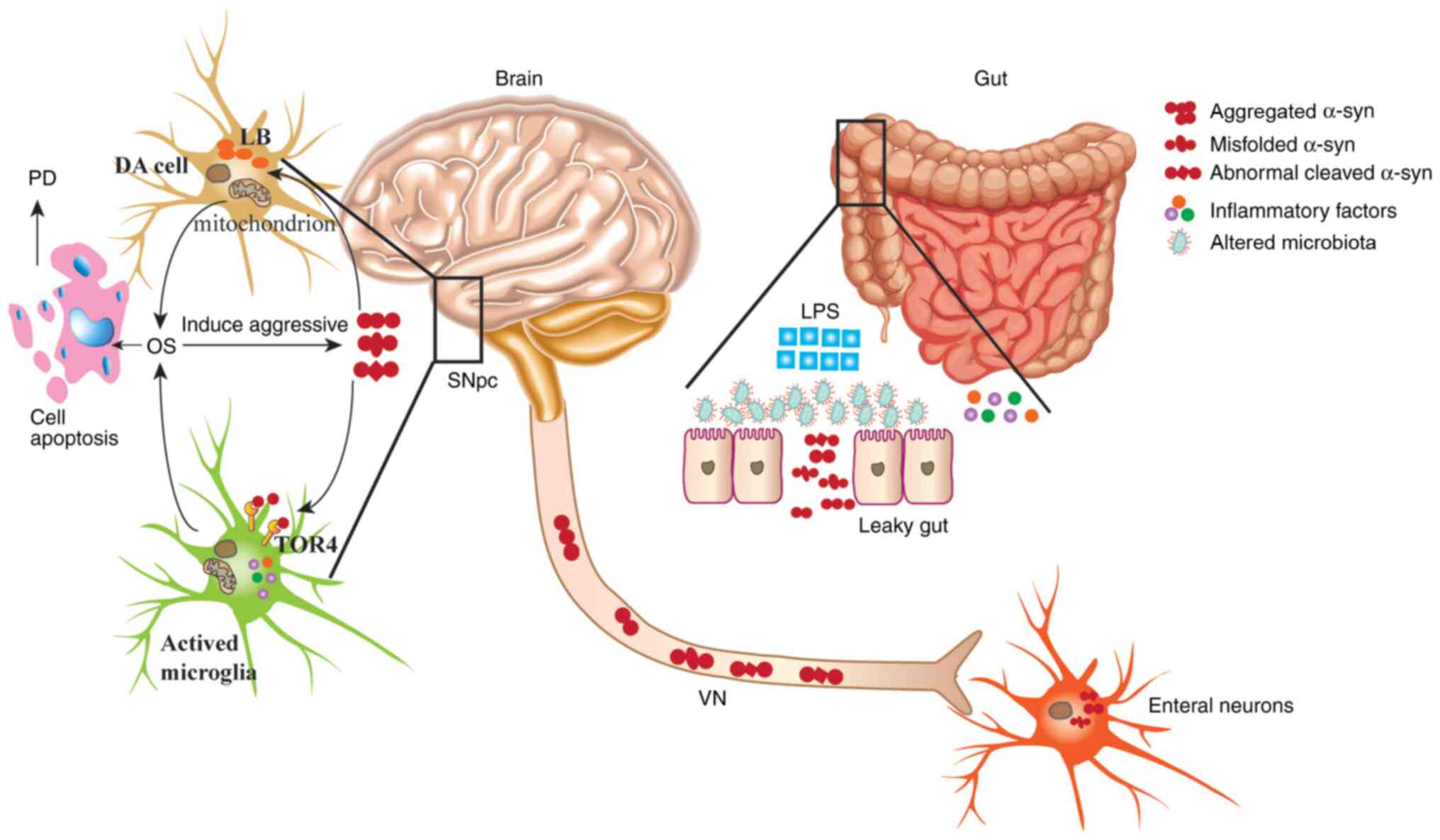
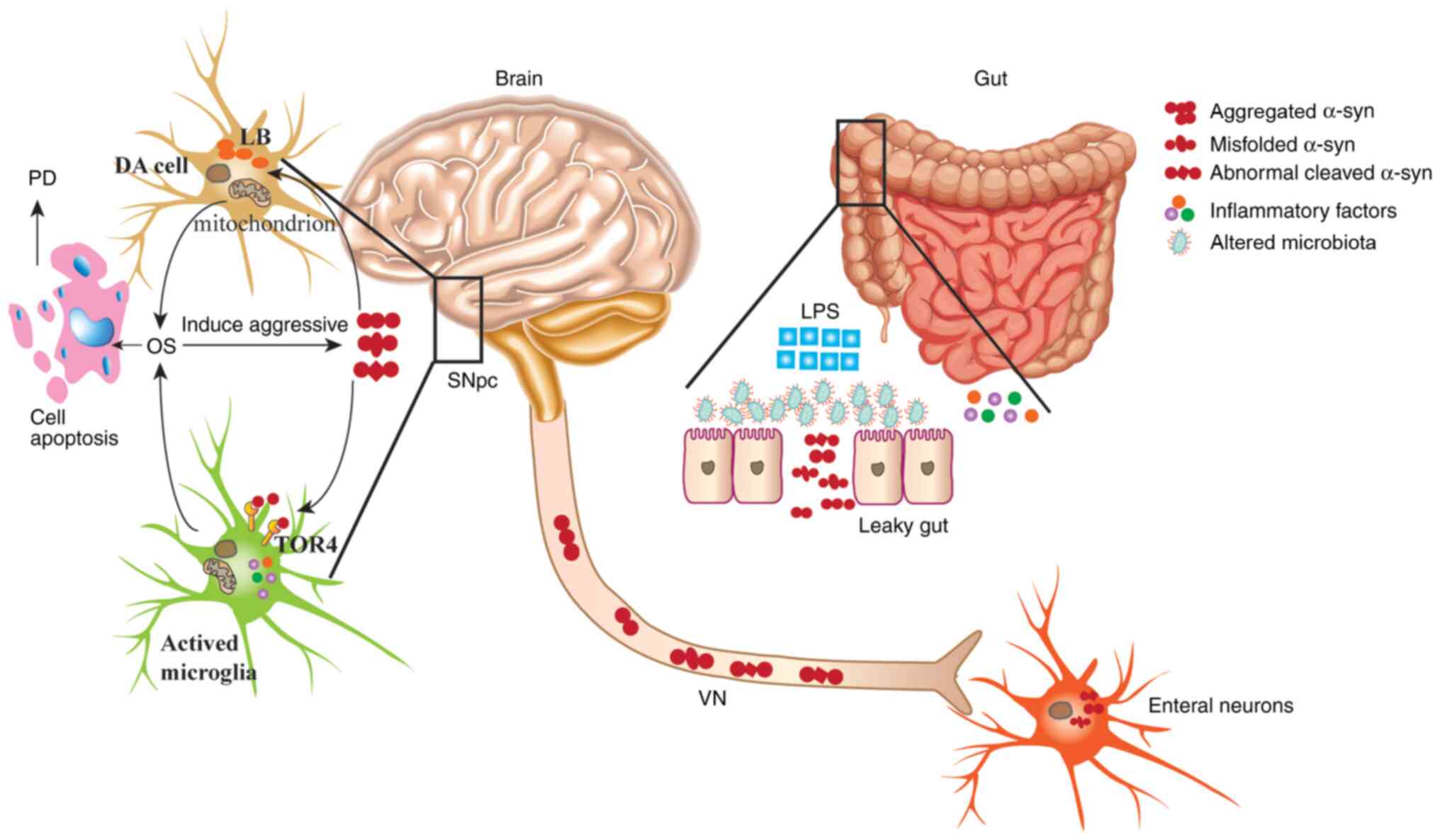
|
1
|
Wu S, Lei L, Song Y, Liu M, Lu S, Lou D,
Shi Y, Wang Z and He D: Mutation of hop-1 and pink-1 attenuates
vulnerability of neurotoxicity in C. elegans: The role of
mitochondria-associated membrane proteins in Parkinsonism. Exp
Neurol. 309:67–78. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Balestrino R and Schapira AHV: Parkinson
disease. Eur J Neurol. 27:27–42. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Mahoney-Sanchez L, Bouchaoui H, Ayton S,
Devos D, Duce JA and Devedjian JC: Ferroptosis and its potential
role in the physiopathology of Parkinson's disease. Prog Neurobiol.
