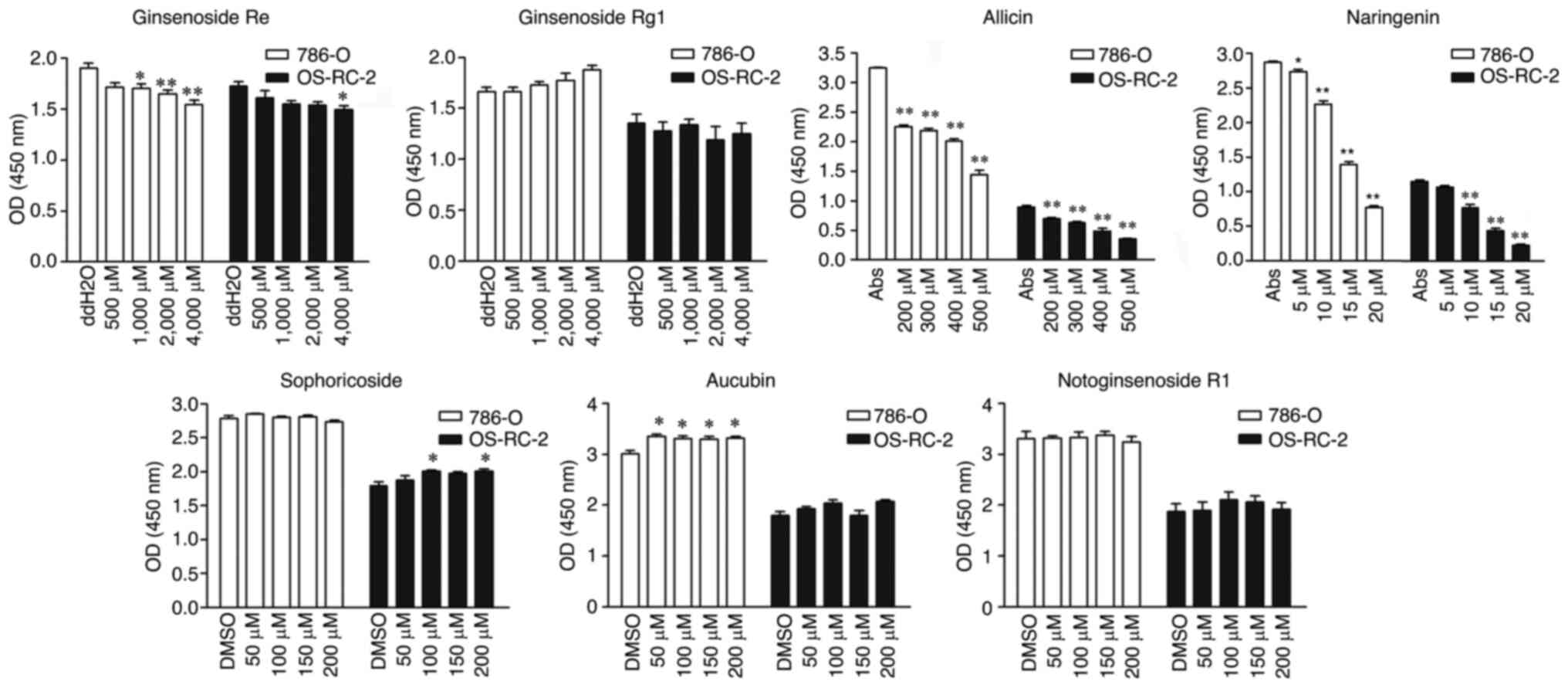
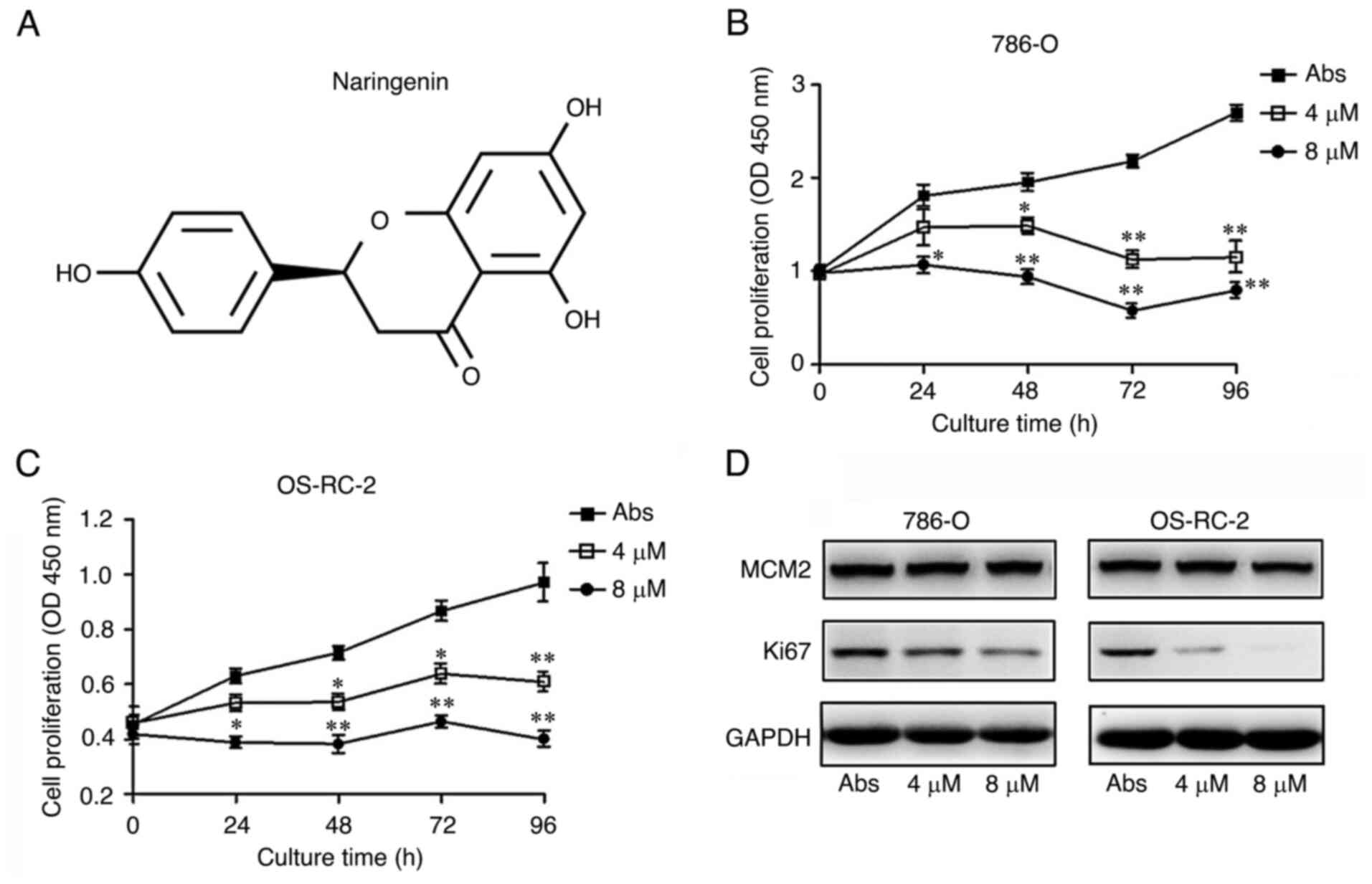
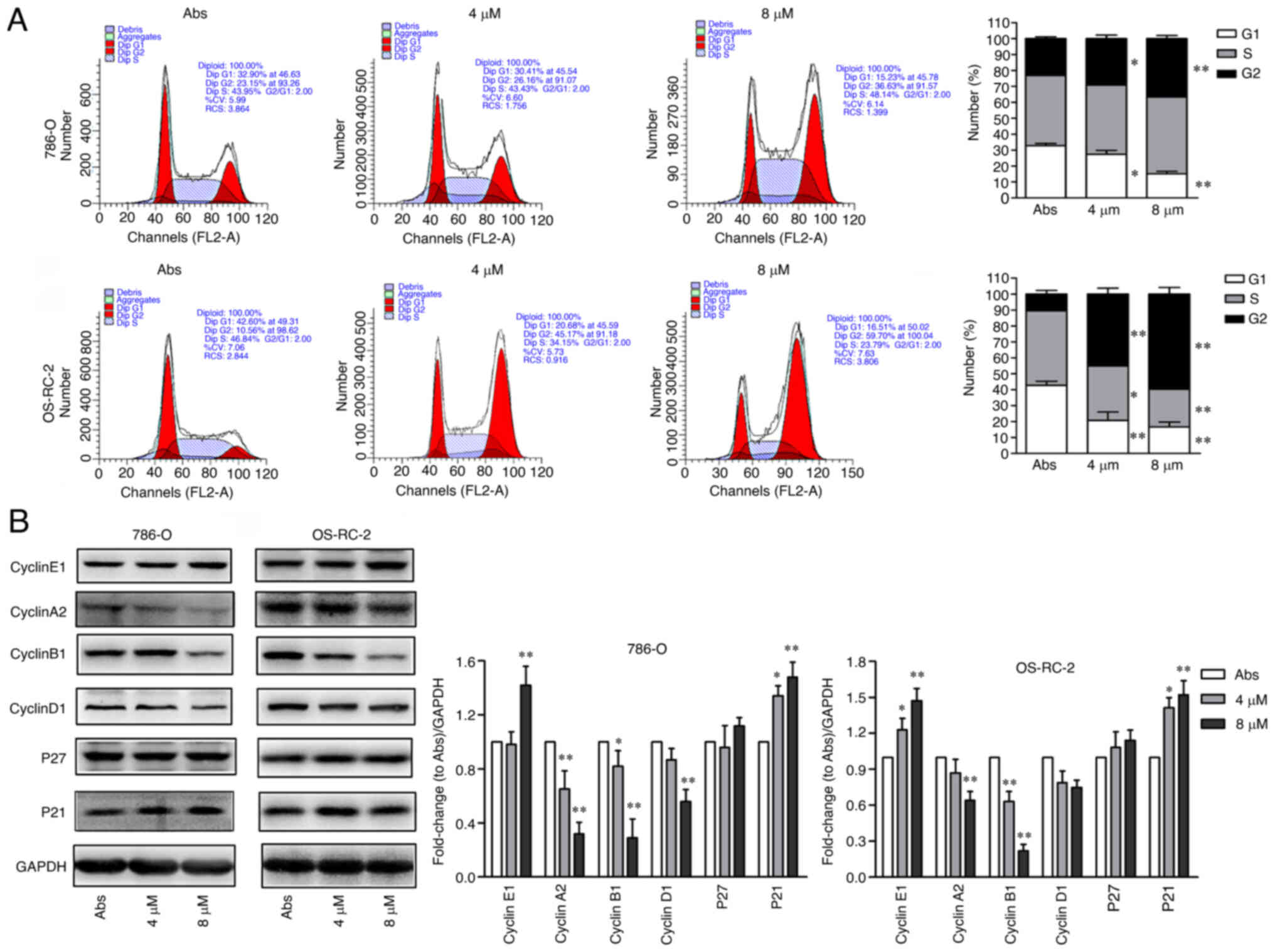
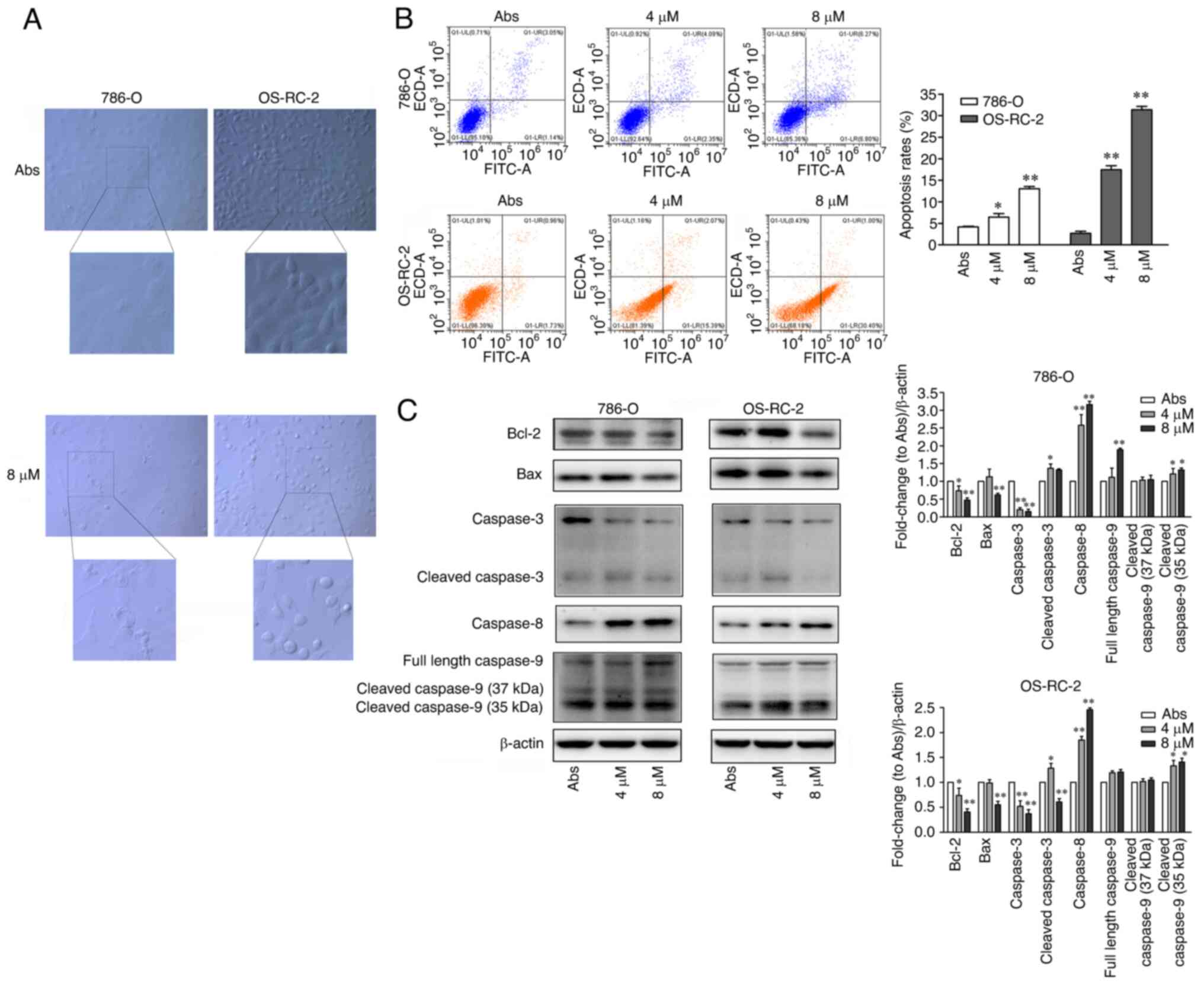
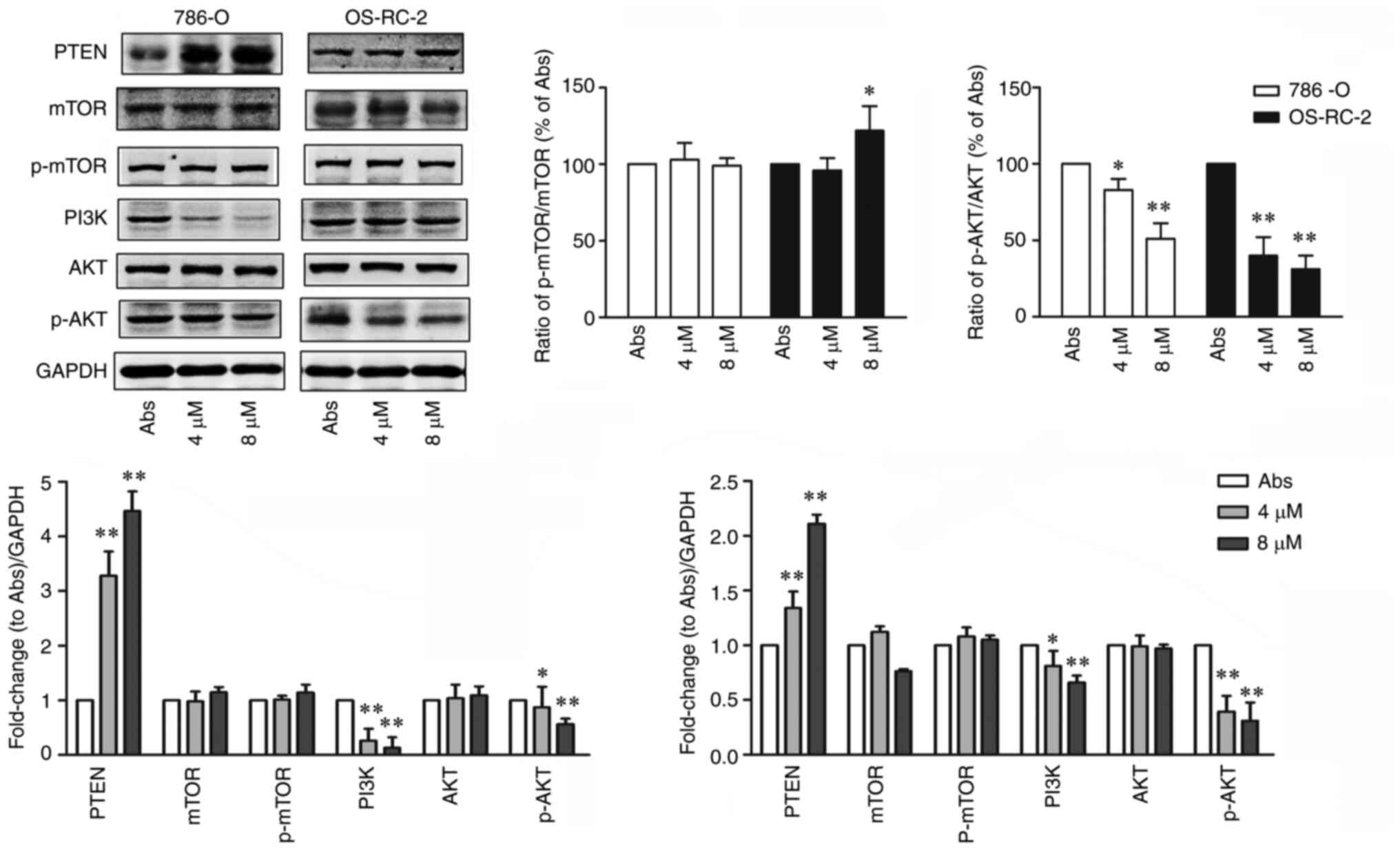
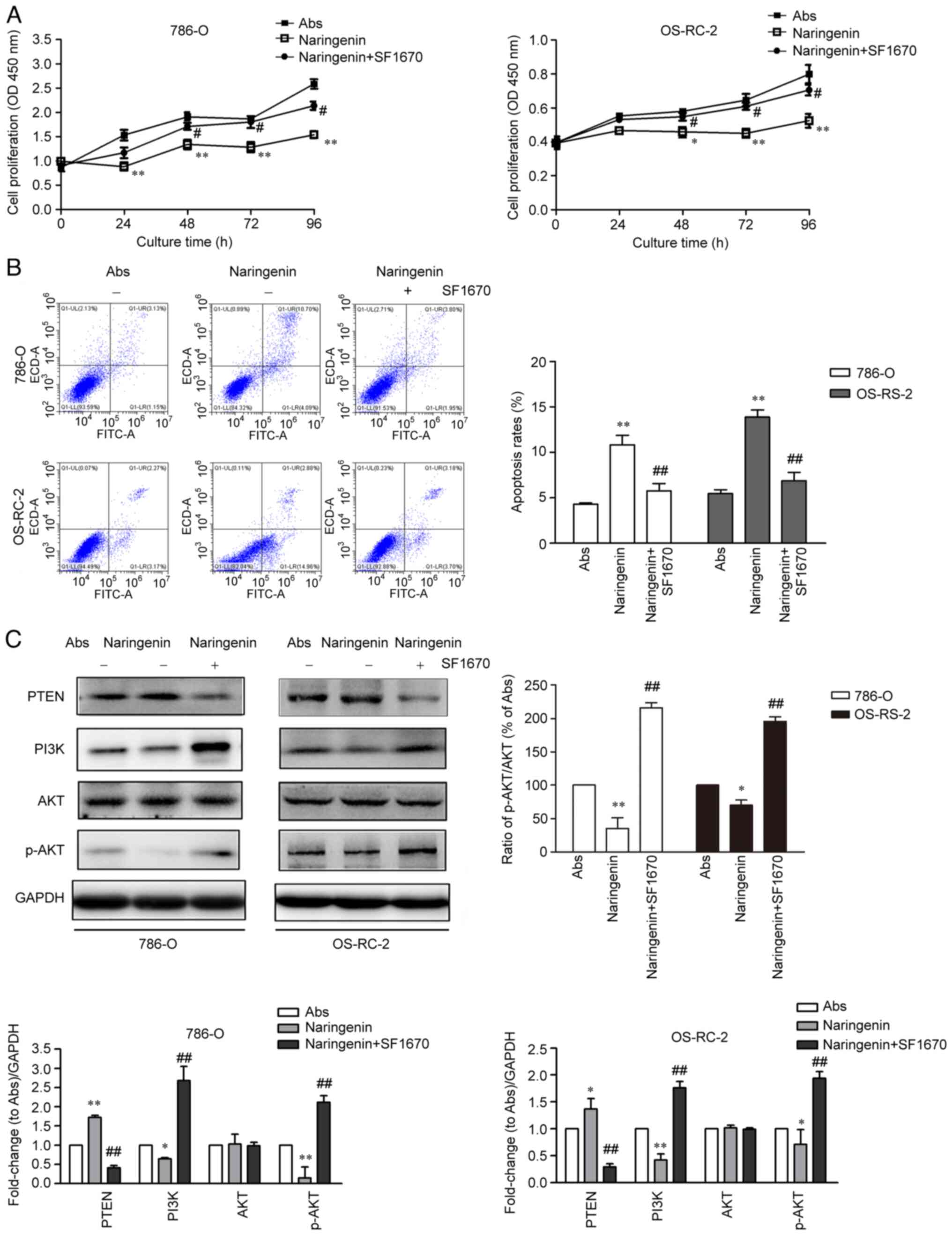
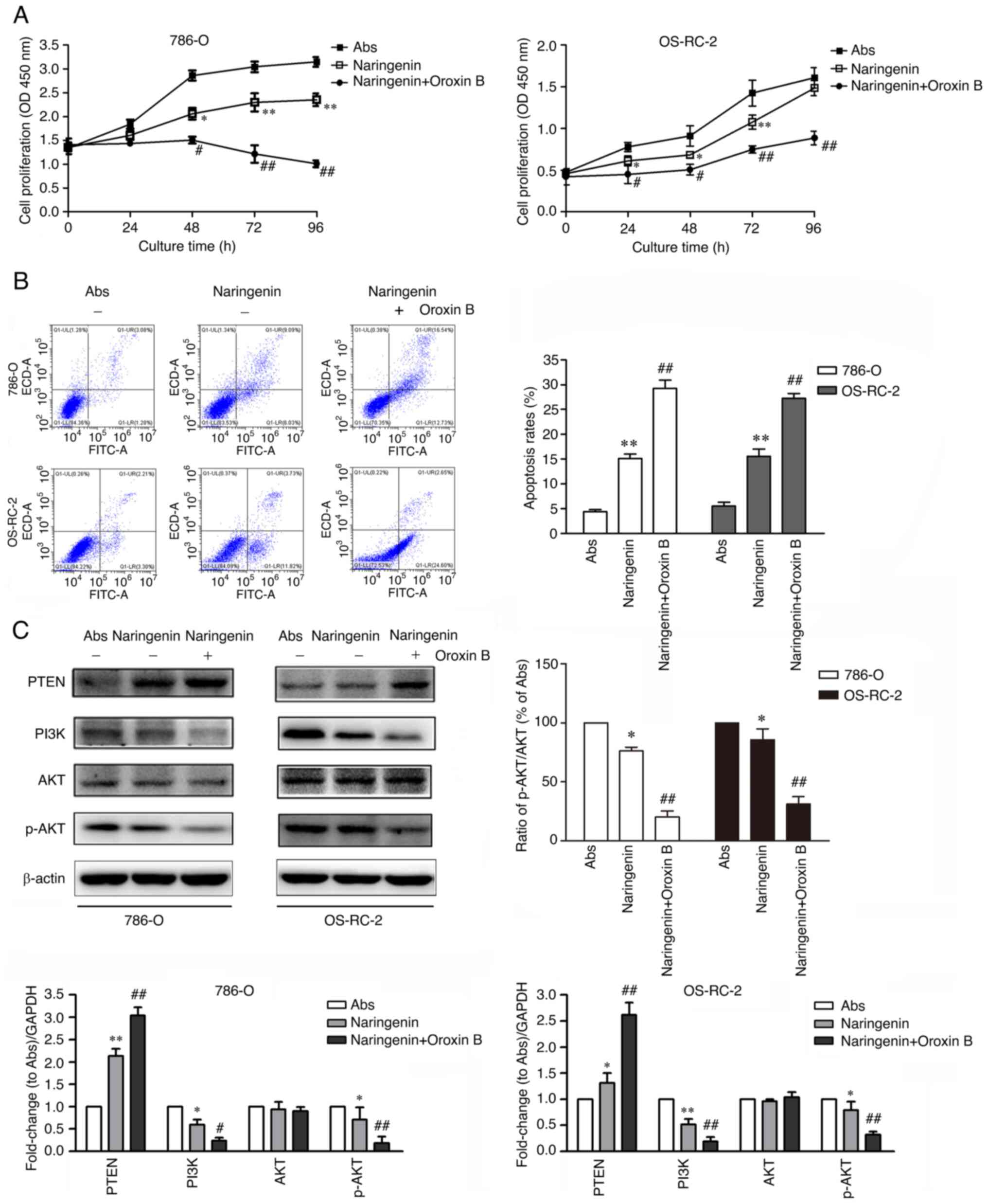
|
1
|
Zhuang H, Meng X, Li Y, Wang X, Huang S,
Liu K, Hehir M, Fang R, Jiang L, Zhou JX, et al: Cyclic AMP
responsive element-binding protein promotes renal cell carcinoma
proliferation probably via the expression of spindle and
kinetochore-associated protein 2. Oncotarget. 7:16325–16337. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2020. CA Cancer J Clin. 70:7–30. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Haque I, Subramanian A, Huang CH, Godwin
