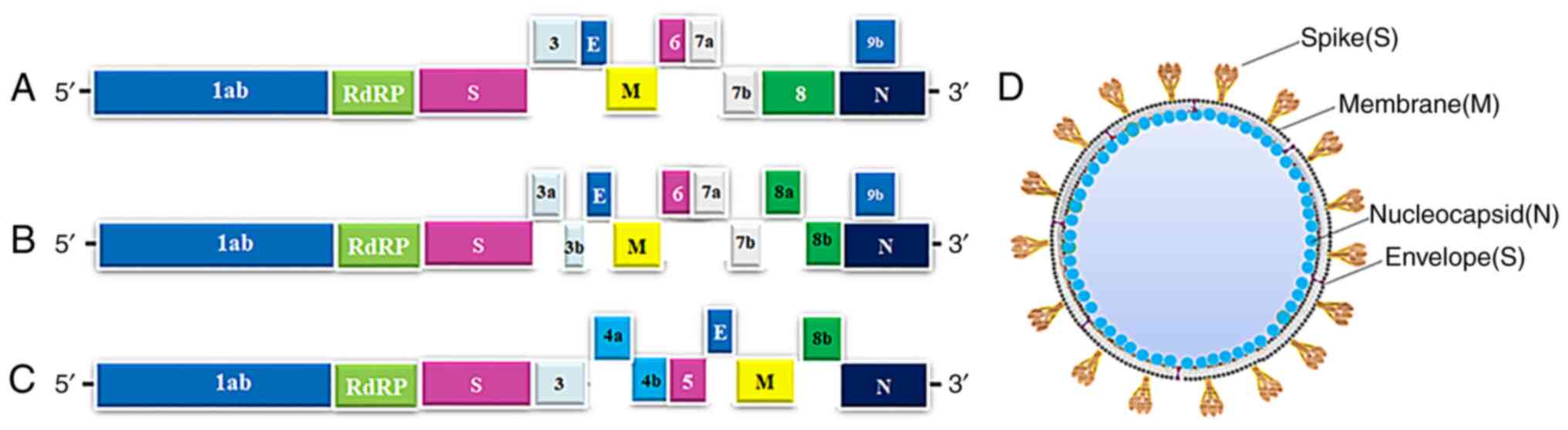
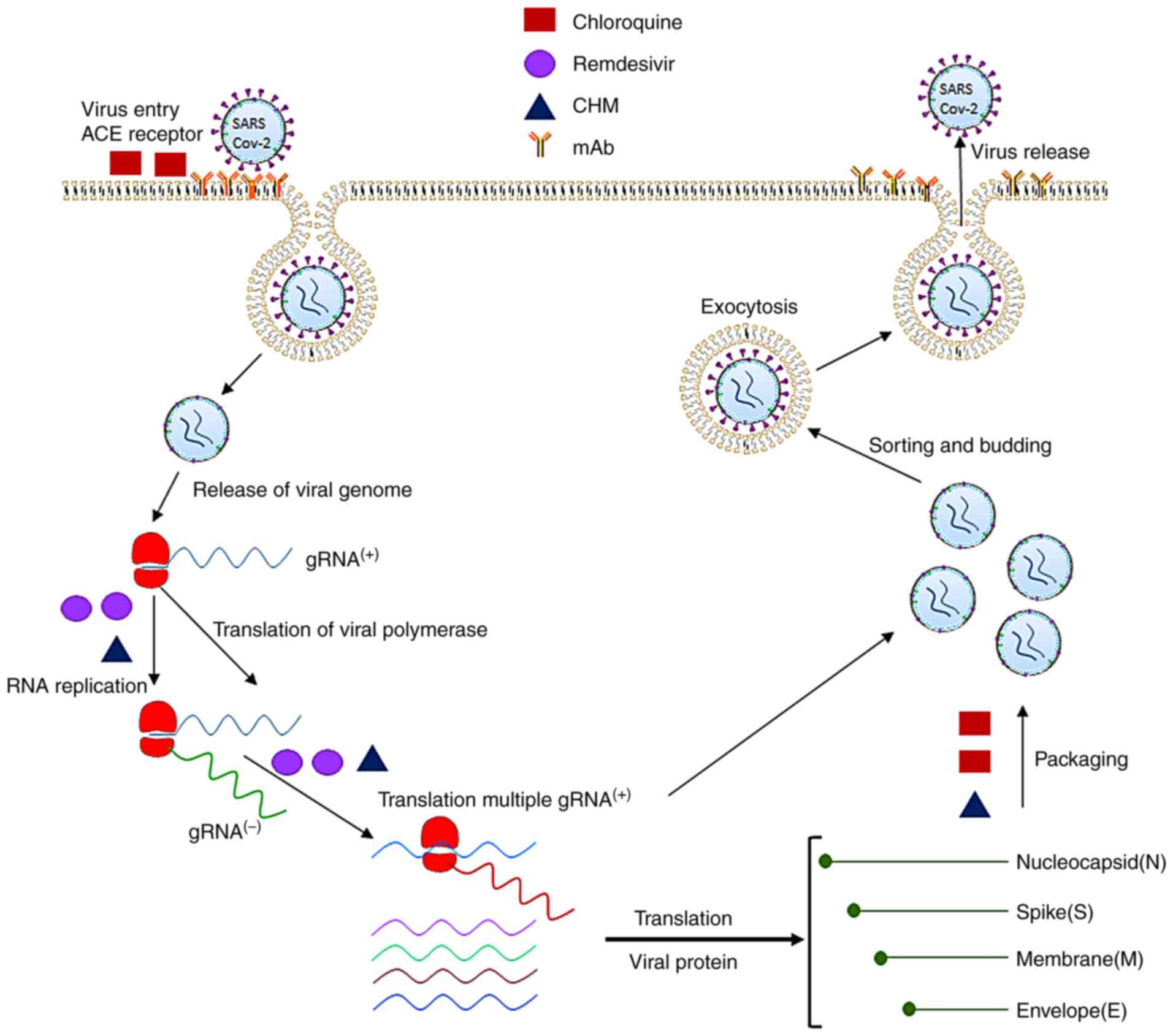
|
1
|
Zhu N, Zhang D, Wang W, Li X, Yang B, Song
J, Zhao X, Huang B, Shi W, Lu R, et al: A novel coronavirus from
patients with pneumonia in China, 2019. N Engl J Med. 382:727–733.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Lu R, Zhao X, Li J, Niu P, Yang B, Wu H,
Wang W, Song H, Huang B, Zhu N, et al: Genomic characterisation and
epidemiology of 2019 novel coronavirus: Implications for virus
origins and receptor binding. Lancet. 395:565–574. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Wang Q, Zhang Y, Wu L, Niu S, Song C,
Zhang Z, Lu G, Qiao C, Hu Y, Yuen KY, et al: Structural and
functional basis of SARS-CoV-2 entry by using human ACE2. Cell.
181:894–904. e9. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Shang J, Ye G, Shi K, Wan Y, Luo C, Aihara
H, Geng Q, Auerbach A and Li F: Structural basis of receptor
recognition by SARS-CoV-2. Nature. 581:221–224. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Kuhn JH, Radoshitzky SR, Li W, Wong SK,
Choe H and Farzan M: The SARS Coronavirus receptor ACE 2 A
potential target for antiviral therapy. New Concepts of Antiviral
Therapy. Holzenburg A and Bogner E: Springer US; Boston, MA: pp.
397–418. 2006, View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Letko M, Marzi A and Munster V: Functional
assessment of cell entry and receptor usage for SARS-CoV-2 and
