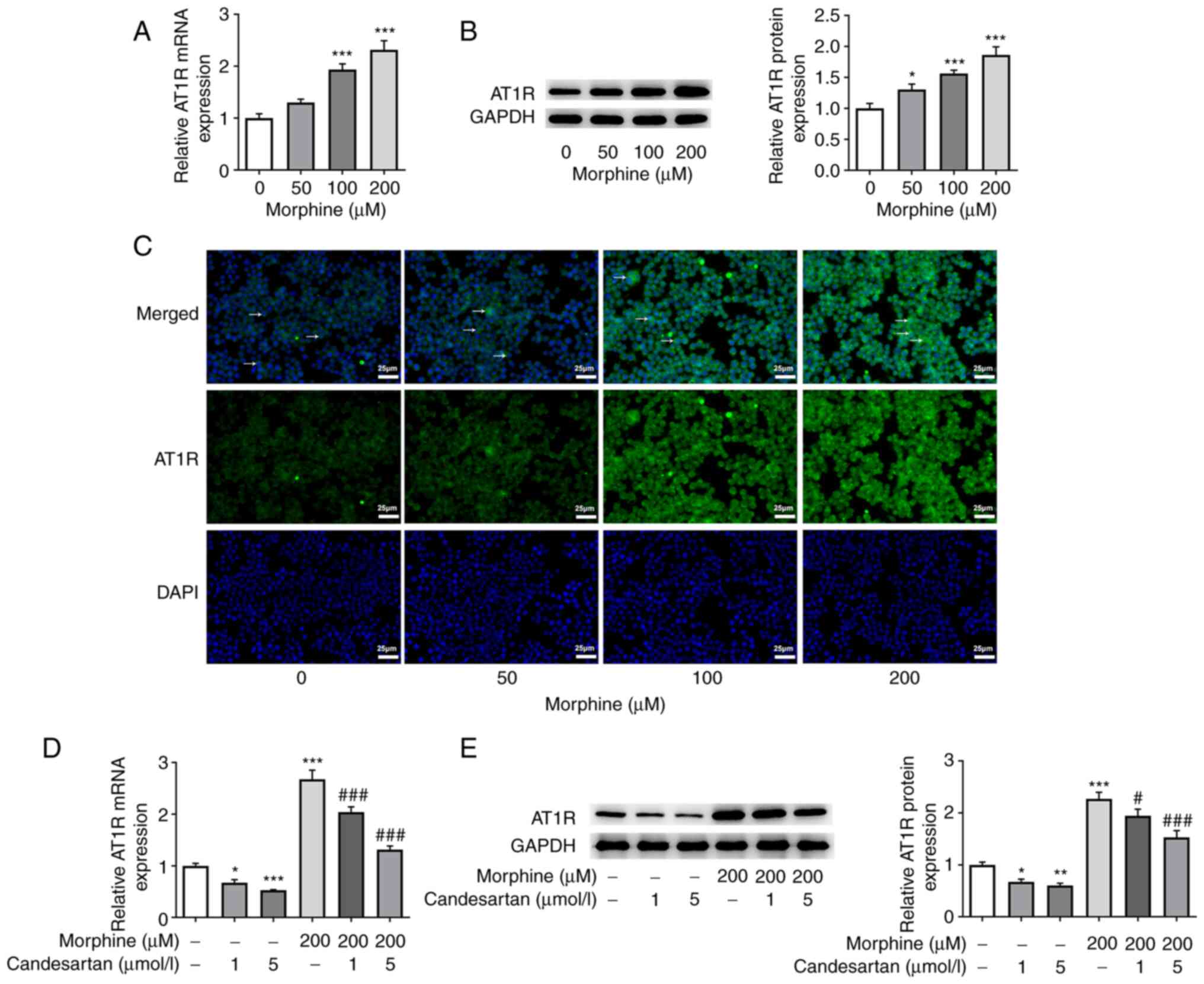
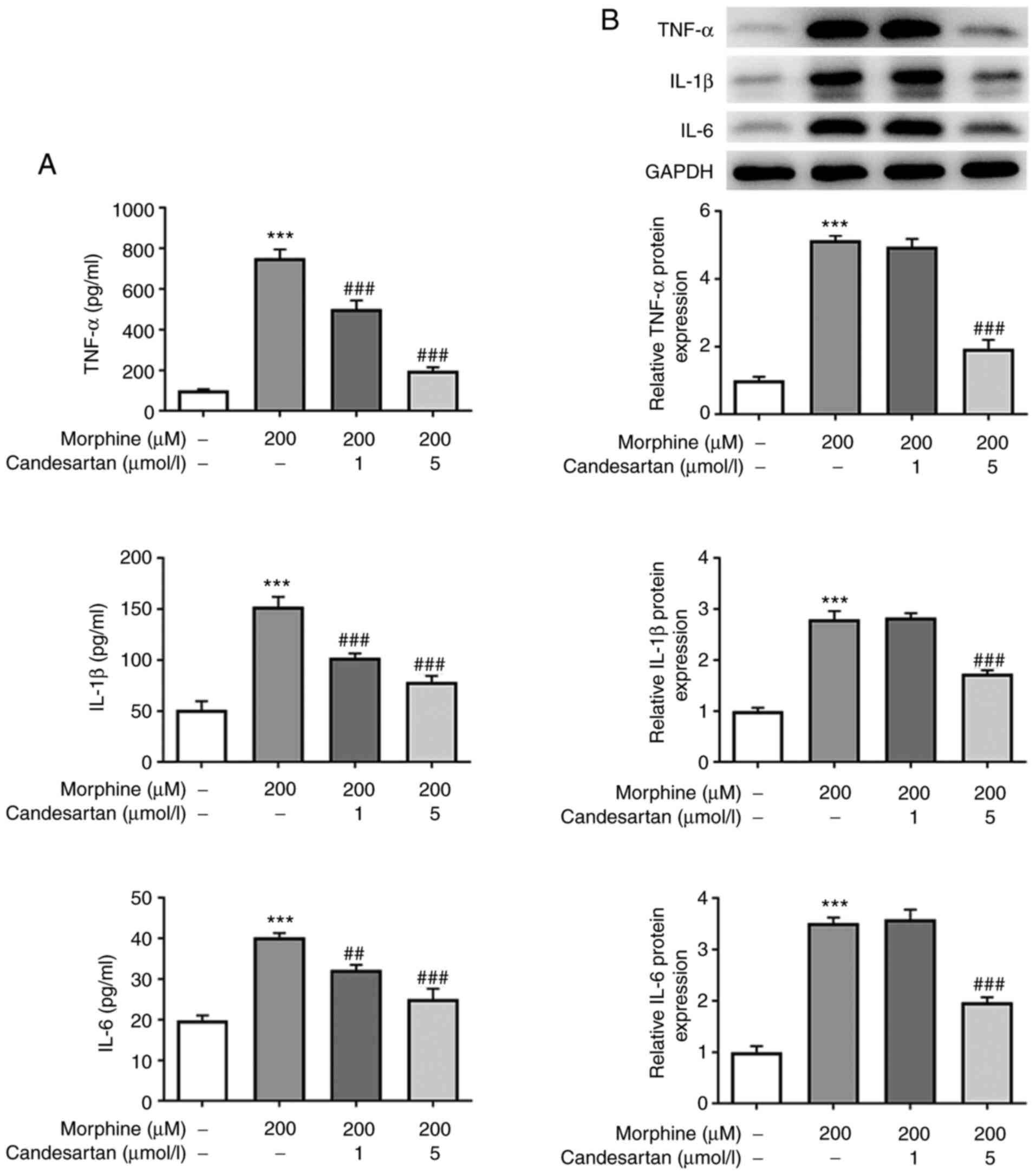
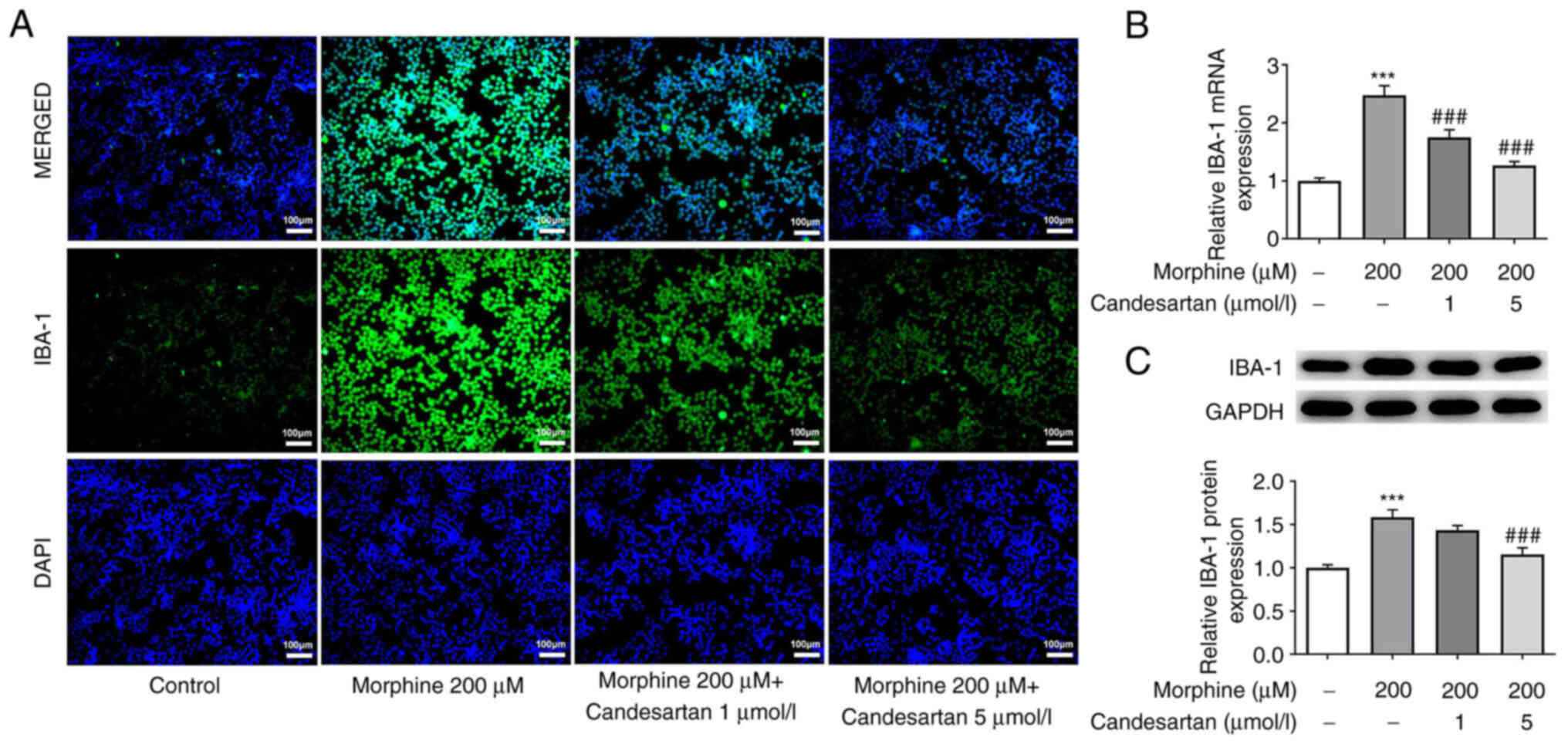
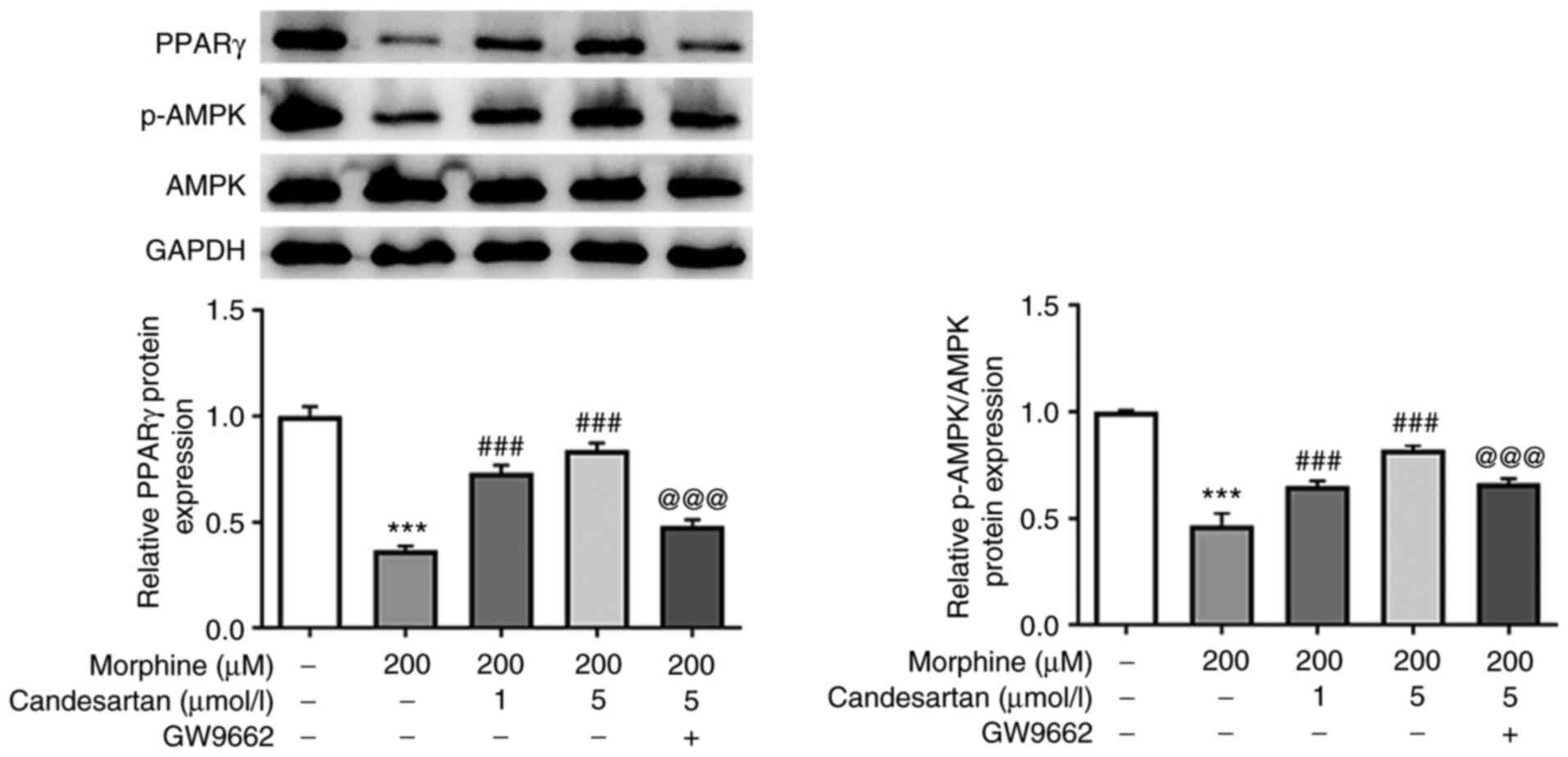
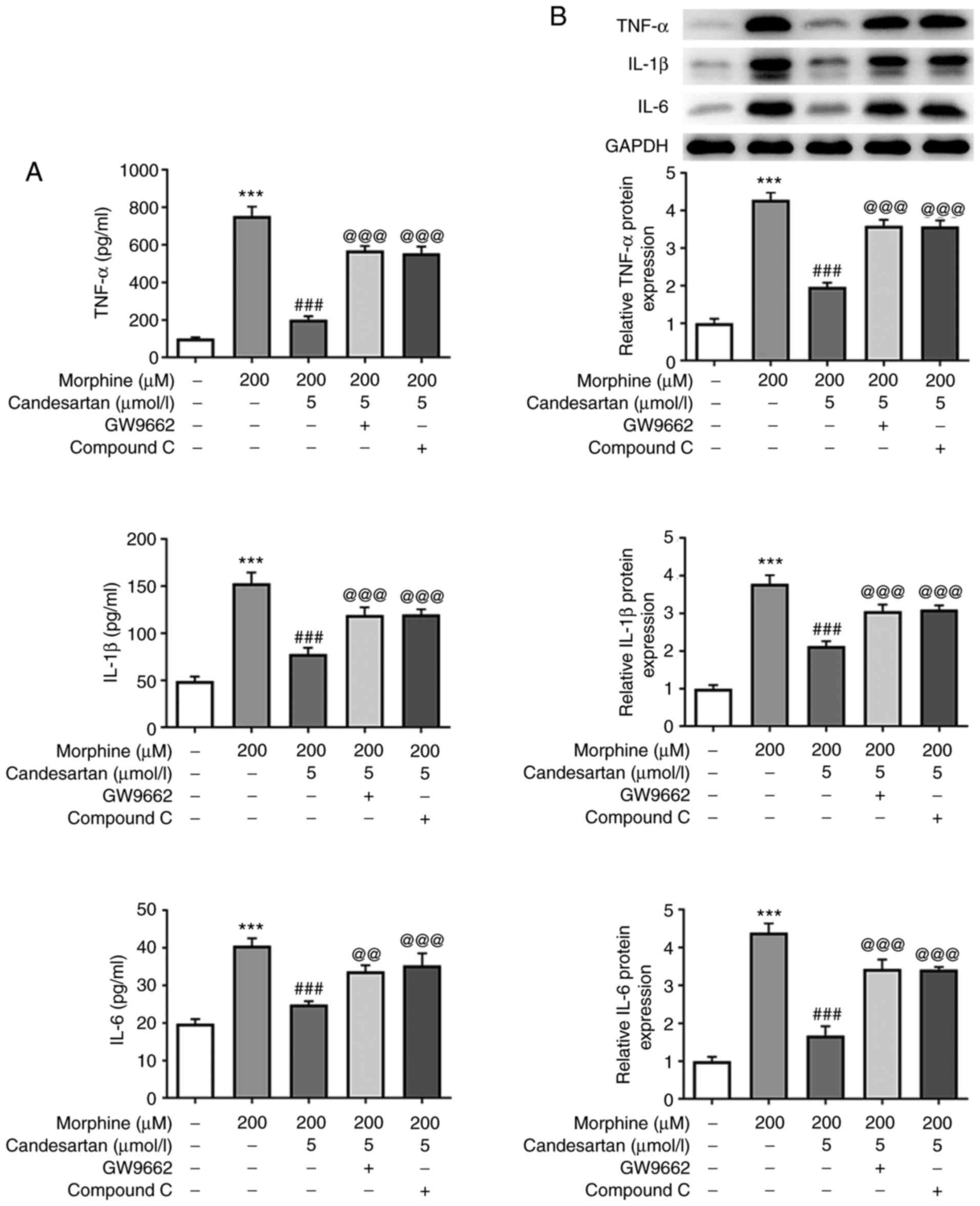
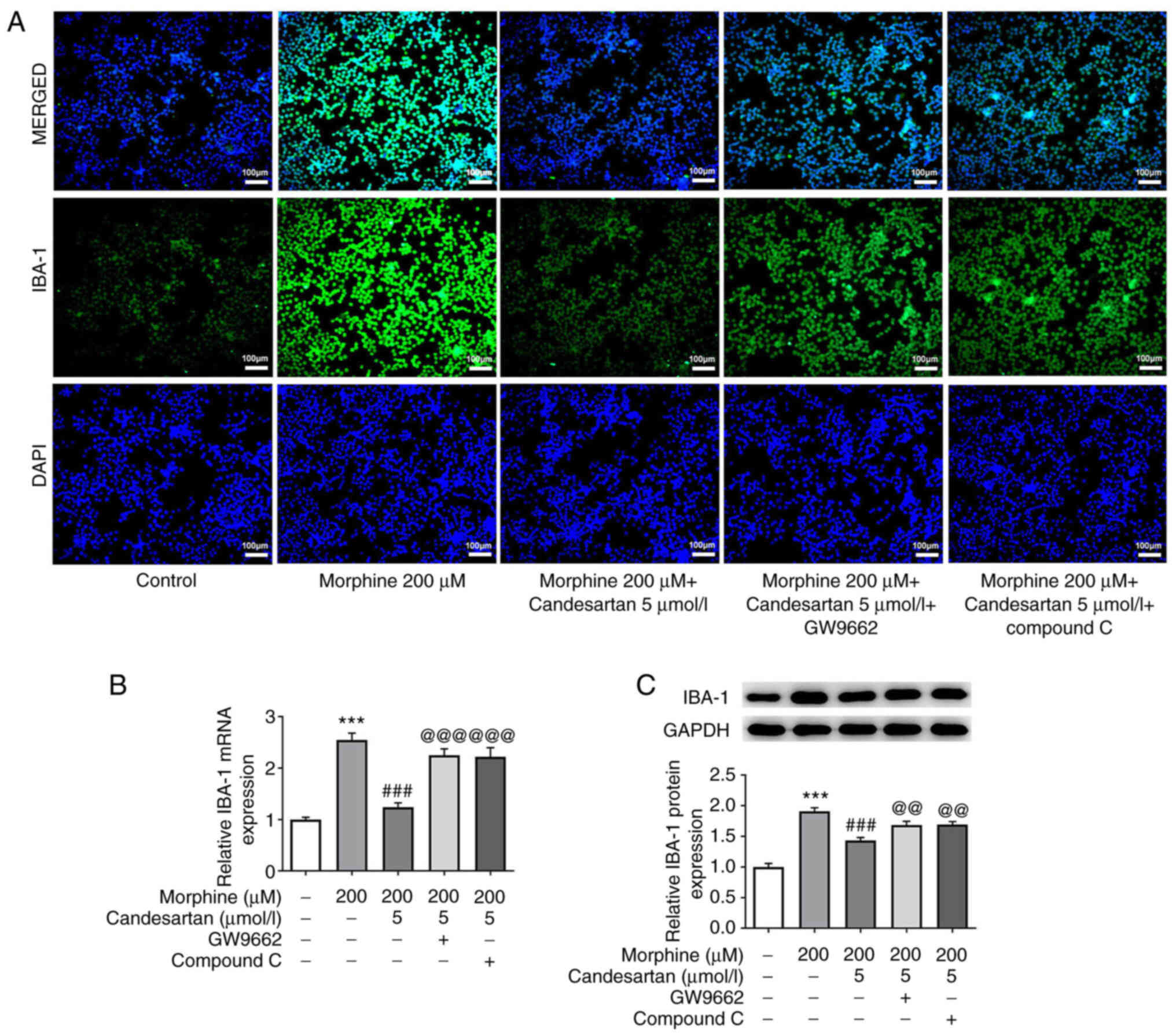
|
1
|
Zhang TJ, Qiu Y and Hua Z: The emerging
perspective of morphine tolerance: MicroRNAs. Pain Res Manag.
2019:94329652019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Kornetsky C and Bain G: Morphine:
Single-dose tolerance. Science. 162:1011–1012. 1968. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Schaefer CP, Tome ME and Davis TP: The
