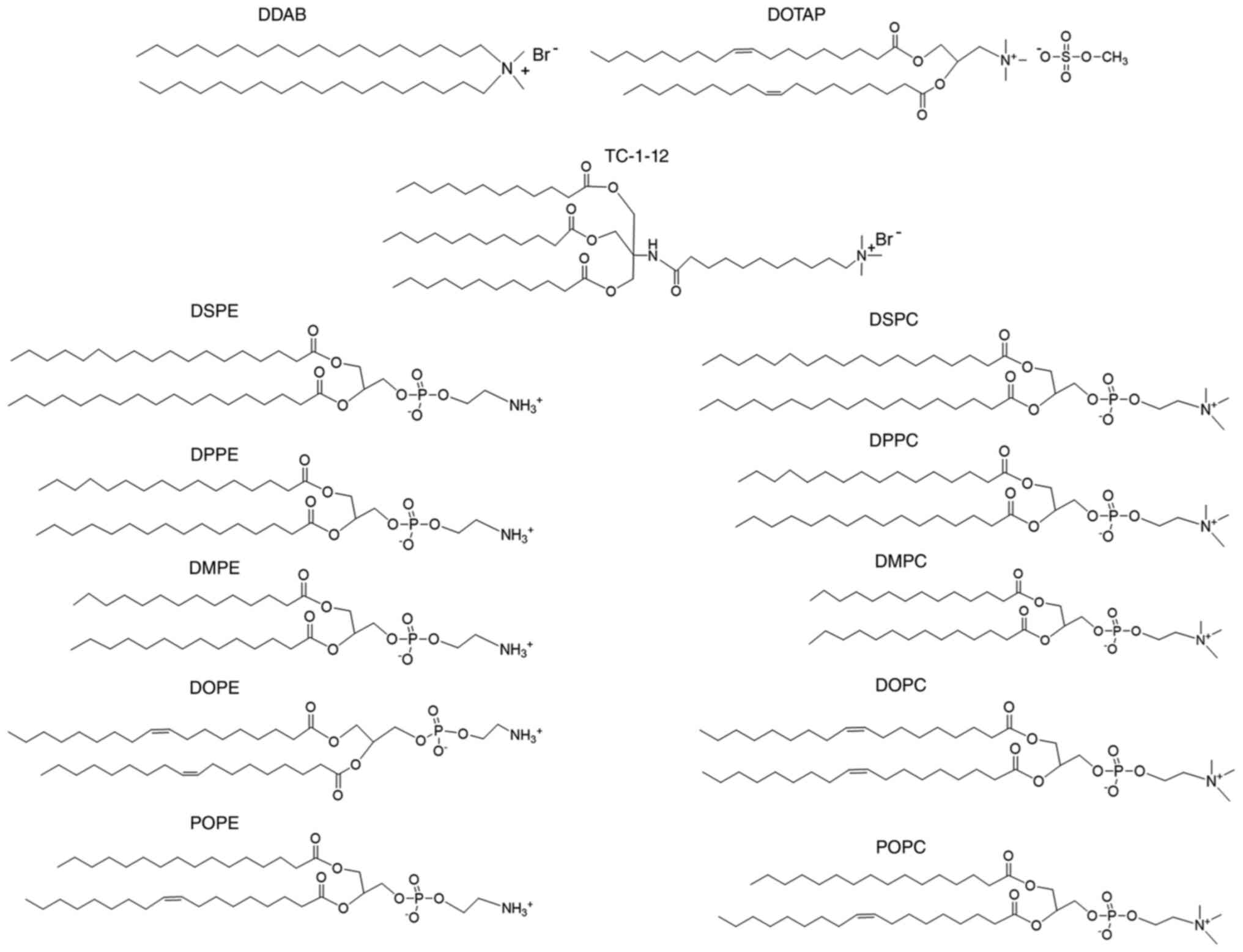
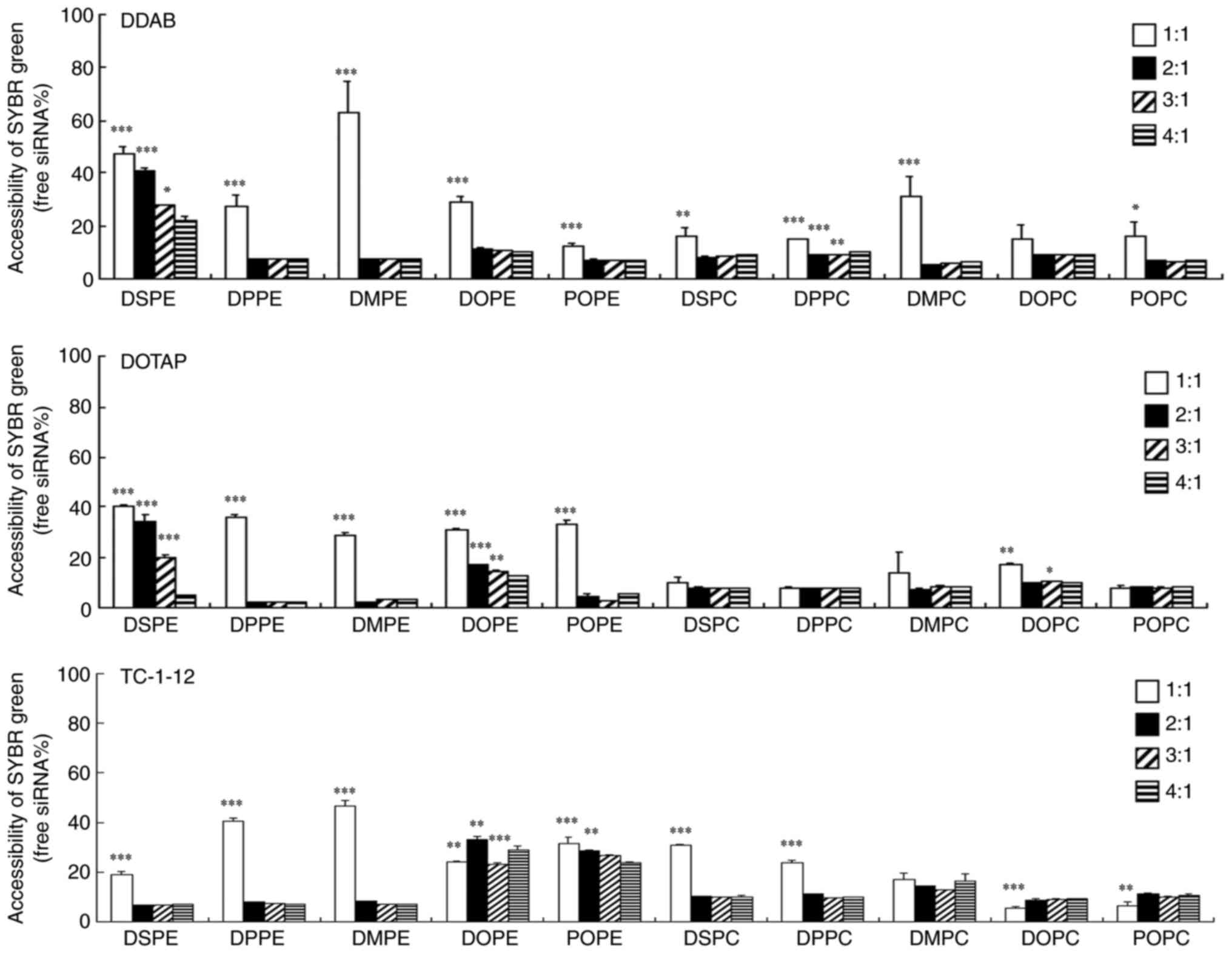
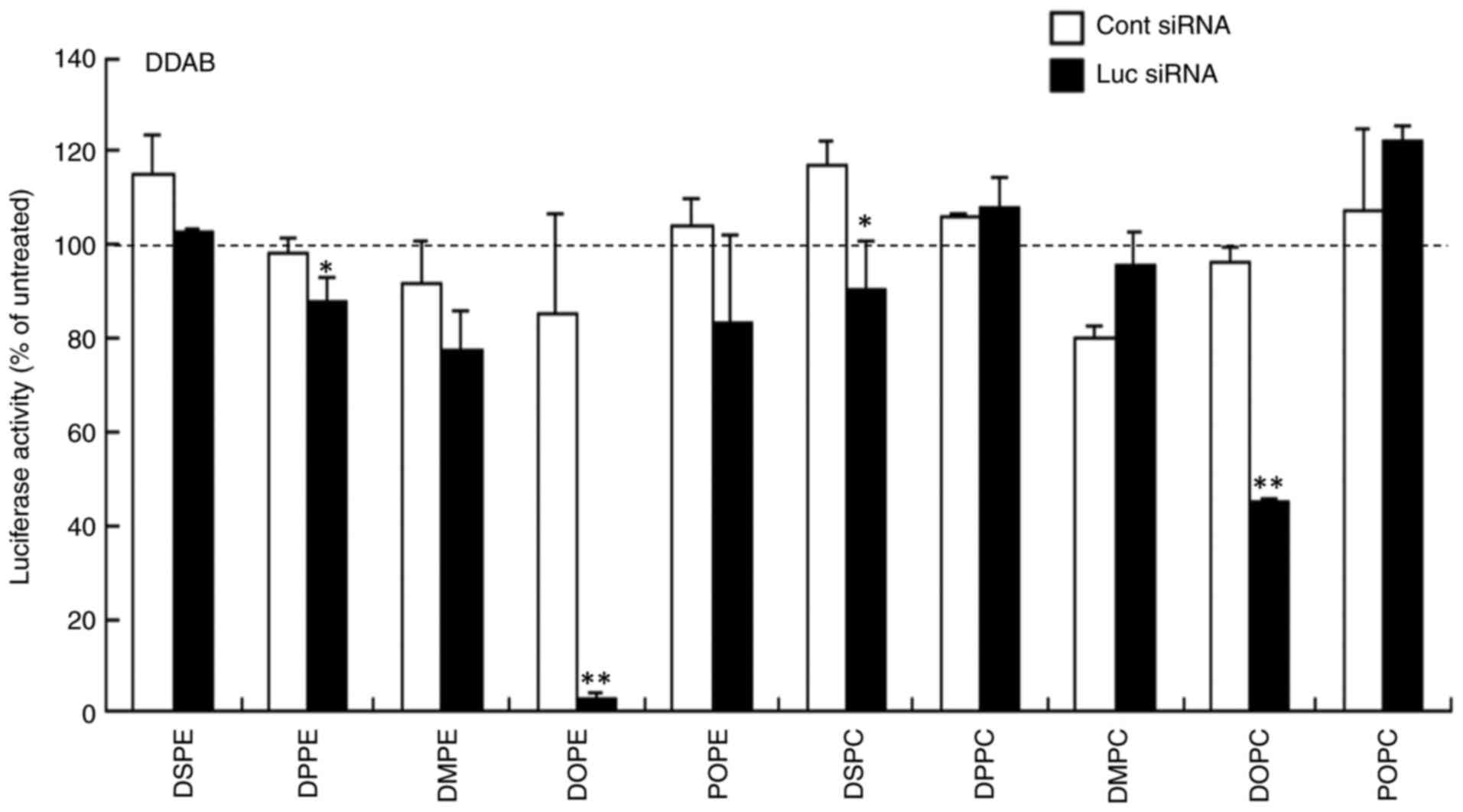
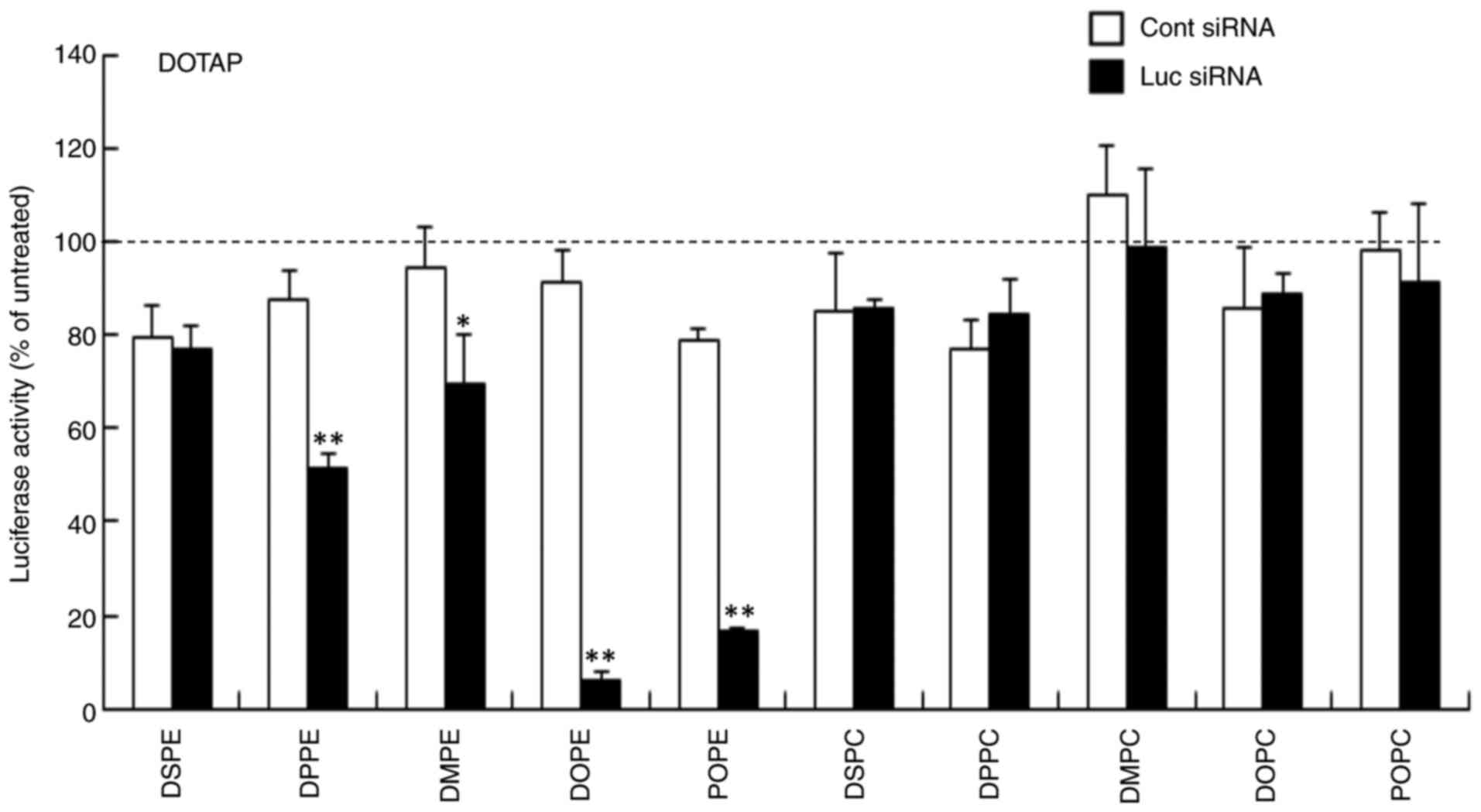
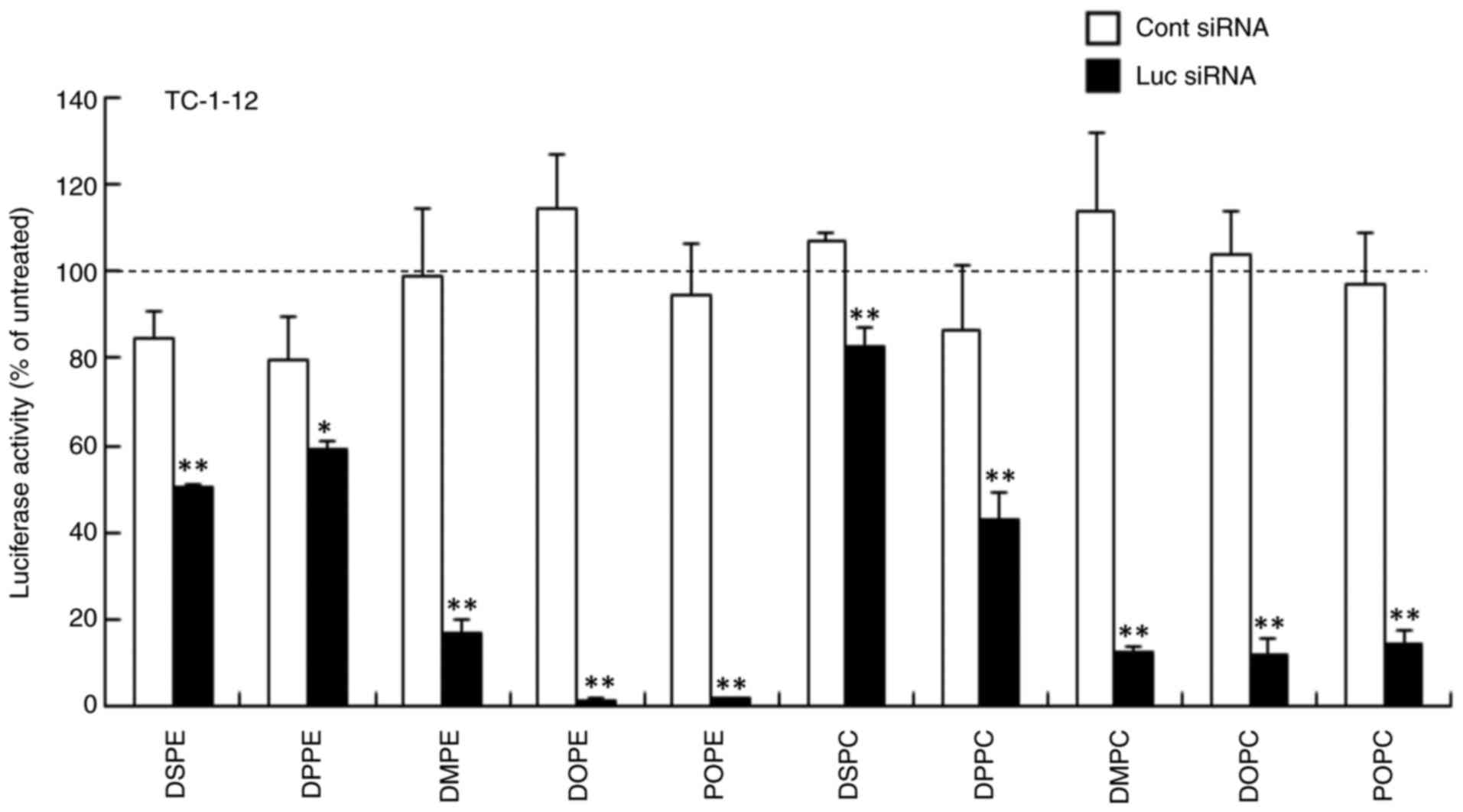
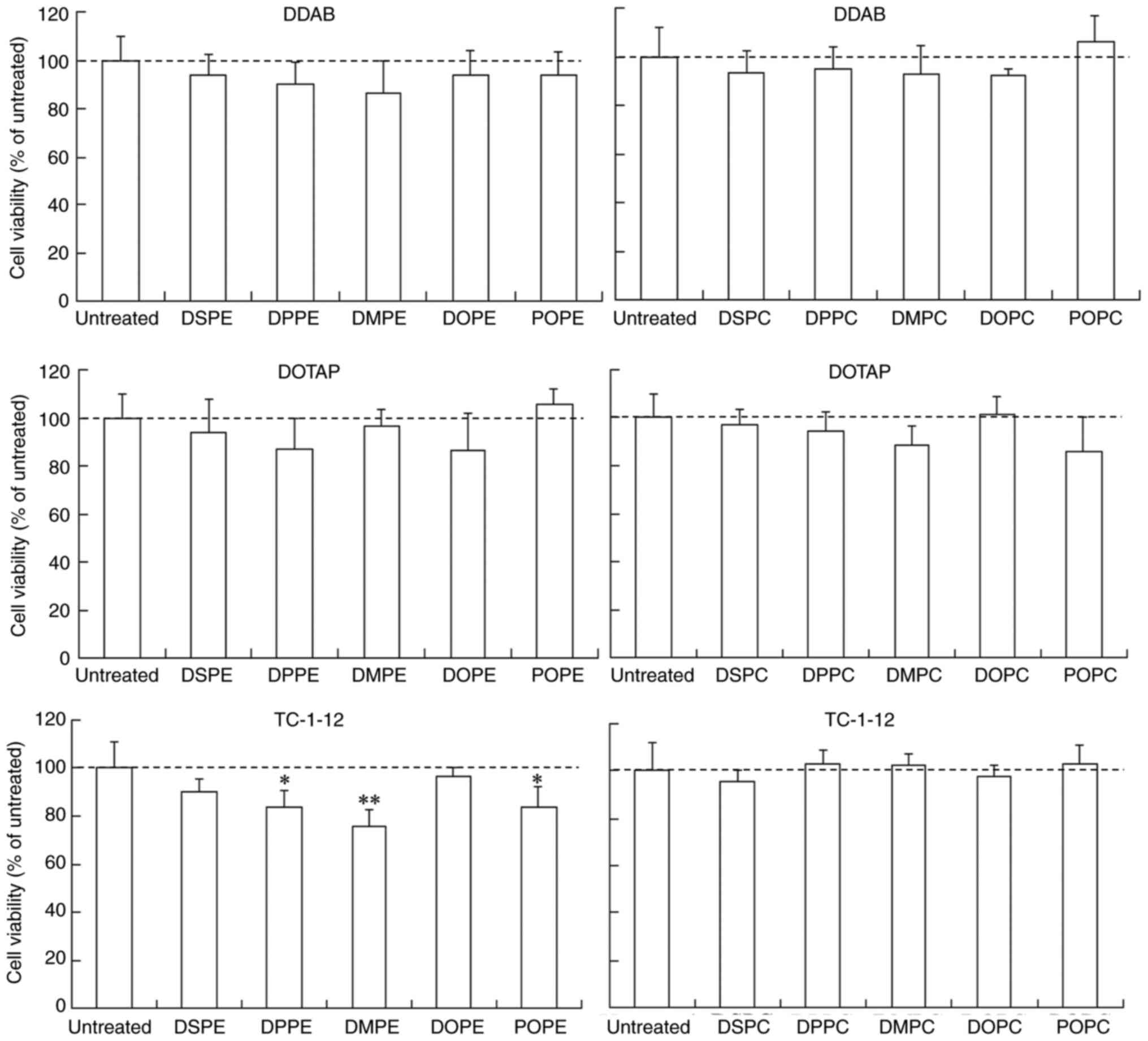
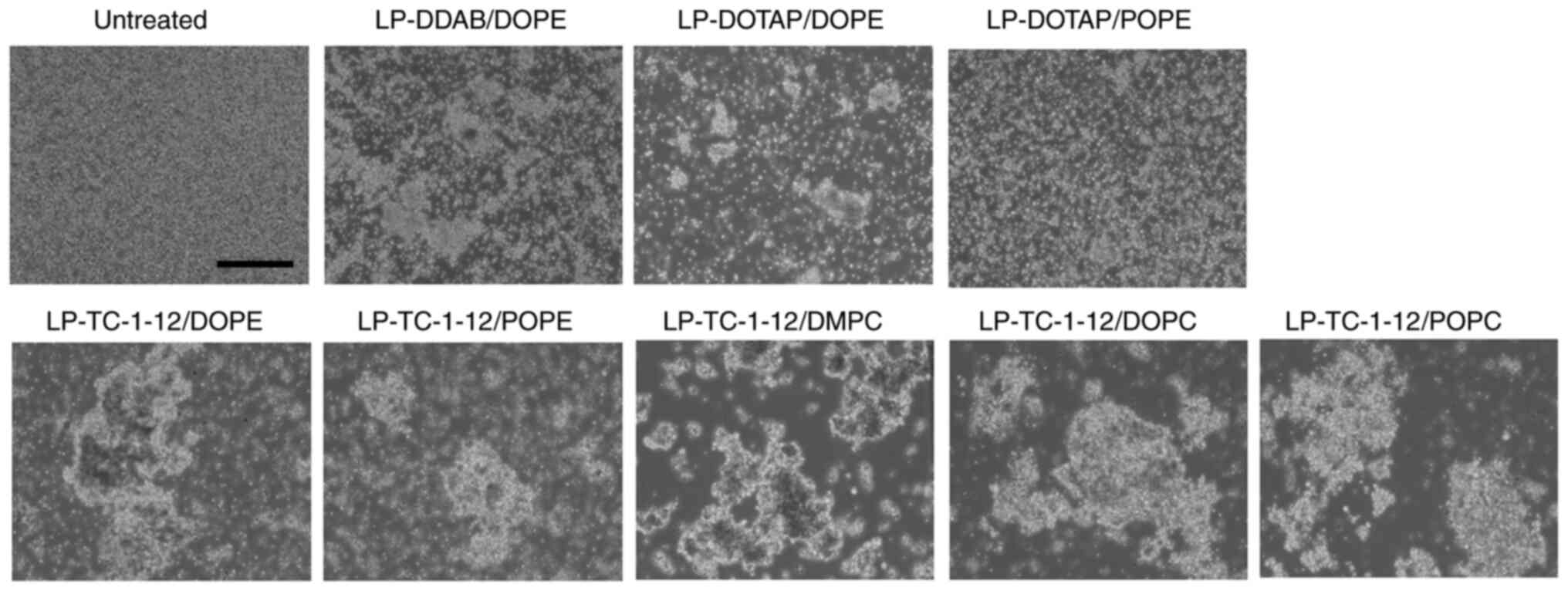
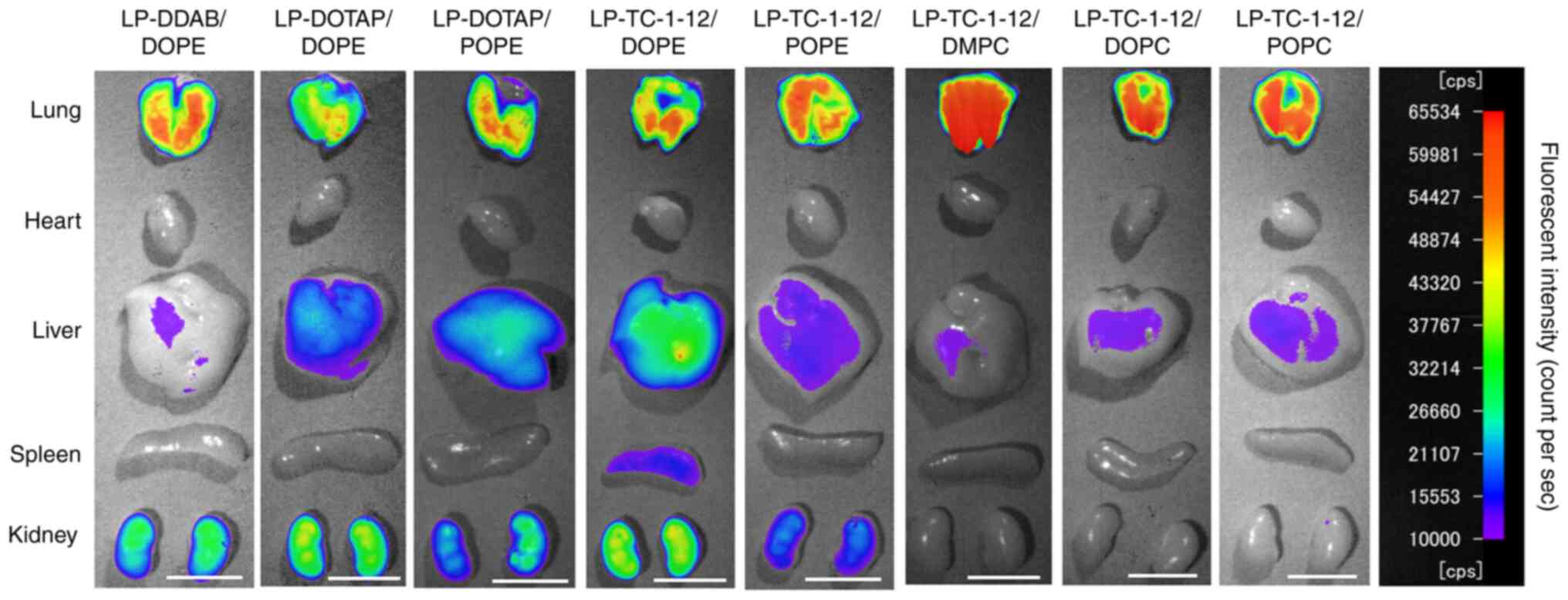
