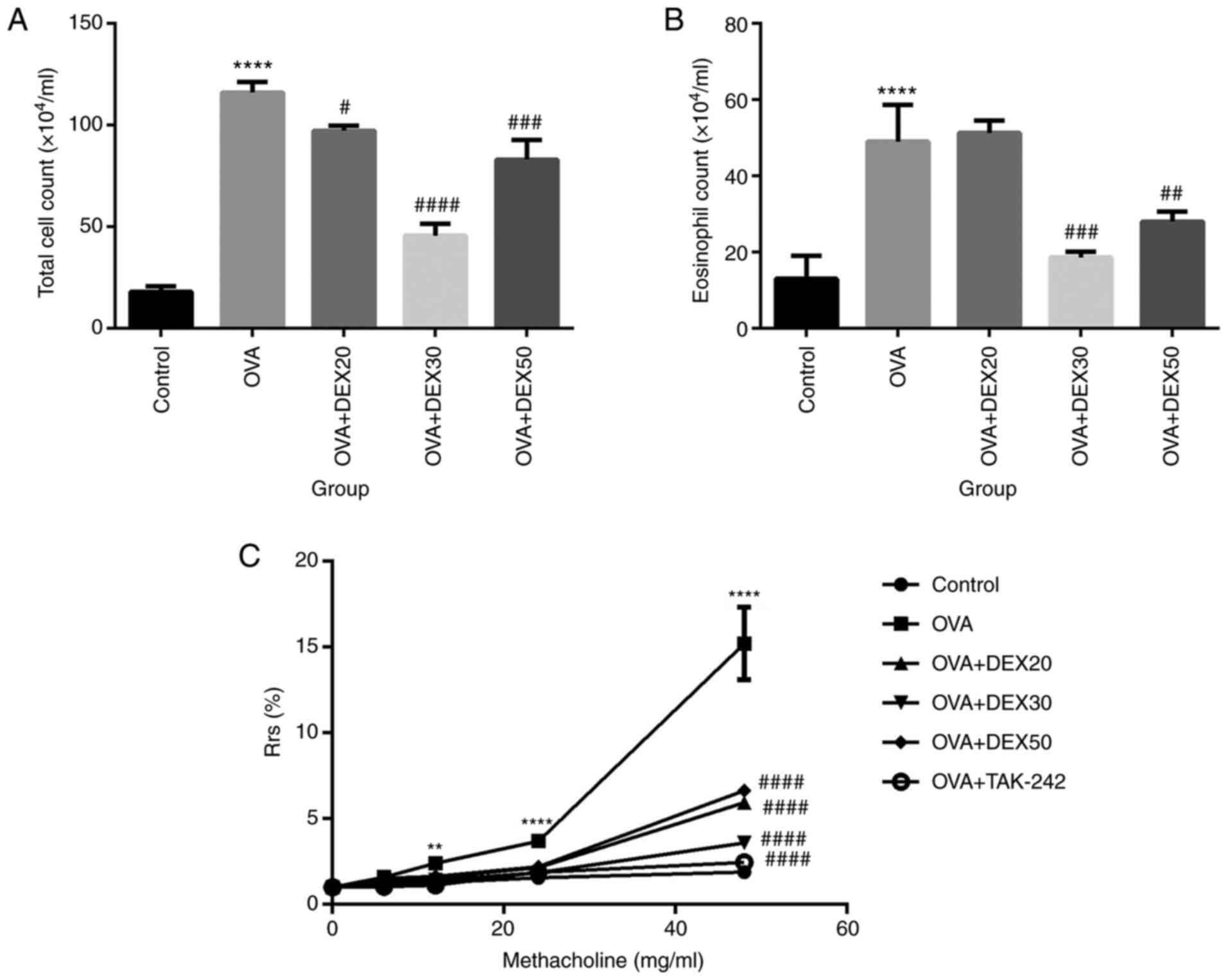
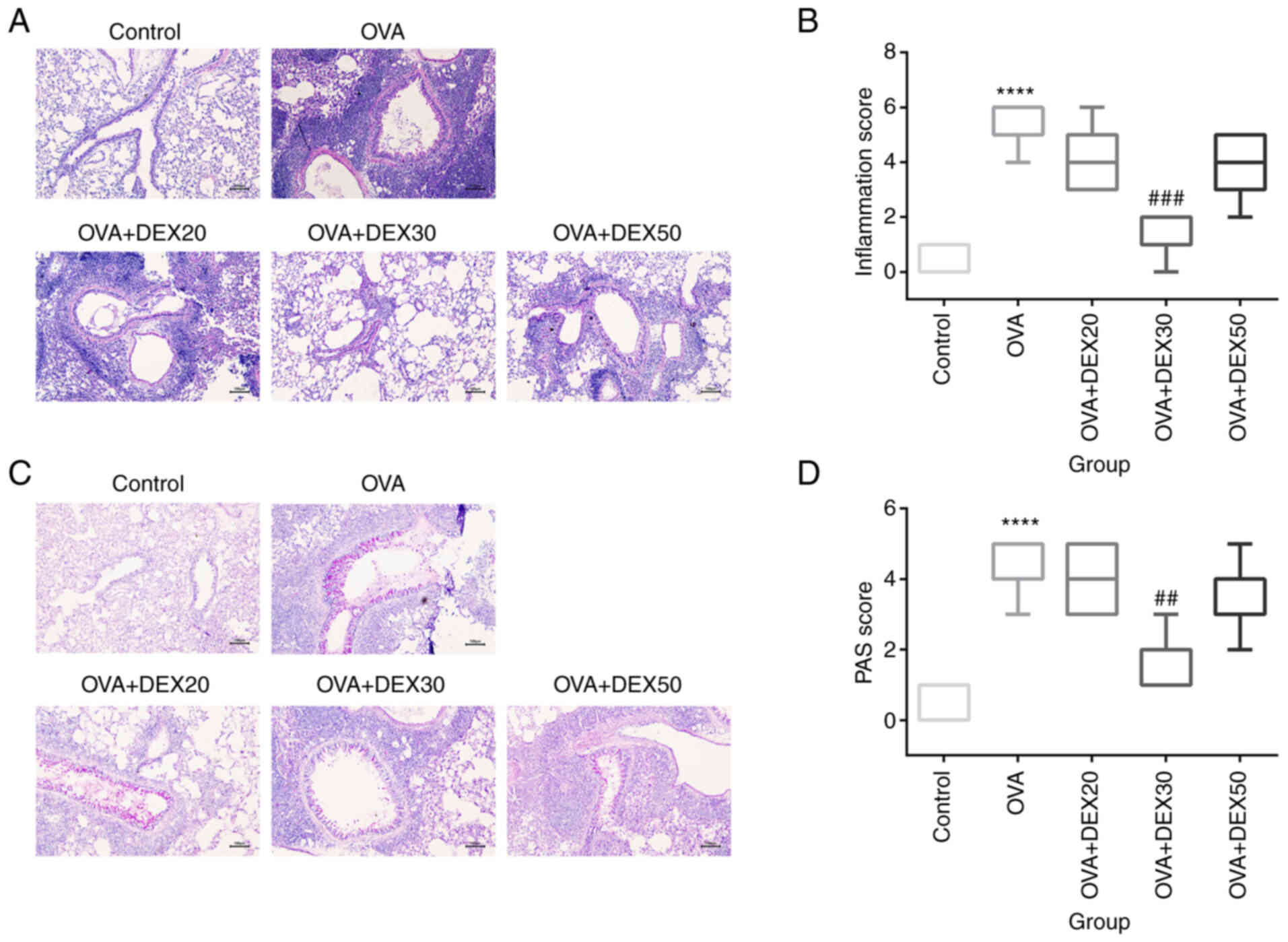
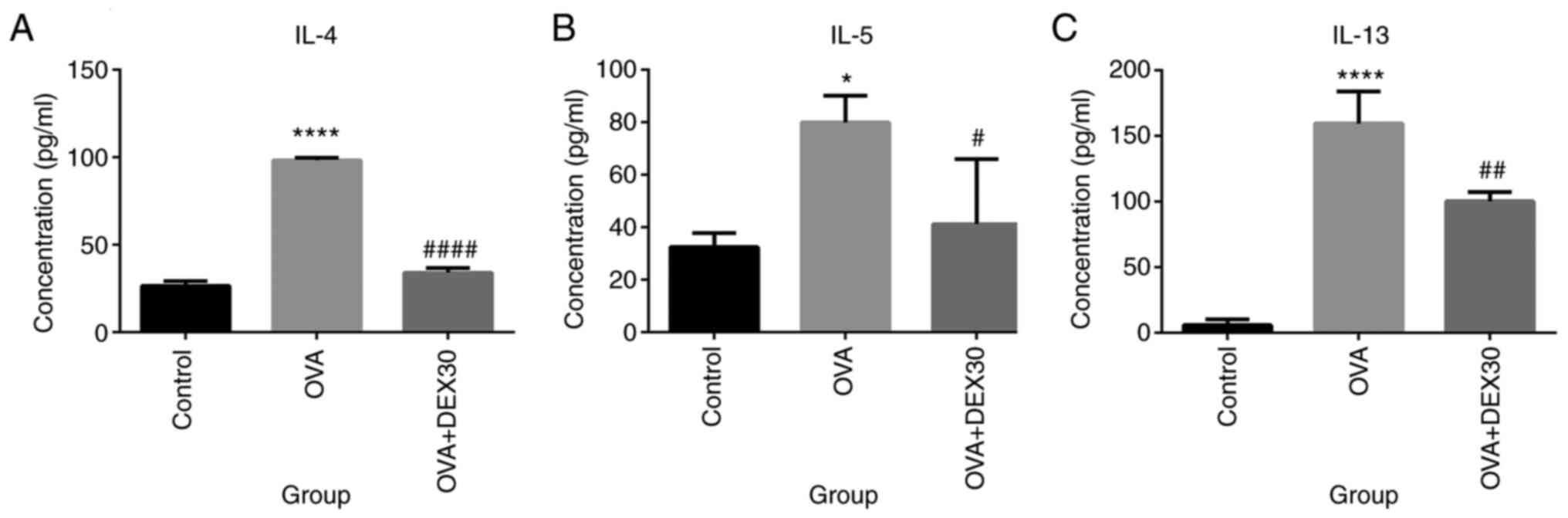
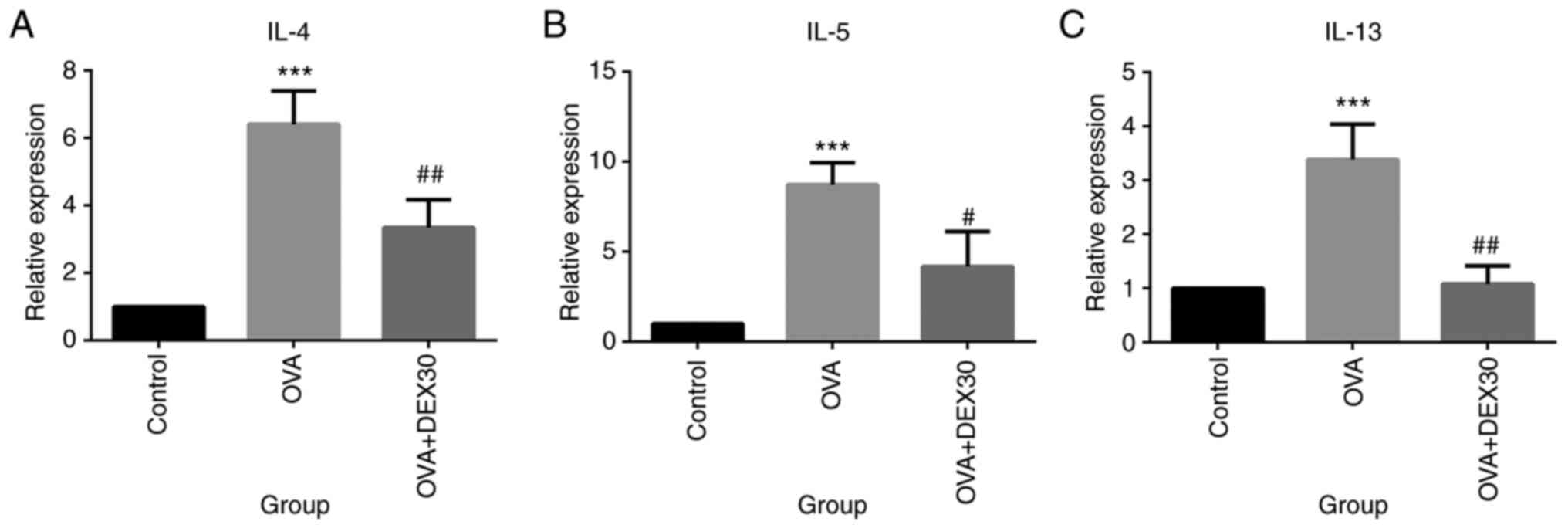
|
1
|
Papi A, Brightling C, Pedersen SE and
Reddel HK: Asthma. Lancet. 391:783–800. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Kong S, So WY and Jang S: The association
between vigorous physical activity and stress in adolescents with
asthma. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 18:34672021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Vasileiadou S, Ekerljung L, Bjerg A and
Goksör E: Asthma increased in young adults from 2008–2016 despite
stable allergic rhinitis and reduced smoking. PLoS One.