other lineage B betacoronaviruses. Nat Microbiol. 5:562–569. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Rodriguez Y, Novelli L, Rojas M, De Santis
M, Acosta-Ampudia Y, Monsalve DM, Ramírez-Santana C, Costanzo A,
Ridgway WM, Ansari AA, et al: Autoinflammatory and autoimmune
conditions at the crossroad of COVID-19. J Autoimmun.
114:1025062020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Tay MZ, Poh CM, Rénia L, MacAry PA and Ng
LFP: The trinity of COVID-19: Immunity, inflammation and
intervention. Nat Rev Immunol. 20:363–374. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Fricke-Galindo I and Falfán-Valencia R:
Genetics insight for COVID-19 susceptibility and severity: A
review. Front Immunol. 12:6221762021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Maggi E, Canonica GW and Moretta L:
COVID-19: Unanswered questions on immune response and pathogenesis.
J Allergy Clin Immunol. 146:18–22. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Ahmed-Hassan H, Sisson B, Shukla RK,
Wijewantha Y, Funderburg NT, Li Z, Hayes D Jr, Demberg T and
Liyanage NPM: Innate immune responses to highly pathogenic
coronaviruses and other significant respiratory viral infections.
Front Immunol. 11:19792020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Li G and De Clercq E: Therapeutic options
for the 2019 novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV). Nat Rev Drug Discov.
