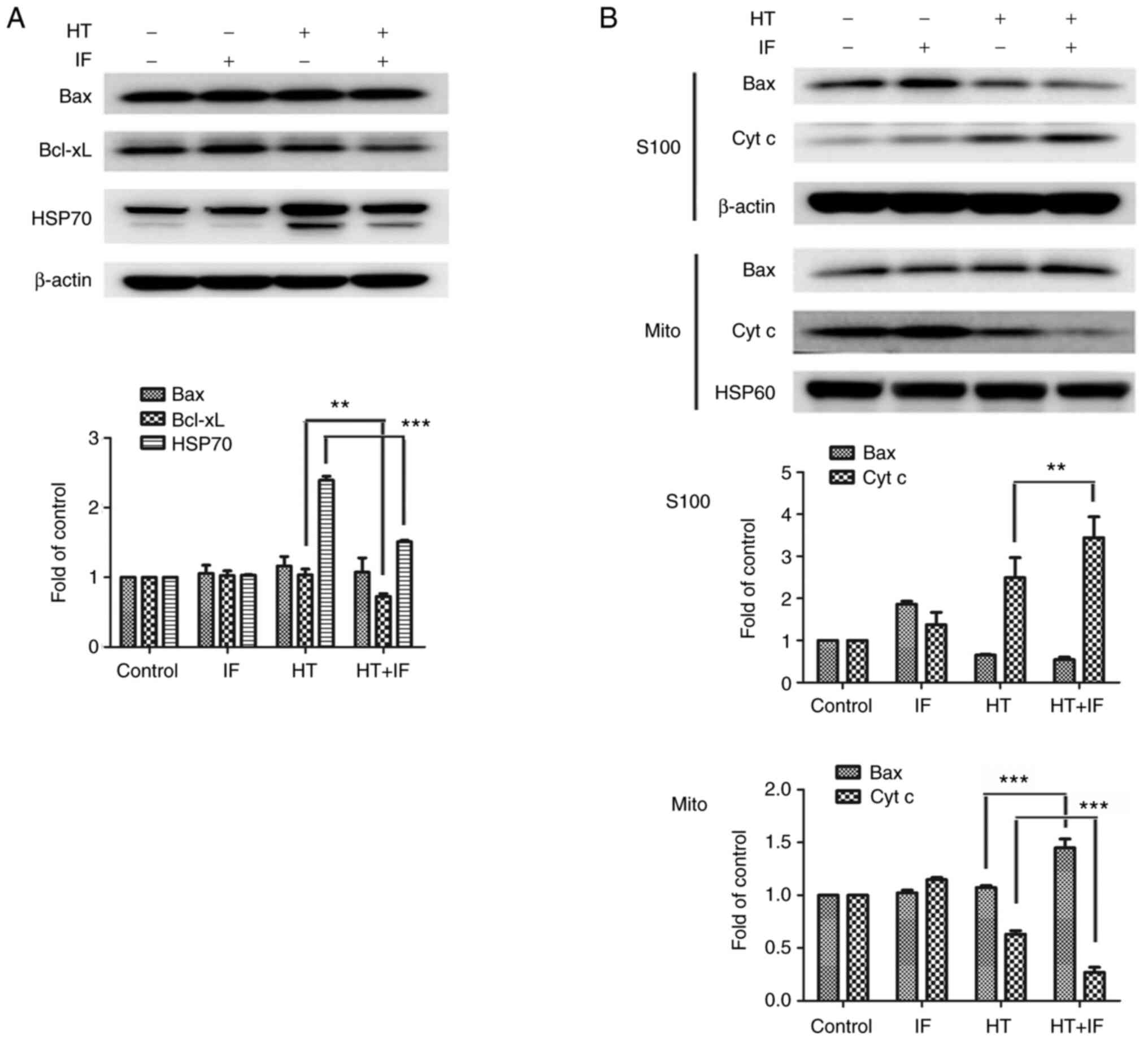
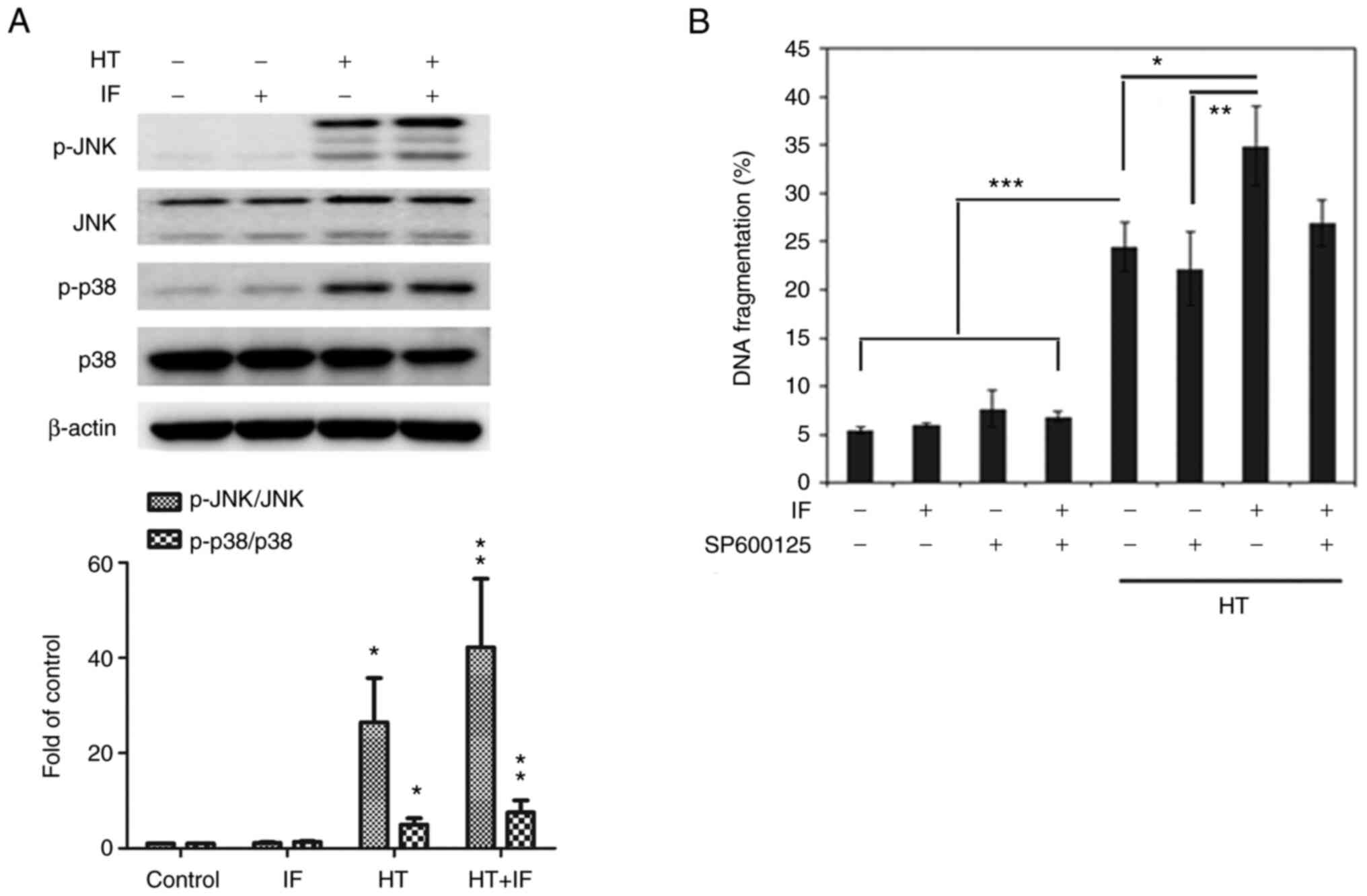
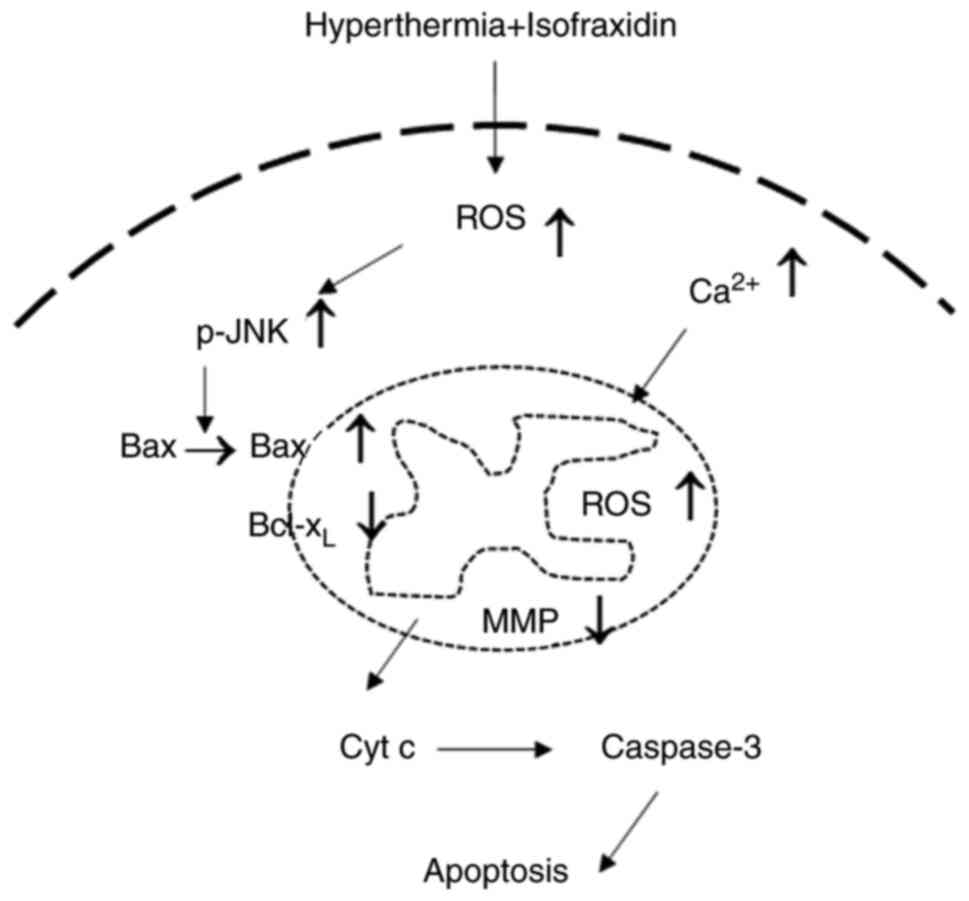
|
1
|
Deyama T, Nishibe S and Nakazawa Y:
Constituents and pharmacological effects of Eucommia and Siberian
ginseng. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 22:1057–1070. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Khan S, Riaz N, Afza N, Malik A, Aziz ur
R, Iqbal L and Lateef M: Antioxidant constituents from Cotoneaster
racemiflora. J Asian Nat Prod Res. 11:44–48. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Li P, Zhao QL, Wu LH, Jawaid P, Jiao YF,
Kadowaki M and Kondo T: Isofraxidin, a potent reactive oxygen
species (ROS) scavenger, protects human leukemia cells from
radiation-induced apoptosis via ROS/mitochondria pathway in
p53-independent manner. Apoptosis. 19:1043–1053. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Niu X, Xing W, Li W, Fan T, Hu H and Li Y:
Isofraxidin exhibited anti-inflammatory effects in vivo and
inhibited TNF-α production in LPS-induced mouse peritoneal
