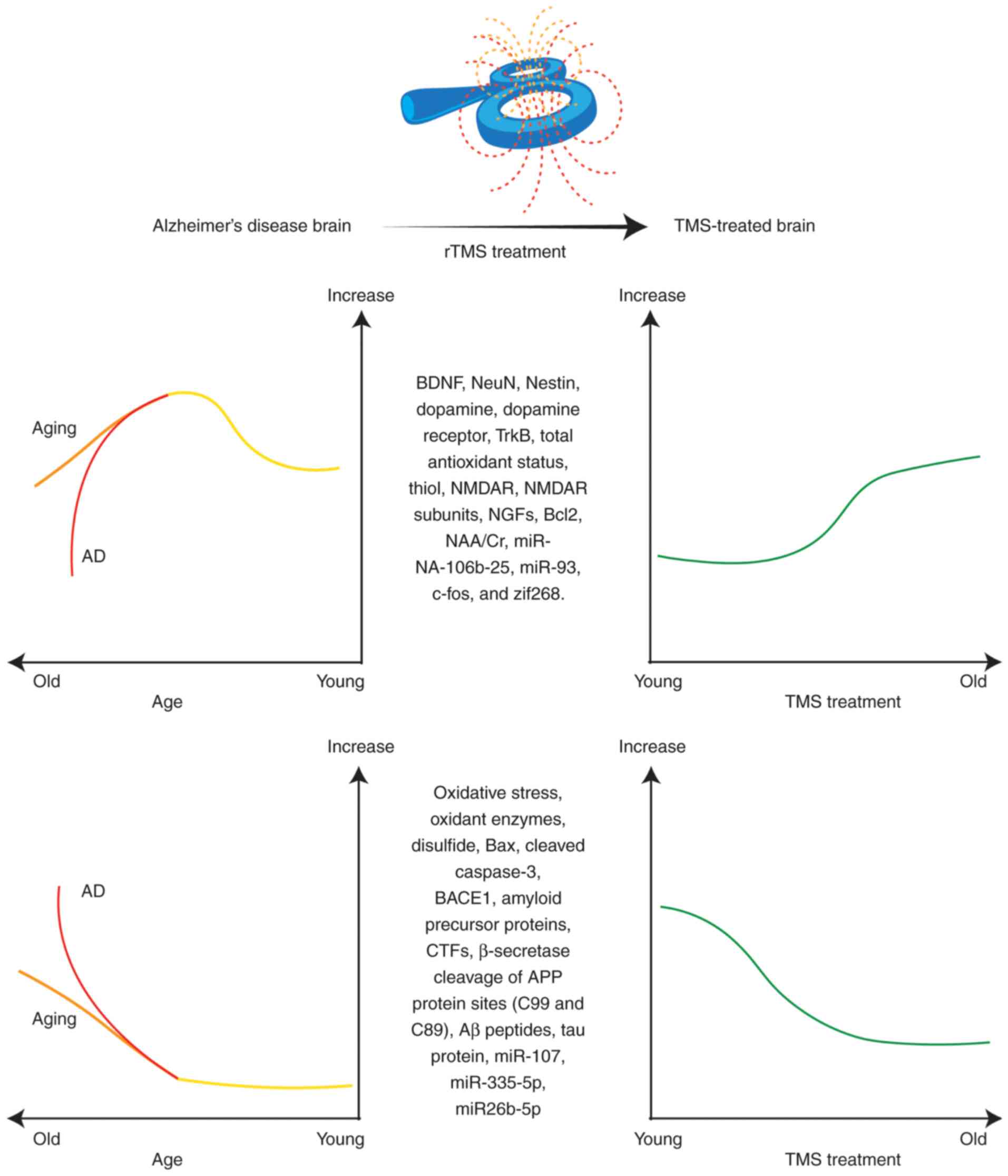
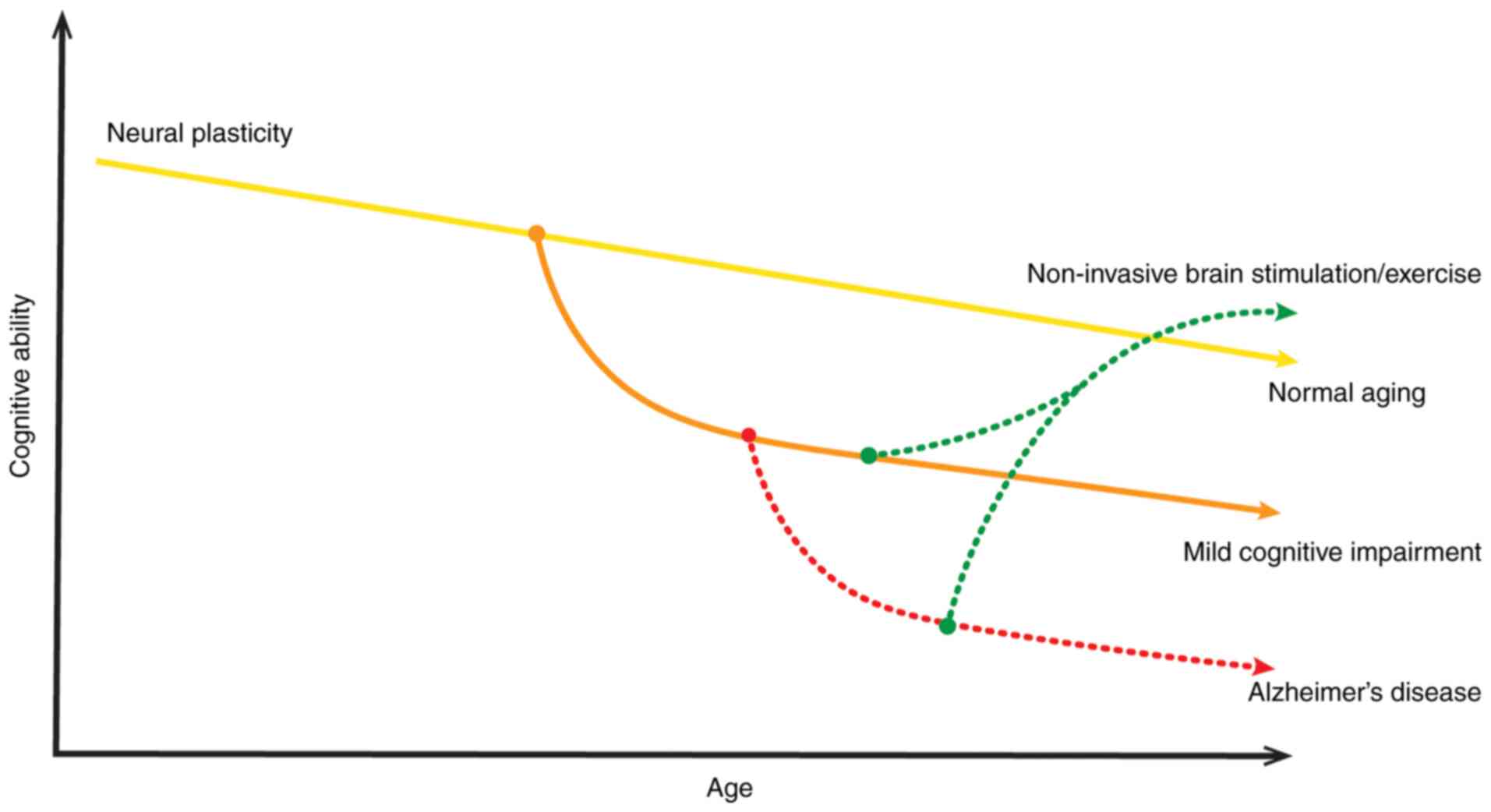
|
1
|
Guarino A, Favieri F, Boncompagni I,
Agostini F, Cantone M and Casagrande M: Executive functions in
Alzheimer disease: A systematic review. Front Aging Neurosci.
10:4372019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Weiler M, Stieger KC, Long JM and Rapp PR:
Transcranial magnetic stimulation in Alzheimer's disease. Are we
ready? eNeuro. 7:2020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Weller J and Budson A: Current
understanding of Alzheimer's disease diagnosis and treatment.
F1000Res. 7:F1000 Faculty Rev. 11612018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
2020 Alzheimer's disease facts and
figures. Alzheimers Dement. 16:391–460. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Uddin M, Kabir M, Jakaria M,
Sobarzo-Sánchez E, Barreto GE, Perveen A, Hafeez A, Bin-Jumah MN,
Abdel-Daim MM and Ashraf GM: Exploring the potential of
neuroproteomics in Alzheimer's disease. Curr Top Med Chem.
20:2263–2278. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Koper MJ, Van Schoor E, Ospitalieri S,
Vandenberghe R, Vandenbulcke M, von Arnim CAF, Tousseyn T, Balusu
S, De Strooper B and Thal DR: Necrosome complex detected in
granulovacuolar degeneration is associated with neuronal loss in
Alzheimer's disease. Acta Neuropathol. 139:463–484. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Hur JY, Frost GR, Wu X, Crump C, Pan SJ,
Wong E, Barros M, Li T, Nie P, Zhai Y, et al: The innate immunity
protein IFITM3 modulates γ-secretase in Alzheimer's disease. Nat
Aust. 586:735–740. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Butterfield DA and Mattson MP:
Apolipoprotein E and oxidative stress in brain with relevance to
Alzheimer's disease. Neurobiol Dis. 138:1047952020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Bhatt S, Puli L and Patil CR: Role of
reactive oxygen species in the progression of Alzheimer's disease.
Drug Discov Today. 26:794–803. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Olajide OJ, Gbadamosi IT, Yawson EO,
Arogundade T, Lewu FS, Ogunrinola KY, Adigun OO, Bamisi O, Lambe E,
Arietarhire LO, et al: Hippocampal degeneration and behavioral
impairment during Alzheimer-like pathogenesis involves glutamate