196:1018902021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Samii A, Nutt JG and Ransom BR:
Parkinson's disease. Lancet. 363:1783–1793. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Khoo TK, Yarnall AJ, Duncan GW, Coleman S,
O'Brien JT, Brooks DJ, Barker RA and Burn DJ: The spectrum of
nonmotor symptoms in early Parkinson disease. Neurology.
80:276–281. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Lopiano L, Modugno N, Marano P, Sensi M,
Meco G, Cannas A, Gusmaroli G, Tamma F, Mancini F, Quatrale R, et
al: Motor outcomes in patients with advanced Parkinson's disease
treated with levodopa/carbidopa intestinal gel in Italy: An interim
analysis from the GREENFIELD observational study. Neurol Sci.
37:1785–1792. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Kalinderi K, Bostantjopoulou S and Fidani
L: The genetic background of Parkinson's disease: Current progress
and future prospects. Acta Neurol Scand. 134:314–326. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Malpartida AB, Williamson M, Narendra DP,
Wade-Martins R and Ryan BJ: Mitochondrial dysfunction and mitophagy
in Parkinson's disease: From mechanism to therapy. Trends Biochem
Sci. 46:329–343. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Tysnes OB and Storstein A: Epidemiology of
Parkinson's disease. J Neural Transm (Vienna). 124:901–905. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Ascherio A and Schwarzschild MA: The
epidemiology of Parkinson's disease: Risk factors and prevention.
Lancet Neurol. 15:1257–1272. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Ahier A, Dai CY, Kirmes I, Cummins N, Hung
GCC, Götz J and Zuryn S: PINK1 and parkin shape the organism-wide
distribution of a deleterious mitochondrial genome. Cell Rep.
35:1092032021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Tolosa E, Vila M, Klein C and Rascol O:
LRRK2 in Parkinson disease: Challenges of clinical trials. Nat Rev
Neurol. 16:97–107. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Wauters F, Cornelissen T, Imberechts D,
Martin S, Koentjoro B, Sue C, Vangheluwe P and Vandenberghe W:
LRRK2 mutations impair depolarization-induced mitophagy through
inhibition of mitochondrial accumulation of RAB10. Autophagy.
16:203–222. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Terbeek J, Martin S, Imberechts D, Kinnart
I, Vangheluwe P, Nicholl D and Vandenberghe W: Increased superoxide
in GCH1 mutant fibroblasts points to a dopamine-independent
toxicity mechanism. Parkinsonism Relat Disord. 82:10–12. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Imai Y, Meng H, Shiba-Fukushima K and
Hattori N: Twin CHCH proteins, CHCHD2, and CHCHD10: Key molecules
of Parkinson's disease, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, and
frontotemporal dementia. Int J Mol Sci. 20:9082019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Sassone J, Reale C, Dati G, Regoni M,
Pellecchia MT and Garavaglia B: The role of VPS35 in the
pathobiology of Parkinson's disease. Cell Mol Neurobiol.
41:199–227. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Gangemi S, Gofita E, Costa C, Teodoro M,
Briguglio G, Nikitovic D, Tzanakakis G, Tsatsakis AM, Wilks MF,
Spandidos DA and Fenga C: Occupational and environmental exposure
to pesticides and cytokine pathways in chronic diseases (Review).
Int J Mol Med. 38:1012–1020. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Teodoro M, Briguglio G, Fenga C and Costa
C: Genetic polymorphisms as determinants of pesticide toxicity:
Recent advances. Toxicol Rep. 6:564–570. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Costa C, Teodoro M, Rugolo CA, Alibrando
C, Giambo F, Briguglio G and Fenga C: MicroRNAs alteration as early
biomarkers for cancer and neurodegenerative diseases: New
challenges in pesticides exposure. Toxicol Rep. 7:759–767. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Srivastav S, Fatima M and Mondal AC:
Important medicinal herbs in Parkinson's disease pharmacotherapy.
Biomed Pharmacother. 92:856–863. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Titze-de-Almeida SS, Soto-Sanchez C,
Fernandez E, Koprich JB, Brotchie JM and Titze-de-Almeida R: The
promise and challenges of developing miRNA-Based therapeutics for
Parkinson's disease. Cells. 9:8412020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Yu Y, Chen H, Hua X, Dang Y, Han Y, Yu Z,
Chen X, Ding P and Li H: Polystyrene microplastics (PS-MPs)
toxicity induced oxidative stress and intestinal injury in nematode
caenorhabditis elegans. Sci Total Environ. 726:1386792020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Schirinzi T, Landi D and Liguori C:
COVID-19: Dealing with a potential risk factor for chronic
neurological disorders. J Neurol. 268:1171–1178. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Ribeiro DE, Oliveira-Giacomelli A, Glaser
T, Arnaud-Sampaio VF, Andrejew R, Dieckmann L, Baranova J, Lameu C,
Ratajczak MZ and Ulrich H: Hyperactivation of P2X7 receptors as a
culprit of COVID-19 neuropathology. Mol Psychiatry. 26:1044–1059.
2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Fasano A, Visanji NP, Liu LW, Lang AE and
Pfeiffer RF: Gastrointestinal dysfunction in Parkinson's disease.
Lancet Neurol. 14:625–639. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Mayer EA, Tillisch K and Gupta A:
Gut/brain axis and the microbiota. J Clin Invest. 125:926–938.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Ghaisas S, Maher J and Kanthasamy A: Gut
microbiome in health and disease: Linking the microbiome-gut-brain
axis and environmental factors in the pathogenesis of systemic and
neurodegenerative diseases. Pharmacol Ther. 158:52–62. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Felice VD, Quigley EM, Sullivan AM,
O'Keeffe GW and O'Mahony SM: Microbiota-gut-brain signalling in
Parkinson's disease: Implications for non-motor symptoms.