macrophages in vitro via the MAPK pathway. Int Immunopharmacol.
14:164–171. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Shen P, Wang HG, Li MM, Ma QY, Zhou CW,
Pan F and Xie R: Isofraxidin inhibited proliferation and induced
apoptosis via blockage of Akt pathway in human colorectal cancer
cells. Biomed Pharmacother. 92:78–85. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Zhang H, Feng QQ, Gong JH and Ma JP:
Anticancer effects of isofraxidin against A549 human lung cancer
cells via the EGFR signaling pathway. Mol Med Rep. 18:407–414.
2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Yamazaki T and Tokiwa T: Isofraxidin, a
coumarin component from Acanthopanax senticosus, inhibits matrix
metalloproteinase-7 expression and cell invasion of human hepatoma
cells. Biol Pharm Bull. 33:1716–1722. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Datta NR, Ordonez SG, Gaipl US, Paulides
MM, Crezee H, Gellermann J, Marder D, Puric E and Bodis S: Local
hyperthermia combined with radiotherapy and-/or chemotherapy:
Recent advances and promises for the future. Cancer Treat Rev.
41:742–753. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Mantso T, Vasileiadis S, Anestopoulos I,
Voulgaridou GP, Lampri E, Botaitis S, Kontomanolis EN, Simopoulos
C, Goussestis G, Franco R, et al: Hyperthermia induces therapeutic
effectiveness and potentiates adjuvant therapy with non-targeted
and targeted drugs in an in vitro model of human malignant
melanoma. Sci Rep. 8:107242018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Plati J, Bucur O and Khosravi-Far R:
Apoptotic cell signaling in cancer progression and therapy. Integr
Biol (Camb). 3:279–296. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Zhao QL, Fujiwara Y and Kondo T: Mechanism
of cell death induction by nitroxide and hyperthermia. Free Radic
Biol Med. 40:1131–1143. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Tabuchi Y, Ahmed K and Kondo T: Induction
of oxidative stress by hyperthermia and enhancement of
hyperthermia-induced apoptosis by oxidative stress modification.
