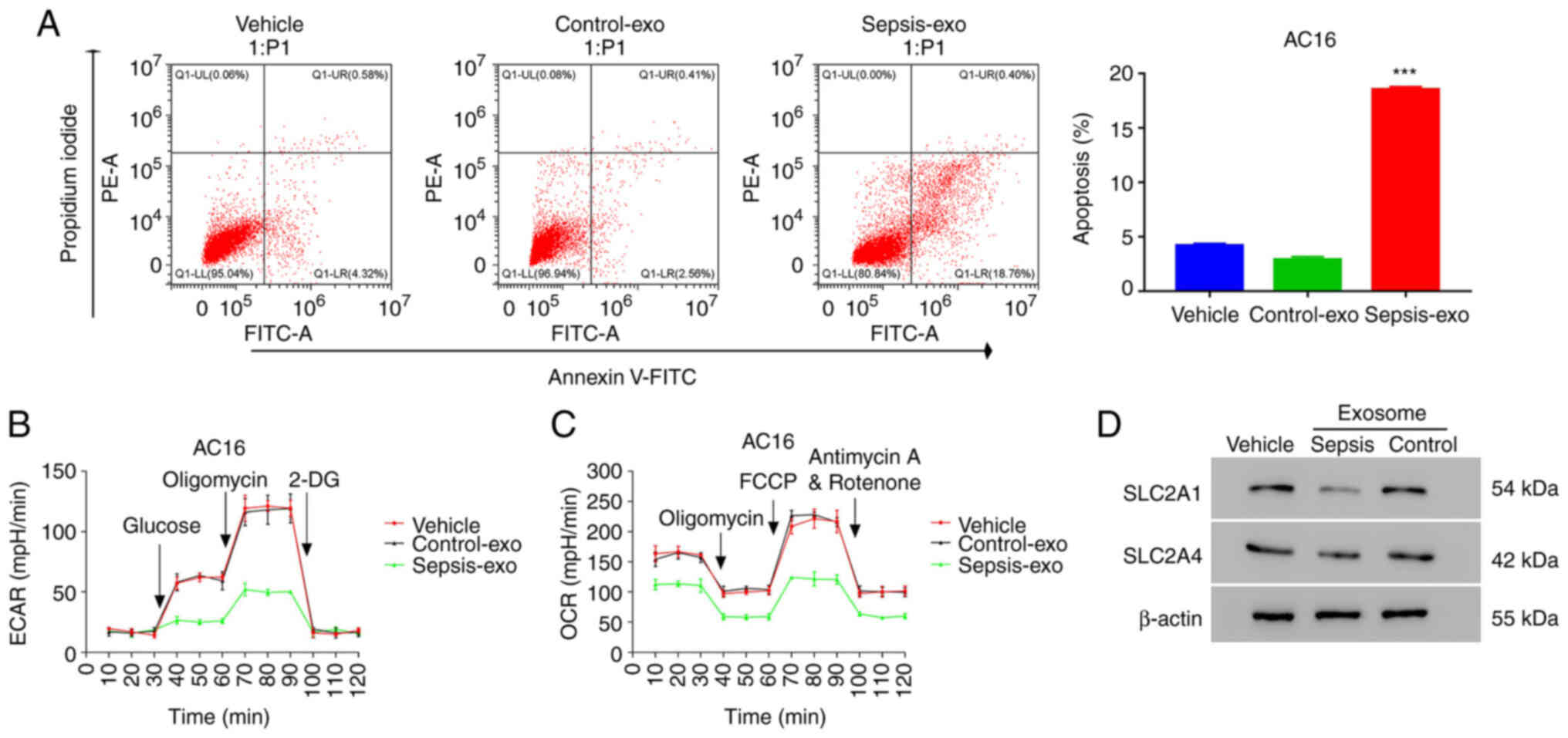
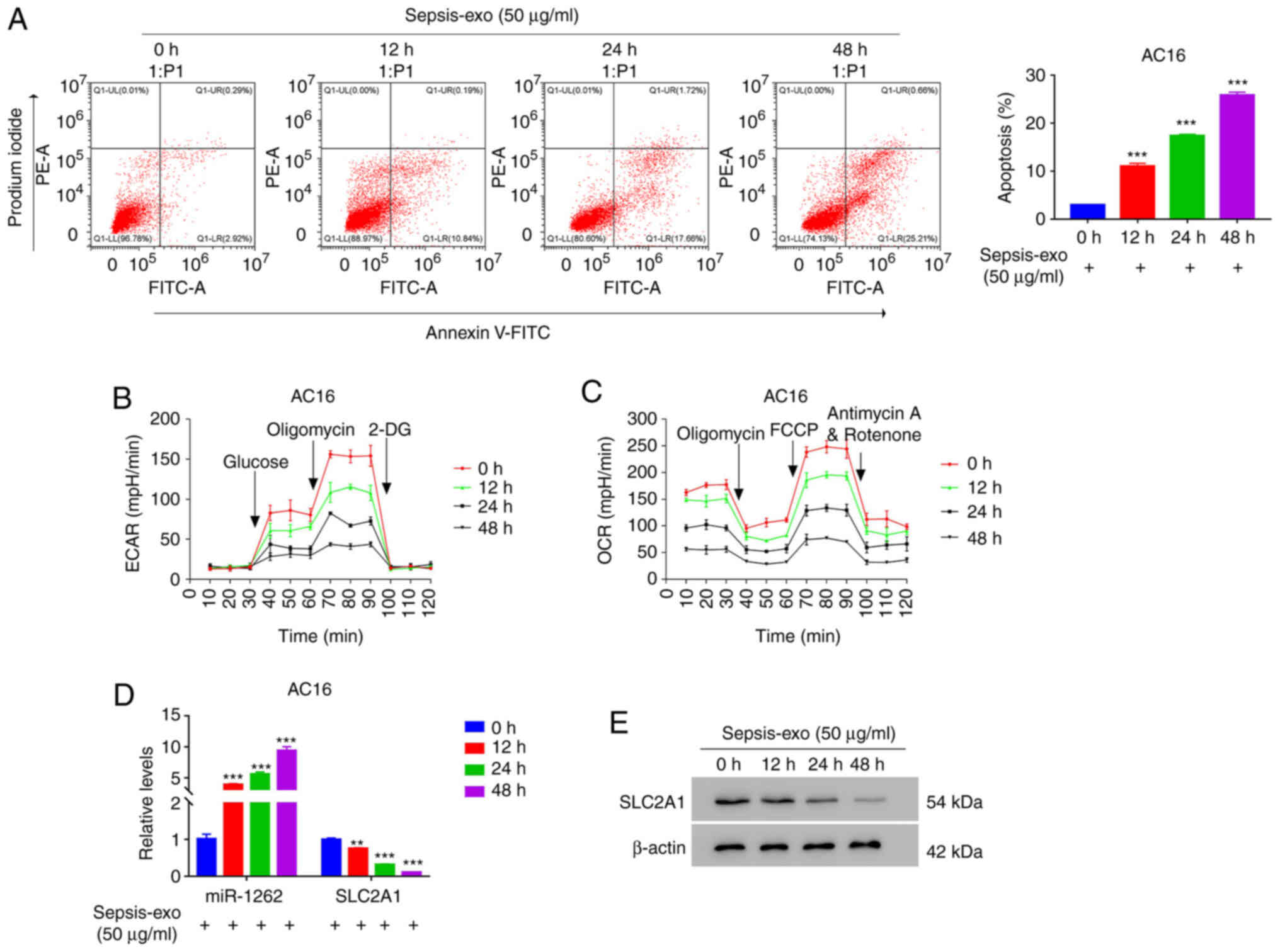
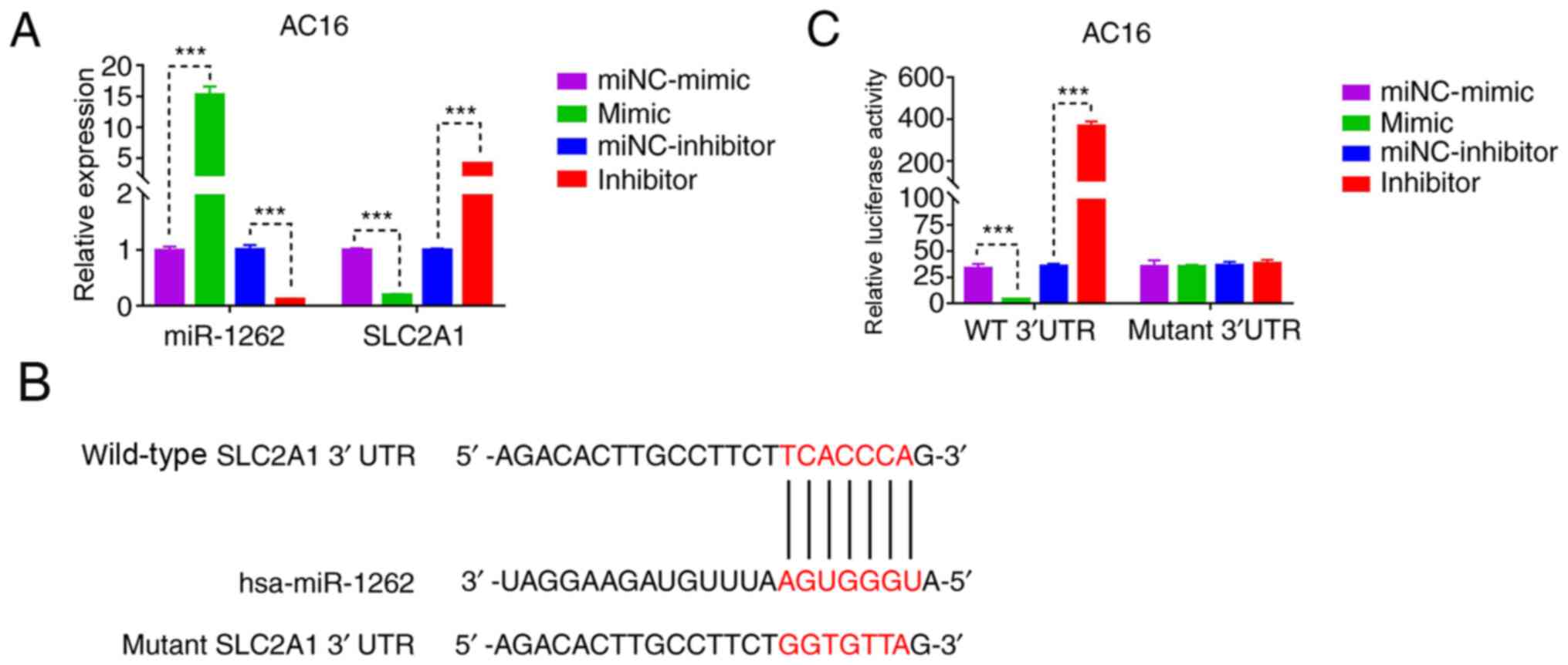
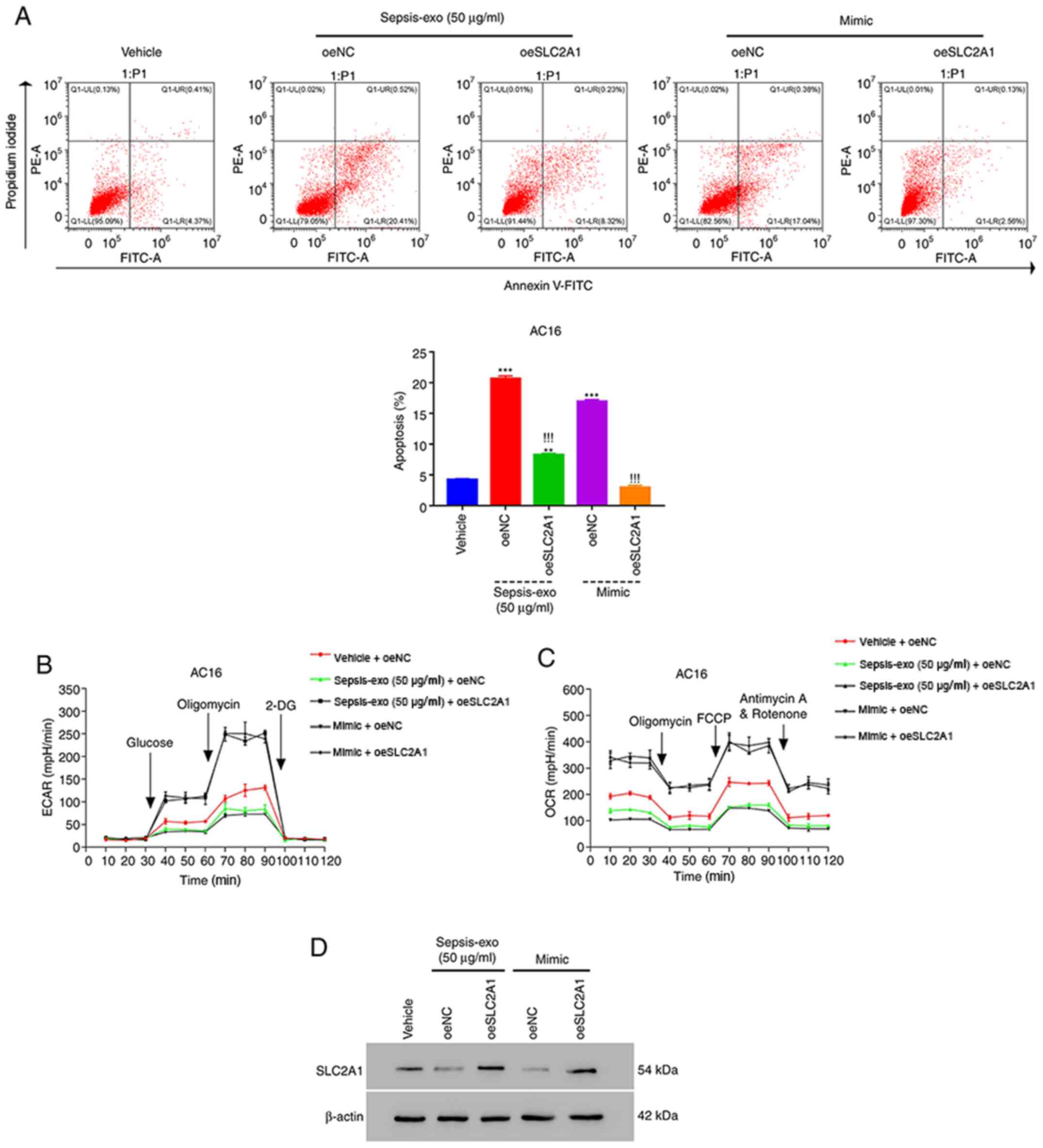
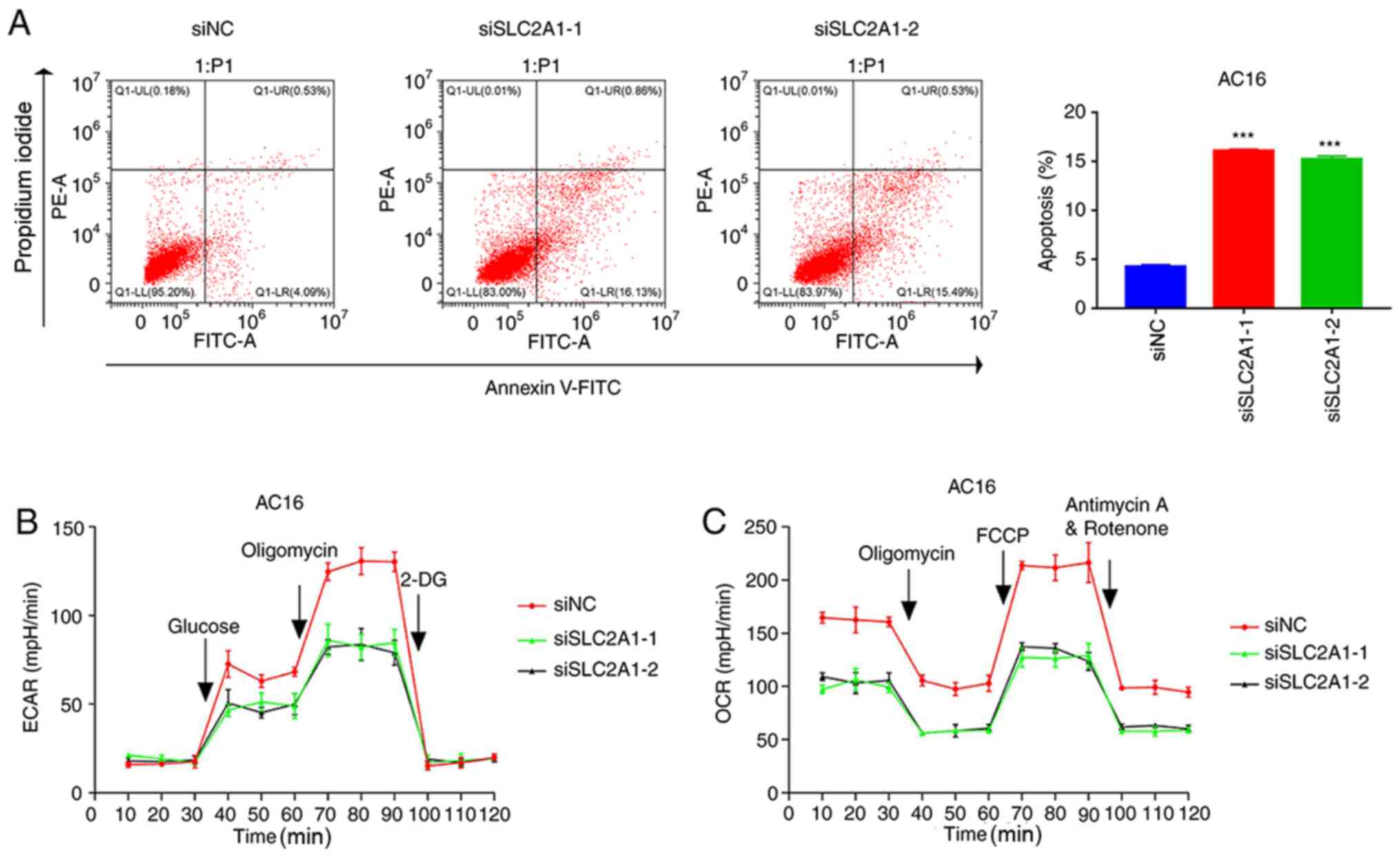
|
1
|
Kakihana Y, Ito T, Nakahara M, Yamaguchi K
and Yasuda T: Sepsis-induced myocardial dysfunction:
Pathophysiology and management. J Intensive Care. 4:222016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Dombrovskiy VY, Martin AA, Sunderram J and
Paz HL: Rapid increase in hospitalization and mortality rates for
severe sepsis in the United States: A trend analysis from 1993 to
2003. Crit Care Med. 35:1244–1250. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Frencken JF, Donker DW, Spitoni C,
Koster-Brouwer ME, Soliman IW, Ong DS, Horn J, van der Poll T, van
Klei WA, Bonten MJ and Cremer OL: Myocardial injury in patients
with sepsis and its association with long-term outcome. Circ
Cardiovasc Qual Outcomes. 11:e0040402018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Parrillo JE, Parker MM, Natanson C,
Suffredini AF, Danner RL, Cunnion RE and Ognibene FP: Septic shock
in humans. Advances in the understanding of pathogenesis,
cardiovascular dysfunction, and therapy. Ann Intern Med.