opioid epidemic: A central role for the blood brain barrier in
opioid analgesia and abuse. Fluids Barriers CNS. 14:322017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Martini L and Whistler JL: The role of mu
opioid receptor desensitization and endocytosis in morphine
tolerance and dependence. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 17:556–564. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Huang M, Luo L, Zhang Y, Wang W, Dong J,
Du W, Jiang W and Xu T: Metabotropic glutamate receptor 5
signalling induced NMDA receptor subunits alterations during the
development of morphine-induced antinociceptive tolerance in mouse
cortex. Biomed Pharmacother. 110:717–726. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Jokinen V, Sidorova Y, Viisanen H,
Suleymanova I, Tiilikainen H, Li Z, Lilius TO, Mätlik K, Anttila
JE, Airavaara M, et al: Differential spinal and supraspinal
activation of Glia in a rat model of morphine tolerance.
Neuroscience. 375:10–24. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Eidson LN and Murphy AZ: Inflammatory
mediators of opioid tolerance: Implications for dependency and
addiction. Peptides. 115:51–58. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Lin CP and Lu DH: Role of
neuroinflammation in opioid tolerance: Translational evidence from
human-to-rodent studies. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1099:125–139. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Berrios I, Castro C and Kuffler DP:
Morphine: Axon regeneration, neuroprotection, neurotoxicity,
tolerance, and neuropathic pain. P R Health Sci J. 27:119–128.
2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Hutchinson MR, Coats BD, Lewis SS, Zhang
Y, Sprunger DB, Rezvani N, Baker EM, Jekich BM, Wieseler JL,
Somogyi AA, et al: Proinflammatory cytokines oppose opioid-induced
acute and chronic analgesia. Brain Behav Immun. 22:1178–1189. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Miyoshi M, Miyano K, Moriyama N, Taniguchi
M and Watanabe T: Angiotensin type 1 receptor antagonist inhibits
lipopolysaccharide-induced stimulation of rat microglial cells by
suppressing nuclear factor kappaB and activator protein-1
activation. Eur J Neurosci. 27:343–351. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Chappell MC: Biochemical evaluation of the
renin-angiotensin system: The good, bad, and absolute? Am J Physiol
Heart Circ Physiol. 310:H137–H152. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Ji J, Tao P and He L: Kangxianling
decoction prevents renal fibrosis in rats with 5/6 nephrectomy and
inhibits Ang II-induced ECM production in glomerular mesangial
cells. J Pharmacol Sci. 139:367–372. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Labandeira-Garcia JL, Rodriguez-Perez AI,
Garrido-Gil P, Rodriguez-Pallares J, Lanciego JL and Guerra MJ:
Brain renin-angiotensin system and microglial polarization:
Implications for aging and neurodegeneration. Front Aging Neurosci.
