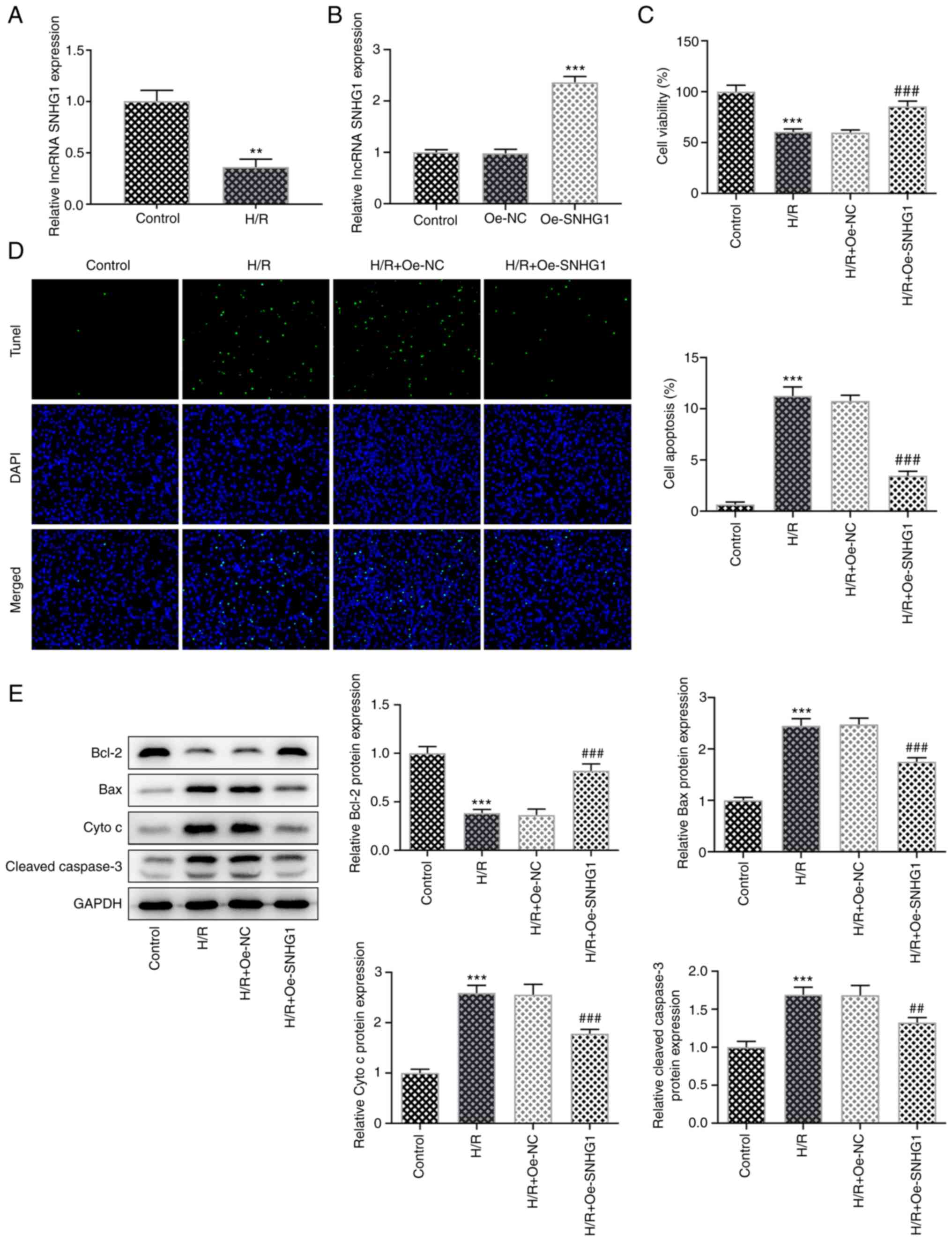
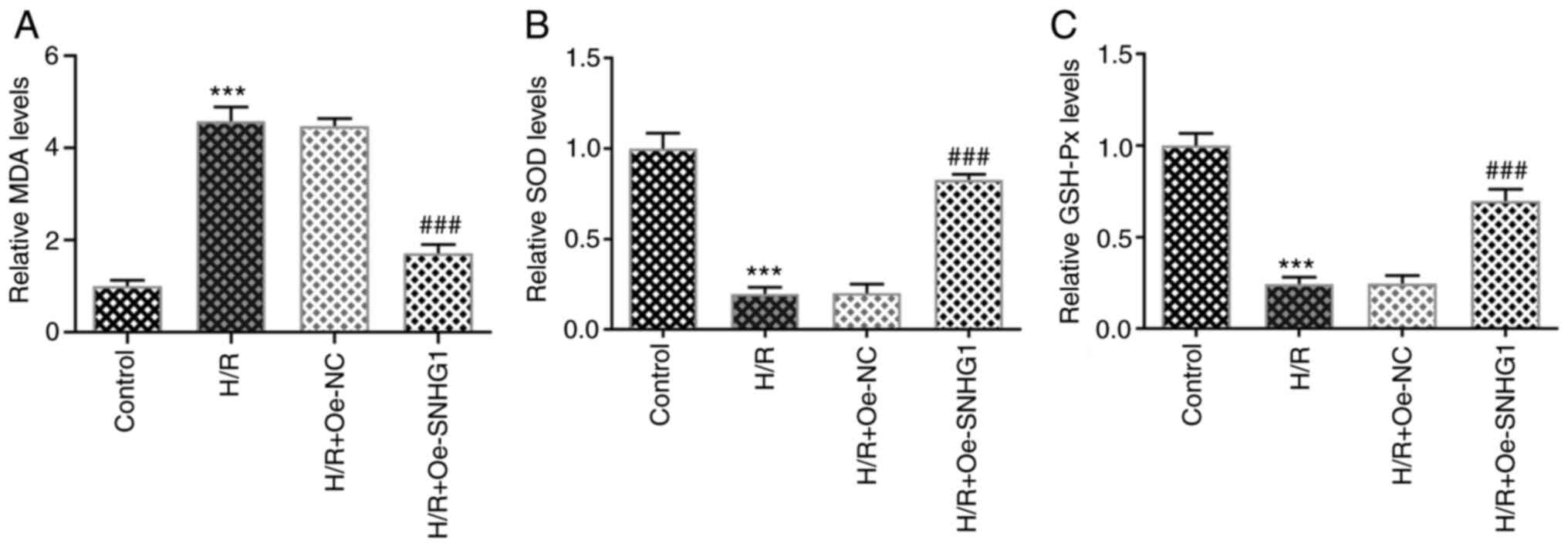
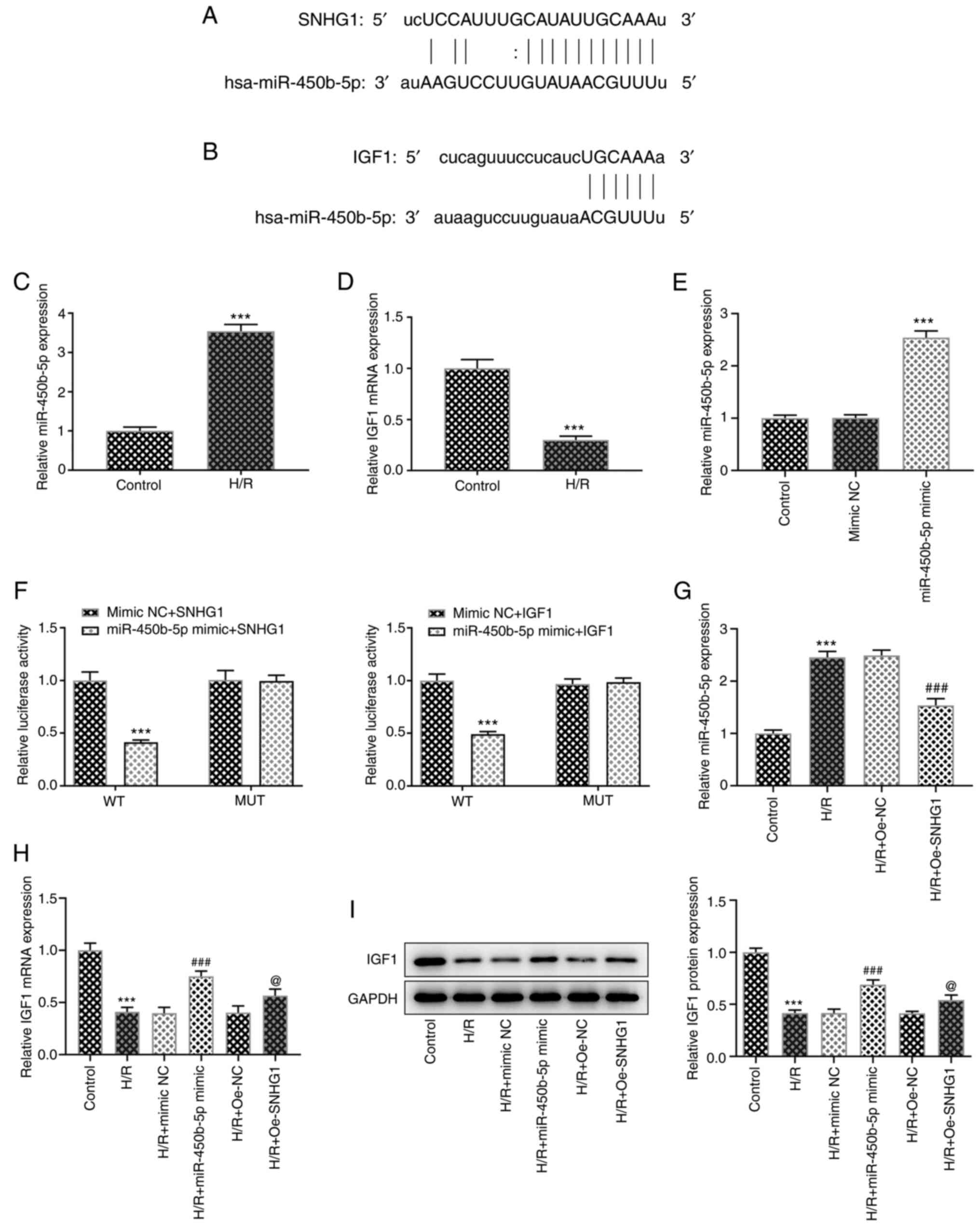
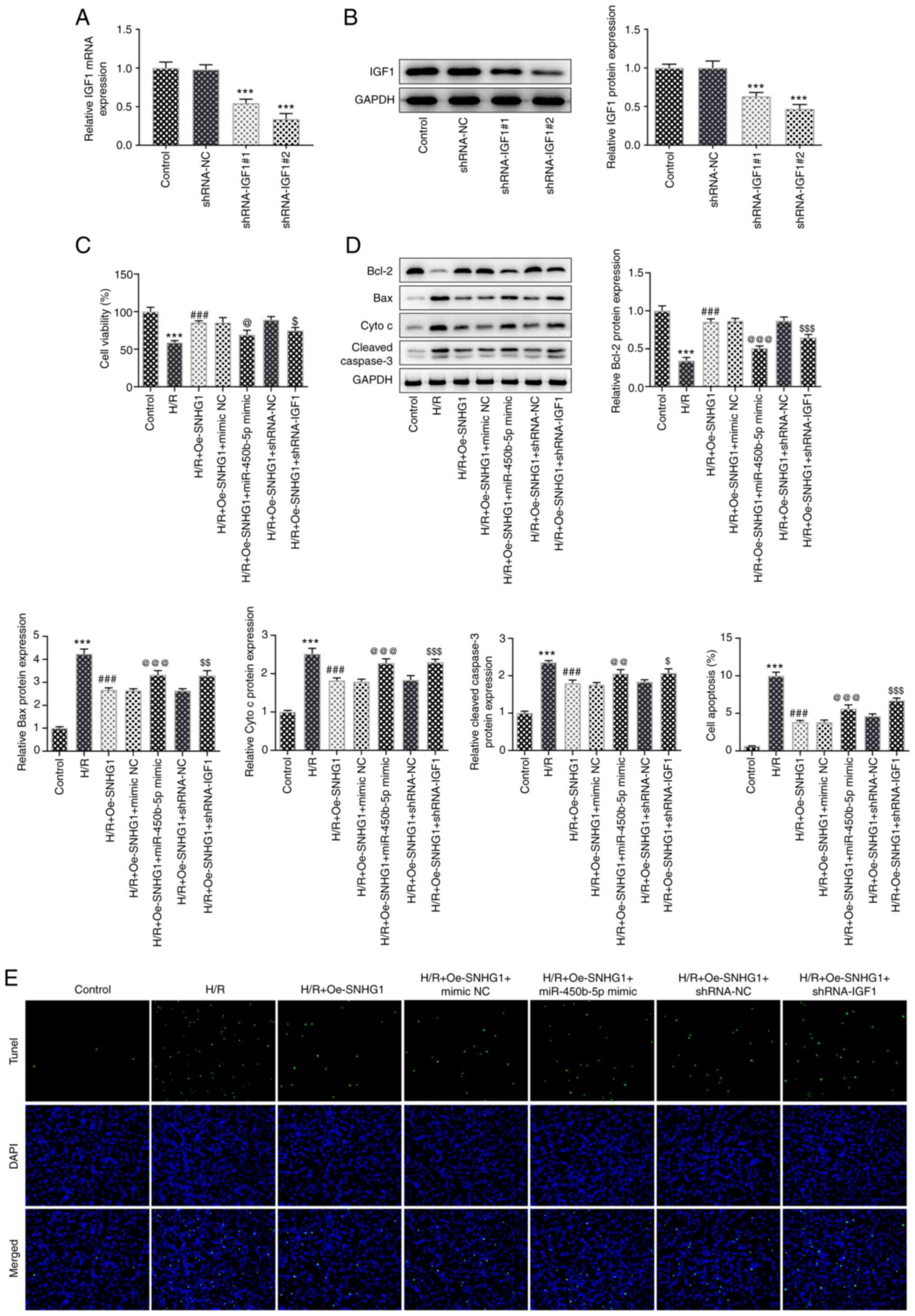
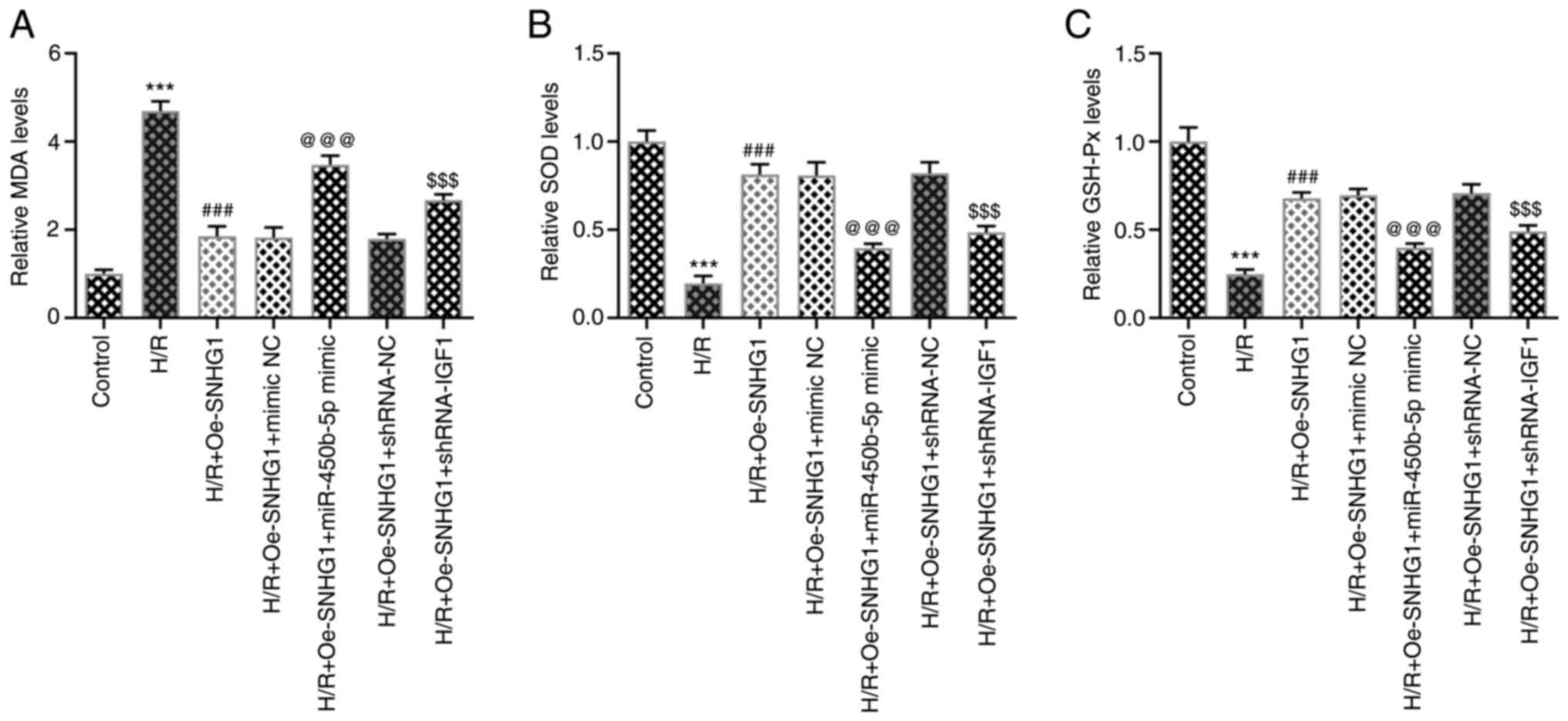
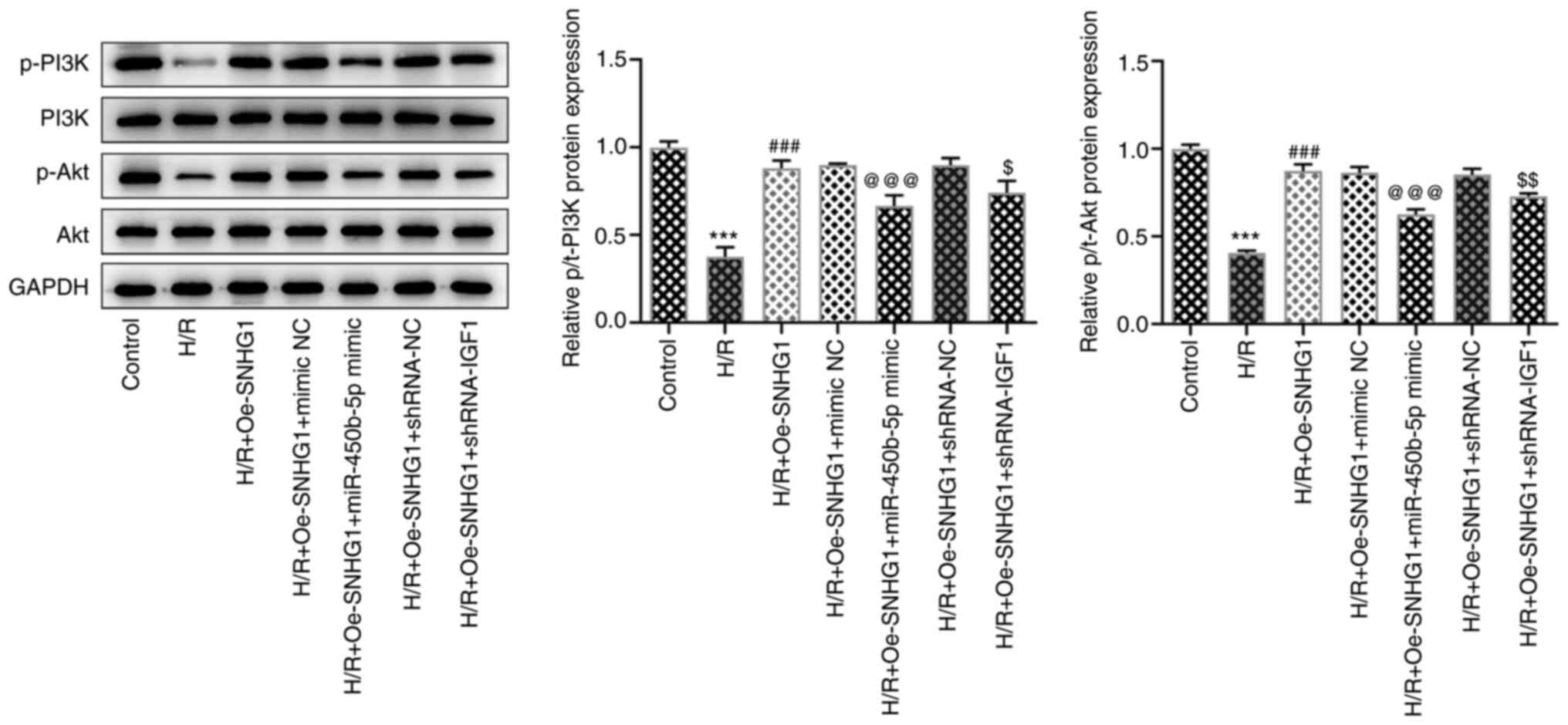
|
1
|
Severino P, D'Amato A, Pucci M, Infusino
F, Adamo F, Birtolo LI, Netti L, Montefusco G, Chimenti C, Lavalle
C, et al: Ischemic heart disease pathophysiology paradigms
overview: From plaque activation to microvascular dysfunction. Int
J Mol Sci. 21:81182020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Kaski JC, Crea F, Gersh BJ and Camici PG:
Reappraisal of ischemic heart disease. Circulation. 138:1463–1480.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Frank A, Bonney M, Bonney S, Weitzel L,
Koeppen M and Eckle T: Myocardial ischemia reperfusion injury: From
basic science to clinical bedside. Semin Cardiothorac Vasc Anesth.
16:123–132. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Wang J, Su Z, Lu S, Fu W, Liu Z, Jiang X
and Tai S: LncRNA HOXA-AS2 and its molecular mechanisms in human
cancer. Clin Chim Acta. 485:229–233. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Thin KZ, Tu JC and Raveendran S: Long
non-coding SNHG1 in cancer. Clin Chim Acta. 494:38–47. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Yan SM, Li H, Shu Q, Wu WJ, Luo XM and Lu
L: LncRNA SNHG1 exerts a protective role in cardiomyocytes
hypertrophy via targeting miR-15a-5p/HMGA1 axis. Cell Biol Int.
44:1009–1019. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Liu Y, Yang Y, Li L, Liu Y, Geng P, Li G
and Song H: LncRNA SNHG1 enhances cell proliferation, migration,
and invasion in cervical cancer. Biochem Cell Biol. 96:38–43. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Zhang Z and Wang H: lncRNA SNHG1
suppresses gastric cancer cell proliferation and promotes apoptosis
via Notch1 pathway. J BUON. 25:302–307. 2020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Chen S, Wang J and Zhou Y: Long non-coding
RNA SNHG1 protects human AC16 cardiomyocytes from doxorubicin
toxicity by regulating miR-195/Bcl-2 axis. Biosci Rep. Jul
25–2019.(Epub ahead of print). doi: 10.1042/BSR20191050. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Liang S, Ren K, Li B, Li F, Liang Z, Hu J,
