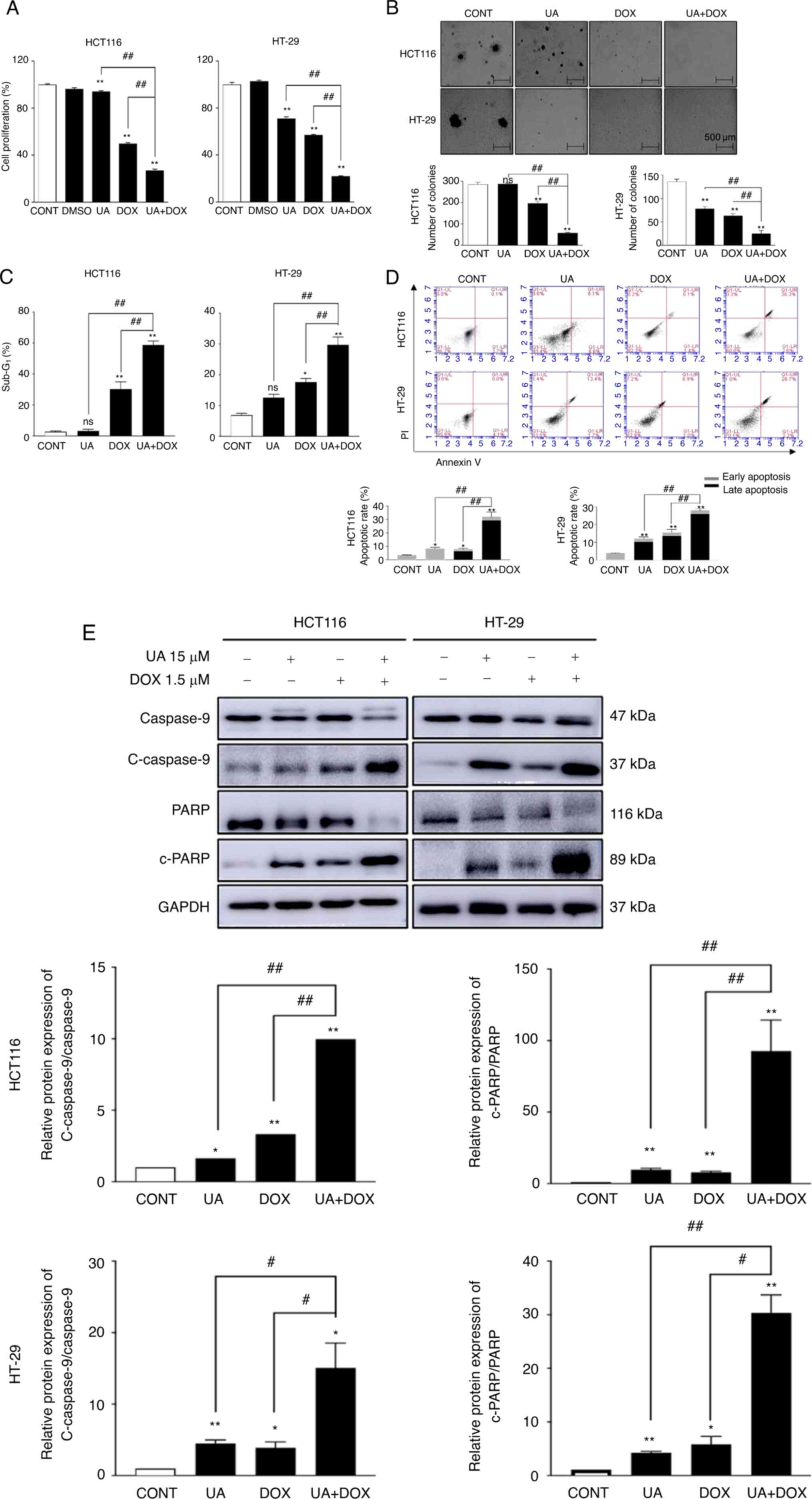
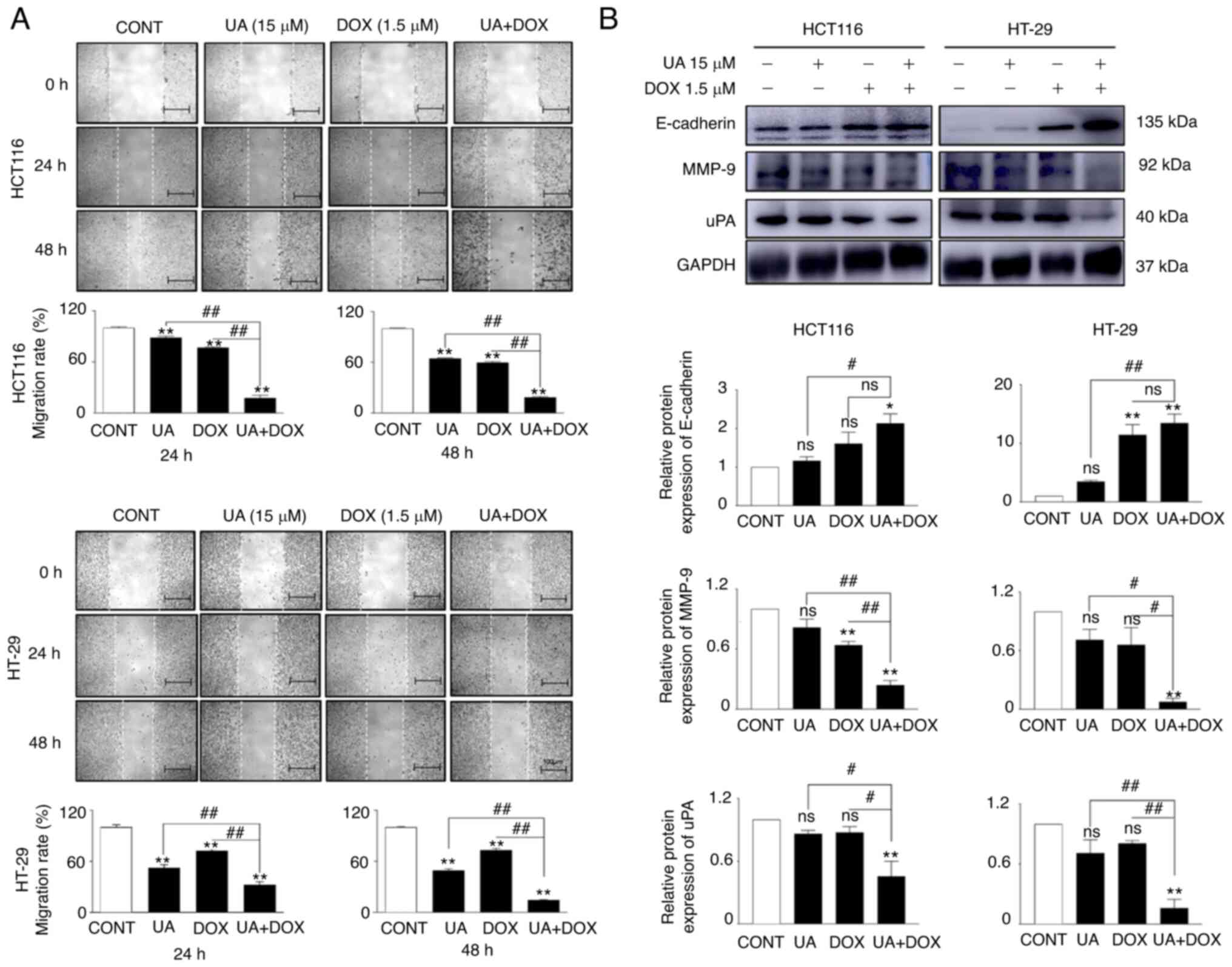
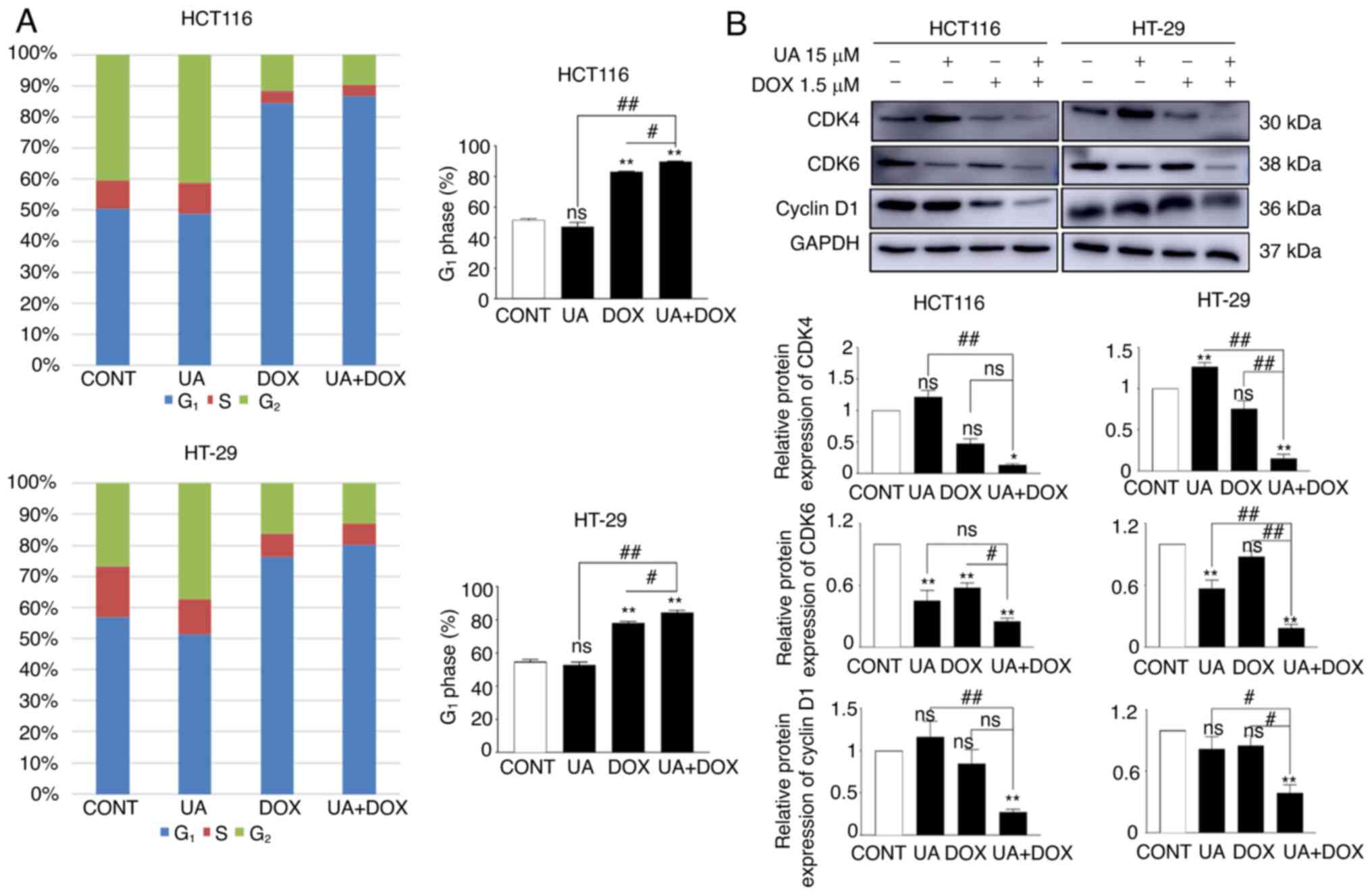
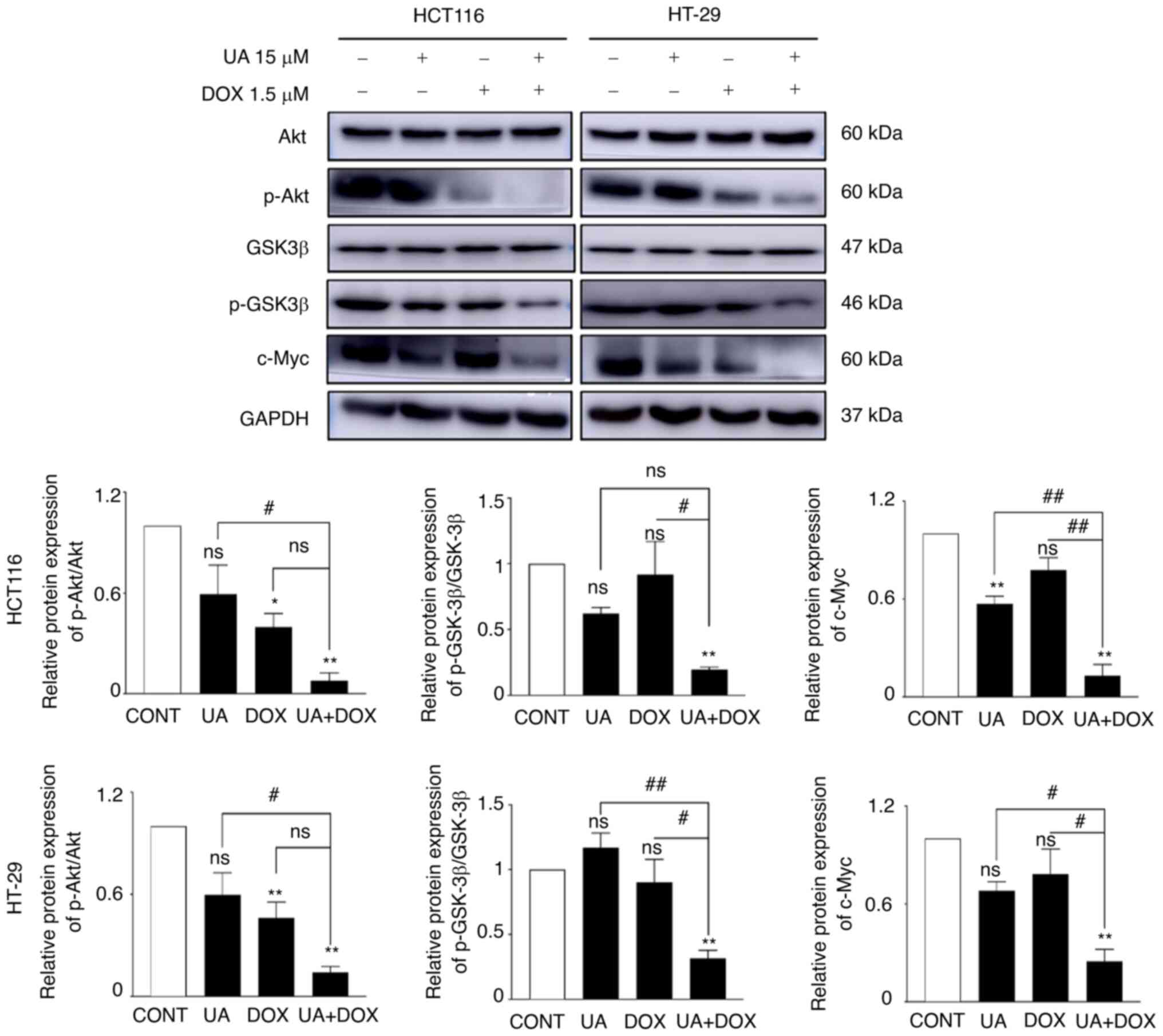
|
1
|
Arnold M, Sierra MS, Laversanne M,
Soerjomataram I, Jemal A and Bray F: Global patterns and trends in
colorectal cancer incidence and mortality. Gut. 66:683–691. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Shin DW, Chang D, Jung JH, Han K, Kim SY,
Choi KS, Lee WC and Park JH and Park JH: Disparities in the
participation rate of colorectal cancer screening by fecal occult
blood test among people with disabilities: A national database
study in South Korea. Cancer Res Treat. 52:60–73. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Yang SY, Cho MS and Kim NK: Difference
between right-sided and left-sided colorectal cancers: From
embryology to molecular subtype. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther.
18:351–358. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
McQuade RM, Stojanovska V, Bornstein JC
and Nurgali K: Colorectal cancer chemotherapy: The evolution of
treatment and new approaches. Curr Med Chem. 24:1537–1557. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Cargnin ST and Gnoatto SB: Ursolic acid
from apple pomace and traditional plants: A valuable triterpenoid
with functional properties. Food Chem. 220:477–489. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Xu C, Liao Y, Fang C, Tsunoda M, Zhang Y,
