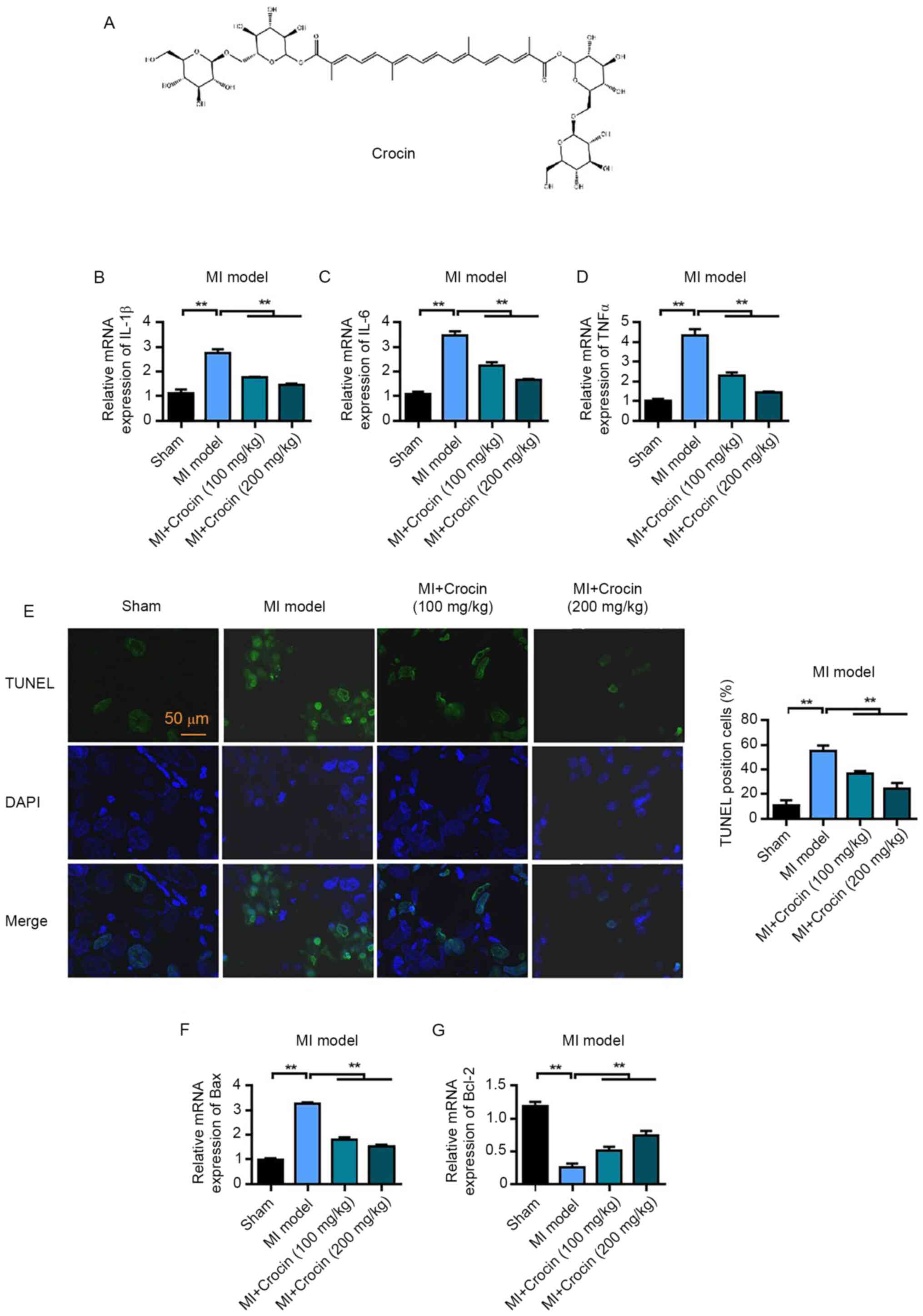
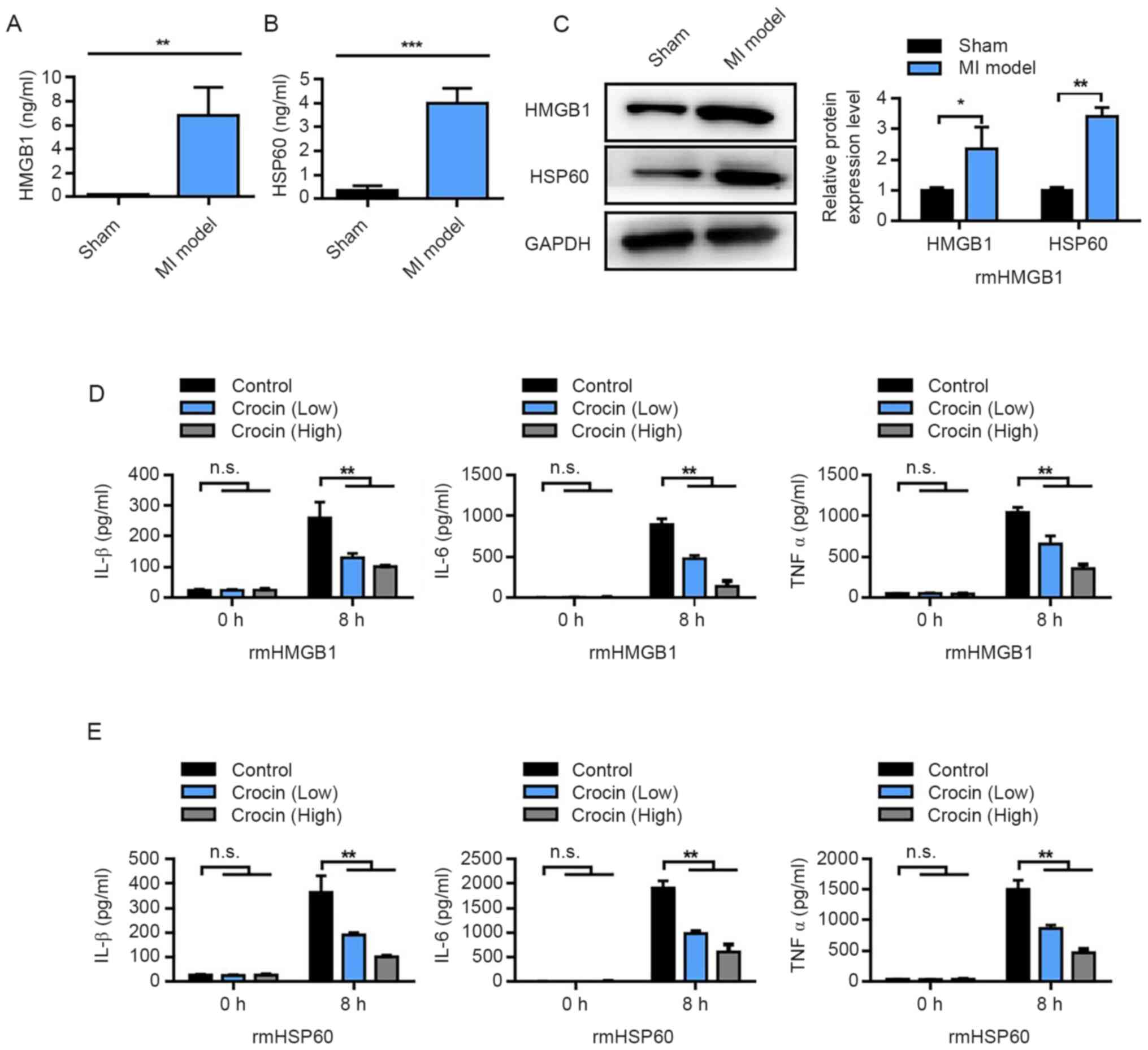
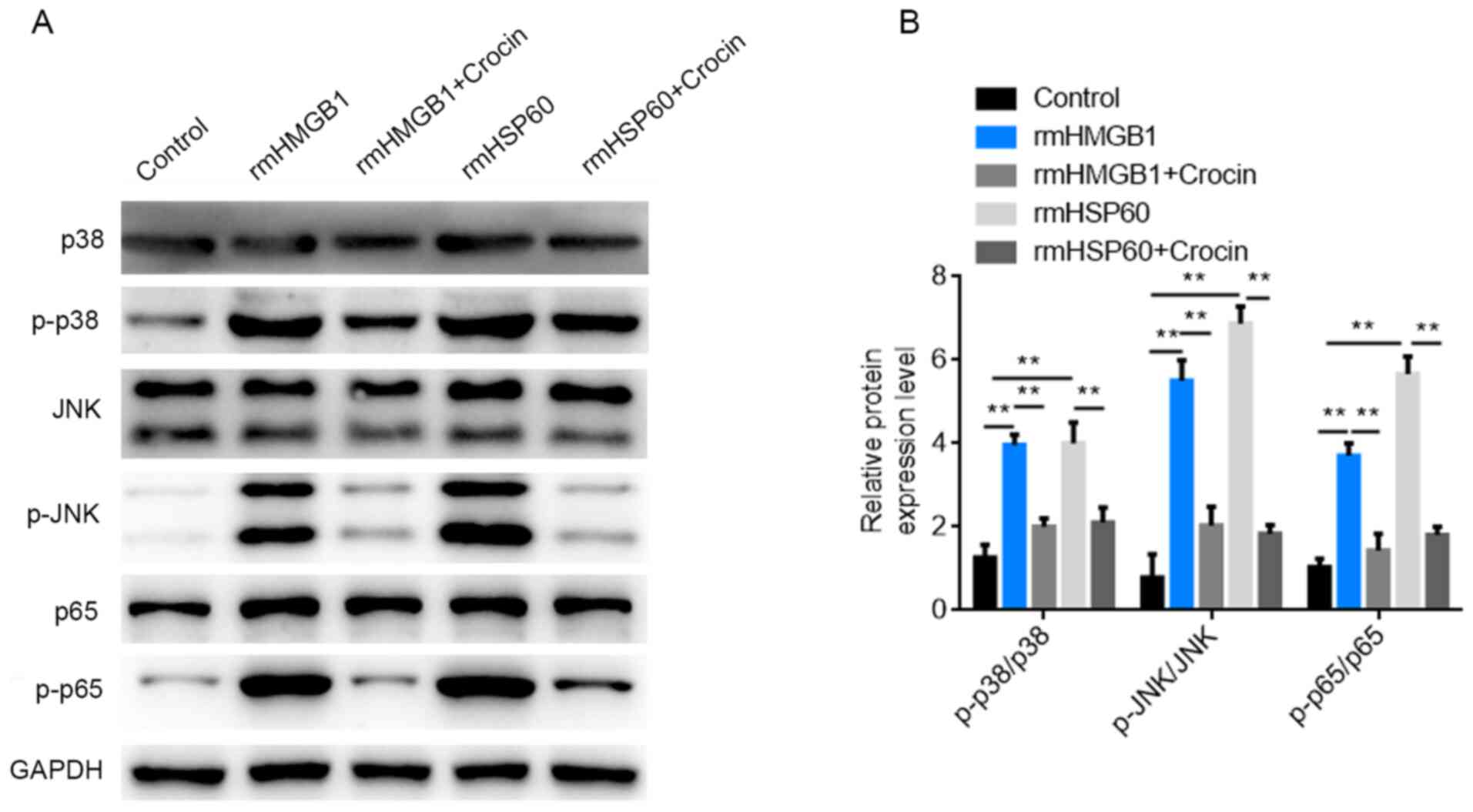
