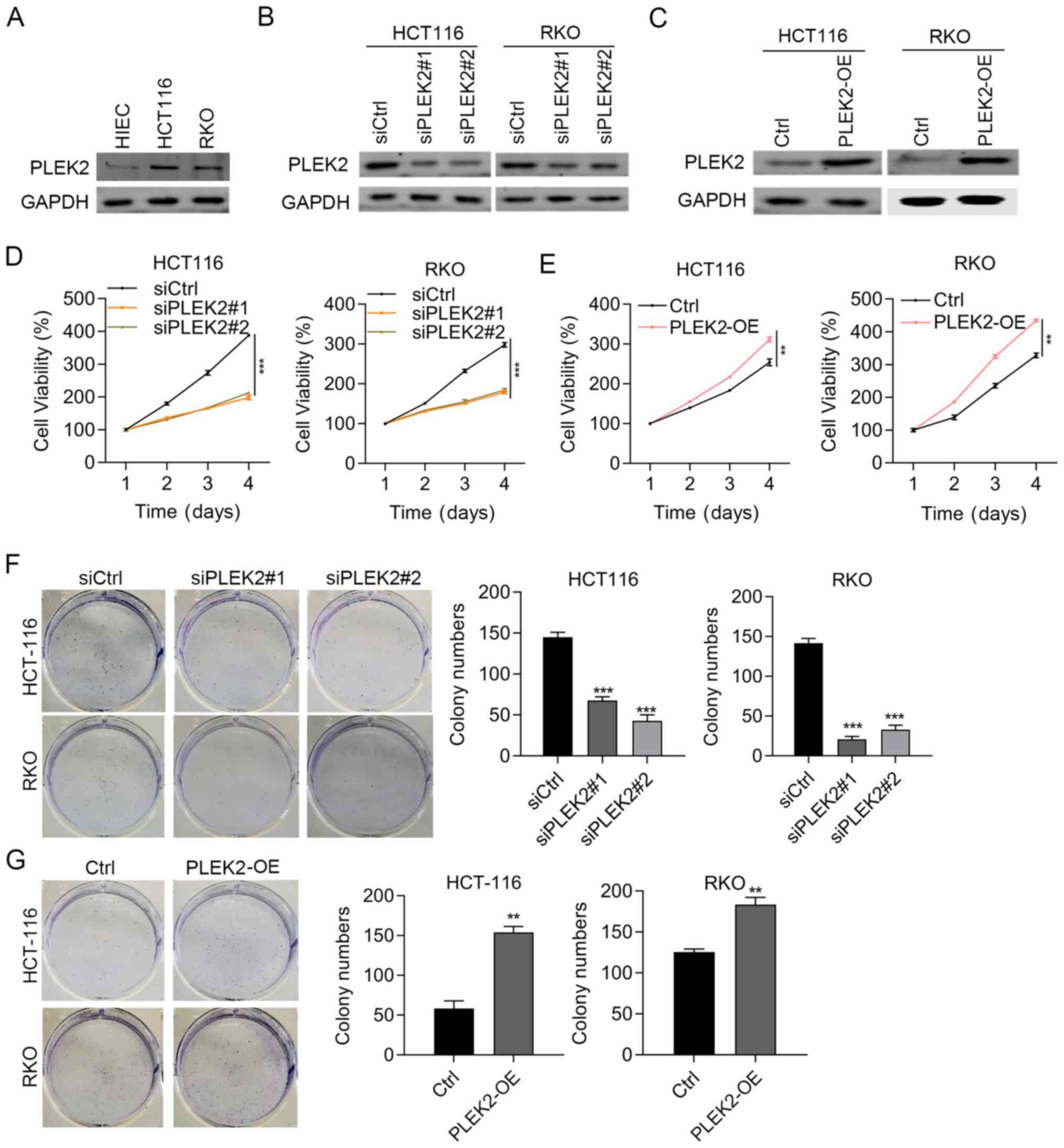
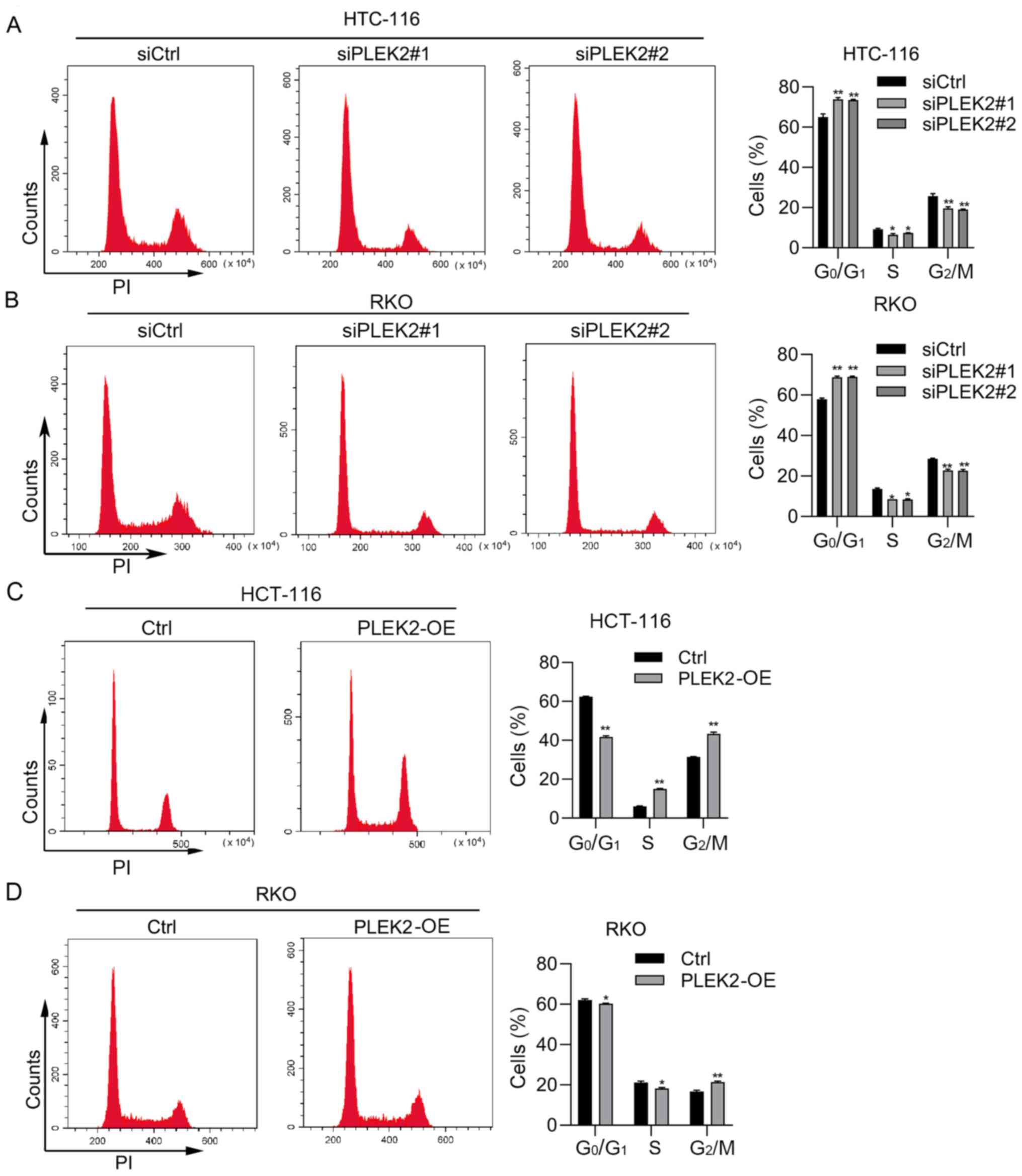