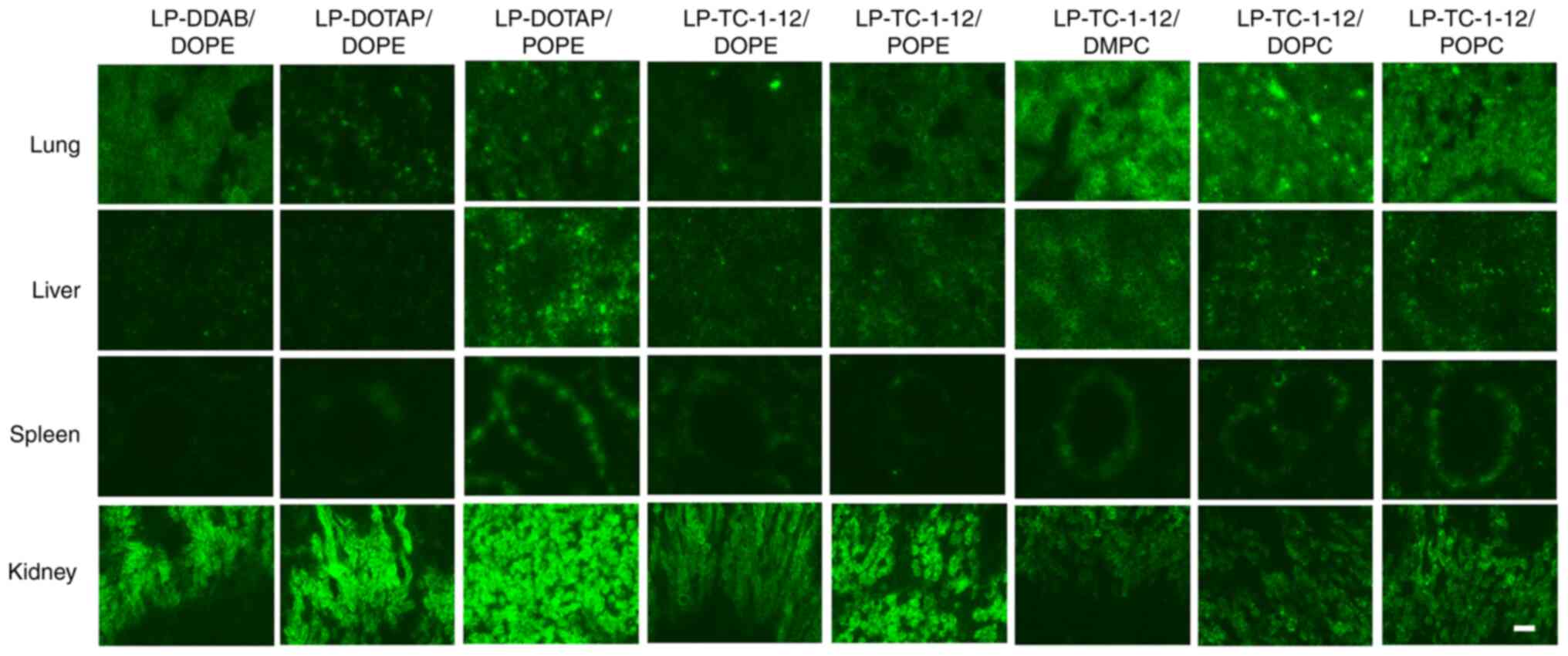
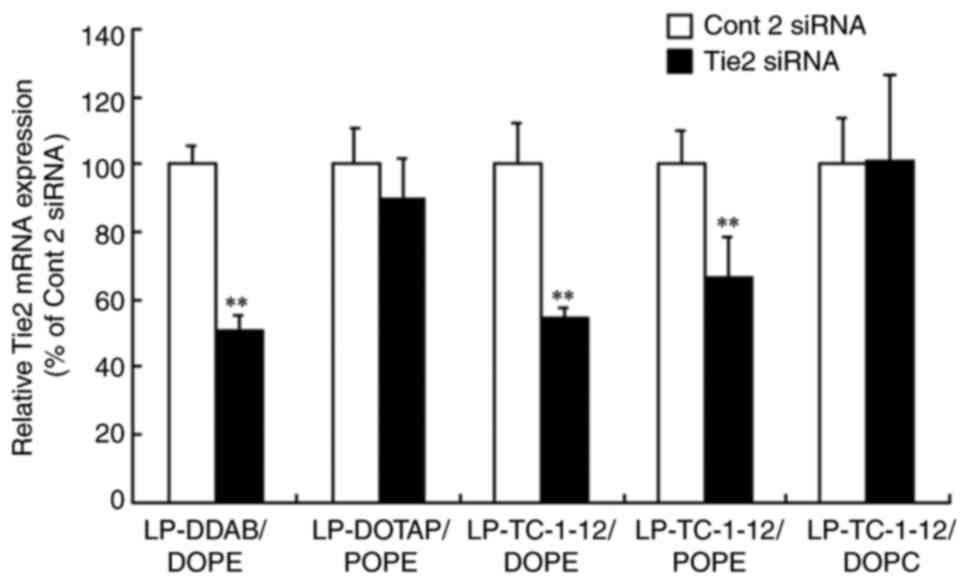
|
1
|
Wilson RC and Doudna JA: Molecular
mechanisms of RNA interference. Annu Rev Biophys. 42:217–239. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Zhang S, Zhi D and Huang L: Lipid-based
vectors for siRNA delivery. J Drug Target. 20:724–735. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Zatsepin TS, Kotelevtsev YV and
Koteliansky V: Lipid nanoparticles for targeted siRNA
delivery-going from bench to bedside. Int J Nanomedicine.
11:3077–3086. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Barba AA, Bochicchio S, Dalmoro A and
Lamberti G: Lipid delivery systems for nucleic-acid-based-drugs:
From production to clinical applications. Pharmaceutics.
11:3602019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Hattori Y, Nakamura M, Takeuchi N, Tamaki
K, Shimizu S, Yoshiike Y, Taguchi M, Ohno H, Ozaki K and Onishi H:
Effect of cationic lipid in cationic liposomes on siRNA delivery
into the lung by intravenous injection of cationic lipoplex. J Drug
Target. 27:217–227. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Hattori Y, Tamaki K, Ozaki KI, Kawano K
and Onishi H: Optimized combination of cationic lipids and neutral
helper lipids in cationic liposomes for siRNA delivery into the
lung by intravenous injection of siRNA lipoplexes. J Drug Deliv Sci
Technol. 52:1042–1050. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Taetz S, Bochot A, Surace C, Arpicco S,
Renoir JM, Schaefer UF, Marsaud V, Kerdine-Roemer S, Lehr CM and
Fattal E: Hyaluronic acid-modified DOTAP/DOPE liposomes for the
targeted delivery of anti-telomerase siRNA to CD44-expressing lung
cancer cells. Oligonucleotides. 19:103–116. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Dakwar GR, Braeckmans K, Ceelen W, De
Smedt SC and Remaut K: Exploring the HYDRAtion method for loading
siRNA on liposomes: The interplay between stability and biological
activity in human undiluted ascites fluid. Drug Deliv Transl Res.