excitotoxicity. J Mol Neurosci. 71:1205–1220. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Zhao Y, Zhan JK and Liu Y: A perspective
on roles played by immunosenescence in the pathobiology of
Alzheimer's disease. Aging Dis. 11:1594–1607. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Uddin MS, Al Mamun A, Rahman M, Behl T,
Perveen A, Hafeez A, Bin-Jumah MN, Abdel-Daim MM and Ashraf GM:
Emerging proof of protein misfolding and interactions in
multifactorial Alzheimer's disease. Curr Top Med Chem.
20:2380–2390. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Butterfield DA and Boyd-Kimball DA:
Mitochondrial oxidative and nitrosative stress and Alzheimer
disease. Antioxidants (Basel). 9:8182020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Sengoku R: Aging and Alzheimer's disease
pathology. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol. 40:22–29. 2020.
|
|
15
|
Wegiel J, Flory M, Kuchna I, Nowicki K, Ma
SY, Wegiel J, Badmaev E, Leon M, Wisniewski T and Reisberg B:
Clinicopathological staging of dynamics of neurodegeneration and
neuronal loss in Alzheimer disease. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol.
80:21–44. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Pei YA, Davies J, Zhang M and Zhang HT:
The role of synaptic dysfunction in Alzheimer's disease. J
Alzheimer's Dis. 76:49–62. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Teipel SJ, Fritz HC and Grothe MJ;
Alzheimer's Disease Neuroimaging Initiative, : Neuropathologic
features associated with basal forebrain atrophy in Alzheimer
disease. Neurology. 95:e1301–e1311. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Amini M, Pedram MM, Moradi A, Jamshidi M
and Ouchani M: Single and combined neuroimaging techniques for
Alzheimer's disease detection. Comput Intell Neurosci.
2021:95230392021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zetterberg H and Burnham SC: Blood-based
molecular biomarkers for Alzheimer's disease. Mol Brain. 12:262019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Jack CR Jr, Bennett DA, Blennow K,
Carrillo MC, Dunn B, Haeberlein SB, Holtzman DM, Jagust W, Jessen
F, Karlawish J, et al: NIA-AA research framework: Toward a
biological definition of Alzheimer's disease. Alzheimer's Dement.
