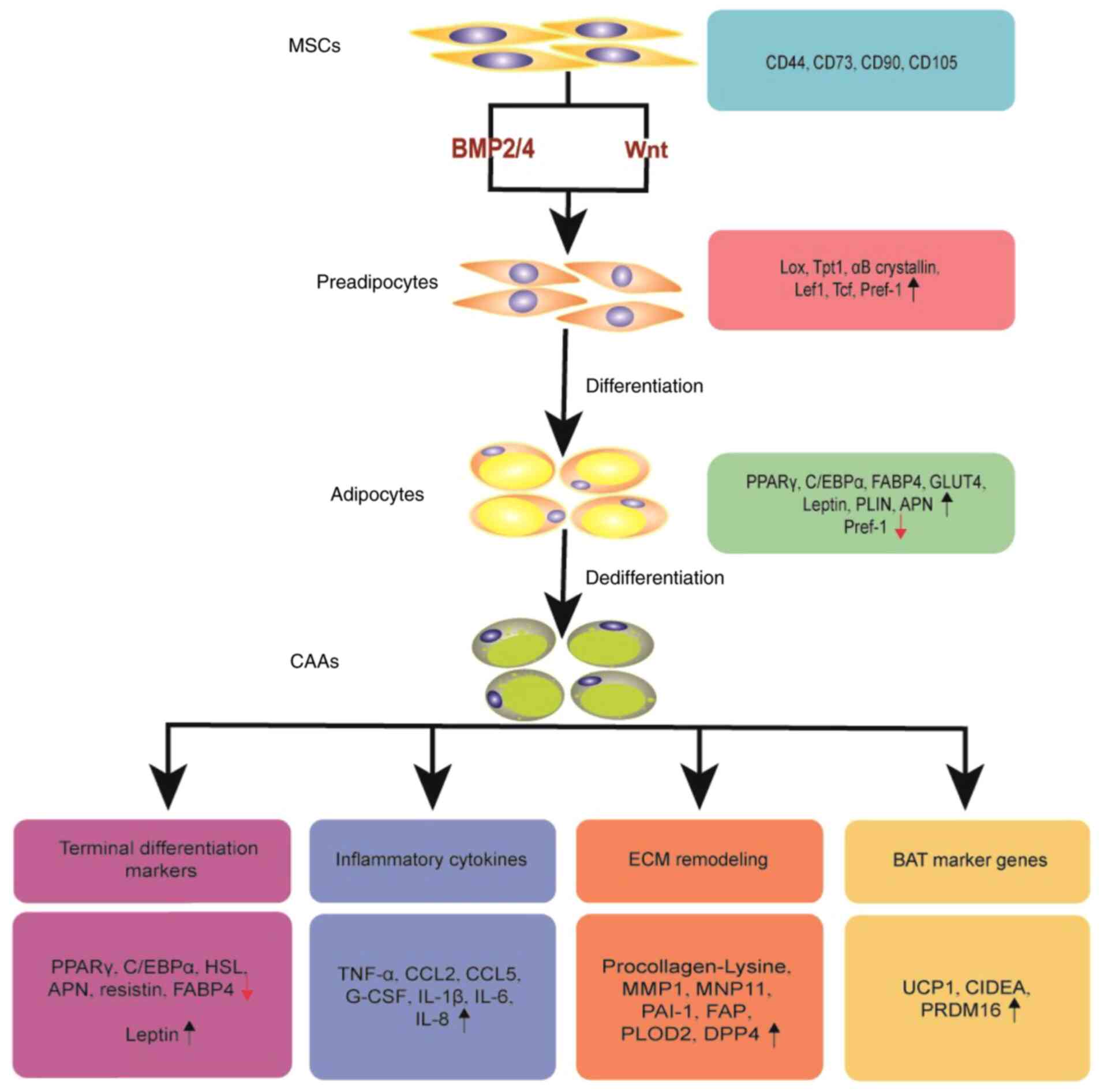
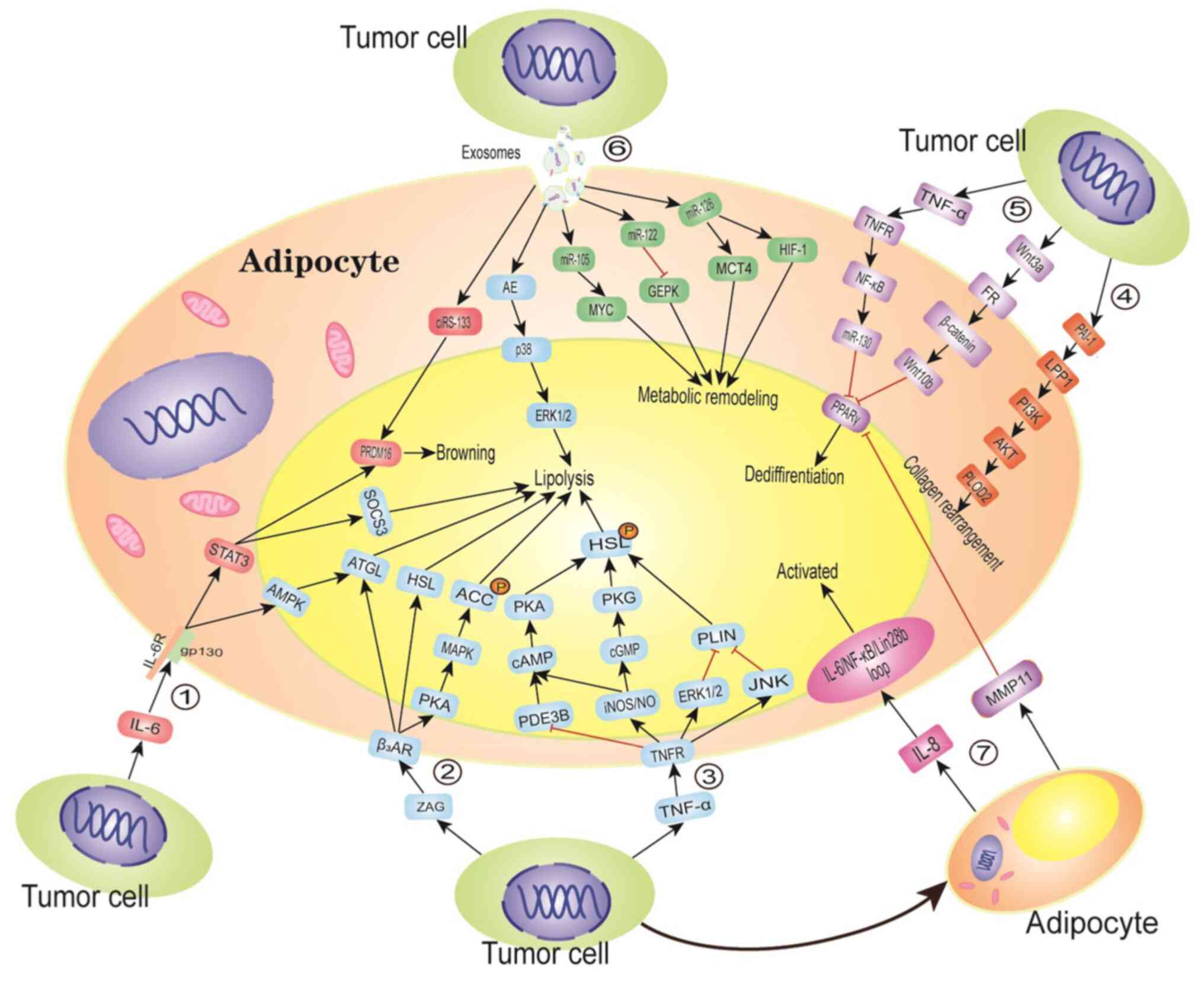
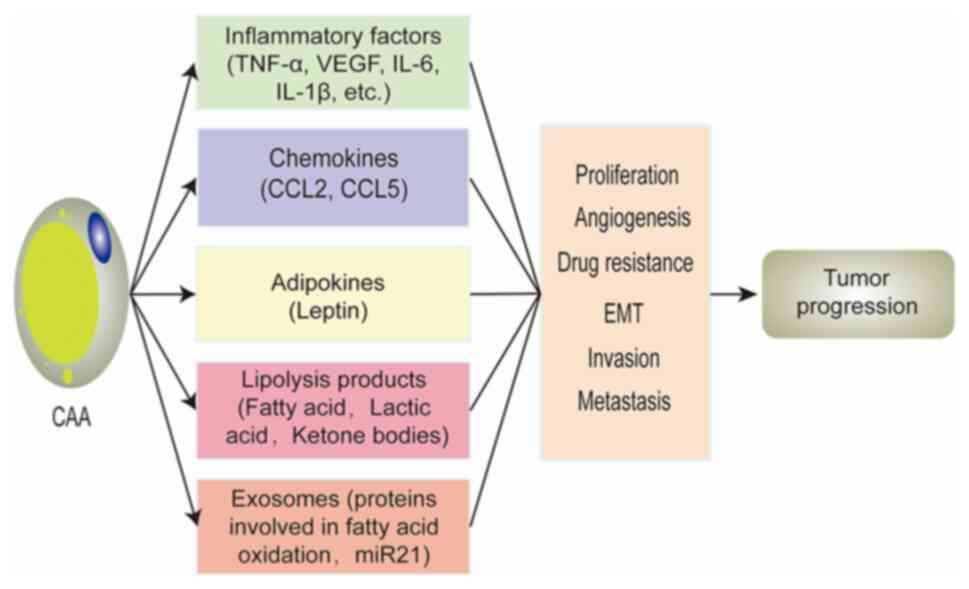
|
1
|
Montel V, Mose ES and Tarin D:
Tumor-stromal interactions reciprocally modulate gene expression
patterns during carcinogenesis and metastasis. Int J Cancer.
119:251–263. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Vandeweyer E and Hertens D: Quantification
of glands and fat in breast tissue: An experimental determination.
Ann Anat. 184:181–184. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Ramsay DT, Kent JC, Hartmann RA and
Hartmann PE: Anatomy of the lactating human breast redefined with
ultrasound imaging. J Anat. 206:525–534. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Luo L and Liu M: Adipose tissue in control
of metabolism. J Endocrinol. 231:R77–R99. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Wang YX, Zhu N, Zhang CJ, Wang YK, Wu HT,
Li Q, Du K, Liao DF and Qin L: Friend or foe: Multiple roles of
adipose tissue in cancer formation and progression. J Cell Physiol.