Hyperthermic Oncology from Bench to Bedside. Springer Singapore;
Singapore: pp. 7–18. 2016
|
|
13
|
Sellins KS and Cohen JJ: Gene induction by
gamma-irradiation leads to DNA fragmentation in lymphocytes. J
Immunol. 139:3199–3206. 1987. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zhao QL, Fujiwara Y and Kondo T:
Synergistic induction of apoptosis and caspase-independent
autophagic cell death by a combination of nitroxide Tempo and heat
shock in human leukemia U937 cells. Apoptosis. 15:1270–1283. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Antonsson B, Montessuit S, Sanchez B and
Martinou JC: Bax is present as a high molecular weight
oligomer/complex in the mitochondrial membrane of apoptotic cells.
J Biol Chem. 276:11615–11623. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Narvaez CJ and Welsh J: Role of
mitochondria and caspases in vitamin D-mediated apoptosis of MCF-7
breast cancer cells. J Biol Chem. 276:9101–9107. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Ott M, Gogvadze V, Orrenius S and
Zhivotovsky B: Mitochondria, oxidative stress and cell death.
Apoptosis. 12:913–922. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Tripathi P and Hildeman D: Sensitization
of T cells to apoptosis-a role for ROS? Apoptosis. 9:515–523. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zhao S, Xiong Z, Mao X, Meng D, Lei Q, Li
Y, Deng P, Chen M, Tu M, Lu X, et al: Atmospheric pressure room
temperature plasma jets facilitate oxidative and nitrative stress
and lead to endoplasmic reticulum stress dependent apoptosis in
HepG2 cells. PLoS One. 8:e736652013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Emam H, Zhao QL, Furusawa Y, Refaat A,
Ahmed K, Kadowak M and Kondo T: Apoptotic cell death by the novel
natural compound, cinobufotalin. Chem Biol Interact. 199:154–160.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
McArthur K and Kile BT: Apoptotic
caspases: Multiple or mistaken identities? Trends Cell Biol.
28:475–493. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Tsujimoto Y and Shimizu S: Bcl-2 family:
Life-or-death switch. FEBS Lett. 466:6–10. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Beere HM, Wolf BB, Cain K, Mosser DD,
Mahboubi A, Kuwana T, Tailor P, Morimoto RI, Cohen GM and Green DR:
Heat-shock protein 70 inhibits apoptosis by preventing recruitment
of procaspase-9 to the Apaf-1 apoptosome. Nat Cell Biol. 2:469–475.
2000. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Lu TH, Hsieh SY, Yen CC, Wu C, Chen KL,
Hung DZ, Chen CH, Wu CC, Su YC, Chen YW, et al: Involvement of
oxidative stress-mediated ERK1/2 and p38 activation regulated
mitochondria-dependent apoptotic signals in methylmercury-induced
neuronal cell injury. Toxicol Lett. 204:71–80. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Gu ZT, Li L, Wu F, Zhao P, Yang H, Liu YS,
Geng Y, Zhao M and Su L: Heat stress induced apoptosis is triggered
by transcription-independent p53, Ca(2+) dyshomeostasis and the
subsequent Bax mitochondrial translocation. Sci Rep. 5:114972015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
McAnulty SR, McAnulty L, Pascoe DD,
Gropper SS, Keith RE, Morrow JD and Gladden LB: Hyperthermia
increases exercise-induced oxidative stress. Int J Sport Med.
26:188–192. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Skibba JL, Powers RH, Stadnicka A,
Cullinane DW, Almagro UA and Kalbfleisch JH: Oxidative stress as a
precursor to the irreversible hepatocellular injury caused by
hyperthermia. Int J Hyperthermia. 7:749–761. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Turrens JF: Mitochondrial formation of
reactive oxygen species. J Physiol. 552:335–344. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Beckman JS and Koppenol WH: Nitric oxide,
superoxide, and peroxynitrite: The good, the bad, and ugly. Am J
Physiol. 271:C1424–C1437. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Krishna MC, Russo A, Mitchell JB,
Goldstein S, Dafni H and Samuni A: Do nitroxide antioxidants act as
scavengers of O2−. or as SOD mimics? J Biol
Chem. 271:26026–26031. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Uchiyama H, Zhao QL, Hassan MA, Andocs G,
Nojima N, Takeda K, Ishikawa K, Hori M and Kondo T: EPR-spin
trapping and flow cytometric studies of free radicals generated
using cold atmospheric argon plasma and X-ray irradiation in
aqueous solutions and intracellular milieu. PLoS One.
