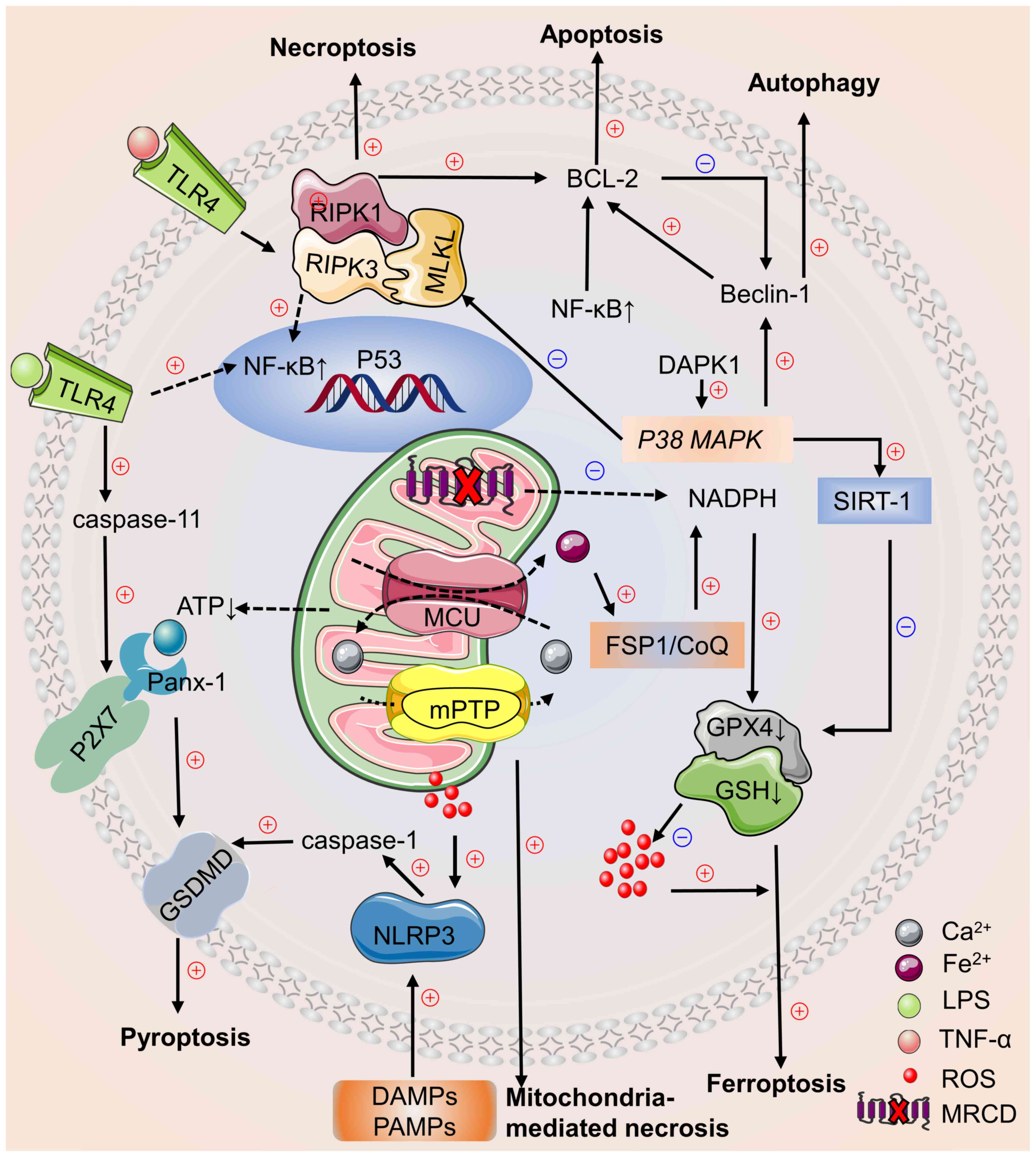
|
1
|
Singer M, Deutschman CS, Seymour CW,
Shankar-Hari M, Annane D, Bauer M, Bellomo R, Bernard GR, Chiche
JD, Coopersmith CM, et al: The third international consensus
definitions for sepsis and septic shock (sepsis-3). JAMA.
315:801–810. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Fleischmann C, Scherag A, Adhikari NKJ,
Hartog CS, Tsaganos T, Schlattmann P, Angus DC and Reinhart K;
International Forum of Acute Care Trialists, : Assessment of global
incidence and mortality of hospital-treated sepsis. Current
estimates and limitations. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 193:259–272.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Bergmann O, Bhardwaj RD, Bernard S, Zdunek
S, Barnabé-Heider F, Walsh S, Zupicich J, Alkass K, Buchholz BA,
Druid H, et al: Evidence for cardiomyocyte renewal in humans.
Science. 324:98–102. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Galluzzi L, Vitale I, Aaronson SA, Abrams
JM, Adam D, Agostinis P, Alnemri ES, Altucci L, Amelio I, Andrews
DW, et al: Molecular mechanisms of cell death: Recommendations of
the nomenclature committee on cell death 2018. Cell Death Differ.
25:486–541. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Mishra PK, Adameova A, Hill JA, Baines CP,
Kang PM, Downey JM, Narula J, Takahashi M, Abbate A, Piristine HC,
et al: Guidelines for evaluating myocardial cell death. Am J
Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 317:H891–H922. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Nedeva C: Inflammation and cell death of
the innate and adaptive immune system during sepsis. Biomolecules.
11:10112021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Picca A, Calvani R, Coelho-Junior HJ and
Marzetti E: Cell death and inflammation: The role of mitochondria
in health and disease. Cells. 10:5372021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Yu Y, Yan Y, Niu F, Wang Y, Chen X, Su G,
Liu Y, Zhao X, Qian L, Liu P and Xiong Y: Ferroptosis: A cell death
connecting oxidative stress, inflammation and cardiovascular
diseases. Cell Death Discov. 7:1932021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Pinheiro Da Silva F and Nizet V: Cell
death during sepsis: Integration of disintegration in the
inflammatory response to overwhelming infection. Apoptosis.
14:509–521. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Lengeler JW: Metabolic networks: A
signal-oriented approach to cellular models. Biol Chem.
381:911–920. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Hotchkiss RS, Strasser A, McDunn JE and
Swanson PE: Cell death. N Engl J Med. 361:1570–1583. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Raff M: Cell suicide for beginners.