AK, Van Veldhuizen PJ, Banerjee S and Banerjee SK: The role of
compounds derived from natural supplement as anticancer agents in
renal cell carcinoma: A review. Int J Mol Sci. 19:1072017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Mendiratta P, Rini BI and Ornstein MC:
Emerging immunotherapy in advanced renal cell carcinoma. Urol
Oncol. 35:687–693. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Wang X, Huang S, Xin X, Ren Y, Weng G and
Wang P: The antitumor activity of umbelliferone in human renal cell
carcinoma via regulation of the p110gamma catalytic subunit of
PI3Kγ. Acta Pharm. 69:111–119. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Ji HF, Li XJ and Zhang HY: Natural
products and drug discovery. Can thousands of years of ancient
medical knowledge lead us to new and powerful drug combinations in
the fight against cancer and dementia? EMBO Rep. 10:194–200. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Reddy D, Kumavath R, Tan TZ, Ampasala DR
and Kumar AP: Peruvoside targets apoptosis and autophagy through
MAPK Wnt/β-catenin and PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathways in human
cancers. Life Sci. 241:1171472020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Krushkal J, Negi S, Yee LM, Evans JR,
Grkovic T, Palmisano A, Fang J, Sankaran H, McShane LM, Zhao Y and
O'Keefe BR: Molecular genomic features associated with in vitro