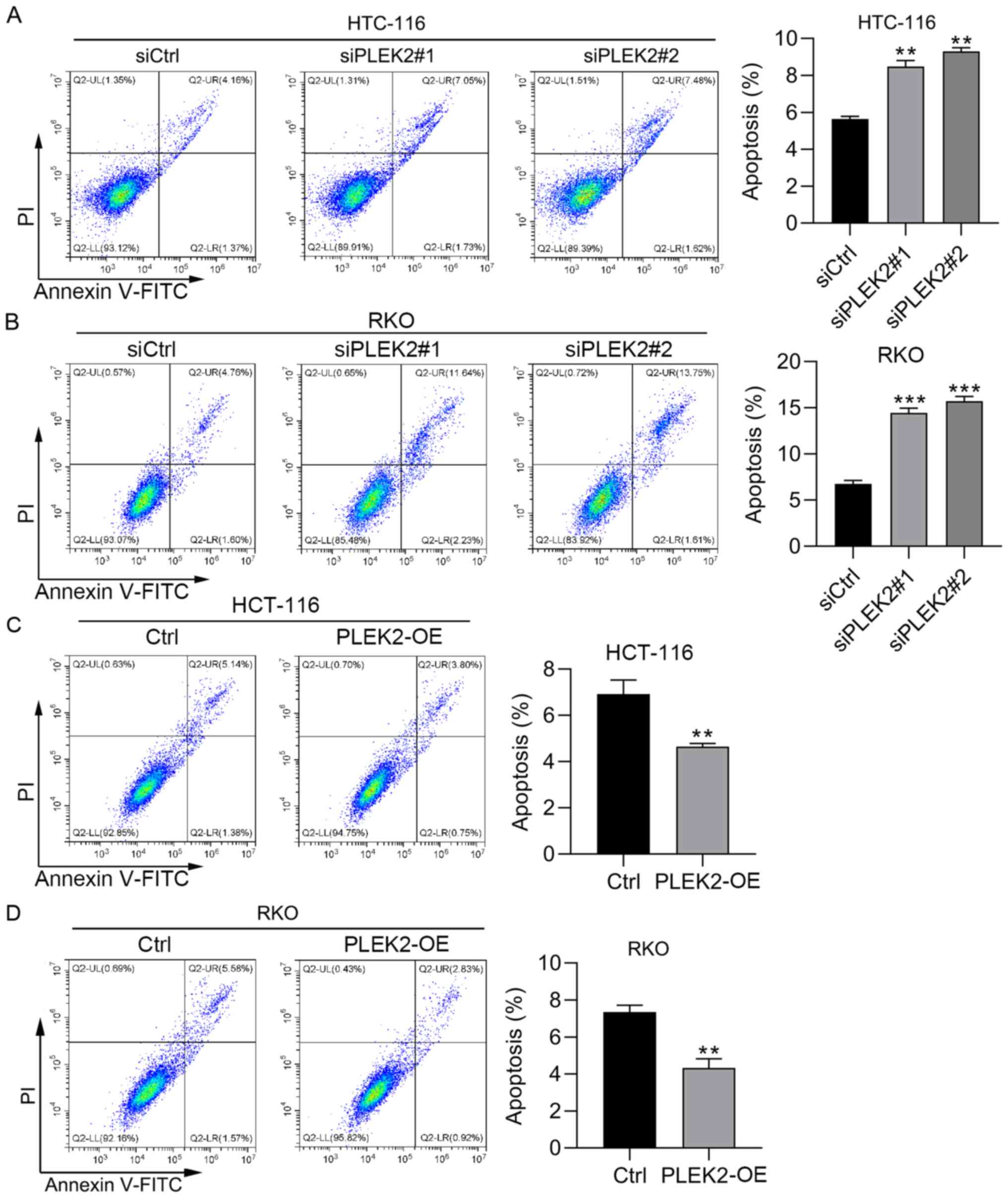
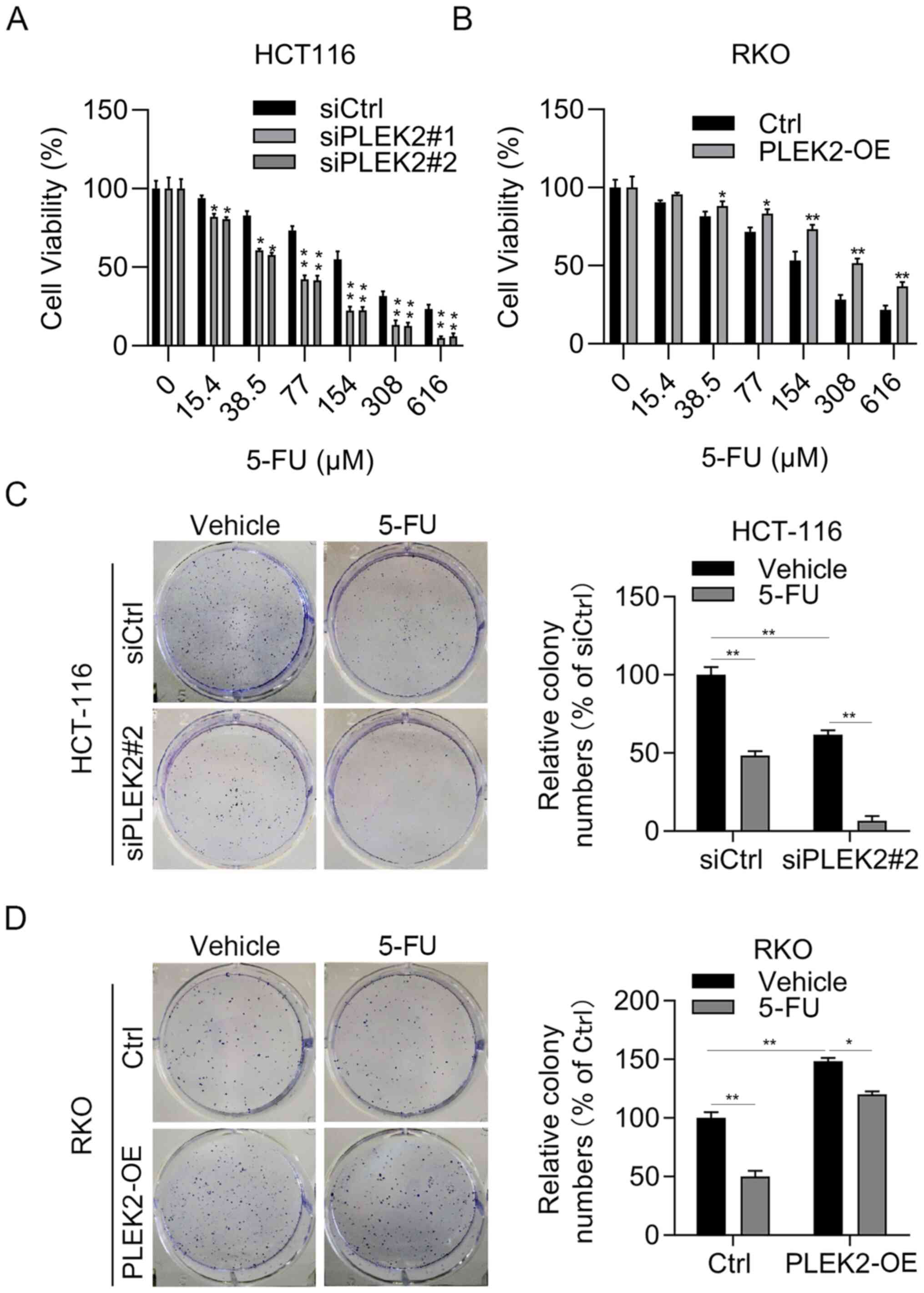
|
1
|
No authors listed. Erratum: Global cancer
statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality
worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin.