7:241–251. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Hattori Y, Nakamura A, Arai S, Kawano K,
Maitani Y and Yonemochi E: siRNA delivery to lung-metastasized
tumor by systemic injection with cationic liposomes. J Liposome
Res. 25:279–286. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Song H, Hart SL and Du Z: Assembly
strategy of liposome and polymer systems for siRNA delivery. Int J
Pharm. 592:1200332021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Kudsiova L, Welser K, Campbell F,
Mohammadi A, Dawson N, Cui L, Hailes HC, Lawrence MJ and Tabor AB:
Delivery of siRNA using ternary complexes containing branched
cationic peptides: The role of peptide sequence, branching and
targeting. Mol Biosyst. 12:934–951. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Tagalakis AD, He L, Saraiva L, Gustafsson
KT and Hart SL: Receptor-targeted liposome-peptide nanocomplexes
for siRNA delivery. Biomaterials. 32:6302–6315. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Hattori Y, Saito H, Oku T and Ozaki K:
Effects of sterol derivatives in cationic liposomes on
biodistribution and gene-knockdown in the lungs of mice
systemically injected with siRNA lipoplexes. Mol Med Rep.
24:5982021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Rehman Z, Zuhorn IS and Hoekstra D: How
cationic lipids transfer nucleic acids into cells and across
cellular membranes: Recent advances. J Control Release. 166:46–56.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Drescher S and van Hoogevest P: The
phospholipid research center: Current research in phospholipids and
their use in drug delivery. Pharmaceutics. 12:12352020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Xue HY, Guo P, Wen WC and Wong HL:
Lipid-based nanocarriers for RNA delivery. Curr Pharm Des.
21:3140–3147. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Hattori Y, Nakamura T, Ohno H, Fujii N and
Maitani Y: siRNA delivery into tumor cells by lipid-based
nanoparticles composed of hydroxyethylated cholesteryl triamine.
Int J Pharm. 443:221–229. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Hattori Y, Kikuchi T, Nakamura M, Ozaki KI
and Onishi H: Therapeutic effects of protein kinase N3 small
interfering RNA and doxorubicin combination therapy on liver and
lung metastases. Oncol Lett. 14:5157–5166. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Fehring V, Schaeper U, Ahrens K, Santel A,
Keil O, Eisermann M, Giese K and Kaufmann J: Delivery of
therapeutic siRNA to the lung endothelium via novel lipoplex
formulation DACC. Mol Ther. 22:811–820. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Hattori Y, Nakamura M, Takeuchi N, Tamaki
K, Ozaki K and Onishi H: Effect of cationic lipid type in PEGylated
liposomes on siRNA delivery following the intravenous injection of
siRNA lipoplexes. Wrld Acd Sci J. 1:74–85. 2019.
|
|
21
|
Hattori Y, Tamaki K, Sakasai S, Ozaki KI
and Onishi H: Effects of PEG anchors in PEGylated siRNA lipoplexes
on in vitro gene-silencing effects and siRNA biodistribution
in mice. Mol Med Rep. 22:4183–4196. 2020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Eliyahu H, Servel N, Domb AJ and Barenholz
Y: Lipoplex-induced hemagglutination: Potential involvement in
intravenous gene delivery. Gene Ther. 9:850–858. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Simberg D, Weisman S, Talmon Y, Faerman A,
Shoshani T and Barenholz Y: The role of organ vascularization and
lipoplex-serum initial contact in intravenous murine lipofection. J
Biol Chem. 278:39858–39865. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Loughna S and Sato TN: Angiopoietin and
Tie signaling pathways in vascular development. Matrix Biol.
20:319–325. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
van der Heijden M, van Nieuw Amerongen GP,
Chedamni S, van Hinsbergh VW and Johan Groeneveld AB: The
angiopoietin-Tie2 system as a therapeutic target in sepsis and
acute lung injury. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 13:39–53. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Du Z, Munye MM, Tagalakis AD, Manunta MD
and Hart SL: The role of the helper lipid on the DNA transfection
efficiency of lipopolyplex formulations. Sci Rep. 4:71072014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Phase transition temperatures for
glycerophospholipids. Tech Support at Avanti Polar Lipids, Inc.;
https://avantilipids.com/tech-support/physical-properties/phase-transition-tempsFebruary
1–2022
|
|
29
|
Koulov AV, Vares L, Jain M and Smith BD:
Cationic triple-chain amphiphiles facilitate vesicle fusion
compared to double-chain or single-chain analogues. Biochim Biophys
Acta. 1564:459–465. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Hirsch-Lerner D and Barenholz Y: Probing
DNA-cationic lipid interactions with the fluorophore
trimethylammonium diphenyl-hexatriene (TMADPH). Biochim Biophys
Acta. 1370:17–30. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Feitosa E, Alves FR, Niemiec A, Real
Oliveira ME, Castanheira EM and Baptista AL: Cationic liposomes in
mixed didodecyldimethylammonium bromide and
dioctadecyldimethylammonium bromide aqueous dispersions studied by
differential scanning calorimetry, Nile red fluorescence, and
turbidity. Langmuir. 22:3579–3585. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|