19:149–150. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zumla A, Chan JF, Azhar EI, Hui DS and
Yuen KY: Coronaviruses-drug discovery and therapeutic options. Nat
Rev Drug Discov. 15:327–347. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Alzaabi MM, Hamdy R, Ashmawy NS, Hamoda
AM, Alkhayat F, Khademi NN, Al Joud SMA, El-Keblawy AA and Soliman
SSM: Flavonoids are promising safe therapy against COVID-19.
Phytochem Rev. May 22–2021.(Epub ahead of print). View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Savarino A, Di Trani L, Donatelli I, Cauda
R and Cassone A: New insights into the antiviral effects of
chloroquine. Lancet Infect Dis. 6:67–69. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Al-Bari MA: Chloroquine analogues in drug
discovery: New directions of uses, mechanisms of actions and toxic
manifestations from malaria to multifarious diseases. J Antimicrob
Chemother. 70:1608–1621. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Keyaerts E, Vijgen L, Maes P, Neyts J and
Van Ranst M: In vitro inhibition of severe acute respiratory
syndrome coronavirus by chloroquine. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
323:264–268. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Wang M, Cao R, Zhang L, Yang X, Liu J, Xu
M, Shi Z, Hu Z, Zhong W and Xiao G: Remdesivir and chloroquine
effectively inhibit the recently emerged novel coronavirus
(2019-nCoV) in vitro. Cell Res. 30:269–271. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Gao J, Tian Z and Yang X: Breakthrough:
Chloroquine phosphate has shown apparent efficacy in treatment of
COVID-19 associated pneumonia in clinical studies. Biosci Trends.
14:72–73. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Huang M, Tang T, Pang P, Li M, Ma R, Lu J,
Shu J, You Y, Chen B, Liang J, et al: Treating COVID-19 with
chloroquine. J Mol Cell Biol. 12:322–325. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Yao X, Ye F, Zhang M, Cui C, Huang B, Niu
P, Liu X, Zhao L, Dong E, Song C, et al: In vitro antiviral
activity and projection of optimized dosing design of
hydroxychloroquine for the treatment of severe acute respiratory
syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). Clin Infect Dis. 71:732–739.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Andreani J, Le Bideau M, Duflot I, Jardot
P, Rolland C, Boxberger M, Wurtz N, Rolain JM, Colson P, La Scola B
and Raoult D: In vitro testing of combined hydroxychloroquine and
azithromycin on SARS-CoV-2 shows synergistic effect. Microb Pathog.
145:1042282020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Gautret P, Lagier JC, Parola P, Hoang VT,
Meddeb L, Mailhe M, Doudier B, Courjon J, Giordanengo V, Vieira VE,
et al: Hydroxychloroquine and azithromycin as a treatment of
COVID-19: Results of an open-label non-randomized clinical trial.
Int J Antimicrob Agents. 56:1059492020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Arshad S, Kilgore P, Chaudhry ZS, Jacobsen
G, Wang DD, Huitsing K, Brar I, Alangaden GJ, Ramesh MS, McKinnon
JE, et al: Treatment with hydroxychloroquine, azithromycin, and
combination in patients hospitalized with COVID-19. Int J Infect
Dis. 97:396–403. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Hernandez AV, Roman YM, Pasupuleti V,
Barboza JJ and White CM: Hydroxychloroquine or chloroquine for
treatment or prophylaxis of COVID-19: A living systematic review.
Ann Intern Med. 173:287–296. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Chowdhury MS, Rathod J and Gernsheimer J:
A rapid systematic review of clinical trials utilizing chloroquine
and hydroxychloroquine as a treatment for COVID-19. Acad Emerg Med.
27:493–504. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Elavarasi A, Prasad M, Seth T, Sahoo RK,
Madan K, Nischal N, Soneja M, Sharma A, Maulik SK, Shalimar and
Garg P: Chloroquine and hydroxychloroquine for the treatment of
COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J Gen Intern Med.
35:3308–3314. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Kumar J, Jain S, Meena J and Yadav A:
Efficacy and safety of hydroxychloroquine/chloroquine against
SARS-CoV-2 infection: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J
Infect Chemother. 27:882–889. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Eckerle LD, Becker MM, Halpin RA, Li K,
Venter E, Lu X, Scherbakova S, Graham RL, Baric RS, Stockwell TB,
et al: Infidelity of SARS-CoV Nsp14-exonuclease mutant virus
replication is revealed by complete genome sequencing. PLoS Pathog.
6:e10008962010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Warren TK, Jordan R, Lo MK, Ray AS,
Mackman RL, Soloveva V, Siegel D, Perron M, Bannister R, Hui HC, et
al: Therapeutic efficacy of the small molecule GS-5734 against
Ebola virus in rhesus monkeys. Nature. 531:381–385. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Dong L, Hu S and Gao J: Discovering drugs
to treat coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). Drug Discov Ther.