70:3132020.Erratum for: CA Cancer J Clin 68: 394-424, 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Dekker E, Tanis PJ, Vleugels JLA, Kasi PM
and Wallace MB: Colorectal cancer. Lancet. 394:1467–1480. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Meyerhardt JA and Mayer RJ: Systemic
therapy for colorectal cancer. N Engl J Med. 352:476–487. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Gustavsson B, Carlsson G, Machover D,
Petrelli N, Roth A, Schmoll HJ, Tveit KM and Gibson F: A review of
the evolution of systemic chemotherapy in the management of
colorectal cancer. Clin Colorectal Cancer. 14:1–10. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Van der Jeught K, Xu HC, Li YJ, Lu XB and
Ji G: Drug resistance and new therapies in colorectal cancer. World
J Gastroenterol. 24:3834–3848. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Rattray NJW, Charkoftaki G, Rattray Z,
Hansen JE, Vasiliou V and Johnson CH: Environmental influences in
the etiology of colorectal cancer: The premise of metabolomics.
Curr Pharmacol Rep. 3:114–125. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Caspi M, Wittenstein A, Kazelnik M,
Shor-Nareznoy Y and Rosin-Arbesfeld R: Therapeutic targeting of the
oncogenic Wnt signaling pathway for treating colorectal cancer and
other colonic disorders. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 169:118–136. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Carethers JM and Jung BH: Genetics and
Genetic Biomarkers in Sporadic Colorectal Cancer. Gastroenterology.
149:1177–1190.e3. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Shang S, Hua F and Hu ZW: The regulation
of β-catenin activity and function in cancer: Therapeutic
opportunities. Oncotarget. 8:33972–33989. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Bian J, Dannappel M, Wan C and Firestein
R: Transcriptional Regulation of Wnt/β-Catenin Pathway in
Colorectal Cancer. Cells. 9:21252020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Cho YH, Ro EJ, Yoon JS, Mizutani T, Kang
DW, Park JC, Il Kim T, Clevers H and Choi KY: 5-FU promotes
stemness of colorectal cancer via p53-mediated WNT/β-catenin
pathway activation. Nat Commun. 11:53212020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Li Y, Wang R, Huang D, Ma X, Mo S, Guo Q,
Fu G, Li Y, Xu X, Hu X, et al: A novel human colon signet-ring cell
carcinoma organoid line: Establishment, characterization and
application. Carcinogenesis. 41:993–1004. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Jung YS and Park JI: Wnt signaling in
cancer: Therapeutic targeting of Wnt signaling beyond β-catenin and
the destruction complex. Exp Mol Med. 52:183–191. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Krishnamurthy N and Kurzrock R: Targeting
the Wnt/beta-catenin pathway in cancer: Update on effectors and
inhibitors. Cancer Treat Rev. 62:50–60. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Zhan T, Rindtorff N and Boutros M: Wnt
signaling in cancer. Oncogene. 36:1461–1473. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Hu MH, Bauman EM, Roll RL, Yeilding N and
Abrams CS: Pleckstrin 2, a widely expressed paralog of pleckstrin
involved in actin rearrangement. J Biol Chem. 274:21515–21518.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Shen H, He M, Lin R, Zhan M, Xu S, Huang
X, Xu C, Chen W, Yao Y, Mohan M and Wang J: PLEK2 promotes
gallbladder cancer invasion and metastasis through EGFR/CCL2
pathway. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 38:2472019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Wang J, He Z, Sun B, Huang W, Xiang J,
Chen Z, Li Z and Gu X: Pleckstrin-2 as a Prognostic Factor and
Mediator of Gastric Cancer Progression. Gastroenterol Res Pract.
2021:55273872021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Wang J, Sun Z, Wang J, Tian Q, Huang R,
Wang H, Wang X and Han F: Expression and prognostic potential of
PLEK2 in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma based on
bioinformatics analysis. Cancer Med. 10:6515–6533. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Cacemiro MDC, Cominal JG, Tognon R, Nunes
NS, Simões BP, Figueiredo-Pontes LL, Catto LFB, Traina F, Souto EX,
Zambuzi FA, et al: Philadelphia-negative myeloproliferative
neoplasms as disorders marked by cytokine modulation. Hematol
Transfus Cell Ther. 40:120–131. 2018.Erratum in: Hematol Transfus
Cell Ther 43: 117, 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Zhao B, Mei Y, Cao L, Zhang J, Sumagin R,
Yang J, Gao J, Schipma MJ, Wang Y, Thorsheim C, et al: Loss of
pleckstrin-2 reverts lethality and vascular occlusions in
JAK2V617F-positive myeloproliferative neoplasms. J Clin Invest.