234:21436–21449. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Iyengar NM, Zhou XK, Mendieta H, Giri DD,
El-Hely O, Winston L, Falcone DJ, Wang H, Meng L, Landa J, et al:
Effects of adiposity and exercise on breast tissue and systemic
metabo-inflammatory factors in women at high risk or diagnosed with
breast cancer. Cancer Prev Res (Phila). 14:541–550. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Nieman KM, Romero IL, Van Houten B and
Lengyel E: Adipose tissue and adipocytes support tumorigenesis and
metastasis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1831:1533–1541. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Zhao C, Wu M, Zeng N, Xiong M, Hu W, Lv W,
Yi Y, Zhang Q and Wu Y: Cancer-associated adipocytes: Emerging
supporters in breast cancer. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 39:1562020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Uehara H, Kobayashi T, Matsumoto M,
Watanabe S, Yoneda A and Bando Y: Adipose tissue: Critical
contributor to the development of prostate cancer. J Med Invest.
65:9–17. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Picon-Ruiz M, Marchal JA and Slingerland
JM: Obtaining human breast adipose cells for breast cancer cell
co-culture studies. STAR Protoc. 1:1001972020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Wu Q, Li B, Li Z, Li J and Sun S and Sun
S: Cancer-associated adipocytes: Key players in breast cancer
progression. J Hematol Oncol. 12:952019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Dirat B, Bochet L, Dabek M, Daviaud D,
Dauvillier S, Majed B, Wang YY, Meulle A, Salles B, Le Gonidec S,
et al: Cancer-associated adipocytes exhibit an activated phenotype
and contribute to breast cancer invasion. Cancer Res. 71:2455–2465.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Kokabu S, Lowery JW and Jimi E: Cell fate
and differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. Stem
Cells Int. 2016:37535812016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Ridge SM, Sullivan FJ and Glynn SA:
Mesenchymal stem cells: Key players in cancer progression. Mol
Cancer. 16:312017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Han Y, Li X, Zhang Y, Han Y, Chang F and
Ding J: Mesenchymal stem cells for regenerative medicine. Cells.
8:8862019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Chen Q, Shou P, Zheng C, Jiang M, Cao G,
Yang Q, Cao J, Xie N, Velletri T, Zhang X, et al: Fate decision of
mesenchymal stem cells: Adipocytes or osteoblasts? Cell Death
Differ. 23:1128–1139. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Shepherd PR, Gnudi L, Tozzo E, Yang H,
Leach F and Kahn BB: Adipose cell hyperplasia and enhanced glucose
disposal in transgenic mice overexpressing GLUT4 selectively in
adipose tissue. J Biol Chem. 268:22243–22246. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Huang HY, Hu LL, Song TJ, Li X, He Q, Sun
X, Li YM, Lu HJ, Yang PY and Tang QQ: Involvement of
cytoskeleton-associated proteins in the commitment of C3H10T1/2
pluripotent stem cells to adipocyte lineage induced by BMP2/4. Mol
Cell Proteomics. 10:M110.002691. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
de Winter TJ and Nusse R: Running against
the Wnt: How Wnt/β-catenin suppresses adipogenesis. Front Cell Dev
Biol. 9:6274292021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Huang H, Song TJ, Li X, Hu L, He Q, Liu M,
Lane MD and Tang QQ: BMP signaling pathway is required for
commitment of C3H10T1/2 pluripotent stem cells to the adipocyte
lineage. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 106:12670–12675. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Tang QQ and Lane MD: Adipogenesis: From
stem cell to adipocyte. Annu Rev Biochem. 81:715–736. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Farmer SR: Transcriptional control of
adipocyte formation. Cell Metab. 4:263–273. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Nielsen R, Pedersen TA, Hagenbeek D,
Moulos P, Siersbaek R, Megens E, Denissov S, Børgesen M, Francoijs
KJ, Mandrup S and Stunnenberg HG: Genome-wide profiling of
PPARgamma:RXR and RNA polymerase II occupancy reveals temporal
activation of distinct metabolic pathways and changes in RXR dimer
composition during adipogenesis. Genes Dev. 22:2953–2967. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Lefterova MI, Zhang Y, Steger DJ, Schupp
M, Schug J, Cristancho A, Feng D, Zhuo D, Stoeckert CJ Jr, Liu XS
and Lazar MA: PPARgamma and C/EBP factors orchestrate adipocyte
biology via adjacent binding on a genome-wide scale. Genes Dev.
22:2941–2952. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Rosen ED, Walkey CJ, Puigserver P and
Spiegelman BM: Transcriptional regulation of adipogenesis. Genes
Dev. 14:1293–1307. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Kaestner KH, Christy RJ, McLenithan JC,
Braiterman LT, Cornelius P, Pekala PH and Lane MD: Sequence, tissue
distribution, and differential expression of mRNA for a putative
insulin-responsive glucose transporter in mouse 3T3-L1 adipocytes.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 86:3150–3154. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Hwang CS, Mandrup S, MacDougald OA, Geiman
DE and Lane MD: Transcriptional activation of the mouse obese (ob)
gene by CCAAT/enhancer binding protein alpha. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 93:873–877. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Hwang CS, Loftus TM, Mandrup S and Lane
MD: Adipocyte differentiation and leptin expression. Annu Rev Cell
Dev Biol. 13:231–259. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Soukas A, Socci ND, Saatkamp BD, Novelli S
and Friedman JM: Distinct transcriptional profiles of adipogenesis
in vivo and in vitro. J Biol Chem. 276:34167–34174. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Kim KH, Lee K, Moon YS and Sul HS: A
cysteine-rich adipose tissue-specific secretory factor inhibits
adipocyte differentiation. J Biol Chem. 276:11252–11256. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Chang E and Kim CY: Natural products and
obesity: A focus on the regulation of mitotic clonal expansion
during adipogenesis. Molecules. 24:11572019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Park A, Kim WK and Bae KH: Distinction of
white, beige and brown adipocytes derived from mesenchymal stem
cells. World J Stem Cells. 6:33–42. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Lapeire L, Hendrix A, Lambein K, Van
Bockstal M, Braems G, Van Den Broecke R, Limame R, Mestdagh P,
Vandesompele J, Vanhove C, et al: Cancer-associated adipose tissue
promotes breast cancer progression by paracrine oncostatin M and
Jak/STAT3 signaling. Cancer Res. 74:6806–6819. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Nieman KM, Kenny HA, Penicka CV, Ladanyi
A, Buell-Gutbrod R, Zillhardt MR, Romero IL, Carey MS, Mills GB,
Hotamisligil GS, et al: Adipocytes promote ovarian cancer
metastasis and provide energy for rapid tumor growth. Nat Med.