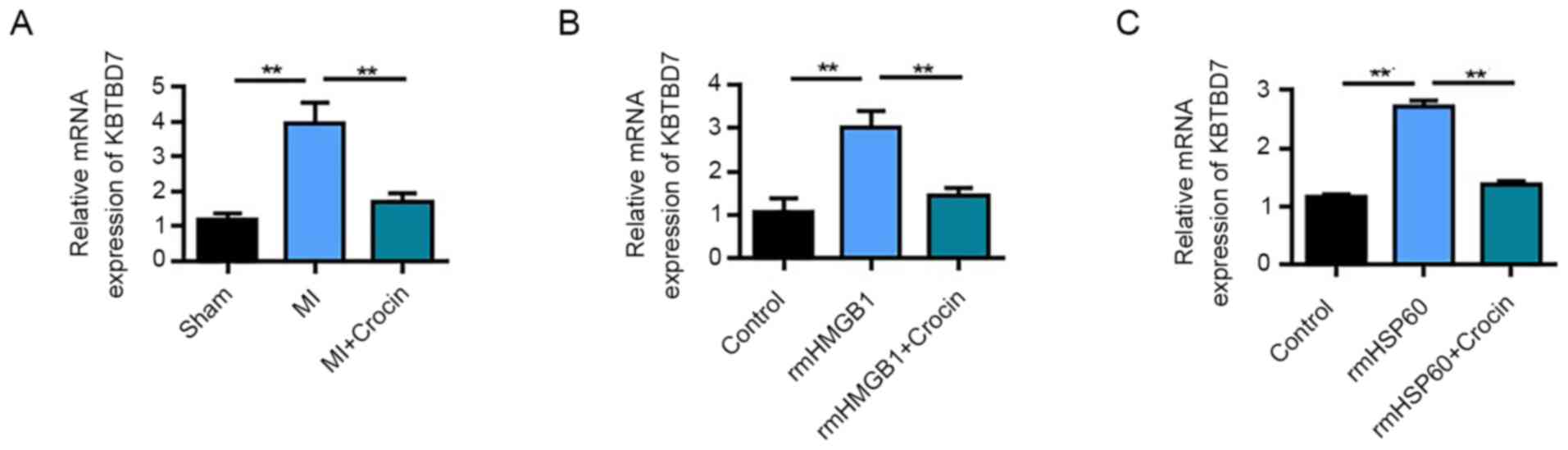
|
1
|
Mui D and Zhang Y: Mitochondrial scenario:
Roles of mitochondrial dynamics in acute myocardial
ischemia/reperfusion injury. J Recept Signal Transduct Res. 41:1–5.
