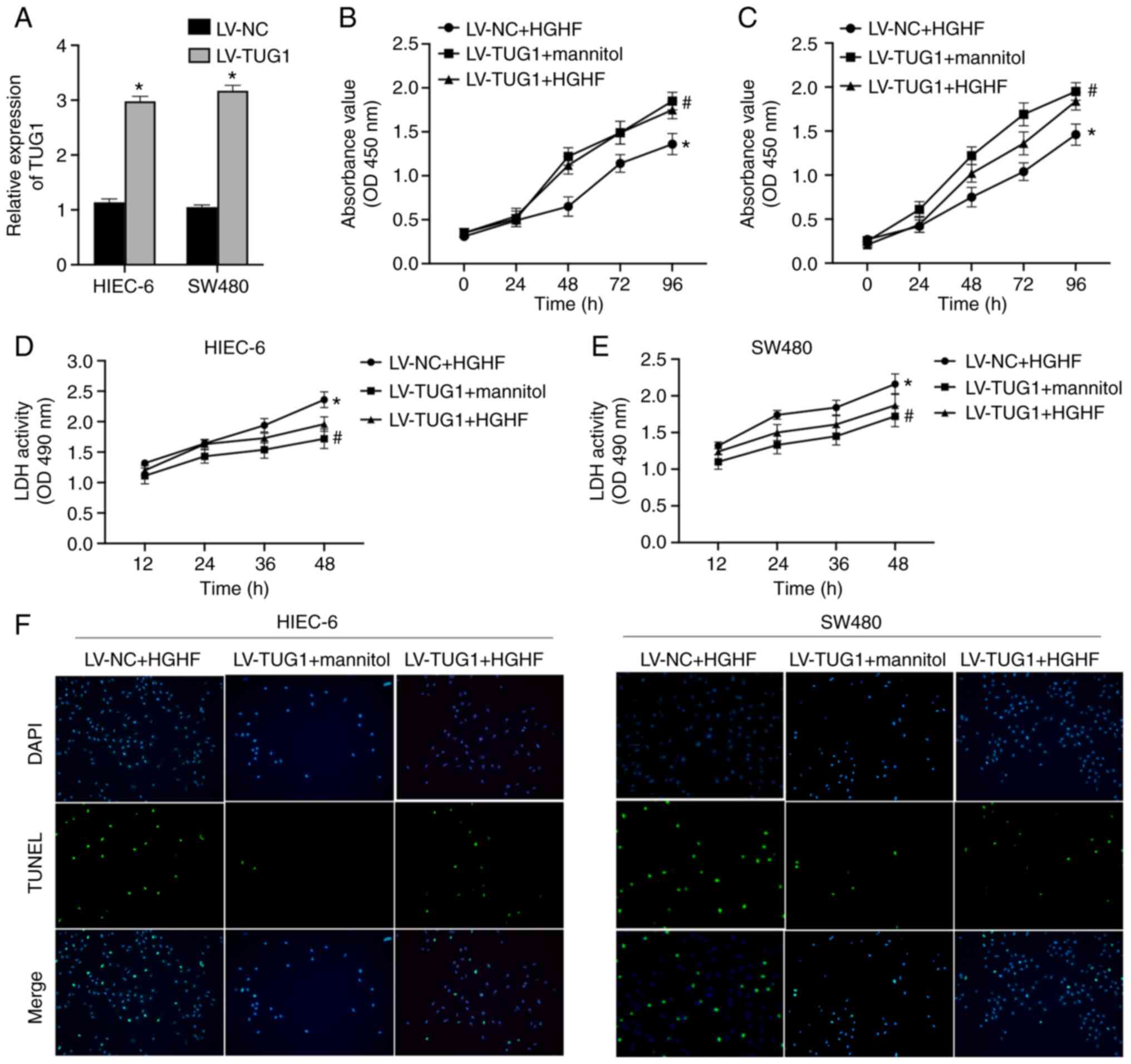
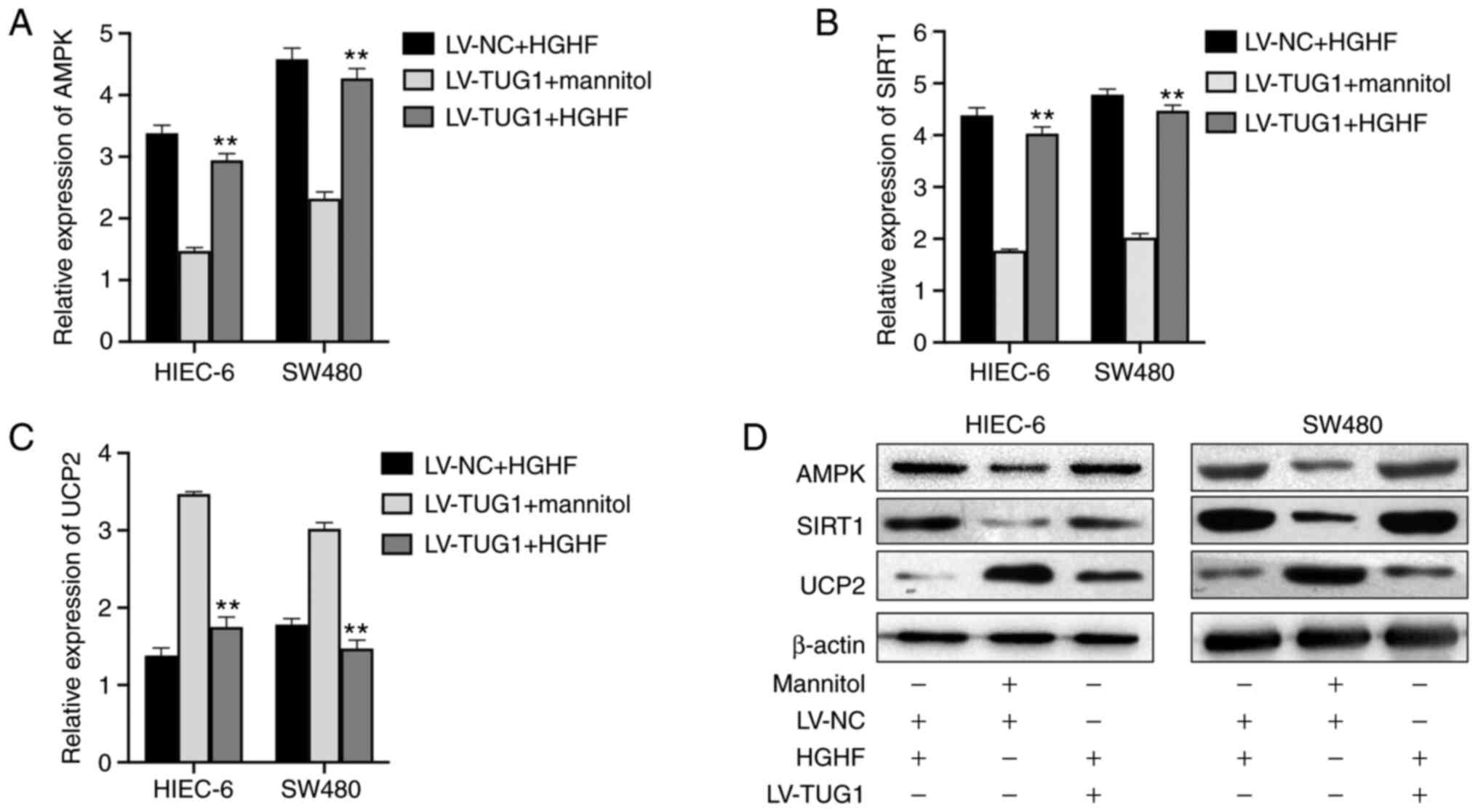
|
1
|
Wang Y, Xue H, Sun M, Zhu X, Zhao L and
Yang Y: Prevention and control of obesity in China. Lancet Glob
Health. 9:e1166–e1167. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Jia W, Weng J, Zhu D, Ji L, Lu J, Zhou Z,
Zou D, Guo L, Ji Q, Chen L, et al: Standards of medical care for
type 2 diabetes in China 2019. Diabetes Metab Res Rev.
35:e31582019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Ortega MA, Fraile-Martínez O, Naya I,
García-Honduvilla N, Álvarez-Mon M, Buján J, Asúnsolo Á and de la
Torre B: Type 2 diabetes mellitus associated with obesity
(diabesity). The central role of gut microbiota and its
translational applications. Nutrients. 12:27492020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Tsilingiris D, Koliaki C and Kokkinos A:
Remission of type 2 diabetes mellitus after bariatric surgery: Fact
or fiction? Int J Environ Res Public Health. 16:31712019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Zeng ZY, Sun J and Kang WM: History,
recent advancements, and prospects in bariatric/metabolic surgery.
Zhongguo Yi Xue Ke Xue Yuan Xue Bao. 40:581–590. 2018.(In Chinese).
PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Macauley M, Percival K, Thelwall PE,
Hollingsworth KG and Taylor R: Altered volume, morphology and
composition of the pancreas in type 2 diabetes. PLoS One.
10:e01268252015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Fan M, Jiang H, Zhang Y, Ma Y, Li L and Wu
J: Liraglutide enhances autophagy and promotes pancreatic β cell
proliferation to ameliorate type 2 diabetes in high-fat-fed and
streptozotocin-treated mice. Med Sci Monit. 24:2310–2316. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Xu H, Wang Q, Sun Q, Qin Y, Han A, Cao Y,
Yang Q, Yang P, Lu J, Liu Q and Xiang Q: In type 2 diabetes induced
by cigarette smoking, activation of p38 MAPK is involved in
pancreatic β-cell apoptosis. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int.
25:9817–9827. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
St Laurent G, Wahlestedt C and Kapranov P:
The landscape of long noncoding RNA classification. Trends Genet.
31:239–251. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Peng WX, Koirala P and Mo YY:
lncRNA-mediated regulation of cell signaling in cancer. Oncogene.
36:5661–5667. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Zhang YX, Yuan J, Gao ZM and Zhang ZG:
lncRNA TUC338 promotes invasion of lung cancer by activating MAPK
pathway. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 22:443–449. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Zhang M, Weng W, Zhang Q, Wu Y, Ni S, Tan
C, Xu M, Sun H, Liu C, Wei P and Du X: The lncRNA NEAT1 activates
Wnt/β-catenin signaling and promotes colorectal cancer progression
via interacting with DDX5. J Hematol Oncol. 11:1132018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Tang J, Yan T, Bao Y, Shen C, Yu C, Zhu X,
Tian X, Guo F, Liang Q, Liu Q, et al: lncRNA GLCC1 promotes
colorectal carcinogenesis and glucose metabolism by stabilizing
c-Myc. Nat Commun. 10:34992019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zheng X, Han H, Liu GP, Ma YX, Pan RL,
Sang LJ, Li RH, Yang LJ, Marks JR, Wang W and Lin A: lncRNA wires
up Hippo and Hedgehog signaling to reprogramme glucose metabolism.
EMBO J. 36:3325–3335. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Young TL, Matsuda T and Cepko CL: The
noncoding RNA taurine upregulated gene 1 is required for
differentiation of the murine retina. Curr Biol. 15:501–512. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Yu G, Zhou H, Yao W, Meng L and Lang B:
lncRNA TUG1 promotes cisplatin resistance by regulating CCND2 via
epigenetically silencing miR-194-5p in bladder cancer. Mol Ther
Nucleic Acids. 16:257–271. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Li J, An G, Zhang M and Ma Q: Long
non-coding RNA TUG1 acts as a miR-26a sponge in human glioma cells.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 477:743–748. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
You G, Long X, Song F, Huang J, Tian M,
Xiao Y, Deng S and Wu Q: Metformin activates the AMPK-mTOR pathway
by modulating lncRNA TUG1 to induce autophagy and inhibit
atherosclerosis. Drug Des Devel Ther. 14:457–468. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Arocho A, Chen B, Ladanyi M and Pan Q:
Validation of the 2-DeltaDeltaCt calculation as an alternate method
of data analysis for quantitative PCR of BCR-ABL P210 transcripts.
Diagn Mol Pathol. 15:56–61. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Umemura A, Sasaki A, Nitta H, Baba S, Ando
T, Kajiwara T and Ishigaki Y: Pancreas volume reduction and
metabolic effects in Japanese patients with severe obesity
following laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy. Endocr J. 64:487–498.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Li YX, Fang DH and Liu TX: Laparoscopic
sleeve gastrectomy combined with single-anastomosis
duodenal-jejunal bypass in the treatment of type 2 diabetes
mellitus of patients with body mass index higher than 27.5 kg/m2
but lower than 32.5 kg/m2. Medicine (Baltimore).