14:535–562. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Lee JC, Kim SJ, Hong S and Kim Y:
Diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease utilizing amyloid and tau as fluid
biomarkers. Exp Mol Med. 51:1–10. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Park JE, Lim DS, Cho YH, Choi KY, Lee JJ,
Kim BC, Lee KH and Lee JS: Plasma contact factors as novel
biomarkers for diagnosing Alzheimer's disease. Biomark Res.
9:52021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Zetterberg H: Blood-based biomarkers for
Alzheimer's disease-An update. J Neurosci Methods. 319:2–6. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Young PNE, Estarellas M, Coomans E,
Srikrishna M, Beaumont H, Maass A, Venkataraman AV, Lissaman R,
Jiménez D, Betts MJ, et al: Imaging biomarkers in
neurodegeneration: Current and future practices. Alzheimers Res
Ther. 12:492020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
O'Dell RS, Mecca AP, Chen MK, Naganawa M,
Toyonaga T, Lu Y, Godek TA, Harris JE, Bartlett HH, Banks ER, et
al: Association of Aβ deposition and regional synaptic density in
early Alzheimer's disease: A PET imaging study with
[11C]UCB-J. Alzheimer's Res Ther. 13:112021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Sujathakumari B, Shetty MC, Lakshitha H,
Mehulkumar PJ and Suma S: Predictive analysis for early detection
of Alzheimer's disease. Data Intelligence and Cognitive
Informatics. Springer; pp. 709–723. 2021, View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Song A, Johnson N, Ayala A and Thompson
AC: Brain Optical coherence tomography in patients with Alzheimer's
disease: What can it tell us? Eye. 13:1–20. 2021.
|
|
28
|
Segal Y, Segal L, Blumenfeld-Katzir T,
Sasson E, Poliansky V, Loeb E, Levy A, Alter A and Bregman N: The
effect of electromagnetic field treatment on recovery from ischemic
stroke in a rat stroke model: Clinical, imaging, and pathological
findings. Stroke Res Treat. 2016:69419462016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Lefaucheur JP, Aleman A, Baeken C,
Benninger DH, Brunelin J, Di Lazzaro V, Filipović SR, Grefkes C,
Hasan A, Hummel FC, et al: Evidence-based guidelines on the
therapeutic use of repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation
(rTMS): An update (2014–2018). Clinical neurophysiology.
131:474–528. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Ba M, Ma G, Ren C, Sun X and Kong M:
Repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation for treatment of
lactacystin-induced Parkinsonian rat model. Oncotarget.
8:50921–50929. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Tasset I, Medina FJ, Jimena I, Agüera E,
Gascón F, Feijóo M, Sánchez-López F, Luque E, Peña J, Drucker-Colín
R and Túnez I: Neuroprotective effects of extremely low-frequency
electromagnetic fields on a Huntington's disease rat model: Effects
on neurotrophic factors and neuronal density. Neuroscience.
209:54–63. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Choung JS, Kim JM, Ko MH, Cho DS and Kim
M: Therapeutic efficacy of repetitive transcranial magnetic
stimulation in an animal model of Alzheimer's disease. Sci Rep.
11:4372021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Chou YH, Ton That V and Sundman M: A
systematic review and meta-analysis of rTMS effects on cognitive
enhancement in mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer's disease.
Neurobiol Aging. 86:1–10. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Weise K, Numssen O, Thielscher A,
Hartwigsen G and Knösche TR: A novel approach to localize cortical
TMS effects. NeuroImage. 209:1164862020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Zorzo C, Higarza SG, Méndez M, Martínez
JA, Pernía AM and Arias JL: High frequency repetitive transcranial
magnetic stimulation improves neuronal activity without affecting
astrocytes and microglia density. Brain Res Bull. 150:13–20. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Velioglu HA, Hanoglu L, Bayraktaroglu Z,
Toprak G, Guler EM, Bektay MY, Mutlu-Burnaz O and Yulug B: Left
lateral parietal rTMS improves cognition and modulates resting
brain connectivity in patients with Alzheimer's disease: Possible
role of BDNF and oxidative stress. Neurobiol Learn Mem.
180:1074102021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Luo J, Zheng H, Zhang L, Zhang Q, Li L,
Pei Z and Hu X: High-frequency repetitive transcranial magnetic
stimulation (rTMS) improves functional recovery by enhancing
neurogenesis and activating BDNF/TrkB signaling in ischemic rats.
Int J Mol Sci. 18:4552017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Heath A, Taylor J and McNerney MW: rTMS
for the treatment of Alzheimer's disease: Where should we be
stimulating? Expert Rev Neurother. 18:903–905. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Bashir S, Mizrahi I, Weaver K, Fregni F
and Pascual-Leone A: Assessment and modulation of neural plasticity
in rehabilitation with transcranial magnetic stimulation. PM R. 2
12 Suppl 2:S253–S268. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Mann SK and Malhi NK: Repetitive
transcranial magnetic stimulation. StatPearls StatPearls Publishing
Copyright©. 2021, StatPearls Publishing LLC.; Treasure
Island (FL): 2021
|
|
41
|
Miniussi C and Ruzzoli M: Transcranial
stimulation and cognition. Handb Clin Neurol. 116:739–750. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Barker AT, Jalinous R and Freeston IL:
Non-invasive magnetic stimulation of human motor cortex. Lancet.
1:1106–1107. 1985. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Uzair M, Abualait T, Arshad M, Yoo WK, Mir
A, Bunyan RF and Bashir S: Transcranial magnetic stimulation in
animal models of neurodegeneration. Neural Regen Res. 17:251–265.
2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Perera T, George MS, Grammer G, Janicak
PG, Pascual-Leone A and Wirecki TS: The clinical TMS society
consensus review and treatment recommendations for TMS therapy for
major depressive disorder. Brain Stimul. 9:336–346. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
George MS: Transcranial magnetic
stimulation for the treatment of depression. Expert Rev Neurother.