16:e02533222021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Loftus PA and Wise SK: Epidemiology and
economic burden of asthma. Int Forum Allergy Rhinol. 5 (Suppl
1):S7–S10. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Woods BD and Sladen RN: Perioperative
considerations for the patient with asthma and bronchospasm. Br J
Anaesth. 103 (Suppl 1):i57–i65. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Buendía JA and Patiño DG: Cost-utility of
triple versus dual inhaler therapy in moderate to severe asthma.
BMC Pulm Med. 21:3982021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Facchinetti F, Civelli M, Singh D, Papi A,
Emirova A and Govoni M: Tanimilast, A Novel Inhaled Pde4 inhibitor
for the treatment of asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary
disease. Front Pharmacol. 12:7408032021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Hall S and Agrawal DK: Key mediators in
the immunopathogenesis of allergic asthma. Int Immunopharmacol.
23:316–329. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Lambrecht BN, Hammad H and Fahy JV: The
cytokines of asthma. Immunity. 50:975–991. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Nagase H, Ueki S and Fujieda S: The roles
of IL-5 and anti-IL-5 treatment in eosinophilic diseases: Asthma,
eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis, and eosinophilic
chronic rhinosinusitis. Allergol Int. 69:178–186. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Bagnasco D, Ferrando M, Varricchi G,
Passalacqua G and Canonica GW: A Critical Evaluation of Anti-IL-13
and Anti-IL-4 strategies in severe asthma. Int Arch Allergy
Immunol. 170:122–131. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Kim G, Hong M, Kashif A, Hong Y, Park BS,
Mun JY, Choi H, Lee JS, Yang EJ, Woo RS, et al: Der f 38 Is a Novel
TLR4-binding allergen related to allergy pathogenesis from
dermatophagoides farinae. Int J Mol Sci. 22:84402021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Lu X, Xu C, Yang R and Zhang G: Ganoderic
acid a alleviates ova-induced asthma in mice. Inflammation.
44:1908–1915. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Kuzmich NN, Sivak KV, Chubarev VN, Porozov
YB, Savateeva-Lyubimova TN and Peri F: TLR4 signaling pathway
modulators as potential therapeutics in inflammation and sepsis.
Vaccines (Basel). 5:342017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Helal MG, Megahed NA and Abd Elhameed AG:
Saxagliptin mitigates airway inflammation in a mouse model of acute
asthma via modulation of NF-kB and TLR4. Life Sci. 239:1170172019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Di Stefano A, Ricciardolo LFM, Caramori G,
Adcock IM, Chung KF, Barnes PJ, Brun P, Leonardi A, Andò F, Vallese
D, et al: Bronchial inflammation and bacterial load in stable COPD
is associated with TLR4 overexpression. Eur Respir J.
49:16020062017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Garantziotis S, Li Z, Potts EN, Lindsey
JY, Stober VP, Polosukhin VV, Blackwell TS, Schwartz DA, Foster WM
and Hollingsworth JW: TLR4 is necessary for hyaluronan-mediated
airway hyperresponsiveness after ozone inhalation. Am J Respir Crit
Care Med. 181:666–675. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Wang K, Wu M, Xu J, Wu C, Zhang B, Wang G
and Ma D: Effects of dexmedetomidine on perioperative stress,
inflammation, and immune function: Systematic review and
meta-analysis. Br J Anaesth. 123:777–794. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Bao N and Tang B: Organ-protective effects
and the underlying mechanism of dexmedetomidine. Mediators Inflamm.
