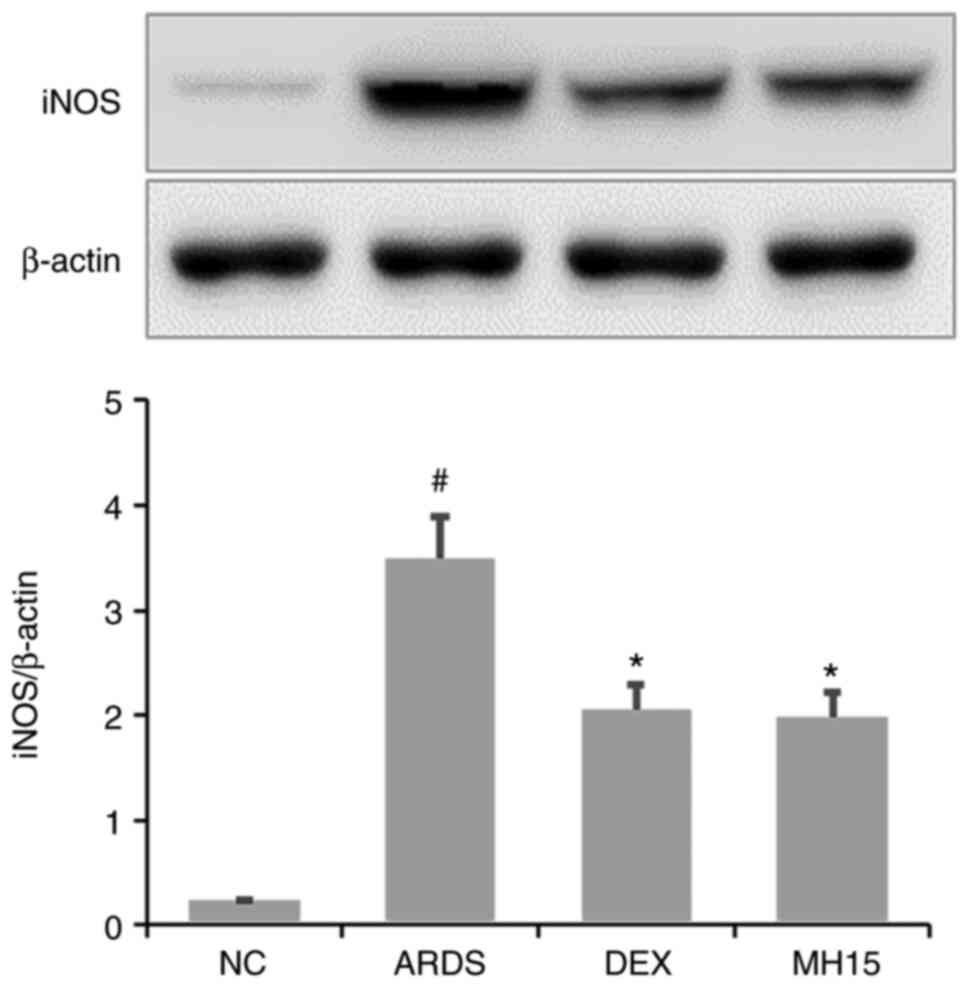
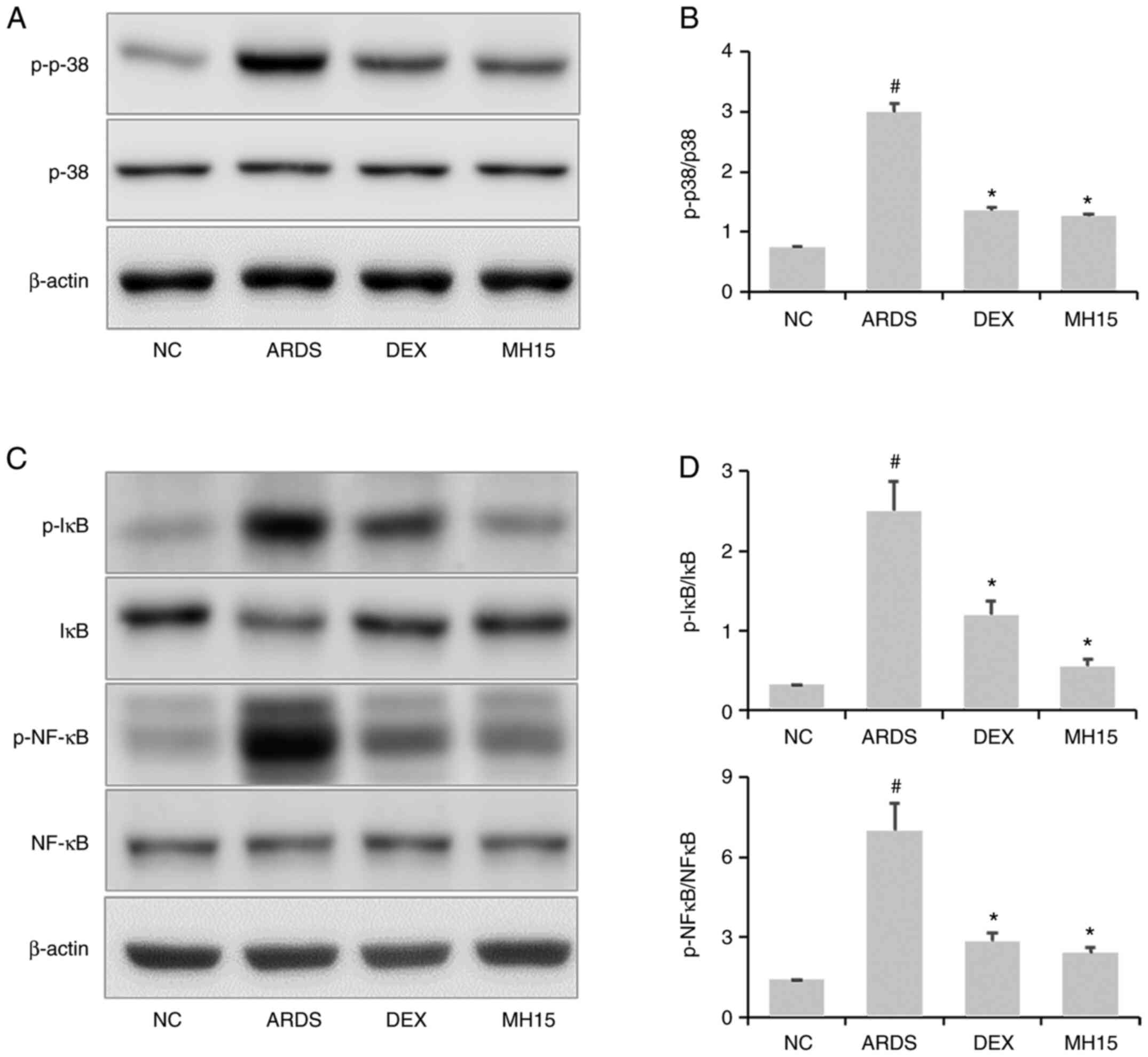
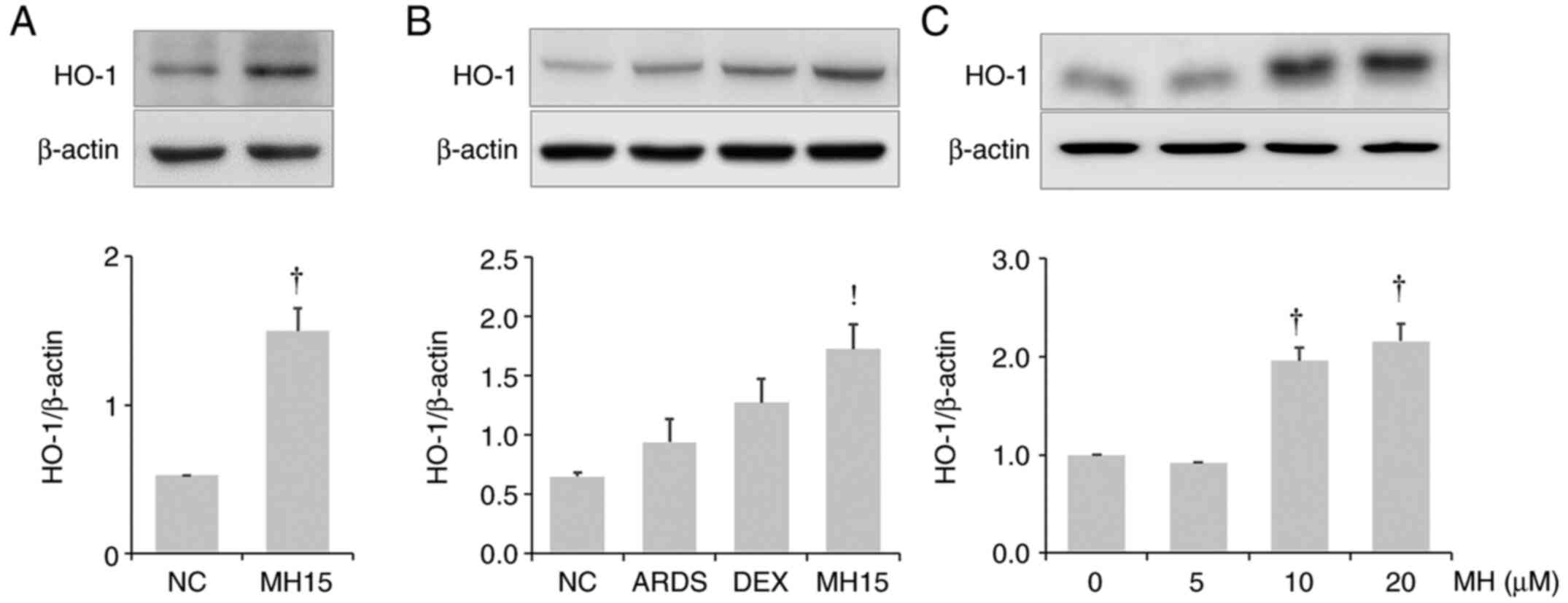
|
1
|
Spadaro S, Park M, Turrini C, Tunstall T,
Thwaites R, Mauri T, Ragazzi R, Ruggeri P, Hansel TT, Caramori G
and Volta CA: Biomarkers for Acute Respiratory Distress syndrome
and prospects for personalised medicine. J Inflamm (Lond).
16:12019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Bhargava M and Wendt CH: Biomarkers in
acute lung injury. Transl Res. 159:205–217. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Barnett N and Ware LB: Biomarkers in acute
lung injury-marking forward progress. Crit Care Clin. 27:661–683.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Kellner M, Noonepalle S, Lu Q, Srivastava
A, Zemskov E and Black SM: ROS signaling in the pathogenesis of
acute lung Injury (ALI) and acute respiratory distress syndrome
(ARDS). Adv Exp Med Biol. 967:105–137. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Lee JW, Chun W, Lee HJ, Min JH, Kim SM,
Seo JY, Ahn KS and Oh SR: The role of macrophages in the
development of acute and chronic inflammatory lung diseases. Cells.
10:8972021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Lee JW, Chun W, Kwon OK, Park HA, Lim Y,
Lee JH, Kim DY, Kim JH, Lee HK, Ryu HW, et al:
3,4,5-Trihydroxycinnamic acid attenuates lipopolysaccharide
(LPS)-induced acute lung injury via downregulating inflammatory
molecules and upregulating HO-1/AMPK activation. Int
Immunopharmacol. 64:123–130. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Lee JW, Park HA, Kwon OK, Park JW, Lee G,
Lee HJ, Lee SJ, Oh SR and Ahn KS: NPS 2143, a selective
calcium-sensing receptor antagonist inhibits
lipopolysaccharide-induced pulmonary inflammation. Mol Immunol.