9:1292017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Rodriguez-Perez AI, Borrajo A,
Rodriguez-Pallares J, Guerra MJ and Labandeira-Garcia JL:
Interaction between NADPH-oxidase and Rho-kinase in angiotensin
II-induced microglial activation. Glia. 63:466–482. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Joglar B, Rodriguez-Pallares J,
Rodriguez-Perez AI, Rey P, Guerra MJ and Labandeira-Garcia JL: The
inflammatory response in the MPTP model of Parkinson's disease is
mediated by brain angiotensin: Relevance to progression of the
disease. J Neurochem. 109:656–669. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Rey P, Lopez-Real A, Sanchez-Iglesias S,
Muñoz A, Soto-Otero R and Labandeira-Garcia JL: Angiotensin
type-1-receptor antagonists reduce 6-hydroxydopamine toxicity for
dopaminergic neurons. Neurobiol Aging. 28:555–567. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Rodriguez-Pallares J, Rey P, Parga JA,
Muñoz A, Guerra MJ and Labandeira-Garcia JL: Brain angiotensin
enhances dopaminergic cell death via microglial activation and
NADPH-derived ROS. Neurobiol Dis. 31:58–73. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Bulsara KG and Makaryus AN: Candesartan.
In: StatPearls. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing;
2022
|
|
20
|
Qie S, Ran Y, Lu X, Su W, Li W, Xi J, Gong
W and Liu Z: Candesartan modulates microglia activation and
polarization via NF-κB signaling pathway. Int J Immunopathol
Pharmacol. 34:20587384209749002020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Timaru-Kast R, Gotthardt P, Luh C, Huang
C, Hummel R, Schäfer MKE and Thal SC: Angiotensin II receptor 1
blockage limits brain damage and improves functional outcome after
brain injury in aged animals despite age-dependent reduction in AT1
Expression. Front Aging Neurosci. 11:632019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Wang L, Yin C, Xu X, Liu T, Wang B, Abdul
M, Zhou Y, Cao J and Lu C: Pellino1 contributes to morphine
tolerance by microglia activation via MAPK signaling in the spinal
cord of mice. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 40:1117–1131. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Torika N, Asraf K, Apte RN and
Fleisher-Berkovich S: Candesartan ameliorates brain inflammation
associated with Alzheimer's disease. CNS Neurosci Ther. 24:231–242.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Stein C: New concepts in opioid analgesia.
Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 27:765–775. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Sverrisdottir E, Lund TM, Olesen AE,
Drewes AM, Christrup LL and Kreilgaard M: A review of morphine and
morphine-6-glucuronide's pharmacokinetic-pharmacodynamic
relationships in experimental and clinical pain. Eur J Pharm Sci.
74:45–62. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Mercadante S, Arcuri E and Santoni A:
Opioid-induced tolerance and hyperalgesia. CNS Drugs. 33:943–955.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Selfridge BR, Wang X, Zhang Y, Yin H,
Grace PM, Watkins LR, Jacobson AE and Rice KC: Structure-activity
relationships of (+)-naltrexone-inspired toll-like receptor 4
(TLR4) antagonists. J Med Chem. 58:5038–5052. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Hickman SE, el Khoury J, Greenberg S,
Schieren I and Silverstein SC: P2Z adenosine triphosphate receptor
activity in cultured human monocyte-derived macrophages. Blood.
84:2452–2456. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Lim KH and Staudt LM: Toll-like receptor
signaling. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 5:a0112472013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Bernier LP: Purinergic regulation of
inflammasome activation after central nervous system injury. J Gen
Physiol. 140:571–575. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Eidson LN and Murphy AZ: Blockade of
Toll-like receptor 4 attenuates morphine tolerance and facilitates
the pain relieving properties of morphine. J Neurosci.
33:15952–15963. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Wang H, Huang M, Wang W, Zhang Y, Ma X,
Luo L, Xu X, Xu L, Shi H, Xu Y, et al: Microglial TLR4-induced TAK1
phosphorylation and NLRP3 activation mediates neuroinflammation and
contributes to chronic morphine-induced antinociceptive tolerance.