2020:61361052020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Heil LB, Santos CL, Santos RS, Samary CS,
Cavalcanti VC, Araújo MM, Poggio H, Maia Lde A, Trevenzoli IH,
Pelosi P, et al: The effects of short-term propofol and
dexmedetomidine on lung mechanics, histology, and biological
markers in experimental obesity. Anesth Analg. 122:1015–1023. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Meng L, Li L, Lu S, Li K, Su Z, Wang Y,
Fan X, Li X and Zhao G: The protective effect of dexmedetomidine on
LPS-induced acute lung injury through the HMGB1-mediated TLR4/NF-κB
and PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathways. Mol Immunol. 94:7–17. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Wang S, Jiang Z, Li L, Zhang J, Zhang C
and Shao C: Ameliorative effects of eosinophil deficiency on immune
response, endoplasmic reticulum stress, apoptosis, and autophagy in
fungus-induced allergic lung inflammation. Respir Res. 22:1732021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Myou S, Leff AR, Myo S, Boetticher E, Tong
J, Meliton AY, Liu J, Munoz NM and Zhu X: Blockade of inflammation
and airway hyperresponsiveness in immune-sensitized mice by
dominant-negative phosphoinositide 3-kinase-TAT. J Exp Med.
198:1573–1582. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Ford JG, Rennick D, Donaldson DD, Venkayya
R, McArthur C, Hansell E, Kurup VP, Warnock M and Grünig G: Il-13
and IFN-gamma: Interactions in lung inflammation. J Immunol.
167:1769–1777. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Feng R, Adeniran SO, Huang F, Li Y, Ma M,
Zheng P and Zhang G: The ameliorative effect of melatonin on
LPS-induced Sertoli cells inflammatory and tight junctions damage
via suppression of the TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB signaling pathway in
newborn calf. Theriogenology. 179:103–116. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
O'Byrne PM and Inman MD: Airway
hyperresponsiveness. Chest. 123 (Suppl 3):411S–6S. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Yamakage M, Iwasaki S and Namiki A:
Guideline-oriented perioperative management of patients with
bronchial asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. J
Anesth. 22:412–428. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Vaschetto R, Bellotti E, Turucz E,
Gregoretti C, Corte FD and Navalesi P: Inhalational anesthetics in
acute severe asthma. Curr Drug Targets. 10:826–832. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Groeben H, Mitzner W and Brown RH: Effects
of the alpha2-adrenoceptor agonist dexmedetomidine on
bronchoconstriction in dogs. Anesthesiology. 100:359–363. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Türktan M, Güleç E, Hatipoğlu Z, Ilgınel
MT and Özcengiz D: The effect of sevoflurane and dexmedetomidine on
pulmonary mechanics in ICU patients. Turk J Anaesthesiol Reanim.
47:206–212. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Ambesh SP and Dubey M: Effect of
intramuscular dexmedetomidine administration before extubation on
post-extubation haemodynamics, postoperative sedation, and
analgesic requirements: A double blind placebo controlled study.
Asian J Anesthesiol. 59:102–110. 2021.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Hwang L, Ko IG, Jin JJ, Kim SH, Kim CJ,
Chang B, Rho JH, Moon EJ and Yi JW: Dexmedetomidine ameliorates
memory impairment in sleep-deprived mice. Anim Cells Syst (Seoul).
23:371–379. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Geng Y, Li R, He SX, Yang HH, Deng QT,
Shao XY, Wu YS, Xu WW and Ma Q: Dexmedetomidine attenuates acute
lung injury induced by heatstroke and improve outcome. Shock.
