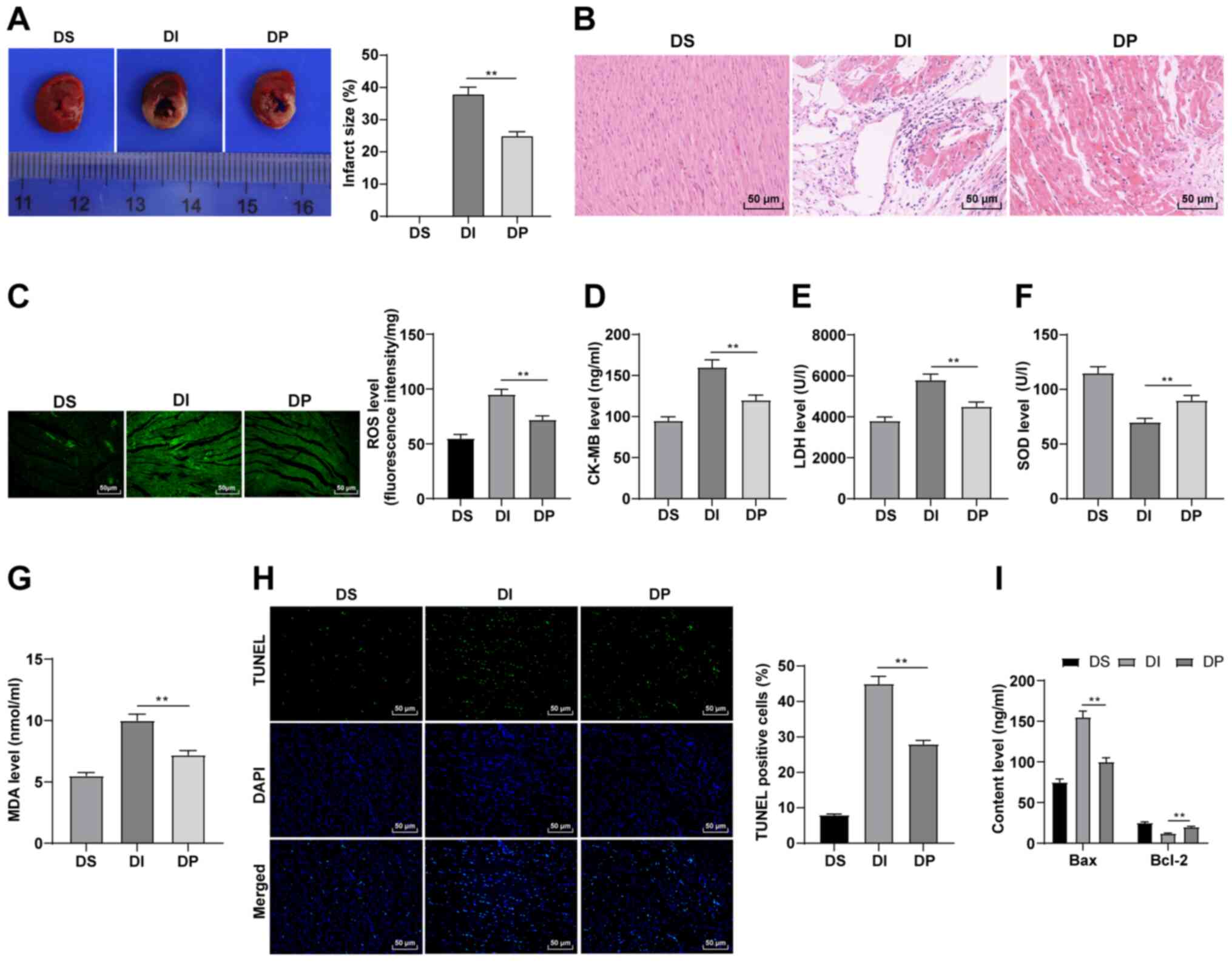
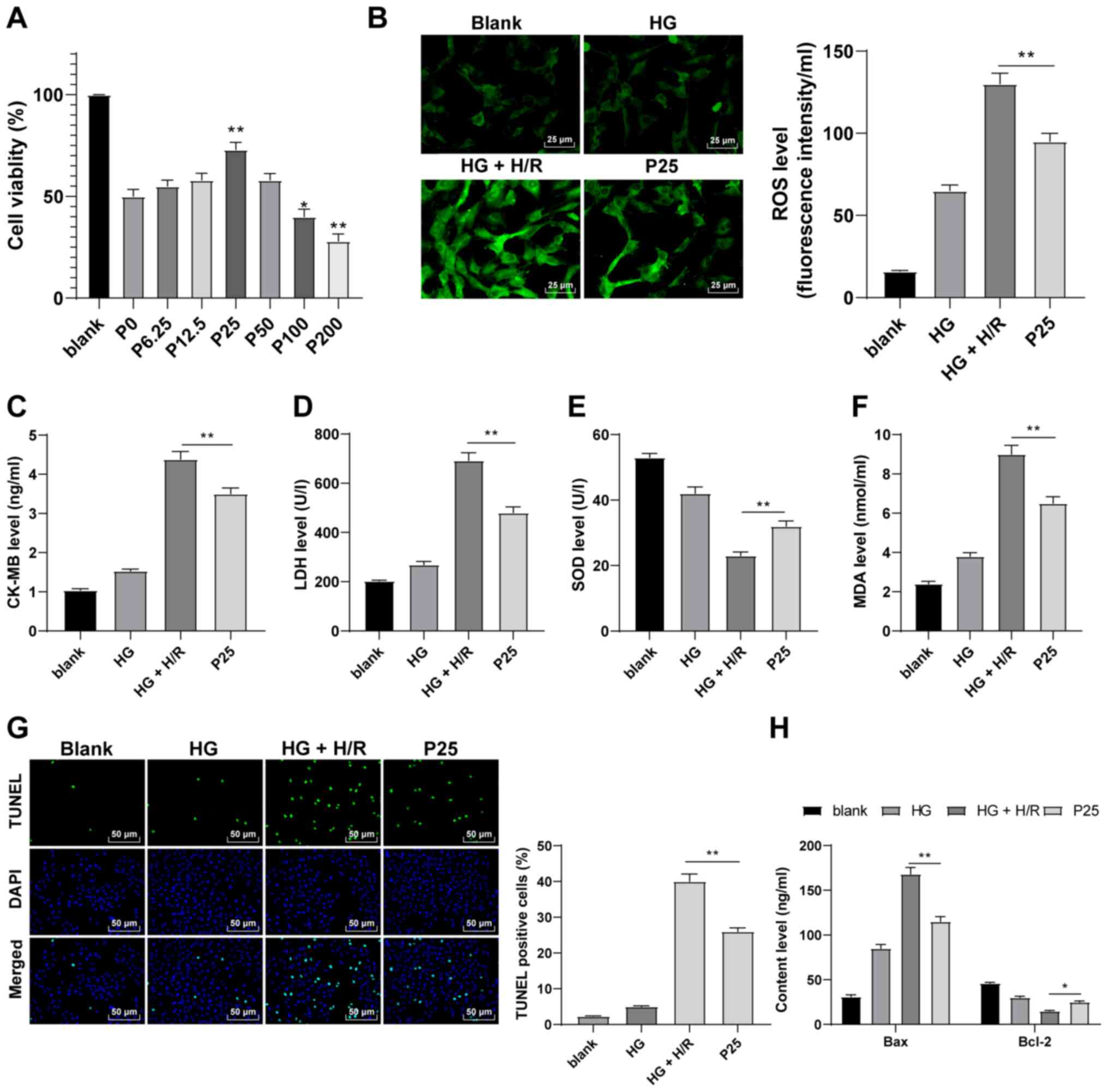
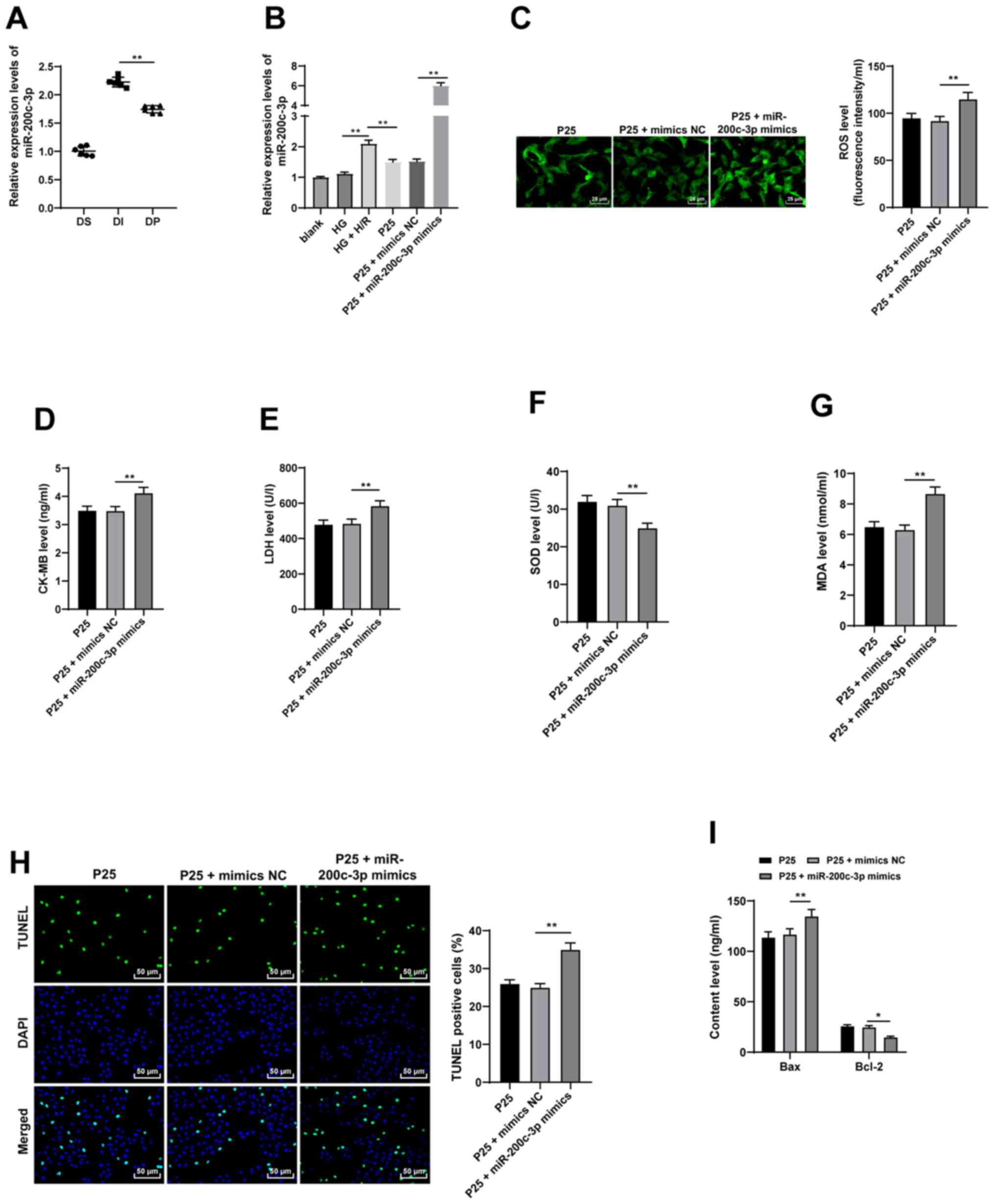
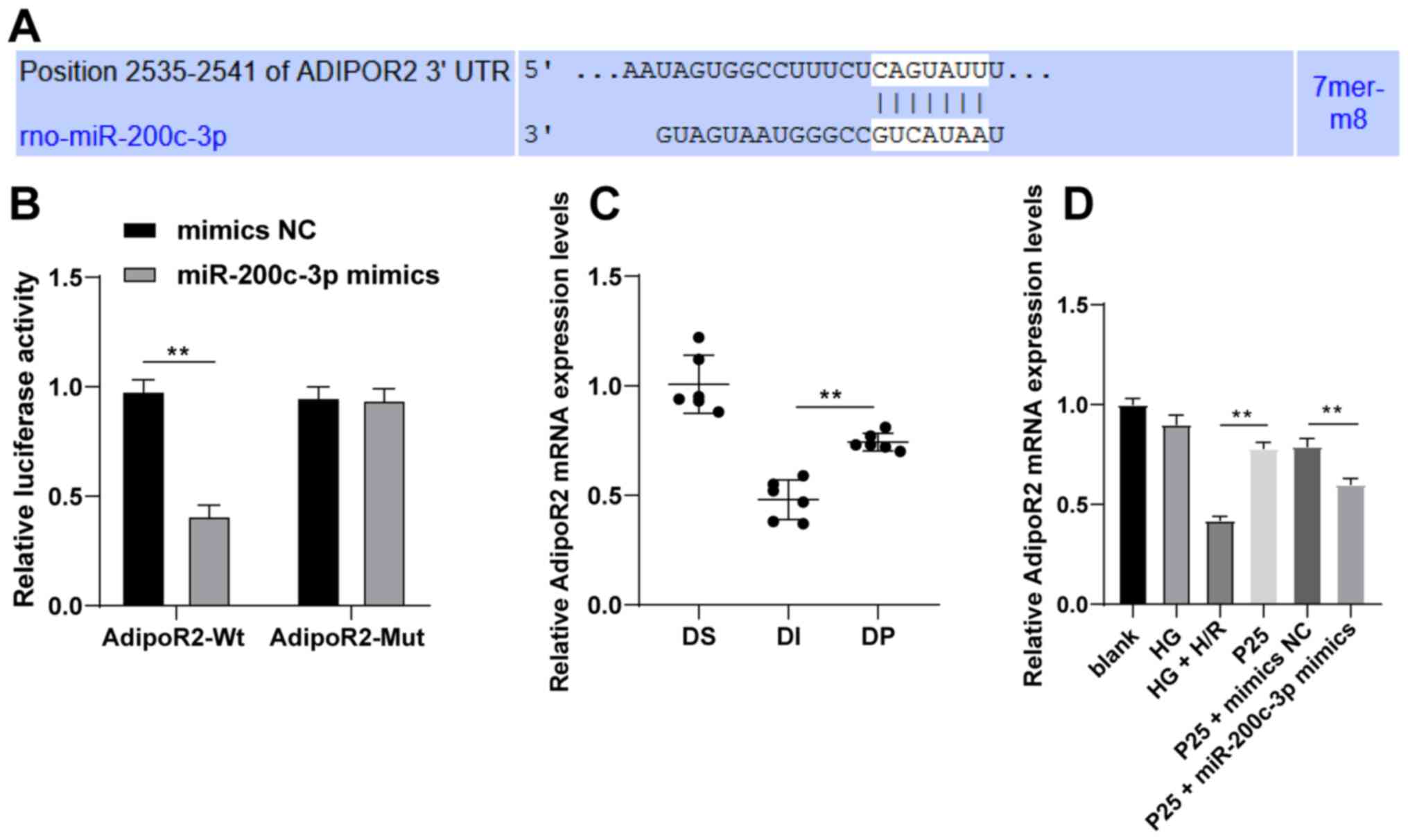
|
1
|
Kerner W and Bruckel J; German Diabetes
Association, : Definition, classification and diagnosis of diabetes
mellitus. Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes. 122:384–386. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Yu SY, Dong B, Fang ZF, Hu XQ, Tang L and
Zhou SH: Knockdown of lncRNA AK139328 alleviates myocardial
Ischaemia/reperfusion injury in diabetic mice via modulating
miR-204-3p and inhibiting autophagy. J Cell Mol Med. 22:4886–4898.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Tao A, Xu X, Kvietys P, Kao R, Martin C
and Rui T: Experimental diabetes mellitus exacerbates
ischemia/reperfusion-induced myocardial injury by promoting
mitochondrial fission: Role of down-regulation of myocardial Sirt1
and subsequent Akt/Drp1 interaction. Int J Biochem Cell Biol.
105:94–103. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Li J, Zhao Y, Zhou N, Li L and Li K:
Dexmedetomidine attenuates myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury
in diabetes mellitus by inhibiting endoplasmic reticulum stress. J
Diabetes Res. 2019:78693182019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Eltzschig HK and Eckle T: Ischemia and
reperfusion-from mechanism to translation. Nat Med. 17:1391–1401.
2011. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Xu Y, Pan S, Jiang W, Xue F and Zhu X:
Effects of propofol on the development of cancer in humans. Cell
Prolif. 53:e128672020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Yan HJ, Qi GQ and Ma Y: Effect of propofol
on myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury through MAPK/ERK pathway.
Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 23:11051–11061. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Facey J, Young L and Nwokocha C:
Relaxation responses of ketamine and propofol to vasoactive agents
in Streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Niger J Physiol Sci.
35:33–39. 2020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Deng F, Wang S, Zhang L, Xie X, Cai S, Li
H, Xie GL, Miao HL, Yang C, Liu X and Xia Z: Propofol through
upregulating Caveolin-3 attenuates Post-hypoxic mitochondrial
damage and cell death in H9C2 cardiomyocytes during hyperglycemia.
Cell Physiol Biochem. 44:279–292. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Lin C, Sui H, Gu J, Yang X, Deng L, Li W,
Ding W, Li D and Yang Y: Effect and mechanism of propofol on
myocardial ischemia reperfusion injury in type 2 diabetic rats.
Microvasc Res. 90:162–168. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Hao W, Zhao ZH, Meng QT, Tie ME, Lei SQ
and Xia ZY: Propofol protects against hepatic ischemia/reperfusion
injury via miR-133a-5p regulating the expression of MAPK6. Cell
Biol Int. 41:495–504. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Lu TX and Rothenberg ME: MicroRNA. J
Allergy Clin Immunol. 141:1202–1207. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zhen W, Hui D, Wenying S and Yulong S:
MicroRNA-20b-5p regulates propofol-preconditioning-induced
inhibition of autophagy in hypoxia-and-reoxygenation-stimulated
endothelial cells. J Biosci. 45:352020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Dehaini H, Awada H, El-Yazbi A, Zouein FA,
Issa K, Eid AA, Ibrahim M, Badran A, Baydoun E, Pintus G and Eid
AH: MicroRNAs as potential pharmaco-targets in ischemia-reperfusion
injury compounded by diabetes. Cells. 8:1522019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Climent M, Viggiani G, Chen YW, Coulis G
and Castaldi A: MicroRNA and ROS crosstalk in cardiac and pulmonary
diseases. Int J Mol Sci. 21:43702020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Zhao B, Gao WW, Liu YJ, Jiang M, Liu L,
Yuan Q, Hou JB and Xia ZY: The role of glycogen synthase kinase 3
beta in brain injury induced by myocardial ischemia/reperfusion
injury in a rat model of diabetes mellitus. Neural Regen Res.
12:1632–1639. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Li H, Yao W, Liu Z, Xu A, Huang Y, Ma XL,
Irwin MG and Xia Z: Hyperglycemia abrogates ischemic
postconditioning cardioprotection by impairing
AdipoR1/Caveolin-3/STAT3 signaling in diabetic rats. Diabetes.
65:942–955. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Wang HY, Wang GL, Yu YH and Wang Y: The
role of phosphoinositide-3-kinase/Akt pathway in propofol-induced
postconditioning against focal cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury
in rats. Brain Res. 1297:177–184. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zhu HJ, Wang DG, Yan J and Xu J:
Up-regulation of microRNA-135a protects against myocardial
ischemia/reperfusion injury by decreasing TXNIP expression in
diabetic mice. Am J Transl Res. 7:2661–2671. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Agarwal V, Bell GW, Nam JW and Bartel DP:
Predicting effective microRNA target sites in mammalian mRNAs.
Elife. 4:e050052015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Wang T, Mao X, Li H, Qiao S, Xu A, Wang J,
Lei S, Liu Z, Ng KF, Wong GT, et al: N-Acetylcysteine and
allopurinol up-regulated the Jak/STAT3 and PI3K/Akt pathways via
adiponectin and attenuated myocardial postischemic injury in
diabetes. Free Radic Biol Med. 63:291–303. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Wang T, Qiao S, Lei S, Liu Y, Ng KF, Xu A,
Lam KS, Irwin MG and Xia Z: N-acetylcysteine and allopurinol
synergistically enhance cardiac adiponectin content and reduce
myocardial reperfusion injury in diabetic rats. PLoS One.
