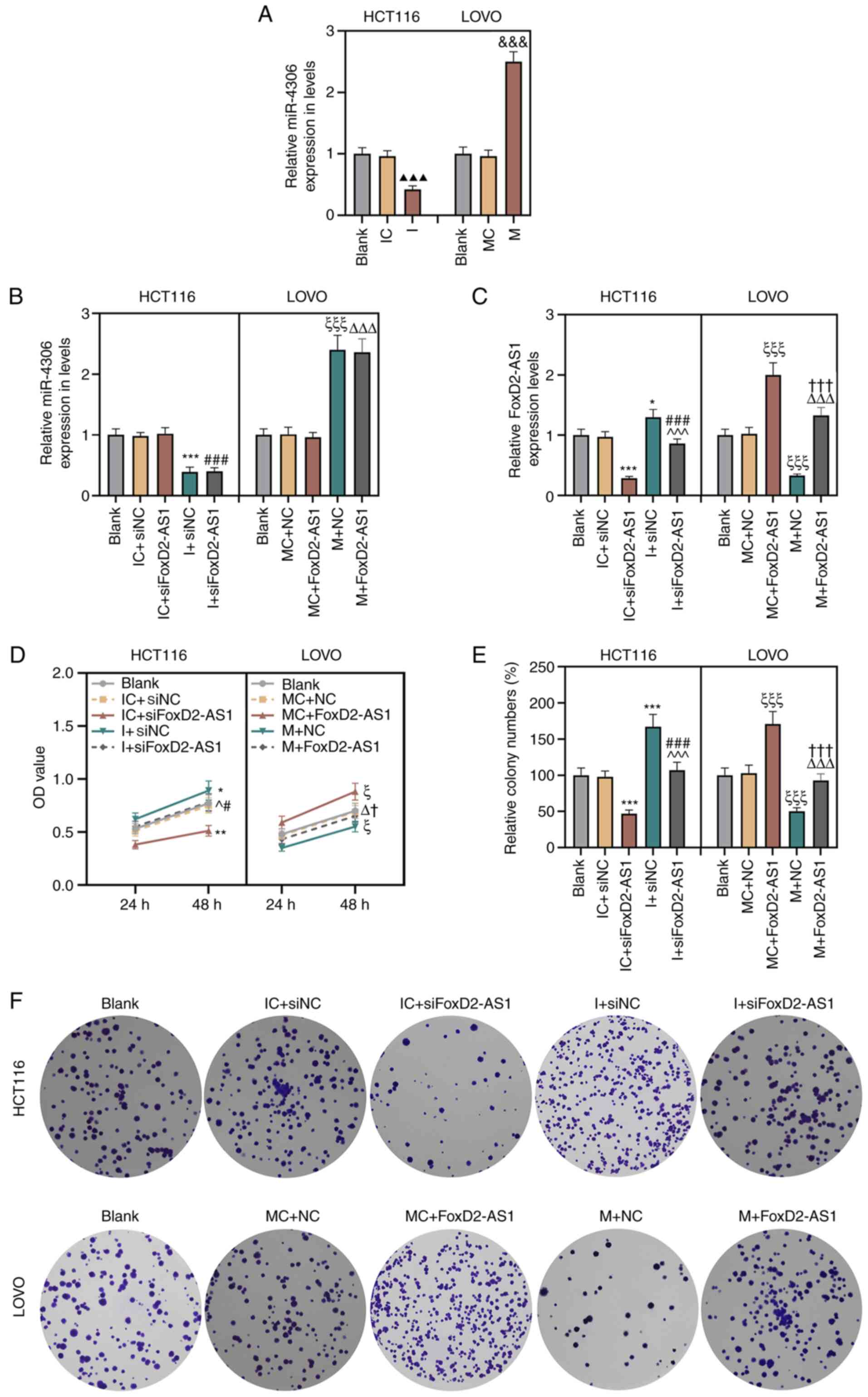
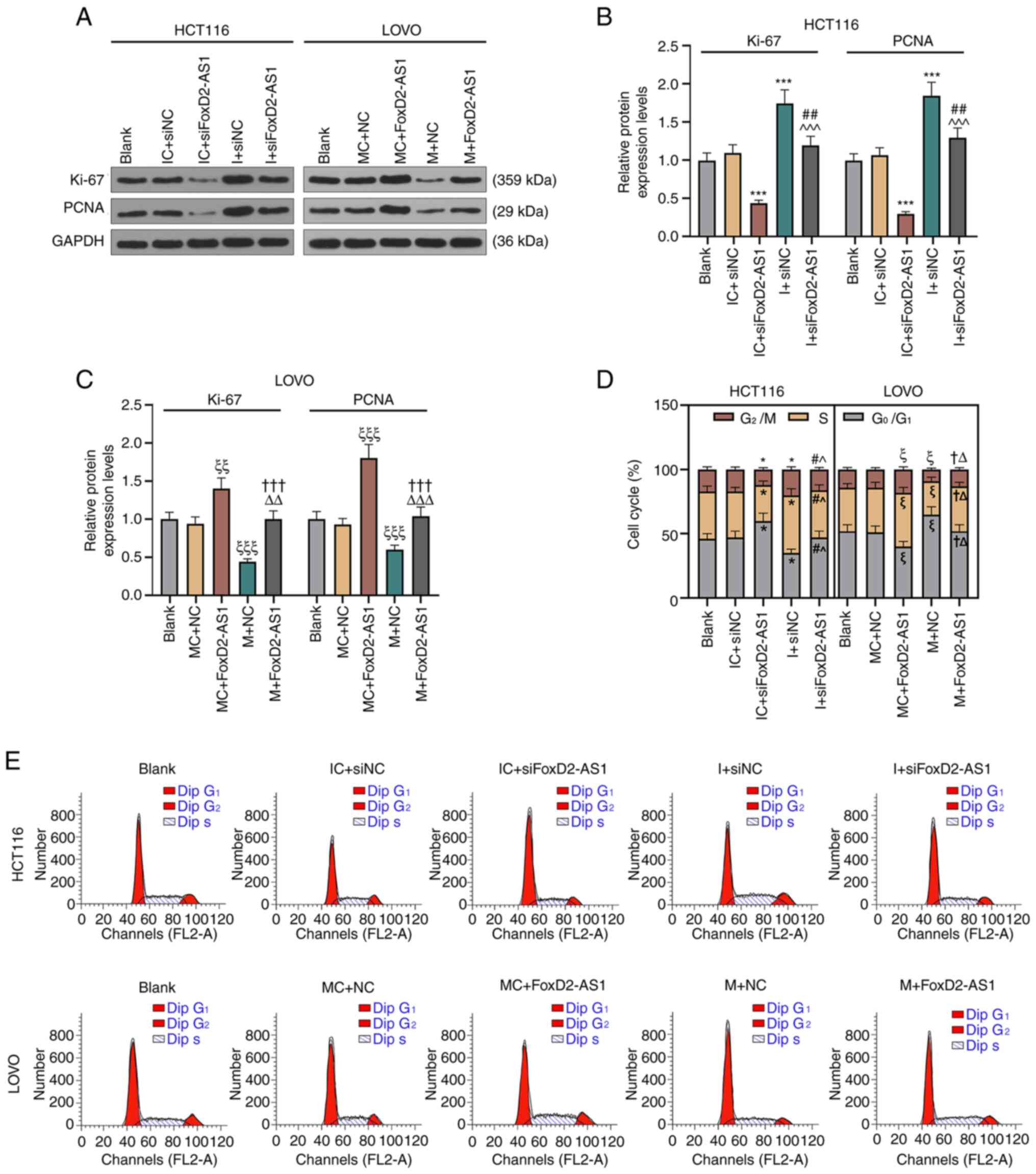
|
1
|
Peng ZY, Gu RH and Yan B: Downregulation
of exosome-encapsulated miR-548c-5p is associated with poor
prognosis in colorectal cancer. J Cell Biochem. 1:10022018.
|
|
2
|
Chen C, Xu ZQ, Zong YP, Ou BC, Shen XH,
Feng H, Zheng MH, Zhao JK and Lu AG: CXCL5 induces tumor
angiogenesis via enhancing the expression of FOXD1 mediated by the
AKT/NF-κB pathway in colorectal cancer. Cell Death Dis. 10:1782019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Jiang X, Zhu Q, Wu P, Zhou F and Chen J:
Upregulated long noncoding RNA LINC01234 predicts unfavorable
prognosis for colorectal cancer and negatively correlates with KLF6
expression. Ann Lab Med. 40:155–163. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Qiang JK, Sutradhar R, Giannakeas V,
Bhatia D, Singh S and Lipscombe LL: Impact of diabetes on
colorectal cancer stage and mortality risk: A population-based
cohort study. Diabetologia. 63:944–953. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Koliarakis I, Psaroulaki A, Nikolouzakis
TK, Kokkinakis M, Sgantzos M, Goulielmos G, Androutsopoulos VP,
Tsatsakis A and Tsiaoussis J: Intestinal microbiota and colorectal
cancer: A new aspect of research. J BUON. 23:1216–1234.