Nature. 396:119–122. 1998. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Norbury CJ and Hickson ID: Cellular
responses to DNA damage. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 41:367–401.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Shi Y: Mechanisms of caspase activation
and inhibition during apoptosis. Mol Cell. 9:459–470. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Guo R and Li G: Tanshinone modulates the
expression of Bcl-2 and Bax in cardiomyocytes and has a protective
effect in a rat model of myocardial ischemia-reperfusion. Hellenic
J Cardiol. 59:323–328. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Savill J and Fadok V: Corpse clearance
defines the meaning of cell death. Nature. 407:784–788. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Haslett C: Granulocyte apoptosis and
inflammatory disease. Br Med Bull. 53:669–683. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Zorc-Pleskovic R, Alibegović A, Zorc M,
Milutinović A, Radovanović N and Petrović D: Apoptosis of
cardiomyocytes in myocarditis. Folia Biol (Praha). 52:6–9.
2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Fajardo G, Zhao M, Powers J and Bernstein
D: Differential cardiotoxic/cardioprotective effects of
beta-adrenergic receptor subtypes in myocytes and fibroblasts in
doxorubicin cardiomyopathy. J Mol Cell Cardiol. l40:375–383. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zechendorf E, O'riordan CE, Stiehler L,
Wischmeyer N, Chiazza F, Collotta D, Denecke B, Ernst S,
Müller-Newen G, Coldewey SM, et al: Ribonuclease 1 attenuates
septic cardiomyopathy and cardiac apoptosis in a murine model of
polymicrobial sepsis. JCI Insight. 5:e1315712020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Díez J: Apoptosis in cardiovascular
diseases. Rev Esp Cardiol. 53:267–274. 2000.(In Spanish).
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Chao J, Yin H, Yao YY, Shen B, Smith RS Jr
and Chao L: Novel role of kallistatin in protection against
myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury by preventing apoptosis and
inflammation. Hum Gene Ther. 17:1201–1213. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Hu X, Dai S, Wu WJ, Tan W, Zhu X, Mu J,
Guo Y, Bolli R and Rokosh G: Stromal cell derived factor-1 alpha
confers protection against myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury:
Role of the cardiac stromal cell derived factor-1 alpha CXCR4 axis.
Circulation. 116:654–663. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Saxena A, Fish JE, White MD, Yu S, Smyth
JW, Shaw RM, Dimaio JM and Srivastava D: Stromal cell-derived
factor-1alpha is cardioprotective after myocardial infarction.
Circulation. 117:2224–2231. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Sun Z, Shen L, Sun X, Tong G, Sun D, Han
T, Yang G, Zhang J, Cao F, Yao L and Wang H: Variation of NDRG2 and
c-Myc expression in rat heart during the acute stage of
ischemia/reperfusion injury. Histochem Cell Biol. 135:27–35. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Oberholzer C, Oberholzer A, Clare-Salzler
M and Moldawer LL: Apoptosis in sepsis: A new target for
therapeutic exploration. FASEB J. 15:879–892. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Wencker D, Chandra M, Nguyen K, Miao W,
Garantziotis S, Factor SM, Shirani J, Armstrong RC and Kitsis RN: A
mechanistic role for cardiac myocyte apoptosis in heart failure. J
Clin Invest. 111:1497–1504. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Nevière R, Fauvel H, Chopin C, Formstecher
P and Marchetti P: Caspase inhibition prevents cardiac dysfunction
and heart apoptosis in a rat model of sepsis. Am J Respir Crit Care
Med. 163:218–225. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Manetti AC, Maiese A, Paolo MD, Matteis
AD, La Russa R, Turillazzi E, Frati P and Fineschi V: MicroRNAs and
sepsis-induced cardiac dysfunction: A systematic review. Int J Mol
Sci. 22:3212020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Lv H, Tian M, Hu P, Wang B and Yang L:
Overexpression of miR-365a-3p relieves sepsis-induced acute
myocardial injury by targeting MyD88/NF-κB pathway. Can J Physiol
Pharmacol. 99:1007–1015. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Mirna M, Paar V, Rezar R, Topf A, Eber M,
Hoppe UC, Lichtenauer M and Jung C: MicroRNAs in inflammatory heart
diseases and sepsis-induced cardiac dysfunction: A potential scope
for the future? Cells. 8:13522019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Pasparakis M and Vandenabeele P:
Necroptosis and its role in inflammation. Nature. 517:311–320.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Han J, Zhong CQ and Zhang DW: Programmed
necrosis: Backup to and competitor with apoptosis in the immune
system. Nat Immunol. 12:1143–1149. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Newton K, Dugger DL, Maltzman A, Greve JM,
Hedehus M, Martin-Mcnulty B, Carano RaD, Cao TC, Van Bruggen N,
Bernstein L, et al: RIPK3 deficiency or catalytically inactive
RIPK1 provides greater benefit than MLKL deficiency in mouse models
of inflammation and tissue injury. Cell Death Differ. 23:1565–1576.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Christofferson DE and Yuan J: Necroptosis
as an alternative form of programmed cell death. Curr Opin Cell
Biol. 22:263–268. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Cho YS, Challa S, Moquin D, Genga R, Ray
TD, Guildford M and Chan FK: Phosphorylation-driven assembly of the
RIP1-RIP3 complex regulates programmed necrosis and virus-induced
inflammation. Cell. 137:1112–1123. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
He S, Wang L, Miao L, Wang T, Du F, Zhao L
and Wang X: Receptor interacting protein kinase-3 determines
cellular necrotic response to TNF-alpha. Cell. 137:1100–1111. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Zhang DW, Shao J, Lin J, Zhang N, Lu BJ,
Lin SC, Dong MQ and Han J: RIP3, an energy metabolism regulator
that switches TNF-induced cell death from apoptosis to necrosis.