10:1761–1772. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Hawken ER, Dilkov D, Kaludiev E, Simek S,
Zhang F and Milev R: Transcranial magnetic stimulation of the
supplementary motor area in the treatment of obsessive-compulsive
disorder: A multi-site study. Int J Mol Sci. 17:4202016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Starling AJ, Tepper SJ, Marmura MJ, Shamim
EA, Robbins MS, Hindiyeh N, Charles AC, Goadsby PJ, Lipton RB,
Silberstein SD, et al: A multicenter, prospective, single arm, open
label, observational study of sTMS for migraine prevention (ESPOUSE
Study). Cephalalgia. 38:1038–1048. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Moussavi Z, Rutherford G, Lithgow B,
Millikin C, Modirrousta M, Mansouri B, Wang X, Omelan C, Fellows L,
Fitzgerald P and Koski L: Repeated transcranial magnetic
stimulation for improving cognition in patients with Alzheimer
disease: Protocol for a randomized, double-blind,
placebo-controlled trial. JMIR Res Protoc. 10:e251442021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Li X, Qi G, Yu C, Lian G, Zheng H, Wu S,
Yuan TF and Zhou D: Cortical plasticity is correlated with
cognitive improvement in Alzheimer's disease patients after rTMS
treatment. Brain Stimul. 14:503–510. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Mi TM, Garg S, Ba F, Liu AP, Liang PP, Gao
LL, Jia Q, Xu EH, Li KC, Chan P and McKeown MJ: Repetitive
transcranial magnetic stimulation improves Parkinson's freezing of
gait via normalizing brain connectivity. NPJ Parkinsons Dis.
6:162020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Yang X, Song L and Liu Z: The effect of
repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation on a model rat of
Parkinson's disease. Neuroreport. 21:268–272. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Spielberg B: What is the success rate of
TMS therapy? 2020.
|
|
53
|
Wagner T, Valero-Cabre A and Pascual-Leone
A: Noninvasive human brain stimulation. Annu Rev Biomed Eng.
9:527–65. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Klomjai W, Katz R and Lackmy-Vallée A:
Basic principles of transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) and
repetitive TMS (rTMS). Ann Phys Rehabil Med. 58:208–213. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Bolognini N and Ro T: Transcranial
magnetic stimulation: Disrupting neural activity to alter and
assess brain function. J Neurosci. 30:9647–9650. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Cuypers K and Marsman A: Transcranial
magnetic stimulation and magnetic resonance spectroscopy:
Opportunities for a bimodal approach in human neuroscience.
Neuroimage. 224:1173942021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Chail A, Saini RK, Bhat P, Srivastava K
and Chauhan V: Transcranial magnetic stimulation: A review of its
evolution and current applications. Ind Psychiatry J. 27:1722018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Habib S, Hamid U, Jamil A, Zainab AZ,
Yousuf T, Habib S, Tariq SM and Ali F: Transcranial magnetic
stimulation as a therapeutic option for neurologic and psychiatric
illnesses. Cureus. 10:e34562018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Eldaief MC, Press DZ and Pascual-Leone A:
Transcranial magnetic stimulation in neurology: A review of
established and prospective applications. Neurol Clin Pract.
3:519–526. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Alomar M, Yoo W-K, Vernet M, Murtaza G,
Rotenberg A and Bashir S: Human brain connectivity in response to
paired pulse TMS paradigm. Brain Stimul. 10:3532017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
61
|
Kim TD, Hong G, Kim J and Yoon S:
Cognitive enhancement in neurological and psychiatric disorders
using transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS): A review of
modalities, potential mechanisms and future implications. Exp
Neurobiol. 28:1–16. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Fried PJ, Jannati A, Davila-Pérez P and
Pascual-Leone A: Reproducibility of single-pulse, paired-pulse, and
intermittent theta-burst TMS measures in healthy aging, type-2
diabetes, and Alzheimer's disease. Front Aging Neurosci. 9:2632017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Chervyakov AV, Chernyavsky AY, Sinitsyn DO
and Piradov MA: Possible mechanisms underlying the therapeutic
effects of transcranial magnetic stimulation. Front Hum Neurosci.
9:3032015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Agarwal S, Koch G, Hillis AE, Huynh W,
Ward NS, Vucic S and Kiernan MC: Interrogating cortical function
with transcranial magnetic stimulation: Insights from
neurodegenerative disease and stroke. J Neurol Neurosurg
Psychiatry. 90:47–57. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Jackson J, Jambrina E, Li J, Marston H,
Menzies F, Phillips K and Gilmour G: Targeting the synapse in
Alzheimer's disease. Front Neurosci. 13:7352019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Wang X, Mao Z, Ling Z and Yu X: Repetitive
transcranial magnetic stimulation for cognitive impairment in
Alzheimer's disease: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled
trials. J Neurol. 267:791–801. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Holczer A, Németh VL, Vékony T, Vécsei L,
Klivényi P and Must A: Non-invasive brain stimulation in
Alzheimer's disease and mild cognitive impairment-a
state-of-the-art review on methodological characteristics and
stimulation parameters. Front Hum Neurosci. 14:1792020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Guerra A, Assenza F, Bressi F, Scrascia F,
Del Duca M, Ursini F, Vollaro S, Trotta L, Tombini M, Chisari C and
Ferreri F: Transcranial magnetic stimulation studies in Alzheimer's
disease. Int J Alzheimers Dis. 2011:2638172011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Yang HY, Liu Y, Xie JC, Liu NN and Tian X:
Effects of repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation on synaptic
plasticity and apoptosis in vascular dementia rats. Behav Brain
Res. 281:149–155. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Capelli E, Torrisi F, Venturini L, Granato
M, Fassina L, Lupo GFD and Ricevuti G: Low-frequency pulsed
electromagnetic field is able to modulate miRNAs in an experimental
cell model of Alzheimer's disease. J Healthcare Eng.