Song Y and Deng S: Simultaneous analysis of ursolic acid and
oleanolic acid in guava leaves using QuEChERS-based extraction
followed by high-performance liquid chromatography. J Anal Methods
Chem. 2017:29845622017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Zheng JL, Wang SS, Shen KP, Huang XW, Li
M, Chen L, Peng X, An HM and Hu B: Ursolic acid potentiated
oxaliplatin to induce apoptosis in colorectal cancer RKO cells.
Pharmazie. 75:246–249. 2020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Wang X, Wang T, Yi F, Duan C, Wang Q, He
N, Zhu L, Li Q and Deng W: Ursolic acid inhibits tumor growth via
epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in colorectal cancer cells.
Biol Pharm Bull. 42:685–691. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Cai Q, Lin J, Zhang L, Lin J, Wang L, Chen
D and Peng J: Comparative proteomics-network analysis of proteins
responsible for ursolic acid-induced cytotoxicity in colorectal
cancer cells. Tumour Biol. 39:10104283176950152017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Wang C, Shu L, Zhang C, Li W, Wu R, Guo Y,
Yang Y and Kong AN: Histone methyltransferase Setd7 regulates Nrf2
signaling pathway by phenethyl isothiocyanate and ursolic acid in
human prostate cancer cells. Mol Nutr Food Res. 62:e17008402018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Yang K, Chen Y, Zhou J, Ma L, Shan Y,