Science. 325:332–336. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Sun L, Wang H, Wang Z, He S, Chen S, Liao
D, Wang L, Yan J, Liu W, Lei X and Wang X: Mixed lineage kinase
domain-like protein mediates necrosis signalling downstream of RIP3
kinase. Cell. 148:213–227. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Zhu H and Sun A: Programmed necrosis in
heart disease: Molecular mechanisms and clinical implications. J
Mol Cell Cardiol. 116:125–134. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Moreno-Gonzalez G, Vandenabeele P and
Krysko DV: Necroptosis: A novel cell death modality and its
potential relevance for critical care medicine. Am J Respir Crit
Care Med. 194:415–428. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Van Der Poll T, Van De Veerdonk FL,
Scicluna BP and Netea MG: The immunopathology of sepsis and
potential therapeutic targets. Nat Rev Immunol. 17:407–420. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Vanden Berghe T, Kaiser WJ, Bertrand MJ
and Vandenabeele P: Molecular crosstalk between apoptosis,
necroptosis, and survival signaling. Mol Cell Oncol. 2:e9750932015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Lafont E, Hartwig T and Walczak H: Paving
trail's path with ubiquitin. Trends Biochem Sci. 43:44–60. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Weinlich R, Oberst A, Beere HM and Green
DR: Necroptosis in development, inflammation and disease. Nat Rev
Mol Cell Biol. 18:127–136. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Oeckinghaus A, Hayden MS and Ghosh S:
Crosstalk in NF-κB signalling pathways. Nat Immunol. 12:695–708.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Newton K and Manning G: Necroptosis and
inflammation. Annu Rev Biochem. 85:743–763. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Wu J, Huang Z, Ren J, Zhang Z, He P, Li Y,
Ma J, Chen W, Zhang Y, Zhou X, et al: Mlkl knockout mice
demonstrate the indispensable role of Mlkl in necroptosis. Cell
Res. 23:994–1006. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Rosenbaum DM, Degterev A, David J,
Rosenbaum PS, Roth S, Grotta JC, Cuny GD, Yuan J and Savitz SI:
Necroptosis, a novel form of caspase-independent cell death,
contributes to neuronal damage in a retinal ischemia-reperfusion
injury model. J Neurosci Res. 88:1569–1576. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Kaczmarek A, Vandenabeele P and Krysko DV:
Necroptosis: The release of damage-associated molecular patterns
and its physiological relevance. Immunity. 38:209–223. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Schenck EJ, Ma KC, Price DR, Nicholson T,
Oromendia C, Gentzler ER, Sanchez E, Baron RM, Fredenburgh LE, Huh
JW, et al: Circulating cell death biomarker trail is associated
with increased organ dysfunction in sepsis. JCI Insight.
4:e1271432019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Kitur K, Wachtel S, Brown A, Wickersham M,
Paulino F, Peñaloza HF, Soong G, Bueno S, Parker D and Prince A:
Necroptosis promotes Staphylococcus aureus clearance by
inhibiting excessive inflammatory signalling. Cell Rep.
16:2219–2230. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Vucur M, Roderburg C, Kaiser L, Schneider
AT, Roy S, Loosen SH, Luedde M, Trautwein C, Koch A, Tacke F and
Luedde T: Elevated serum levels of mixed lineage kinase domain-like
protein predict survival of patients during intensive care unit
treatment. Dis Markers. 2018:19834212018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Peng S, Xu J, Ruan W, Li S and Xiao F:
PPAR-γ activation prevents septic cardiac dysfunction via
inhibition of apoptosis and necroptosis. Oxid Med Cell Longev.
2017:83267492017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Beno SM, Riegler AN, Gilley RP, Brissac T,
Wang Y, Kruckow KL, Jadapalli JK, Wright GM, Shenoy AT, Stoner SN,
et al: Inhibition of necroptosis to prevent long-term cardiac
damage during pneumococcal pneumonia and invasive disease. J Infect
Dis. 222:1882–1893. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Zechendorf E, Vaßen P, Zhang J, Hallawa A,
Martincuks A, Krenkel O, Müller-Newen G, Schuerholz T, Simon TP,
Marx G, et al: Heparan sulfate induces necroptosis in murine
cardiomyocytes: A medical-in silico approach combining in vitro
experiments and machine learning. Front Immunol. 9:3932018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Yu S, Yang H, Guo X and Sun Y: Klotho
attenuates angiotensin II-induced cardiotoxicity through
suppression of necroptosis and oxidative stress. Mol Med Rep.
23:662021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Yu X, Ruan Y, Huang X, Dou L, Lan M, Cui
J, Chen B, Gong H, Wang Q, Yan M, et al: Dexrazoxane ameliorates
doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity by inhibiting both apoptosis and
necroptosis in cardiomyocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
523:140–146. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Drosatos K, Khan RS, Trent CM, Jiang H,
Son NH, Blaner WS, Homma S, Schulze PC and Goldberg IJ: Peroxisome
proliferator-activated receptor-γ activation prevents
sepsis-related cardiac dysfunction and mortality in mice. Circ
Heart Fail. 6:550–562. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Yang X, Lu H, Xie H, Zhang B, Nie T, Fan
C, Yang T, Xu Y, Su H, Tang W and Zhou B: Potent and selective
RIPK1 inhibitors targeting dual-pockets for the treatment of
systemic inflammatory response syndrome and sepsis. Angew Chem Int
Ed Engl. 61:e2021149222022.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Fu G, Wang B, He B, Feng M and Yu Y: LPS
induces cardiomyocyte necroptosis through the Ripk3/Pgam5 signaling
pathway. J Recept Signal Transduct Res. 41:32–37. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Kroemer G, Galluzzi L, Vandenabeele P,
Abrams J, Alnemri ES, Baehrecke EH, Blagosklonny MV, El-Deiry WS,
Golstein P, Green DR, et al: Classification of cell death:
Recommendations of the nomenclature committee on cell death 2009.
Cell Death Differ. 16:3–11. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Kayar SR and Banchero N: Volume density
and distribution of mitochondria in myocardial growth and
hypertrophy. Respir Physiol. 70:275–286. 1987. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Beretta M, Santos CX, Molenaar C, Hafstad
AD, Miller CC, Revazian A, Betteridge K, Schröder K,
Streckfuß-Bömeke K, Doroshow JH, et al: Nox4 regulates
InsP3 receptor-dependent Ca2+ release into
mitochondria to promote cell survival. EMBO J. 39:e1035302020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Kim J, Kwon J, Kim M, Do J, Lee D and Han
H: Low-dielectric-constant polyimide aerogel composite films with
low water uptake. Polym J. 48:829–834. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
66
|
Weiss JN, Korge P, Honda HM and Ping P:
Role of the mitochondrial permeability transition in myocardial
disease. Circ Res. 93:292–301. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Kroemer G, Galluzzi L and Brenner C:
Mitochondrial membrane permeabilization in cell death. Physiol Rev.
87:99–163. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Izzo V, Bravo-San Pedro JM, Sica V,
Kroemer G and Galluzzi L: Mitochondrial permeability transition:
New findings and persisting uncertainties. Trends Cell Biol.