Parkinsonism Relat Disord. 27:1–8. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Pfeiffer R: Beyond here be dragons: SIBO
in Parkinson's disease. Mov Disord. 28:1764–1765. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Nielsen HH, Qiu J, Friis S, Wermuth L and
Ritz B: Treatment for helicobacter pylori infection and risk of
Parkinson's disease in denmark. Eur J Neurol. 19:864–869. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Devos D, Lebouvier T, Lardeux B, Biraud M,
Rouaud T, Pouclet H, Coron E, Bruley des Varannes S, Naveilhan P,
Nguyen JM, et al: Colonic inflammation in Parkinson's disease.
Neurobiol Dis. 50:42–48. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Mehra S, Sahay S and Maji SK: α-synuclein
misfolding and aggregation: Implications in Parkinson's disease
pathogenesis. Biochim Biophys Acta Proteins Proteom. 1867:890–908.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Li X, Li YH, Han JY, Yu S and Chen B: cDNA
cloning, prokaryotic expression and purification of rat
alpha-synuclein. Neurosci Bull. 22:29–33. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Pogorelov VM, Kao HT, Augustine GJ and
Wetsel WC: Postsynaptic mechanisms render Syn I/II/III mice highly
responsive to psychostimulants. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol.
22:453–465. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Thiel G: Synapsin I, synapsin II, and
synaptophysin: Marker proteins of synaptic vesicles. Brain Pathol.
3:87–95. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Zhang L, Zhang C, Zhu Y, Cai Q, Chan P,
Uéda K, Yu S and Yang H: Semi-quantitative analysis of
alpha-synuclein in subcellular pools of rat brain neurons: An
immunogold electron microscopic study using a C-terminal specific
monoclonal antibody. Brain Res. 1244:40–52. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Braak H, Rub U, Gai WP and Del Tredici K;
Idiopathic Parkinson's disease, : Possible routes by which
vulnerable neuronal types may be subject to neuroinvasion by an
unknown pathogen. J Neural Transm (Vienna). 110:517–536. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Luk KC, Kehm VM, Zhang B, O'Brien P,
Trojanowski JQ and Lee VM: Intracerebral inoculation of
pathological alpha-synuclein initiates a rapidly progressive
neurodegenerative alpha-synucleinopathy in mice. J Exp Med.
209:975–986. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Zheng H, Shi C, Luo H, Fan L, Yang Z, Hu
X, Zhang Z, Zhang S, Hu Z, Fan Y, et al: alpha-synuclein in
Parkinson's disease: Does a prion-like mechanism of propagation
from periphery to the brain play a role? Neuroscientist.
27:367–387. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Perez-Pardo P, Kliest T, Dodiya HB,
Broersen LM, Garssen J, Keshavarzian A and Kraneveld AD: The
gut-brain axis in Parkinson's disease: Possibilities for food-based
therapies. Eur J Pharmacol. 817:86–95. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Dogra N, Mani RJ and Katare DP: The
gut-brain axis: Two ways signaling in Parkinson's disease. Cell Mol
Neurobiol. 2:10072021.
|
|
42
|
Kuo YM, Li Z, Jiao Y, Gaborit N, Pani AK,
Orrison BM, Bruneau BG, Giasson BI, Smeyne RJ, Gershon MD and
Nussbaum RL: Extensive enteric nervous system abnormalities in mice
transgenic for artificial chromosomes containing Parkinson
disease-associated alpha-synuclein gene mutations precede central
nervous system changes. Hum Mol Genet. 19:1633–1650. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Braak H, Del Tredici K, Rüb U, de Vos RA,
Steur EN and Braak E: Staging of brain pathology related to
sporadic Parkinson's disease. Neurobiol Aging. 24:197–211. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Borghammer P and Van Den Berge N:
Brain-first versus gut-first Parkinson's disease: A hypothesis. J
Parkinsons Dis. 9:S281–S295. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Comi C, Magistrelli L, Oggioni GD,
Carecchio M, Fleetwood T, Cantello R, Mancini F and Antonini A:
Peripheral nervous system involvement in Parkinson's disease:
Evidence and controversies. Parkinsonism Relat Disord.
20:1329–1334. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Nair AT, Ramachandran V, Joghee NM, Antony
S and Ramalingam G: Gut microbiota dysfunction as reliable
non-invasive early diagnostic biomarkers in the pathophysiology of
Parkinson's disease: A critical review. J Neurogastroenterol Motil.
24:30–42. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Rani L and Mondal AC: Unravelling the role
of gut microbiota in Parkinson's disease progression: Pathogenic
and therapeutic implications. Neurosci Res. 168:100–112. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Scheperjans F, Aho V, Pereira PA, Koskinen
K, Paulin L, Pekkonen E, Haapaniemi E, Kaakkola S, Eerola-Rautio J,
Pohja M, et al: Gut microbiota are related to Parkinson's disease
and clinical phenotype. Mov Disord. 30:350–358. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Mulak A and Boaz B: Brain-gut-microbiota
axis in Parkinson's disease. World J Gastroenterol. 21:10609–10620.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Cirstea MS, Yu AC, Golz E, Sundvick K,
Kliger D, Radisavljevic N, Foulger LH, Mackenzie M, Huan T, Finlay
BB and Appel-Cresswell S: Microbiota composition and metabolism are
associated with gut function in Parkinson's disease. Mov Disord.
35:1208–1217. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Lee HS, Lobbestael E, Vermeire S, Sabino J
and Cleynen I: Inflammatory bowel disease and Parkinson's disease:
Common pathophysiological links. Gut. 70:408–417. 2021.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Gerhardt S and Mohajeri MH: Changes of
colonic bacterial composition in Parkinson's disease and other
neurodegenerative diseases. Nutrients. 10:7082018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Lubomski M, Tan AH, Lim SY, Holmes AJ,
Davis RL and Sue CM: Parkinson's disease and the gastrointestinal
microbiome. J Neurol. 267:2507–2523. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Keshavarzian A, Green SJ, Engen PA, Voigt
RM, Naqib A, Forsyth CB, Mutlu E and Shannon KM: Colonic bacterial
composition in Parkinson's disease. Mov Disord. 30:1351–1360. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Baizabal-Carvallo JF and Alonso-Juarez M:
The link between gut dysbiosis and neuroinflammation in Parkinson's
disease. Neuroscience. 432:160–173. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Li F, Wang P, Chen Z, Sui X, Xie X and
Zhang J: Alteration of the fecal microbiota in North-Eastern Han
Chinese population with sporadic Parkinson's disease. Neurosci
Lett. 707:1342972019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Hill-Burns EM, Debelius JW, Morton JT,
Wissemann WT, Lewis MR, Wallen ZD, Peddada SD, Factor SA, Molho E,
Zabetian CP, et al: Parkinson's disease and Parkinson's disease
medications have distinct signatures of the gut microbiome. Mov
Disord. 32:739–749. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Elfil M, Kamel S, Kandil M, Koo BB and
Schaefer SM: Implications of the gut microbiome in Parkinson's
disease. Movement disorders: Mov Disord. 35:921–933. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Sorrentino ZA, Xia Y, Gorion KM, Hass E
and Giasson BI: Carboxy-terminal truncations of mouse α-synuclein
alter aggregation and prion-like seeding. FEBS Lett. 594:1271–1283.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Cryan JF, O'Riordan KJ, Cowan CSM, Sandhu
KV, Bastiaanssen TFS, Boehme M, Codagnone MG, Cussotto S, Fulling
C, Golubeva AV, et al: The microbiota-gut-brain axis. Physiol Rev.
