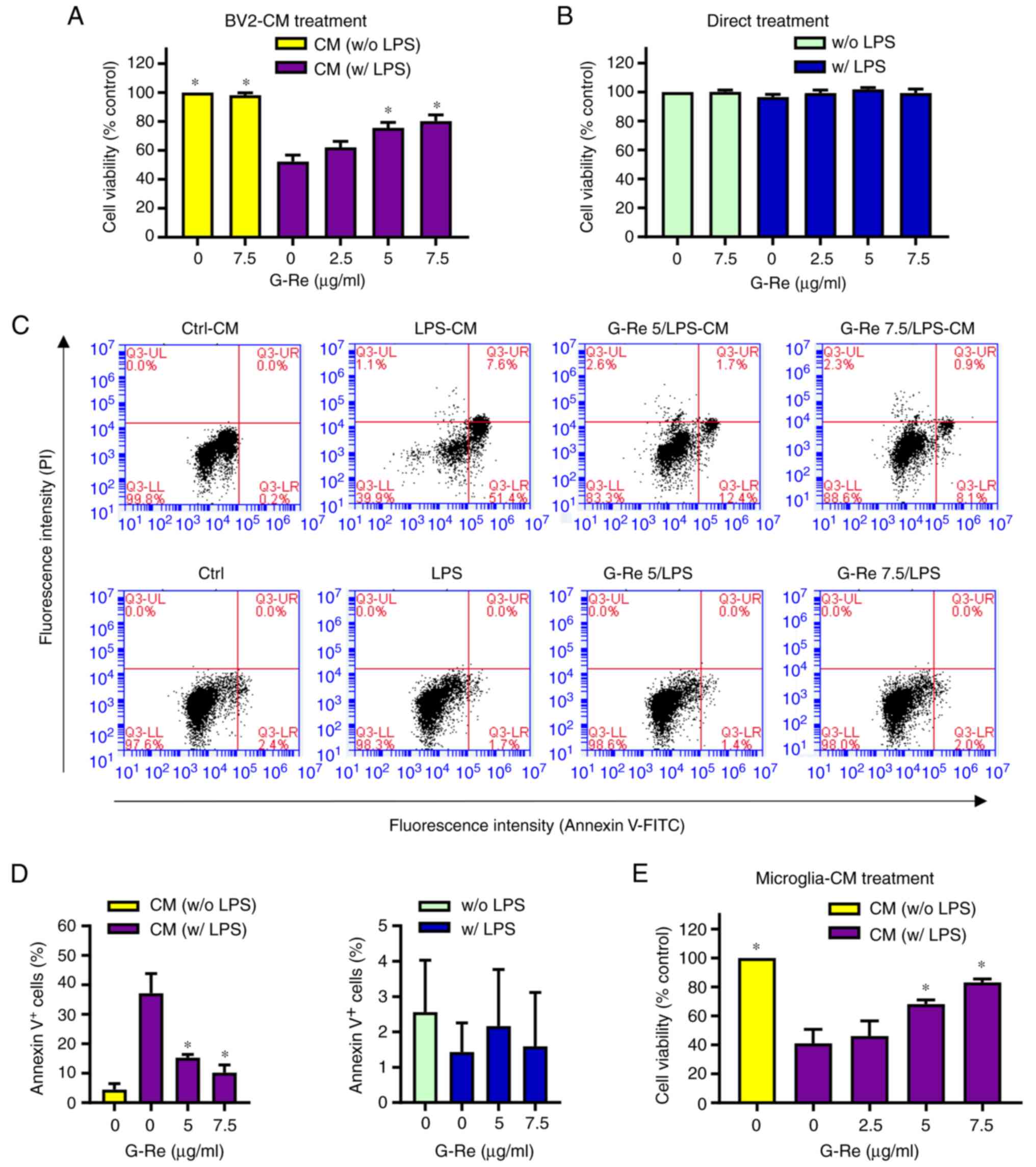
|
1
|
Yang I, Han SJ, Kaur G, Crane C and Parsa
AT: The role of microglia in central nervous system immunity and
glioma immunology. J Clin Neurosci. 17:6–10. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Streit WJ, Conde JR, Fendrick SE, Flanary
BE and Mariani CL: Role of microglia in the central nervous
system's immune response. Neurol Res. 27:685–691. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Boje KM and Arora PK: Microglial-produced
nitric oxide and reactive nitrogen oxides mediate neuronal cell
death. Brain Res. 587:250–256. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Block ML, Zecca L and Hong JS:
Microglia-mediated neurotoxicity: Uncovering the molecular
mechanisms. Nat Rev Neurosci. 8:57–69. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Hickman S, Izzy S, Sen P, Morsett L and El
Khoury J: Microglia in neurodegeneration. Nat Neurosci.