14:58–60. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Agostini ML, Andres EL, Sims AC, Graham
RL, Sheahan TP, Lu X, Smith EC, Case JB, Feng JY, Jordan R, et al:
Coronavirus susceptibility to the antiviral remdesivir (GS-5734) is
mediated by the viral polymerase and the proofreading
exoribonuclease. mBio. 9:e00221–e00228. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Fu L, Ye F, Feng Y, Yu F, Wang Q, Wu Y,
Zhao C, Sun H, Huang B, Niu P, et al: Both boceprevir and GC376
efficaciously inhibit SARS-CoV-2 by targeting its main protease.
Nat Commun. 11:44172020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Holshue ML, DeBolt C, Lindquist S, Lofy
KH, Wiesman J, Bruce H, Spitters C, Ericson K, Wilkerson S, Tural
A, et al: First case of 2019 Novel Coronavirus in the United
States. N Engl J Med. 382:929–936. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Grein J, Ohmagari N, Shin D, Diaz G,
Asperges E, Castagna A, Feldt T, Green G, Green ML, Lescure FX, et
al: Compassionate use of remdesivir for patients with severe
Covid-19. N Engl J Med. 382:2327–2336. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Spinner CD, Gottlieb RL, Criner GJ,
Arribas López JR, Cattelan AM, Soriano Viladomiu A, Ogbuagu O,
Malhotra P, Mullane KM, Castagna A, et al: Effect of remdesivir vs
standard care on clinical status at 11 days in patients with
moderate COVID-19: A randomized clinical trial. JAMA.
324:1048–1057. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Beigel JH, Tomashek KM, Dodd LE, Mehta AK,
Zingman BS, Kalil AC, Hohmann E, Chu HY, Luetkemeyer A, Kline S, et
al: Remdesivir for the treatment of Covid-19-final report. N Engl J
Med. 383:1813–1826. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Garibaldi BT, Wang K, Robinson ML, Zeger
SL, Bandeen-Roche K, Wang MC, Alexander GC, Gupta A, Bollinger R
and Xu Y: Comparison of time to clinical improvement with vs
without remdesivir treatment in hospitalized patients with
COVID-19. JAMA Netw Open. 4:e2130712021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Aleissa MM, Silverman EA, Paredes Acosta
LM, Nutt CT, Richterman A and Marty FM: New perspectives on
antimicrobial agents: Remdesivir treatment for COVID-19. Antimicrob
Agents Chemother. 65:e01814–20. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Elfiky AA: Ribavirin, remdesivir,
sofosbuvir, galidesivir, and tenofovir against SARS-CoV-2 RNA
dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp): A molecular docking study. Life
Sci. 253:1175922020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Falzarano D, de Wit E, Martellaro C,
Callison J, Munster VJ and Feldmann H: Inhibition of novel β
coronavirus replication by a combination of interferon-α2b and
ribavirin. Sci Rep. 3:16862013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Falzarano D, de Wit E, Rasmussen AL,
Feldmann F, Okumura A, Scott DP, Brining D, Bushmaker T, Martellaro
C, Baseler L, et al: Treatment with interferon-α2b and ribavirin
improves outcome in MERS-CoV-infected rhesus macaques. Nat Med.
19:1313–1317. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
De Clercq E: New nucleoside analogues for
the treatment of hemorrhagic fever virus infections. Chem Asian J.
14:3962–3968. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Choy KT, Wong AY, Kaewpreedee P, Sia SF,
Chen D, Hui KPY, Chu DKW, Chan MCW, Cheung PP, Huang X, et al:
Remdesivir, lopinavir, emetine, and homoharringtonine inhibit
SARS-CoV-2 replication in vitro. Antiviral Res. 178:1047862020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Chen C, Zhang Y, Huang J, Yin P, Cheng Z,
Wu J, Chen S, Zhang Y, Chen B, Lu M, et al: Favipiravir versus
Arbidol for COVID-19: A randomized clinical trial. medRxiv:
2020.03.17.20037432. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Taylor R, Kotian P, Warren T, Panchal R,
Bavari S, Julander J, Dobo S, Rose A, El-Kattan Y, Taubenheim B, et
al: BCX4430-A broad-spectrum antiviral adenosine nucleoside analog
under development for the treatment of Ebola virus disease. J
Infect Public Health. 9:220–226. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Shu H, Wang S, Ruan S, Wang Y, Zhang J,
Yuan Y, Liu H, Wu Y, Li R, Pan S, et al: Dynamic changes of
antibodies to SARS-CoV-2 in COVID-19 patients at early stage of
outbreak. Virol Sin. 35:744–751. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Brouwer PJM, Caniels TG, van der Straten
K, Snitselaar JL, Aldon Y, Bangaru S, Torres JL, Okba NMA,
Claireaux M, Kerster G, et al: Potent neutralizing antibodies from
COVID-19 patients define multiple targets of vulnerability.