17:1498–1503. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Wu Q, Li J, Li Z, Sun S, Zhu S, Wang L, Wu
J, Yuan J, Zhang Y, Sun S and Wang C: Exosomes from the
tumour-adipocyte interplay stimulate beige/brown differentiation
and reprogram metabolism in stromal adipocytes to promote tumour
progression. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 38:2232019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Balaban S, Shearer RF, Lee LS, van
Geldermalsen M, Schreuder M, Shtein HC, Cairns R, Thomas KC,
Fazakerley DJ, Grewal T, et al: Adipocyte lipolysis links obesity
to breast cancer growth: Adipocyte-derived fatty acids drive breast
cancer cell proliferation and migration. Cancer Metab. 5:12017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Notarnicola M, Miccolis A, Tutino V,
Lorusso D and Caruso MG: Low levels of lipogenic enzymes in
peritumoral adipose tissue of colorectal cancer patients. Lipids.
47:59–63. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Choi J, Cha YJ and Koo JS: Adipocyte
biology in breast cancer: From silent bystander to active
facilitator. Prog Lipid Res. 69:11–20. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Fujisaki K, Fujimoto H, Sangai T,
Nagashima T, Sakakibara M, Shiina N, Kuroda M, Aoyagi Y and
Miyazaki M: Cancer-mediated adipose reversion promotes cancer cell
migration via IL-6 and MCP-1. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 150:255–263.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
D'Esposito V, Liguoro D, Ambrosio MR,
Collina F, Cantile M, Spinelli R, Raciti GA, Miele C, Valentino R,
Campiglia P, et al: Adipose microenvironment promotes triple
negative breast cancer cell invasiveness and dissemination by
producing CCL5. Oncotarget. 7:24495–24509. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Kim EJ, Kim YK, Kim S, Kim JE, Tian YD,
Doh EJ, Lee DH and Chung JH: Adipochemokines induced by ultraviolet
irradiation contribute to impaired fat metabolism in subcutaneous
fat cells. Br J Dermatol. 178:492–501. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Liu L, Wu Y, Zhang C, Zhou C, Li Y, Zeng
Y, Zhang C, Li R, Luo D, Wang L, et al: Cancer-associated
adipocytes-derived G-CSF promotes breast cancer malignancy via
Stat3 signaling. J Mol Cell Biol. 12:723–737. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Andarawewa KL, Motrescu ER, Chenard MP,
Gansmuller A, Stoll I, Tomasetto C and Rio MC: Stromelysin-3 is a
potent negative regulator of adipogenesis participating to cancer
cell-adipocyte interaction/crosstalk at the tumor invasive front.
Cancer Res. 65:10862–10871. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Iyengar P, Espina V, Williams TW, Lin Y,
Berry D, Jelicks LA, Lee H, Temple K, Graves R, Pollard J, et al:
Adipocyte-derived collagen VI affects early mammary tumor
progression in vivo, demonstrating a critical interaction in the
tumor/stroma microenvironment. J Clin Invest. 115:1163–1176. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Bochet L, Lehuédé C, Dauvillier S, Wang
YY, Dirat B, Laurent V, Dray C, Guiet R, Maridonneau-Parini I, Le
Gonidec S, et al: Adipocyte-derived fibroblasts promote tumor
progression and contribute to the desmoplastic reaction in breast
cancer. Cancer Res. 73:5657–5668. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Côté JA, Guénard F, Lessard J, Lapointe M,
Biron S, Vohl MC and Tchernof A: Temporal changes in gene
expression profile during mature adipocyte dedifferentiation. Int J
Genomics. 2017:51493622017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Wei X, Li S, He J, Du H, Liu Y, Yu W, Hu
H, Han L, Wang C, Li H, et al: Tumor-secreted PAI-1 promotes breast
cancer metastasis via the induction of adipocyte-derived collagen
remodeling. Cell Commun Signal. 17:582019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Master SR, Hartman JL, D'Cruz CM, Moody
SE, Keiper EA, Ha SI, Cox JD, Belka GK and Chodosh LA: Functional
microarray analysis of mammary organogenesis reveals a
developmental role in adaptive thermogenesis. Mol Endocrinol.