Cheng X, Wang Y, Zhang Z, Ji X, Chen L, et al: Ursolic acid
promotes apoptosis and mediates transcriptional suppression of
CT45A2 gene expression in non-small-cell lung carcinoma harbouring
EGFR T790M mutations. Br J Pharmacol. 176:4609–4624. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Mendes VIS, Bartholomeusz GA, Ayres M,
Gandhi V and Salvador JAR: Synthesis and cytotoxic activity of
novel A-ring cleaved ursolic acid derivatives in human non-small
cell lung cancer cells. Eur J Med Chem. 123:317–331. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Chan EWC, Soon CY, Tan JBL, Wong SK and
Hui YW: Ursolic acid: An overview on its cytotoxic activities
against breast and colorectal cancer cells. J Integr Med.
17:155–160. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Kim K, Shin EA, Jung JH, Park JE, Kim DS,
Shim BS and Kim SH: Ursolic acid induces apoptosis in colorectal
cancer cells partially via upregulation of MicroRNA-4500 and
inhibition of JAK2/STAT3 phosphorylation. Int J Mol Sci.
20:1142018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Prasad S, Yadav VR, Sung B, Reuter S,
Kannappan R, Deorukhkar A, Diagaradjane P, Wei C,
Baladandayuthapani V, Krishnan S, et al: Ursolic acid inhibits
growth and metastasis of human colorectal cancer in an orthotopic
nude mouse model by targeting multiple cell signaling pathways:
Chemosensitization with capecitabine. Clin Cancer Res.
