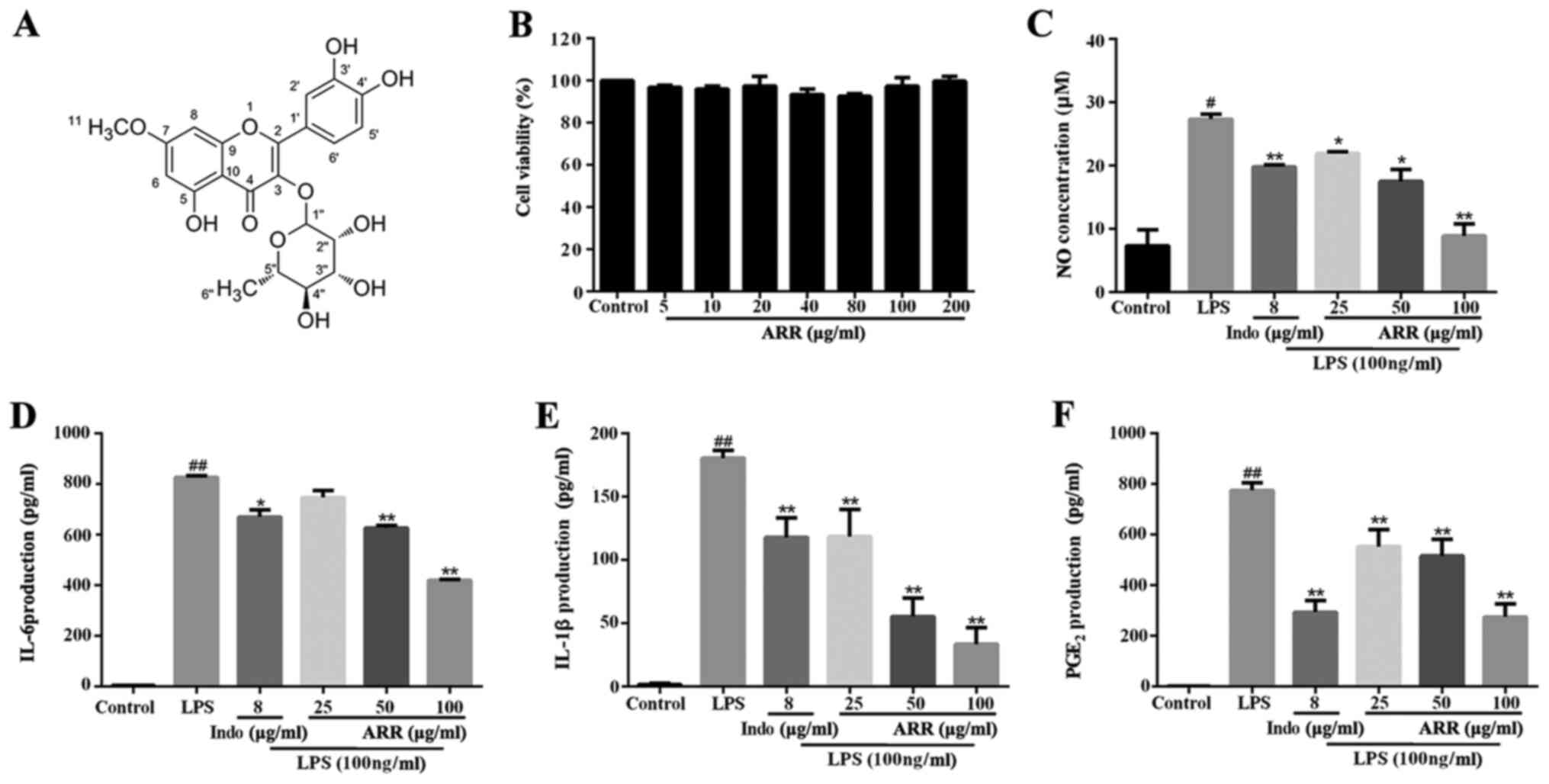
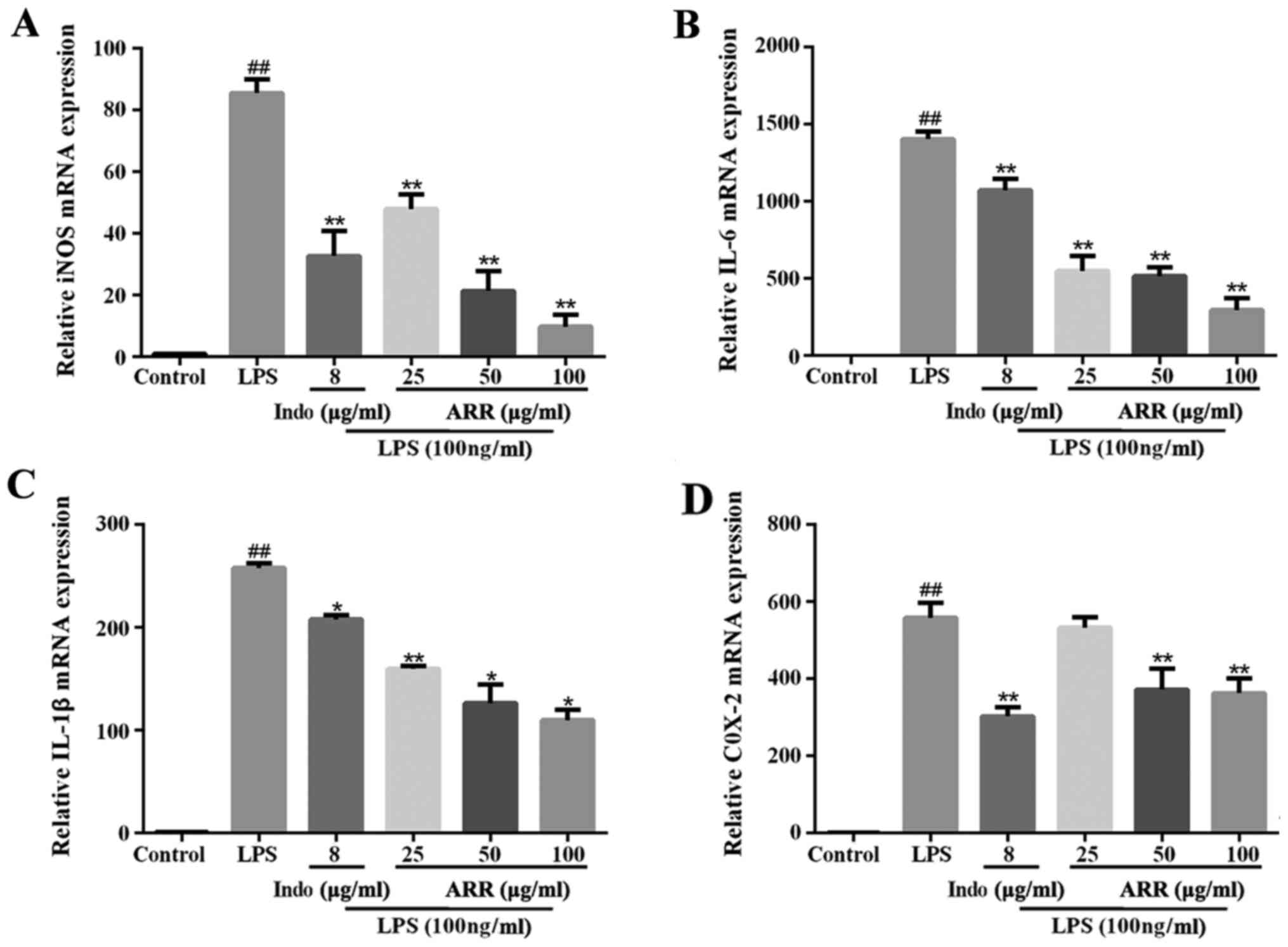
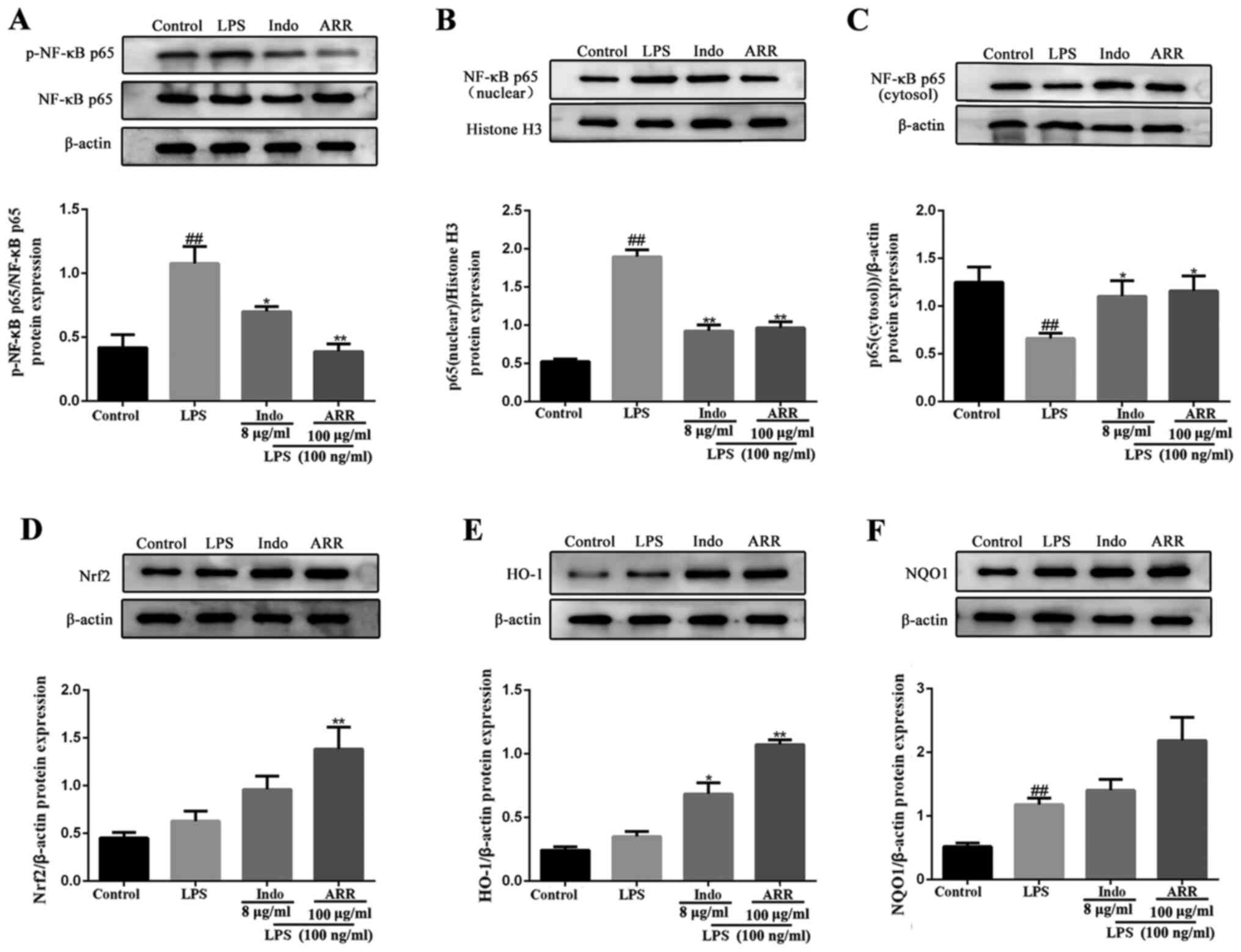
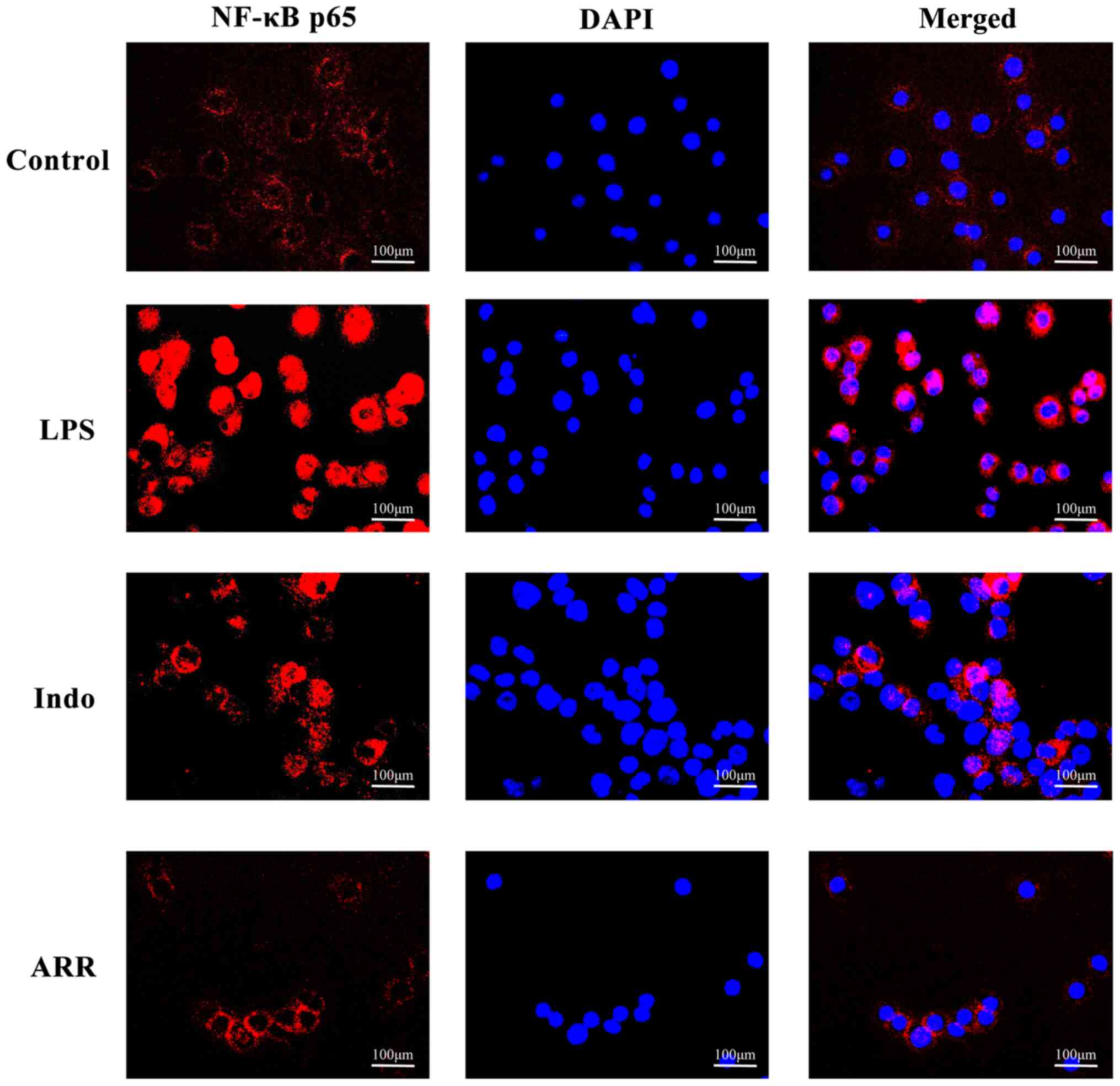
|
1
|
Yang SH, Le B, Androutsopoulos VP,
Tsukamoto C, Shin TS, Tsatsakis AM and Chung G: Anti-inflammatory
effects of soyasapogenol I-αa via downregulation of the MAPK
signaling pathway in LPS-induced RAW 264.7 macrophages. Food Chem
Toxicol. 113:211–217. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Venkatesan T, Park EJ, Choi YW, Lee J and
Kim YK: Anti-inflammatory activity of Ternstroemia gymnanthera stem
bark extracts in bacterial lipopolysaccharide-stimulated RAW264.7
murine macrophage cells. Pharm Biol. 55:837–846. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Venkatesan T, Choi YW, Lee J and Kim YK:
Falcarindiol inhibits LPS-induced inflammation via attenuating MAPK
and JAK-STAT signaling pathways in murine macrophage RAW 264.7
cells. Mol Cell Biochem. 445:169–178. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Vašíček O, Lojek A and Číž M: Serotonin
and its metabolites reduce oxidative stress in murine RAW264.7
macrophages and prevent inflammation. J Physiol Biochem. 76:49–60.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Park SM, Lee TH, Zhao R, Kim YS, Jung JY,
Park CA, Jegal KH, Ku SK, Kim JK, Lee CW, et al: Amelioration of
inflammatory responses by Socheongryong-Tang, a traditional herbal
medicine, in RAW 264.7 cells and rats. Int J Mol Med. 41:2771–2783.