26:655–667. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Isoyama S and Nitta-Komatsubara Y: Acute
and chronic adaptation to hemodynamic overload and ischemia in the
aged heart. Heart Fail Rev. 7:63–69. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Larche J, Lancel S, Hassoun SM, Favory R,
Decoster B, Marchetti P, Chopin C and Neviere R: Inhibition of
mitochondrial permeability transition prevents sepsis-induced
myocardial dysfunction and mortality. J Am Coll Cardiol.
48:377–385. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Nesci S: The mitochondrial permeability
transition pore in cell death: A promising drug binding
bioarchitecture. Med Res Rev. 40:811–817. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Bauer TM and Murphy E: Role of
mitochondrial calcium and the permeability transition pore in
regulating cell death. Circ Res. 126:280–293. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Azzolin L, Antolini N, Calderan A, Ruzza
P, Sciacovelli M, Marin O, Mammi S, Bernardi P and Rasola A:
Antamanide, a derivative of amanita phalloides, is a novel
inhibitor of the mitochondrial permeability transition pore. PLoS
One. 6:e162802011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Zhou Q, Xie M, Zhu J, Yi Q, Tan B, Li Y,
Ye L, Zhang X, Zhang Y, Tian J and Xu H: PINK1 contained in
huMSC-derived exosomes prevents cardiomyocyte mitochondrial calcium
overload in sepsis via recovery of mitochondrial Ca2+
efflux. Stem Cell Res Ther. 12:2692021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Fernandes-Alnemri T, Wu J, Yu JW, Datta P,
Miller B, Jankowski W, Rosenberg S, Zhang J and Alnemri ES: The
pyroptosome: A supramolecular assembly of ASC dimers mediating
inflammatory cell death via caspase-1 activation. Cell Death
Differ. 14:1590–1604. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Bergsbaken T, Fink SL and Cookson BT:
Pyroptosis: Host cell death and inflammation. Nat Rev Microbiol.
7:99–109. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Robinson N, Ganesan R, Hegedűs C, Kovács
K, Kufer TA and Virág L: Programmed necrotic cell death of
macrophages: Focus on pyroptosis, necroptosis, and parthanatos.
Redox Biol. 26:1012392019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Jorgensen I and Miao EA: Pyroptotic cell
death defends against intracellular pathogens. Immunol Rev.
265:130–142. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Frank D and Vince JE: Pyroptosis versus
necroptosis: Similarities, differences, and crosstalk. Cell Death
Differ. 26:99–114. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Shi J, Gao W and Shao F: Pyroptosis:
Gasdermin-mediated programmed necrotic cell death. Trends Biochem
Sci. 42:245–254. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Fink SL and Cookson BT:
Caspase-1-dependent pore formation during pyroptosis leads to
osmotic lysis of infected host macrophages. Cell Microbiol.
8:1812–1825. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Kayagaki N, Stowe IB, Lee BL, O'Rourke K,
Anderson K, Warming S, Cuellar T, Haley B, Roose-Girma M, Phung QT,
et al: Caspase-11 cleaves gasdermin D for non-canonical
inflammasome signalling. Nature. 526:666–671. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Espinosa-Oliva AM, García-Revilla J,
Alonso-Bellido IM and Burguillos MA: Brainiac caspases: Beyond the
wall of apoptosis. Front Cell Neurosci. 13:5002019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Zhang Y, Liu X, Bai X, Lin Y, Li Z, Fu J,
Li M, Zhao T, Yang H, Xu R, et al: Melatonin prevents endothelial
cell pyroptosis via regulation of long noncoding RNA
MEG3/miR-223/NLRP3 axis. J Pineal Res. 64:e124492018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
85
|
Vande Walle L and Lamkanfi M: Pyroptosis.
Curr Biol. 26:R568–R572. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Kang R, Zeng L, Zhu S, Xie Y, Liu J, Wen
Q, Cao L, Xie M, Ran Q, Kroemer G, et al: Lipid peroxidation drives
gasdermin D-mediated pyroptosis in lethal polymicrobial sepsis.
Cell Host Microbe. 24:97–108.e4. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Xue Z, Xi Q, Liu H, Guo X, Zhang J, Zhang
Z, Li Y, Yang G, Zhou D, Yang H, et al: miR-21 promotes NLRP3
inflammasome activation to mediate pyroptosis and endotoxic shock.
Cell Death Dis. 10:4612019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Hagar JA, Powell DA, Aachoui Y, Ernst RK
and Miao EA: Cytoplasmic LPS activates caspase-11: Implications in
TLR4-independent endotoxic shock. Science. 341:1250–1253. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Cheng KT, Xiong S, Ye Z, Hong Z, Di A,
Tsang KM, Gao X, An S, Mittal M, Vogel SM, et al:
Caspase-11-mediated endothelial pyroptosis underlies
endotoxemia-induced lung injury. J Clin Invest. 127:4124–4135.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Nierhaus A, Winkler MS, Holzmann M,
Mudersbach E, Bauer A, Robbe L, Zahrte C, Schwedhelm E, Daum G,
Kluge S and Zoellner C: Sphingosine-1-phosphate is a novel
biomarker in sepsis severity. Intensive Care Med Exp. 3 (Suppl
1):A7892015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
91
|
Song F, Hou J, Chen Z, Cheng B, Lei R, Cui
P, Sun Y, Wang H and Fang X: Sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor 2
signalling promotes caspase-11-dependent macrophage pyroptosis and
worsens scherichia coli sepsis outcome. Anesthesiology.
129:311–320. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Bordon Y: Mucosal immunology:
Inflammasomes induce sepsis following community breakdown. Nat Rev
Immunol. 12:400–401. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Guo H, Callaway JB and Ting JP:
Inflammasomes: Mechanism of action, role in disease, and
therapeutics. Nat Med. 21:677–687. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Pu Q, Gan C, Li R, Li Y, Tan S, Li X, Wei
Y, Lan L, Deng X, Liang H, et al: Atg7 deficiency intensifies
inflammasome activation and pyroptosis in pseudomonas sepsis. J
Immunol. 198:3205–3213. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Man SM and Kanneganti TD: Regulation of
inflammasome activation. Immunol Rev. 265:6–21. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
96
|
Lamkanfi M and Dixit VM: In retrospect:
The inflammasome turns 15. Nature. 548:534–535. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Chu LH, Indramohan M, Ratsimandresy RA,
Gangopadhyay A, Morris EP, Monack DM, Dorfleutner A and Stehlik C:
The oxidized phospholipid oxPAPC protects from septic shock by
targeting the non-canonical inflammasome in macrophages. Nat
Commun. 9:9962018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98
|
Lee SK, Kim YS, Bae GH, Lee HY and Bae YS:
VU0155069 inhibits inflammasome activation independent of
phospholipase D1 activity. Sci Rep. 9:143492019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
99
|
Li Z, Jia Y, Feng Y, Cui R, Miao R, Zhang
X, Qu K, Liu C and Zhang J: Methane alleviates sepsis-induced
injury by inhibiting pyroptosis and apoptosis: In vivo and in vitro
experiments. Aging (Albany NY). 11:1226–1239. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
100
|
Li N, Zhou H, Wu H, Wu Q, Duan M, Deng W
and Tang Q: STING-IRF3 contributes to lipopolysaccharide-induced
cardiac dysfunction, inflammation, apoptosis and pyroptosis by
activating NLRP3. Redox Biol. 24:1012152019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
101
|
Liu J, Zhao N, Shi G and Wang H:
Geniposide ameliorated sepsis-induced acute kidney injury by
activating PPARγ. Aging (Albany NY). 12:22744–22758.