21:1359–1369. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Song WM and Colonna M: The identity and
function of microglia in neurodegeneration. Nat Immunol.
19:1048–1058. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Liu Y, Yin H, Zhao M and Lu Q: TLR2 and
TLR4 in autoimmune diseases: A comprehensive review. Clin Rev
Allergy Immunol. 47:136–147. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Kaminska B, Gozdz A, Zawadzka M,
Ellert-Miklaszewska A and Lipko M: MAPK signal transduction
underlying brain inflammation and gliosis as therapeutic target.
Aanat Rec. 292:1902–1913. 2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Sun J and Nan G: The extracellular
signal-regulated kinase 1/2 pathway in neurological diseases: A
potential therapeutic target (Review). Int J Mol Med. 39:1338–1346.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Song Q, Fan C, Wang P, Li Y, Yang M and Yu
SY: Hippocampal CA1 βCaMKII mediates neuroinflammatory responses
via COX-2/PGE2 signaling pathways in depression. J
Neuroinflammation. 15:3382018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Wang HH, Hsieh HL and Yang CM: Calmodulin
kinase II-dependent transactivation of PDGF receptors mediates
astrocytic MMP-9 expression and cell motility induced by
lipoteichoic acid. J Neuroinflammation. 7:842010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Leung KW and Wong AS: Pharmacology of
ginsenosides: A literature review. Chin Med. 5:202010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Huang GD, Zhong XF, Deng ZY and Zeng R:
Proteomic analysis of ginsenoside Re attenuates hydrogen
peroxide-induced oxidative stress in human umbilical vein
endothelial cells. Food Funct. 7:2451–2461. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Lee GH, Lee WJ, Hur J, Kim E, Lee HG and
Seo HG: Ginsenoside Re mitigates 6-hydroxydopamine-induced
oxidative stress through upregulation of GPX4. Molecules.
25:1882020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Xie JT, Shao ZH, Vanden Hoek TL, Chang WT,
Li J, Mehendale S, Wang CZ, Hsu CW, Becker LB, Yin JJ and Yuan CS:
Antioxidant effects of ginsenoside Re in cardiomyocytes. Eur J
Pharmacol. 532:201–207. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
López MV, Cuadrado MP, Ruiz-Poveda OM, Del
Fresno AM and Accame ME: Neuroprotective effect of individual
ginsenosides on astrocytes primary culture. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1770:1308–1316. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Bae HM, Cho OS, Kim SJ, Im BO, Cho SH, Lee
S, Kim MG, Kim KT, Leem KH and Ko SK: Inhibitory effects of
ginsenozside Re isolated from ginseng berry on histamine and
cytokine release in human mast cells and human alveolar epithelial
cells. J Ginseng Res. 36:369–374. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Lee IA, Hyam SR, Jang SE, Han MJ and Kim
DH: Ginsenoside Re ameliorates inflammation by inhibiting the
binding of lipopolysaccharide to TLR4 on macrophages. J Agric Food
Chem. 60:9595–9602. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Lee KW, Jung SY, Choi SM and Yang EJ:
Effects of ginsenoside Re on LPS-induced inflammatory mediators in
BV2 microglial cells. BMC Complement Altern Med. 12:1962012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Huang YC, Chen CT, Chen SC, Lai PH, Liang
HC, Chang Y, Yu LC and Sung HW: A natural compound (ginsenoside Re)
isolated from Panax ginseng as a novel angiogenic agent for
tissue regeneration. Pharm Res. 22:636–646. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Yu Y, Sun J, Liu J, Wang P and Wang C:
Ginsenoside Re preserves cardiac function and ameliorates left
ventricular remodeling in a rat model of myocardial infarction. J
Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 75:91–97. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Chen RC, Wang J, Yang L, Sun GB and Sun
XB: Protective effects of ginsenoside Re on
lipopolysaccharide-induced cardiac dysfunction in mice. Food Funct.