99:1877–2013. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Koszewicz M, Jaroch J, Brzecka A, Ejma M,
Budrewicz S, Mikhaleva LM, Muresanu C, Schield P, Somasundaram SG,
Kirkland CE, et al: Dysbiosis is one of the risk factor for stroke
and cognitive impairment and potential target for treatment.
Pharmacol Res. 164:1052772021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Tan AH, Lim SY, Chong KK, Manap AM, Hor
JW, Lim JL, Low SC, Chong CW, Mahadeva S and Lang AE: Probiotics
for constipation in Parkinson disease: A randomized
placebo-controlled study. Neurology. 96:e772–e782. 2021.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Hou YF, Shan C, Zhuang SY, Zhuang QQ,
Ghosh A, Zhu KC, Kong XK, Wang SM, Gong YL, Yang YY, et al: Gut
microbiota-derived propionate mediates the neuroprotective effect
of osteocalcin in a mouse model of Parkinson's disease. Microbiome.
9:342021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Sun MF, Zhu YL, Zhou ZL, Jia XB, Xu YD,
Yang Q, Cui C and Shen YQ: Neuroprotective effects of fecal
microbiota transplantation on MPTP-induced Parkinson's disease
mice: Gut microbiota, glial reaction and TLR4/TNF-α signaling
pathway. Brain Behav Immun. 70:48–60. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Kayisoglu O, Weiss F, Niklas C, Pierotti
I, Pompaiah M, Wallaschek N, Germer CT, Wiegering A and Bartfeld S:
Location-specific cell identity rather than exposure to GI
microbiota defines many innate immune signalling cascades in the
gut epithelium. Gut. 70:687–697. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Kelly LP, Carvey PM, Keshavarzian A,
Shannon KM, Shaikh M, Bakay RA and Kordower JH: Progression of
intestinal permeability changes and alpha-synuclein expression in a
mouse model of Parkinson's disease. Mov Disord. 29:999–1009. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Uemura N, Yagi H, Uemura MT, Hatanaka Y,
Yamakado H and Takahashi R: Inoculation of α-synuclein preformed
fibrils into the mouse gastrointestinal tract induces lewy
body-like aggregates in the brainstem via the vagus nerve. Mol
Neurodegener. 13:212018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Forsyth CB, Shannon KM, Kordower JH, Voigt
RM, Shaikh M, Jaglin JA, Estes JD, Dodiya HB and Keshavarzian A:
Increased intestinal permeability correlates with sigmoid mucosa
alpha-synuclein staining and endotoxin exposure markers in early
Parkinson's disease. PLoS One. 6:e280322011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
George S and Brundin P: Immunotherapy in
Parkinson's disease: Micromanaging alpha-synuclein aggregation. J
Parkinsons Dis. 5:413–424. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Wang Y, Liu Y, Sidhu A, Ma Z, McClain C
and Feng W: Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG culture supernatant
ameliorates acute alcohol-induced intestinal permeability and liver
injury. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 303:G32–G41. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Bischoff SC, Barbara G, Buurman W,
Ockhuizen T, Schulzke JD, Serino M, Tilg H, Watson A and Wells JM:
Intestinal permeability-a new target for disease prevention and
therapy. BMC Gastroenterol. 14:1892014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Ploger S, Stumpff F, Penner GB, Schulzke
JD, Gäbel G, Martens H, Shen Z, Günzel D and Aschenbach JR:
Microbial butyrate and its role for barrier function in the
gastrointestinal tract. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1258:52–59. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Unger MM, Spiegel J, Dillmann KU,
Grundmann D, Philippeit H, Burmann J, Faßbender K, Schwiertz A and
Schäfer KH: Short chain fatty acids and gut microbiota differ
between patients with Parkinson's disease and age-matched controls.
Parkinsonism Relat Disord. 32:66–72. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Zhou X, Zhang B, Zhao X, Lin Y, Wang J,
Wang X, Hu N and Wang S: Chlorogenic acid supplementation
ameliorates hyperuricemia, relieves renal inflammation, and
modulates intestinal homeostasis. Food Funct. 12:5637–5649. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Chen ZJ, Liang CY, Yang LQ, Ren SM, Xia
YM, Cui L, Li XF and Gao BL: Association of Parkinson's disease
with microbes and microbiological therapy. Front Cell Infect
Microbiol. 11:6193542021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Watson AJ and Hughes KR: TNF-α-induced
intestinal epithelial cell shedding: Implications for intestinal
barrier function. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1258:1–8. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Resnikoff H, Metzger JM, Lopez M,
Bondarenko V, Mejia A, Simmons HA and Emborg ME: Colonic
inflammation affects myenteric alpha-synuclein in nonhuman
primates. J Inflamm Res. 12:113–126. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Choi JG, Kim N, Ju IG, Eo H, Lim SM, Jang
SE, Kim DH and Oh MS: Oral administration of proteus mirabilis
damages dopaminergic neurons and motor functions in mice. Sci Rep.
8:12752018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Brown GC: The endotoxin hypothesis of
neurodegeneration. J Neuroinflammation. 16:1802019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Bhattacharyya D, Mohite GM, Krishnamoorthy
J, Gayen N, Mehra S, Navalkar A, Kotler SA, Ratha BN, Ghosh A,
Kumar R, et al: Lipopolysaccharide from gut microbiota modulates
α-synuclein aggregation and alters its biological function. ACS
Chem Neurosci. 10:2229–2236. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Huang C, Zhu L, Li H, Shi FG, Wang GQ, Wei
YZ, Liu J and Zhang F: Adulthood exposure to lipopolysaccharide
exacerbates the neurotoxic and inflammatory effects of rotenone in
the substantia nigra. Front Mol Neurosci. 10:1312017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Wang W, Nguyen LT, Burlak C, Chegini F,
Guo F, Chataway T, Ju S, Fisher OS, Miller DW, Datta D, et al:
Caspase-1 causes truncation and aggregation of the Parkinson's
disease-associated protein alpha-synuclein. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
113:9587–9592. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Terada M, Suzuki G, Nonaka T, Kametani F,
Tamaoka A and Hasegawa M: The effect of truncation on prion-like
properties of α-synuclein. J Biol Chem. 293:13910–13920. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Woerman AL, Kazmi SA, Patel S, Freyman Y,
Oehler A, Aoyagi A, Mordes DA, Halliday GM, Middleton LT, Gentleman
SM, et al: MSA prions exhibit remarkable stability and resistance
to inactivation. Acta Neuropathol. 135:49–63. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Davie CA: A review of Parkinson's disease.