2020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
102
|
Wong WT, Li LH, Rao YK, Yang SP, Cheng SM,
Lin WY, Cheng CC, Chen A and Hua KF: Repositioning of the β-blocker
carvedilol as a novel autophagy inducer that inhibits the NLRP3
inflammasome. Front Immunol. 9:19202018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
103
|
Tong R, Jia T, Shi R and Yan F: Inhibition
of microRNA-15 protects H9c2 cells against CVB3-induced myocardial
injury by targeting NLRX1 to regulate the NLRP3 inflammasome. Cell
Mol Biol Lett. 25:62020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
104
|
Chen J, Wang B, Lai J, Braunstein Z, He M,
Ruan G, Yin Z, Wang J, Cianflone K, Ning Q, et al: Trimetazidine
attenuates cardiac dysfunction in endotoxemia and sepsis by
promoting neutrophil migration. Front Immunol. 9:20152018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
105
|
Dev S and Babitt JL: Overview of iron
metabolism in health and disease. Hemodial Int. 21 (Suppl
1):S6–S20. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
106
|
Drakesmith H and Prentice AM: Hepcidin and
the iron-infection axis. Science. 338:768–772. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
107
|
Flo TH, Smith KD, Sato S, Rodriguez DJ,
Holmes MA, Strong RK, Akira S and Aderem A: Lipocalin 2 mediates an
innate immune response to bacterial infection by sequestrating
iron. Nature. 432:917–921. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
108
|
Sheldon JR, Laakso HA and Heinrichs DE:
Iron acquisition strategies of bacterial pathogens. Virulence Mech
Bact Pathog. 4:43–85. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
109
|
Liu Q, Wu J, Zhang X, Wu X, Zhao Y and Ren
J: Iron homeostasis and disorders revisited in the sepsis. Free
Radic Biol Med. 165:1–13. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
110
|
Ganz T: Iron in innate immunity: Starve
the invaders. Curr Opin Immunol. 21:63–67. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
111
|
Hentze MW, Muckenthaler MU and Andrews NC:
Balancing acts: Molecular control of mammalian iron metabolism.
Cell. 117:285–297. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
112
|
Dixon SJ, Lemberg KM, Lamprecht MR, Skouta
R, Zaitsev EM, Gleason CE, Patel DN, Bauer AJ, Cantley AM, Yang WS,
et al: Ferroptosis: An iron-dependent form of nonapoptotic cell
death. Cell. 149:1060–1072. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
113
|
Gaschler MM, Andia AA, Liu H, Csuka JM,
Hurlocker B, Vaiana CA, Heindel DW, Zuckerman DS, Bos PH, Reznik E,
et al: FINO2 initiates ferroptosis through GPX4 inactivation and
iron oxidation. Nat Chem Biol. 14:507–515. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
114
|
Lei P, Bai T and Sun Y: Mechanisms of
ferroptosis and relations with regulated cell death: A review.
Front Physiol. 10:1392019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
115
|
Zhu S, Zhang Q, Sun X, Zeh HJ III, Lotze
MT, Kang R and Tang D: HSPA5 regulates ferroptotic cell death in
cancer cells. Cancer Res. 77:2064–2077. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
116
|
Yuan H, Li X, Zhang X, Kang R and Tang D:
CISD1 inhibits ferroptosis by protection against mitochondrial
lipid peroxidation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 478:838–844. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
117
|
Gao M, Monian P, Quadri N, Ramasamy R and
Jiang X: Glutaminolysis and transferrin regulate ferroptosis. Mol
Cell. 59:298–308. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
118
|
Stockwell BR, Friedmann Angeli JP, Bayir
H, Bush AI, Conrad M, Dixon SJ, Fulda S, Gascón S, Hatzios SK,
Kagan VE, et al: Ferroptosis: A regulated cell death nexus linking
metabolism, redox biology, and disease. Cell. 171:273–285. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
119
|
Yang WS, Kim KJ, Gaschler MM, Patel M,
Shchepinov MS and Stockwell BR: Peroxidation of polyunsaturated
fatty acids by lipoxygenases drives ferroptosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 113:E4966–E4975. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
120
|
Doll S, Proneth B, Tyurina YY, Panzilius
E, Kobayashi S, Ingold I, Irmler M, Beckers J, Aichler M, Walch A,
et al: ACSL4 dictates ferroptosis sensitivity by shaping cellular
lipid composition. Nat Chem Biol. 13:91–98. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
121
|
Yu H, Guo P, Xie X, Wang Y and Chen G:
Ferroptosis, a new form of cell death, and its relationships with
tumourous diseases. J Cell Mol Med. 21:648–657. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
122
|
Cao JY and Dixon SJ: Mechanisms of
ferroptosis. Cell Mol Life Sci. 73:2195–2209. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
123
|
Xie Y, Hou W, Song X, Yu Y, Huang J, Sun
X, Kang R and Tang D: Ferroptosis: Process and function. Cell Death
Differ. 23:369–379. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
124
|
Fang X, Wang H, Han D, Xie E, Yang X, Wei
J, Gu S, Gao F, Zhu N, Yin X, et al: Ferroptosis as a target for
protection against cardiomyopathy. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
116:2672–2680. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
125
|
Park SJ, Cho SS, Kim KM, Yang JH, Kim JH,
Jeong EH, Yang JW, Han CY, Ku SK, Cho IJ and Ki SH: Protective
effect of sestrin2 against iron overload and ferroptosis-induced
liver injury. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 379:1146652019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
126
|
Weiland A, Wang Y, Wu W, Lan X, Han X, Li
Q and Wang J: Ferroptosis and its role in diverse brain diseases.