7:2278–2287. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Cho WC, Chung WS, Lee SK, Leung AW, Cheng
CH and Yue KK: Ginsenoside Re of Panax ginseng possesses
significant antioxidant and antihyperlipidemic efficacies in
streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Eur J Pharmacol. 550:173–179.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Quan HY, Yuan HD, Jung MS, Ko SK, Park YG
and Chung SH: Ginsenoside Re lowers blood glucose and lipid levels
via activation of AMP-activated protein kinase in HepG2 cells and
high-fat diet fed mice. Int J Mol Med. 29:73–80. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Gao Y, Yang MF, Su YP, Jiang HM, You XJ,
Yang YJ and Zhang HL: Ginsenoside Re reduces insulin resistance
through activation of PPAR-γ pathway and inhibition of TNF-α
production. J Ethnopharmacol. 147:509–516. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Shi Y, Wan X, Shao N, Ye R, Zhang N and
Zhang Y: Protective and anti-angiopathy effects of ginsenoside Re
against diabetes mellitus via the activation of p38 MAPK, ERK1/2
and JNK signaling. Mol Med Rep. 14:4849–4856. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Lian H, Roy E and Zheng H: Protocol for
primary microglial culture preparation. Bio Protoc.
6:e19892016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Kim Y, Moon JS, Lee KS, Park SY, Cheong J,
Kang HS, Lee HY and Kim HD: Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent
protein phosphatase calcineurin mediates the expression of iNOS
through IKK and NF-kappaB activity in LPS-stimulated mouse
peritoneal macrophages and RAW 264.7 cells. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 314:695–703. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Park SY, Kim YH, Kim Y and Lee SJ:
Aromatic-turmerone's anti-inflammatory effects in microglial cells
are mediated by protein kinase A and heme oxygenase-1 signaling.
Neurochem Int. 61:767–777. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Song JS, Shin JE, Kim JH and Kim Y:
Gardenia jasminoides exerts anti-inflammatory activity via
Akt and p38-dependent heme oxygenase-1 upregulation in microglial
cells. J Life Sci. 27:8–14. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
You MM, Chen YF, Pan YM, Liu YC, Tu J,
Wang K and Hu FL: Royal jelly attenuates lps-induced inflammation
in BV-2 microglial cells through modulating NF-κB and p38/JNK
signaling pathways. Mediators Inflamm. 2018:78343812018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Ardito F, Giuliani M, Perrone D, Troiano G
and Muzio LL: The crucial role of protein phosphorylation in cell
signaling and its use as targeted therapy (Review). Int J Mol Med.
40:271–280. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Zhou YQ, Liu Z, Liu ZH, Chen SP, Li M,
Shahveranov A, Ye DW and Tian YK: Interleukin-6: An emerging
regulator of pathological pain. J Neuroinflammation. 13:1412016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Petkovic F and Castellano B: The role of
interleukin-6 in central nervous system demyelination. Neural Regen
Res. 11:19222016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Gyengesi E, Rangel A, Ullah F, Liang H,
Niedermayer G, Asgarov R, Venigalla M, Gunawardena D, Karl T and
Münch G: Chronic Microglial activation in the GFAP-IL6 mouse
contributes to age-dependent cerebellar volume loss and impairment
in motor function. Front Neurosci. 13:3032019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Hirohata S and Miyamoto T: Elevated levels
of interleukin-6 in cerebrospinal fluid from patients with systemic
lupus erythematosus and central nervous system involvement.
Arthritis Rheum. 33:644–649. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Frei K, Leist TP, Meager A, Gallo P,
Leppert D, Zinkernagel RM and Fontana A: Production of B cell
stimulatory factor-2 and interferon gamma in the central nervous
system during viral meningitis and encephalitis. Evaluation in a
murine model infection and in patients. J Exp Med. 168:449–453.
1988. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Bodro M, Compta Y, Llansó L, Esteller D,
Doncel-Moriano A, Mesa A, Rodríguez A, Sarto J, Martínez-Hernandez
E, Vlagea A, et al: Increased CSF levels of IL-1β, IL-6, and ACE in
SARS-CoV-2-associated encephalitis. Neurol Neuroimmunol
Neuroinflamm. 7:e8212020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Tarkowski E, Rosengren L, Blomstrand C,
Wikkelsö C, Jensen C, Ekholm S and Tarkowski A: Early intrathecal
production of interleukin-6 predicts the size of brain lesion in
stroke. Stroke. 26:1393–1398. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Qiu Z and Gruol DL: Interleukin-6,
beta-amyloid peptide and NMDA interactions in rat cortical neurons.