18:4942–4953. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Liu P, Du R and Yu X: Ursolic acid
exhibits potent anticancer effects in human metastatic melanoma
cancer cells (SK-MEL-24) via apoptosis induction, inhibition of
cell migration and invasion, cell cycle arrest, and inhibition of
mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK)/ERK signaling pathway. Med
Sci Monit. 25:1283–1290. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Liu T, Ma H, Shi W, Duan J, Wang Y, Zhang
C, Li C, Lin J, Li S, Lv J and Lin L: Inhibition of STAT3 signaling
pathway by ursolic acid suppresses growth of hepatocellular
carcinoma. Int J Oncol. 51:555–562. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Zhang L, Cai QY, Liu J, Peng J, Chen YQ,
Sferra TJ and Lin JM: Ursolic acid suppresses the invasive
potential of colorectal cancer cells by regulating the
TGF-β1/ZEB1/miR-200c signaling pathway. Oncol Lett. 18:3274–3282.
2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Cheng J, Liu Y, Liu Y, Liu D, Liu Y, Guo
Y, Wu Z, Li H and Wang H: Ursolic acid alleviates lipid
accumulation by activating the AMPK signaling pathway in vivo and
in vitro. J Food Sci. 85:3998–4008. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Kim GH, Kan SY, Kang H, Lee S, Ko HM, Kim
JH and Lim JH: Ursolic acid suppresses cholesterol biosynthesis and
exerts anti-cancer effects in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Int J
Mol Sci. 20:47672019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Lin CW, Chin HK, Lee SL, Chiu CF, Chung
JG, Lin ZY, Wu CY, Liu YC, Hsiao YT, Feng CH, et al: Ursolic acid
induces apoptosis and autophagy in oral cancer cells. Environ
Toxicol. 34:983–991. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Lin JH, Chen SY, Lu CC, Lin JA and Yen GC:
Ursolic acid promotes apoptosis, autophagy, and chemosensitivity in
gemcitabine-resistant human pancreatic cancer cells. Phytother Res.
34:2053–2066. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Lin W and Ye H: Anticancer activity of
ursolic acid on human ovarian cancer cells via ROS and MMP mediated
apoptosis, cell cycle arrest and downregulation of PI3K/AKT
pathway. J BUON. 25:750–756. 2020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Li W, Zhang H, Nie M, Tian Y, Chen X, Chen
C, Chen H and Liu R: Ursolic acid derivative FZU-03,010 inhibits
STAT3 and induces cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in renal and
breast cancer cells. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai).
49:367–373. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Ruan JS, Zhou H, Yang L, Wang L, Jiang ZS,
Sun H and Wang SM: Ursolic acid attenuates TGF-β1-induced
epithelial-mesenchymal transition in NSCLC by targeting integrin
αVβ5/MMPs signaling. Oncol Res. 27:593–600. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Sohn EJ, Won G, Lee J, Yoon SW, Lee I, Kim
HJ and Kim SH: Blockage of epithelial to mesenchymal transition and
upregulation of let 7b are critically involved in ursolic acid
induced apoptosis in malignant mesothelioma cell. Int J Biol Sci.
12:1279–1288. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Lee NR, Meng RY, Rah SY, Jin H, Ray N, Kim
SH, Park BH and Kim SM: Reactive oxygen species-mediated autophagy
by ursolic acid inhibits growth and metastasis of esophageal cancer
cells. Int J Mol Sci. 21:94092020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Park HJ, Jo DS, Choi DS, Bae JE, Park NY,
Kim JB, Chang JH, Shin JJ and Cho DH: Ursolic acid inhibits
pigmentation by increasing melanosomal autophagy in B16F1 cells.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 531:209–214. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Arcamone F, Cassinelli G, Fantini G, Grein
A, Orezzi P, Pol C and Spalla C: Adriamycin, 14-hydroxydaunomycin,
a new antitumor antibiotic from S. peucetius var. caesius.
Reprinted from biotechnology and bioengineering, Vol. XI, Issue 6,
Pages 1101–1110 (1969). Biotechnol Bioeng. 67:704–713. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Cortés-Funes H and Coronado C: Role of
anthracyclines in the era of targeted therapy. Cardiovasc Toxicol.
7:56–60. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Weiss RB: The anthracyclines: Will we ever
find a better doxorubicin? Semin Oncol. 19:670–686. 1992.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Sarmento-Ribeiro AB, Scorilas A, Goncalves
AC, Efferth T and Trougakos IP: The emergence of drug resistance to
targeted cancer therapies: Clinical evidence. Drug Resist Updat.
47:1006462019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Rui M, Xin Y, Li R, Ge Y, Feng C and Xu X:
Targeted biomimetic nanoparticles for synergistic combination
chemotherapy of paclitaxel and doxorubicin. Mol Pharm. 14:107–123.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Fan YP, Liao JZ, Lu YQ, Tian DA, Ye F,
Zhao PX, Xiang GY, Tang WX and He XX: MiR-375 and doxorubicin
co-delivered by liposomes for combination therapy of hepatocellular
carcinoma. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 7:181–189. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Minotti G, Menna P, Salvatorelli E, Cairo
G and Gianni L: Anthracyclines: Molecular advances and
pharmacologic developments in antitumor activity and
cardiotoxicity. Pharmacol Rev. 56:185–229. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Guo NF, Cao YJ, Chen X, Zhang Y, Fan YP,
Liu J and Chen XL: Lixisenatide protects doxorubicin-induced renal
fibrosis by activating wNF-κB/TNF-α and TGF-β/Smad pathways. Eur
Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 23:4017–4026. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Saleh D, Abdelbaset M, Hassan A, Sharaf O,
Mahmoud S and Hegazy R: Omega-3 fatty acids ameliorate
doxorubicin-induced cardiorenal toxicity: In-vivo regulation of
oxidative stress, apoptosis and renal Nox4, and in-vitro
preservation of the cytotoxic efficacy. PLoS One. 15:e02421752020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Prasanna PL, Renu K and Valsala
Gopalakrishnan A: New molecular and biochemical insights of
doxorubicin-induced hepatotoxicity. Life Sci. 250:1175992020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Zhou X, Xu P, Dang R, Guo Y, Li G, Qiao Y,
Xie R, Liu Y and Jiang P: The involvement of autophagic flux in the
development and recovery of doxorubicin-induced neurotoxicity. Free
Radic Biol Med. 129:440–445. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Yu FX, Zhao B and Guan KL: Hippo pathway
in organ size control, tissue homeostasis, and cancer. Cell.