Mol Neurobiol. 56:4880–4893. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
127
|
Bogdan AR, Miyazawa M, Hashimoto K and
Tsuji Y: Regulators of iron homeostasis: New players in metabolism,
cell death, and disease. Trends Biochem Sci. 41:274–286. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
128
|
Zhu H, Santo A, Jia Z and Li YR: GPx4 in
bacterial infection and polymicrobial sepsis: Involvement of
ferroptosis and pyroptosis. React Oxyg Species (Apex). 7:154–160.
2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
129
|
Beatty A, Singh T, Tyurina YY, Tyurin VA,
Samovich S, Nicolas E, Maslar K, Zhou Y, Cai KQ, Tan Y, et al:
Ferroptotic cell death triggered by conjugated linolenic acids is
mediated by ACSL1. Nat Commun. 12:22442021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
130
|
Friedmann Angeli JP, Schneider M, Proneth
B, Tyurina YY, Tyurin VA, Hammond VJ, Herbach N, Aichler M, Walch
A, Eggenhofer E, et al: Inactivation of the ferroptosis regulator
Gpx4 triggers acute renal failure in mice. Nat Cell Biol.
16:1180–1191. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
131
|
Gao G and Chang YZ: Mitochondrial ferritin
in the regulation of brain iron homeostasis and neurodegenerative
diseases. Front Pharmacol. 5:192014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
132
|
Fang X, Cai Z, Wang H, Han D, Cheng Q,
Zhang P, Gao F, Yu Y, Song Z, Wu Q, et al: Loss of cardiac ferritin
H facilitates cardiomyopathy via Slc7a11-mediated ferroptosis. Circ
Res. 127:486–501. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
133
|
Liu Y, Zeng L, Yang Y, Chen C, Wang D and
Wang H: Acyl-CoA thioesterase 1 prevents cardiomyocytes from
doxorubicin-induced ferroptosis via shaping the lipid composition.
Cell Death Dis. 11:7562020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
134
|
Ma S, Sun L, Wu W, Wu J, Sun Z and Ren Z:
USP22 protects against myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury via
the SIRT1-P53/SLC7A11-dependent inhibition of ferroptosis-induced
cardiomyocyte death. Front Physiol. 11:5513182020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
135
|
Lillo-Moya J, Rojas-Solé C,
Muñoz-Salamanca D, Panieri E, Saso L and Rodrigo R: Targeting
ferroptosis against ischemia/reperfusion cardiac injury.
Antioxidants (Basel). 10:6672021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
136
|
Wang N, Ma H, Li J, Meng C, Zou J, Wang H,
Liu K, Liu M, Xiao X, Zhang H and Wang K: HSF1 functions as a key
defender against palmitic acid-induced ferroptosis in
cardiomyocytes. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 150:65–76. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
137
|
Li N, Wang W, Zhou H, Wu Q, Duan M, Liu C,
Wu H, Deng W, Shen D and Tang Q: Ferritinophagy-mediated
ferroptosis is involved in sepsis-induced cardiac injury. Free
Radic Biol Med. 160:303–318. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
138
|
Hu H, Chen Y, Jing L, Zhai C and Shen L:
The link between ferroptosis and cardiovascular diseases: A novel
target for treatment. Front Cardiovasc Med. 8:7109632021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
139
|
Wang C, Yuan W, Hu A, Lin J, Xia Z, Yang
CF, Li Y and Zhang Z: Dexmedetomidine alleviated sepsis-induced
myocardial ferroptosis and septic heart injury. Mol Med Rep.
22:175–184. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
140
|
Antonioli M, Di Rienzo M, Piacentini M and
Fimia GM: Emerging mechanisms in initiating and terminating
autophagy. Trends Biochem Sci. 42:28–41. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
141
|
Zheng L, Terman A, Hallbeck M, Dehvari N,
Cowburn RF, Benedikz E, Kågedal K, Cedazo-Minguez A and Marcusson
J: Macroautophagy-generated increase of lysosomal amyloid β-protein
mediates oxidant-induced apoptosis of cultured neuroblastoma cells.
Autophagy. 7:1528–1545. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
142
|
Levine B, Mizushima N and Virgin HW:
Autophagy in immunity and inflammation. Nature. 469:323–335. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
143
|
Anand SK, Sharma A, Singh N and Kakkar P:
Entrenching role of cell cycle checkpoints and autophagy for
maintenance of genomic integrity. DNA Repair (Amst). 86:1027482020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
144
|
Denton D and Kumar S: Autophagy-dependent
cell death. Cell Death Differ. 26:605–616. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
145
|
Jiang Y, Gao M, Wang W, Lang Y, Tong Z,
Wang K, Zhang H, Chen G, Liu M, Yao Y and Xiao X: Sinomenine
hydrochloride protects against polymicrobial sepsis via autophagy.
Int J Mol Sci. 16:2559–2573. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
146
|
Chung MT, Lee YM, Shen HH, Cheng PY, Huang
YC, Lin YJ, Huang YY and Lam KK: Activation of autophagy is
involved in the protective effect of 17β-oestradiol on
endotoxaemia-induced multiple organ dysfunction in ovariectomized
rats. J Cell Mol Med. 21:3705–3717. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
147
|
Jia J, Gong X, Zhao Y, Yang Z, Ji K, Luan
T, Zang B and Li G: Autophagy enhancing contributes to the organ
protective effect of alpha-lipoic acid in septic rats. Front
Immunol. 10:14912019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
148
|
Lu LH, Chao CH and Yeh TM: Inhibition of
autophagy protects against sepsis by concurrently attenuating the
cytokine storm and vascular leakage. J Infect. 78:178–186. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
149
|
Cui SN, Chen ZY, Yang XB, Chen L, Yang YY,
Pan SW, Wang YX, Xu JQ, Zhou T, Xiao HR, et al: Trichostatin A
modulates the macrophage phenotype by enhancing autophagy to reduce
inflammation during polymicrobial sepsis. Int Immunopharmacol.
77:1059732019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
150
|
Oami T, Watanabe E, Hatano M, Sunahara S,
Fujimura L, Sakamoto A, Ito C, Toshimori K and Oda S: Suppression
of t cell autophagy results in decreased viability and function of
T cells through accelerated apoptosis in a murine sepsis model.