2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Novilla A, Djamhuri DS, Nurhayati B,
Rihibiha DD, Afifah E and Widowati W: Anti-inflammatory properties
of oolong tea (Camellia sinensis) ethanol extract and
epigallocatechin gallate in LPS-induced RAW 264.7 cells. Asian
Pacific J Tropical Biomed. 7:1005–1009. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Liang N, Sang Y, Liu W, Yu W and Wang X:
Anti-inflammatory effects of gingerol on
lipopolysaccharide-stimulated RAW 264.7 cells by inhibiting NF-κB
signaling pathway. Inflammation. 41:835–845. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Shim SY, Sung SH and Lee M:
Anti-inflammatory activity of mulberrofuran K isolated from the
bark of Morus bombycis. Int Immunopharmacol. 58:117–124. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Alam MB, Ju MK, Kwon YG and Lee SH:
Protopine attenuates inflammation stimulated by carrageenan and LPS
via the MAPK/NF-κB pathway. Food Chem Toxicol. 131:1105832019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Olajide OA, Akande IS, Filho C,
Lepiarz-Raba I and de Sousa DP: Methyl 3,4,5-trimethoxycinnamate
suppresses inflammation in RAW264.7 macrophages and blocks
macrophage-adipocyte interaction. Inflammopharmacology.
28:1315–1326. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Gültekin Y, Eren E and Özören N:
Overexpressed NLRC3 acts as an anti-inflammatory cytosolic protein.
J Innate Immun. 7:25–36. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Schneider M, Zimmermann AG, Roberts RA,
Zhang L, Swanson KV, Wen H, Davis BK, Allen IC, Holl EK, Ye Z, et
al: The innate immune sensor NLRC3 attenuates toll-like receptor
signaling via modification of the signaling adaptor TRAF6 and
transcription factor NF-κB. Nat Immunol. 13:823–831. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zhang L, Mo J, Swanson KV, Wen H,
Petrucelli A, Gregory SM, Zhang Z, Schneider M, Jiang Y, Fitzgerald
KA, et al: NLRC3, a member of the NLR family of proteins, is a
negative regulator of innate immune signaling induced by the DNA
sensor STING. Immunity. 40:329–341. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Wu A, Yang Z, Huang Y, Yuan H, Lin C, Wang
T, Zhao Z, Zhou Y and Zhu C: Natural phenylethanoid glycosides
isolated from Callicarpa kwangtungensis suppressed
lipopolysaccharide-mediated inflammatory response via activating
Keap1/Nrf2/HO-1 pathway in RAW 264.7 macrophages cell. J
Ethnopharmacol. 258:1128572020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Younis NS and Mohamed ME: Protective
effects of myrrh essential oil on isoproterenol-induced myocardial
infarction in rats through antioxidant, anti-inflammatory,
Nrf2/HO-1 and apoptotic pathways. J Ethnopharmacol. 270:1137932021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Kobayashi EH, Suzuki T, Funayama R,
Nagashima T, Hayashi M, Sekine H, Tanaka N, Moriguchi T, Motohashi
H, Nakayama K and Yamamoto M: Nrf2 suppresses macrophage
inflammatory response by blocking proinflammatory cytokine
transcription. Nat Commun. 7:116242016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Kim HN, Kim JD, Park SB, Son HJ, Park GH,
Eo HJ, Kim HS and Jeong JB: Anti-inflammatory activity of the
extracts from Rodgersia podophylla leaves through activation of
Nrf2/HO-1 pathway, and inhibition of NF-κB and MAPKs pathway in
mouse macrophage cells. Inflamm Res. 69:233–244. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Qiu HX and Lin YR: Loranthaceae Juss.
Flora of China. Editorial Committee of Flora of China, Chinese
Academy of Sciences (eds), . 24. Science Press; Beijing: pp.
p1011988
|
|
19
|
Kim YK, Kim YS, Choi SU and Ryu SY:
Isolation of flavonol rhamnosides from Loranthus tanakae and
cytotoxic effect of them on human tumor cell lines. Arch Pharm Res.
27:44–47. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Chen Y, Lin Y, Li Y and Li C: Total
flavonoids of Hedyotis diffusa willd inhibit inflammatory responses
in LPS-activated macrophages via suppression of the NF-kappaB and
MAPK signaling pathways. Exp Ther Med. 11:1116–1122. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Feng H, He Y, La L, Hou C, Song L, Yang Q,
Wu F, Liu W, Hou L, Li Y, et al: The flavonoid-enriched extract
from the root of Smilax China L. inhibits inflammatory responses
via the TLR-4-mediated signaling pathway. J Ethnopharmacol.