113:227–242. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Gyawali B, Ramakrishna K and Dhamoon AS:
Sepsis: The evolution in definition, pathophysiology, and
management. SAGE Open Med. 7:20503121198350432019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Ooi AT and Gomperts BN: Molecular
pathways: Targeting cellular energy metabolism in cancer via
inhibition of SLC2A1 and LDHA. Clin Cancer Res. 21:2440–2444. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Di Dedda C, Vignali D, Piemonti L and
Monti P: Pharmacological targeting of GLUT1 to control autoreactive
T cell responses. Int J Mol Sci. 20:49622019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Jiang B: Aerobic glycolysis and high level
of lactate in cancer metabolism and microenvironment. Genes Dis.
4:25–27. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Krzeslak A, Wojcik-Krowiranda K, Forma E,
Jozwiak P, Romanowicz H, Bienkiewicz A and Brys M: Expression of
GLUT1 and GLUT3 glucose transporters in endometrial and breast
cancers. Pathol Oncol Res. 18:721–728. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Guo W, Sun S, Guo L, Song P, Xue X, Zhang
H, Zhang G, Li R, Gao Y, Qiu B, et al: Elevated SLC2A1 expression
correlates with poor prognosis in patients with surgically resected
lung adenocarcinoma: A study based on immunohistochemical analysis
and bioinformatics. DNA Cell Biol. 39:631–644. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Palmer CS, Cherry CL, Sada-Ovalle I, Singh
A and Crowe SM: Glucose metabolism in T cells and monocytes: New
perspectives in HIV pathogenesis. EBioMedicine. 6:31–41. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Vary TC, Drnevich D, Jurasinski C and
Brennan WA Jr: Mechanisms regulating skeletal muscle glucose
metabolism in sepsis. Shock. 3:403–410. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zhang Y, Liu Y, Liu H and Tang WH:
Exosomes: Biogenesis, biologic function and clinical potential.
Cell Biosci. 9:192019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Pegtel DM and Gould SJ: Exosomes. Annu Rev
Biochem. 88:487–514. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Cai Y, Yu X, Hu S and Yu J: A brief review
on the mechanisms of miRNA regulation. Genomics Proteomics
Bioinformatics. 7:147–154. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Sato-Kuwabara Y, Melo SA, Soares FA and
Calin GA: The fusion of two worlds: Non-coding RNAs and
extracellular vesicles-diagnostic and therapeutic implications
(Review). Int J Oncol. 46:17–27. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Zhang J, Li S, Li L, Li M, Guo C, Yao J
and Mi S: Exosome and exosomal microRNA: Trafficking, sorting, and
function. Genomics Proteomics Bioinformatics. 13:17–24. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Lei T, Zhang L, Song Y, Wang B, Shen Y,
Zhang N and Yang M: miR-1262 transcriptionally modulated by an
enhancer genetic variant improves efficiency of epidermal growth
factor receptor-tyrosine kinase inhibitors in advanced lung
adenocarcinoma. DNA Cell Biol. 39:1111–1118. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Ahmad S, Ahmed MM, Hasan PMZ, Sharma A,
Bilgrami AL, Manda K, Ishrat R and Syed MA: Identification and
validation of potential miRNAs, as biomarkers for sepsis and
associated lung injury: A network-based approach. Genes.