Science. 369:643–650. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Chan KH, Chan JF, Tse H, Chen H, Lau CC,
Cai JP, Tsang AK, Xiao X, To KK, Lau SK, et al: Cross-reactive
antibodies in convalescent SARS patients' sera against the emerging
novel human coronavirus EMC (2012) by both immunofluorescent and
neutralizing antibody tests. J Infect. 67:130–140. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Mair-Jenkins J, Saavedra-Campos M, Baillie
JK, Cleary P, Khaw FM, Lim WS, Makki S, Rooney KD, Nguyen-Van-Tam
JS and Beck CR; Convalescent Plasma Study Group, : The
effectiveness of convalescent plasma and hyperimmune immunoglobulin
for the treatment of severe acute respiratory infections of viral
etiology: A systematic review and exploratory meta-analysis. J
Infect Dis. 211:80–90. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Tian X, Li C, Huang A, Xia S, Lu S, Shi Z,
Lu L, Jiang S, Yang Z, Wu Y and Ying T: Potent binding of 2019
novel coronavirus spike protein by a SARS coronavirus-specific
human monoclonal antibody. Emerg Microbes Infect. 9:382–385. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Sui J, Deming M, Rockx B, Liddington RC,
Zhu QK, Baric RS and Marasco WA: Effects of human anti-spike
protein receptor binding domain antibodies on severe acute
respiratory syndrome coronavirus neutralization escape and fitness.
J Virol. 88:13769–13780. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Jiang S, Hillyer C and Du L: Neutralizing
antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 and other human coronaviruses:
(Trends in Immunology 41, 355–359; 2020). Trends Immunol.
41:5452020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Mulangu S, Dodd LE, Davey RT Jr, Tshiani
Mbaya O, Proschan M, Mukadi D, Lusakibanza Manzo M, Nzolo D,
Tshomba Oloma A, Ibanda A, et al: A randomized, controlled trial of
Ebola virus disease therapeutics. N Engl J Med. 381:2293–2303.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Shi R, Shan C, Duan X, Chen Z, Liu P, Song
J, Song T, Bi X, Han C, Wu L, et al: A human neutralizing antibody
targets the receptor-binding site of SARS-CoV-2. Nature.
584:120–124. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Valdez-Cruz NA, García-Hernández E,
Espitia C, Cobos-Marín L, Altamirano C, Bando-Campos CG,
Cofas-Vargas LF, Coronado-Aceves EW, González-Hernández RA,
Hernández-Peralta P, et al: Integrative overview of antibodies
against SARS-CoV-2 and their possible applications in COVID-19
prophylaxis and treatment. Microb Cell Fact. 20:882021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Chen P, Nirula A, Heller B, Gottlieb RL,
Boscia J, Morris J, Huhn G, Cardona J, Mocherla B, Stosor V, et al:
SARS-CoV-2 neutralizing antibody LY-CoV555 in outpatients with
Covid-19. N Engl J Med. 384:229–237. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Katia F, Myriam DP, Ucciferri C, Auricchio
A, Di Nicola M, Marchioni M, Eleonora C, Emanuela S, Cipollone F
and Vecchiet J: Efficacy of canakinumab in mild or severe COVID-19
pneumonia. Immun Inflamm Dis. 9:399–405. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Hung IF, To KK, Lee CK, Lee KL, Chan K,
Yan WW, Liu R, Watt CL, Chan WM, Lai KY, et al: Convalescent plasma
treatment reduced mortality in patients with severe pandemic
influenza A (H1N1) 2009 virus infection. Clin Infect Dis.
52:447–456. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Ko JH, Seok H, Cho SY, Ha YE, Baek JY, Kim
SH, Kim YJ, Park JK, Chung CR, Kang ES, et al: Challenges of
convalescent plasma infusion therapy in Middle East respiratory
coronavirus infection: A single centre experience. Antivir Ther.