256:1127852020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Cho BO, Che DN, Kim JS, Kim JH, Shin JY,
Kang HJ and Jang SI: In vitro anti-inflammatory and anti-oxidative
stress activities of kushenol C isolated from the roots of sophora
flavescens. Molecules. 25:17682020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Chiu YH, Wu YW, Hung JI and Chen MC:
Epigallocatechin gallate/L-ascorbic acid-loaded poly-γ-glutamate
microneedles with antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and
immunomodulatory effects for the treatment of atopic dermatitis.
Acta Biomater. 130:223–233. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Ningning X, Yune B, Qiangqiang X, Shouyuan
Z and Guane Y: Preliminary experiments on the chemical constituents
of the parasitic mulberry. Chinese Medicines and Clinics.
12:762–763. 2012.(In Chinese).
|
|
25
|
Zhou J, Wang T, Dou Y, Huang Y, Qu C, Gao
J, Huang Z, Xie Y, Huang P, Lin Z and Su Z: Brusatol ameliorates
2,4,6-trinitrobenzenesulfonic acid-induced experimental colitis in
rats: Involvement of NF-κB pathway and NLRP3 inflammasome. Int
Immunopharmacol. 64:264–274. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Liu S, Man Y and Zhao L: Sinomenine
inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory injury by
regulation of miR-101/MKP-1/JNK pathway in keratinocyte cells.
Biomed Pharmacother. 101:422–429. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Yuan S, Liu H, Yuan D, Xu J, Chen Y, Xu X,
Xu F and Liang H: PNPLA3 I148M mediates the regulatory effect of
NF-kB on inflammation in PA-treated HepG2 cells. J Cell Mol Med.
24:1541–1552. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Son ES, Park JW, Kim SH, Park HR, Han W,
Kwon OC, Nam JY, Jeong SH and Lee CS: Anti-inflammatory activity of
3,5,6,7,3′,4′-hexamethoxyflavone via repression of the NF-κB and
MAPK signaling pathways in LPS-stimulated RAW264.7 cells. Mol Med
Rep. 22:1985–1993. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Li LQ, Song AX, Yin JY, Siu KC, Wong WT
and Wu JY: Anti-inflammation activity of exopolysaccharides
produced by a medicinal fungus Cordyceps sinensis Cs-HK1 in cell
and animal models. Int J Biol Macromol. 149:1042–1050. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Lee M, Hong S, Park C, Han MH, Kim SO,
Hong SH, Kim GY and Choi YH: Anti-inflammatory effects of
Daehwangmokdantang, a traditional herbal formulation, in
lipopolysaccharide-stimulated RAW 264.7 macrophages. Exp Ther Med.
14:5809–5816. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Leal NRF, Vigliano MV, Pinto FA, de Sousa
TV, Velozo LSM, Sabino KC, da Graça Justo M and Coelho MG:
Anti-inflammatory effect of diterpenes-enriched fractions from
Pterodon polygalaeflorus through inhibition of macrophage migration
and cytokine production. J Pharm Pharmacol. 70:808–820. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Kim SJ, Ko WK, Jo MJ, Arai Y, Choi H,
Kumar H, Han IB and Sohn S: Anti-inflammatory effect of
Tauroursodeoxycholic acid in RAW 264.7 macrophages, Bone
marrow-derived macrophages, BV2 microglial cells, and spinal cord
injury. Sci Rep. 8:31762018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Kim YJ: Rhamnetin attenuates melanogenesis
by suppressing oxidative stress and pro-inflammatory mediators.