2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Rout A, Tantry US, Novakovic M, Sukhi A
and Gurbel PA: Targeted pharmacotherapy for ischemia reperfusion
injury in acute myocardial infarction. Expert Opin Pharmacother.
21:1851–1865. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Hausenloy DJ and Yellon DM: Myocardial
ischemia-reperfusion injury: A neglected therapeutic target. J Clin
Invest. 123:92–100. 2013. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Turer AT and Hill JA: Pathogenesis of
myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury and rationale for therapy.
Am J Cardiol. 106:360–368. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Davidson SM, Ferdinandy P, Andreadou I,
Bøtker HE, Heusch G, Ibáñez B, Ovize M, Schulz R, Yellon DM,
Hausenloy DJ, et al: Multitarget strategies to reduce myocardial
ischemia/reperfusion injury: JACC review topic of the week. J Am
Coll Cardiol. 73:89–99. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Yang L, Wang B, Zhou Q, Wang Y, Liu X, Liu
Z and Zhan Z: MicroRNA-21 prevents excessive inflammation and
cardiac dysfunction after myocardial infarction through targeting
KBTBD7. Cell Death Dis. 9:7692018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Frantz S and Nahrendorf M: Cardiac
macrophages and their role in ischaemic heart disease. Cardiovasc
Res. 102:240–248. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Lambert JM, Lopez EF and Lindsey ML:
Macrophage roles following myocardial infarction. Int J Cardiol.
130:147–158. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Zhang Y, Wang Y, Xu J, Tian F, Hu S, Chen
Y and Fu Z: Melatonin attenuates myocardial ischemia-reperfusion
injury via improving mitochondrial fusion/mitophagy and activating
the AMPK-OPA1 signaling pathways. J Pineal Res. 66:e125422019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Ye B, Chen X, Dai S, Han J, Liang X, Lin
S, Cai X, Huang Z and Huang W: Emodin alleviates myocardial
ischemia/reperfusion injury by inhibiting gasdermin D-mediated
pyroptosis in cardiomyocytes. Drug Des Devel Ther. 13:975–990.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Ryu SM, Kim HJ, Cho KR and Jo WM:
Myocardial protective effect of tezosentan, an endothelin receptor
antagonist, for ischemia-reperfusion injury in experimental heart
failure models. J Korean Med Sci. 24:782–788. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Xi X, Liu N, Wang Q, Chu Y, Yin Z, Ding Y
and Lu Y: ACT001, a novel PAI-1 inhibitor, exerts synergistic
effects in combination with cisplatin by inhibiting PI3K/AKT
pathway in glioma. Cell Death Dis. 10:7572019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Wang H, Zhong W, Zhao J, Zhang H, Zhang Q,
Liang Y, Chen S, Liu H, Zong S, Tian Y, et al: Oleanolic acid
inhibits epithelial-mesenchymal transition of hepatocellular
carcinoma by promoting iNOS dimerization. Mol Cancer Ther.
18:62–74. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zhong W, Sun B, Gao W, Qin Y, Zhang H,
Huai L, Tang Y, Liang Y, He L, Zhang X, et al: Salvianolic acid A
targeting the transgelin-actin complex to enhance vasoconstriction.