response of the NCI-60 cancer cell line panel to natural products.
Mol Oncol. 15:381–406. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Atanasov AG, Waltenberger B,
Pferschy-Wenzig EM, Linder T, Wawrosch C, Uhrin P, Temml V, Wang L,
Schwaiger S, Heiss EH, et al: Discovery and resupply of
pharmacologically active plant-derived natural products: A review.
Biotechnol Adv. 33:1582–1614. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Fang J, Wu Z, Cai C, Wang Q, Tang Y and
Cheng F: Quantitative and systems pharmacology. 1. in silico
prediction of drug-target interactions of natural products enables
new targeted cancer therapy. J Chem Inf Model. 57:2657–2671. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Ha MW, Song BR, Chung HJ and Paek SM:
Design and synthesis of anti-cancer chimera molecules based on
marine natural products. Mar Drugs. 17:5002019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Czarnik AW and Keene JD: Combinatorial
chemistry. Curr Biol. 8:R705–R707. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Siddiqui M and Rajkumar SV: The high cost
of cancer drugs and what we can do about it. Mayo Clin Proc.
87:935–943. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Kang Q, Gong J, Wang M, Wang Q, Chen F and
Cheng KW: 6-C-(E-Phenylethenyl)naringenin attenuates the stemness
of hepatocellular carcinoma cells by suppressing wnt/beta-catenin
signaling. J Agric Food Chem. 67:13939–13947. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
O'Brien CA, Kreso A and Jamieson CH:
Cancer stem cells and self-renewal. Clin Cancer Res. 16:3113–3120.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Sui M, Zhang H, Di X, Chang J, Shen Y and
Fan W: G2 checkpoint abrogator abates the antagonistic interaction
between antimicrotubule drugs and radiation therapy. Radiother
Oncol. 104:243–248. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Sezer ED, Oktay LM, Karadadas E, Memmedov
H, Gunel NS and Sözmen E: Assessing anticancer potential of
blueberry flavonoids, quercetin, kaempferol, and gentisic acid,
through oxidative stress and apoptosis parameters on HCT-116 cells.