Br Med Bull. 86:109–127. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Prusiner SB: Cell biology. A unifying role
for prions in neurodegenerative diseases. Science. 336:1511–1513.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Bhattacharyya D and Bhunia A: Gut-brain
axis in Parkinson's disease etiology: The role of
lipopolysaccharide. Chem Phys Lipids. 235:1050292021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Lee SJ, Desplats P, Sigurdson C, Tsigelny
I and Masliah E: Cell-to-cell transmission of non-prion protein
aggregates. Nat Rev Neurol. 6:702–706. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Luk KC, Kehm V, Carroll J, Zhang B,
O'Brien P, Trojanowski JQ and Lee VM: Pathological α-synuclein
transmission initiates Parkinson-like neurodegeneration in
nontransgenic mice. Science. 338:949–953. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Pan-Montojo F, Schwarz M, Winkler C,
Arnhold M, O'Sullivan GA, Pal A, Said J, Marsico G, Verbavatz JM,
Rodrigo-Angulo M, et al: Environmental toxins trigger PD-like
progression via increased alpha-synuclein release from enteric
neurons in mice. Sci Rep. 2:8982012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Mezias C, Rey N, Brundin P and Raj A:
Neural connectivity predicts spreading of alpha-synuclein pathology
in fibril-injected mouse models: Involvement of retrograde and
anterograde axonal propagation. Neurobiol Dis. 134:1046232020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Holmqvist S, Chutna O, Bousset L,
Aldrin-Kirk P, Li W, Björklund T, Wang ZY, Roybon L, Melki R and Li
JY: Direct evidence of Parkinson pathology spread from the
gastrointestinal tract to the brain in rats. Acta Neuropathol.
128:805–820. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Kim S, Kwon SH, Kam TI, Panicker N,
Karuppagounder SS, Lee S, Lee JH, Kim WR, Kook M, Foss CA, et al:
Transneuronal propagation of pathologic alpha-synuclein from the
gut to the brain models Parkinson's disease. Neuron. 103:627–641.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Braak H, Sastre M, Bohl JR, de Vos RA and
Del Tredici K: Parkinson's disease: Lesions in dorsal horn layer I,
involvement of parasympathetic and sympathetic pre- and
postganglionic neurons. Acta Neuropathol. 113:421–429. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Dodiya HB, Forsyth CB, Voigt RM, Engen PA,
Patel J, Shaikh M, Green SJ, Naqib A, Roy A, Kordower JH, et al:
Chronic stress-induced gut dysfunction exacerbates Parkinson's
disease phenotype and pathology in a rotenone-induced mouse model
of Parkinson's disease. Neurobiol Dis. 135:1043522020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
96
|
Santos SF, de Oliveira HL, Yamada ES,
Neves BC and Pereira A Jr: The gut and Parkinson's disease-a
bidirectional pathway. Front Neurol. 10:5742019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Hsu LJ, Sagara Y, Arroyo A, Rockenstein E,
Sisk A, Mallory M, Wong J, Takenouchi T, Hashimoto M and Masliah E:
alpha-synuclein promotes mitochondrial deficit and oxidative
stress. Am J Pathol. 157:401–410. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98
|
Hu D, Sun X, Liao X, Zhang X, Zarabi S,
Schimmer A, Hong Y, Ford C, Luo Y and Qi X: Alpha-synuclein
suppresses mitochondrial protease ClpP to trigger mitochondrial
oxidative damage and neurotoxicity. Acta Neuropathol. 137:939–960.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
99
|
Chong W, Jimenez J, Mc IM, Saito MA and
Kwakye GF: α-Synuclein enhances cadmium uptake and neurotoxicity
via oxidative stress and caspase activated cell death mechanisms in
a dopaminergic cell model of Parkinson's disease. Neurotox Res.
32:231–246. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
100
|
Dryanovski DI, Guzman JN, Xie Z, Galteri
DJ, Volpicelli-Daley LA, Lee VM, Miller RJ, Schumacker PT and
Surmeier DJ: Calcium entry and α-synuclein inclusions elevate
dendritic mitochondrial oxidant stress in dopaminergic neurons. J
Neurosci. 33:10154–10164. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
101
|
Tapias V, Hu X, Luk KC, Sanders LH, Lee VM
and Greenamyre JT: Synthetic alpha-synuclein fibrils cause
mitochondrial impairment and selective dopamine neurodegeneration
in part via iNOS-mediated nitric oxide production. Cell Mol Life
Sci. 74:2851–2874. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
102
|
Musgrove RE, Helwig M, Bae EJ, Aboutalebi
H, Lee SJ, Ulusoy A and Di Monte DA: Oxidative stress in vagal
neurons promotes parkinsonian pathology and intercellular
alpha-synuclein transfer. J Clin Invest. 129:3738–3753. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
103
|
Martin LJ, Pan Y, Price AC, Sterling W,
Copeland NG, Jenkins NA, Price DL and Lee MK: Parkinson's disease
alpha-synuclein transgenic mice develop neuronal mitochondrial
degeneration and cell death. J Neurosci. 26:41–50. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
104
|
Stichel CC, Zhu XR, Bader V, Linnartz B,
Schmidt S and Lübbert H: Mono- and double-mutant mouse models of
Parkinson's disease display severe mitochondrial damage. Hum Mol
Genet. 16:2377–2393. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
105
|
Ding H, Xiong Y, Sun J, Chen C, Gao J and
Xu H: Asiatic acid prevents oxidative stress and apoptosis by
inhibiting the translocation of α-synuclein into mitochondria.
Front Neurosci. 12:4312018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
106
|
Ho MS: Microglia in Parkinson's disease.
Adv Exp Med Biol. 1175:335–353. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
107
|
Harms AS, Delic V, Thome AD, Bryant N, Liu
Z, Chandra S, Jurkuvenaite A and West AB: α-synuclein fibrils
recruit peripheral immune cells in the rat brain prior to
neurodegeneration. Neuropathol Commun. 5:852017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
108
|
Politis M, Su P and Piccini P: Imaging of
microglia in patients with neurodegenerative disorders. Front
Pharmacol. 3:962012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
109
|
Joers V, Tansey MG, Mulas G and Carta AR:
Microglial phenotypes in Parkinson's disease and animal models of
the disease. Prog Neurobiol. 155:57–75. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
110
|
Whitton PS: Inflammation as a causative
factor in the aetiology of Parkinson's disease. Br J Pharmacol.
150:963–976. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
111
|
Zhang YN, Fan JK, Gu L, Yang HM, Zhan SQ
and Zhang H: Metabotropic glutamate receptor 5 inhibits
α-synuclein-induced microglia inflammation to protect from
neurotoxicity in Parkinson's disease. J Neuroinflammation.