EBioMedicine. 37:246–258. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Zhong W, Hou H, Liu T, Su S, Xi X, Liao Y,
Xie R, Jin G, Liu X, Zhu L, et al: Cartilage oligomeric matrix
protein promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition by interacting
with transgelin in colorectal cancer. Theranostics. 10:8790–8806.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Zhong W, Yang W, Qin Y, Gu W, Xue Y, Tang
Y, Xu H, Wang H, Zhang C, Wang C, et al: 6-Gingerol stabilized the
p-VEGFR2/VE-cadherin/β-catenin/actin complex promotes microvessel
normalization and suppresses tumor progression. J Exp Clin Cancer
Res. 38:2852019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Chen L, Qi Y and Yang X: Neuroprotective
effects of crocin against oxidative stress induced by
ischemia/reperfusion injury in rat retina. Ophthalmic Res.
54:157–168. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Lee IA, Lee JH, Baek NI and Kim DH:
Antihyperlipidemic effect of crocin isolated from the fructus of
Gardenia jasminoides and its metabolite crocetin. Biol Pharm
Bull. 28:2106–2110. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Hashemzaei M, Mamoulakis C, Tsarouhas K,
Georgiadis G, Lazopoulos G, Tsatsakis A, Shojaei Asrami E and
Rezaee R: Crocin: A fighter against inflammation and pain. Food
Chem Toxicol. 143:1115212020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Hashemzaei M, Rezaee R, Nabatzehi M,
Tsarouhas K, Konstantinos Nikolouzakis T, Lazopoulos G, A Spandidos
D, Tsatsakis A and Shahraki J: Anti-hypertensive effect of crocin
and hesperidin combination in high-fat diet treated rats. Exp Ther
Med. 19:3840–3844. 2020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Rezaee R, Mahmoudi M, Abnous K, Zamani
Taghizadeh Rabe S, Tabasi N, Hashemzaei M and Karimi G: Cytotoxic
effects of crocin on MOLT-4 human leukemia cells. J Complement
Integr Med. 10:1–8. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
El-Baz FK, Aly HF and Abd-Alla HI: The
ameliorating effect of carotenoid rich fraction extracted from
Dunaliella salina microalga against inflammation-associated cardiac
dysfunction in obese rats. Toxicol Rep. 7:118–124. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Tian Y, Pu X, Yu H, Ji A, Gao R, Hu Y, Xu
Z and Wang H: Genome-wide characterization and analysis of bHLH
transcription factors related to crocin biosynthesis in Gardenia
jasminoides ellis (rubiaceae). Biomed Res Int.
2020:29038612020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Xu G, Gong Z, Yu W, Gao L, He S and Qian
Z: Increased expression ratio of Bcl-2/Bax is associated with
crocin-mediated apoptosis in bovine aortic endothelial cells. Basic
Clin Pharmacol Toxicol. 100:31–35. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Ochiai T, Ohno S, Soeda S, Tanaka H,
Shoyama Y and Shimeno H: Crocin prevents the death of rat
pheochromyctoma (PC-12) cells by its antioxidant effects stronger
than those of alpha-tocopherol. Neurosci Lett. 362:61–64. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Sebastin Santhosh M, Hemshekhar M,
Thushara RM, Devaraja S, Kemparaju K and Girish KS: Vipera russelli
venom-induced oxidative stress and hematological alterations:
Amelioration by crocin a dietary colorant. Cell Biochem Funct.