Crit Care Med. 45:e77–e85. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
151
|
Patoli D, Mignotte F, Deckert V, Dusuel A,
Dumont A, Rieu A, Jalil A, Van Dongen K, Bourgeois T, Gautier T, et
al: Inhibition of mitophagy drives macrophage activation and
antibacterial defense during sepsis. J Clin Invest. 130:5858–5874.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
152
|
Dong G, Si C, Zhang Q, Yan F, Li C, Zhang
H, Ma Q, Dai J, Li Z, Shi H, et al: Autophagy regulates
accumulation and functional activity of granulocytic
myeloid-derived suppressor cells via STAT3 signaling in endotoxin
shock. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 1863:2796–2807. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
153
|
Jin L, Batra S and Jeyaseelan S: Deletion
of NLRP3 augments survival during polymicrobial sepsis by
decreasing autophagy and enhancing phagocytosis. J Immunol.
198:1253–1262. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
154
|
Ge Y, Huang M, Dong N and Yao YM: Effect
of interleukin-36β on activating autophagy of CD4+CD25+ regulatory
T cells and its immune regulation in sepsis. J Infect Dis.
222:1517–1530. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
155
|
Park SY, Shrestha S, Youn YJ, Kim JK, Kim
SY, Kim HJ, Park SH, Ahn WG, Kim S, Lee MG, et al: Autophagy primes
neutrophils for neutrophil extracellular trap formation during
sepsis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 196:577–589. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
156
|
Napolitano LM: Sepsis 2018: Definitions
and guideline changes. Surg Infect (Larchmt). 19:117–125. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
157
|
Jiang P and Mizushima N: Autophagy and
human diseases. Cell Res. 24:69–79. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
158
|
Lemasters JJ: Selective mitochondrial
autophagy, or mitophagy, as a targeted defense against oxidative
stress, mitochondrial dysfunction, and aging. Rejuvenation Res.
8:3–5. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
159
|
Carchman EH, Whelan S, Loughran P, Mollen
K, Stratamirovic S, Shiva S, Rosengart MR and Zuckerbraun BS:
Experimental sepsis-induced mitochondrial biogenesis is dependent
on autophagy, TLR4, and TLR9 signaling in liver. FASEB J.
27:4703–4711. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
160
|
Murphy MP: How mitochondria produce
reactive oxygen species. Biochem J. 417:1–13. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
161
|
Kubli DA, Quinsay MN, Huang C, Lee Y and
Gustafsson AB: Bnip3 functions as a mitochondrial sensor of
oxidative stress during myocardial ischemia and reperfusion. Am J
Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 295:H2025–H2031. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
162
|
Pohl C and Dikic I: Cellular quality
control by the ubiquitin-proteasome system and autophagy. Science.
366:818–822. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
163
|
Ma J, Wang Y, Zheng D, Wei M, Xu H and
Peng T: Rac1 signalling mediates doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity
through both reactive oxygen species-dependent and -independent
pathways. Cardiovasc Res. 97:77–87. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
164
|
Wu C, Zhou XX, Li JZ, Qiang HF, Wang Y and
Li G: Pretreatment of cardiac progenitor cells with bradykinin
attenuates H2O2-induced cell apoptosis and
improves cardiac function in rats by regulating autophagy. Stem
Cell Res Ther. 12:4372021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
165
|
Jiang YJ, Sun SJ, Cao WX, Lan XT, Ni M, Fu
H, Li DJ, Wang P and Shen FM: Excessive ROS production and enhanced
autophagy contribute to myocardial injury induced by branched-chain
amino acids: Roles for the AMPK-ULK1 signaling pathway and α7nAChR.
Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 1867:1659802021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
166
|
Huang J, Lam GY and Brumell JH: Autophagy
signalling through reactive oxygen species. Antioxid Redox Signal.
14:2215–2231. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
167
|
Takahashi W, Watanabe E, Fujimura L,
Watanabe-Takano H, Yoshidome H, Swanson PE, Tokuhisa T, Oda S and
Hatano M: Kinetics and protective role of autophagy in a mouse
cecal ligation and puncture-induced sepsis. Crit Care. 17:R1602013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
168
|
Yen YT, Yang HR, Lo HC, Hsieh YC, Tsai SC,
Hong CW and Hsieh CH: Enhancing autophagy with activated protein C
and rapamycin protects against sepsis-induced acute lung injury.
Surgery. 153:689–698. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
169
|
Sun Y, Yao X, Zhang QJ, Zhu M, Liu ZP, Ci
B, Xie Y, Carlson D, Rothermel BA, Sun Y, et al: Beclin-1-dependent
autophagy protects the heart during sepsis. Circulation.
138:2247–2262. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
170
|
Liu JJ, Li Y, Yang MS, Chen R and Cen CQ:
SP1-induced ZFAS1 aggravates sepsis-induced cardiac dysfunction via
miR-590-3p/NLRP3-mediated autophagy and pyroptosis. Arch Biochem
Biophys. 695:1086112020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
171
|
Wang Q, Yang X, Song Y, Sun X, Li W, Zhang
L, Hu X, Wang H, Zhao N, Zhuang R, et al: Astragaloside
IV-targeting miRNA-1 attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced cardiac
dysfunction in rats through inhibition of apoptosis and autophagy.
Life Sci. 275:1194142021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
172
|
Wu B, Song H, Fan M, You F, Zhang L, Luo
J, Li J, Wang L, Li C and Yuan M: Luteolin attenuates
sepsis-induced myocardial injury by enhancing autophagy in mice.
Int J Mol Med. 45:1477–1487. 2020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
173
|
Han W, Wang H, Su L, Long Y, Cui N and Liu
D: Inhibition of the mTOR pathway exerts cardioprotective effects
partly through autophagy in CLP rats. Mediators Inflamm.