18:232021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
112
|
Croisier E, Moran LB, Dexter DT, Pearce RK
and Graeber MB: Microglial inflammation in the parkinsonian
substantia nigra: Relationship to alpha-synuclein deposition. J
Neuroinflammation. 2:142005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
113
|
Williams GP, Marmion DJ, Schonhoff AM,
Jurkuvenaite A, Won WJ, Standaert DG, Kordower JH and Harms AS: T
cell infiltration in both human multiple system atrophy and a novel
mouse model of the disease. Acta Neuropathol. 139:855–874. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
114
|
Roodveldt C, Labrador-Garrido A,
Gonzalez-Rey E, Fernandez-Montesinos R, Caro M, Lachaud CC, Waudby
CA, Delgado M, Dobson CM and Pozo D: Glial innate immunity
generated by non-aggregated alpha-synuclein in mouse: Differences
between wild-type and Parkinson's disease-linked mutants. PLoS One.
5:e134812010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
115
|
Vaure C and Liu Y: A comparative review of
toll-like receptor 4 expression and functionality in different
animal species. Front Immunol. 5:3162014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
116
|
Uhlén M, Fagerberg L, Hallström BM,
Lindskog C, Oksvold P, Mardinoglu A, Sivertsson A, Kampf C,
Sjöstedt E, Asplund A, et al: Proteomics. Tissue-based map of the
human proteome. Science. 347:12604192015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
117
|
Wardill HR, Van Sebille YZ, Mander KA,
Gibson RJ, Logan RM, Bowen JM and Sonis ST: Toll-like receptor 4
signaling: A common biological mechanism of regimen-related
toxicities: An emerging hypothesis for neuropathy and
gastrointestinal toxicity. Cancer Treat Rev. 41:122–128. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
118
|
Rahimifard M, Maqbool F, Moeini-Nodeh S,
Niaz K, Abdollahi M, Braidy N, Nabavi SM and Nabavi SF: Targeting
the TLR4 signaling pathway by polyphenols: A novel therapeutic
strategy for neuroinflammation. Ageing Res Rev. 36:11–19. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
119
|
Fellner L, Irschick R, Schanda K, Reindl
M, Klimaschewski L, Poewe W, Wenning GK and Stefanova N: Toll-like
receptor 4 is required for α-synuclein dependent activation of
microglia and astroglia. Glia. 61:349–360. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
120
|
Mariucci G, Pagiotti R, Galli F, Romani L
and Conte C: The potential role of toll-like receptor 4 in
mediating dopaminergic cell loss and alpha-synuclein expression in
the acute MPTP mouse model of Parkinson's disease. J Mol Neurosci.
64:611–618. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
121
|
Choi I, Zhang Y, Seegobin SP, Pruvost M,
Wang Q, Purtell K, Zhang B and Yue Z: Microglia clear
neuron-released α-synuclein via selective autophagy and prevent
neurodegeneration. Nat Commun. 11:13862020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
122
|
Wilms H, Rosenstiel P, Romero-Ramos M,
Arlt A, Schäfer H, Seegert D, Kahle PJ, Odoy S, Claasen JH,
Holzknecht C, et al: Suppression of MAP kinases inhibits microglial
activation and attenuates neuronal cell death induced by
alpha-synuclein protofibrils. Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol.
22:897–909. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
123
|
Lee EJ, Woo MS, Moon PG, Baek MC, Choi IY,
Kim WK, Junn E and Kim HS: Alpha-synuclein activates microglia by
inducing the expressions of matrix metalloproteinases and the
subsequent activation of protease-activated receptor-1. J Immunol.
185:615–623. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
124
|
Zhang W, Dallas S, Zhang D, Guo JP, Pang
H, Wilson B, Miller DS, Chen B, Zhang W, McGeer PL, et al:
Microglial PHOX and Mac-1 are essential to the enhanced
dopaminergic neurodegeneration elicited by A30P and A53T mutant
alpha-synuclein. Glia. 55:1178–1188. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
125
|
Lastres-Becker I, Ulusoy A, Innamorato NG,
Sahin G, Rábano A, Kirik D and Cuadrado A: α-Synuclein expression
and Nrf2 deficiency cooperate to aggravate protein aggregation,
neuronal death and inflammation in early-stage Parkinson's disease.
Hum Mol Genet. 21:3173–3192. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
126
|
Sanchez-Guajardo V, Tentillier N and
Romero-Ramos M: The relation between α-synuclein and microglia in
Parkinson's disease: Recent developments. Neuroscience. 302:47–58.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
127
|
Shavali S, Combs CK and Ebadi M: Reactive
macrophages increase oxidative stress and alpha-synuclein nitration
during death of dopaminergic neuronal cells in co-culture:
Relevance to Parkinson's disease. Neurochem Res. 31:85–94. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
128
|
Stefanova N, Fellner L, Reindl M, Masliah
E, Poewe W and Wenning GK: Toll-like receptor 4 promotes
alpha-synuclein clearance and survival of nigral dopaminergic
neurons. Am J Pathol. 179:954–963. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
129
|
Campos SS, Alza NP and Salvador GA: Lipid
metabolism alterations in the neuronal response to A53T α-synuclein
and Fe-induced injury. Arch Biochem Biophys. 655:43–54. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
130
|
Liao JF, Cheng YF, You ST, Kuo WC, Huang
CW, Chiou JJ, Hsu CC, Hsieh-Li HM, Wang S and Tsai YC:
Lactobacillus plantarum PS128 alleviates neurodegenerative
progression in 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine-induced
mouse models of Parkinson's disease. Brain Behav Immun. 90:26–46.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
131
|
Martin WRW, Miles M, Zhong Q, Hartlein J,
Racette BA, Norris SA, Ushe M, Maiti B, Criswell S, Davis AA, et
al: Is levodopa response a valid indicator of parkinson's disease?
Mov Disord. 36:948–954. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
132
|
Tomlinson CL, Stowe R, Patel S, Rick C,
Gray R and Clarke CE: Systematic review of levodopa dose
equivalency reporting in Parkinson's disease. Mov Disord.
25:2649–2653. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
133
|
Epprecht L, Schreglmann SR, Goetze O,
Woitalla D, Baumann CR and Waldvogel D: Unchanged gastric emptying
and visceral perception in early Parkinson's disease after a high
caloric test meal. J Neurol. 262:1946–1953. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
134
|
Schrag A and Quinn N: Dyskinesias and
motor fluctuations in Parkinson's disease. A community-based study.
Brain. 123((Pt 11)): 2297–2305. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
135
|
Nonnekes J, Timmer MH, de Vries NM, Rascol
O, Helmich RC and Bloem BR: Unmasking levodopa resistance in
Parkinson's disease. Mov Disord. 31:1602–1609. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
136
|
Zhu H, Xu G, Zhang K, Kong X, Han R, Zhou
J and Ni Y: Crystal structure of tyrosine decarboxylase and
identification of key residues involved in conformational swing and
substrate binding. Sci Rep. 6:277792016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
137
|
Rekdal VM, Bess EN, Bisanz JE, Turnbaugh
PJ and Balskus EP: Discovery and inhibition of an interspecies gut
bacterial pathway for levodopa metabolism. Science.