31:41–50. 2013. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Ordoudi SA, Befani CD, Nenadis N, Koliakos
GG and Tsimidou MZ: Further examination of antiradical properties
of Crocus sativus stigmas extract rich in crocins. J Agric
Food Chem. 57:3080–3086. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Oruc S, Gönül Y, Tunay K, Oruc OA, Bozkurt
MF, Karavelioğlu E, Bağcıoğlu E, Coşkun KS and Celik S: The
antioxidant and antiapoptotic effects of crocin pretreatment on
global cerebral ischemia reperfusion injury induced by four vessels
occlusion in rats. Life Sci. 154:79–86. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Genau HM, Huber J, Baschieri F, Akutsu M,
Dötsch V, Farhan H, Rogov V and Behrends C: CUL3-KBTBD6/KBTBD7
ubiquitin ligase cooperates with GABARAP proteins to spatially
restrict TIAM1-RAC1 signaling. Mol Cell. 57:995–1010. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Hu J, Yuan W, Tang M, Wang Y, Fan X, Mo X,
Li Y, Ying Z, Wan Y, Ocorr K, et al: KBTBD7, a novel human
BTB-kelch protein, activates transcriptional activities of SRE and
AP-1. BMB Rep. 43:17–22. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Liu YT, Liu F, Cao L, Xue L, Gu WT, Zheng
YZ, Tang H, Wang Y, Yao H, Zhang Y, et al: The KBTBD6/7-DRD2 axis
regulates pituitary adenoma sensitivity to dopamine agonist
treatment. Acta Neuropathol. 140:377–396. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Gao Y, Wang C, Wang Z, Li W, Liu Y, Shou S
and Chai Y: Semaphorin 3A contributes to sepsis-induced
immunosuppression by impairing CD4+ T cell anergy. Mol
Med Rep. 23:3022021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Li J, Wang X, Ma C, Xu S, Xu M, Yang J,
Wang R and Xue L: Dual PI3K/mTOR inhibitor NVP-BEZ235 decreases the
proliferation of doxorubicin-resistant K562 cells. Mol Med Rep.
23:3012021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Wu H, Tao Y, Zhang W, Wang G and Zhang Q:
circ-0000212 promotes cell proliferation of colorectal cancer by
sponging miR-491 and modulating FOXP4 expression. Mol Med Rep.
23:3002021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Liu NB, Wu M, Chen C, Fujino M, Huang JS,
Zhu P and Li XK: Novel molecular targets participating in
myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury and cardioprotection.
Cardiol Res Pract. 2019:69351472019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Mozaffari MS, Liu JY, Abebe W and Baban B:
Mechanisms of load dependency of myocardial ischemia reperfusion
injury. Am J Cardiovasc Dis. 3:180–196. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Fischesser DM, Bo B, Benton RP, Su H,
Jahanpanah N and Haworth KJ: Controlling reperfusion injury with
controlled reperfusion: Historical perspectives and new paradigms.
J Cardiovasc Pharmacol Ther. 26:504–523. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Liu H, Wu X, Luo J, Wang X, Guo H, Feng D,
Zhao L, Bai H, Song M, Liu X, et al: Pterostilbene attenuates
astrocytic inflammation and neuronal oxidative injury after
ischemia-reperfusion by inhibiting NF-κB phosphorylation. Front
Immunol. 10:24082019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Wang C, Sun H, Song Y, Ma Z, Zhang G, Gu X
and Zhao L: Pterostilbene attenuates inflammation in rat heart
subjected to ischemia-reperfusion: Role of TLR4/NF-κB signaling
pathway. Int J Clin Exp Med. 8:1737–1746. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Farkhondeh T and Samarghandian S: The
effect of saffron (Crocus sativus L.) and its ingredients on
the management of diabetes mellitus and dislipidemia. Afr J Pharm
Pharmacol. 8:541–549. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Razavi BM, Hosseinzadeh H, Movassaghi AR,
Imenshahidi M and Abnous K: Protective effect of crocin on diazinon
induced cardiotoxicity in rats in subchronic exposure. Chem Biol
Interact. 203:547–555. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Sarshoori JR, Asadi MH and Mohammadi MT:
Neuroprotective effects of crocin on the histopathological
alterations following brain ischemia-reperfusion injury in rat.
Iran J Basic Med Sci. 17:895–902. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Thushara RM, Hemshekhar M, Santhosh MS,
Jnaneshwari S, Nayaka SC, Naveen S, Kemparaju K and Girish KS:
Crocin, a dietary additive protects platelets from oxidative
stress-induced apoptosis and inhibits platelet aggregation. Mol
Cell Biochem. 373:73–83. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Vakili A, Einali MR and Bandegi AR:
Protective effect of crocin against cerebral ischemia in a
dose-dependent manner in a rat model of ischemic stroke. J Stroke
Cerebrovasc Dis. 23:106–113. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Zhang X, Fan Z and Jin T: Crocin protects
against cerebral-ischemia-induced damage in aged rats through
maintaining the integrity of blood-brain barrier. Restor Neurol
Neurosci. 35:65–75. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Naghizadeh B, Boroushaki MT, Vahdati
Mashhadian N and Mansouri MT: Protective effects of crocin against
cisplatin-induced acute renal failure and oxidative stress in rats.