6:e239672011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Zhan L, Zhang Y, Su W, Zhang Q, Chen R,
Zhao B, Li W, Xue R, Xia Z and Lei S: The roles of autophagy in
acute lung injury induced by myocardial ischemia reperfusion in
diabetic rats. J Diabetes Res. 2018:50475262018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Li YM, Sun JG, Hu LH, Ma XC, Zhou G and
Huang XZ: Propofol-mediated cardioprotection dependent of
microRNA-451/HMGB1 against myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury.
J Cell Physiol. 234:23289–23301. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Wang Y, Che J, Zhao H, Tang J and Shi G:
Platycodin D inhibits oxidative stress and apoptosis in H9c2
cardiomyocytes following hypoxia/reoxygenation injury. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 503:3219–3224. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Rahimi R, Karimi J, Khodadadi I, Tayebinia
H, Kheiripour N, Hashemnia M and Goli F: Silymarin ameliorates
expression of urotensin II (U-II) and its receptor (UTR) and
attenuates toxic oxidative stress in the heart of rats with type 2
diabetes. Biomed Pharmacother. 101:244–250. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Hu C, Zhang X, Wei W, Zhang N, Wu H, Ma Z,
Li L, Deng W and Tang Q: Matrine attenuates oxidative stress and
cardiomyocyte apoptosis in doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity via
maintaining AMPKα/UCP2 pathway. Acta Pharm Sin B. 9:690–701. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Chen Y and Li Z: Protective effects of
propofol on rats with cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury via the
PI3K/Akt Pathway. J Mol Neurosci. 71:810–820. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Li H, Zhang X, Tan J, Sun L, Xu LH, Jiang
YG, Lou JS, Shi XY and Mi WD: Propofol postconditioning protects
H9c2 cells from hypoxia/reoxygenation injury by inducing autophagy
via the SAPK/JNK pathway. Mol Med Rep. 17:4573–4580.
2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Tang M, Liu P, Li X, Wang JW, Zhu XC and
He FP: Protective action of B1R antagonist against cerebral
ischemia-reperfusion injury through suppressing miR-200c expression
of Microglia-derived microvesicles. Neurol Res. 39:612–620. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Wu Y, Gu C and Huang X: Sevoflurane
protects against hepatic ischemia/reperfusion injury by modulating
microRNA-200c regulation in mice. Biomed Pharmacother.
84:1126–1136. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Shi D, Guo L, Sun X, Shang M, Meng D, Zhou
X, Liu X, Zhao Y and Li J: UTMD inhibit EMT of breast cancer
through the ROS/miR-200c/ZEB1 axis. Sci Rep. 10:66572020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Nunomura A and Perry G: RNA and oxidative
stress in Alzheimer's disease: Focus on microRNAs. Oxid Med Cell
Longev. 2020:26381302020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Zhang Y, Zhao J, Li R, Lau WB, Yuan YX,
Liang B, Li R, Gao EH, Koch WJ, Ma XL and Wang YJ: AdipoRon, the
first orally active adiponectin receptor activator, attenuates
postischemic myocardial apoptosis through both AMPK-mediated and
AMPK-independent signalings. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab.
309:E275–E282. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Li D, Song LL, Wang J, Meng C and Cui XG:
Adiponectin protects against lung ischemia-reperfusion injury in
rats with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Mol Med Rep. 17:7191–7201.
2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Wang Y, Liang B, Lau WB, Du Y, Guo R, Yan
Z, Gan L, Yan W, Zhao J, Gao E, et al: Restoring diabetes-induced
autophagic flux arrest in ischemic/reperfused heart by ADIPOR
(adiponectin receptor) activation involves both AMPK-dependent and
AMPK-independent signaling. Autophagy. 13:1855–1869. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Zhang Y, Zheng LM, Wang CX, Gu JM and Xue
S: SENP3 protects H9C2 cells from apoptosis triggered by H/R via
STAT3 pathway. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 22:2778–2786.
2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Chen X, Wang Y, Xiao ZY, Hou DN, Li DB and
Zhang XP: Effect of propofol on myocardial ischemia/reperfusion
injury in rats through JAK/STAT signaling pathway. Eur Rev Med
Pharmacol Sci. 23:6330–6338. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Li K, Zhou P, Li S, Zheng S and Wang D:
MicroRNA-29b reduces myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats
via down-regulating PTEN and activating the Akt/eNOS signaling
pathway. J Thromb Thrombolysis. 53:123–135. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|