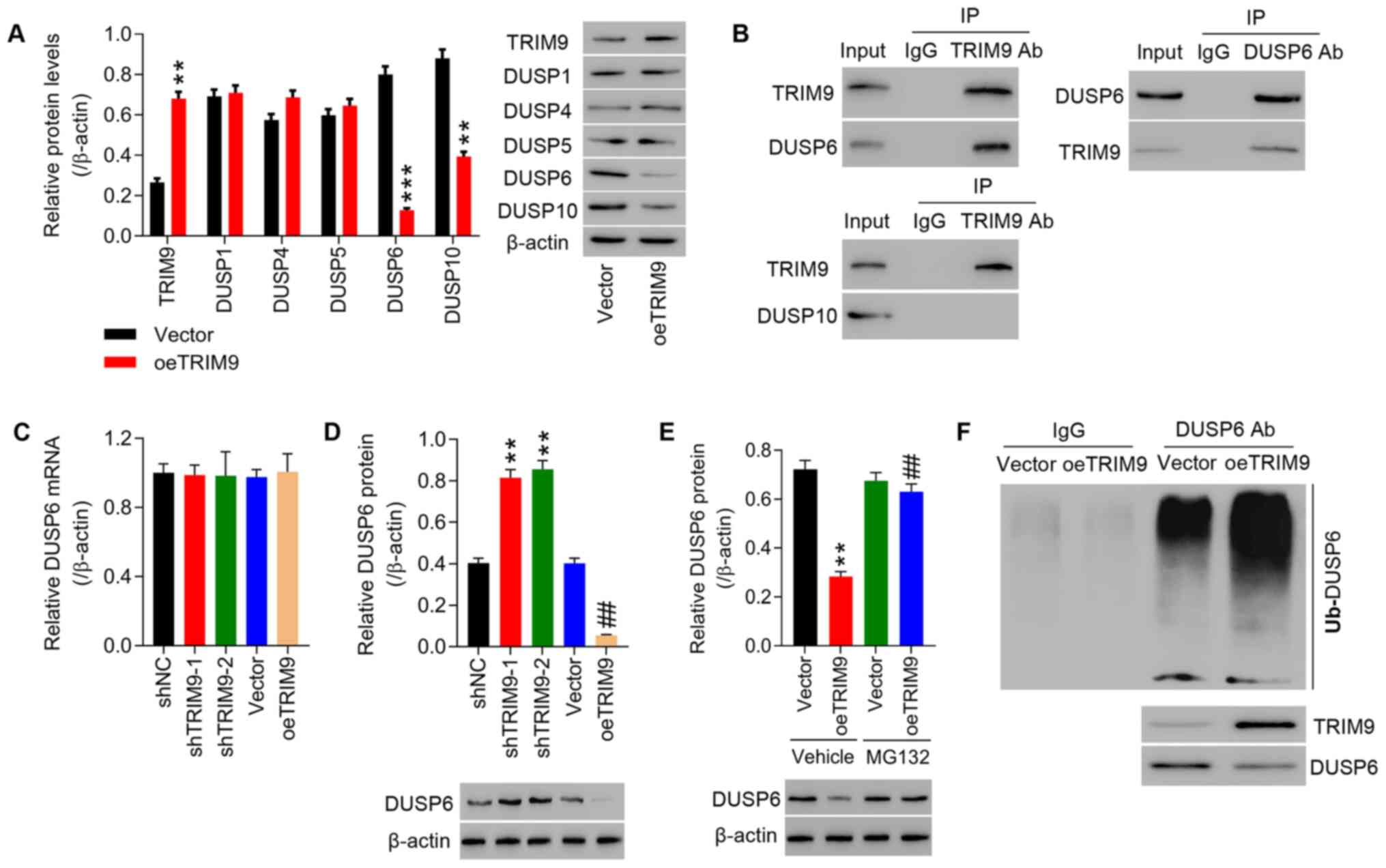
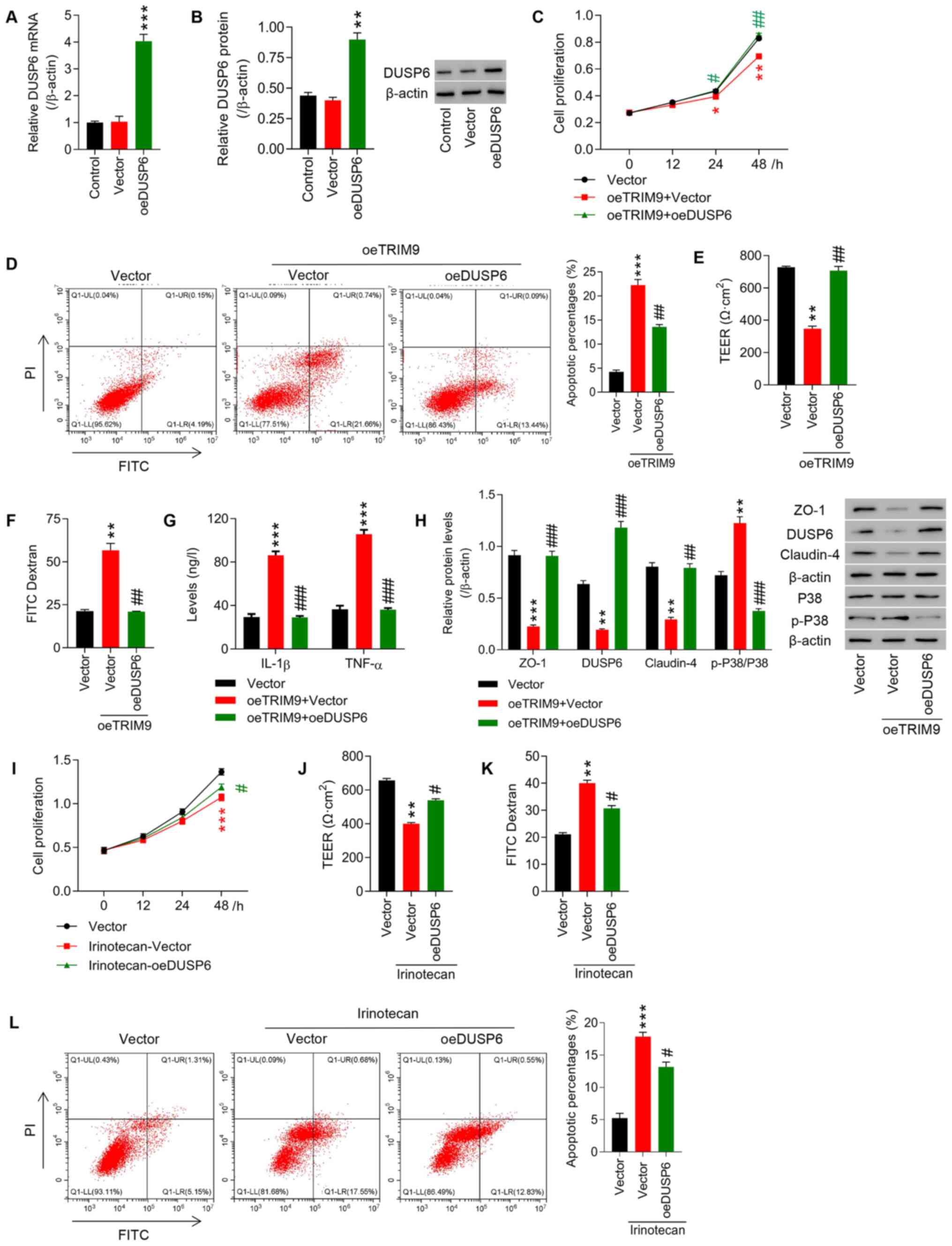
|
1
|
Sougiannis AT, VanderVeen BN, Davis JM,
Fan D and Murphy EA: Understanding chemotherapy-induced intestinal
mucositis and strategies to improve gut resilience. Am J Physiol
Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 320:G712–G719. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Wu ZQ, Han XD, Wang Y, Yuan KL, Jin ZM, Di
JZ, Yan J, Pan Y, Zhang P, Huang XY, et al: Interleukin-1 receptor
antagonist reduced apoptosis and attenuated intestinal mucositis in
a 5-fluorouracil chemotherapy model in mice. Cancer Chemother
Pharmacol. 68:87–96. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Murata Y, Hirose T, Yamaoka T, Shirai T,
Okuda K, Sugiyama T, Kusumoto S, Nakashima M, Ohmori T and Adachi
M: Phase II trial of the combination of carboplatin and irinotecan
in elderly patients with small-cell lung cancer. Eur J Cancer.
