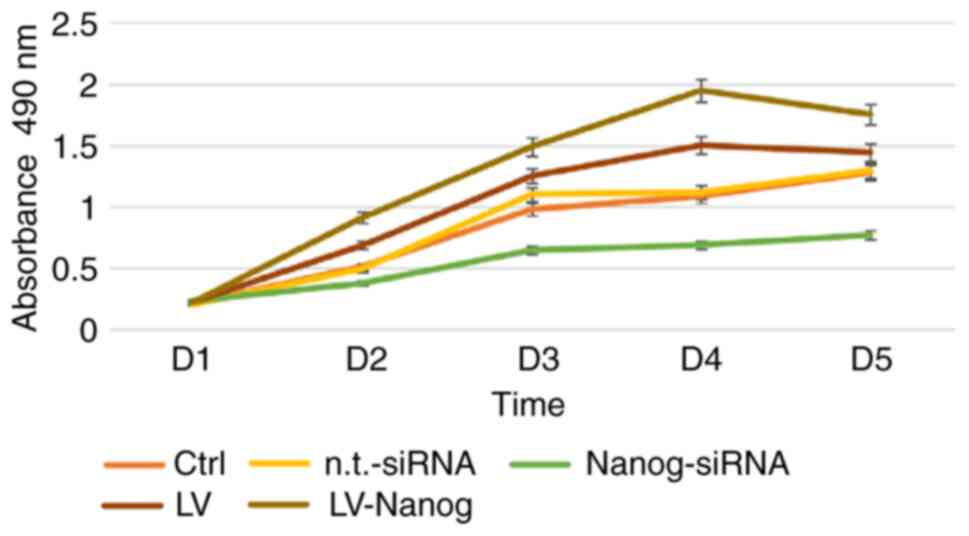
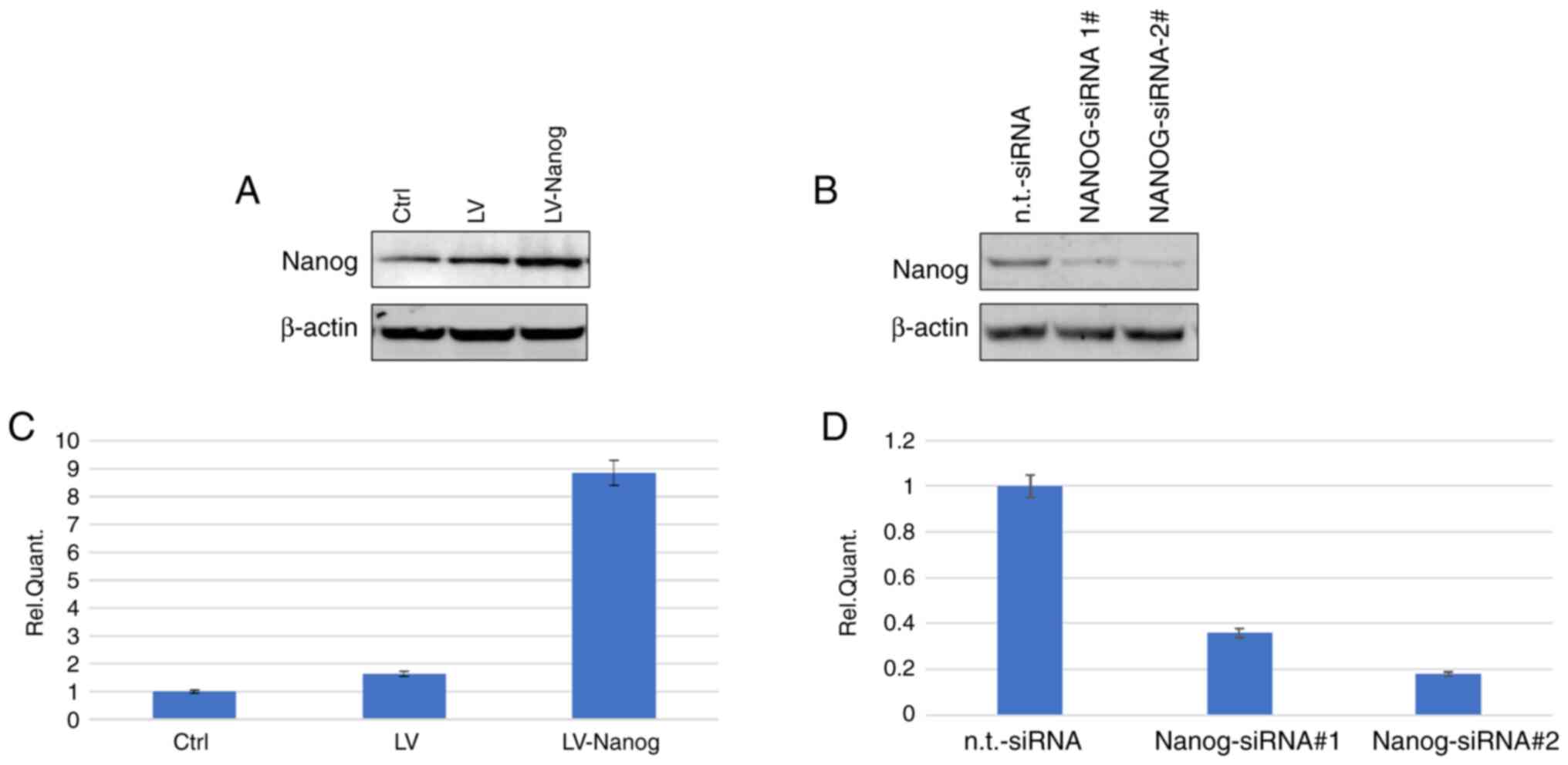
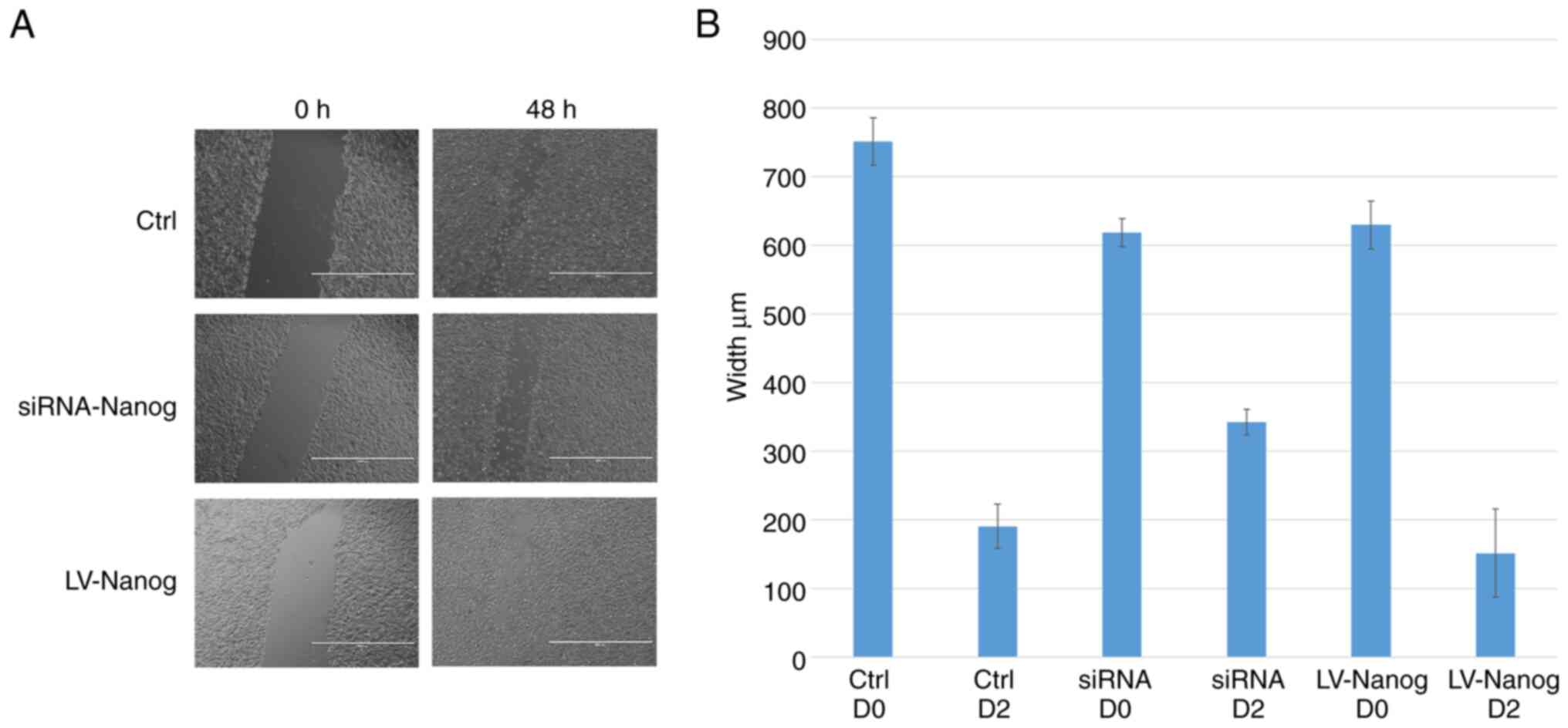
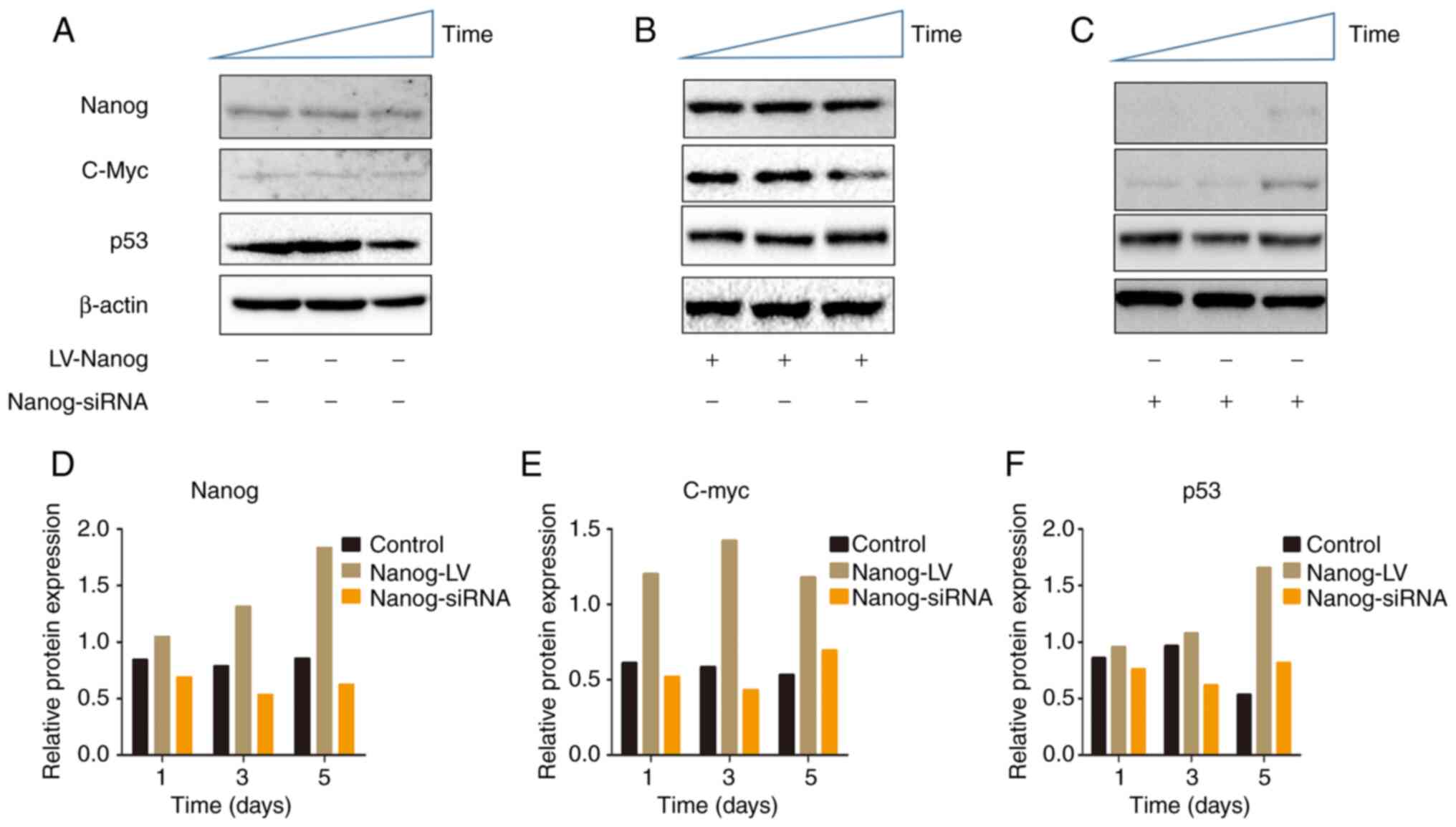
|
1
|
Wei X, Yang X, Han ZP, Qu FF, Shao L and
Shi YF: Mesenchymal stem cells: A new trend for cell therapy. Acta
Pharmacol Sin. 34:747–754. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Jeschke MG, Rehou S, McCann MR and
Shahrokhi S: Allogeneic mesenchymal stem cells for treatment of