2017:25302702017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Xiao N and Le QT: Neurotrophic factors and
their potential applications in tissue regeneration. Arch Immunol
Ther Exp (Warsz). 64:89–99. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Sampaio TB, Savall AS, Gutierrez MEZ and
Pinton S: Neurotrophic factors in Alzheimer's and Parkinson's
diseases: Implications for pathogenesis and therapy. Neural Regen
Res. 12:549–557. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Budni J, Bellettini-Santos T, Mina F,
Garcez ML and Zugno AI: The involvement of BDNF, NGF and GDNF in
aging and Alzheimer's disease. Aging Dis. 6:331–341. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Miranda M, Morici JF, Zanoni MB and
Bekinschtein P: Brain-derived neurotrophic factor: A key molecule
for memory in the healthy and the pathological brain. Front Cell
Neurosci. 13:3632019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Ballinger EC, Ananth M, Talmage DA and
Role LW: Basal forebrain cholinergic circuits and signaling in
cognition and cognitive decline. Neuron. 91:1199–1218. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Martinez JL, Zammit MD, West NR, Christian
BT and Bhattacharyya A: Basal forebrain cholinergic neurons:
Linking down syndrome and Alzheimer's disease. Front Aging
Neurosci. 13:7038762021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Serrano-Pozo A, Frosch MP, Masliah E and
Hyman BT: Neuropathological alterations in Alzheimer disease. Cold
Spring Harb Perspect Med. 1:a0061892011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Pang Y and Shi M: Repetitive transcranial
magnetic stimulation improves mild cognitive impairment associated
with Alzheimer's disease in mice by modulating the
miR-567/NEUROD2/PSD95 axis. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 17:2151–2161.
2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Wang ZH, Xiang J, Liu X, Yu SP,
Manfredsson FP, Sandoval IM, Wu S, Wang JZ and Ye K: Deficiency in
BDNF/TrkB neurotrophic activity stimulates δ-secretase by
upregulating C/EBPβ in Alzheimer's disease. Cell Rep.
28:655–669.e5. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Ng TKS, Ho CSH, Tam WWS, Kua EH and Ho RC:
Decreased serum brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) levels in
patients with Alzheimer's disease (AD): A systematic review and
meta-analysis. Int J Mol Sci. 20:2572019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Chen X, Dong GY and Wang LX:
High-frequency transcranial magnetic stimulation protects APP/PS1
mice against Alzheimer's disease progress by reducing APOE and
enhancing autophagy. Brain Behavior. 10:e017402020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Tan T, Xie J, Liu T, Chen X, Zheng X, Tong
Z and Tian X: Low-frequency (1Hz) repetitive transcranial magnetic
stimulation (rTMS) reverses Aβ(1–42)-mediated memory deficits in
rats. Exp Gerontol. 48:786–794. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Chen X, Chen S, Liang W and Ba F:
Administration of repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation
attenuates A β1-42-induced Alzheimer's disease in mice
by activating β-catenin signaling. Biomed Res Int.
2019:14317602019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Schaller G, Sperling W,
Richter-Schmidinger T, Mühle C, Heberlein A, Maihöfner C, Kornhuber
J and Lenz B: Serial repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation
(rTMS) decreases BDNF serum levels in healthy male volunteers. J
Neural Transm (Vienna). 121:307–313. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Gaede G, Hellweg R, Zimmermann H, Brandt
AU, Dörr J, Bellmann-Strobl J, Zangen A, Paul F and Pfueller CF:
Effects of deep repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation on
brain-derived neurotrophic factor serum concentration in healthy
volunteers. Neuropsychobiology. 69:112–119. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Yulug B, Hanoglu L, Khanmammadov E, Duz
OA, Polat B, Hanoglu T, Gunal MY and Kilic E: Beyond the
therapeutic effect of rTMS in Alzheimer's disease: A possible
neuroprotective role of hippocampal BDNF?: A minireview. Mini Rev
Med Chem. 18:1479–1485. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Huang WJ, Zhang X and Chen WW: Role of
oxidative stress in Alzheimer's disease. Biomed Rep. 4:519–522.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Cheignon C, Tomas M, Bonnefont-Rousselot
D, Faller P, Hureau C and Collin F: Oxidative stress and the
amyloid beta peptide in Alzheimer's disease. Redox Biol.
14:450–464. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Chen Z and Zhong C: Oxidative stress in
Alzheimer's disease. Neurosci Bull. 30:271–281. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Perry G, Cash AD and Smith MA: Alzheimer
disease and oxidative stress. J Biomed Biotechnol. 2:120–123. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Butterfield DA and Halliwell B: Oxidative
stress, dysfunctional glucose metabolism and Alzheimer disease. Nat
Rev Neurosci. 20:148–160. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Molinari C, Morsanuto V, Ruga S, Notte F,
Farghali M, Galla R and Uberti F: The role of BDNF on
aging-modulation markers. Brain Sci. 10:2852020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Umeno A, Biju V and Yoshida Y: In vivo ROS
production and use of oxidative stress-derived biomarkers to detect
the onset of diseases such as Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's
disease, and diabetes. Free Radical Res. 51:413–427. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Durmaz O, Ispir E, Baykan H, Alisik M and
Erel Ö: The impact of repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation
on oxidative stress in subjects with medication-resistant
depression. J ECT. 34:127–131. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Niimi M, Hashimoto K, Kakuda W, Miyano S,
Momosaki R, Ishima T and Abo M: Role of brain-derived neurotrophic
factor in beneficial effects of repetitive transcranial magnetic
stimulation for upper limb hemiparesis after stroke. PLoS One.
11:e01522412016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
96
|
Medina-Fernandez FJ, Escribano BM, Agüera
E, Aguilar-Luque M, Feijoo M, Luque E, Garcia-Maceira FI,
Pascual-Leone A, Drucker-Colin R and Tunez I: Effects of
transcranial magnetic stimulation on oxidative stress in
experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Free Radical Res.