Pharmacol Res. 165:1054822021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Wang H, Zhang Y, Ma X, Wang W, Xu X, Huang
M, Xu L, Shi H, Yuan T, Jiang W, et al: Spinal TLR4/P2X7
receptor-dependent NLRP3 inflammasome activation contributes to the
development of tolerance to morphine-induced antinociception. J
Inflamm Res. 13:571–582. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Biancardi VC, Stranahan AM, Krause EG, de
Kloet AD and Stern JE: Cross talk between AT1 receptors and
Toll-like receptor 4 in microglia contributes to angiotensin
II-derived ROS production in the hypothalamic paraventricular
nucleus. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 310:H404–H415. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Sun H, Wu H, Yu X, Zhang G, Zhang R, Zhan
S, Wang H, Bu N, Ma X and Li Y: Angiotensin II and its receptor in
activated microglia enhanced neuronal loss and cognitive impairment
following pilocarpine-induced status epilepticus. Mol Cell
Neurosci. 65:58–67. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Rodriguez-Perez AI, Garrido-Gil P, Pedrosa
MA, Garcia-Garrote M, Valenzuela R, Navarro G, Franco R and
Labandeira-Garcia JL: Angiotensin type 2 receptors: Role in aging
and neuroinflammation in the substantia nigra. Brain Behav Immun.
87:256–271. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Chandel N, Sharma B, Salhan D, Husain M,
Malhotra A, Buch S and Singhal PC: Vitamin D receptor activation
and downregulation of renin-angiotensin system attenuate
morphine-induced T cell apoptosis. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol.
303:C607–C615. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Bhat SA, Goel R, Shukla R and Hanif K:
Angiotensin receptor blockade modulates NFκB and STAT3 signaling
and inhibits glial activation and neuroinflammation better than
angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibition. Mol Neurobiol.
53:6950–6967. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Tiyerili V, Becher UM, Aksoy A, Lütjohann
D, Wassmann S, Nickenig G and Mueller CF: AT1-receptor-deficiency
induced atheroprotection in diabetic mice is partially mediated via
PPARγ. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 12:302013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
de Guglielmo G, Kallupi M, Scuppa G,
Stopponi S, Demopulos G, Gaitanaris G and Ciccocioppo R: Analgesic
tolerance to morphine is regulated by PPARγ. Br J Pharmacol.
171:5407–5416. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Ghavimi H, Hassanzadeh K, Maleki-Dizaji N,
Azarfardian A, Ghasami S, Zolali E and Charkhpour M: Pioglitazone
prevents morphine antinociception tolerance and withdrawal symptoms
in rats. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 387:811–821. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Xu X, Wang Y, Wei Z, Wei W, Zhao P, Tong
B, Xia Y and Dai Y: Madecassic acid, the contributor to the
anti-colitis effect of madecassoside, enhances the shift of Th17
toward Treg cells via the PPARγ/AMPK/ACC1 pathway. Cell Death Dis.
8:e27232017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Huang H, Wang ZJ, Zhang HB, Liang JX, Cao
WD, Wu Q, He CP and Chen C: The function of PPARγ/AMPK/SIRT-1
pathway in inflammatory response of human articular chondrocytes
stimulated by advanced glycation end products. Biol Pharm Bull.
42:1303–1309. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Chao YM, Wu KLH, Tsai PC, Tain YL, Leu S,
Lee WC and Chan JYH: Anomalous AMPK-regulated angiotensin AT1R
expression and SIRT1-mediated mitochondrial biogenesis at RVLM in
hypertension programming of offspring to maternal high fructose
exposure. J Biomed Sci. 27:682020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Zhao Y, Shang F, Shi W, Zhang J, Zhang J,
Liu X, Li B, Hu X and Wang L: Angiotensin II receptor type 1
antagonists modulate vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation and
migration via AMPK/mTOR. Cardiology. 143:1–10. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Shu S, Zhang Y, Li W, Wang L, Wu Y, Yuan Z
and Zhou J: The role of monocyte chemotactic protein-induced
protein 1 (MCPIP1) in angiotensin II-induced macrophage apoptosis
and vulnerable plaque formation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
515:378–385. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Zhang Y, Tao GJ, Hu L, Qu J, Han Y, Zhang
G, Qian Y, Jiang CY and Liu WT: Lidocaine alleviates morphine
tolerance via AMPK-SOCS3-dependent neuroinflammation suppression in
the spinal cord. J Neuroinflammation. 14:2112017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|