Biol Pharm Bull. 36:1341–1347. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Jnawali HN, Lee E, Jeong KW, Shin A, Heo
YS and Kim Y: Anti-inflammatory activity of rhamnetin and a model
of its binding to c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase 1 and p38 MAPK. J Nat
Prod. 77:258–263. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Mendis S, Lindholm LH, Anderson SG, Alwan
A, Koju R, Onwubere BJ, Kayani AM, Abeysinghe N, Duneas A, Tabagari
S, et al: Total cardiovascular risk approach to improve efficiency
of cardiovascular prevention in resource constrain settings. J Clin
Epidemiol. 64:1451–1462. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Kim KH, Kim EJ, Kwun MJ, Lee JY, Bach TT,
Eum SM, Choi JY, Cho S, Kim SJ, Jeong SI and Joo M: Suppression of
lung inflammation by the methanol extract of Spilanthes acmella
Murray is related to differential regulation of NF-κB and Nrf2. J
Ethnopharmacol. 217:89–97. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Wu H, Wang Y, Zhang Y, Xu F, Chen J, Duan
L, Zhang T, Wang J and Zhang F: Breaking the vicious loop between
inflammation, oxidative stress and coagulation, a novel
anti-thrombus insight of nattokinase by inhibiting LPS-induced
inflammation and oxidative stress. Redox Biol. 32:1015002020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Ying Y, Sun CB, Zhang SQ, Chen BJ, Yu JZ,
Liu FY, Wen J, Hou J, Han SS, Yan JY, et al: Induction of autophagy
via the TLR4/NF-κB signaling pathway by astragaloside contributes
to the amelioration of inflammation in RAW264.7 cells. Biomed
Pharmacother. 137:1112712021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Li M, Dong L, Du H, Bao Z and Lin S:
Potential mechanisms underlying the protective effects of
Tricholoma matsutake singer peptides against LPS-induced
inflammation in RAW264.7 macrophages. Food Chem. 353:1294522021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Guo C, Bi J, Li X, Lyu J, Liu X, Wu X and
Liu J: Immunomodulation effects of polyphenols from thinned peach
treated by different drying methods on RAW264.7 cells through the
NF-κB and Nrf2 pathways. Food Chem. 340:1279312021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Kim ME, Na JY and Lee JS:
Anti-inflammatory effects of trans-cinnamaldehyde on
lipopolysaccharide-stimulated macrophage activation via MAPKs
pathway regulation. Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol. 40:219–224.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Hwang SJ, Ahn EY, Park Y and Lee HJ: An
aqueous extract of Nomura's jellyfish ameliorates inflammatory
responses in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated RAW264.7 cells and a
zebrafish model of inflammation. Biomed Pharmacother. 100:583–589.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Khajuria V, Gupta S, Sharma N, Tiwari H,
Bhardwaj S, Dutt P, Satti N, Nargotra A, Bhagat A and Ahmed Z:
Kaempferol-3-o-β-d-glucuronate exhibit potential anti-inflammatory
effect in LPS stimulated RAW 264.7 cells and mice model. Int
Immunopharmacol. 57:62–71. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Su Y, Xiong S, Lan H, Xu L and Wei X:
Molecular mechanism underlying anti-inflammatory activities of
lirioresinol B dimethyl ether through suppression of NF-κB and MAPK
signaling in in vitro and in vivo models. Int Immunopharmacol.
73:321–332. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Hunto ST, Kim HG, Baek KS, Jeong D, Kim E,
Kim JH and Cho JY: Loratadine, an antihistamine drug, exhibits
anti-inflammatory activity through suppression of the NF-κB
pathway. Biochem Pharmacol. 177:1139492020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Ha DT, Long PT, Hien TT, Tuan DT, An NT,
Khoi NM, Oanh HV and Hung TM: Anti-inflammatory effect of
oligostilbenoids from Vitis heyneana in LPS-stimulated RAW 264.7
macrophages via suppressing the NF-κB activation. Chem Cent J.
12:142018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Tao MQ, Ji CL, Wu YJ, Dong JY, Li Y,
Olatunji OJ and Zuo J: 1,7-Dihydroxy-3,4-dimethoxyxanthone inhibits
lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation in RAW264.7 macrophages by
suppressing TLR4/NF-κB signaling cascades. Inflammation.
43:1821–1831. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Eleazu C, Suleiman JB, Othman ZA, Zakaria
Z, Nna VU, Hussain NH and Mohamed M: Bee bread attenuates high fat
diet induced renal pathology in obese rats via modulation of
oxidative stress, downregulation of NF-κB mediated inflammation and
Bax signalling. Arch Physiol Biochem. 2:1–17. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Huang YF, Zhou JT, Qu C, Dou YX, Huang QH,
Lin ZX, Xian YF, Xie JH, Xie YL, Lai XP and Su ZR:
Anti-inflammatory effects of Brucea javanica oil emulsion by
suppressing NF-kappaB activation on dextran sulfate sodium-induced
ulcerative colitis in mice. J Ethnopharmacol. 198:389–398. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Huang C, Li W, Zhang Q, Chen L, Chen W,
Zhang H and Ni Y: Anti-inflammatory activities of Guang-Pheretima
extract in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated RAW 264.7 murine
macrophages. BMC Complement Altern Med. 18:462018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Lee SG, Brownmiller CR, Lee SO and Kang
HW: Anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects of anthocyanins of
trifolium pratense (Red Clover) in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated
RAW-267.4 macrophages. Nutrients. 12:10892020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Karki S, Park HJ, Nugroho A, Kim EJ, Jung
HA and Choi JS: Quantification of major compounds fromIxeris
dentata, Ixeris dentata Var. albiflora, and Ixeris sonchifolia and
their comparative anti-inflammatoryactivity in
lipopolysaccharide-stimulated RAW 264.7 cells. J Med Food.