23:617–622. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Soo YO, Cheng Y, Wong R, Hui DS, Lee CK,
Tsang KK, Ng MH, Chan P, Cheng G and Sung JJ: Retrospective
comparison of convalescent plasma with continuing high-dose
methylprednisolone treatment in SARS patients. Clin Microbiol
Infect. 10:676–678. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Casadevall A, Grossman BJ, Henderson JP,
Joyner MJ, Shoham S, Pirofski LA and Paneth N: The assessment of
convalescent plasma efficacy against COVID-19. Med (N Y). 1:66–77.
2020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Arabi Y, Balkhy H, Hajeer AH, Bouchama A,
Hayden FG, Al-Omari A, Al-Hameed FM, Taha Y, Shindo N, Whitehead J,
et al: Feasibility, safety, clinical, and laboratory effects of
convalescent plasma therapy for patients with Middle East
respiratory syndrome coronavirus infection: A study protocol.
Springerplus. 4:7092015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Ahn JY, Sohn Y, Lee SH, Cho Y, Hyun JH,
Baek YJ, Jeong SJ, Kim JH, Ku NS, Yeom JS, et al: Use of
convalescent plasma therapy in two COVID-19 patients with acute
respiratory distress syndrome in Korea. J Korean Med Sci.
35:e1492020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Duan K, Liu B, Li C, Zhang H, Yu T, Qu J,
Zhou M, Chen L, Meng S, Hu Y, et al: Effectiveness of convalescent
plasma therapy in severe COVID-19 patients. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
117:9490–9496. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Liu S, Shergis J, Chen X, Yu X, Guo X,
Zhang AL, Lu C and Xue CC: Chinese herbal medicine (weijing
decoction) combined with pharmacotherapy for the treatment of acute
exacerbations of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Evid Based
Complement Alternat Med. 2014:2570122014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Leung PC: The efficacy of Chinese medicine
for SARS: A review of Chinese publications after the crisis. Am J
Chin Med. 35:575–581. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Cinatl J, Morgenstern B, Bauer G, Chandra
P, Rabenau H and Doerr HW: Glycyrrhizin, an active component of
liquorice roots, and replication of SARS-associated coronavirus.
Lancet. 361:2045–2046. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Wang SQ, Du QS, Zhao K, Li AX, Wei DQ and
Chou KC: Virtual screening for finding natural inhibitor against
cathepsin-L for SARS therapy. Amino Acids. 33:129–135. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Ho TY, Wu SL, Chen JC, Li CC and Hsiang
CY: Emodin blocks the SARS coronavirus spike protein and
angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 interaction. Antiviral Res.
74:92–101. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Niu M, Wang RL, Wang ZX, Zhang P, Bai ZF,
Jing J, Guo YM, Zhao X, Zhan XY, Zhang ZT, et al: Rapid
establishment of traditional Chinese medicine prevention and
treatment of 2019-nCoV based on clinical experience and molecular
docking. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 45:1213–1218. 2020.(In
Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Runfeng L, Yunlong H, Jicheng H, Weiqi P,
Qinhai M, Yongxia S, Chufang L, Jin Z, Zhenhua J, Haiming J, et al:
Lianhuaqingwen exerts anti-viral and anti-inflammatory activity
against novel coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2). Pharmacol Res.
156:1047612020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Liu H, Ye F, Sun Q, Liang H, Li C, Li S,
Lu R, Huang B, Tan W and Lai L: Scutellaria baicalensis
extract and baicalein inhibit replication of SARS-CoV-2 and its
3C-like protease in vitro. bioRxiv: 2020.04.10.035824. 2020.
|
|
74
|
Zhu J, Deng YQ, Wang X, Li XF, Zhang NN,
Liu Z, Zhang B, Qin CF and Xie Z: An artificial intelligence system
reveals liquiritin inhibits SARS-CoV-2 by mimicking type I
interferon. bioRxiv: doi:
https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.05.02.074021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
75
|
Chen Z and Nakamura T: Statistical
evidence for the usefulness of Chinese medicine in the treatment of
SARS. Phytother Res. 18:592–594. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Luo H, Tang QL, Shang YX, Liang SB, Yang
M, Robinson N and Liu JP: Can Chinese medicine be used for
prevention of corona virus disease 2019 (COVID-19)? A review of
historical classics, research evidence and current prevention
programs. Chin J Integr Med. 26:243–250. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Ang L, Lee HW, Choi JY, Zhang J and Soo
Lee M: Herbal medicine and pattern identification for treating
COVID-19: A rapid review of guidelines. Integr Med Res.
9:1004072020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Yu S, Wang J and Shen H: Network
pharmacology-based analysis of the role of traditional Chinese
herbal medicines in the treatment of COVID-19. Ann Palliat Med.