163:811–828. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Kim CL, Choi SH and Mo JS: Role of the
Hippo pathway in fibrosis and cancer. Cells. 8:4682019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Dong J, Feldmann G, Huang J, Wu S, Zhang
N, Comerford SA, Gayyed MF, Anders RA, Maitra A and Pan D:
Elucidation of a universal size-control mechanism in
Drosophila and mammals. Cell. 130:1120–1233. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Avruch J, Zhou D and Bardeesy N: YAP
oncogene overexpression supercharges colon cancer proliferation.
Cell Cycle. 11:1090–1096. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Liu XF, Han Q, Rong XZ, Yang M, Han YC, Yu
JH and Lin XY: ANKHD1 promotes proliferation and invasion of
non-small-cell lung cancer cells via regulating YAP oncoprotein
expression and inactivating the Hippo pathway. Int J Oncol.
56:1175–1185. 2020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Niu K, Liu Y, Zhou Z, Wu X, Wang H and Yan
J: Antitumor effects of paeoniflorin on Hippo signaling pathway in
gastric cancer cells. J Oncol. 2021:47249382021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Hou L, Chen L and Fang L: Scutellarin
inhibits proliferation, invasion, and tumorigenicity in human
breast cancer cells by regulating HIPPO-YAP signaling pathway. Med
Sci Monit. 23:5130–5138. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Driskill JH and Pan D: The Hippo pathway
in liver homeostasis and pathophysiology. Annu Rev Pathol.
16:299–322. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Masliantsev K, Karayan-Tapon L and Guichet
PO: Hippo signaling pathway in gliomas. Cells. 10:1842021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Ansari D, Ohlsson H, Althini C, Bauden M,
Zhou Q, Hu D and Andersson R: The Hippo signaling pathway in
pancreatic cancer. Anticancer Res. 39:3317–3321. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Llado V, Nakanishi Y, Duran A,
Reina-Campos M, Shelton PM, Linares JF, Yajima T, Campos A,
Aza-Blanc P, Leitges M, et al: Repression of intestinal stem cell
function and tumorigenesis through direct phosphorylation of
β-catenin and Yap by PKCζ. Cell Rep. 10:740–754. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Chen L, Qin F, Deng X, Avruch J and Zhou
D: Hippo pathway in intestinal homeostasis and tumorigenesis.
Protein Cell. 3:305–310. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Gu Y, Zhang L and Yu FX: Functions and
regulations of the Hippo signaling pathway in intestinal
homeostasis, regeneration and tumorigenesis. Yi Chuan. 39:588–596.
2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Zhou D, Zhang Y, Wu H, Barry E, Yin Y,
Lawrence E, Dawson D, Willis JE, Markowitz SD, Camargo FD and
Avruch J: Mst1 and Mst2 protein kinases restrain intestinal stem
cell proliferation and colonic tumorigenesis by inhibition of
Yes-associated protein (Yap) overabundance. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
108:E1312–E1320. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Xiao Y, Liu Q, Peng N, Li Y, Qiu D, Yang
T, Kang R, Usmani A, Amadasu E, Borlongan CV and Yu G: Lovastatin
inhibits RhoA to suppress canonical Wnt/β-catenin signaling and
alternative Wnt-YAP/TAZ signaling in colon cancer. Cell Transplant.
31:96368972210757492022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Touil Y, Igoudjil W, Corvaisier M, Dessein
AF, Vandomme J, Monté D, Stechly L, Skrypek N, Langlois C, Grard G,
et al: Colon cancer cells escape 5FU chemotherapy-induced cell
death by entering stemness and quiescence associated with the
c-Yes/YAP axis. Clin Cancer Res. 20:837–846. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Shamekhi S, Abdolalizadeh J, Ostadrahimi
A, Mohammadi SA, Barzegari A, Lotfi H, Bonabi E and Zarghami N:
Apoptotic effect of saccharomyces cerevisiae on human colon cancer
SW480 cells by regulation of Akt/NF-ĸB signaling pathway.
Probiotics Antimicrob Proteins. 12:311–319. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Goel S, Huang J and Klampfer L: K-Ras,
intestinal homeostasis and colon cancer. Curr Clin Pharmacol.
10:73–81. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Tumaneng K, Schlegelmilch K, Russell RC,
Yimlamai D, Basnet H, Mahadevan N, Fitamant J, Bardeesy N, Camargo
FD and Guan KL: YAP mediates crosstalk between the Hippo and
PI(3)K-TOR pathways by suppressing PTEN via miR-29. Nat Cell Biol.
14:1322–1329. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Yu FX, Zhao B, Panupinthu N, Jewell JL,
Lian I, Wang LH, Zhao J, Yuan H, Tumaneng K, Li H, et al:
Regulation of the Hippo-YAP pathway by G-protein-coupled receptor
signaling. Cell. 150:780–791. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Kawai K, Viars C, Arden K, Tarin D,
Urquidi V and Goodison S: Comprehensive karyotyping of the HT-29
colon adenocarcinoma cell line. Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 34:1–8.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Grada A, Otero-Vinas M, Prieto-Castrillo
F, Obagi Z and Falanga V: Research techniques made simple: Analysis
of collective cell migration using the wound healing assay. J
Invest Dermatol. 137:e11–e16. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Vang Mouritzen M and Jenssen H: Optimized
scratch assay for in vitro testing of cell migration with an
automated optical camera. J Vis Exp. 576912018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Martinotti S and Ranzato E: Scratch wound
healing assay. Methods Mol Biol. 2109:225–229. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Meng RY, Jin H, Nguyen TV, Chai OH, Park
BH and Kim SM: Ursolic acid accelerates paclitaxel-induced cell
death in esophageal cancer cells by suppressing Akt/FOXM1 signaling
cascade. Int J Mol Sci. 22:114862021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Stephenson W: Deficiencies in the national
institute of health's guidelines for the care and protection of
laboratory animals. J Med Philos. 18:375–88. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Kilkenny C, Browne WJ, Cuthill IC, Emerson
M and Altman DG: Improving bioscience research reporting: The
ARRIVE guidelines for reporting animal research. Osteoarthritis
Cartilage. 20:256–260. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Spangenberg EM and Keeling LJ: Assessing
the welfare of laboratory mice in their home environment using
animal-based measures-a benchmarking tool. Lab Anim. 50:30–38.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Clayden EC: Practical section cutting and
staining. 5th edition. Edinburgh: (15 Teviot Place, Edinburgh 1).