severe burn injury. Stem Cell Res Ther. 10:3372019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Kosaric N, Kiwanuka H and Gurtner GC: Stem
cell therapies for wound healing. Expert Opin Biol Ther.
19:575–585. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Yang R, Liu F, Wang J, Chen X, Xie J and
Xiong K: Epidermal stem cells in wound healing and their clinical
applications. Stem Cell Res Ther. 10:2292019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Morasso MI and Tomic-Canic M: Epidermal
stem cells: The cradle of epidermal determination, differentiation
and wound healing. Biol Cell. 97:173–183. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Li Y, Zhang J, Yue J, Gou X and Wu X:
Epidermal stem cells in skin wound healing. Adv Wound Care (New
Rochelle). 6:297–307. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Brockmann I, Ehrenpfordt J, Sturmheit T,
Brandenburger M, Kruse C, Zille M, Rose D and Boltze J:
Skin-derived stem cells for wound treatment using cultured
epidermal autografts: Clinical applications and challenges. Stem
Cells Int. 2018:46236152018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Teng M, Huang Y and Zhang H: Application
of stems cells in wound healing-an update. Wound Repair Regen.
22:151–160. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Dash BC, Xu Z, Lin L, Koo A, Ndon S,
Berthiaume F, Dardik A and Hsia H: Stem cells and engineered
scaffolds for regenerative wound healing. Bioengineering (Basel).
5:232018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Silva J, Chambers I, Pollard S and Smith
A: Nanog promotes transfer of pluripotency after cell fusion.