47:1336–1342. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Gao J, Gao J, Qian L, Wang X, Wu M, Zhang
Y, Ye H, Zhu S, Yu Y and Han W: Activation of p38-MAPK by
CXCL4/CXCR3 axis contributes to p53-dependent intestinal apoptosis
initiated by 5-fluorouracil. Cancer Biol Ther. 15:982–991. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Thomsen M and Vitetta L: Adjunctive
treatments for the prevention of chemotherapy- and
radiotherapy-induced mucositis. Integr Cancer Ther. 17:1027–1047.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Lu H, Qin J, Han N, Xie F, Gong L and Li
C: Banxia Xiexin decoction is effective to prevent and control
irinotecan-induced delayed diarrhea in recurrent small cell lung
cancer. Integr Cancer Ther. 17:1109–1114. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Paulík A, Nekvindová J and Filip S:
Irinotecan toxicity during treatment of metastatic colorectal
cancer: Focus on pharmacogenomics and personalized medicine.
Tumori. 106:87–94. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Ottaiano A, Scala S, Normanno N,
Napolitano M, Capozzi M, Rachiglio AM, Roma C, Trotta AM, D'Alterio
C, Portella L, et al: Cetuximab, irinotecan and fluorouracile in
fiRst-line treatment of immunologically-selected advanced
colorectal cancer patients: The CIFRA study protocol. BMC Cancer.
19:8992019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Spyropoulos BG: Interleukin-18 as a target
for modulation of irinotecan-induced intestinal toxicity: a step
towards a better therapeutic index? Commentary on Lima-Junior et
al., . Br J Pharmacol. 171:2335–2350, Br J Pharmacol 172:
4779-4781. 2015.
|
|
10
|
Ouyang M, Luo Z, Zhang W, Zhu D, Lu Y, Wu
J and Yao X: Protective effect of curcumin against
irinotecan-induced intestinal mucosal injury via attenuation of
NF-κB activation, oxidative stress and endoplasmic reticulum
stress. Int J Oncol. 54:1376–1386. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Wardill HR, Gibson RJ, Van Sebille YZ,
Secombe KR, Coller JK, White IA, Manavis J, Hutchinson MR,
Staikopoulos V, Logan RM, et al: Irinotecan-induced
gastrointestinal dysfunction and pain are mediated by common
TLR4-dependent mechanisms. Mol Cancer Ther. 15:1376–1386. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Hatakeyama S: TRIM family proteins: Roles
in autophagy, immunity, and carcinogenesis. Trends Biochem Sci.
42:297–311. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Jaworska AM, Wlodarczyk NA, Mackiewicz A
and Czerwinska P: The role of TRIM family proteins in the
regulation of cancer stem cell self-renewal. Stem Cells.
38:165–173. 2020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Esposito D, Koliopoulos MG and Rittinger
K: Structural determinants of TRIM protein function. Biochem Soc
Trans. 45:183–191. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Fiorentini F, Esposito D and Rittinger K:
Does it take two to tango? RING domain self-association and
activity in TRIM E3 ubiquitin ligases. Biochem Soc Trans.