16:1185–1203. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Wang F, Gao S, Chen F, Fu Z, Yin H, Lu X,
Yu J and Lu C: Mammary fat of breast cancer: Gene expression
profiling and functional characterization. PLoS One. 9:e1097422014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Tsoli M, Schweiger M, Vanniasinghe AS,
Painter A, Zechner R, Clarke S and Robertson G: Depletion of white
adipose tissue in cancer cachexia syndrome is associated with
inflammatory signaling and disrupted circadian regulation. PLoS
One. 9:e929662014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Wu Q, Sun S, Li Z, Yang Q, Li B, Zhu S,
Wang L, Wu J, Yuan J, Yang C, et al: Tumour-originated exosomal
miR-155 triggers cancer-associated cachexia to promote tumour
progression. Mol Cancer. 17:1552018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Guerrero J, Tobar N, Cáceres M, Espinoza
L, Escobar P, Dotor J, Smith PC and Martinez J: Soluble factors
derived from tumor mammary cell lines induce a stromal mammary
adipose reversion in human and mice adipose cells. Possible role of
TGF-beta1 and TNF-alpha. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 119:497–508.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Stephens JM and Pekala PH: Transcriptional
repression of the C/EBP-alpha and GLUT4 genes in 3T3-L1 adipocytes
by tumor necrosis factor-alpha. Regulations is coordinate and
independent of protein synthesis. J Biol Chem. 267:13580–13584.
1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Kim C, Lee H, Cho YM, Kwon OJ, Kim W and
Lee EK: TNFalpha-induced miR-130 resulted in adipocyte dysfunction
during obesity-related inflammation. FEBS Lett. 587:3853–3858.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Lien CC, Au LC, Tsai YL, Ho LT and Juan
CC: Short-term regulation of tumor necrosis factor-alpha-induced
lipolysis in 3T3-L1 adipocytes is mediated through the inducible
nitric oxide synthase/nitric oxide-dependent pathway.
Endocrinology. 150:4892–4900. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Ryden M, Dicker A, van Harmelen V, Hauner
H, Brunnberg M, Perbeck L, Lonnqvist F and Arner P: Mapping of
early signaling events in tumor necrosis factor-alpha -mediated
lipolysis in human fat cells. J Biol Chem. 277:1085–1091. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Zhang HH, Halbleib M, Ahmad F, Manganiello
VC and Greenberg AS: Tumor necrosis factor-alpha stimulates
lipolysis in differentiated human adipocytes through activation of
extracellular signal-related kinase and elevation of intracellular
cAMP. Diabetes. 51:2929–2935. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Rydén M, Arvidsson E, Blomqvist L, Perbeck
L, Dicker A and Arner P: Targets for TNF-alpha-induced lipolysis in
human adipocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 318:168–175. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Souza SC, de Vargas LM, Yamamoto MT, Lien
P, Franciosa MD, Moss LG and Greenberg AS: Overexpression of
perilipin A and B blocks the ability of tumor necrosis factor alpha
to increase lipolysis in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. J Biol Chem.
273:24665–24669. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Tsoli M and Robertson G: Cancer cachexia:
Malignant inflammation, tumorkines, and metabolic mayhem. Trends
Endocrinol Metab. 24:174–183. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Arner P and Langin D: Lipolysis in lipid
turnover, cancer cachexia, and obesity-induced insulin resistance.
Trends Endocrinol Metab. 25:255–262. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Petersen EW, Carey AL, Sacchetti M,
Steinberg GR, Macaulay SL, Febbraio MA and Pedersen BK: Acute IL-6
treatment increases fatty acid turnover in elderly humans in vivo
and in tissue culture in vitro. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab.
288:E155–E162. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Ahmadian M, Abbott MJ, Tang T, Hudak CS,
Kim Y, Bruss M, Hellerstein MK, Lee HY, Samuel VT, Shulman GI, et
al: Desnutrin/ATGL is regulated by AMPK and is required for a brown
adipose phenotype. Cell Metab. 13:739–748. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Wang YY, Attané C, Milhas D, Dirat B,
Dauvillier S, Guerard A, Gilhodes J, Lazar I, Alet N, Laurent V, et
al: Mammary adipocytes stimulate breast cancer invasion through
metabolic remodeling of tumor cells. JCI Insight. 2:e874892017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Ueki K, Kondo T and Kahn CR: Suppressor of
cytokine signaling 1 (SOCS-1) and SOCS-3 cause insulin resistance
through inhibition of tyrosine phosphorylation of insulin receptor
substrate proteins by discrete mechanisms. Mol Cell Biol.
24:5434–5446. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Seale P, Conroe HM, Estall J, Kajimura S,
Frontini A, Ishibashi J, Cohen P, Cinti S and Spiegelman BM: Prdm16
determines the thermogenic program of subcutaneous white adipose
tissue in mice. J Clin Invest. 121:96–105. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Cannon B and Nedergaard J: Brown adipose
tissue: Function and physiological significance. Physiol Rev.
84:277–359. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Lee J, Hong BS, Ryu HS, Lee HB, Lee M,
Park IA, Kim J, Han W, Noh DY and Moon HG: Transition into
inflammatory cancer-associated adipocytes in breast cancer
microenvironment requires microRNA regulatory mechanism. PLoS One.