9:437–446. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Wu C, Liu Y, Yang Y, Zhang P, Zhong W,
Wang Y, Wang Q, Xu Y, Li M, Li X, et al: Analysis of therapeutic
targets for SARS-CoV-2 and discovery of potential drugs by
computational methods. Acta Pharm Sin B. 10:766–788. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Zhang DH, Wu KL, Zhang X, Deng SQ and Peng
B: In silico screening of Chinese herbal medicines with the
potential to directly inhibit 2019 novel coronavirus. J Integr Med.
18:152–158. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Zhang Q, Wang Y, Qi C, Shen L and Li J:
Clinical trial analysis of 2019-nCoV therapy registered in China. J
Med Virol. 92:540–545. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Kulanthaivel S, Kaliberdenko VB,
Balasundaram K, Shterenshis MV, Scarpellini E and Abenavoli L:
Tocilizumab in SARS-CoV-2 patients with the syndrome of cytokine
storm: A narrative review. Rev Recent Clin Trials. 16:138–145.
2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Toniati P, Piva S, Cattalini M, Garrafa E,
Regola F, Castelli F, Franceschini F, Airò P, Bazzani C, Beindorf
EA, et al: Tocilizumab for the treatment of severe COVID-19
pneumonia with hyperinflammatory syndrome and acute respiratory
failure: A single center study of 100 patients in Brescia, Italy.
Autoimmun Rev. 19:1025682020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Caly L, Druce JD, Catton MG, Jans DA and
Wagstaff KM: The FDA-approved drug ivermectin inhibits the
replication of SARS-CoV-2 in vitro. Antiviral Res. 178:1047872020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Yang SNY, Atkinson SC, Wang C, Lee A,
Bogoyevitch MA, Borg NA and Jans DA: The broad spectrum antiviral
ivermectin targets the host nuclear transport importin α/β1
heterodimer. Antiviral Res. 177:1047602020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Monteagudo LA, Boothby A and Gertner E:
Continuous intravenous anakinra infusion to calm the cytokine storm
in macrophage activation syndrome. ACR Open Rheumatol. 2:276–282.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Franzetti M, Forastieri A, Borsa N,
Pandolfo A, Molteni C, Borghesi L, Pontiggia S, Evasi G, Guiotto L,
Erba M, et al: IL-1 receptor antagonist anakinra in the treatment
of COVID-19 acute respiratory distress syndrome: A retrospective,
observational study. J Immunol. 206:1569–1575. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Romani L, Tomino C, Puccetti P and Garaci
E: Off-label therapy targeting pathogenic inflammation in COVID-19.
Cell Death Discov. 6:492020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Puccetti M, Costantini C, Ricci M and
Giovagnoli S: Tackling immune pathogenesis of COVID-19 through
molecular pharmaceutics. Pharmaceutics. 13:4942021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
D'Ardes D, Pontolillo M, Esposito L,
Masciarelli M, Boccatonda A, Rossi I, Bucci M, Guagnano MT,
Ucciferri C, Santilli F, et al: Duration of COVID-19: Data from an
Italian cohort and potential role for steroids. Microorganisms.
8:13272020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Horby P, White NJ and Landray MJ:
Hydroxychloroquine in hospitalized patients with Covid-19. Reply. N
Engl J Med. 384:8822021.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Ucciferri C, Barone M, Vecchiet J and
Falasca K: Pidotimod in paucisymptomatic SARS-CoV2 infected
patients. Mediterr J Hematol Infect Dis. 12:e20200482020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Saakre M, Mathew D and Ravisankar V:
Perspectives on plant flavonoid quercetin-based drugs for novel
SARS-CoV-2. Beni Suef Univ J Basic Appl Sci. 10:212021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
López-Cortés A, Guevara-Ramírez P,
Kyriakidis NC, Barba-Ostria C, León Cáceres Á, Guerrero S,
Ortiz-Prado E, Munteanu CR, Tejera E, Cevallos-Robalino D, et al:
In silico analyses of immune system protein interactome network,
single-cell rna sequencing of human tissues, and artificial neural
networks reveal potential therapeutic targets for drug repurposing
against COVID-19. Front Pharmacol. 12:5989252021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Hong W: Combating COVID-19 with
chloroquine. J Mol Cell Biol. 12:249–250. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
96
|
Lan J, Ge J, Yu J, Shan S, Zhou H, Fan S,
Zhang Q, Shi X, Wang Q, Zhang L and Wang X: Structure of the
SARS-CoV-2 spike receptor-binding domain bound to the ACE2
receptor. Nature. 581:215–220. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Liu J, Cao R, Xu M, Wang X, Zhang H, Hu H,
Li Y, Hu Z, Zhong W and Wang M: Hydroxychloroquine, a less toxic
derivative of chloroquine, is effective in inhibiting SARS-CoV-2
infection in vitro. Cell Discov. 6:162020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
98
|
Hoffmann M, Kleine-Weber H, Schroeder S,
Krüger N, Herrler T, Erichsen S, Schiergens TS, Herrler G, Wu NH,
Nitsche A, et al: SARS-CoV-2 cell entry depends on ACE2 and TMPRSS2
and is blocked by a clinically proven protease inhibitor. Cell.