48:2615–2624. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Tanji K, Kamitani T, Mori F, Kakita A,
Takahashi H and Wakabayashi K: TRIM9, a novel brain-specific E3
ubiquitin ligase, is repressed in the brain of Parkinson's disease
and dementia with Lewy bodies. Neurobiol Dis. 38:210–218. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Winkle CC, Olsen RH, Kim H, Moy SS, Song J
and Gupton SL: Trim9 deletion alters the morphogenesis of
developing and adult-born hippocampal neurons and impairs spatial
learning and memory. J Neurosci. 36:4940–4958. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Menon S, Boyer NP, Winkle CC, McClain LM,
Hanlin CC, Pandey D, Rothenfußer S, Taylor AM and Gupton SL: The E3
ubiquitin ligase TRIM9 is a filopodia off switch required for
netrin-dependent axon guidance. Dev Cell. 35:698–712. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zeng J, Wang Y, Luo Z, Chang LC, Yoo JS,
Yan H, Choi Y, Xie X, Deverman BE, Gradinaru V, et al:
TRIM9-mediated resolution of neuroinflammation confers
neuroprotection upon ischemic stroke in mice. Cell Rep.
27:549–560.e6. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Wu J, Gan Y, Li M, Chen L, Liang J, Zhuo
J, Luo H, Xu N, Wu X, Wu Q, et al: Patchouli alcohol attenuates
5-fluorouracil-induced intestinal mucositis via TLR2/MyD88/NF-κB
pathway and regulation of microbiota. Biomed Pharmacother.
124:1098832020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Tokarz DA, Heffelfinger AK, Jima DD,
Gerlach J, Shah RN, Rodriguez-Nunez I, Kortum AN, Fletcher AA,
Nordone SK, Law JM, et al: Disruption of Trim9 function abrogates
macrophage motility in vivo. J Leukoc Biol. 102:1371–1380. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Beaudry K, Langlois M-J, Montagne A,
Cagnol S, Carrier JC and Rivard N: Dual-specificity phosphatase 6
deletion protects the colonic epithelium against inflammation and
promotes both proliferation and tumorigenesis. J Cell Physiol.
234:6731–6745. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Noguchi T, Metz R, Chen L, Mattéi MG,
Carrasco D and Bravo R: Structure, mapping, and expression of erp,
a growth factor-inducible gene encoding a nontransmembrane protein
tyrosine phosphatase, and effect of ERP on cell growth. Mol Cell
Biol. 13:5195–5205. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Ruan JW, Statt S, Huang CT, Tsai YT, Kuo
CC, Chan HL, Liao YC, Tan TH and Kao CY: Dual-specificity
phosphatase 6 deficiency regulates gut microbiome and transcriptome
response against diet-induced obesity in mice. Nat Microbiol.
2:162202016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Muda M, Boschert U, Dickinson R, Martinou
JC, Martinou I, Camps M, Schlegel W and Arkinstall S: MKP-3, a
novel cytosolic protein-tyrosine phosphatase that exemplifies a new
class of mitogen-activated protein kinase phosphatase. J Biol Chem.
271:4319–4326. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Muda M, Theodosiou A, Rodrigues N,
Boschert U, Camps M, Gillieron C, Davies K, Ashworth A and
Arkinstall S: The dual specificity phosphatases M3/6 and MKP-3 are
highly selective for inactivation of distinct mitogen-activated
protein kinases. J Biol Chem. 271:27205–27208. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Groom LA, Sneddon AA, Alessi DR, Dowd S
and Keyse SM: Differential regulation of the MAP, SAP and RK/p38
kinases by Pyst1, a novel cytosolic dual-specificity phosphatase.