12:e01741262017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Arora GK, Gupta A, Narayanan S, Guo T,
Iyengar P and Infante RE: Cachexia-associated adipose loss induced
by tumor-secreted leukemia inhibitory factor is counterbalanced by
decreased leptin. JCI Insight. 3:e1212212018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Zoico E, Darra E, Rizzatti V, Budui S,
Franceschetti G, Mazzali G, Rossi AP, Fantin F, Menegazzi M, et al:
Adipocytes WNT5a mediated dedifferentiation: a possible target in
pancreatic cancer microenvironment. Oncotarget. 7:20223–20235.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Kang MI, Baker AR, Dextras CR, Cabarcas
SM, Young MR and Colburn NH: (2012). Targeting of Noncanonical
Wnt5a Signaling by AP-1 Blocker Dominant-Negative Jun When It
Inhibits Skin Carcinogenesis. Genes cancer. 3:37–50. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Gustafson B and Smith U: Activation of
canonical wingless-type MMTV integration site family (Wnt)
signaling in mature adipocytes increases beta-catenin levels and
leads to cell dedifferentiation and insulin resistance. J Biol
Chem. 285:14031–14041. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Christodoulides C, Lagathu C, Sethi JK and
Vidal-Puig A: Adipogenesis and WNT signalling. Trends Endocrinol
Metab. 20:16–24. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Zoico E, Darra E, Rizzatti V, Budui S,
Franceschetti G, Mazzali G, Rossi AP, Fantin F, Menegazzi M, Cinti
S and Zamboni M: Adipocytes WNT5a mediated dedifferentiation: A
possible target in pancreatic cancer microenvironment. Oncotarget.
7:20223–20235. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Bilkovski R, Schulte DM, Oberhauser F,
Mauer J, Hampel B, Gutschow C, Krone W and Laudes M: Adipose tissue
macrophages inhibit adipogenesis of mesenchymal precursor cells via
wnt-5a in humans. Int J Obes (Lond). 35:1450–1454. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Klaus A and Birchmeier W: Wnt signalling
and its impact on development and cancer. Nat Rev Cancer.
8:387–398. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Bauer M, Bénard J, Gaasterland T, Willert
K and Cappellen D: WNT5A encodes two isoforms with distinct
functions in cancers. PLoS One. 8:e805262013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Zhuang Y, Li X, Zhan P, Pi G and Wen G:
MMP11 promotes the proliferation and progression of breast cancer
through stabilizing Smad2 protein. Oncol Rep. 45:162021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Rio MC: From a unique cell to metastasis
is a long way to go: Clues to stromelysin-3 participation.
Biochimie. 87:299–306. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Xu G, Zhang B, Ye J, Cao S, Shi J, Zhao Y,
Wang Y, Sang J, Yao Y, Guan W, et al: Exosomal miRNA-139 in
cancer-associated fibroblasts inhibits gastric cancer progression
by repressing MMP11 expression. Int J Biol Sci. 15:2320–2329. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Motrescu ER, Blaise S, Etique N, Messaddeq
N, Chenard MP, Stoll I, Tomasetto C and Rio MC: Matrix
metalloproteinase-11/stromelysin-3 exhibits collagenolytic function
against collagen VI under normal and malignant conditions.
Oncogene. 27:6347–6355. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Kozlova N, Jensen JK, Chi TF, Samoylenko A
and Kietzmann T: PAI-1 modulates cell migration in a LRP1-dependent
manner via β-catenin and ERK1/2. Thromb Haemost. 113:988–998. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Benesch MG, Ko YM, McMullen TP and
Brindley DN: Autotaxin in the crosshairs: Taking aim at cancer and
other inflammatory conditions. FEBS Lett. 588:2712–2727. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Brindley DN, Lin FT and Tigyi GJ: Role of
the autotaxin-lysophosphatidate axis in cancer resistance to
chemotherapy and radiotherapy. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1831:74–85.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Choi JW and Chun J: Lysophospholipids and
their receptors in the central nervous system. Biochim Biophys
Acta. 1831:20–32. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Samadi N, Bekele R, Capatos D, Venkatraman
G, Sariahmetoglu M and Brindley DN: Regulation of lysophosphatidate
signaling by autotaxin and lipid phosphate phosphatases with
respect to tumor progression, angiogenesis, metastasis and
chemo-resistance. Biochimie. 93:61–70. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
So J, Wang FQ, Navari J, Schreher J and
Fishman DA: LPA-induced epithelial ovarian cancer (EOC) in vitro
invasion and migration are mediated by VEGF receptor-2 (VEGF-R2).
Gynecol Oncol. 97:870–878. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Murph MM, Hurst-Kennedy J, Newton V,
Brindley DN and Radhakrishna H: Lysophosphatidic acid decreases the
nuclear localization and cellular abundance of the p53 tumor
suppressor in A549 lung carcinoma cells. Mol Cancer Res.
5:1201–1211. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Popnikolov NK, Dalwadi BH, Thomas JD,
Johannes GJ and Imagawa WT: Association of autotaxin and
lysophosphatidic acid receptor 3 with aggressiveness of human
breast carcinoma. Tumour Biol. 33:2237–2243. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Brindley DN, Tang X, Meng G and Benesch
MGK: Role of adipose tissue-derived autotaxin, lysophosphatidate
signaling, and inflammation in the progression and treatment of
breast cancer. Int J Mol Sci. 21:59382020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Benesch MG, Tang X, Maeda T, Ohhata A,
Zhao YY, Kok BP, Dewald J, Hitt M, Curtis JM, McMullen TP and
Brindley DN: Inhibition of autotaxin delays breast tumor growth and
lung metastasis in mice. FASEB J. 28:2655–2666. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Benesch MG, Zhao YY, Curtis JM, McMullen
TP and Brindley DN: Regulation of autotaxin expression and
secretion by lysophosphatidate and sphingosine 1-phosphate. J Lipid
Res. 56:1134–1144. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Benesch MG, Tang X, Dewald J, Dong WF,
Mackey JR, Hemmings DG, McMullen TP and Brindley DN: Tumor-induced
inflammation in mammary adipose tissue stimulates a vicious cycle
of autotaxin expression and breast cancer progression. FASEB J.