181:271–280.e8. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
99
|
Kong Q, Wu Y, Gu Y, Lv Q, Qi F, Gong S and
Chen X: Analysis of the molecular mechanism of Pudilan (PDL)
treatment for COVID-19 by network pharmacology tools. Biomed
Pharmacother. 128:1103162020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
100
|
Chu CK, Gadthula S, Chen X, Choo H, Olgen
S, Barnard DL and Sidwell RW: Antiviral activity of nucleoside
analogues against SARS-coronavirus (SARS-coV). Antivir Chem
Chemother. 17:285–289. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
101
|
Gordon CJ, Tchesnokov EP, Woolner E, Perry
JK, Feng JY, Porter DP and Götte M: Remdesivir is a direct-acting
antiviral that inhibits RNA-dependent RNA polymerase from severe
acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 with high potency. J Biol
Chem. 295:6785–6797. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
102
|
Shannon A, Selisko B, Le NT, Huchting J,
Touret F, Piorkowski G, Fattorini V, Ferron F, Decroly E, Meier C,
et al: Rapid incorporation of Favipiravir by the fast and
permissive viral RNA polymerase complex results in SARS-CoV-2
lethal mutagenesis. Nat Commun. 11:46822020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
103
|
Khan A, Khan M, Saleem S, Babar Z, Ali A,
Khan AA, Sardar Z, Hamayun F, Ali SS and Wei DQ: Phylogenetic
analysis and structural perspectives of RNA-dependent
RNA-polymerase inhibition from SARs-CoV-2 with natural products.
Interdiscip Sci. 12:335–348. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
104
|
Lin CW, Tsai FJ, Tsai CH, Lai CC, Wan L,
Ho TY, Hsieh CC and Chao PD: Anti-SARS coronavirus 3C-like protease
effects of Isatis indigotica root and plant-derived phenolic
compounds. Antiviral Res. 68:36–42. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
105
|
Park T, Lee SY, Kim S, Kim MJ, Kim HG, Jun
S, Kim SI, Kim BT, Park EC and Park D: Spike protein binding
prediction with neutralizing antibodies of SARS-CoV-2. bioRxiv:
doi: 2020.02.22.951178. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
106
|
Anand K, Ziebuhr J, Wadhwani P, Mesters JR
and Hilgenfeld R: Coronavirus main proteinase (3CLpro) structure:
Basis for design of anti-SARS drugs. Science. 300:1763–1767. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
107
|
Zhou G and Zhao Q: Perspectives on
therapeutic neutralizing antibodies against the novel coronavirus
SARS-CoV-2. Int J Biol Sci. 16:1718–1723. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
108
|
Quiros Roldan E, Biasiotto G, Magro P and
Zanella I: The possible mechanisms of action of 4-aminoquinolines
(chloroquine/hydroxychloroquine) against Sars-Cov-2 infection
(COVID-19): A role for iron homeostasis? Pharmacol Res.
158:1049042020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
109
|
Zhou D, Dai SM and Tong Q: COVID-19: A
recommendation to examine the effect of hydroxychloroquine in
preventing infection and progression. J Antimicrob Chemother.
75:1667–1670. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
110
|
Devaux CA, Rolain JM, Colson P and Raoult
D: New insights on the antiviral effects of chloroquine against
coronavirus: What to expect for COVID-19? Int J Antimicrob Agents.
55:1059382020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
111
|
Adhikari B, Marasini BP, Rayamajhee B,
Bhattarai BR, Lamichhane G, Khadayat K, Adhikari A, Khanal S and
Parajuli N: Potential roles of medicinal plants for the treatment
of viral diseases focusing on COVID-19: A review. Phytother Res.
35:1298–1312. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
112
|
Lee DYW, Li QY, Liu J and Efferth T:
Traditional Chinese herbal medicine at the forefront battle against
COVID-19: Clinical experience and scientific basis. Phytomedicine.
80:1533372021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|