90:150–157. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Liu B, Cheng Y, Wu Y, Zheng X, Li X, Yang
G, He T, Li S and Shen F: Emodin improves alveolar hypercoagulation
and inhibits pulmonary inflammation in LPS-provoked ARDS in mice
via NF-κB inactivation. Int Immunopharmacol. 88:1070202020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Frank JA, Pittet JF, Lee H, Godzich M and
Matthay MA: High tidal volume ventilation induces NOS2 and impairs
cAMP- dependent air space fluid clearance. Am J Physiol Lung Cell
Mol Physiol. 284:L791–L798. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Xiao Q, Cui Y, Zhao Y, Liu L, Wang H and
Yang L: Orientin relieves lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung
injury in mice: The involvement of its anti-inflammatory and
anti-oxidant properties. Int Immunopharmacol. 90:1071892021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Lee SA, Lee SH, Kim JY and Lee WS: Effects
of glycyrrhizin on lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury in
a mouse model. J Thorac Dis. 11:1287–1302. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Moine P, McIntyre R, Schwartz MD, Kaneko
D, Shenkar R, Le Tulzo Y, Moore EE and Abraham E: NF-kappaB
regulatory mechanisms in alveolar macrophages from patients with
acute respiratory distress syndrome. Shock. 13:85–91. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zhong WT, Wu YC, Xie XX, Zhou X, Wei MM,
Soromou LW, Ci XX and Wang DC: Phillyrin attenuates LPS-induced
pulmonary inflammation via suppression of MAPK and NF-κB activation
in acute lung injury mice. Fitoterapia. 90:132–139. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Guo S, Jiang K, Wu H, Yang C, Yang Y, Yang
J, Zhao G and Deng G: Magnoflorine ameliorates
lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury via suppressing NF-κB
and MAPK activation. Front Pharmacol. 9:9822018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Lei J, Wei Y, Song P, Li Y, Zhang T, Feng
Q and Xu G: Cordycepin inhibits LPS-induced acute lung injury by
inhibiting inflammation and oxidative stress. Eur J Pharmacol.
818:110–114. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Pooladanda V, Thatikonda S, Bale S,
Pattnaik B, Sigalapalli DK, Bathini NB, Singh SB and Godugu C:
Nimbolide protects against endotoxin-induced acute respiratory
distress syndrome by inhibiting TNF-α mediated NF-κB and HDAC-3
nuclear translocation. Cell Death Dis. 10:812019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Kwon YS and Kim CM: Antioxidant
constituents from the stem of Sorghum bicolor. Arch Pharm Res.
26:535–539. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Vo VA, Lee JW, Shin SY, Kwon JH, Lee HJ,
Kim SS, Kwon YS and Chun W: Methyl p-Hydroxycinnamate suppresses
lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory responses through akt
phosphorylation in RAW264.7 cells. Biomol Ther (Seoul). 22:10–16.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Park JW, Ryu HW, Ahn HI, Min JH, Kim SM,
Kim MG, Kwon OK, Hwang D, Kim SY, Choi S, et al: The
anti-inflammatory effect of trichilia martiana C. DC. in the
lipopolysaccharide-stimulated inflammatory response in macrophages
and airway epithelial cells and in LPS-challenged mice. J Microbiol
Biotechnol. 30:1614–1625. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Lee JW, Ryu HW, Lee SU, Kim MG, Kwon OK,
Kim MO, Oh TK, Lee JK, Kim TY, Lee SW, et al: Pistacia
weinmannifolia ameliorates cigarette smoke and
lipopolysaccharide-induced pulmonary inflammation by inhibiting
interleukin8 production and NF-κB activation. Int J Mol Med.
44:949–959. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Tian M, Peng S, Wang S, Li X, Li H and
Shen L: Pristimerin reduces dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis
in mice by inhibiting microRNA-155. Int Immunopharmacol.
94:1074912021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Bhatia M and Moochhala S: Role of
inflammatory mediators in the pathophysiology of acute respiratory
distress syndrome. J Pathol. 202:145–156. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Parsons PE, Eisner MD, Thompson BT,
Matthay MA, Ancukiewicz M, Bernard GR and Wheeler AP; NHLBI Acute
Respiratory Distress Syndrome Clinical Trials Network, : Lower
tidal volume ventilation and plasma cytokine markers of
inflammation in patients with acute lung injury. Crit Care Med.
