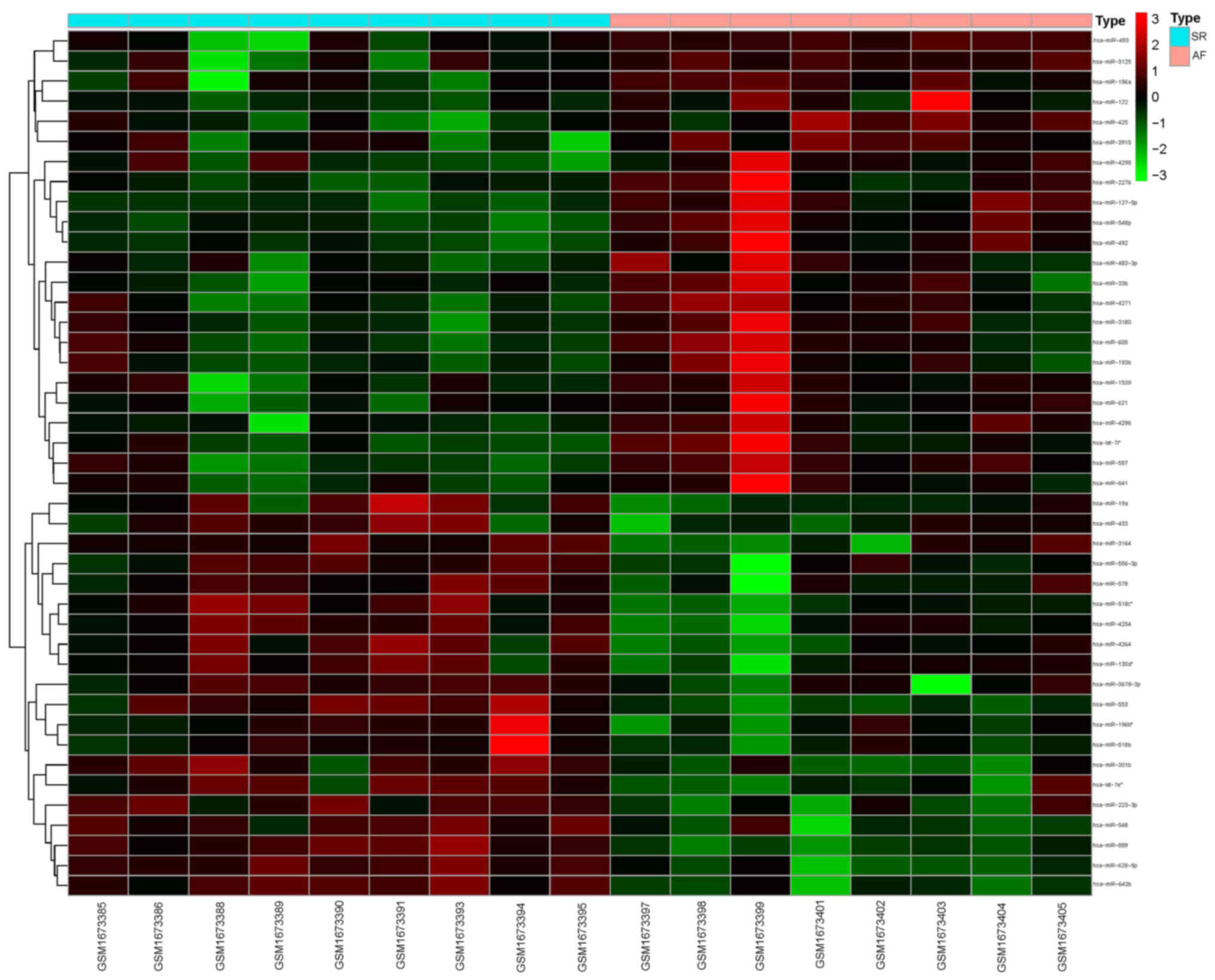
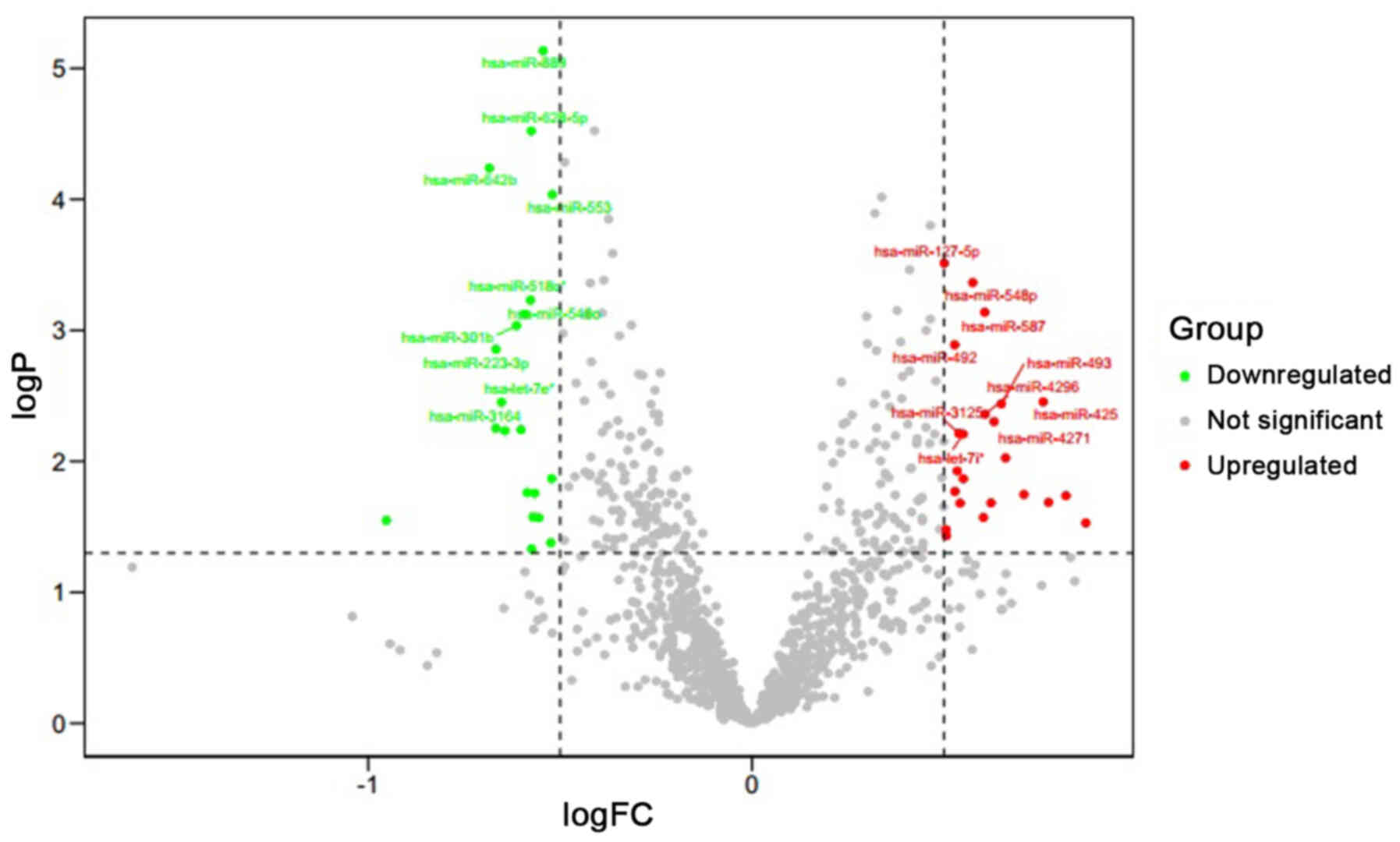
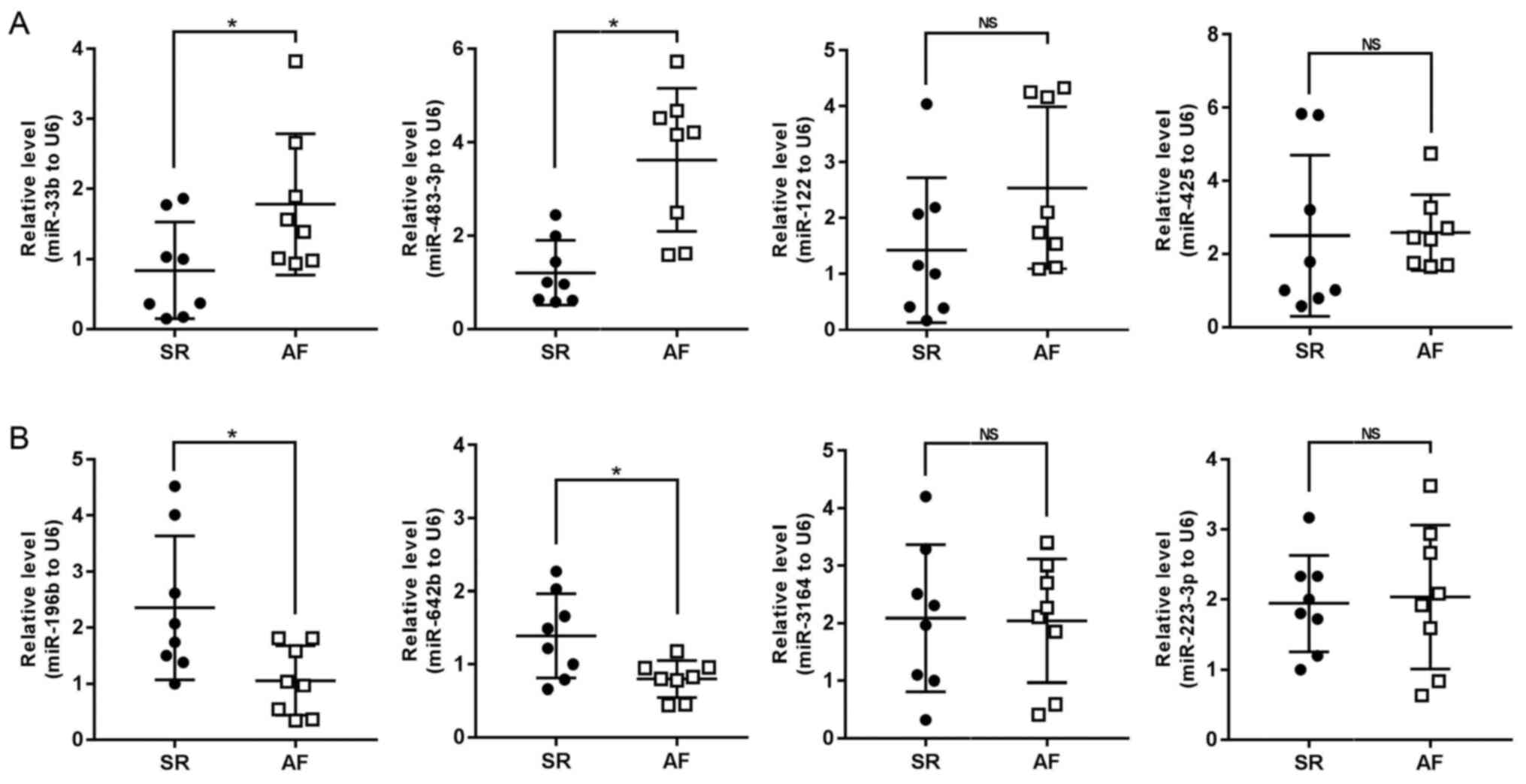
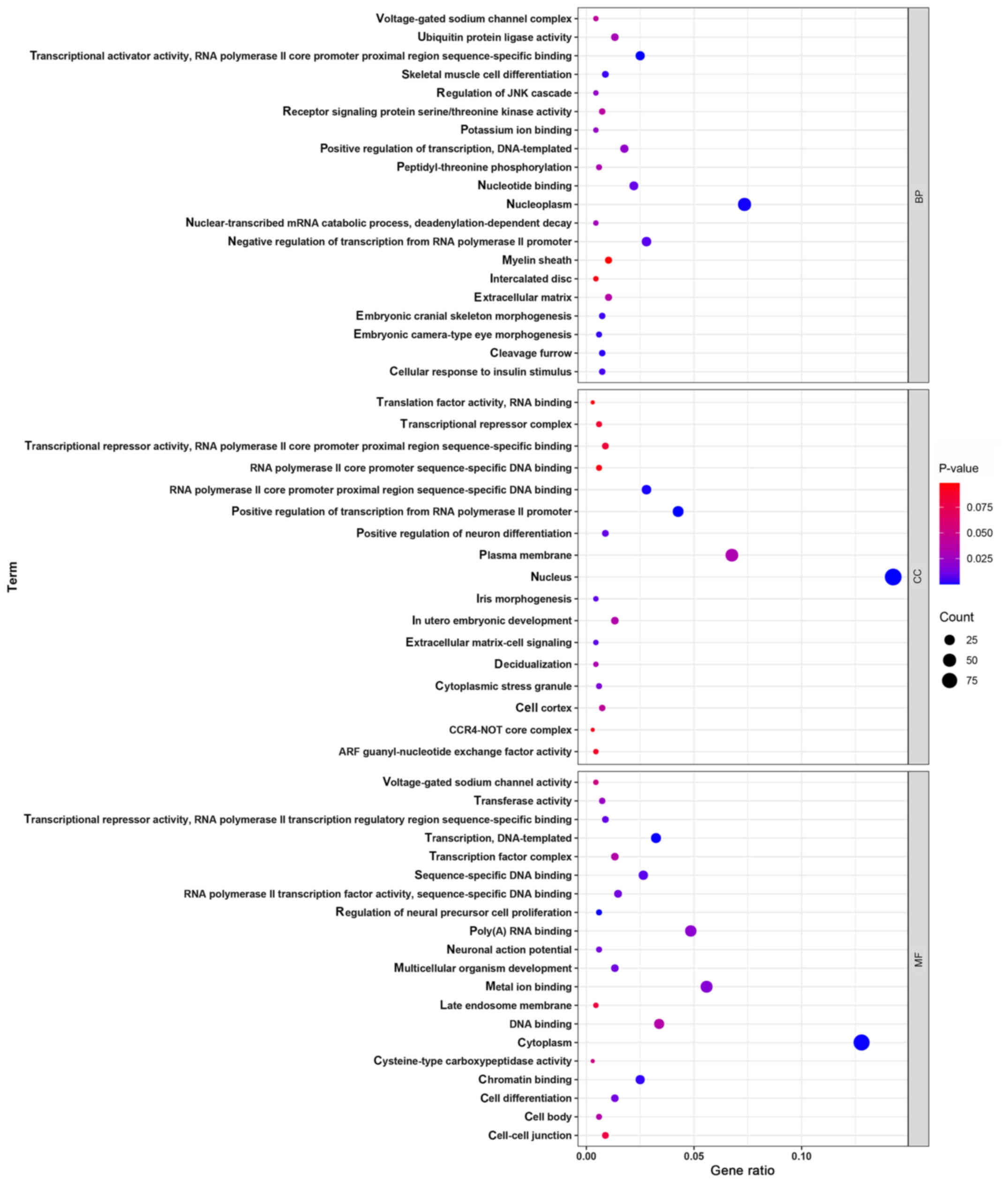
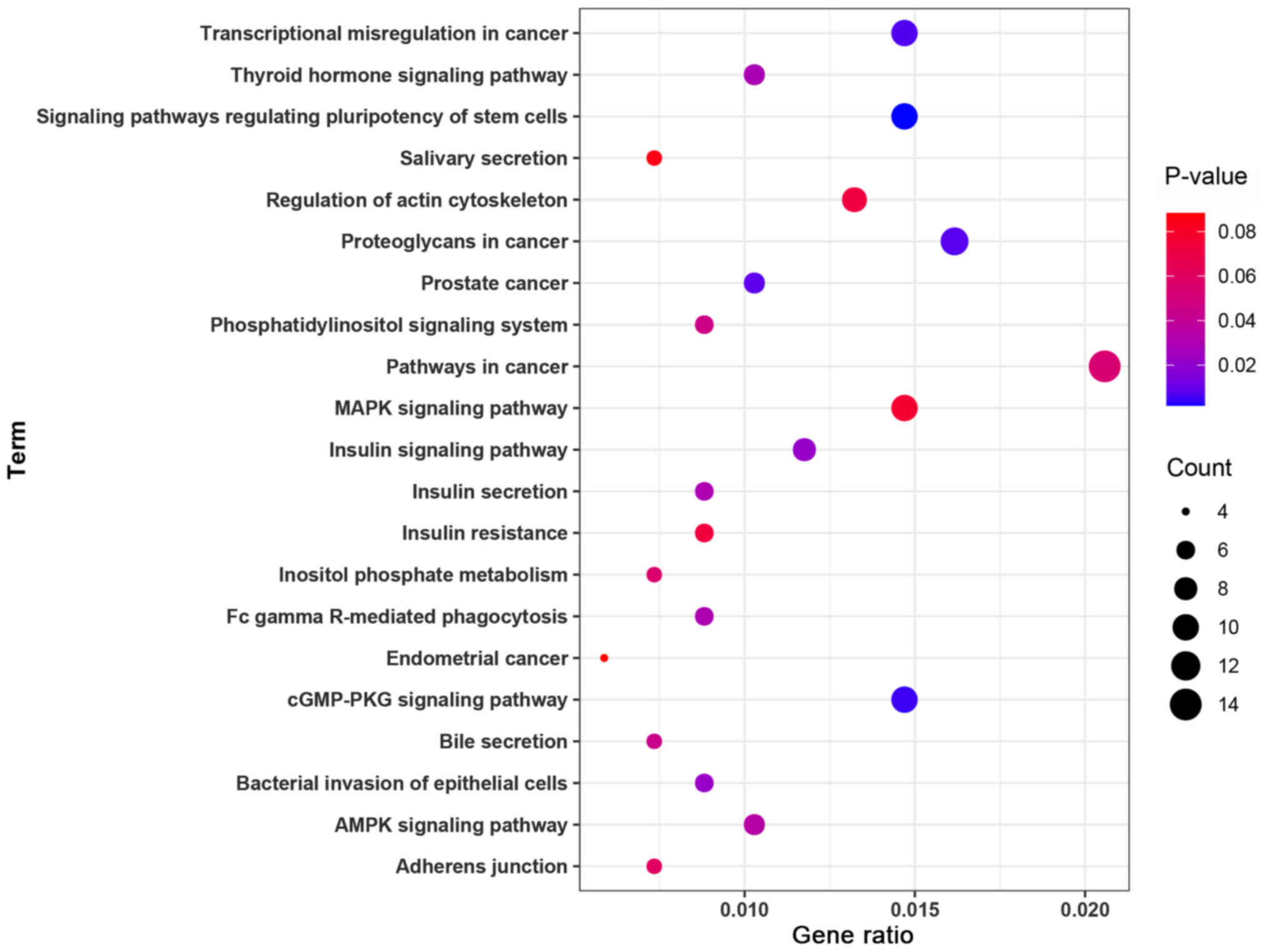
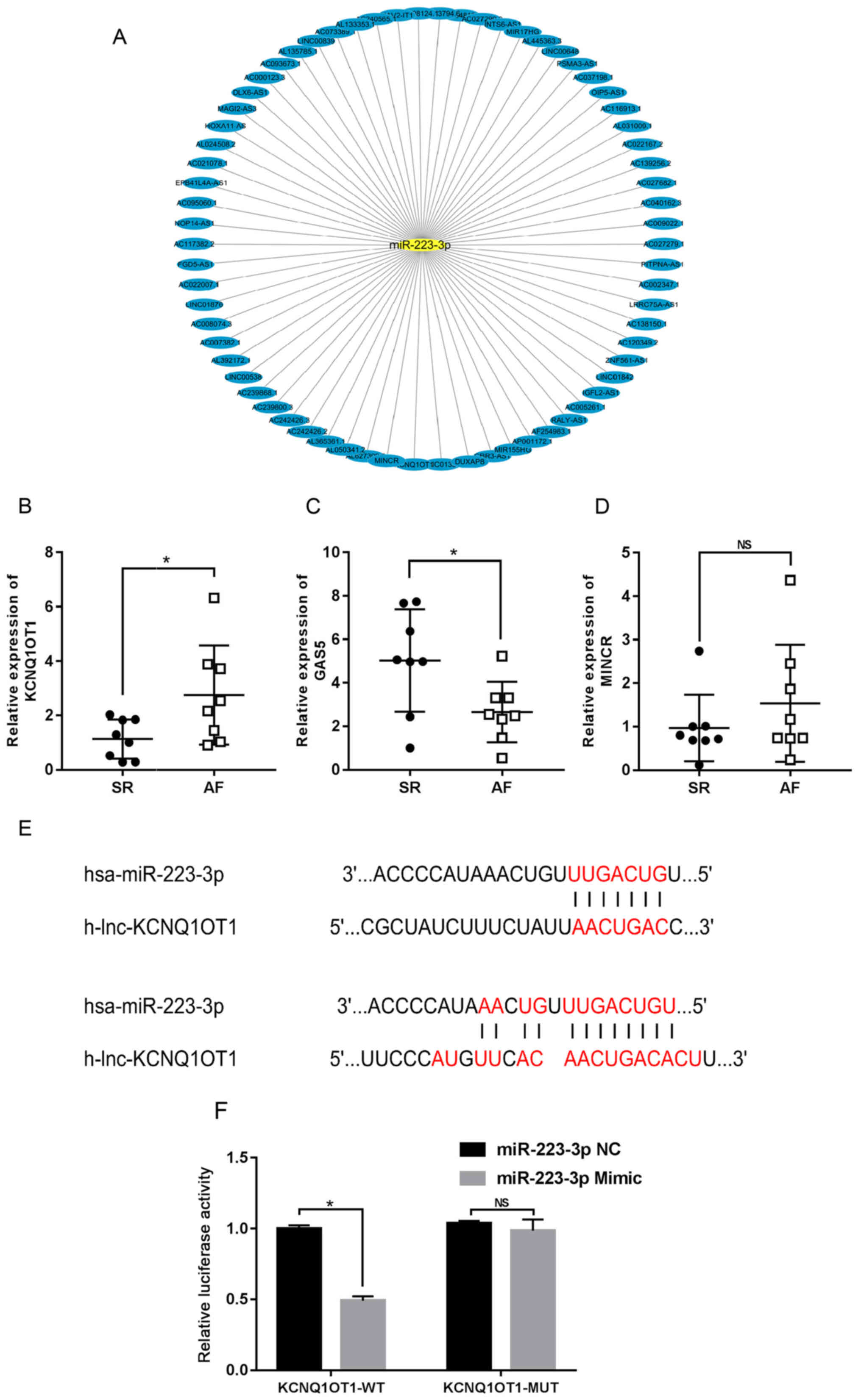
|
1
|
Chugh SS, Havmoeller R, Narayanan K, Singh
D, Rienstra M, Benjamin EJ, Gillum RF, Kim YH, McAnulty JH Jr,
Zheng ZJ, et al: Worldwide epidemiology of atrial fibrillation: A