52:532–539. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Yang C, He L, Wang C, Huang Y, Wang A, Li
X and Ao J: Dexmedetomidine alleviated
lipopolysaccharide/D-galactosamine-induced acute liver injury in
mice. Int Immunopharmacol. 72:367–373. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Zhi Y, Huang H and Liang L:
MFG-E8/integrin β3 signaling contributes to airway inflammation
response and airway remodeling in an ovalbumin-induced murine model
of asthma. J Cell Biochem. 119:8887–8896. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Fahy JV: Type 2 inflammation in
asthma-present in most, absent in many. Nat Rev Immunol. 15:57–65.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Ren M, Feng M, Long Z, Ma J, Peng X and He
G: Allergic asthma-induced cognitive impairment is alleviated by
dexamethasone. Front Pharmacol. 12:6808152021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Lo D, Kennedy JL, Kurten RC, Panettieri RA
Jr and Koziol-White CJ: Modulation of airway hyperresponsiveness by
rhinovirus exposure. Respir Res. 19:2082018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Yang M, Kumar RK and Foster PS:
Interferon-gamma and pulmonary macrophages contribute to the
mechanisms underlying prolonged airway hyperresponsiveness. Clin
Exp Allergy. 40:163–173. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Duan J, Kang J, Qin W, Deng T, Liu H, Li
B, Yu W, Gong S, Yang X and Chen M: Exposure to formaldehyde and
diisononyl phthalate exacerbate neuroinflammation through NF-κB
activation in a mouse asthma model. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf.
163:356–364. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Kim E, Kim HC, Lee S, Ryu HG, Park YH, Kim
JH, Lim YJ and Park HP: Dexmedetomidine confers neuroprotection
against transient global cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury in
rats by inhibiting inflammation through inactivation of the
TLR-4/NF-κB pathway. Neurosci Lett. 649:20–27. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Huang W, Li ML, Xia MY and Shao JY:
Fisetin-treatment alleviates airway inflammation through inhbition
of MyD88/NF-κB signaling pathway. Int J Mol Med. 42:208–218.
2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Tanic M, Yanowsky K, Rodriguez-Antona C,
Andrés R, Márquez-Rodas I, Osorio A, Benitez J and Martinez-Delgado
B: Deregulated miRNAs in hereditary breast cancer revealed a role
for miR-30c in regulating KRAS oncogene. PLoS One. 7:e388472012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Gao ZJ, Yuan WD, Yuan JQ, Yuan K and Wang
Y: MiR-486-5p functions as an oncogene by targeting PTEN in
non-small cell lung cancer. Pathol Res Pract. 214:700–705. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Fan HP, Wang SY, Shi YY and Sun J:
MicroRNA-340-5p inhibits the malignant phenotypes of osteosarcoma
by directly targeting NRF2 and deactivating the PI3K/AKT pathway.
Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 25:3661–3669. 2021.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Bao Y, Zhu Y, He G, Ni H, Liu C, Ma L,
Zhang L and Shi D: Dexmedetomidine attenuates neuroinflammation in
LPS-Stimulated BV2 microglia cells through upregulation of miR-340.
Drug Des Devel Ther. 13:3465–3475. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
He L, Wang Z, Zhou R, Xiong W, Yang Y,
Song N and Qian J: Dexmedetomidine exerts cardioprotective effect
through miR-146a-3p targeting IRAK1 and TRAF6 via inhibition of the
NF-κB pathway. Biomed Pharmacother. 133:1109932021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Wei W, Sun Z, He S, Zhang W and Chen S:
Protective role of dexmedetomidine against sevoflurane-induced
postoperative cognitive dysfunction via the microRNA-129/TLR4 axis.
J Clin Neurosci. 92:89–97. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Du XH, Li SS, Xiong GS, Yang GM, Shen W,
Sun SB, Ye XL, Li L and Weng ZY: Therapeutic efficacy of
dexmedetomidine on chronic obstructive pulmonary disease via
downregulating lncRNA PACER. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci.
24:12963–12970. 2020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Deng F, Cai L, Zhou B, Zhou Z and Xu G:
Whole transcriptome sequencing reveals dexmedetomidine-improves
postoperative cognitive dysfunction in rats via modulating lncRNA.
3 Biotech. 10:2022020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Zhou Z, Chen Q, Wan L, Zheng D, Li Z and
Wu Z: Dexmedetomidine protects hepatic cells against oxygen-glucose
deprivation/reperfusion injury via lncRNA CCAT1. Cell Biol Int.
42:1250–1258. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Takasaki Y, Kido T and Semba K:
Dexmedetomidine facilitates induction of noninvasive positive
pressure ventilation for acute respiratory failure in patients with
severe asthma. J Anesth. 23:147–150. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Lee JA, Rowen DW and Rose DD: Bronchial
thermoplasty: A novel treatment for severe asthma requiring
monitored anesthesia care. AANA J. 79:480–483. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|