33:1–6; discussion 230-2. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Dong Z and Yuan Y: Accelerated
inflammation and oxidative stress induced by LPS in acute lung
injury: Inhibition by ST1926. Int J Mol Med. 41:3405–3421.
2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Guimarães LMF, Rossini CVT and Lameu C:
Implications of SARS-Cov-2 infection on eNOS and iNOS activity:
Consequences for the respiratory and vascular systems. Nitric
Oxide. 111-112:64–71. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Chen JR, Tang Y, Wang YL, Cui Q, Inam M,
Kong LC and Ma HX: Serine protease inhibitor MDSPI16 ameliorates
LPS-induced acute lung injury through its anti-inflammatory
activity. Int Immunopharmacol. 88:1070152020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Wu YX, Zeng S, Wan BB, Wang YY, Sun HX,
Liu G, Gao ZQ, Chen D, Chen YQ, Lu MD and Pang QF: Sophoricoside
attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury by
activating the AMPK/Nrf2 signaling axis. Int Immunopharmacol.
90:1071872021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Sun WH, Liu F, Chen Y and Zhu YC: Hydrogen
sulfide decreases the levels of ROS by inhibiting mitochondrial
complex IV and increasing SOD activities in cardiomyocytes under
ischemia/reperfusion. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 421:164–169.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Lan A, Liao X, Mo L, Yang C, Yang Z, Wang
X, Hu F, Chen P, Feng J, Zheng D and Xiao L: Hydrogen sulfide
protects against chemical hypoxia-induced injury by inhibiting
ROS-activated ERK1/2 and p38MAPK signaling pathways in PC12 cells.
PLoS One. 6:e259212011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Fang W, Cai SX, Wang CL, Sun XX, Li K, Yan
XW, Sun YB, Sun XZ, Gu CK, Dai MY, et al: Modulation of
mitogen-activated protein kinase attenuates sepsis-induced acute
lung injury in acute respiratory distress syndrome rats. Mol Med
Rep. 16:9652–9658. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Wu H, Zhao G, Jiang K, Chen X, Zhu Z, Qiu
C, Li C and Deng G: Plantamajoside ameliorates
lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury via suppressing NF-κB
and MAPK activation. Int Immunopharmacol. 35:315–322. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Jha P and Das H: KLF2 in Regulation of
NF-κB-Mediated immune cell function and inflammation. Int J Mol
Sci. 18:23832017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Meng L, Li L, Lu S, Li K, Su Z, Wang Y,
Fan X, Li X and Zhao G: The protective effect of dexmedetomidine on
LPS-induced acute lung injury through the HMGB1-mediated TLR4/NF-κB
and PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathways. Mol Immunol. 94:7–17. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Tang J, Xu L, Zeng Y and Gong F: Effect of
gut microbiota on LPS-induced acute lung injury by regulating the
TLR4/NF-kB signaling pathway. Int Immunopharmacol. 91:1072722021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Zhang WB, Yang F, Wang Y, Jiao FZ, Zhang
HY, Wang LW and Gong ZJ: Inhibition of HDAC6 attenuates LPS-induced
inflammation in macrophages by regulating oxidative stress and
suppressing the TLR4-MAPK/NF-κB pathways. Biomed Pharmacother.
117:1091662019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Dong Q, Li Y, Chen J and Wang N:
Azilsartan Suppressed LPS-Induced Inflammation in U937 Macrophages
through Suppressing Oxidative Stress and Inhibiting the TLR2/MyD88
Signal Pathway. ACS Omega. 6:113–118. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Liu Q, Ci X, Wen Z and Peng L: Diosmetin
Alleviates Lipopolysaccharide-Induced acute lung injury through
activating the Nrf2 Pathway and inhibiting the NLRP3 Inflammasome.
Biomol Ther (Seoul). 26:157–166. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Liu Y, Song M, Zhu G, Xi X, Li K, Wu C and
Huang L: Corynoline attenuates LPS-induced acute lung injury in
mice by activating Nrf2. Int Immunopharmacol. 48:96–101. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|