Global Burden of Disease 2010 Study. Circulation. 129:837–847.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Zimetbaum P: Atrial Fibrillation. Ann
Intern Med. 166:ITC33–ITC48. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Nattel S and Harada M: Atrial remodeling
and atrial fibrillation: Recent advances and translational
perspectives. J Am Coll Cardiol. 63:2335–2345. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Ferrari R, Bertini M, Blomstrom-Lundqvist
C, Dobrev D, Kirchhof P, Pappone C, Ravens U, Tamargo J, Tavazzi L
and Vicedomini GG: An update on atrial fibrillation in 2014: From
pathophysiology to treatment. Int J Cardiol. 203:22–29. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Liu Y, Shi Q, Ma Y and Liu Q: The role of
immune cells in atrial fibrillation. J Mol Cell Cardiol.
123:198–208. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Vyas V, Hunter RJ, Longhi MP and Finlay
MC: Inflammation and adiposity: New frontiers in atrial
fibrillation. Europace. 22:1609–1618. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Arroyo AB, de Los Reyes-García AM,
Rivera-Caravaca JM, Valledor P, García-Barberá N, Roldán V, Vicente
V, Martínez C and González-Conejero R: miR-146a regulates
neutrophil extracellular trap formation that predicts adverse
cardiovascular events in patients with atrial fibrillation.
Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 38:892–902. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Farazi TA, Hoell JI, Morozov P and Tuschl
T: MicroRNAs in human cancer. Adv Exp Med Biol. 774:1–20. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Zhao Y, Yuan Y and Qiu C: Underexpression
of CACNA1C caused by overexpression of microRNA-29a underlies the
pathogenesis of atrial fibrillation. Med Sci Monit. 22:2175–2181.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Cañón S, Caballero R, Herraiz-Martínez A,
Pérez-Hernández M, López B, Atienza F, Jalife J, Hove-Madsen L,
Delpón E and Bernad A: miR-208b upregulation interferes with
calcium handling in HL-1 atrial myocytes: Implications in human
chronic atrial fibrillation. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 99:162–173. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Lv X, Li J, Hu Y, Wang S, Yang C, Li C and
Zhong G: Overexpression of miR-27b-3p targeting Wnt3a regulates the
signaling pathway of Wnt/β-catenin and attenuates atrial fibrosis
in rats with atrial fibrillation. Oxid Med Cell Longev.