Churchill Livingstone; 7. pp. pp2701971
|
|
69
|
Kim DH, Kang DY, Sp N, Jo ES, Rugamba A,
Jang KJ and Yang YM: Methylsulfonylmethane induces cell cycle
arrest and apoptosis, and suppresses the stemness potential of
HT-29 cells. Anticancer Res. 40:5191–5200. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Ombrato L and Malanchi I: The EMT
universe: Space between cancer cell dissemination and metastasis
initiation. Crit Rev Oncog. 19:349–361. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Wang C, Li Z, Lu Y, Du R, Katiyar S, Yang
J, Fu M, Leader JE, Quong A, Novikoff PM and Pestell RG: Cyclin D1
repression of nuclear respiratory factor 1 integrates nuclear DNA
synthesis and mitochondrial function. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
103:11567–11572. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Bishnupuri KS, Alvarado DM, Khouri AN,
Shabsovich M, Chen B, Dieckgraefe BK and Ciorba MA: IDO1 and
kynurenine pathway metabolites activate PI3K-Akt signaling in the
neoplastic colon epithelium to promote cancer cell proliferation
and inhibit apoptosis. Cancer Res. 79:1138–1150. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Ji J, Wang Z, Sun W, Li Z, Cai H, Zhao E
and Cui H: Effects of cynaroside on cell proliferation, apoptosis,
migration and invasion though the MET/AKT/mTOR axis in gastric
cancer. Int J Mol Sci. 22:121252021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Zhang P, Yuan X, Yu T, Huang H, Yang C,
Zhang L, Yang S, Luo X and Luo J: Lycorine inhibits cell
proliferation, migration and invasion, and primarily exerts in
vitro cytostatic effects in human colorectal cancer via
activating the ROS/p38 and AKT signaling pathways. Oncol Rep.
45:192021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Yang L, Liu Y, Wang M, Qian Y, Dong X, Gu
H, Wang H, Guo S and Hisamitsu T: Quercetin-induced apoptosis of
HT-29 colon cancer cells via inhibition of the Akt-CSN6-Myc
signaling axis. Mol Med Rep. 14:4559–4566. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Guo C, Zhang X and Pfeifer GP: The tumor
suppressor RASSF1A prevents dephosphorylation of the mammalian
STE20-like kinases MST1 and MST2. J Biol Chem. 286:6253–6261. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Kim M, Kim M, Lee MS, Kim CH and Lim DS:
The MST1/2-SAV1 complex of the Hippo pathway promotes ciliogenesis.
Nat Commun. 5:53702014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Shome D, von Woedtke T, Riedel K and Masur
K: The HIPPO transducer YAP and its targets CTGF and Cyr61 drive a
paracrine signalling in cold atmospheric plasma-mediated wound
healing. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2020:49102802020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Wang Y, Kuramitsu Y, Baron B, Kitagawa T,
Tokuda K, Akada J, Maehara SI, Maehara Y and Nakamura K: PI3K
inhibitor LY294002, as opposed to wortmannin, enhances AKT
phosphorylation in gemcitabine-resistant pancreatic cancer cells.
Int J Oncol. 50:606–612. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Lin J, Chen Y, Wei L, Hong Z, Sferra TJ
and Peng J: Ursolic acid inhibits colorectal cancer angiogenesis
through suppression of multiple signaling pathways. Int J Oncol.
43:1666–1674. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Zhang Y, Huang L, Shi H, Chen H, Tao J,
Shen R and Wang T: Ursolic acid enhances the therapeutic effects of
oxaliplatin in colorectal cancer by inhibition of drug resistance.
Cancer Sci. 109:94–102. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Zeng Q, Che Y, Zhang Y, Chen M, Guo Q and
Zhang W: Thymol isolated from thymus vulgaris L. inhibits
colorectal cancer cell growth and metastasis by suppressing the
Wnt/β-catenin pathway. Drug Des Devel Ther. 14:2535–2547. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Yao M, Ma X, Zhang X, Shi L, Liu T, Liang
X, Zhao H, Li X, Li L, Gao H, et al: Lectin-mediated pH-sensitive
doxorubicin prodrug for pre-targeted chemotherapy of colorectal
cancer with enhanced efficacy and reduced side effects.
Theranostics. 9:747–760. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
O'Bryan RM, Baker LH, Gottlieb JE, Rivkin
SE, Balcerzak SP, Grumet GN, Salmon SE, Moon TE and Hoogstraten B:
Dose response evaluation of adriamycin in human neoplasia. Cancer.
39:1940–1948. 1977. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Gabizon A, Shmeeda H and Barenholz Y:
Pharmacokinetics of pegylated liposomal doxorubicin: Review of
animal and human studies. Clin Pharmacokinet. 42:419–436. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Marina NM, Cochrane D, Harney E, Zomorodi
K, Blaney S, Winick N, Bernstein M and Link MP: Dose escalation and
pharmacokinetics of pegylated liposomal doxorubicin (Doxil) in
children with solid tumors: A pediatric oncology group study. Clin
Cancer Res. 8:413–418. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Nair AB and Jacob S: A simple practice
guide for dose conversion between animals and human. J Basic Clin
Pharm. 7:27–31. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2019. CA Cancer J Clin. 69:7–34. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Xie YH, Chen YX and Fang JY: Comprehensive
review of targeted therapy for colorectal cancer. Signal Transduct
Target Ther. 5:222020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Li J, Ma X, Chakravarti D, Shalapour S and
DePinho RA: Genetic and biological hallmarks of colorectal cancer.
Genes Dev. 35:787–820. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Tiwari A, Saraf S, Verma A, Panda PK and
Jain SK: Novel targeting approaches and signaling pathways of
colorectal cancer: An insight. World J Gastroenterol. 24:4428–4435.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Krishnamurthy N and Kurzrock R: Targeting
the Wnt/beta-catenin pathway in cancer: Update on effectors and
inhibitors. Cancer Treat Rev. 62:50–60. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Chen Z, Oh D, Dubey AK, Yao M, Yang B,
Groves JT and Sheetz M: EGFR family and Src family kinase
interactions: Mechanics matters? Curr Opin Cell Biol. 51:97–102.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Lopez A, Harada K, Vasilakopoulou M,
Shanbhag N and Ajani JA: Targeting angiogenesis in colorectal
carcinoma. Drugs. 79:63–74. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Ahmad R, Singh JK, Wunnava A, Al-Obeed O,
Abdulla M and Srivastava SK: Emerging trends in colorectal cancer:
Dysregulated signaling pathways (Review). Int J Mol Med. 47:142021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
96
|
Kassi E, Sourlingas TG, Spiliotaki M,
Papoutsi Z, Pratsinis H, Aligiannis N and Moutsatsou P: Ursolic
acid triggers apoptosis and Bcl-2 downregulation in MCF-7 breast
cancer cells. Cancer Invest. 27:723–733. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Yim EK, Lee KH, Namkoong SE, Um SJ and
Park JS: Proteomic analysis of ursolic acid-induced apoptosis in
cervical carcinoma cells. Cancer Lett. 235:209–220. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98
|
Argenziano M, Gigliotti CL, Clemente N,
Boggio E, Ferrara B, Trotta F, Pizzimenti S, Barrera G, Boldorini
R, Bessone F, et al: Improvement in the anti-tumor efficacy of
doxorubicin nanosponges in in vitro and in mice bearing breast
tumor models. Cancers (Basel). 12:1622020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
99
|
Brattain MG, Brattain DE, Fine WD, Khaled
FM, Marks ME, Kimball PM, Arcolano LA and Danbury BH: Initiation
and characterization of cultures of human colonic carcinoma with
different biological characteristics utilizing feeder layers of
confluent fibroblasts. Oncodev Biol Med. 2:355–366. 1981.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
100
|
Brattain MG, Fine WD, Khaled FM, Thompson
J and Brattain DE: Heterogeneity of malignant cells from a human
colonic carcinoma. Cancer Res. 41:1751–1756. 1981.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
101
|
Ahmed D, Eide PW, Eilertsen IA, Danielsen
SA, Eknaes M, Hektoen M, Lind GE and Lothe RA: Epigenetic and
genetic features of 24 colon cancer cell lines. Oncogenesis.