18:83–94. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Kim MS, Park JS, Chung YC, Jang S, Hyun CG
and Kim SY: Anti-inflammatory effects of formononetin
7-O-phosphate, a novel biorenovation product, on LPS-stimulated RAW
264.7 macrophage cells. Molecules. 24:39102019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Li ZT, Liu H and Zhang WQ: NLRC3
alleviates hypoxia/reoxygenation induced inflammation in RAW264.7
cells by inhibiting K63-linked ubiquitination of TRAF6.
Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int. 19:455–460. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Biliktu M, Senol SP, Temiz-Resitoglu M,
Guden DS, Horat MF, Sahan-Firat S, Sevim S and Tunctan B:
Pharmacological inhibition of soluble epoxide hydrolase attenuates
chronic experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis by modulating
inflammatory and anti-inflammatory pathways in an
inflammasome-dependent and -independent manner.
Inflammopharmacology. 28:1509–1524. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Cho YC, Park J and Cho S:
Anti-inflammatory and anti-oxidative effects of
luteolin-7-O-glucuronide in LPS-stimulated murine macrophages
through TAK1 inhibition and Nrf2 activation. Int J Mol Sci.
21:20072020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Kwon MY, Park J, Kim SM, Lee J, Cho H,
Park JH and Han IO: An alpha-lipoic acid-decursinol hybrid compound
attenuates lipopolysaccharide-mediated inflammation in BV2 and
RAW264.7 cells. BMB Rep. 52:508–513. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Li CL, Liu XH, Qiao Y, Ning LN, Li WJ, Sun
YS, Liu DS, Gao W and Ma CM: Allicin alleviates inflammation of
diabetic macroangiopathy via the Nrf2 and NF-κB pathway. Eur J
Pharmacol. 876:1730522020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Wardyn JD, Ponsford AH and Sanderson CM:
The Keap1/Nrf2 pathway in health and disease dissecting molecular
cross-talk between Nrf2 and NF-κB response pathways. Biochem Soc
Trans. 43:621–626. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Ren J, Su D, Li L, Cai H, Zhang M, Zhai J,
Li M, Wu X and Hu K: Anti-inflammatory effects of Aureusidin in
LPS-stimulated RAW264.7 macrophages via suppressing NF-κB and
activating ROS- and MAPKs-dependent Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathways.
Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 387:1148462019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Zheng Y, Tian C, Fan C, Xu N, Xiao J, Zhao
X, Lu Z, Cao H, Liu J and Yu L: Sheng-Mai Yin exerts
anti-inflammatory effects on RAW 264.7 cells and zebrafish. J
Ethnopharmacol. 267:1134972020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Park YJ, Cheon SY, Lee DS, Cominguez DC,
Zhang Z, Lee S and An HJ: Anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects
of carpesium cernuum L. Methanolic extract in LPS-stimulated RAW
264.7 macrophages. Mediators Inflammation. 2020:31642392020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Baek SH, Park T, Kang MG and Park D:
Anti-inflammatory activity and ROS regulation effect of
sinapaldehyde in LPS-stimulated RAW 264.7 macrophages. Molecules.
25:40892020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Kumar A, Sawhney G, Nagar RK, Chauhan N,
Gupta N, Kaul A, Ahmed Z, Sangwan PL, Kumar PS and Yadav G:
Evaluation of the immunomodulatory and anti-inflammatory activity
of Bakuchiol using RAW 264.7 macrophage cell lines and in animal
models stimulated by lipopolysaccharide (LPS). Int Immunopharmacol.
91:1072642021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Sewwandi S, Dissanayake CY, Natraj P, Lee
YJ and Han CH: Anti-inflammatory effect of sulforaphane on
LPS-stimulated RAW 264.7 cells and ob/ob mice. J Vet Sci.
21:e912020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|