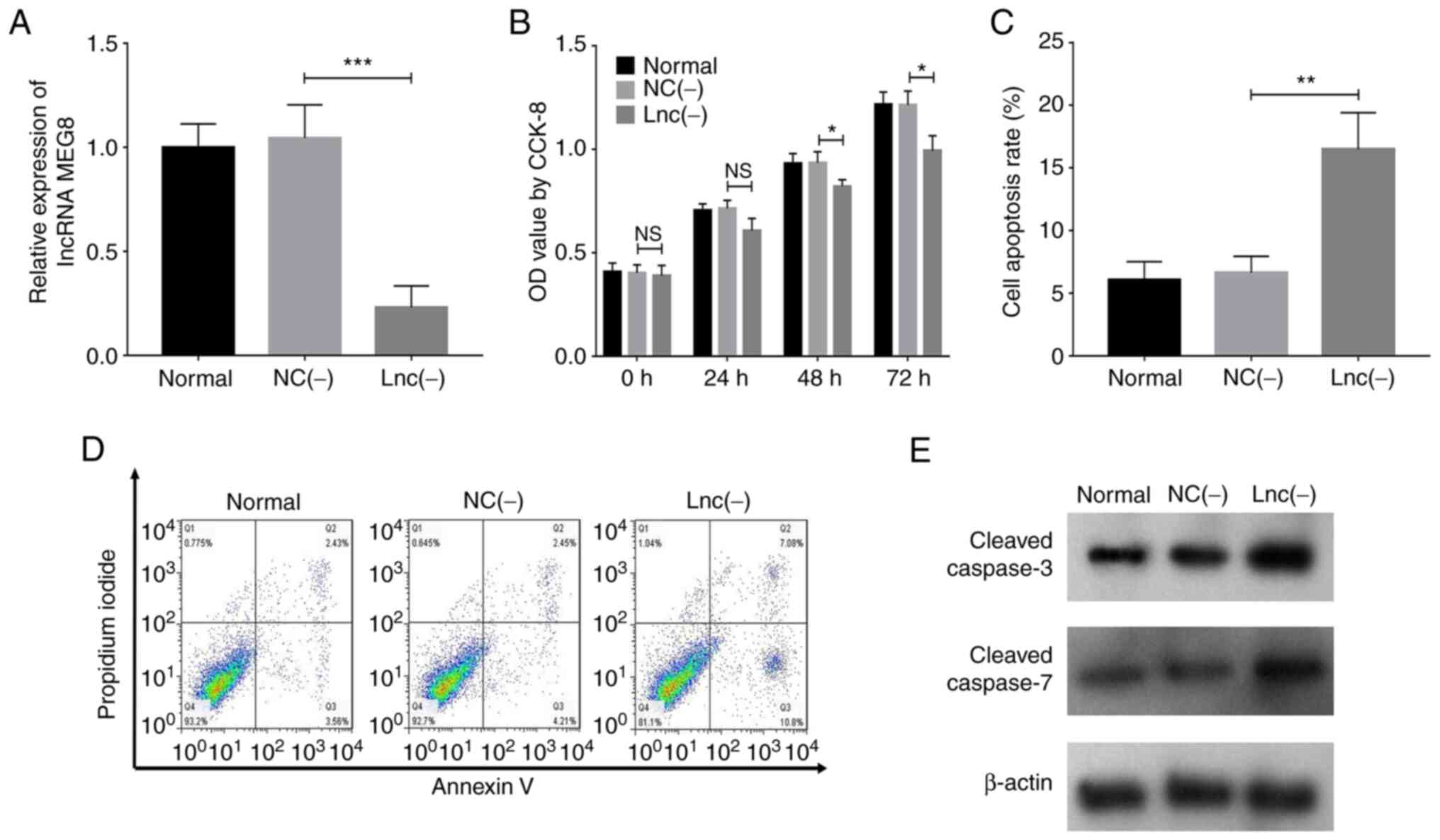
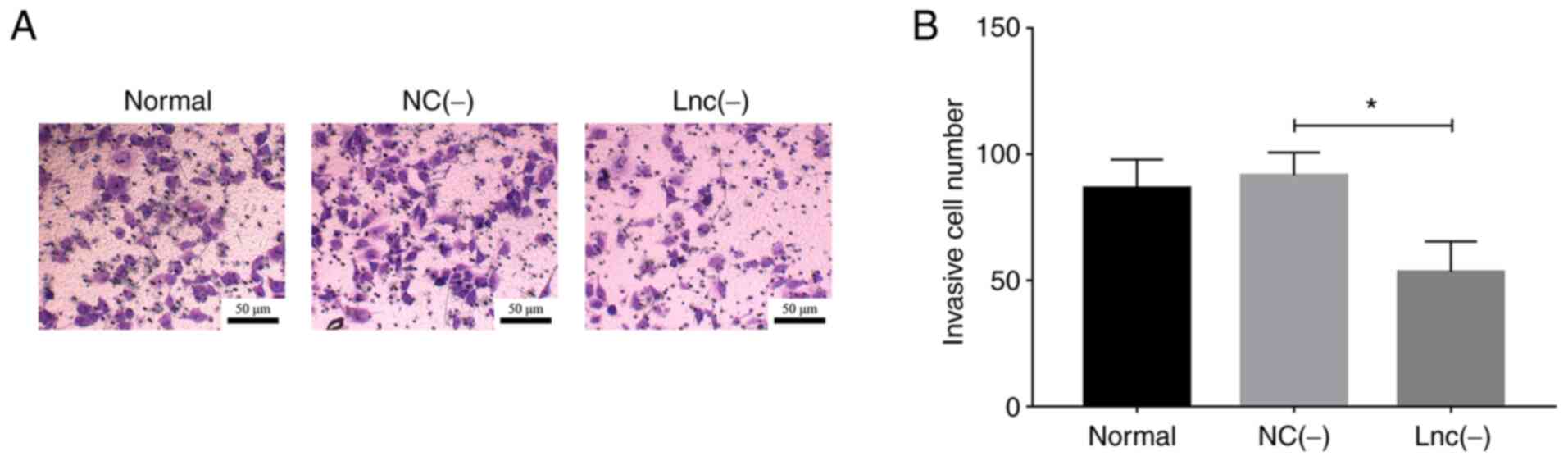
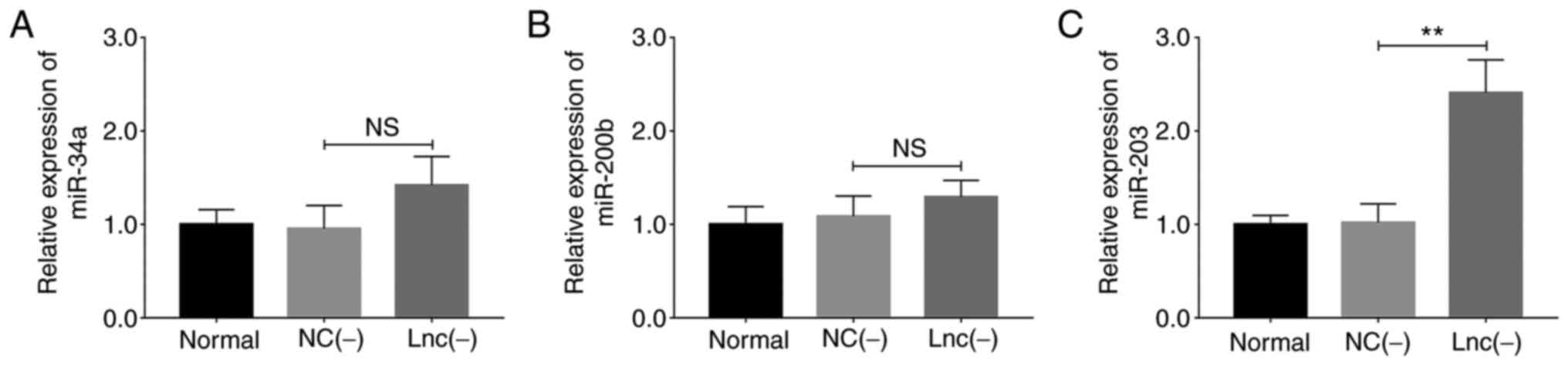
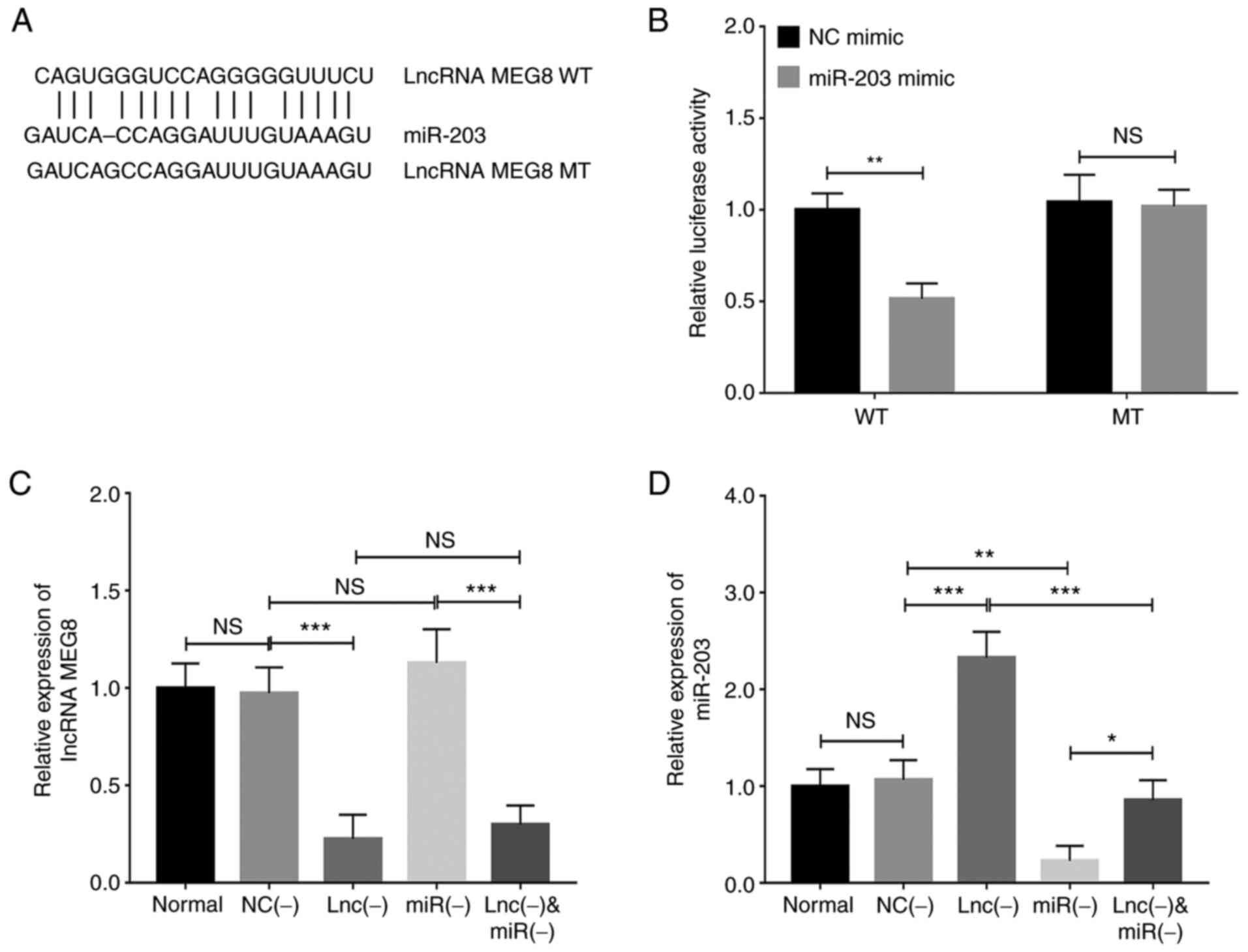
|
1
|
DeHart A and Richter G: Hemangioma: Recent
advances. F1000Res. 8:F1000 Faculty Rev-1926. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Li X, Chen B, Chi D, Zhang Y and Jiang W:
lncRNA CASC9 regulates cell migration and invasion in hemangioma
endothelial cells by targeting miR-125a-3p/Nrg1. Onco Targets Ther.
12:423–432. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Valdebran M and Wine Lee L:
Hemangioma-related syndromes. Curr Opin Pediatr. 32:498–505. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Chi Y, Wang D, Wang J, Yu W and Yang J:
Long non-coding RNA in the pathogenesis of cancers. Cells.
8:10152019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Gutschner T and Diederichs S: The
hallmarks of cancer: A long non-coding RNA point of view. RNA Biol.