364:eaau63232019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
138
|
van Kessel SP, Frye AK, El-Gendy AO,
Castejon M, Keshavarzian A, van Dijk G and El Aidy S: Gut bacterial
tyrosine decarboxylases restrict levels of levodopa in the
treatment of Parkinson's disease. Nat Commun. 10:3102019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
139
|
Sampson TR, Debelius JW, Thron T, Janssen
S, Shastri GG, Ilhan ZE, Challis C, Schretter CE, Rocha S,
Gradinaru V, et al: Gut microbiota regulate motor deficits and
neuroinflammation in a model of Parkinson's disease. Cell.
167:1469–1480. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
140
|
Varankovich NV, Nickerson MT and Korber
DR: Probiotic-based strategies for therapeutic and prophylactic use
against multiple gastrointestinal diseases. Front Microbiol.
6:6852015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
141
|
Liu Y, Yin F, Huang L, Teng H, Shen T and
Qin H: Long-term and continuous administration of Bacillus subtilis
during remission effectively maintains the remission of
inflammatory bowel disease by protecting intestinal integrity,
regulating epithelial proliferation, and reshaping microbial
structure and function. Food Funct. 12:2201–2210. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
142
|
Ait-Belgnaoui A, Durand H, Cartier C,
Chaumaz G, Eutamene H, Ferrier L, Houdeau E, Fioramonti J, Bueno L
and Theodorou V: Prevention of gut leakiness by a probiotic
treatment leads to attenuated HPA response to an acute
psychological stress in rats. Psychoneuroendocrinology.
37:1885–1895. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
143
|
Evrensel A and Ceylan ME: Fecal microbiota
transplantation and its usage in neuropsychiatric disorders. Clin
Psychopharm Neu. 14:231–237. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
144
|
Goya ME, Xue F, Sampedro-Torres-Quevedo C,
Arnaouteli S, Riquelme-Dominguez L, Romanowski A, Brydon J, Ball
KL, Stanley-Wall NR and Doitsidou M: Probiotic bacillus subtilis
protects against α-synuclein aggregation in C. elegans. Cell Rep.
30:367–380. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
145
|
Metta V, Leta V, Mrudula KR, Prashanth LK,
Goyal V, Borgohain R, Chung-Faye G and Chaudhuri KR:
Gastrointestinal dysfunction in Parkinson's disease: Molecular
pathology and implications of gut microbiome, probiotics, and fecal
microbiota transplantation. J Neurol. 21:10072021.
|
|
146
|
Khoruts A: Faecal microbiota
transplantation in 2013: Developing human gut microbiota as a class
of therapeutics. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 11:79–80. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
147
|
Liang S, Wang T, Hu X, Luo J, Li W, Wu X,
Duan Y and Jin F: Administration of Lactobacillus helveticus NS8
improves behavioral, cognitive, and biochemical aberrations caused
by chronic restraint stress. Neuroscience. 310:561–577. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
148
|
Vendrik KEW, Ooijevaar RE, de Jong PRC,
Laman JD, van Oosten BW, van Hilten JJ, Ducarmon QR, Keller JJ,
Kuijper EJ and Contarino MF: Fecal microbiota transplantation in
neurological disorders. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 10:982020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
149
|
Fang X: Microbial treatment: The potential
application for Parkinson's disease. Neurol Sci. 40:51–58. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
150
|
Gibson GR, Hutkins R, Sanders ME, Prescott
SL, Reimer RA, Salminen SJ, Scott K, Stanton C, Swanson KS, Cani
PD, et al: Expert consensus document: The international scientific
association for probiotics and prebiotics (ISAPP) consensus
statement on the definition and scope of prebiotics. Nat Rev
Gastroenterol Hepatol. 14:491–502. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
151
|
Gibson GR and Roberfroid MB: Dietary
modulation of the human colonic microbiota: Introducing the concept
of prebiotics. J Nutr. 125:1401–1412. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
152
|
Kovacs Z, Benjamins E, Grau K, Ur Rehman
A, Ebrahimi M and Czermak P: Recent developments in manufacturing
oligosaccharides with prebiotic functions. Adv Biochem Eng
Biotechnol. 143:257–295. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
153
|
Savignac HM, Corona G, Mills H, Chen L,
Spencer JP, Tzortzis G and Burnet PW: Prebiotic feeding elevates
central brain derived neurotrophic factor, N-methyl-D-aspartate
receptor subunits and D-serine. Neurochem Int. 63:756–764. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
154
|
Armstrong MJ and Okun MS: Diagnosis and
treatment of Parkinson disease: A review. JAMA. 323:548–560. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
155
|
Emamzadeh FN and Surguchov A: Parkinson's
disease: Biomarkers, treatment, and risk factors. Front Neurosci.
12:6122018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
156
|
Takahashi M, Suzuki M, Fukuoka M, Fujikake
N, Watanabe S, Murata M, Wada K, Nagai Y and Hohjoh H:
Normalization of overexpressed α-synuclein causing Parkinson's
disease by a moderate gene silencing with RNA interference. Mol
Ther Nucleic Acids. 4:e2412015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
157
|
Ding L, Gu H, Xiong X, Ao H, Cao J, Lin W,
Yu M, Lin J and Cui Q: MicroRNAs involved in carcinogenesis,
prognosis, therapeutic resistance and applications in human
triple-negative breast cancer. Cells. 8:14922019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
158
|
Junn E, Lee KW, Jeong BS, Chan TW, Im JY
and Mouradian MM: Repression of alpha-synuclein expression and
toxicity by microRNA-7. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 106:13052–13057.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
159
|
Masliah E, Rockenstein E, Adame A, Alford
M, Crews L, Hashimoto M, Seubert P, Lee M, Goldstein J, Chilcote T,
et al: Effects of alpha-synuclein immunization in a mouse model of
Parkinson's disease. Neuron. 46:857–868. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
160
|
Ghochikyan A, Petrushina I, Davtyan H,
Hovakimyan A, Saing T, Davtyan A, Cribbs DH and Agadjanyan MG:
Immunogenicity of epitope vaccines targeting different B cell
antigenic determinants of human alpha-synuclein: Feasibility study.
Neurosci Lett. 560:86–91. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
161
|
Vaikath NN, Hmila I, Gupta V, Erskine D,
Ingelsson M and El-Agnaf OMA: Antibodies against alpha-synuclein:
Tools and therapies. J Neurochem. 150:612–625. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
162
|
Rabenstein M, Agbo DB, Wolf E, Dams J,
Nicolai M, Roeder A, Bacher M, Dodel RC and Noelker C: Effect of
naturally occurring α-synuclein-antibodies on toxic
alpha-synuclein-fragments. Neurosci Lett. 704:181–188. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
163
|
Wang Z, Gao G, Duan C and Yang H: Progress
of immunotherapy of anti-alpha-synuclein in Parkinson's disease.