29:3990–4000. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Russell ST, Zimmerman TP, Domin BA and
Tisdale MJ: Induction of lipolysis in vitro and loss of body fat in
vivo by zinc-alpha2-glycoprotein. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1636:59–68.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Bing C, Bao Y, Jenkins J, Sanders P,
Manieri M, Cinti S, Tisdale MJ and Trayhurn P:
Zinc-alpha2-glycoprotein, a lipid mobilizing factor, is expressed
in adipocytes and is up-regulated in mice with cancer cachexia.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 101:2500–2505. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
96
|
Delort L, Perrier S, Dubois V, Billard H,
Mracek T, Bing C, Vasson MP and Caldefie-Chézet F:
Zinc-α2-glycoprotein: A proliferative factor for breast cancer?
In vitro study and molecular mechanisms. Oncol Rep.
29:2025–2029. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Zhu H, Liu M, Zhang N, Pan H, Lin G, Li N,
Wang L, Yang H, Yan K and Gong F: Circulating and adipose tissue
mRNA levels of Zinc-α2-glycoprotein, leptin, high-molecular-weight
adiponectin, and tumor necrosis factor-alpha in colorectal cancer
patients with or without obesity. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne).
9:1902018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98
|
Henshall SM, Horvath LG, Quinn DI,
Eggleton SA, Grygiel JJ, Stricker PD, Biankin AV, Kench JG and
Sutherland RL: Zinc-alpha2-glycoprotein expression as a predictor
of metastatic prostate cancer following radical prostatectomy. J
Natl Cancer Inst. 98:1420–1424. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
99
|
Elattar S, Dimri M and Satyanarayana A:
The tumor secretory factor ZAG promotes white adipose tissue
browning and energy wasting. FASEB J. 32:4727–4743. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
100
|
Gong FY, Zhang SJ, Deng JY, Zhu HJ, Pan H,
Li NS and Shi YF: Zinc-alpha2-glycoprotein is involved in
regulation of body weight through inhibition of lipogenic enzymes
in adipose tissue. Int J Obes (Lond). 33:1023–1030. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
101
|
Xiao XH, Qi XY, Wang YD, Ran L, Yang J,
Zhang HL, Xu CX, Wen GB and Liu JH: Zinc alpha2 glycoprotein
promotes browning in adipocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
496:287–293. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
102
|
Vlassov AV, Magdaleno S, Setterquist R and
Conrad R: Exosomes: Current knowledge of their composition,
biological functions, and diagnostic and therapeutic potentials.
Biochim Biophys Acta. 1820:940–948. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
103
|
Minciacchi VR, Freeman MR and Di Vizio D:
Extracellular vesicles in cancer: Exosomes, microvesicles and the
emerging role of large oncosomes. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 40:41–51.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
104
|
Wang H, Liu L, Lin JZ, Aprahamian TR and
Farmer SR: Browning of white adipose tissue with roscovitine
induces a distinct population of UCP1(+) adipocytes. Cell Metab.
24:835–847. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
105
|
Tomasetti M, Nocchi L, Staffolani S,
Manzella N, Amati M, Goodwin J, Kluckova K, Nguyen M, Strafella E,
Bajzikova M, et al: MicroRNA-126 suppresses mesothelioma malignancy
by targeting IRS1 and interfering with the mitochondrial function.
Antioxid Redox Signal. 21:2109–2125. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
106
|
Fong MY, Zhou W, Liu L, Alontaga AY,
Chandra M, Ashby J, Chow A, O'Connor ST, Li S, Chin AR, et al:
Breast-cancer-secreted miR-122 reprograms glucose metabolism in
premetastatic niche to promote metastasis. Nat Cell Biol.
17:183–194. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
107
|
Yan W, Wu X, Zhou W, Fong MY, Cao M, Liu
J, Liu X, Chen CH, Fadare O, Pizzo DP, et al: Cancer-cell-secreted
exosomal miR-105 promotes tumour growth through the MYC-dependent
metabolic reprogramming of stromal cells. Nat Cell Biol.
20:597–609. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
108
|
Wang S, Xu M, Li X, Su X, Xiao X, Keating
A and Zhao RC: Exosomes released by hepatocarcinoma cells endow
adipocytes with tumor-promoting properties. J Hematol Oncol.
11:822018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
109
|
Sagar G, Sah RP, Javeed N, Dutta SK, Smyrk
TC, Lau JS, Giorgadze N, Tchkonia T, Kirkland JL, Chari ST and
Mukhopadhyay D: Pathogenesis of pancreatic cancer exosome-induced
lipolysis in adipose tissue. Gut. 65:1165–1174. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
110
|
Kong F, Li L, Du Y, Zhu H, Li Z and Kong
X: Exosomal adrenomedullin derived from cancer-associated
fibroblasts promotes lipolysis in adipose tissue. Gut.
67:2226–2227. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
111
|
Hu W, Ru Z, Zhou Y, Xiao W, Sun R, Zhang
S, Gao Y, Li X, Zhang X and Yang H: Lung cancer-derived
extracellular vesicles induced myotube atrophy and adipocyte
lipolysis via the extracellular IL-6-mediated STAT3 pathway.
Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Biol Lipids. 1864:1091–1102. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
112
|
Zhang H, Zhu L, Bai M, Liu Y, Zhan Y, Deng
T, Yang H, Sun W, Wang X, Zhu K, et al: Exosomal circRNA derived
from gastric tumor promotes white adipose browning by targeting the
miR-133/PRDM16 pathway. Int J Cancer. 144:2501–2515. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
113
|
Bhome R, Goh RW, Bullock MD, Pillar N,
Thirdborough SM, Mellone M, Mirnezami R, Galea D, Veselkov K, Gu Q,
et al: Exosomal microRNAs derived from colorectal cancer-associated
fibroblasts: Role in driving cancer progression. Aging (Albany NY).
9:2666–2694. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
114
|
Au Yeung CL, Co NN, Tsuruga T, Yeung TL,
Kwan SY, Leung CS, Li Y, Lu ES, Kwan K, Wong KK, et al: Exosomal
transfer of stroma-derived miR21 confers paclitaxel resistance in
ovarian cancer cells through targeting APAF1. Nat Commun.
7:111502016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
115
|
Zheng Z, Liu L, Zhan Y, Yu S and Kang T:
Adipose-derived stem cell-derived microvesicle-released miR-210
promoted proliferation, migration and invasion of endothelial cells
by regulating RUNX3. Cell Cycle. 17:1026–1033. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
116
|
Lazar I, Clement E, Dauvillier S, Milhas
D, Ducoux-Petit M, LeGonidec S, Moro C, Soldan V, Dalle S, Balor S,
et al: Adipocyte exosomes promote melanoma aggressiveness through
fatty acid oxidation: A novel mechanism linking obesity and cancer.
Cancer Res. 76:4051–4057. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
117
|
Wang J, Wu Y, Guo J, Fei X, Yu L and Ma S:
Adipocyte-derived exosomes promote lung cancer metastasis by
increasing MMP9 activity via transferring MMP3 to lung cancer
cells. Oncotarget. 8:81880–81891. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
118
|
Zaidi N, Lupien L, Kuemmerle NB, Kinlaw
WB, Swinnen JV and Smans K: Lipogenesis and lipolysis: The pathways
exploited by the cancer cells to acquire fatty acids. Prog Lipid
Res. 52:585–589. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
119
|
Kedia-Mehta N and Finlay DK: Competition
for nutrients and its role in controlling immune responses. Nat
Commun. 10:21232019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
120
|
Gonzalez-Perez RR, Xu Y, Guo S, Watters A,
Zhou W and Leibovich SJ: Leptin upregulates VEGF in breast cancer
via canonic and non-canonical signalling pathways and
NFkappaB/HIF-1alpha activation. Cell Signal. 22:1350–1362. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
121
|
Liu S, Lee JS, Jie C, Park MH, Iwakura Y,
Patel Y, Soni M, Reisman D and Chen H: HER2 overexpression triggers
an IL1α proinflammatory circuit to drive tumorigenesis and promote
chemotherapy resistance. Cancer Res. 78:2040–2051. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
122
|
Zhao J, Liu J, Wu N, Zhang H, Zhang S, Li
L and Wang M: ANGPTL4 overexpression is associated with progression
and poor prognosis in breast cancer. Oncol Lett. 20:2499–2505.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
123
|
Meng L, Zhou J, Sasano H, Suzuki T,
Zeitoun KM and Bulun SE: Tumor necrosis factor alpha and
interleukin 11 secreted by malignant breast epithelial cells
inhibit adipocyte differentiation by selectively down-regulating
CCAAT/enhancer binding protein alpha and peroxisome
proliferator-activated receptor gamma: Mechanism of desmoplastic
reaction. Cancer Res. 61:2250–2255. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
124
|
Gray NE, Lam LN, Yang K, Zhou AY, Koliwad
S and Wang JC: Angiopoietin-like 4 (Angptl4) protein is a
physiological mediator of intracellular lipolysis in murine
adipocytes. J Biol Chem. 287:8444–8456. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
125
|
Kogo R, Shimamura T, Mimori K, Kawahara K,
Imoto S, Sudo T, Tanaka F, Shibata K, Suzuki A, Komune S, et al:
Long noncoding RNA HOTAIR regulates polycomb-dependent chromatin
modification and is associated with poor prognosis in colorectal
cancers. Cancer Res. 71:6320–6326. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
126
|
Gupta RA, Shah N, Wang KC, Kim J, Horlings
HM, Wong DJ, Tsai MC, Hung T, Argani P, Rinn JL, et al: Long
non-coding RNA HOTAIR reprograms chromatin state to promote cancer
metastasis. Nature. 464:1071–1076. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
127
|
Ma X, Li Z, Li T, Zhu L, Li Z and Tian N:
Long non-coding RNA HOTAIR enhances angiogenesis by induction of
VEGFA expression in glioma cells and transmission to endothelial
cells via glioma cell derived-extracellular vesicles. Am J Transl
Res. 9:5012–5021. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
128
|
Sanchez-Alvarez R, Martinez-Outschoorn UE,
Lamb R, Hulit J, Howell A, Gandara R, Sartini M, Rubin E, Lisanti
MP and Sotgia F: Mitochondrial dysfunction in breast cancer cells
prevents tumor growth: Understanding chemoprevention with
metformin. Cell Cycle. 12:172–182. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
129
|
Munteanu R, Onaciu A, Moldovan C, Zimta
AA, Gulei D, Paradiso AV, Lazar V and Berindan-Neagoe I:
Adipocyte-based cell therapy in oncology: The role of
cancer-associated adipocytes and their reinterpretation as delivery
platforms. Pharmaceutics. 12:4022020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|