Nature. 441:997–1001. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Hayashi Y, Caboni L, Das D, Yumoto F,
Clayton T, Deller MC, Nguyen P, Farr CL, Chiu HJ, Miller MD, et al:
Structure-based discovery of NANOG variant with enhanced properties
to promote self-renewal and reprogramming of pluripotent stem
cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 112:4666–4671. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Mitsui K, Tokuzawa Y, Itoh H, Segawa K,
Murakami M, Takahashi K, Maruyama M, Maeda M and Yamanaka S: The
homeoprotein Nanog is required for maintenance of pluripotency in
mouse epiblast and ES cells. Cell. 113:631–642. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Pashaiasl M, Khodadadi K, Kayvanjoo AH,
Pashaei-Asl R, Ebrahimie E and Ebrahimi M: Unravelling evolution of
Nanog, the key transcription factor involved in self-renewal of
undifferentiated embryonic stem cells, by pattern recognition in
nucleotide and tandem repeats characteristics. Gene. 578:194–204.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Yin D, Tian L, Ye Y, Li K, Wang J, Cheng
P, Chen A, Guo F and Huang H: Nanog and β-catenin: A new
convergence point in EpSC proliferation and differentiation. Int J
Mol Med. 29:587–592. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Cheng P, Sun X, Yin D, Xu F, Yang K, Qin
L, Dong Y, Guo F, Chen A, Zhang W and Huang H: Nanog down-regulates
the Wnt signaling pathway via β-catenin phosphorylation during
epidermal stem cell proliferation and differentiation. Cell Biosci.
5:52015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
National Research Council, . Guide for the
care and use of laboratory animals. 8th edition. The National
Academies Press; Washington, DC: pp. 2462011
|
|
17
|
Liu Y, Zhou H and Gao F: Isolation and
identification of stem cells from adult cashmere goat skin. Int J
Dermatol. 47:551–556. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Jensen KB, Driskell RR and Watt FM:
Assaying proliferation and differentiation capacity of stem cells
using disaggregated adult mouse epidermis. Nat Protoc. 5:898–911.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Wong D, Makowska IJ and Weary DM: Rat
aversion to isoflurane versus carbon dioxide. Biol Lett.
9:201210002012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Hickman DL and Johnson SW: Evaluation of
the aesthetics of physical methods of euthanasia of anesthetized
rats. J Am Assoc Lab Anim Sci. 50:695–701. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Dang CV: MYC on the path to cancer. Cell.
149:22–35. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Gabay M, Li Y and Felsher DW: MYC
activation is a hallmark of cancer initiation and maintenance. Cold
Spring Harb Perspect Med. 4:a0142412014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Li L, Gu W, Du J, Reid B, Deng X, Liu Z,
Zong Z, Wang H, Yao B, Yang C, et al: Electric fields guide
migration of epidermal stem cells and promote skin wound healing.
Wound Repair Regen. 20:840–851. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Yang R, Wang J, Chen X, Shi Y and Xie J:
Epidermal stem cells in wound healing and regeneration. Stem Cells
Int. 2020:91483102020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Finley LWS, Vardhana SA, Carey BW,
Alonso-Curbelo D, Koche R, Chen Y, Wen D, King B, Radler MR, Rafii
S, et al: Pluripotency transcription factors and Tet1/2 maintain
Brd4-independent stem cell identity. Nat Cell Biol. 20:565–574.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Pan G and Thomson JA: Nanog and
transcriptional networks in embryonic stem cell pluripotency. Cell
Res. 17:42–49. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Bijonowski BM, Yuan X, Jeske R, Li Y and
Grant SC: Cyclical aggregation extends in vitro expansion potential
of human mesenchymal stem cells. Sci Rep. 10:204482020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Kim J, Chu J, Shen X, Wang J and Orkin SH:
An extended transcriptional network for pluripotency of embryonic
stem cells. Cell. 132:1049–1061. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Cartwright P, McLean C, Sheppard A, Rivett
D, Jones K and Dalton S: LIF/STAT3 controls ES cell self-renewal
and pluripotency by a Myc-dependent mechanism. Development.