Xu B and Zhang A: LncRNA SNHG1 alleviates
hypoxia-reoxygenation-induced vascular endothelial cell injury as a
competing endogenous RNA through the HIF-1α/VEGF signal pathway.
Mol Cell Biochem. 465:1–11. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Huang Y: The novel regulatory role of
lncRNA-miRNA-mRNA axis in cardiovascular diseases. J Cell Mol Med.
22:5768–5775. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Huang Z, Mou T, Luo Y, Pu X, Pu J, Wan L,
Gong J, Yang H, Liu Y, Li Z, et al: Inhibition of miR-450b-5p
ameliorates hepatic ischemia/reperfusion injury via targeting
CRYAB. Cell Death Dis. 11:4552020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Liao Y, Li H, Pi Y, Li Z and Jin S:
Cardioprotective effect of IGF-1 against myocardial
ischemia/reperfusion injury through activation of PI3K/Akt pathway
in rats in vivo. J Int Med Res. 47:3886–3897. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Sheng M, Huang Z, Pan L, Yu M, Yi C, Teng
L, He L, Gu C, Xu C and Li J: SOCS2 exacerbates myocardial injury
induced by ischemia/reperfusion in diabetic mice and H9c2 cells
through inhibiting the JAK-STAT-IGF-1 pathway. Life Sci.