51:460–469. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Snowden SG, Ebshiana AA, Hye A, Pletnikova
O, O'Brien R, Yang A, Troncoso J, Legido-Quigley C and Thambisetty
M: Neurotransmitter imbalance in the brain and Alzheimer's disease
pathology. J Alzheimers Dis. 72:35–43. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98
|
Svob Strac D, Muck-Seler D and Pivac N:
Neurotransmitter measures in the cerebrospinal fluid of patients
with Alzheimer's disease: A review. Psychiatr Danub. 27:14–24.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
99
|
Kaur S, DasGupta G and Singh S: Altered
neurochemistry in Alzheimer's disease: Targeting neurotransmitter
receptor mechanisms and therapeutic strategy. Neurophysiology.
51:293–309. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
100
|
Speranza L, di Porzio U, Viggiano D, de
Donato A and Volpicelli F: Dopamine: The neuromodulator of
long-term synaptic plasticity, reward and movement control. Cells.
10:7352021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
101
|
He Z, Jiang Y, Gu S, Wu D, Feng G, Ma X,
Huang JH and Wang F: The aversion function of the limbic
dopaminergic neurons and their roles in functional neurological
disorders. Front Cell Dev Biol. 9:7137622021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
102
|
Pan X, Kaminga AC, Wen SW, Wu X,
Acheampong K and Liu A: Dopamine and dopamine receptors in
Alzheimer's disease: A systematic review and network meta-analysis.
Front Aging Neurosci. 11:1752019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
103
|
D'Amelio M, Puglisi-Allegra S and Mercuri
N: The role of dopaminergic midbrain in Alzheimer's disease:
Translating basic science into clinical practice. Pharmacol Res.
130:414–419. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
104
|
Nobili A, Latagliata EC, Viscomi MT,
Cavallucci V, Cutuli D, Giacovazzo G, Krashia P, Rizzo FR, Marino
R, Federici M, et al: Dopamine neuronal loss contributes to memory
and reward dysfunction in a model of Alzheimer's disease. Nat
Commun. 8:147272017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
105
|
Malik S, Jacobs M, Cho SS, Boileau I,
Blumberger D, Heilig M, Wilson A, Daskalakis ZJ, Strafella AP,
Zangen A and Le Foll B: Deep TMS of the insula using the H-coil
modulates dopamine release: A crossover [11C] PHNO-PET
pilot trial in healthy humans. Brain Imaging Behav. 12:1306–1317.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
106
|
Cho SS and Strafella AP: rTMS of the left
dorsolateral prefrontal cortex modulates dopamine release in the
ipsilateral anterior cingulate cortex and orbitofrontal cortex.
PLoS One. 4:e67252009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
107
|
Liu J, Chang L, Song Y, Li H and Wu Y: The
role of NMDA receptors in Alzheimer's disease. Front Neurosci.
13:432019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
108
|
Zhang Y, Li P, Feng J and Wu M:
Dysfunction of NMDA receptors in Alzheimer's disease. Neurol Sci.
37:1039–1047. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
109
|
Kodis EJ, Choi S, Swanson E, Ferreira G
and Bloom GS: Dementia N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor-mediated
calcium influx connects amyloid-β oligomers to ectopic neuronal
cell cycle reentry in Alzheimer's disease. Alzheimers Dement.
14:1302–1312. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
110
|
Tsang SW, Vinters HV, Cummings JL, Wong
PT, Chen CP and Lai MK: Alterations in NMDA receptor subunit
densities and ligand binding to glycine recognition sites are
associated with chronic anxiety in Alzheimer's disease. Neurobiol.
Aging. 29:1524–1532. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
111
|
Battaglia F, Wang HY, Ghilardi MF, Gashi
E, Quartarone A, Friedman E and Nixon RA: Cortical plasticity in
Alzheimer's disease in humans and rodents. Biol Psychiatry.
62:1405–1412. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
112
|
Zhang N, Xing M, Wang Y, Tao H and Cheng
Y: Repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation enhances spatial
learning and synaptic plasticity via the VEGF and BDNF-NMDAR
pathways in a rat model of vascular dementia. Neuroscience.
311:284–291. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
113
|
Niimi M, Fujita Y, Ishima T, Hashimoto K,
Sasaki N, Hara T, Yamada N and Abo M: Role of D-serine in the
beneficial effects of repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation
in post-stroke patients. Acta Neuropsychiatr. 32:1–22. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
114
|
Chi H, Chang H-Y and Sang TK: Neuronal
cell death mechanisms in major neurodegenerative diseases. Int J
Mol Sci. 19:30822018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
115
|
Obulesu M and Lakshmi MJ: Apoptosis in
Alzheimer's disease: An understanding of the physiology, pathology
and therapeutic avenues. Neurochem Res. 39:2301–2312. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
116
|
Paradis E, Douillard H, Koutroumanis M,
Goodyer C and LeBlanc A: Amyloid beta peptide of Alzheimer's
disease downregulates Bcl-2 and upregulates bax expression in human
neurons. J Neurosci. 16:7533–7539. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
117
|
Guo F, Lou J, Han X, Deng Y and Huang X:
Repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation ameliorates cognitive
impairment by enhancing neurogenesis and suppressing apoptosis in
the hippocampus in rats with ischemic stroke. Front Physiol.
8:5592017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
118
|
Yulug B, Hanoglu L, Kilic E, Polat B and
Rüdiger Schabitz W: The neuroprotective role of repetitive
transcranial magnetic stimulation (rTMS) for neurodegenerative
diseases: A short review on experimental studies. Mini Rev Med
Chem. 16:1269–1273. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
119
|
Cappa SF, Binetti G, Pezzini A, Padovani
A, Rozzini L and Trabucchi M: Object and action naming in
Alzheimer's disease and frontotemporal dementia [see comment].