128:125–140. 2018. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Wu DM, Deng SH, Zhou J, Han R, Liu T,
Zhang T, Li J, Chen JP and Xu Y: PLEK2 mediates metastasis and
vascular invasion via the ubiquitin-dependent degradation of SHIP2
in non-small cell lung cancer. Int J Cancer. 146:2563–2575.
2020.Erratum in: Int J Cancer 149: E11, 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Weinstein JN, Collisson EA, Mills GB, Shaw
KR, Ozenberger BA, Ellrott K, Shmulevich I, Sander C and Stuart JM;
Cancer Genome Atlas Research Network, : The Cancer Genome Atlas
Pan-Cancer analysis project. Nat Genet. 45:1113–1120. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Chai B, Guo Y, Cui X, Liu J, Suo Y, Dou Z
and Li N: MiR-223-3p promotes the proliferation, invasion and
migration of colon cancer cells by negative regulating PRDM1. Am J
Transl Res. 11:4516–4523. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Xie YH, Chen YX and Fang JY: Comprehensive
review of targeted therapy for colorectal cancer. Signal Transduct
Target Ther. 5:222020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Michels BE, Mosa MH, Streibl BI, Zhan T,
Menche C, Abou-El-Ardat K, Darvishi T, Członka E, Wagner S, Winter
J, et al: Pooled In Vitro and In Vivo CRISPR-Cas9 Screening
Identifies Tumor Suppressors in Human Colon Organoids. Cell Stem
Cell. 26:782–792.e7. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Ragusa S, Prat-Luri B, González-Loyola A,
Nassiri S, Squadrito ML, Guichard A, Cavin S, Gjorevski N, Barras
D, Marra G, et al: Antiangiogenic immunotherapy suppresses
desmoplastic and chemoresistant intestinal tumors in mice. J Clin
Invest. 130:1199–1216. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Zhang L and Shay J: Multiple Roles of APC
and its Therapeutic Implications in Colorectal Cancer. J Natl
Cancer Inst. 109:djw3322017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Gao C, Xiao G and Hu J: Regulation of
Wnt/β-catenin signaling by posttranslational modifications. Cell
Biosci. 4:132014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Yang B, Mao L, Li Y, Li Q, Li X, Zhang Y
and Zhai Z: β-catenin, leucine-rich repeat-containing G
protein-coupled receptor 5 and GATA-binding factor 6 are associated
with the normal mucosa-adenoma-adenocarcinoma sequence of
colorectal tumorigenesis. Oncol Lett. 15:2287–2295. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Inazu T, Yamada K and Miyamoto K: Cloning
and expression of pleckstrin 2, a novel member of the pleckstrin
family. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 265:87–93. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Hamaguchi N, Ihara S, Ohdaira T, Nagano H,
Iwamatsu A, Tachikawa H and Fukui Y: Pleckstrin-2 selectively
interacts with phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase lipid products and
regulates actin organization and cell spreading. Biochem Biophys
Res Commun. 361:270–275. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Zhang W, Li T, Hu B and Li H: PLEK2 Gene
Upregulation Might Independently Predict Shorter Progression-Free
Survival in Lung Adenocarcinoma. Technol Cancer Res Treat.
19:15330338209570302020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Luo Y, Robinson S, Fujita J, Siconolfi L,
Magidson J, Edwards CK, Wassmann K, Storm K, Norris DA,
Bankaitis-Davis D, et al: Transcriptome profiling of whole blood
cells identifies PLEK2 and C1QB in human melanoma. PLoS One.
6:e209712011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|