Biomed Pharmacother. 115:1088432019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
164
|
Lashuel HA, Overk CR, Oueslati A and
Masliah E: The many faces of alpha-synuclein: From structure and
toxicity to therapeutic target. Nat Rev Neurosci. 14:38–48. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
165
|
Sulzer D, Alcalay RN, Garretti F, Cote L,
Kanter E, Agin-Liebes J, Liong C, McMurtrey C, Hildebrand WH, Mao
X, et al: T cells from patients with Parkinson's disease recognize
α-synuclein peptides. Nature. 546:656–661. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
166
|
Tran HT, Chung CH, Iba M, Zhang B,
Trojanowski JQ, Luk KC and Lee VM: Alpha-synuclein immunotherapy
blocks uptake and templated propagation of misfolded
alpha-synuclein and neurodegeneration. Cell Rep. 7:2054–2065. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
167
|
Zhou C, Emadi S, Sierks MR and Messer A: A
human single-chain Fv intrabody blocks aberrant cellular effects of
overexpressed alpha-synuclein. Mol Ther. 10:1023–1031. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
168
|
El-Agnaf O, Overk C, Rockenstein E, Mante
M, Florio J, Adame A, Vaikath N, Majbour N, Lee SJ, Kim C, et al:
Differential effects of immunotherapy with antibodies targeting
alpha-synuclein oligomers and fibrils in a transgenic model of
synucleinopathy. Neurobiol Dis. 104:85–96. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
169
|
Rutherford NJ, Brooks M and Giasson BI:
Novel antibodies to phosphorylated α-synuclein serine 129 and NFL
serine 473 demonstrate the close molecular homology of these
epitopes. Acta Neuropathol Commun. 4:802016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
170
|
Wang N, Garcia J, Freeman R and Gibbons
CH: Phosphorylated alpha-synuclein within cutaneous autonomic
nerves of patients with Parkinson's disease: The implications of
sample thickness on results. J Histochem Cytochem. 68:669–678.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
171
|
Ciesielska A, Matyjek M and Kwiatkowska K:
TLR4 and CD14 trafficking and its influence on LPS-induced
pro-inflammatory signaling. Cell Mol Life Sci. 78:1233–1261. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
172
|
Perez-Pardo P, Dodiya HB, Engen PA,
Forsyth CB, Huschens AM, Shaikh M, Voigt RM, Naqib A, Green SJ,
Kordower JH, et al: Role of TLR4 in the gut-brain axis in
Parkinson's disease: A translational study from men to mice. Gut.
68:829–843. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
173
|
Brundin L, Bryleva EY and Rajamani KT:
Role of inflammation in suicide: From mechanisms to treatment.
Neuropsychopharmacology. 42:271–283. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
174
|
Decressac M, Mattsson B, Weikop P,
Lundblad M, Jakobsson J and Bjorklund A: TFEB-mediated autophagy
rescues midbrain dopamine neurons from α-synuclein toxicity. Proc
Natl Acad Sci USA. 110:E1817–E1826. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
175
|
Maiese K, Chong ZZ, Shang YC and Wang S:
mTOR: On target for novel therapeutic strategies in the nervous
system. Trends Mol Med. 19:51–60. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
176
|
Sardi SP, Cedarbaum JM and Brundin P:
Targeted therapies for Parkinson's Disease: From genetics to the
clinic. Mov Disord. 33:684–696. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
177
|
Ghosh A, Tyson T, George S, Hildebrandt
EN, Steiner JA, Madaj Z, Schulz E, Machiela E, McDonald WG, Escobar
Galvis ML, et al: Mitochondrial pyruvate carrier regulates
autophagy, inflammation, and neurodegeneration in experimental
models of Parkinson's disease. Sci Transl Med. 8:368ra1742016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
178
|
Erlich S, Shohami E and Pinkas-Kramarski
R: Neurodegeneration induces upregulation of beclin 1. Autophagy.
2:49–51. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
179
|
Spencer B, Potkar R, Trejo M, Rockenstein
E, Patrick C, Gindi R, Adame A, Wyss-Coray T and Masliah E: Beclin
1 gene transfer activates autophagy and ameliorates the
neurodegenerative pathology in alpha-synuclein models of
Parkinson's and lewy body diseases. J Neurosci. 29:13578–13588.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
180
|
Savitt D and Jankovic J: Targeting
α-synuclein in Parkinson's disease: Progress towards the
development of disease-modifying therapeutics. Drugs. 79:797–810.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
181
|
Hussain T, Zhao D, Shah SZA, Sabir N, Wang
J, Liao Y, Song Y, Dong H, Mangi MH, Ni J, et al: Nilotinib: A
tyrosine kinase inhibitor mediates resistance to intracellular
mycobacterium via regulating autophagy. Cells. 8:5062019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
182
|
Pagan F, Hebron M, Valadez EH,
Torres-Yaghi Y, Huang X, Mills RR, Wilmarth BM, Howard H, Dunn C,
Carlson A, et al: Nilotinib effects in Parkinson's disease and
dementia with lewy bodies. J Parkinsons Dis. 6:503–517. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
183
|
de Groot P, Nikolic T, Pellegrini S, Sordi
V, Imangaliyev S, Rampanelli E, Hanssen N, Attaye I, Bakker G,
Duinkerken G, et al: Faecal microbiota transplantation halts
progression of human new-onset type 1 diabetes in a randomised
controlled trial. Gut. 70:92–105. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
184
|
Gurung M, Li Z, You H, Rodrigues R, Jump
DB, Morgun A and Shulzhenko N: Role of gut microbiota in type 2
diabetes pathophysiology. EBioMedicine. 51:1025902020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
185
|
Horsager J, Andersen KB, Knudsen K,
Skjærbæk C, Fedorova TD, Okkels N, Schaeffer E, Bonkat SK, Geday J,
Otto M, et al: Brain-first versus body-first Parkinson's disease: A
multimodal imaging case-control study. Brain. 143:3077–3088. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
186
|
Barbut D, Stolzenberg E and Zasloff M:
Gastrointestinal immunity and alpha-synuclein. J Parkinsons Dis.
9:S313–S322. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
187
|
Perni M, Galvagnion C, Maltsev A, Meisl G,
Müller MB, Challa PK, Kirkegaard JB, Flagmeier P, Cohen SI,
Cascella R, et al: A natural product inhibits the initiation of
α-synuclein aggregation and suppresses its toxicity. Proc Natl Acad
Sci USA. 114:E1009–E1017. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
188
|
Das T and Eliezer D: Membrane interactions
of intrinsically disordered proteins: The example of
alpha-synuclein. Biochim Biophys Acta Proteins Proteom.
1867:879–889. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
189
|
Abbott SK, Li H, Muñoz SS, Knoch B,
Batterham M, Murphy KE, Halliday GM and Garner B: Altered ceramide
acyl chain length and ceramide synthase gene expression in
Parkinson's disease. Mov Disord. 29:518–526. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|