Neurology. 50:351–355. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
120
|
Almor A, Aronoff JM, MacDonald MC,
Gonnerman LM, Kempler D, Hintiryan H, Hayes UL, Arunachalam S and
Andersen ES: A common mechanism in verb and noun naming deficits in
Alzheimer's patients. Brain Lang. 111:8–19. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
121
|
de Almeida RG, Mobayyen F, Antal C,
Kehayia E, Nair VP and Schwartz G: Category-specific verb-semantic
deficits in Alzheimer's disease: Evidence from static and dynamic
action naming. Cogn Neuropsychol. 38:1–26. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
122
|
Kumar S, Zomorrodi R, Ghazala Z, Goodman
MS, Blumberger DM, Cheam A, Fischer C, Daskalakis ZJ, Mulsant BH,
Pollock BG and Rajji TK: Extent of dorsolateral prefrontal cortex
plasticity and its association with working memory in patients with
Alzheimer disease. JAMA Psychiatry. 74:1266–1274. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
123
|
Kumar S, Iwata Y, Zomorrodi R, Blumberger
DM, Fischer CE, Daskalakis ZJ, Mulsant BH, Pollock BG,
Graff-Guerrero A and Rajji TK: Dorsolateral prefrontal cortex
metabolites and their relationship with plasticity in Alzheimer's
disease: Biomarkers (non-neuroimaging)/novel biomarkers. Alzheimers
Dement. 16:e0458792020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
124
|
Alder G, Signal N, Olsen S and Taylor D: A
systematic review of paired associative stimulation (PAS) to
modulate lower limb corticomotor excitability: Implications for
stimulation parameter selection and experimental design. Front
Neurosci. 13:8952019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
125
|
Silverstein J, Cortes M, Tsagaris KZ,
Climent A, Gerber LM, Oromendia C, Fonzetti P, Ratan RR, Kitago T,
Iacoboni M, et al: Paired associative stimulation as a tool to
assess plasticity enhancers in chronic stroke. Front Neurosci.
13:7922019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
126
|
Motta C, Di Lorenzo F, Ponzo V,
Pellicciari MC, Bonnì S, Picazio S, Mercuri NB, Caltagirone C,
Martorana A and Koch G: Transcranial magnetic stimulation predicts
cognitive decline in patients with Alzheimer's disease. J Neurol
Neurosurg Psychiatry. 89:1237–1242. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
127
|
Bashir S, Al-Hussain F, Hamza A, Shareefi
GF, Abualait T and Yoo WK: Role of single low pulse intensity of
transcranial magnetic stimulation over the frontal cortex for
cognitive function. Front Hum Neurosci. 14:2052020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
128
|
Nardone R, Tezzon F, Höller Y, Golaszewski
S, Trinka E and Brigo F: Transcranial magnetic stimulation
(TMS)/repetitive TMS in mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer's
disease. Acta Neurol Scand. 129:351–366. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
129
|
Cappa SF, Sandrini M, Rossini PM, Sosta K
and Miniussi C: The role of the left frontal lobe in action naming
rTMS evidence. Neurology. 59:720–723. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
130
|
Cotelli M, Manenti R, Cappa SF, Geroldi C,
Zanetti O, Rossini PM and Miniussi C: Effect of transcranial
magnetic stimulation on action naming in patients with Alzheimer
disease. Arch Neurol. 63:1602–1604. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
131
|
Cotelli M, Manenti R, Cappa SF, Zanetti O
and Miniussi C: Transcranial magnetic stimulation improves naming
in Alzheimer disease patients at different stages of cognitive
decline. Eur J Neurol. 15:1286–1292. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
132
|
Cotelli M, Calabria M, Manenti R, Rosini
S, Zanetti O, Cappa SF and Miniussi C: Improved language
performance in Alzheimer disease following brain stimulation. J
Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 82:794–797. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
133
|
Ahmed MA, Darwish ES, Khedr EM, El Serogy
YM and Ali AM: Effects of low versus high frequencies of repetitive
transcranial magnetic stimulation on cognitive function and
cortical excitability in Alzheimer's dementia. J Neurology.
259:83–92. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
134
|
Zhang F, Qin Y, Xie L, Zheng C, Huang X
and Zhang M: High-frequency repetitive transcranial magnetic
stimulation combined with cognitive training improves cognitive
function and cortical metabolic ratios in Alzheimer's disease. J
Neural Transm (Vienna). 126:1081–1094. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
135
|
Turriziani P, Smirni D, Mangano GR,
Zappalà G, Giustiniani A, Cipolotti L and Oliveri M: Low-frequency
repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation of the right
dorsolateral prefrontal cortex enhances recognition Memory in
Alzheimer's disease. J Alzheimers Dis. 72:613–622. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
136
|
Huang Z, Tan T, Du Y, Chen L, Fu M, Yu Y,
Zhang L, Song W and Dong Z: Low-frequency repetitive transcranial
magnetic stimulation ameliorates cognitive function and synaptic
plasticity in APP23/PS45 mouse model of Alzheimer's disease. Front
Aging Neurosci. 9:2922017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
137
|
Bagattini C, Zanni M, Barocco F, Caffarra
P, Brignani D, Miniussi C and Defanti CA: Enhancing cognitive
training effects in Alzheimer's disease: rTMS as an add-on
treatment. Brain Stimul. 13:1655–1664. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
138
|
Huerta PT and Volpe BT: Transcranial
magnetic stimulation, synaptic plasticity and network oscillations.
J Neuroeng Rehabil. 6:72009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
139
|
Liu W, Ma R and Yuan Y:
Post-transcriptional regulation of genes related to biological
behaviors of gastric cancer by long noncoding RNAs and MicroRNAs. J
Cancer. 8:4141–4154. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
140
|
Catalanotto C, Cogoni C and Zardo G:
MicroRNA in control of gene expression: An overview of nuclear
functions. Int J Mol Sci. 17:17122016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
141
|
Zhao J, Yue D, Zhou Y, Jia L, Wang H, Guo
M, Xu H, Chen C, Zhang J and Xu L: The role of MicroRNAs in Aβ
deposition and Tau phosphorylation in Alzheimer's disease. Front
Neurol. 8:3422017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
142
|
Konovalova J, Gerasymchuk D, Parkkinen I,
Chmielarz P and Domanskyi A: Interplay between MicroRNAs and
oxidative stress in neurodegenerative diseases. Int J Mol Sci.