Iran Biomed J. 12:93–100. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
He SY, Qian ZY, Tang FT, Wen N, Xu GL and
Sheng L: Effect of crocin on experimental atherosclerosis in quails
and its mechanisms. Life Sci. 77:907–921. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Roshankhah S, Salahshoor MR, Jalili F,
Karimi F, Sohrabi M and Jalili C: Crocin effects on the
nicotine-induce ovary injuries in female rat. Int J Life Sci Pharm
Res. 7:1–8. 2017.
|
|
50
|
Hussain MA, Abogresha NM, AbdelKader G,
Hassan R, Abdelaziz EZ and Greish SM: Antioxidant and
anti-inflammatory effects of crocin ameliorate doxorubicin-induced
nephrotoxicity in rats. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2021:88417262021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Khwaja B, Thankam FG and Agrawal DK:
Mitochondrial DAMPs and altered mitochondrial dynamics in OxLDL
burden in atherosclerosis. Mol Cell Biochem. 476:1915–1928. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Yang H, Wang H and Andersson U: Targeting
Inflammation Driven by HMGB1. Front Immunol. 11:4842020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Andrassy M, Volz HC, Riedle N, Gitsioudis
G, Seidel C, Laohachewin D, Zankl AR, Kaya Z, Bierhaus A,
Giannitsis E, et al: HMGB1 as a predictor of infarct transmurality
and functional recovery in patients with myocardial infarction. J
Intern Med. 270:245–253. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Ding HS, Yang J, Chen P, Yang J, Bo SQ,
Ding JW and Yu QQ: The HMGB1-TLR4 axis contributes to myocardial
ischemia/reperfusion injury via regulation of cardiomyocyte
apoptosis. Gene. 527:389–393. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Hu X, Fu W and Jiang H: HMGB1: A potential
therapeutic target for myocardial ischemia and reperfusion injury.
Int J Cardiol. 155:4892012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Li Q, Xu M, Li Z, Li T, Wang Y, Chen Q,
Wang Y, Feng J, Yin X and Lu C: Maslinic acid attenuates
ischemia/reperfusion injury-induced myocardial inflammation and
apoptosis by regulating HMGB1-TLR4 axis. Front Cardiovasc Med.
8:7689472021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Giallauria F, Cirillo P, D'agostino M,
Petrillo G, Vitelli A, Pacileo M, Angri V, Chiariello M and
Vigorito C: Effects of exercise training on high-mobility group
box-1 levels after acute myocardial infarction. J Card Fail.
17:108–114. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Vinten-Johansen J, Jiang R, Reeves JG,
Mykytenko J, Deneve J and Jobe LJ: Inflammation, proinflammatory
mediators and myocardial ischemia-reperfusion Injury. Hematol Oncol
Clin North Am. 21:123–145. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Hou M, Wu X, Zhao Z, Deng Q, Chen Y and
Yin L: Endothelial cell-targeting, ROS-ultrasensitive drug/siRNA
co-delivery nanocomplexes mitigate early-stage neutrophil
recruitment for the anti-inflammatory treatment of myocardial
ischemia reperfusion injury. Acta Biomater. 143:344–355. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Gao C, Liu Y, Yu Q, Yang Q, Li B, Sun L,
Yan W, Cai X, Gao E, Xiong L, et al: TNF-α antagonism ameliorates
myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury in mice by upregulating
adiponectin. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 308:H1583–H1591.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Cao J, Xie H, Sun Y, Zhu J, Ying M, Qiao
S, Shao Q, Wu H and Wang C: Sevoflurane post-conditioning reduces
rat myocardial ischemia reperfusion injury through an increase in
NOS and a decrease in phopshorylated NHE1 levels. Int J Mol Med.
36:1529–1537. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Xie C, Li X, Zhu J, Wu J, Geng S and Zhong
C: Magnesium isoglycyrrhizinate suppresses LPS-induced inflammation
and oxidative stress through inhibiting NF-κB and MAPK pathways in
RAW264.7 cells. Bioorg Med Chem. 27:516–524. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Wang HW, Liu HJ, Cao H, Qiao ZY and Xu YW:
Diosgenin protects rats from myocardial inflammatory injury induced
by ischemia-reperfusion. Med Sci Monit. 24:246–253. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
National Research Council (US) Committee
for the Update of the Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory
Animals, . Guide for the care and use of laboratory animals. 8th
edition. Washington (DC): National Academies Press (US); 2011
|