188:101–109. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Li W, Dong X, He C, Tan G, Li Z, Zhai B,
Feng J, Jiang X, Liu C, Jiang H and Sun X: LncRNA SNHG1 contributes
to sorafenib resistance by activating the Akt pathway and is
positively regulated by miR-21 in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. J
Exp Clin Cancer Res. 38:1832019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Chen J, Zhang W, Wu YQ, Chen H and Zhao
JF: LncRNA SNHG1 inhibits neuronal apoptosis in cerebral infarction
rats through PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci.
23:5366–5373. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Tang M, Pan H, Zheng Z, Guo Y, Peng J,
Yang J, Luo Y, He J, Yan S, Wang P, et al: Prostaglandin E1
protects cardiomyocytes against hypoxia-reperfusion induced injury
via the miR-21-5p/FASLG axis. Biosci Rep. 39:BSR201905972019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Eltzschig HK and Eckle T: Ischemia and
reperfusion-from mechanism to translation. Nat Med. 17:1391–1401.
2011. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Xiao X, Tan Z, Jia M, Zhou X, Wu K, Ding Y
and Li W: Long Noncoding RNA SNHG1 knockdown ameliorates apoptosis,
oxidative stress and inflammation in models of Parkinson's disease
by inhibiting the miR-125b-5p/MAPK1 Axis. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat.
17:1153–1163. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Zhang N, Meng X, Mei L, Hu J, Zhao C and
Chen W: The long non-coding RNA SNHG1 attenuates cell apoptosis by
regulating miR-195 and BCL2-Like protein 2 in human cardiomyocytes.
Cell Physiol Biochem. 50:1029–1040. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Delic D, Dkhil M, Al-Quraishy S and
Wunderlich F: Hepatic miRNA expression reprogrammed by Plasmodium
chabaudi malaria. Parasitol Res. 108:1111–1121. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Ohuchi K, Watanabe M, Hirasawa N,
Tsurufuji S, Ozeki T and Fujiki H: Inhibition by gossypol of tumor
promoter-induced arachidonic acid metabolism in rat peritoneal
macrophages. Biochim Biophys Acta. 971:85–91. 1988. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Wang L, Niu X, Hu J, Xing H, Sun M, Wang
J, Jian Q and Yang H: After myocardial ischemia-reperfusion,
miR-29a, and Let7 could affect apoptosis through regulating IGF-1.
Biomed Res Int. 2015:2454122015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Song CL, Liu B, Diao HY, Shi YF, Zhang JC,
Li YX, Liu N, Yu YP, Wang G, Wang JP and Li Q: Down-regulation of
microRNA-320 suppresses cardiomyocyte apoptosis and protects
against myocardial ischemia and reperfusion injury by targeting
IGF-1. Oncotarget. 7:39740–39757. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Tejada T, Tan L, Torres RA, Calvert JW,
Lambert JP, Zaidi M, Husain M, Berce MD, Naib H, Pejler G, et al:
IGF-1 degradation by mouse mast cell protease 4 promotes cell death
and adverse cardiac remodeling days after a myocardial infarction.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 113:6949–6954. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Arslan F, Lai RC, Smeets MB, Akeroyd L,
Choo A, Aguor EN, Timmers L, van Rijen HV, Doevendans PA,
Pasterkamp G, et al: Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes
increase ATP levels, decrease oxidative stress and activate
PI3K/Akt pathway to enhance myocardial viability and prevent
adverse remodeling after myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury.
Stem Cell Res. 10:301–312. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Chen E, Chen C, Niu Z, Gan L, Wang Q, Li
M, Cai X, Gao R, Katakam S, Chen H, et al: Poly(I:C)
preconditioning protects the heart against myocardial
ischemia/reperfusion injury through TLR3/PI3K/Akt-dependent
pathway. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 5:2162020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|