20:60552019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
143
|
Friedman RC, Farh KK, Burge CB and Bartel
DP: Most mammalian mRNAs are conserved targets of microRNAs. Genome
Res. 19:92–105. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
144
|
Rooda I, Hensen K, Kaselt B, Kasvandik S,
Pook M, Kurg A, Salumets A and Velthut-Meikas A: Target prediction
and validation of microRNAs expressed from FSHR and aromatase genes
in human ovarian granulosa cells. Sci Rep. 10:23002020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
145
|
Song M: miRNAs-dependent regulation of
synapse formation and function. Genes Genomics. 42:837–845. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
146
|
Hu Z and Li Z: miRNAs in synapse
development and synaptic plasticity. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 45:24–31.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
147
|
Siedlecki-Wullich D, Català-Solsona J,
Fábregas C, Hernández I, Clarimon J, Lleó A, Boada M, Saura CA,
Rodríguez-Álvarez J and Miñano-Molina AJ: Altered microRNAs related
to synaptic function as potential plasma biomarkers for Alzheimer's
disease. Alzheimers Res Ther. 11:462019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
148
|
Wei W, Wang ZY, Ma LN, Zhang TT, Cao Y and
Li H: MicroRNAs in Alzheimer's disease: Function and potential
applications as diagnostic biomarkers. Front Mol Neurosci.
13:1602020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
149
|
Angelucci F, Cechova K, Valis M, Kuca K,
Zhang B and Hort J: MicroRNAs in Alzheimer's disease: Diagnostic
markers or therapeutic agents? Front Pharmacol. 10:6652019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
150
|
Amakiri N, Kubosumi A, Tran J and Reddy
PH: Amyloid beta and microRNAs in Alzheimer's disease. Front
Neurosci. 13:4302019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
151
|
Liu H, Han XH, Chen H, Zheng CX, Yang Y
and Huang XL: Repetitive magnetic stimulation promotes neural stem
cells proliferation by upregulating MiR-106b in vitro. J Huazhong
Univ Sci Technolog Med Sci. 35:766–772. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
152
|
Liu H, Li G, Ma C, Chen Y, Wang J and Yang
Y: Repetitive magnetic stimulation promotes the proliferation of
neural progenitor cells via modulating the expression of miR-106b.
Int J Mol Med. 42:3631–3639. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
153
|
Aydin-Abidin S, Trippe J, Funke K, Eysel
UT and Benali A: High- and low-frequency repetitive transcranial
magnetic stimulation differentially activates c-Fos and zif268
protein expression in the rat brain. Exp Brain Res. 188:249–261.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
154
|
Perez FP, Maloney B, Chopra N, Morisaki JJ
and Lahiri DK: Repeated electromagnetic field stimulation lowers
amyloid-β peptide levels in primary human mixed brain tissue
cultures. Sci Rep. 11:6212021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
155
|
Loo CK, McFarquhar TF and Mitchell PB: A
review of the safety of repetitive transcranial magnetic
stimulation as a clinical treatment for depression. Int J
Neuropsychopharmacol. 11:131–147. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
156
|
Najib U and Horvath J: Transcranial
magnetic stimulation (TMS) safety considerations and
recommendations. Neuromethods. 89:15–30. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
157
|
Wassermann EM: Side effects of repetitive
transcranial magnetic stimulation. Depress Anxiety. 12:124–129.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
158
|
Dhamne SC, Kothare RS, Yu C, Hsieh TH,
Anastasio EM, Oberman L, Pascual-Leone A and Rotenberg A: A measure
of acoustic noise generated from transcranial magnetic stimulation
coils. Brain Stimul. 7:432–434. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
159
|
Varone G, Hussain Z, Sheikh Z, Howard A,
Boulila W, Mahmud M, Howard N, Morabito FC and Hussain A: Real-time
artifacts reduction during TMS-EEG co-registration: A comprehensive
review on technologies and procedures. Sensors (Basel). 21:6372021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
160
|
Duecker F and Sack AT: Rethinking the role
of sham TMS. Front Psychol. 6:2102015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
161
|
Wassermann EM: Risk and safety of
repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation: Report and suggested
guidelines from the International Workshop on the Safety of
Repetitive Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation, June 5–7, 1996.
Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 108:1–16. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
162
|
Chen R, Gerloff C, Classen J, Wassermann
EM, Hallett M and Cohen LG: Safety of different inter-train
intervals for repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation and
recommendations for safe ranges of stimulation parameters.
Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 105:415–421. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
163
|
Rossi S, Hallett M, Rossini PM and
Pascual-Leone A; Safety of TMS Consensus Group, : Safety, ethical
considerations, and application guidelines for the use of
transcranial magnetic stimulation in clinical practice and
research. Clin Neurophysiol. 120:2008–2039. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
164
|
DeTure MA and Dickson DW: The
neuropathological diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease. Mol
Neurodegener. 14:322019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
165
|
Jellinger KA: Neuropathology of the
Alzheimer's continuum: An update. Free Neuropathol. 1:32. 2020.
|
|
166
|
Speer AM, Kimbrell TA, Wassermann EM, D
Repella J, Willis MW, Herscovitch P and Post RM: Opposite effects
of high and low frequency rTMS on regional brain activity in
depressed patients. Biol Psychiatry. 48:1133–1141. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
167
|
Ilmoniemi RJ, Mäki H, Saari J, Salvador R
and Miranda PC: The frequency-dependent neuronal length constant in
transcranial magnetic stimulation. Front Cell Neurosci. 10:1942016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
168
|
Freedberg M, Reeves JA, Hussain SJ,
Zaghloul KA and Wassermann EM: Identifying site- and
stimulation-specific TMS-evoked EEG potentials using a quantitative
cosine similarity metric. PLoS One. 15:e02161852020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|