132:885–896. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Wernig M, Meissner A, Cassady JP and
Jaenisch R: c-Myc is dispensable for direct reprogramming of mouse
fibroblasts. Cell Stem Cell. 2:10–12. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Fagnocchi L, Cherubini A, Hatsuda H,
Fasciani A, Mazzoleni S, Poli V, Berno V, Rossi RL, Reinbold R,
Endele M, et al: A Myc-driven self-reinforcing regulatory network
maintains mouse embryonic stem cell identity. Nat Commun.
7:119032016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Carroll PA, Freie BW, Mathsyaraja H and
Eisenman RN: The MYC transcription factor network: Balancing
metabolism, proliferation and oncogenesis. Front Med. 12:412–425.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Maoz M, Devir M, Inbar M, Inbar-Daniel Z,
Sherill-Rofe D, Bloch I, Meir K, Edelman D, Azzam S, Nechushtan H,
et al: Clinical implications of sub-grouping HER2 positive tumors
by amplicon structure and co-amplified genes. Sci Rep. 9:187952019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Spencer CA and Groudine M: Control of
c-myc regulation in normal and neoplastic cells. Adv Cancer Res.
56:1–48. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Eilers M, Schirm S and Bishop JM: The MYC
protein activates transcription of the alpha-prothymosin gene. EMBO
J. 10:133–141. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Yoon K, Lim YS, Yu SB, Kim DS, Ryu SJ, Kim
KH, Jang TH and Kim SH: The expression of survivin and its related
genes in adipocyte-derived stem cell by demethylation. Korean J
Anesthesiol. 58:383–390. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Levens D: You don't muck with MYC. Genes
Cancer. 1:547–554. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Farrell AS and Sears RC: MYC degradation.
Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 4:a0143652014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Swaidan NT, Salloum-Asfar S, Palangi F,
Errafii K, Soliman NH, Aboughalia AT, Wali AHS, Abdulla SA and
Emara MM: Identification of potential transcription factors that
enhance human iPSC generation. Sci Rep. 10:219502020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Pitolli C, Wang Y, Candi E, Shi Y, Melino
G and Amelio I: p53-mediated tumor suppression: DNA-damage response
and alternative mechanisms. Cancers (Basel). 11:19832019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Parfenyev S, Singh A, Fedorova O, Daks A,
Kulshreshtha R and Barlev NA: Interplay between p53 and non-coding
RNAs in the regulation of EMT in breast cancer. Cell Death Dis.
12:172021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Yang P, Jiang Y, Pan Y, Ding X, Rhea P,
Ding J, Hawke DH, Felsher D, Narla G, Lu Z and Lee RT: Mistletoe
extract Fraxini inhibits the proliferation of liver cancer by
down-regulating c-Myc expression. Sci Rep. 9:64282019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Nakagawa R, Toboso-Navasa A, Schips M,
Young G, Bhaw-Rosun L, Llorian-Sopena M, Chakravarty P, Sesay AK,
Kassiotis G, Meyer-Hermann M and Calado DP: Permissive selection
followed by affinity-based proliferation of GC light zone B cells
dictates cell fate and ensures clonal breadth. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 118:e20164251182021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Kin K, Chen X, Gonzalez-Garay M and
Fakhouri WD: The effect of non-coding DNA variations on P53 and
cMYC competitive inhibition at cis-overlapping motifs. Hum Mol
Genet. 25:1517–1527. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Brandner S: Nanog, Gli, and p53: A new
network of stemness in development and cancer. EMBO J.
29:2475–2476. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Nourian Dehkordi A, Mirahmadi Babaheydari
F, Chehelgerdi M and Raeisi Dehkordi S: Skin tissue engineering:
Wound healing based on stem-cell-based therapeutic strategies. Stem
Cell Res Ther. 10:1112019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Pastar I, Stojadinovic O, Yin NC, Ramirez
H, Nusbaum AG, Sawaya A, Patel SB, Khalid L, Isseroff RR and
Tomic-Canic M: Epithelialization in wound healing: A comprehensive
review. Adv Wound Care (New Rochelle). 3:445–464. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|