11:13272020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Ding X, Liu J, Liu T, Ma Z, Wen D and Zhu
J: miR-148b inhibits glycolysis in gastric cancer through targeting
SLC2A1. Cancer Med. 6:1301–1310. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Xia X, Wang Y, Huang Y, Zhang H, Lu H and
Zheng JC: Exosomal miRNAs in central nervous system diseases:
Biomarkers, pathological mediators, protective factors and
therapeutic agents. Prog Neurobiol. 183:1016942019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Hu C, Meiners S, Lukas C, Stathopoulos GT
and Chen J: Role of exosomal microRNAs in lung cancer biology and
clinical applications. Cell Prolif. 53:e128282020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Singh A: Exosome-mediated transfer of
integrins promotes cell-cell communication in prostate cancer.
(2017). ETD Collection for Thomas Jefferson University.
AAI10617823. https://jdc.jefferson.edu/dissertations/AAI10617823/February
24–2021
|
|
24
|
Kenneth JL and Thomas DS: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2-ΔΔCT method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Xie K, Chen M, Zhu M, Wang C, Qin N, Liang
C, Song C, Dai J, Jin G, Shen H, et al: A polymorphism in miR-1262
regulatory region confers the risk of lung cancer in Chinese
population. Int J Cancer. 141:958–966. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Li L, Qu WH, Ma HP, Wang LL, Zhang YB and
Ma Y: LRP8, modulated by miR-1262, promotes tumour progression and
forecasts the prognosis of patients in breast cancer. Arch Physiol
Biochem. 29:1–9. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Macintyre AN, Gerriets VA, Nichols AG,
Michalek RD, Rudolph MC, Deoliveira D, Anderson SM, Abel ED, Chen
BJ, Hale LP and Rathmell JC: The glucose transporter Glut1 is
selectively essential for CD4 T cell activation and effector
function. Cell Metab. 20:61–72. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Szablewski L: Expression of glucose
transporters in cancers. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1835:164–169.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Lang CH and Dobrescu C: Sepsis-induced
increases in glucose uptake by macrophage-rich tissues persist
during hypoglycemia. Metabolism. 40:585–593. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Fukuzumi M, Shinomiya H, Shimizu Y, Ohishi
K and Utsumi S: Endotoxin-induced enhancement of glucose influx
into murine peritoneal macrophages via GLUT1. Infect Immun.
64:108–112. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Tan Q, Huang Q, Ma YL, Mao K, Yang G, Luo
P, Ma G, Mei P and Jin Y: Potential roles of IL-1 subfamily members
in glycolysis in disease. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 44:18–27.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Taylor DJ: Interleukin-1 stimulation of
fibroblast glycolysis is accompanied by reduced glucose oxidation
in the tricarboxylic acid cycle. Biochem Soc Trans. 18:982–983.
1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Zheng Z, Ma H, Zhang X, Tu F, Wang X, Ha
T, Fan M, Liu L, Xu J, Yu K, et al: Enhanced glycolytic metabolism
contributes to cardiac dysfunction in polymicrobial sepsis. J
Infect Dis. 215:1396–1406. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Yang L, Xie M, Yang M, Yu Y, Zhu S, Hou W,
Kang R, Lotze MT, Billiar TR, Wang H, et al: PKM2 regulates the
Warburg effect and promotes HMGB1 release in sepsis. Nat Commun.
5:44362014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
MacFarlane M, Robinson GL and Cain K:
Glucose-a sweet way to die: Metabolic switching modulates tumor
cell death. Cell Cycle. 11:3919–3925. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Mason EF, Zhao Y, Goraksha-Hicks P, Coloff
JL, Gannon H, Jones SN and Rathmell JC: Aerobic glycolysis
suppresses p53 activity to provide selective protection from
apoptosis upon loss of growth signals or inhibition of BCR-Abl.
Cancer Res. 70:8066–8076. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|