EMBO J. 15:3621–3632. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Caunt CJ and Keyse SM: Dual-specificity
MAP kinase phosphatases (MKPs): Shaping the outcome of MAP kinase
signalling. FEBS J. 280:489–504. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Wales S, Hashemi S, Blais A and McDermott
JC: Global MEF2 target gene analysis in cardiac and skeletal muscle
reveals novel regulation of DUSP6 by p38MAPK-MEF2 signaling.
Nucleic Acids Res. 42:11349–11362. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Hu X, Tang Z, Ma S, Yu Y, Chen X and Zang
G: Tripartite motif-containing protein 7 regulates hepatocellular
carcinoma cell proliferation via the DUSP6/p38 pathway. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 511:889–895. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Hsu SF, Lee YB, Lee YC, Chung AL, Apaya
MK, Shyur LF, Cheng CF, Ho FM and Meng TC: Dual specificity
phosphatase DUSP6 promotes endothelial inflammation through
inducible expression of ICAM-1. FEBS J. 285:1593–1610. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Quaroni A, Wands J, Trelstad RL and
Isselbacher KJ: Epithelioid cell cultures from rat small intestine.
Characterization by morphologic and immunologic criteria. J Cell
Biol. 80:248–265. 1979. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Ferrell N, Desai RR, Fleischman AJ, Roy S,
Humes HD and Fissell WH: A microfluidic bioreactor with integrated
transepithelial electrical resistance (TEER) measurement electrodes
for evaluation of renal epithelial cells. Biotechnol Bioeng.
107:707–716. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Wardill HR, Gibson RJ, Van Sebille YZ,
Secombe KR, Logan RM and Bowen JM: A novel in vitro platform for
the study of SN38-induced mucosal damage and the development of
Toll-like receptor 4-targeted therapeutic options. Exp Biol Med
(Maywood). 241:1386–1394. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Meddings JB, Sutherland LR, Byles NI and
Wallace JL: Sucrose: A novel permeability marker for gastroduodenal
disease. Gastroenterology. 104:1619–1626. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Liu Y, Wang G, Jiang X, Li W, Zhai C,
Shang F, Chen S, Zhao Z and Yu W: TRIM67 inhibits tumor
proliferation and metastasis by mediating MAPK11 in colorectal
cancer. J Cancer. 11:6025–6037. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Li Y, Xu S, Xu Q and Chen Y: Clostridium
difficile toxin B induces colonic inflammation through the
TRIM46/DUSP1/MAPKs and NF-κB signalling pathway. Artif Cells
Nanomed Biotechnol. 48:452–462. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Chen Q, Gao C, Wang M, Fei X and Zhao N:
TRIM18-regulated STAT3 signaling pathway via PTP1B promotes renal
epithelial-mesenchymal transition, inflammation, and fibrosis in
diabetic kidney disease. Front Physiol. 12:7095062021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Jeffrey MP, MacPherson CW, Mathieu O,
Tompkins TA and Green-Johnson JM: Secretome-mediated interactions
with intestinal epithelial cells: A role for secretome components
from Lactobacillus rhamnosus R0011 in the attenuation of
Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium secretome and
TNF-α-induced proinflammatory responses. J Immunol. 204:2523–2534.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Wu F, Huang Y, Dong F and Kwon JH:
Ulcerative colitis-associated long noncoding RNA, BC012900,
regulates intestinal epithelial cell apoptosis. Inflamm Bowel Dis.
22:782–795. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Wang R, Kwon IK, Singh N, Islam B, Liu K,
Sridhar S, Hofmann F and Browning DD: Type 2 cGMP-dependent protein
kinase regulates homeostasis by blocking c-Jun N-terminal kinase in
the colon epithelium. Cell Death Differ. 21:427–437. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Do LD, Gupton SL, Tanji K, Bastien J,
Brugière S, Couté Y, Quadrio I, Rogemond V, Fabien N, Desestret V,
et al: TRIM9 and TRIM67 are new targets in paraneoplastic
cerebellar degeneration. Cerebellum. 18:245–254. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Mishima C, Kagara N, Matsui S, Tanei T,
Naoi Y, Shimoda M, Shimomura A, Shimazu K, Kim SJ and Noguchi S:
Promoter methylation of TRIM9 as a marker for detection of
circulating tumor DNA in breast cancer patients. Springerplus.