10:e01369562015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Rohan M, Rehman MU, Zhao QL, Jawaid P,
Mitsuhashi Y, Sakurai K, Heshiki W, Ogawa R, Tomihara K, Saitoh JI,
et al: Combination of 5-aminosalicylic acid and hyperthermia
synergistically enhances apoptotic cell death in HSC-3 cells due to
intracellular nitric oxide/peroxynitrite generation. Cancer Lett.
451:58–67. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Rohan M, Rehman MU, Zhao QL, Jawaid P,
Takeda K, Ishikawa K, Hori M, Tomihara K, Noguchi K, Kondo T and
Noguchi M: Cold atmospheric plasma causes synergistic enhancement
in cell death with hyperthermia and an additive enhancemnt with
radiation. Sci Rep. 7:116592017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Elmore S: Apoptosis: A review of
programmed cell death. Toxicol Pathol. 35:495–516. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Neumann S, El Maadidi S, Faletti L, Haun
F, Labib S, Schejtman A, Maurer U and Borner C: How do viruses
control mitochondria-mediated apoptosis? Virus Res. 209:45–55.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Fulda S and Debatin KM: Extrinsic versus
intrinsic apoptosis pathways in anticancer chemotherapy. Oncogene.
25:4798–4811. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Bruin JE, Gerstein HC, Morrison KM and
Holloway AC: Increased pancreatic beta-cell apoptosis following
fetal and neonatal exposure to nicotine is mediated via the
mitochondria. Toxicol Sci. 103:362–370. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Borner C and Andrews DW: The apoptotic
pore on mitochondria: Are we breaking through or still stuck? Cell
Death Differ. 21:187–191. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Youle RJ and Strasser A: The BCL-2 protein
family: Opposing activities that mediate cell death. Nat Rev Mol
Cell Biol. 9:47–59. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Haneef J, Parvathy M, Thankayyan RS,
Sithul H and Sreeharshan S: Bax translocation mediated
mitochondrial apoptosis and caspase dependent photosensitizing
effect of Ficus religiosa on cancer cells. PLoS One. 7:e400552012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Wang Z, Lu W, Li Y and Tang B: Alpinetin
promotes Bax translocation, induces apoptosis through the
mitochondrial pathway and arrests human gastric cancer cells at the
G2/M phase. Mol Med Rep. 7:915–920. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Kim BJ, Ryu SW and Song BJ: JNK- and p38
kinase-mediated phosphorylation of Bax leads to its activation and
mitochondrial translocation and to apoptosis of human hepatoma
HepG2 cells. J Biol Chem. 281:21256–21265. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Gaitanaki C, Mastri M, Aggeli IK and Beis
I: Differential roles of p38-MAPK and JNKs in mediating early
protection or apoptosis in the hyperthermic perfused amphibian
heart. J Exp Biol. 211:2524–2532. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Speidel D: Transcription-independent p53
apoptosis: An alternative route to death. Trends Cell Biol.
20:14–24. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Wold LE, Ceylan-Isik AF, Fang CX, Yang X,
Li SY, Sreejayan N, Privratsky JR and Ren J: Metallothionein
alleviates cardiac dysfunction in streptozotocin-induced diabetes:
Role of Ca2+ cycling proteins, NADPH oxidase, poly(ADP-Ribose)
polymerase and myosin heavy chain isozyme. Free Radic Biol Med.
40:1419–1429. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Yu T, Robotham JL and Yoon Y: Increased
production of reactive oxygen species in hyperglycemic conditions
requires dynamic change of mitochondrial morphology. Proc Natl Acad
Sci USA. 103:2653–2658. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Orrenius S, Zhivotovsky B and Nicotera P:
Regulation of cell death: The calcium-apoptosis link. Nat Rev Mol
Cell Biol. 4:552–565. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Crompton M, Barksby E, Johnson N and
Capano M: Mitochondrial intermembrane junctional complexes and
their involvement in cell death. Biochimie. 84:143–152. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Toledo FD, Perez LM, Basiglio CL, Ochoa
JE, Pozzi EJ and Roma MG: The
Ca(2)(+)-calmodulin-Ca(2)(+)/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II
signaling pathway is involved in oxidative stress-induced
mitochondrial permeability transition and apoptosis in isolated rat
hepatocytes. Arch Toxicol. 88:1695–1709. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Seynhaeve ALB, Amin M, Haemmerich D, van
Rhoon GC and Hagen TLM: Hyperthermia and smart drug delivery
systems for solid tumor therapy. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 163:125–144.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|