2:e712013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
102
|
Bazan V, Migliavacca M, Zanna I, Tubiolo
C, Grassi N, Latteri MA, La Farina M, Albanese I, Dardanoni G,
Salerno S, et al: Specific codon 13 K-ras mutations are predictive
of clinical outcome in colorectal cancer patients, whereas codon 12
K-ras mutations are associated with mucinous histotype. Ann Oncol.
13:1438–1446. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
103
|
Lupertz R, Watjen W, Kahl R and Chovolou
Y: Dose- and time-dependent effects of doxorubicin on cytotoxicity,
cell cycle and apoptotic cell death in human colon cancer cells.
Toxicology. 271:115–121. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
104
|
Nie W, Zan X, Yu T, Ran M, Hong Z, He Y,
Yang T, Ju Y and Gao X: Synergetic therapy of glioma mediated by a
dual delivery system loading α-mangostin and doxorubicin through
cell cycle arrest and apoptotic pathways. Cell Death Dis.
11:9282020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
105
|
Tilija Pun N, Jang WJ and Jeong CH: Role
of autophagy in regulation of cancer cell death/apoptosis during
anti-cancer therapy: Focus on autophagy flux blockade. Arch Pharm
Res. 43:475–488. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
106
|
Lin YJ, Liang WM, Chen CJ, Tsang H, Chiou
JS, Liu X, Cheng CF, Lin TH, Liao CC, Huang SM, et al: Network
analysis and mechanisms of action of Chinese herb-related natural
compounds in lung cancer cells. Phytomedicine. 58:1528932019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
107
|
Doğan Şiğva ZÖ, Balci Okcanoğlu T, Biray
Avci Ç, Yilmaz Süslüer S, Kayabaşi Ç, Turna B, Dodurga Y, Nazli O
and Gündüz C: Investigation of the synergistic effects of
paclitaxel and herbal substances and endemic plant extracts on cell
cycle and apoptosis signal pathways in prostate cancer cell lines.
Gene. 687:261–271. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
108
|
Aiello P, Sharghi M, Mansourkhani SM,
Ardekan AP, Jouybari L, Daraei N, Peiro K, Mohamadian S, Rezaei M,
Heidari M, et al: Medicinal plants in the prevention and treatment
of colon cancer. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2019:20756142019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
109
|
Phan T, Nguyen VH, A'Lincourt Salazar M,
Wong P, Diamond DJ, Yim JH and Melstrom LG: Inhibition of autophagy
amplifies baicalein-induced apoptosis in human colorectal cancer.
Mol Ther Oncolytics. 19:1–7. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
110
|
Mandal S, Gamit N, Varier L, Dharmarajan A
and Warrier S: Inhibition of breast cancer stem-like cells by a
triterpenoid, ursolic acid, via activation of Wnt antagonist, sFRP4
and suppression of miRNA-499a-5p. Life Sci. 265:1188542021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
111
|
Zheng JL, Wang SS, Shen KP, Chen L, Peng
X, Chen JF, An HM and Hu B: Ursolic acid induces apoptosis and
anoikis in colorectal carcinoma RKO cells. BMC Complement Med Ther.
21:522021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
112
|
Yang S, Zhang X, Qu H, Qu B, Yin X and
Zhao H: Cabozantinib induces PUMA-dependent apoptosis in colon
cancer cells via AKT/GSK-3β/NF-κB signaling pathway. Cancer Gene
Ther. 27:368–377. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
113
|
Qin J, Fu M, Wang J, Huang F, Liu H,
Huangfu M, Yu D, Liu H, Li X, Guan X and Chen X: PTEN/AKT/mTOR
signaling mediates anticancer effects of epigallocatechin-3-gallate
in ovarian cancer. Oncol Rep. 43:1885–1896. 2020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
114
|
Zhu ML, Zhang PM, Jiang M, Yu SW and Wang
L: Myricetin induces apoptosis and autophagy by inhibiting
PI3K/Akt/mTOR signalling in human colon cancer cells. BMC
Complement Med Ther. 20:2092020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
115
|
Li W, Li C, Ma L and Jin F: Resveratrol
inhibits viability and induces apoptosis in the small-cell lung
cancer H446 cell line via the PI3K/Akt/c-Myc pathway. Oncol Rep.
44:1821–1830. 2020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
116
|
Tian J, Zhang H, Mu L, Wang M, Li X, Zhang
X, Xie E, Ma M, Wu D and Du Y: The miR-218/GAB2 axis regulates
proliferation, invasion and EMT via the PI3K/AKT/GSK-3β pathway in
prostate cancer. Exp Cell Res. 394:1121282020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
117
|
Qi X, Sun L, Wan J, Xu R, He S and Zhu X:
Tensin4 promotes invasion and migration of gastric cancer cells via
regulating AKT/GSK-3β/snail signaling pathway. Pathol Res Pract.
216:1530012020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
118
|
Chang YX, Lin YF, Chen CL, Huang MS, Hsiao
M and Liang PH: Chaperonin-containing TCP-1 promotes cancer
chemoresistance and metastasis through the AKT-GSK3β-β-catenin and
XIAP-survivin pathways. Cancers (Basel). 12:38652020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
119
|
Ding L, Cao J, Lin W, Chen H, Xiong X, Ao
H, Yu M, Lin J and Cui Q: The roles of cyclin-dependent kinases in
cell-cycle progression and therapeutic strategies in human breast
cancer. Int J Mol Sci. 21:19602020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
120
|
Xu S, Zhang H, Liu T, Yang W, Lv W, He D,
Guo P and Li L: 6-Gingerol induces cell-cycle G1-phase arrest
through AKT-GSK 3β-cyclin D1 pathway in renal-cell carcinoma.
Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 85:379–390. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
121
|
Zhou C, Du J, Zhao L, Liu W, Zhao T, Liang
H, Fang P, Zhang K and Zeng H: GLI1 reduces drug sensitivity by
regulating cell cycle through PI3K/AKT/GSK3/CDK pathway in acute
myeloid leukemia. Cell Death Dis. 12:2312021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
122
|
Zhang S, Liu X, Bawa-Khalfe T, Lu LS, Lyu
YL, Liu LF and Yeh ET: Identification of the molecular basis of
doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity. Nat Med. 18:1639–1642. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
123
|
Desai VG, Lee T, Moland CL, Vijay V, Han
T, Lewis SM, Herman EH and Fuscoe JC: Candidate early predictive
plasma protein markers of doxorubicin-induced chronic
cardiotoxicity in B6C3F1 mice. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol.
363:164–173. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
124
|
Kuenzi BM and Ideker T: Author correction:
A census of pathway maps in cancer systems biology. Nat Rev Cancer.
21:2122021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
125
|
Kuenzi BM and Ideker T: A census of
pathway maps in cancer systems biology. Nat Rev Cancer. 20:233–246.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
126
|
Chang YC, Wu JW, Wang CW and Jang AC:
Hippo signaling-mediated mechanotransduction in cell movement and
cancer metastasis. Front Mol Biosci. 6:1572020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
127
|
Kennedy MB: Origin of PDZ (DHR, GLGF)
domains. Trends Biochem Sci. 20:3501995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
128
|
Zheng Y and Pan D: The Hippo signaling
pathway in development and disease. Dev Cell. 50:264–282. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
129
|
Furth N and Aylon Y: The LATS1 and LATS2
tumor suppressors: Beyond the Hippo pathway. Cell Death Differ.
24:1488–1501. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
130
|
Kim SH, Jin H, Meng RY, Kim DY, Liu YC,
Chai OH, Park BH and Kim SM: Activating Hippo pathway via Rassf1 by
ursolic acid suppresses the tumorigenesis of gastric cancer. Int J
Mol Sci. 20:47092019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
131
|
Jeong SH, Kim HB, Kim MC, Lee JM, Lee JH,
Kim JH, Kim JW, Park WY, Kim SY, Kim JB, et al: Hippo-mediated
suppression of IRS2/AKT signaling prevents hepatic steatosis and
liver cancer. J Clin Invest. 128:1010–1025. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
132
|
Zhang S, Chen Q, Liu Q, Li Y, Sun X, Hong
L, Ji S, Liu C, Geng J, Zhang W, et al: Hippo signaling suppresses
cell ploidy and tumorigenesis through Skp2. Cancer Cell.
31:669–684.e7. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
133
|
Ahmed AA, Abedalthagafi M, Anwar AE and
Bui MM: Akt and Hippo pathways in Ewing's sarcoma tumors and their
prognostic significance. J Cancer. 6:1005–1010. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
134
|
Berthold R, Isfort I, Erkut C, Heinst L,
Grunewald I, Wardelmann E, Kindler T, Åman P, Grünewald TGP,
Cidre-Aranaz F, et al: Fusion protein-driven IGF-IR/PI3K/AKT
signals deregulate Hippo pathway promoting oncogenic cooperation of
YAP1 and FUS-DDIT3 in myxoid liposarcoma. Oncogenesis. 11:202022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
135
|
Ma W, Han C, Zhang J, Song K, Chen W, Kwon
H and Wu T: The histone methyltransferase G9a promotes
cholangiocarcinogenesis through regulation of the Hippo pathway
kinase LATS2 and YAP signaling pathway. Hepatology. 72:1283–1297.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
136
|
Xu W, Yang Z, Xie C, Zhu Y, Shu X, Zhang
Z, Li N, Chai N, Zhang S, Wu K, et al: PTEN lipid phosphatase
inactivation links the hippo and PI3K/Akt pathways to induce
gastric tumorigenesis. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 37:1982018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
137
|
Jang SW, Yang SJ, Srinivasan S and Ye K:
Akt phosphorylates MstI and prevents its proteolytic activation,
blocking FOXO3 phosphorylation and nuclear translocation. J Biol
Chem. 282:30836–30844. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
138
|
Romano D, Matallanas D, Weitsman G,
Preisinger C, Ng T and Kolch W: Proapoptotic kinase MST2
coordinates signaling crosstalk between RASSF1A, Raf-1, and Akt.
Cancer Res. 70:1195–1203. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
139
|
Kim D, Shu S, Coppola MD, Kaneko S, Yuan
ZQ and Cheng JQ: Regulation of proapoptotic mammalian ste20-like
kinase MST2 by the IGF1-Akt pathway. PLoS One. 5:e96162010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
140
|
Kim SM, Ye S, Rah SY, Park BH, Wang H, Kim
JR, Kim SH, Jang KY and Lee KB: RhBMP-2 activates Hippo signaling
through RASSF1 in esophageal cancer cells. Sci Rep. 6:268212016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
141
|
Pankova D, Jiang Y, Chatzifrangkeskou M,
Vendrell I, Buzzelli J, Ryan A, Brown C and O'Neill E: RASSF1A
controls tissue stiffness and cancer stem-like cells in lung
adenocarcinoma. EMBO J. 38:e1005322019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
142
|
Gupta V, Agarwal P and Deshpande P: Impact
of RASSF1A gene methylation on clinico-pathological features of
tumor and non-tumor tissue of breast cancer. Ann Diagn Pathol.
52:1517222021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
143
|
Lee NH, Kim SJ and Hyun J: MicroRNAs
regulating Hippo-YAP signaling in liver cancer. Biomedicines.
9:3472021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
144
|
Agarwal S, Amin KS, Jagadeesh S, Baishay
G, Rao PG, Barua NC, Bhattacharya S and Banerjee PP: Mahanine
restores RASSF1A expression by down-regulating DNMT1 and DNMT3B in
prostate cancer cells. Mol Cancer. 12:992013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
145
|
Blanchard TG, Lapidus R, Banerjee V,
Bafford AC, Czinn SJ, Ahmed H and Banerjee A: Upregulation of
RASSF1A in colon cancer by suppression of angiogenesis signaling
and Akt activation. Cell Physiol Biochem. 48:1259–1273. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|