2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
ENCODE Project Consortium, ; Birney E,
Stamatoyannopoulos JA, Dutta A, Guigó R, Gingeras TR, Margulies EH,
Weng Z, Snyder M, Dermitzakis ET, et al: Identification and
analysis of functional elements in 1% of the human genome by the
ENCODE pilot project. Nature. 447:799–816. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Mercer TR, Dinger ME and Mattick JS: Long
non-coding RNAs: Insights into functions. Nat Rev Genet.
10:155–159. 2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Yao RW, Wang Y and Chen LL: Cellular
functions of long noncoding RNAs. Nat Cell Biol. 21:542–551. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Wang H, Yin Y, Li W, Zhao X, Yu Y, Zhu J,
Qin Z, Wang Q, Wang K, Lu W, et al: Over-expression of PDGFR-β
promotes PDGF-induced proliferation, migration, and angiogenesis of
EPCs through PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. PLoS One. 7:e305032012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Xu Y, Li J, Wang P, Zhang Z and Wang X:
LncRNA HULC promotes lung squamous cell carcinoma by regulating
PTPRO via NF-κB. J Cell Biochem. 120:19415–19421. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Xia S, Wang C, Ni X, Ni Z, Dong Y and Zhan
W: NONHSAT076754 aids ultrasonography in predicting lymph node
metastasis and promotes migration and invasion of papillary thyroid
cancer cells. Oncotarget. 8:2293–2306. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Vitiello M, Tuccoli A and Poliseno L: Long
non-coding RNAs in cancer: Implications for personalized therapy.
Cell Oncol (Dordr). 38:17–28. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Bartonicek N, Maag JL and Dinger ME: Long
noncoding RNAs in cancer: Mechanisms of action and technological
advancements. Mol Cancer. 15:432016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Slaby O, Laga R and Sedlacek O:
Therapeutic targeting of non-coding RNAs in cancer. Biochem J.
474:4219–4251. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Zhang C, Liu C, Wu J, Zheng Y, Xu H, Cheng
G and Hua L: Upregulation of long noncoding RNA LOC440040 promotes
tumor progression and predicts poor prognosis in patients with
prostate cancer. Onco Targets Ther. 10:4945–4954. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Cai Q, Wang ZQ, Wang SH, Li C, Zhu ZG,
Quan ZW and Zhang WJ: Upregulation of long non-coding RNA LINC00152
by SP1 contributes to gallbladder cancer cell growth and tumor
metastasis via PI3K/AKT pathway. Am J Transl Res. 8:4068–4081.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Qiao Q and Li H: LncRNA FER1L4 suppresses
cancer cell proliferation and cycle by regulating PTEN expression
in endometrial carcinoma. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 478:507–512.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Wu Q, Meng WY, Jie Y and Zhao H: LncRNA
MALAT1 induces colon cancer development by regulating
miR-129-5p/HMGB1 axis. J Cell Physiol. 233:6750–6757. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Chai J, Guo D, Ma W, Han D, Dong W, Guo H
and Zhang Y: A feedback loop consisting of
RUNX2/LncRNA-PVT1/miR-455 is involved in the progression of
colorectal cancer. Am J Cancer Res. 8:538–550. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Song W, Mei JZ and Zhang M: Long noncoding
RNA PlncRNA-1 promotes colorectal cancer cell progression by
regulating the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. Oncol Res. 26:261–268.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Gu ZG, Shen GH, Lang JH, Huang WX, Qian ZH
and Qiu J: Effects of long non-coding RNA URHC on proliferation,
apoptosis and invasion of colorectal cancer cells. Eur Rev Med
Pharmacol Sci. 22:1658–1664. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Chen G, Sun W, Hua X, Zeng W and Yang L:
Long non-coding RNA FOXD2-AS1 aggravates nasopharyngeal carcinoma
carcinogenesis by modulating miR-363-5p/S100A1 pathway. Gene.
645:76–84. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Yang X, Duan B and Zhou X: Long non-coding
RNA FOXD2-AS1 functions as a tumor promoter in colorectal cancer by
regulating EMT and notch signaling pathway. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol
Sci. 21:3586–3591. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
An Q, Zhou L and Xu N: Long noncoding RNA
FOXD2-AS1 accelerates the gemcitabine-resistance of bladder cancer
by sponging miR-143. Biomed Pharmacother. 103:415–420. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Zhu Y, Qiao L, Zhou Y, Ma N, Wang C and
Zhou J: Long non-coding RNA FOXD2-AS1 contributes to colorectal
cancer proliferation through its interaction with microRNA-185-5p.