2019:57037642019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Kong F, Jin J, Lv X, Han Y, Liang X, Gao Y
and Duan X: Long noncoding RNA RMRP upregulation aggravates
myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury by sponging miR-206 to
target ATG3 expression. Biomed Pharmacother. 109:716–725. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Salmena L, Poliseno L, Tay Y, Kats L and
Pandolfi PP: A ceRNA hypothesis: the Rosetta Stone of a hidden RNA
language? Cell. 146:353–358. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Lou W, Ding B and Fu P: Pseudogene-derived
lncRNAs and their miRNA sponging mechanism in human cancer. Front
Cell Dev Biol. 8:852020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Wang LY, Shen H, Yang Q, Min J, Wang Q, Xi
W, Yin L, Le SG, Zhang YF, Xiao J, et al: LncRNA-LINC00472
contributes to the pathogenesis of atrial fibrillation (Af) by
reducing expression of JP2 and RyR2 via miR-24. Biomed
Pharmacother. 120:1093642019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Kirchhof P, Benussi S, Kotecha D, Ahlsson
A, Atar D, Casadei B, Castella M, Diener HC, Heidbuchel H, Hendriks
J, et al ESC Scientific Document Group, : 2016 ESC Guidelines for
the management of atrial fibrillation developed in collaboration
with EACTS. Eur Heart J. 37:2893–2962. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Gene Ontology Consortium, . The Gene
Ontology (GO) project in 2006. Nucleic Acids Res. 34:D322–D326.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Kanehisa M, Sato Y, Kawashima M, Furumichi
M and Tanabe M: KEGG as a reference resource for gene and protein
annotation. Nucleic Acids Res. 44(D1): D457–D462. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Morishima M, Iwata E, Nakada C, Tsukamoto
Y, Takanari H, Miyamoto S, Moriyama M and Ono K: Atrial
Fibrillation-Mediated Upregulation of miR-30d Regulates Myocardial
Electrical Remodeling of the G-Protein-Gated K(+) Channel, IK.ACh.
Circ J. 80:1346–1355. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Zhang H, Yang G, Zhong N, Shan J, Li X, Wu
Y, Xu Y and Yuan Y: Possible key microRNAs and corresponding
molecular mechanisms for atrial fibrillation. Anatol J Cardiol.
23:324–333. 2020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Hu J, Wang X, Cui X, Kuang W, Li D and
Wang J: Quercetin prevents isoprenaline-induced myocardial fibrosis
by promoting autophagy via regulating miR-223-3p/FOXO3. Cell Cycle.
20:1253–1269. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Li Z, Wang X, Wang W, Du J, Wei J, Zhang
Y, Wang J and Hou Y: Altered long non-coding RNA expression profile
in rabbit atria with atrial fibrillation: TCONS_00075467 modulates
atrial electrical remodeling by sponging miR-328 to regulate
CACNA1C. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 108:73–85. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Ji Q, Xu X, Song Q, Xu Y, Tai Y, Goodman
SB, Bi W, Xu M, Jiao S, Maloney WJ, et al: miR-223-3p inhibits
human osteosarcoma metastasis and progression by directly targeting
CDH6. Mol Ther. 26:1299–1312. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Matsuzaki J and Ochiya T: Extracellular
microRNAs and oxidative stress in liver injury: A systematic mini
review. J Clin Biochem Nutr. 63:6–11. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Boxberger N, Hecker M and Zettl UK:
Dysregulation of Inflammasome Priming and Activation by MicroRNAs
in Human Immune-Mediated Diseases. J Immunol. 202:2177–2187. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Qin D, Wang X, Li Y, Yang L, Wang R, Peng
J, Essandoh K, Mu X, Peng T, Han Q, et al: MicroRNA-223-5p and −3p
Cooperatively Suppress Necroptosis in Ischemic/Reperfused Hearts. J
Biol Chem. 291:20247–20259. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Singh S, de Ronde MWJ, Kok MGM, Beijk MA,
De Winter RJ, van der Wal AC, Sondermeijer BM, Meijers JCM,
Creemers EE and Pinto-Sietsma SJ: MiR-223-3p and miR-122-5p as
circulating biomarkers for plaque instability. Open Heart.
7:e0012232020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Hardie DG: The AMP-activated protein
kinase pathway--new players upstream and downstream. J Cell Sci.
117:5479–5487. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Chakraborty P, Nattel S and Nanthakumar K:
Linking cellular energy state to atrial fibrillation pathogenesis:
Potential role of adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase.