2018:47982092018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
174
|
Sang Z, Zhang P, Wei Y and Dong S:
miR-214-3p attenuates sepsis-induced myocardial dysfunction in mice
by inhibiting autophagy through PTEN/AKT/mTOR pathway. Biomed Res
Int. 2020:14090382020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
175
|
Hsieh CH, Pai PY, Hsueh HW, Yuan SS and
Hsieh YC: Complete induction of autophagy is essential for
cardioprotection in sepsis. Ann Surg. 253:1190–1200. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
176
|
Yu T, Liu D, Gao M, Yang P, Zhang M, Song
F, Zhang X and Liu Y: Dexmedetomidine prevents septic myocardial
dysfunction in rats via activation of α7nAChR and PI3K/Akt-mediated
autophagy. Biomed Pharmacother. 120:1092312019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
177
|
Zhang E, Zhao X, Zhang L, Li N, Yan J, Tu
K, Yan R, Hu J, Zhang M, Sun D and Hou L: Minocycline promotes
cardiomyocyte mitochondrial autophagy and cardiomyocyte autophagy
to prevent sepsis-induced cardiac dysfunction by Akt/mTOR
signaling. Apoptosis. 24:369–381. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
178
|
Yuan X, Chen G, Guo D, Xu L and Gu Y:
Polydatin alleviates septic myocardial injury by promoting
SIRT6-mediated autophagy. Inflammation. 43:785–795. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
179
|
Gao J, Chen X, Shan C, Wang Y, Li P and
Shao K: Autophagy in cardiovascular diseases: Role of noncoding
RNAs. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 23:101–118. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
180
|
Leng Y, Zhang Y, Li X, Wang Z, Zhuang Q
and Lu Y: Receptor interacting protein kinases 1/3: The potential
therapeutic target for cardiovascular inflammatory diseases. Front
Pharmacol. 12:7623342021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
181
|
Hsieh YC, Athar M and Chaudry IH: When
apoptosis meets autophagy: Deciding cell fate after trauma and
sepsis. Trends Mol Med. 15:129–138. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
182
|
Nishida K, Yamaguchi O and Otsu K:
Crosstalk between autophagy and apoptosis in heart disease. Circ
Res. 103:343–351. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
183
|
Galluzzi L, Bravo-San Pedro JM, Vitale I,
Aaronson SA, Abrams JM, Adam D, Alnemri ES, Altucci L, Andrews D,
Annicchiarico-Petruzzelli M, et al: Essential versus accessory
aspects of cell death: Recommendations of the NCCD 2015. Cell Death
Differ. 22:58–73. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
184
|
Speir M and Lawlor KE: RIP-roaring
inflammation: RIPK1 and RIPK3 driven NLRP3 inflammasome activation
and autoinflammatory disease. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 109:114–124.
2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
185
|
Kunchithapautham K and Rohrer B: Apoptosis
and autophagy in photoreceptors exposed to oxidative stress.
Autophagy. 3:433–441. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
186
|
Nagata S, Hanayama R and Kawane K:
Autoimmunity and the clearance of dead cells. Cell. 140:619–630.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
187
|
Humphries F, Yang S, Wang B and Moynagh
PN: RIP kinases: Key decision makers in cell death and innate
immunity. Cell Death Differ. 22:225–236. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
188
|
Feoktistova M, Makarov R, Yazdi AS and
Panayotova-Dimitrova D: RIPK1 and TRADD regulate TNF-induced
signaling and ripoptosome formation. Int J Mol Sci. 22:124592021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
189
|
Ofengeim D and Yuan J: Regulation of rip1
kinase signalling at the crossroads of inflammation and cell death.
Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 14:727–736. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
190
|
Degterev A, Huang Z, Boyce M, Li Y, Jagtap
P, Mizushima N, Cuny GD, Mitchison TJ, Moskowitz MA and Yuan J:
Chemical inhibitor of nonapoptotic cell death with therapeutic
potential for ischemic brain injury. Nat Chem Biol. 1:112–119.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
191
|
Hou W, Xie Y, Song X, Sun X, Lotze MT, Zeh
HJ III, Kang R and Tang D: Autophagy promotes ferroptosis by
degradation of ferritin. Autophagy. 12:1425–1428. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
192
|
Lu ZY, Cheng MH, Yu CY, Lin YS, Yeh TM,
Chen CL, Chen CC, Wan SW and Chang CP: Dengue nonstructural protein
1 maintains autophagy through retarding caspase-mediated cleavage
of beclin-1. Int J Mol Sci. 21:97022020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
193
|
Korsmeyer SJ, Wei MC, Saito M, Weiler S,
Oh KJ and Schlesinger PH: Pro-apoptotic cascade activates BID,
which oligomerizes BAK or BAX into pores that result in the release
of cytochrome c. Cell Death Differ. 7:1166–1173. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
194
|
Almeida RD, Manadas BJ, Carvalho AP and
Duarte CB: Intracellular signaling mechanisms in photodynamic
therapy. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1704:59–86. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
195
|
Fefelova N, Wongjaikam S, Siri-Angkul N,
Gwathmey J, Chattipakorn N, Chattipakorn S and Xie LH: Abstract
15737: Deficiency of mitochondrial calcium uniporter protects mouse
hearts from iron overload by attenuating ferroptosis. Circulation.
142 (Suppl 3):A157372020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
196
|
Yin Z, Ding G, Chen X, Qin X, Xu H, Zeng
B, Ren J, Zheng Q and Wang S: Beclin1 haploinsufficiency rescues
low ambient temperature-induced cardiac remodeling and contractile
dysfunction through inhibition of ferroptosis and mitochondrial
injury. Metabolism. 113:1543972020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
197
|
Kang R, Zhu S, Zeh HJ, Klionsky DJ and
Tang D: BECN1 is a new driver of ferroptosis. Autophagy.
14:2173–2175. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
198
|
Shao W, Yeretssian G, Doiron K, Hussain SN
and Saleh M: The caspase-1 digestome identifies the glycolysis
pathway as a target during infection and septic shock. J Biol Chem.
282:36321–36329. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
199
|
Rogers C, Fernandes-Alnemri T, Mayes L,
Alnemri D, Cingolani G and Alnemri ES: Cleavage of DFNA5 by
caspase-3 during apoptosis mediates progression to secondary
necrotic/pyroptotic cell death. Nat Commun. 8:141282017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
200
|
Mandal P, Feng Y, Lyons JD, Berger SB,
Otani S, Delaney A, Tharp GK, Maner-Smith K, Burd EM, Schaeffer M,
et al: Caspase-8 collaborates with caspase-11 to drive tissue
damage and execution of endotoxic shock. Immunity. 49:42–55.e6.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
201
|
Russo AJ and Rathinam VAK: Lipid
peroxidation adds fuel to pyr(optosis). Cell Host Microbe. 24:8–9.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
202
|
Bruni A, Bornstein S, Linkermann A and
Shapiro AMJ: Regulated cell death seen through the lens of islet
transplantation. Cell Transplant. 27:890–901. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
203
|
Zhou W, Chen C, Chen Z, Liu L, Jiang J, Wu
Z, Zhao M and Chen Y: NLRP3: A novel mediator in cardiovascular
disease. J Immunol Res. 2018:57021032018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|