4:6352015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Yang J, Wang Y, Liu H, Bi J and Lu Y:
C2-ceramide influences alveolar epithelial barrier function by
downregulating Zo-1, occludin and claudin-4 expression. Toxicol
Mech Methods. 27:293–297. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Hamada K, Kakigawa N, Sekine S, Shitara Y
and Horie T: Disruption of ZO-1/claudin-4 interaction in relation
to inflammatory responses in methotrexate-induced intestinal
mucositis. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 72:757–765. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Logan RM, Gibson RJ, Bowen JM, Stringer
AM, Sonis ST and Keefe DM: Characterisation of mucosal changes in
the alimentary tract following administration of irinotecan:
Implications for the pathobiology of mucositis. Cancer Chemother
Pharmacol. 62:33–41. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Koga Y, Tsurumaki H, Aoki-Saito H, Sato M,
Yatomi M, Takehara K and Hisada T: Roles of cyclic AMP response
element binding activation in the ERK1/2 and p38 MAPK signalling
pathway in central nervous system, cardiovascular system,
osteoclast differentiation and mucin and cytokine production. Int J
Mol Sci. 20:202019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Gallo S, Vitacolonna A, Bonzano A,
Comoglio P and Crepaldi T: ERK: A key player in the pathophysiology
of cardiac hypertrophy. Int J Mol Sci. 20:202019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Craige SM, Chen K, Blanton RM, Keaney JF
Jr and Kant S: JNK and cardiometabolic dysfunction. Biosci Rep.
39:392019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Xiang DC, Yang JY, Xu YJ, Zhang S, Li M,
Zhu C, Zhang CL and Liu D: Protective effect of Andrographolide on
5-Fu induced intestinal mucositis by regulating p38 MAPK signaling
pathway. Life Sci. 252:1176122020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Yamaguchi H, Igarashi M, Hirata A,
Tsuchiya H, Susa S, Tominaga M, Daimon M and Kato T:
Characterization of platelet-derived growth factor-induced p38
mitogen-activated protein kinase activation in vascular smooth
muscle cells. Eur J Clin Invest. 31:672–680. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Piya S, Kim JY, Bae J, Seol DW, Moon AR
and Kim TH: DUSP6 is a novel transcriptional target of p53 and
regulates p53-mediated apoptosis by modulating expression levels of
Bcl-2 family proteins. FEBS Lett. 586:4233–4240. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Bermudez O, Pagès G and Gimond C: The
dual-specificity MAP kinase phosphatases: Critical roles in
development and cancer. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 299:C189–C202.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Furukawa T, Fujisaki R, Yoshida Y, Kanai
N, Sunamura M, Abe T, Takeda K, Matsuno S and Horii A: Distinct
progression pathways involving the dysfunction of DUSP6/MKP-3 in
pancreatic intraepithelial neoplasia and intraductal
papillary-mucinous neoplasms of the pancreas. Mod Pathol.
18:1034–1042. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Chan DW, Liu VW, Tsao GS, Yao KM, Furukawa
T, Chan KK and Ngan HY: Loss of MKP3 mediated by oxidative stress
enhances tumorigenicity and chemoresistance of ovarian cancer
cells. Carcinogenesis. 29:1742–1750. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Okudela K, Yazawa T, Woo T, Sakaeda M,
Ishii J, Mitsui H, Shimoyamada H, Sato H, Tajiri M, Ogawa N, et al:
Down-regulation of DUSP6 expression in lung cancer: Its mechanism
and potential role in carcinogenesis. Am J Pathol. 175:867–881.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|