Heart Rhythm. 17:1398–1404. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Harada M, Tadevosyan A, Qi X, Xiao J, Liu
T, Voigt N, Karck M, Kamler M, Kodama I, Murohara T, et al: Atrial
Fibrillation Activates AMP-Dependent Protein Kinase and its
Regulation of Cellular Calcium Handling: Potential Role in
Metabolic Adaptation and Prevention of Progression. J Am Coll
Cardiol. 66:47–58. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Zhang Y, Zhang S, Liu Z, Zhao X, Yuan Y,
Sheng L and Li Y: Correction to: Resveratrol prevents atrial
fibrillation by inhibiting atrial structural and metabolic
remodeling in collagen-induced arthritis rats. Naunyn Schmiedebergs
Arch Pharmacol. 393:927–928. 2020.Erratum for: Naunyn Schmiedebergs
Arch Pharmacol 391: 1179-1190, 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Abe I, Teshima Y, Kondo H, Kaku H, Kira S,
Ikebe Y, Saito S, Fukui A, Shinohara T, Yufu K, et al: Association
of fibrotic remodeling and cytokines/chemokines content in
epicardial adipose tissue with atrial myocardial fibrosis in
patients with atrial fibrillation. Heart Rhythm. 15:1717–1727.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Maesen B, Nijs J, Maessen J, Allessie M
and Schotten U: Post-operative atrial fibrillation: A maze of
mechanisms. Europace. 14:159–174. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Liu L, Gan S, Li B, Ge X, Yu H and Zhou H:
Fisetin Alleviates Atrial Inflammation, Remodeling, and
Vulnerability to Atrial Fibrillation after Myocardial Infarction.
Int Heart J. 60:1398–1406. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Kanduri C: Kcnq1ot1: A chromatin
regulatory RNA. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 22:343–350. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Jiang Y, Du W, Chu Q, Qin Y, Tuguzbaeva G,
Wang H, Li A, Li G, Li Y, Chai L, et al: Downregulation of Long
Non-Coding RNA Kcnq1ot1: An Important Mechanism of Arsenic
Trioxide-Induced Long QT Syndrome. Cell Physiol Biochem.
45:192–202. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Li X, Dai Y, Yan S, Shi Y, Han B, Li J,
Cha L and Mu J: Down-regulation of lncRNA KCNQ1OT1 protects against
myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury following acute myocardial
infarction. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 491:1026–1033. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Shen C, Kong B, Liu Y, Xiong L, Shuai W,
Wang G, Quan D and Huang H: YY1-induced upregulation of lncRNA
KCNQ1OT1 regulates angiotensin II-induced atrial fibrillation by
modulating miR-384b/CACNA1C axis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
505:134–140. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Yang F, Qin Y, Wang Y, Li A, Lv J, Sun X,
Che H, Han T, Meng S, Bai Y, et al: LncRNA KCNQ1OT1 Mediates
Pyroptosis in Diabetic Cardiomyopathy. Cell Physiol Biochem.
50:1230–1244. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Wang YN, Shan K, Yao MD, Yao J, Wang JJ,
Li X, Liu B, Zhang YY, Ji Y, Jiang Q, et al: Long Noncoding
RNA-GAS5: A Novel Regulator of Hypertension-Induced Vascular
Remodeling. Hypertension. 68:736–748. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Lu J, Xu FQ, Guo JJ, Lin PL, Meng Z, Hu
LG, Li J, Li D, Lu XH and An Y: Long noncoding RNA GAS5 attenuates
cardiac fibroblast proliferation in atrial fibrillation via
repressing ALK5. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 23:7605–7610.
2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Zhou XH, Chai HX, Bai M and Zhang Z:
LncRNA-GAS5 regulates PDCD4 expression and mediates myocardial
infarction-induced cardiomyocytes apoptosis via targeting miR-21.
Cell Cycle. 19:1363–1377. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Dong X, Kong C, Liu X, Bi J, Li Z, Li Z,
Zhu Y and Zhang Z: GAS5 functions as a ceRNA to regulate hZIP1
expression by sponging miR-223 in clear cell renal cell carcinoma.
Am J Cancer Res. 8:1414–1426. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Yao J, Shi Z, Ma X, Xu D and Ming G:
lncRNA GAS5/miR-223/NAMPT axis modulates the cell proliferation and
senescence of endothelial progenitor cells through PI3K/AKT
signaling. J Cell Biochem. 120:14518–14530. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Wang JG, Meng X, Han J, Li Y, Luo TG, Wang
J, Xin M and Xi JZ: Differential expressions of miRNAs in patients
with nonvalvular atrial fibrillation. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi.
92:1816–1819. 2012.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Wang S, Min J, Yu Y, Yin L, Wang Q, Shen
H, Yang J, Zhang P, Xiao J and Wang Z: Differentially expressed
miRNAs in circulating exosomes between atrial fibrillation and
sinus rhythm. J Thorac Dis. 11:4337–4348. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|