J Neuroimmunol. 139:51–57. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Belarbi K, Jopson T, Tweedie D, Arellano
C, Luo W, Greig NH and Rosi S: TNF-α protein synthesis inhibitor
restores neuronal function and reverses cognitive deficits induced
by chronic neuroinflammation. J Neuroinflammation. 9:232012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Shamim D and Laskowski M: Inhibition of
inflammation mediated through the tumor necrosis factor α
biochemical pathway can lead to favorable outcomes in Alzheimer
disease. J Cent Nerv Syst Dis. 9:11795735177225122017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Singh A, Kukreti R, Saso L and Kukreti S:
Oxidative stress: A key modulator in neurodegenerative diseases.
Molecules. 24:15832019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Kim GH, Kim JE, Rhie SJ and Yoon S: The
role of oxidative stress in neurodegenerative diseases. Exp
Neurobiol. 24:325–340. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Tewari D, Sah AN, Bawari S, Nabavi SF,
Dehpour AR, Shirooie S, Braidy N, Fiebich BL, Vacca RA and Nabavi
SM: Role of Nitric oxide in neurodegeneration: Function,
regulation, and inhibition. Curr Neuropharmacol. 19:114–126. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Wang L, Hagemann TL, Kalwa H, Michel T,
Messing A and Feany MB: Nitric oxide mediates glial-induced
neurodegeneration in Alexander disease. Nat Commun. 6:89662015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Wei T, Chen C, Hou J, Xin W and Mori A:
Nitric oxide induces oxidative stress and apoptosis in neuronal
cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1498:72–79. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Pacher P, Beckman JS and Liaudet L: Nitric
oxide and peroxynitrite in health and disease. Physiol Rev.
87:315–424. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Ahn KS and Aggarwal BB: Transcription
factor NF-kappaB: A sensor for smoke and stress signals. Ann N Y
Acad Sci. 1056:218–233. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Sivandzade F, Prasad S, Bhalerao A and
Cucullo L: NRF2 and NF-κB interplay in cerebrovascular and
neurodegenerative disorders: Molecular mechanisms and possible
therapeutic approaches. Redox Biol. 21:1010592019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Shih RH, Wang CY and Yang CM: NF-kappaB
signaling pathways in neurological inflammation: A mini review.
Front Mol Neurosci. 8:772015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Giridharan S and Srinivasan M: Mechanisms
of NF-kappaB p65 and strategies for therapeutic manipulation. J
inflamm Res. 11:407–419. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Zhao J, Bi W, Xiao S, Lan X, Cheng X,
Zhang J, Lu D, Wei W, Wang Y, Li H, et al: Neuroinflammation
induced by lipopolysaccharide causes cognitive impairment in mice.
Sci Rep. 9:57902019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Lee JW, Lee YK, Yuk DY, Choi DY, Ban SB,
Oh KW and Hong JT: Neuro-inflammation induced by lipopolysaccharide
causes cognitive impairment through enhancement of beta-amyloid
generation. J Neuroinflammation. 5:372008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Czerniawski J, Miyashita T, Lewandowski G
and Guzowski JF: Systemic lipopolysaccharide administration impairs
retrieval of context-object discrimination, but not spatial,
memory: Evidence for selective disruption of specific
hippocampus-dependent memory functions during acute
neuroinflammation. Brain Behav Immun. 44:159–166. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Dean JM, Wang X, Kaindl AM, Gressens P,
Fleiss B, Hagberg H and Mallard C: Microglial MyD88 signaling
regulates acute neuronal toxicity of LPS-stimulated microglia in
vitro. Brain Behav Immun. 24:776–783. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Chao CC, Hu S, Molitor TW, Shaskan EG and
Peterson PK: Activated microglia mediate neuronal cell injury via a
nitric oxide mechanism. J Immunol. 149:2736–2741. 1992.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Banati RB, Gehrmann J, Schubert P and
Kreutzberg GW: Cytotoxicity of microglia. Glia. 7:111–118. 1993.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Vitner EB, Farfel-Becker T, Eilam R, Biton
I and Futerman AH: Contribution of brain inflammation to neuronal
cell death in neuronopathic forms of Gaucher's disease. Brain.
135:1724–1735. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Cai M and Yang EJ: Ginsenoside Re
attenuates neuroinflammation in a symptomatic ALS animal model. Am
J Chin Med. 44:401–413. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|