J Med Food. 22:1118–1126. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Deleuze A, Saout J, Dugay F, Peyronnet B,
Mathieu R, Verhoest G, Bensalah K, Crouzet L, Laguerre B,
Belaud-Rotureau MA, et al: Immunotherapy in renal cell carcinoma:
The future is now. Int J Mol Sci. 21:25322020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Gu B, Ding Q, Xia G and Fang Z: EGCG
inhibits growth and induces apoptosis in renal cell carcinoma
through TFPI-2 overexpression. Oncol Rep. 21:635–640.
2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Meng FD, Li Y, Tian X, Ma P, Sui CG, Fu LY
and Jiang YH: Synergistic effects of snail and quercetin on renal
cell carcinoma Caki-2 by altering AKT/mTOR/ERK1/2 signaling
pathways. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 8:6157–6168. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Batova A, Altomare D, Creek KE, Naviaux
RK, Wang L, Li K, Green E, Williams R, Naviaux JC, Diccianni M and
Yu AL: Englerin A induces an acute inflammatory response and
reveals lipid metabolism and ER stress as targetable
vulnerabilities in renal cell carcinoma. PLoS One. 12:e01726322017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Hamedani Y, Chakraborty S, Sabarwal A, Pal
S, Bhowmick S and Balan M: Novel Honokiol-eluting PLGA-based
scaffold effectively restricts the growth of renal cancer cells.
PLoS One. 15:e02438372020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Zhang T, Zhao L, Zhang TT, Wu W, Liu J,
Wang X, Wan Y, Geng H, Sun X, Qian W and Yu D: Curcumin negatively
regulates cigarette smoke-induced renal cell carcinoma
epithelial-mesenchymal transition through the ERK5/AP-1 pathway.
Onco Targets Ther. 13:9689–9700. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Dai L, Chen L, Wang W and Lin P:
Resveratrol inhibits ACHN cells via regulation of histone
acetylation. Pharm Biol. 58:231–238. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Kim BH, Chung EY, Min BK, Lee SH, Kim MK,
Min KR and Kim Y: Anti-inflammatory action of legume isoflavonoid
sophoricoside through inhibition on cyclooxygenase-2 activity.
Planta Med. 69:474–476. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Wu C, Luan H, Wang S, Zhang X, Wang R, Jin
L, Guo P and Chen X: Modulation of lipogenesis and glucose
consumption in HepG2 cells and C2C12 myotubes by sophoricoside.
Molecules. 18:15624–15635. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Yang Z, Wu QQ, Xiao Y, Duan MX, Liu C,
Yuan Y, Meng YY, Liao HH and Tang QZ: Aucubin protects against
myocardial infarction-induced cardiac remodeling via
nNOS/NO-regulated oxidative stress. Oxid Med Cell Longev.
2018:43279012018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Liu H, Yang J, Yang W, Hu S, Wu Y, Zhao B,
Hu H and Du S: Focus on notoginsenoside R1 in metabolism and
prevention against human diseases. Drug Des Devel Ther. 14:551–565.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Shen B, Zhao C, Wang Y, Peng Y, Cheng J,
Li Z, Wu L, Jin M and Feng H: Aucubin inhibited lipid accumulation
and oxidative stress via Nrf2/HO-1 and AMPK signalling pathways. J
Cell Mol Med. 23:4063–4075. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Qin Q, Lin N, Huang H, Zhang X, Cao X,
Wang Y and Li P: Ginsenoside Rg1 ameliorates cardiac oxidative
stress and inflammation in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats.
Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 12:1091–1103. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Li W, Li G, She W, Hu X and Wu X: Targeted
antitumor activity of Ginsenoside (Rg1) in paclitaxel-resistant
human nasopharyngeal cancer cells are mediated through activation
of autophagic cell death, cell apoptosis, endogenous ROS
production, S phase cell cycle arrest and inhibition of
m-TOR/PI3K/AKT signalling pathway. J BUON. 24:2056–2061.
2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Hou Y, Gu D, Peng J, Jiang K, Li Z, Shi J,
Yang S, Li S and Fan X: Ginsenoside Rg1 regulates liver lipid
factor metabolism in NAFLD model rats. ACS Omega. 5:10878–10890.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Nan B, Yang C, Li L, Ye H, Yan H, Wang M
and Yuan Y: Allicin alleviated acrylamide-induced NLRP3
inflammasome activation via oxidative stress and endoplasmic
reticulum stress in Kupffer cells and SD rats liver. Food Chem
Toxicol. 148:1119372021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Salehi B, Fokou PVT, Sharifi-Rad M, Zucca
P, Pezzani R, Martins N and Sharifi-Rad J: The therapeutic
potential of naringenin: A review of clinical trials.
Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 12:112019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Huang B, Hu P, Hu A, Li Y, Shi Q, Huang J,
Jiang Q, Xu S, Li L and Wu Q: Naringenin attenuates carotid
restenosis in rats after balloon injury through its
anti-inflammation and anti-oxidative effects via the RIP1-RIP3-MLKL
signaling pathway. Eur J Pharmacol. 855:167–174. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Chanput W, Krueyos N and Ritthiruangdej P:
Anti-oxidative assays as markers for anti-inflammatory activity of
flavonoids. Int Immunopharmacol. 40:170–175. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Pinho-Ribeiro FA, Zarpelon AC, Fattori V,
Manchope MF, Mizokami SS, Casagrande R and Verri WA Jr: Naringenin
reduces inflammatory pain in mice. Neuropharmacology. 105:508–519.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Zhang C, Zeng W, Yao Y, Xu B, Wei X, Wang
L, Yin X, Barman AK, Zhang F, Zhang C, et al: Naringenin
ameliorates radiation-induced lung injury by lowering IL-1beta
level. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 366:341–348. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Joshi R, Kulkarni YA and Wairkar S:
Pharmacokinetic, pharmacodynamic and formulations aspects of
Naringenin: An update. Life Sci. 215:43–56. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Latif AD, Gonda T, Vagvolgyi M, Kúsz N,
Kulmány A, Ocsovszki I, Zomborszki ZP, Zupkó I and Hunyadi A:
Synthesis and in vitro antitumor activity of naringenin oxime and
oxime ether derivatives. Int J Mol Sci. 20:21842019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Tarantino G, Citro V and Capone D:
Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: A challenge from mechanisms to
therapy. J Clin Med. 9:152019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Fu S, Zhang Y, Shi J, Hao D and Zhang P:
Identification of gene-phenotype connectivity associated with
flavanone naringenin by functional network analysis. PeerJ.
7:e66112019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Hermawan A, Ikawati M, Jenie RI, Khumaira
A, Putri H, Nurhayati IP, Angraini SM and Muflikhasari HA:
Identification of potential therapeutic target of naringenin in
breast cancer stem cells inhibition by bioinformatics and in vitro
studies. Saudi Pharm J. 29:12–26. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Han KY, Chen PN, Hong MC, Hseu YC, Chen
KM, Hsu LS and Chen WJ: Naringenin attenuated prostate cancer
invasion via reversal of epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and
inhibited uPA activity. Anticancer Res. 38:6753–6758. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Tan Z, Sun Y, Liu M, Xia L, Cao F, Qi Y
and Song Y: Naringenin inhibits cell migration, invasion, and tumor
growth by regulating circFOXM1/miR-3619-5p/SPAG5 axis in lung
cancer. Cancer Biother Radiopharm. 27:10892020.
|
|
46
|
Choi J, Lee DH, Jang H, Park SY and Seol
JW: Naringenin exerts anticancer effects by inducing tumor cell
death and inhibiting angiogenesis in malignant melanoma. Int J Med
Sci. 17:3049–3057. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Bao L, Liu F, Guo HB, Li Y, Tan BB, Zhang
WX and Peng YH: Naringenin inhibits proliferation, migration, and
invasion as well as induces apoptosis of gastric cancer SGC7901
cell line by downregulation of AKT pathway. Tumour Biol.
37:11365–11374. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Md S, Alhakamy NA, Aldawsari HM, Husain M,
Kotta S, Abdullah ST, Fahmy UA, Alfaleh MA and Asfour HZ:
Formulation design, statistical optimization, and in vitro
evaluation of a naringenin nanoemulsion to enhance apoptotic
activity in A549 lung cancer cells. Pharmaceuticals (Basel).
13:1522020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Arul D and Subramanian P: Naringenin
(citrus flavonone) induces growth inhibition, cell cycle arrest and
apoptosis in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Pathol Oncol
Res. 19:763–770. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Yan N, Wen L, Peng R, Li H, Liu H, Peng H,
Sun Y, Wu T, Chen L, Duan Q, et al: Naringenin ameliorated kidney
injury through Let-7a/TGFBR1 signaling in diabetic nephropathy. J
Diabetes Res. 2016:87387602016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Zhao Z, Jin G, Ge Y and Guo Z: Naringenin
inhibits migration of breast cancer cells via inflammatory and
apoptosis cell signaling pathways. Inflammopharmacology.
27:1021–1036. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Wang R, Wang J, Dong T, Shen J, Gao X and
Zhou J: Naringenin has a chemoprotective effect in MDA-MB-231
breast cancer cells via inhibition of caspase-3 and −9 activities.
Oncol Lett. 17:1217–1222. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Wang Y, Liu Z, Liu Q, Han Y, Zang Y, Zhang
H, Du X, Qin T and Wu Y: Honokiol suppressed pancreatic cancer
progression via miR-101/Mcl-1 axis. Cancer Manag Res. 12:5243–5254.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Newton K, Wickliffe KE, Maltzman A, Dugger
DL, Reja R, Zhang Y, Roose-Girma M, Modrusan Z, Sagolla MS, Webster
JD and Dixit VM: Activity of caspase-8 determines plasticity
between cell death pathways. Nature. 575:679–682. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Zhou J, Xia L and Zhang Y: Naringin
inhibits thyroid cancer cell proliferation and induces cell
apoptosis through repressing PI3K/AKT pathway. Pathol Res Pract.
215:1527072019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Lim W, Park S, Bazer FW and Song G:
Naringenin-induced apoptotic cell death in prostate cancer cells is
mediated via the PI3K/AKT and MAPK signaling pathways. J Cell
Biochem. 118:1118–1131. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|