97:e115372018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Ramos AC, Bastos EL, Ramos MG, Bertin NT,
Galvão TD, de Lucena RT and Campos JM: Medium-term follow-up
results with laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy. Arq Bras Cir Dig. 28
Suppl 1:S61–S64. 2015.(In English, Portuguese).s. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Murillo-Maldonado JM and Riesgo-Escovar
JR: The various and shared roles of lncRNAs during development. Dev
Dyn. 248:1059–1069. 2019. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Wei GH and Wang X: lncRNA MEG3 inhibit
proliferation and metastasis of gastric cancer via p53 signaling
pathway. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 21:3850–3856. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Xiong H, Ni Z, He J, Jiang S, Li X, He J,
Gong W, Zheng L, Chen S, Li B, et al: lncRNA HULC triggers
autophagy via stabilizing Sirt1 and attenuates the chemosensitivity
of HCC cells. Oncogene. 36:3528–3540. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Sun Y, Zhong L, He X, Wang S, Lai Y, Wu W,
Song H, Chen Y, Yang Y, Liao W, et al: lncRNA H19 promotes vascular
inflammation and abdominal aortic aneurysm formation by functioning
as a competing endogenous RNA. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 131:66–81. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Wang X, Chang X, Zhang P, Fan L, Zhou T
and Sun K: Aberrant expression of long non-coding RNAs in newly
diagnosed type 2 diabetes indicates potential roles in chronic
inflammation and insulin resistance. Cell Physiol Biochem.
43:2367–2378. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Sathishkumar C, Prabu P, Mohan V and
Balasubramanyam M: Linking a role of lncRNAs (long non-coding RNAs)
with insulin resistance, accelerated senescence, and inflammation
in patients with type 2 diabetes. Hum Genomics. 12:412018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Chen J, Ke S, Zhong L, Wu J, Tseng A,
Morpurgo B, Golovko A, Wang G, Cai JJ, Ma X, et al: Long noncoding
RNA MALAT1 regulates generation of reactive oxygen species and the
insulin responses in male mice. Biochem Pharmacol. 152:94–103.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Zhu X, Li H, Wu Y, Zhou J, Yang G, Wang W,
Kang D and Ye S: CREB-upregulated lncRNA MEG3 promotes hepatic
gluconeogenesis by regulating miR-302a-3p-CRTC2 axis. J Cell
Biochem. 120:4192–4202. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Liu S, Sheng L, Miao H, Saunders TL,
MacDougald OA, Koenig RJ and Xu B: SRA gene knockout protects
against diet-induced obesity and improves glucose tolerance. J Biol
Chem. 289:13000–13009. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Long J, Galvan DL, Mise K, Kanwar YS, Li
L, Poungavrin N, Overbeek PA, Chang BH and Danesh FR: Role for
carbohydrate response element-binding protein (ChREBP) in high
glucose-mediated repression of long noncoding RNA Tug1. J Biol
Chem. 295:15840–15852. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Li Y, Zhi K, Han S, Li X, Li M, Lian W,
Zhang H and Zhang X: TUG1 enhances high glucose-impaired
endothelial progenitor cell function via miR-29c-3p/PDGF-BB/Wnt
signaling. Stem Cell Res Ther. 11:4412020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Zhao L, Li W and Zhao H: Inhibition of
long non-coding RNA TUG1 protects against diabetic cardiomyopathy
induced diastolic dysfunction by regulating miR-499-5p. Am J Transl
Res. 12:718–730. 2020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Rajendran R, Garva R, Krstic-Demonacos M
and Demonacos C: Sirtuins: Molecular traffic lights in the
crossroad of oxidative stress, chromatin remodeling, and
transcription. J Biomed Biotechnol. 2011:3682762011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
D'Onofrio N, Servillo L and Balestrieri
ML: SIRT1 and SIRT6 signaling pathways in cardiovascular disease
protection. Antioxid Redox Signal. 28:711–732. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Kitada M, Ogura Y, Monno I and Koya D:
Sirtuins and type 2 diabetes: Role in inflammation, oxidative
stress, and mitochondrial function. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne).
10:1872019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Herzig S and Shaw RJ: AMPK: Guardian of
metabolism and mitochondrial homeostasis. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol.
19:121–135. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Bai B, Man AW, Yang K, Guo Y, Xu C, Tse
HF, Han W, Bloksgaard M, De Mey JG, Vanhoutte PM, et al:
Endothelial SIRT1 prevents adverse arterial remodeling by
facilitating HERC2-mediated degradation of acetylated LKB1.
Oncotarget. 7:39065–39081. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Sun LY, Li XJ, Sun YM, Huang W, Fang K,
Han C, Chen ZH, Luo XQ, Chen YQ and Wang WT: lncRNA ANRIL regulates
AML development through modulating the glucose metabolism pathway
of AdipoR1/AMPK/SIRT1. Mol Cancer. 17:1272018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Bordone L, Motta MC, Picard F, Robinson A,
Jhala US, Apfeld J, McDonagh T, Lemieux M, McBurney M, Szilvasi A,
et al: Sirt1 regulates insulin secretion by repressing UCP2 in
pancreatic beta cells. PLoS Biol. 4:e312006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|