Cancer Sci. 109:2235–2242. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Zhang M, Jiang X, Jiang S, Guo Z, Zhou Q
and He J: LncRNA FOXD2-AS1 regulates miR-25-3p/Sema4c axis to
promote the invasion and migration of colorectal cancer cells.
Cancer Manag Res. 11:10633–10639. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Chen R and Zhang L: MiR-29a inhibits cell
proliferation and migration by targeting the CDC42/PAK1 signaling
pathway in cervical cancer. Anticancer Drugs. 30:579–587. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Liu B and Sun X: miR-25 promotes invasion
of human non-small cell lung cancer via CDH1. Bioengineered.
10:271–281. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Zhao Z, Li L, Du P, Ma L, Zhang W, Zheng
L, Lan B, Zhang B, Ma F, Xu B, et al: Transcriptional
downregulation of miR-4306 serves as a new therapeutic target for
triple negative breast cancer. Theranostics. 9:1401–1416. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Ni W, Yao S, Zhou Y, Liu Y, Huang P, Zhou
A, Liu J, Che L and Li J: Long noncoding RNA GAS5 inhibits
progression of colorectal cancer by interacting with and triggering
YAP phosphorylation and degradation and is negatively regulated by
the m6A reader YTHDF3. Mol Cancer. 18:1432019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Ogunwobi OO, Mahmood F and Akingboye A:
Biomarkers in colorectal cancer: Current research and future
prospects. Int J Mol Sci. 21:53112020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Dastmalchi N, Safaralizadeh R and Nargesi
MM: LncRNAs: Potential novel prognostic and diagnostic biomarkers
in colorectal cancer. Curr Med Chem. 27:5067–5077. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Han Q, Xu L, Lin W, Yao X, Jiang M, Zhou
R, Sun X and Zhao L: Long noncoding RNA CRCMSL suppresses tumor
invasive and metastasis in colorectal carcinoma through
nucleocytoplasmic shuttling of HMGB2. Oncogene. 38:3019–3032. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Shang AQ, Wang WW, Yang YB, Gu CZ, Ji P,
Chen C, Zeng BJ, Wu JL, Lu WY, Sun ZJ and Li D: Knockdown of long
noncoding RNA PVT1 suppresses cell proliferation and invasion of
colorectal cancer via upregulation of microRNA-214-3p. Am J Physiol
Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 317:G222–G232. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Ni W, Xia Y, Bi Y, Wen F, Hu D and Luo L:
FoxD2-AS1 promotes glioma progression by regulating
miR-185-5P/HMGA2 axis and PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. Aging (Albany
NY). 11:1427–1439. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Ge P, Cao L, Yao YJ, Jing RJ, Wang W and
Li HJ: lncRNA FOXD2-AS1 confers cisplatin resistance of
non-small-cell lung cancer via regulation of miR185-5p-SIX1 axis.
Onco Targets Ther. 12:6105–6117. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Bao J, Zhou C, Zhang J, Mo J, Ye Q, He J
and Diao J: Upregulation of the long noncoding RNA FOXD2-AS1
predicts poor prognosis in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.
Cancer Biomark. 21:527–533. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Iguchi T, Uchi R, Nambara S, Saito T,
Komatsu H, Hirata H, Ueda M, Sakimura S, Takano Y, Kurashige J, et
al: A long noncoding RNA, lncRNA-ATB, is involved in the
progression and prognosis of colorectal cancer. Anticancer Res.
35:1385–1388. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Han P, Li JW, Zhang BM, Lv JC, Li YM, Gu
XY, Yu ZW, Jia YH, Bai XF, Li L, et al: The lncRNA CRNDE promotes
colorectal cancer cell proliferation and chemoresistance via
miR-181a-5p-mediated regulation of Wnt/β-catenin signaling. Mol
Cancer. 16:92017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Li J, Zhao LM, Zhang C, Li M, Gao B, Hu
XH, Cao J and Wang GY: The lncRNA FEZF1-AS1 promotes the
progression of colorectal cancer through regulating OTX1 and
targeting miR-30a-5p. Oncol Res. 28:51–63. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Xie JJ, Li WH, Li X, Ye W and Shao CF:
LncRNA MALAT1 promotes colorectal cancer development by sponging
miR-363-3p to regulate EZH2 expression. J Biol Regul Homeost
Agents. 33:331–343. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Zhou Y and Mu T: LncRNA LINC00958 promotes
tumor progression through miR-4306/CEMIP axis in osteosarcoma. Eur
Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 25:3182–3199. 2021.PubMed/NCBI
|