9:703–719. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Lin H, Wang J, Wang T, Wu J, Wang P, Huo
X, Zhang J, Pan H and Fan Y: The LncRNA MIR503HG/miR-224-5p/TUSC3
signaling cascade suppresses gastric cancer development via
modulating ATF6 Branch of unfolded protein response. Front Oncol.
11:7085012021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Cen X, Huang Y, Lu Z, Shao W, Zhuo C, Bao
C, Feng S, Wei C, Tang X, Cen L, et al: LncRNA IGFL2-AS1 promotes
the proliferation, migration, and invasion of colon cancer cells
and is associated with patient prognosis. Cancer Manag Res.
13:5957–5968. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Lou J, Yan W, Li QY, Zhu AK, Tan BQ, Dong
R, Zou XZ and Liu T: LncRNA MEG8 plays an oncogenic role in
hepatocellular carcinoma progression through
miR-367-3p/14-3-3ζ/TGFβR1 axis. Neoplasma. 68:273–282. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Liu Y, Li L, Shang P and Song X: LncRNA
MEG8 promotes tumor progression of non-small cell lung cancer via
regulating miR-107/CDK6 axis. Anticancer Drugs. 31:1065–1073. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Terashima M, Ishimura A, Wanna-Udom S and
Suzuki T: MEG8 long noncoding RNA contributes to epigenetic
progression of the epithelial-mesenchymal transition of lung and
pancreatic cancer cells. J Biol Chem. 293:18016–18030. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Guo K, Qi D and Huang B: LncRNA MEG8
promotes NSCLC progression by modulating the
miR-15a-5p-miR-15b-5p/PSAT1 axis. Cancer Cell Int. 21:842021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Chen T, Lin H, Chen X, Li G, Zhao Y, Zheng
L, Shi Z, Zhang K, Hong W and Han T: LncRNA Meg8 suppresses
activation of hepatic stellate cells and epithelial-mesenchymal
transition of hepatocytes via the Notch pathway. Biochem Biophys
Res Commun. 521:921–927. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Ji Y, Chen S, Li K, Li L, Xu C and Xiang
B: Signaling pathways in the development of infantile hemangioma. J
Hematol Oncol. 7:132014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Khan ZA, Melero-Martin JM, Wu X, Paruchuri
S, Boscolo E, Mulliken JB and Bischoff J: Endothelial progenitor
cells from infantile hemangioma and umbilical cord blood display
unique cellular responses to endostatin. Blood. 108:915–921. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Zhang H, Wei T, Johnson A, Sun R, Richter
G and Strub GM: NOTCH pathway activation in infantile hemangiomas.
J Vasc Surg Venous Lymphat Disord. 9:489–496. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Liu X, Lv R, Zhang L, Xu G, Bi J, Gao F,
Zhang J, Xue F, Wang F, Wu Y, et al: Long noncoding RNA expression
profile of infantile hemangioma identified by microarray analysis.
Tumour Biol. Oct 5–2016.(Epub ahead of print). doi:
10.1007/s13277-016-5434-y. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Zhang B, Dong Y and Zhao Z: LncRNA MEG8
regulates vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation, migration and
apoptosis by targeting PPARα. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
510:171–176. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Yuan SM, Guo Y, Xu Y, Wang M, Chen HN and
Shen WM: The adipogenesis in infantile hemangioma and the
expression of adipogenic-related genes. Int J Clin Exp Pathol.
10:11596–11602. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Fang Y and Fullwood MJ: Roles, functions,
and mechanisms of long non-coding RNAs in cancer. Genomics
Proteomics Bioinformatics. 14:42–54. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Eich ML, Athar M, Ferguson JE III and
Varambally S: EZH2-targeted therapies in cancer: Hype or a reality.
Cancer Res. 80:5449–5458. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Carmeliet P and Jain RK: Molecular
mechanisms and clinical applications of angiogenesis. Nature.
473:298–307. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
He S, Zhang G, Dong H, Ma M and Sun Q:
MiR-203 facilitates tumor growth and metastasis by targeting
fibroblast growth factor 2 in breast cancer. Onco Targets Ther.
9:6203–6210. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Wang B, Li X, Zhao G, Yan H, Dong P,
Watari H, Sims M, Li W, Pfeffer LM, Guo Y and Yue J: MiR-203
inhibits ovarian tumor metastasis by targeting BIRC5 and
attenuating the TGFβ pathway. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 37:2352018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|